A Novel Approach for Data Feature Weighting Using Correlation Coefficients and Min–Max Normalization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Datasets and Experiments
| Algorithm 1 CCMMW algorithm |
| Algorithm: Normalization + Weighting data using Min-Max01 and CC to improve the accuracy of classification methods Input: Un-Data: un-normalize data Output: CCoT Correlation Coefficient of Label feature, Normalized data (No-Data), Correlation Weighted Normalized Data (CCMMW-Data) CCoT = Calculate the correlation coefficient of each feature with the Label feature corr(Vj,VTarget) using the PCC method as in Equation (1) Calculate No-Data using MMN normalization method, Equation (2) For i = 1 to , where n is the number of features in the data Calculate CCMMW-Data using the proposed method as in Equation (3) |
3. Results
3.1. The Evaluation of Different Classifiers Based on the Best Result of CCMMW
3.2. Logistic Regression (LR) Classifier
3.3. Support Vector Machine Classifier
3.4. k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) Classifier
3.5. Neural Network (NN) Classifier
3.6. Naive Bayes Classifier
4. Discussion
The Effect of C Parameter on the CCMMW Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCMMW | Correlation Coefficient with Min–Max Weighted |
| PCC | Pearson correlation coefficient |
| MMN | Min–Max normalization |
| CC | correlation coefficient |
| 2S-P | Two-Stage Min–Max with Pearson |
| 2S-RF | Two-Stage Min–Max with RF Feature Importance |
| NAMM | New Approach Min–Max |
| NB | naive Bayes |
| NN | neural network |
| LR | logistic regression |
| kNN | k-nearest neighbor |
References
- Niño-Adan, I.; Manjarres, D.; Landa-Torres, I.; Portillo, E. Feature weighting methods: A review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 184, 115424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Xie, W.; Pei, Z. Semi-supervised adversarial discriminative learning approach for intelligent fault diagnosis of wind turbine. Inf. Sci. 2023, 648, 119496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, K. A note on transformation, standardization and normalization. Int. J. Oper. Quant. Manag. 2010, IX, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- García, S.; Luengo, J.; Herrera, F. Data Preprocessing in Data Mining; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 72. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamad Mohsin, M.F.; Hamdan, A.R.; Abu Bakar, A. The Effect of Normalization for Real Value Negative Selection Algorithm. In Soft Computing Applications and Intelligent Systems; Noah, S.A., Abdullah, A., Arshad, H., Abu Bakar, A., Othman, Z.A., Sahran, S., Omar, N., Othman, Z., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 194–205. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Kamber, M.; Pei, J. 3—Data Preprocessing. In Data Mining, 3rd ed.; Han, J., Kamber, M., Pei, J., Eds.; Morgan Kaufmann: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 83–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, D.; Huang, J. Optimize TSK Fuzzy Systems for Classification Problems: Minibatch Gradient Descent With Uniform Regularization and Batch Normalization. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebuňa, P.; Halčinová, J.; Fil’o, M.; Markovič, J. The importance of normalization and standardization in the process of clustering. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics (SAMI), Herl’any, Slovakia, 23–25 January 2014; pp. 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyemo, A.; Wimmer, H.; Powell, L.M. Effects of Normalization Techniques on Logistic Regression in Data Science. J. Inf. Syst. Appl. Res. 2019, 12, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeswari, D.; Thangavel, K. The Performance of Data Normalization Techniques on Heart Disease Datasets. Int. J. Adv. Res. Eng. Technol. 2020, 11, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar]
- Shanker, M.; Hu, M.Y.; Hung, M.S. Effect of data standardization on neural network training. Omega 1996, 24, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Han, T. Data-driven lithium-ion batteries capacity estimation based on deep transfer learning using partial segment of charging/discharging data. Energy 2023, 271, 127033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandanaarachchi, S.; Muñoz, M.A.; Hyndman, R.J.; Smith-Miles, K. On normalization and algorithm selection for unsupervised outlier detection. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 34, 309–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D. Adaptive Deep Sparse Semantic Modeling Framework for High Spatial Resolution Image Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6180–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, B. Investigating the impact of data normalization on classification performance. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 97, 105524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dialameh, M.; Jahromi, M.Z. A general feature-weighting function for classification problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 72, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Lu, Z.; Song, J. Variable importance analysis: A comprehensive review. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 142, 399–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Kong, G. Two feature weighting approaches for naive Bayes text classifiers. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 100, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataliani, Y.; Yang, M.-S. Feature-Weighted Fuzzy K-Modes Clustering. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Metaheuristics & Swarm Intelligence, Male, Maldives, 23–24 March 2019; pp. 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Malarvizhi, K.; Amshakala, K. Feature Linkage Weight Based Feature Reduction using Fuzzy Clustering Method. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 4563–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Martinez, T.R. Feature weighting using neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37541), Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 July 2004; pp. 1327–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Dalwinder, S.; Birmohan, S.; Manpreet, K. Simultaneous feature weighting and parameter determination of neural networks using ant lion optimization for the classification of breast cancer. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.; Fan, Z.; Lee, Y.; Li, Z. Feature and sample weighted support vector machine. In Knowledge Engineering and Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Kong, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B. Maximum weight and minimum redundancy: A novel framework for feature subset selection. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, L. A new hybrid feature selection based on multi-filter weights and multi-feature weights. Appl. Intell. 2019, 49, 4033–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, B. Hybridization of feature selection and feature weighting for high dimensional data. Appl. Intell. 2019, 49, 1580–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, Z.; Shan, S.W.; Yusoff, I.; Kee, C.P. Classification techniques for predicting graduate employability. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2018, 8, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swesi, I.; Abu Bakar, A. Feature Clustering for PSO-Based Feature Construction on High-Dimensional Data. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2019, 18, 439–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation coefficients: Appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamis, H. Measures of association: How to choose? J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2008, 24, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, B. The correlation coefficient: Its values range between +1/−1, or do they? J. Target. Meas. Anal. Mark. 2009, 17, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.A. Correlation-Based Feature Selection of Discrete and Numeric Class Machine Learning; Department of Computer Science, University of Waikato: Hamilton, New Zealand, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Saidi, R.; Bouaguel, W.; Essoussi, N. Hybrid Feature Selection Method Based on the Genetic Algorithm and Pearson Correlation Coefficient. In Machine Learning Paradigms: Theory and Application; Hassanien, A.E., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-H.; Hsieh, C.-W. Feature Selection via Correlation Coefficient Clustering. J. Softw. 2010, 5, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, G.; Islam, Z. A decision tree-based missing value imputation technique for data pre-processing. In Proceedings of the Ninth Australasian Data Mining Conference, Ballarat, Australia, 1–2 December 2011; pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, Z.; Liang, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, B. Ensemble correlation-based low-rank matrix completion with applications to traffic data imputation. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2017, 132, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefidian, A.M.; Daneshpour, N. Estimating missing data using novel correlation maximization based methods. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 91, 106249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. A Pearson’s correlation coefficient based decision tree and its parallel implementation. Inf. Sci. 2018, 435, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Fong, S. The Impact of Data Normalization on Stock Market Prediction: Using SVM and Technical Indicators. In Soft Computing in Data Science; Berry, M.W., Mohamed, A.H., Yap, B.W., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 72–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, B.; Swarnkar, T. Importance of data standardization methods on stock indices prediction accuracy. In Advanced Computing and Intelligent Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Singh, B. Effective and efficient classification of gastrointestinal lesions: Combining data preprocessing, feature weighting, and improved ant lion optimization. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 8683–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Omer, Z.M. Improving accuracy of missing data imputation in data mining. Kurd. J. Appl. Res. 2017, 2, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Henderi, H.; Wahyuningsih, T.; Rahwanto, E. Comparison of Min-Max normalization and Z-Score Normalization in the K-nearest neighbor (kNN) Algorithm to Test the Accuracy of Types of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Inform. Inf. Syst. 2021, 4, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriyari, L. Effect of normalization methods on the performance of supervised learning algorithms applied to HTSeq-FPKM-UQ data sets: 7SK RNA expression as a predictor of survival in patients with colon adenocarcinoma. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 20, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayalakshmi, T.; Santhakumaran, A. Statistical normalization and back propagation for classification. Int. J. Comput. Theory Eng. 2011, 3, 1793–8201. [Google Scholar]
- Patro, S.; Sahu, K.K. Normalization: A preprocessing stage. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.06462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalatu, P.I.; Midi, H. New Approaches to Normalization Techniques to Enhance K-Means Clustering Algorithm. Malays. J. Math. Sci. 2020, 14, 41–62. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.; Yang, M.; Qin, Z.; Peng, J.; Ying, S. A Weighting Method for Feature Dimension by Semisupervised Learning With Entropy. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, K.; Sentürk, U. A novel ML approach to prediction of breast cancer: Combining of mad normalization, KMC based feature weighting and AdaBoostM1 classifier. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 19–21 October 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Poongodi, K.; Kumar, D. Support vector machine with information gain based classification for credit card fraud detection system. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 2021, 18, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Niño-Adan, I.; Landa-Torres, I.; Portillo, E.; Manjarres, D. Analysis and Application of Normalization Methods with Supervised Feature Weighting to Improve K-means Accuracy. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2019), Seville, Spain, 13–15 May 2019; Martínez Álvarez, F., Troncoso Lora, A., Sáez Muñoz, J.A., Quintián, H., Corchado, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Dialameh, M.; Hamzeh, A. Dynamic feature weighting for multi-label classification problems. Prog. Artif. Intell. 2021, 10, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lai, X.; Zhang, L. A Hierarchical Missing Value Imputation Method by Correlation-Based K-Nearest Neighbors. In Intelligent Systems and Applications: Proceedings of the 2019 Intelligent Systems Conference (IntelliSys), London, UK, 5–6 September 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 486–496. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-i.; Noh, Y.; Kang, Y.-J.; Park, S.; Lee, J.-W.; Chin, S.-W. Hybrid data-scaling method for fault classification of compressors. Measurement 2022, 201, 111619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| the new weighted value | Minimum value of column j | ||
| each original value | Maximum value of column j | ||
| the parameter to adjust the new range | New minimum value (0) | ||
| the correlation coefficient among column j and column label using PCC | New maximum value (1) |
| Original Normalized Min–Max (0,1) Data | CCMMW (1) | CCMMW (5) | CCMMW (10) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 |
| 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.56 | 0.88 | 1.25 | 1.50 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.88 | 1.50 | 2.25 | 2.75 |
| 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.75 | 1.13 | 1.75 | 2.50 | 3.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.75 | 3.00 | 4.50 | 5.50 |
| 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.83 | 0.94 | 1.13 | 1.35 | 1.50 | 0.75 | 1.13 | 1.69 | 2.63 | 3.75 | 4.50 | 0.75 | 1.50 | 2.63 | 4.50 | 6.75 | 8.25 |
| 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 1.25 | 1.50 | 1.80 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 2.25 | 3.50 | 5.00 | 6.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 3.50 | 6.00 | 9.00 | 11.00 |
| Feature | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC value | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.80 | 1.00 |
| Datasets | Type of Data | # of Instances | # of Features | # Classes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer 1 | real | 569 | 30 | 2 |
| QSAR | real | 1055 | 41 | 2 |
| Sonar | real | 208 | 60 | 2 |
| PARKINSON | real | 195 | 22 | 2 |
| Wine | Integer + real | 6463 | 12 | 2 |
| Monkey | Integer | 556 | 6 | 2 |
| German | real | 1000 | 24 | 2 |
| Musk | Integer | 6598 | 166 | 2 |
| liver | Integer + real | 345 | 6 | 2 |
| wholesale | Integer | 440 | 8 | 2 |
| Spam | real | 4601 | 57 | 2 |
| Heart s Cleveland | Integer + real | 1190 | 11 | 2 |
| Magic | real | 19,020 | 10 | 2 |
| Blood | Integer | 748 | 4 | 2 |
| Breast Cancer Coimbra | real | 116 | 9 | 2 |
| Vehicle | Integer | 846 | 18 | 4 |
| Bupa | Integer + real | 345 | 6 | 2 |
| Glass | real | 214 | 9 | 6 |
| Letter | Integer | 20,000 | 16 | 26 |
| Ecoli | real | 336 | 7 | 8 |
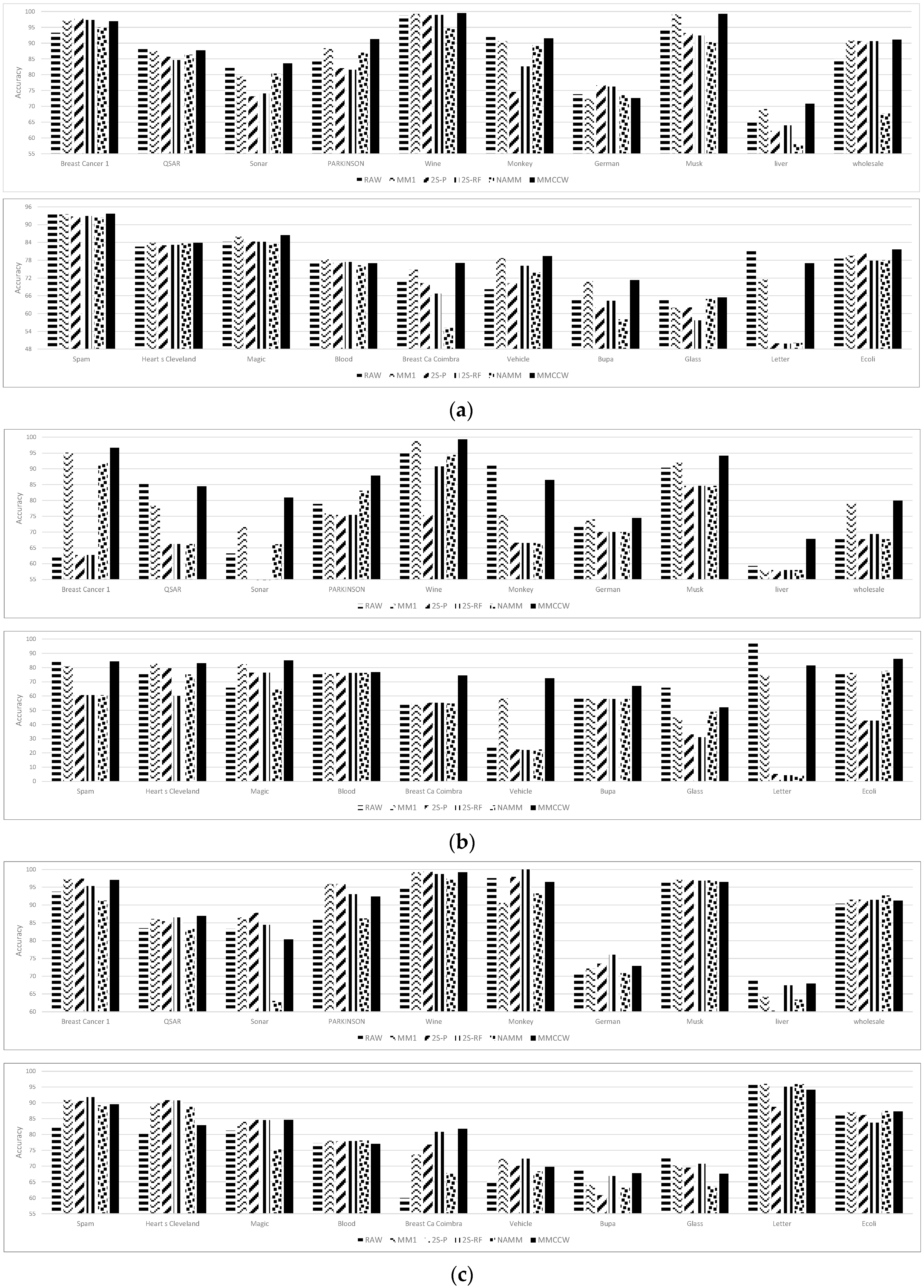
| Dataset | RAW | MM | 2S-P | 2S-RF | NAMM | CCMMW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer 1 | 93.29 | 97.05 | 97.73 | 97.29 | 94.97 | 96.89 |
| QSAR | 88.11 | 87.46 | 85.69 | 84.61 | 86.33 | 87.75 |
| Sonar | 82.16 | 79.42 | 73.19 | 74.02 | 80.32 | 83.56 |
| PARKINSON | 84.13 | 88.35 | 82.08 | 81.58 | 86.98 | 91.27 |
| Wine | 98.82 | 99.25 | 98.87 | 98.93 | 94.66 | 99.47 |
| Monkey | 91.88 | 90.64 | 74.55 | 82.59 | 89.34 | 91.50 |
| German | 73.82 | 72.35 | 76.66 | 76.20 | 73.53 | 72.56 |
| Musk | 94.33 | 99.12 | 93.18 | 92.38 | 90.26 | 99.27 |
| liver | 65.33 | 69.17 | 62.26 | 63.91 | 57.98 | 70.85 |
| wholesale | 84.98 | 90.75 | 90.59 | 90.61 | 67.73 | 91.14 |
| Spam | 94.10 | 93.47 | 92.72 | 92.86 | 92.41 | 93.68 |
| Heart s Cleveland | 82.58 | 83.86 | 82.99 | 83.13 | 83.65 | 83.83 |
| Magic | 84.22 | 85.87 | 84.28 | 84.21 | 83.48 | 86.40 |
| Blood | 76.88 | 78.22 | 77.16 | 77.38 | 76.21 | 76.98 |
| Breast Ca Coimbra | 71.49 | 74.80 | 70.28 | 66.74 | 55.19 | 77.05 |
| Vehicle | 68.14 | 78.68 | 70.24 | 76.08 | 73.85 | 79.41 |
| Bupa | 65.23 | 70.94 | 62.09 | 64.35 | 57.98 | 71.25 |
| Glass | 64.88 | 61.98 | 62.11 | 57.65 | 64.87 | 65.45 |
| Letter | 81.94 | 71.46 | 49.96 | 49.81 | 50.14 | 76.92 |
| Ecoli | 78.51 | 79.55 | 80.22 | 77.80 | 78.00 | 81.65 |
| Dataset | RAW | MM | 2S-P | 2S-RF | NAMM | CCMMW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer 1 | 62.74 | 95.11 | 62.74 | 62.74 | 91.79 | 96.61 |
| QSAR | 85.41 | 78.34 | 66.25 | 66.25 | 66.25 | 84.47 |
| Sonar | 63.19 | 71.54 | 53.38 | 52.69 | 66.13 | 80.87 |
| PARKINSON | 78.86 | 75.89 | 75.38 | 75.39 | 83.07 | 87.86 |
| Wine | 95.03 | 98.81 | 75.35 | 90.77 | 94.37 | 99.30 |
| Monkey | 91.37 | 75.30 | 66.56 | 66.54 | 66.55 | 86.48 |
| German | 71.78 | 74.07 | 70.00 | 70.00 | 70.00 | 74.45 |
| Musk | 90.39 | 91.93 | 84.59 | 84.59 | 84.59 | 94.16 |
| liver | 59.28 | 57.97 | 57.98 | 57.95 | 58.00 | 67.80 |
| wholesale | 67.73 | 79.27 | 67.73 | 69.32 | 67.73 | 79.93 |
| Spam | 83.90 | 80.92 | 60.60 | 60.60 | 60.60 | 84.30 |
| Heart s Cleveland | 76.97 | 82.62 | 79.50 | 59.96 | 75.10 | 83.03 |
| Magic | 65.87 | 82.28 | 76.38 | 76.49 | 64.84 | 85.08 |
| Blood | 75.24 | 76.21 | 76.21 | 76.21 | 76.20 | 76.70 |
| Breast Ca Coimbra | 55.20 | 54.67 | 55.18 | 55.17 | 54.69 | 74.31 |
| Vehicle | 23.99 | 58.22 | 22.33 | 22.03 | 22.31 | 72.48 |
| Bupa | 59.34 | 57.98 | 57.95 | 57.97 | 57.97 | 67.05 |
| Glass | 65.75 | 44.93 | 32.88 | 31.06 | 48.97 | 51.95 |
| Letter | 97.52 | 74.82 | 5.20 | 4.30 | 3.85 | 81.42 |
| Ecoli | 75.84 | 76.22 | 42.55 | 42.56 | 77.71 | 86.05 |
| Dataset | RAW | MM | 2S-P | 2S-RF | NAMM | CCMMW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer 1 | 93.75 | 97.24 | 97.38 | 95.36 | 91.20 | 97.02 |
| QSAR | 83.47 | 86.06 | 85.43 | 86.53 | 83.25 | 86.97 |
| Sonar | 83.34 | 86.53 | 87.83 | 84.40 | 63.02 | 80.28 |
| PARKINSON | 85.75 | 95.86 | 95.89 | 93.01 | 86.20 | 92.37 |
| Wine | 95.34 | 99.23 | 99.32 | 98.71 | 97.42 | 99.23 |
| Monkey | 97.59 | 90.61 | 97.88 | 100.00 | 93.27 | 96.50 |
| German | 71.00 | 72.12 | 73.48 | 76.05 | 70.87 | 72.89 |
| Musk | 96.92 | 97.08 | 96.97 | 96.84 | 96.87 | 96.48 |
| liver | 69.20 | 64.15 | 60.30 | 67.44 | 63.37 | 67.87 |
| wholesale | 90.39 | 91.55 | 91.50 | 91.43 | 92.70 | 91.20 |
| Spam | 82.47 | 90.88 | 90.55 | 91.83 | 89.20 | 89.57 |
| Hearts Cleveland | 80.74 | 89.79 | 90.86 | 90.78 | 88.71 | 82.89 |
| Magic | 81.23 | 83.99 | 84.67 | 84.56 | 75.24 | 84.64 |
| Blood | 77.23 | 78.00 | 77.85 | 77.92 | 78.06 | 77.05 |
| Breast Ca Coimbra | 59.97 | 73.64 | 76.78 | 80.84 | 67.82 | 81.82 |
| Vehicle | 65.50 | 72.26 | 70.12 | 72.32 | 68.31 | 69.73 |
| Bupa | 69.24 | 64.12 | 60.89 | 66.84 | 63.24 | 67.75 |
| Glass | 73.33 | 70.18 | 69.50 | 70.74 | 63.68 | 67.61 |
| Letter | 96.00 | 96.01 | 88.73 | 95.09 | 95.93 | 94.11 |
| Ecoli | 86.71 | 87.09 | 86.14 | 83.73 | 87.47 | 87.26 |
| Dataset | RAW | MM | 2S-P | 2S-RF | NAMM | CCMMW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer 1 | 91.39 | 96.70 | 97.50 | 96.73 | 92.20 | 96.77 |
| QSAR | 85.48 | 87.19 | 85.33 | 84.67 | 86.01 | 87.44 |
| Sonar | 80.45 | 80.39 | 77.64 | 76.68 | 57.38 | 81.16 |
| PARKINSON | 78.28 | 87.30 | 84.36 | 86.14 | 83.29 | 89.54 |
| Wine | 96.11 | 99.55 | 99.16 | 98.00 | 96.23 | 99.57 |
| Monkey | 77.13 | 84.91 | 78.32 | 86.33 | 80.23 | 77.61 |
| German | 76.02 | 72.73 | 76.58 | 76.26 | 71.52 | 72.62 |
| Musk | 94.36 | 97.26 | 91.64 | 90.23 | 84.59 | 97.50 |
| liver | 67.29 | 70.72 | 69.10 | 69.36 | 57.99 | 71.38 |
| wholesale | 83.55 | 90.66 | 90.50 | 90.86 | 67.73 | 91.73 |
| Spam | 83.64 | 93.18 | 90.16 | 90.16 | 89.51 | 93.40 |
| Heart s Cleveland | 73.61 | 85.08 | 82.89 | 83.77 | 83.90 | 83.66 |
| Magic | 77.93 | 84.25 | 82.35 | 82.32 | 76.60 | 85.65 |
| Blood | 78.20 | 79.05 | 78.34 | 78.14 | 76.27 | 75.95 |
| Breast Ca Coimbra | 64.01 | 67.11 | 71.56 | 71.83 | 68.85 | 75.40 |
| Vehicle | 50.64 | 79.14 | 61.62 | 63.87 | 54.78 | 77.17 |
| Bupa | 65.89 | 71.17 | 69.47 | 69.45 | 57.97 | 71.51 |
| Glass | 54.53 | 60.36 | 62.09 | 55.73 | 54.68 | 63.57 |
| Letter | 24.62 | 34.36 | 21.77 | 33.60 | 34.11 | 44.27 |
| Ecoli | 81.34 | 82.67 | 71.16 | 75.06 | 82.31 | 82.82 |
| Dataset | RAW | MM | 2S-P | 2S-RF | NAMM | CCMMW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer 1 | 96.08 | 95.91 | 96.33 | 96.22 | 96.24 | 96.45 |
| QSAR | 87.00 | 87.13 | 87.20 | 87.05 | 87.17 | 87.13 |
| Sonar | 82.73 | 82.77 | 83.16 | 82.42 | 82.38 | 83.71 |
| PARKINSON | 91.06 | 90.85 | 90.38 | 90.70 | 90.63 | 91.58 |
| Wine | 99.52 | 99.50 | 99.50 | 99.52 | 99.50 | 99.51 |
| Monkey | 99.79 | 99.68 | 99.66 | 99.87 | 99.53 | 100.0 |
| German | 76.22 | 76.33 | 76.47 | 76.39 | 76.28 | 76.81 |
| Musk | 97.81 | 97.81 | 97.84 | 97.83 | 97.86 | 97.86 |
| liver | 72.36 | 72.88 | 73.46 | 72.99 | 72.80 | 70.76 |
| wholesale | 91.23 | 91.11 | 91.25 | 91.18 | 90.80 | 91.39 |
| Spam | 95.44 | 95.49 | 95.47 | 95.42 | 95.41 | 95.55 |
| Heart s Cleveland | 93.79 | 93.85 | 93.57 | 93.71 | 93.41 | 90.01 |
| Magic | 88.15 | 88.05 | 88.09 | 88.12 | 88.09 | 87.85 |
| Blood | 73.88 | 74.25 | 73.82 | 73.95 | 73.89 | 76.69 |
| Breast Ca Coimbra | 70.39 | 71.61 | 71.47 | 69.48 | 71.67 | 73.58 |
| Vehicle | 74.93 | 74.77 | 74.96 | 74.98 | 74.82 | 74.96 |
| Bupa | 72.42 | 73.23 | 72.47 | 72.91 | 72.77 | 70.81 |
| Glass | 78.78 | 78.40 | 78.61 | 79.39 | 79.86 | 78.98 |
| Letter | 96.62 | 96.60 | 96.57 | 96.61 | 96.60 | 96.18 |
| Ecoli | 86.79 | 86.91 | 87.13 | 86.63 | 86.73 | 85.89 |
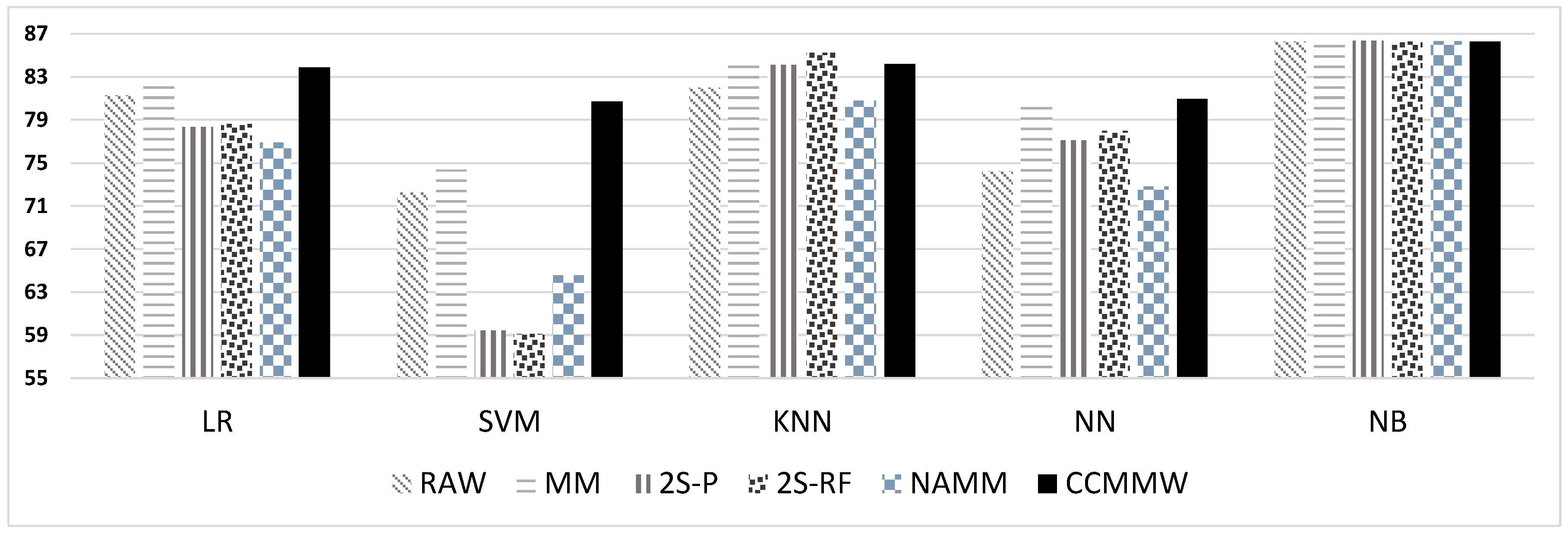
| Method | RAW | MM | 2S-P | 2S-RF | NAMM | CCMMW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 81.24 | 82.62 | 78.34 | 78.61 | 76.9 | 83.84 |
| SVM | 72.27 | 74.36 | 59.44 | 59.13 | 64.54 | 80.72 |
| KNN | 81.96 | 84.32 | 84.10 | 85.22 | 80.79 | 84.16 |
| NN | 74.22 | 80.19 | 77.08 | 77.96 | 72.81 | 80.94 |
| NB | 86.25 | 86.36 | 86.37 | 86.27 | 86.32 | 86.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shantal, M.; Othman, Z.; Bakar, A.A. A Novel Approach for Data Feature Weighting Using Correlation Coefficients and Min–Max Normalization. Symmetry 2023, 15, 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15122185
Shantal M, Othman Z, Bakar AA. A Novel Approach for Data Feature Weighting Using Correlation Coefficients and Min–Max Normalization. Symmetry. 2023; 15(12):2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15122185
Chicago/Turabian StyleShantal, Mohammed, Zalinda Othman, and Azuraliza Abu Bakar. 2023. "A Novel Approach for Data Feature Weighting Using Correlation Coefficients and Min–Max Normalization" Symmetry 15, no. 12: 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15122185
APA StyleShantal, M., Othman, Z., & Bakar, A. A. (2023). A Novel Approach for Data Feature Weighting Using Correlation Coefficients and Min–Max Normalization. Symmetry, 15(12), 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15122185






