An Improved Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Based on Angle Preference
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Multi-Objective Optimization
2.2. Particle Swarm Optimization
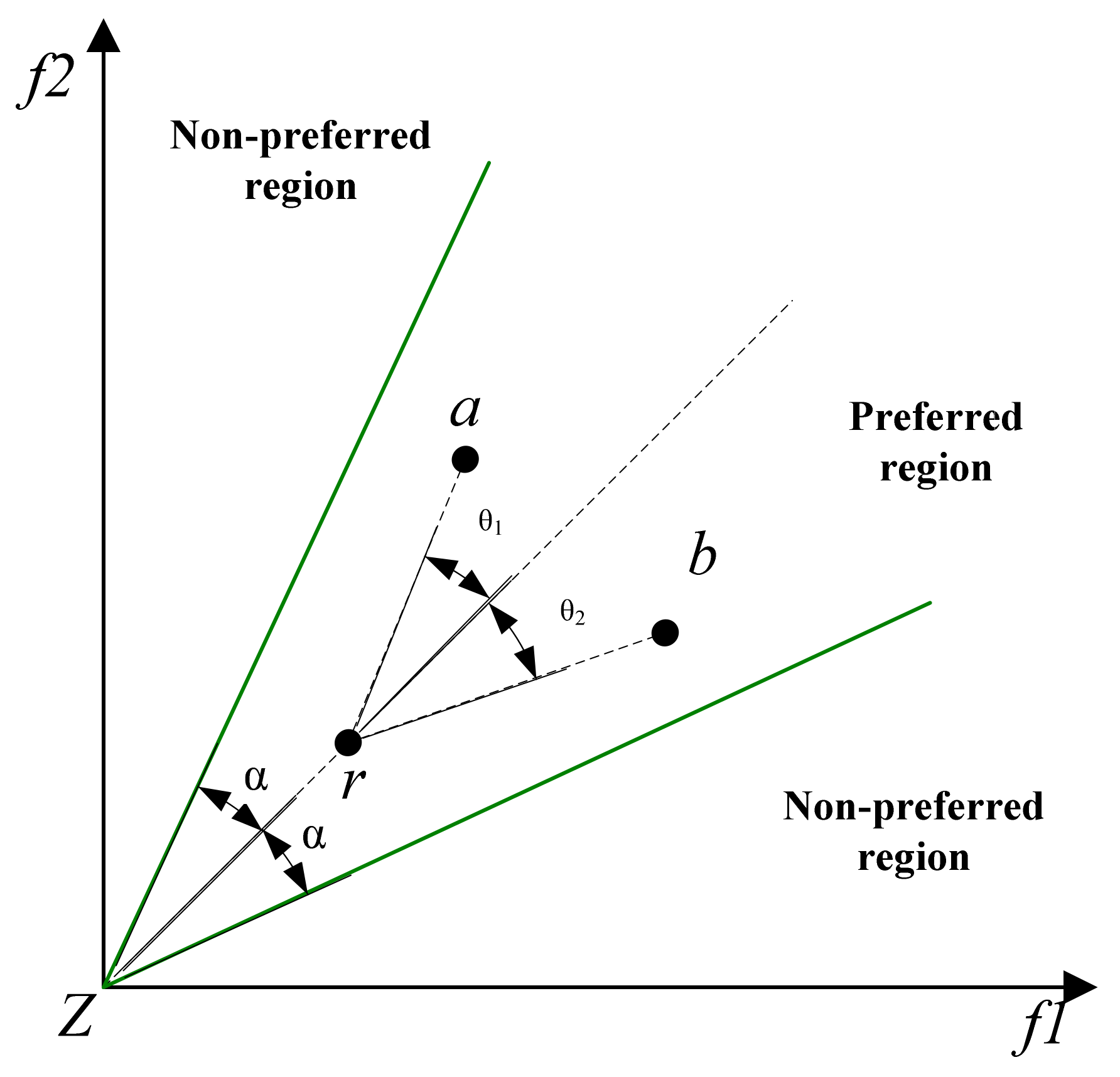
2.3. Angle Preference Domination Relationship
3. The Proposed MOPSO Algorithm Based on Angle Preference
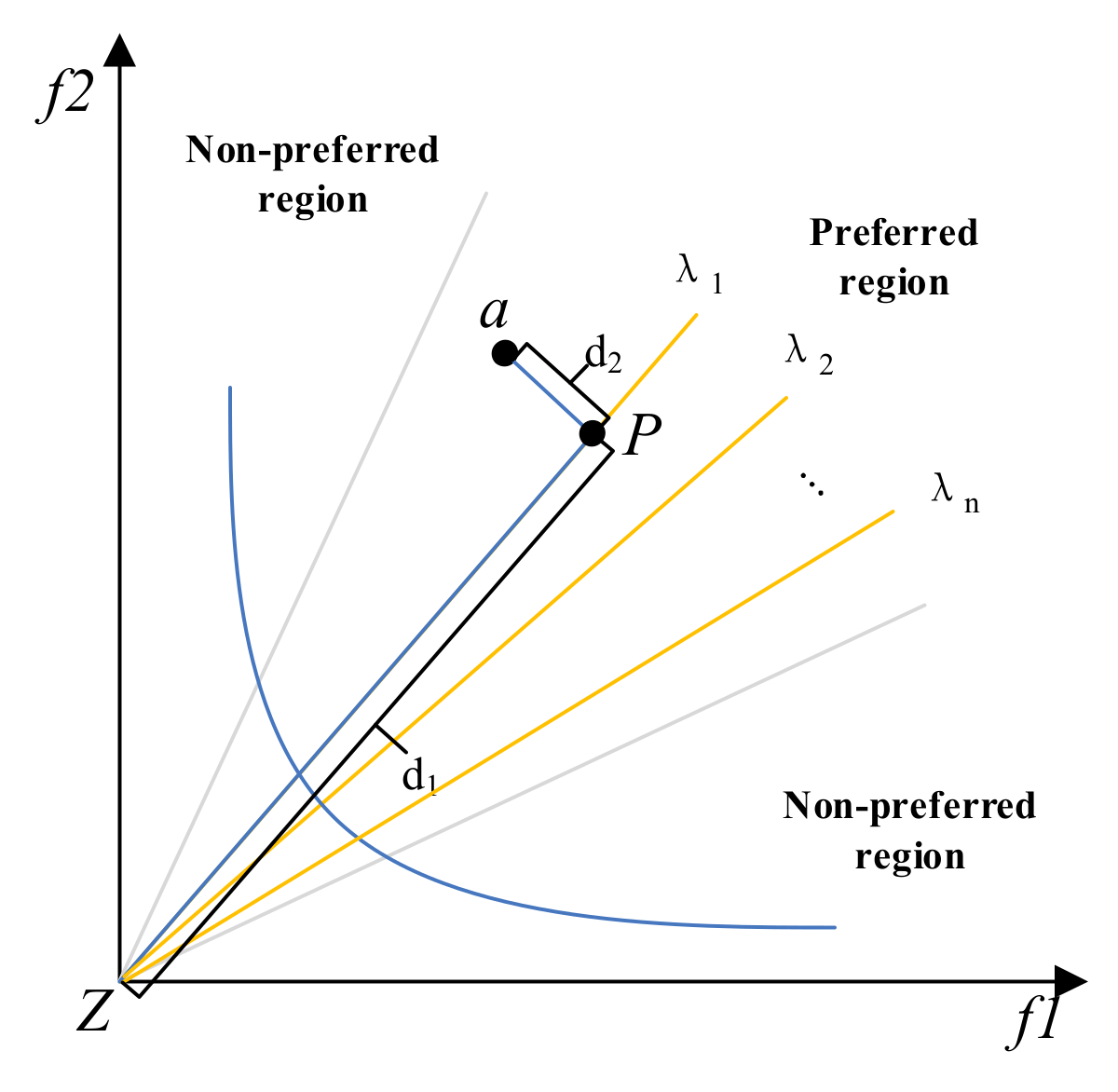
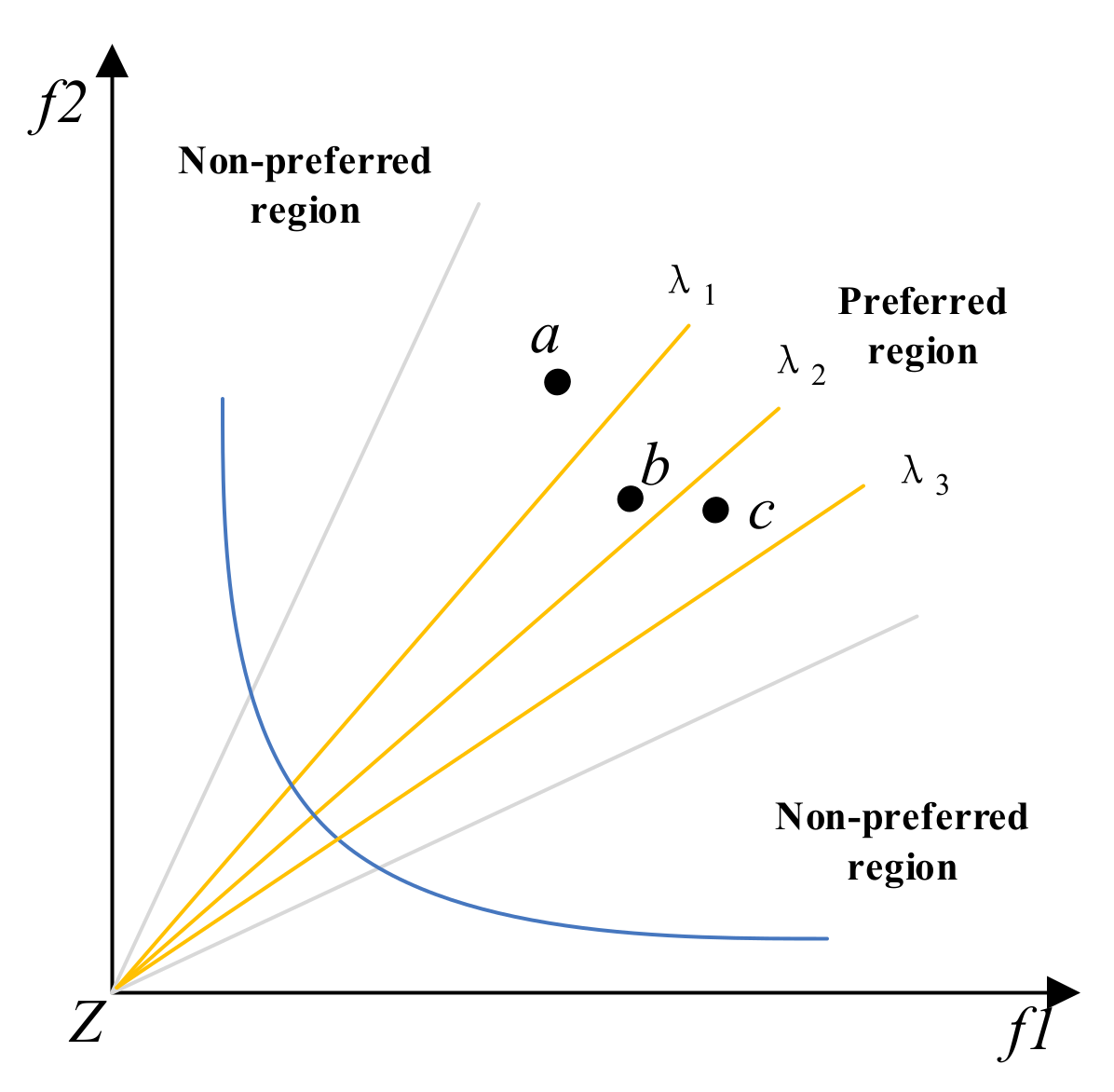
3.1. The Update Strategy of the Angle Preference-Based External Archive
| Algorithm 1 Update external archive. |
| Input:Ar (external archive), λ (reference vector), α (preference angle) Output: Ar’ (updated external archive), |
| Generating a set of uniformly distributed reference vectors in the range of preference angle. For i = 1 to size (Ar) do Associate the closest reference vector with particle Pi. End While size (Ar‘) < size (Ar) While not all the reference vectors have been selected λi ← Randomly select an unselected reference vector Pi ← Select a particle from search particle with minimum d forλi Remove Pi from search particle Ar‘ = Ar‘ Pi Associate λi with Pi End Remove the selection trace of the reference vector. End |
3.2. The Update Strategy of Individual Optimum
| Algorithm 2 Update individual optima |
| Input: P (population), λ (reference vector), α (preference angle) Output: optima (updated individual optima) |
| For i = 1 to size (P) do λi ← Associate the closest reference vector with Pi. λj ← Select the neighborhood vector of λi Ni ← Select the associating individual of λj If Ni: Pn ← Randomly take a particle in Ni If there exists dominance relationship between Pi and Pn optimai = non-dominated(Pi,Pn) else optimai = Randomly select from (Pi,Pn) End End End |
3.3. The Adaptive Adjustment Strategy of Preference Angle
3.4. The Steps of the Improved Angle Preference-Based MOPSO
| Algorithm 3 The proposed algorithm (IAPMOPSO) |
| Input:N (population size), λ (reference vector), α (preference angle), maxgen (maximal generation number) Output: Ar (archive) |
| P ← InitializeParticles (𝑁) Ar = ; Ar = Ar non-dominated solutions For i = 1 to maxgen do: Apply polynomial mutation strategy to particles according to Equation (11). optima = update individual optimum(P,λ, α) proposed in Algorithm 2. Update α with the strategy proposed in Section 3.3. Select the global leader and update the velocities and positions of the particles according to Equations (6) and (7). Ar = Update external archive (Ar,λ, α) proposed in Algorithm 1. End |
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Comparison on Test Functions
4.1.1. Test Functions and Parameters Setting
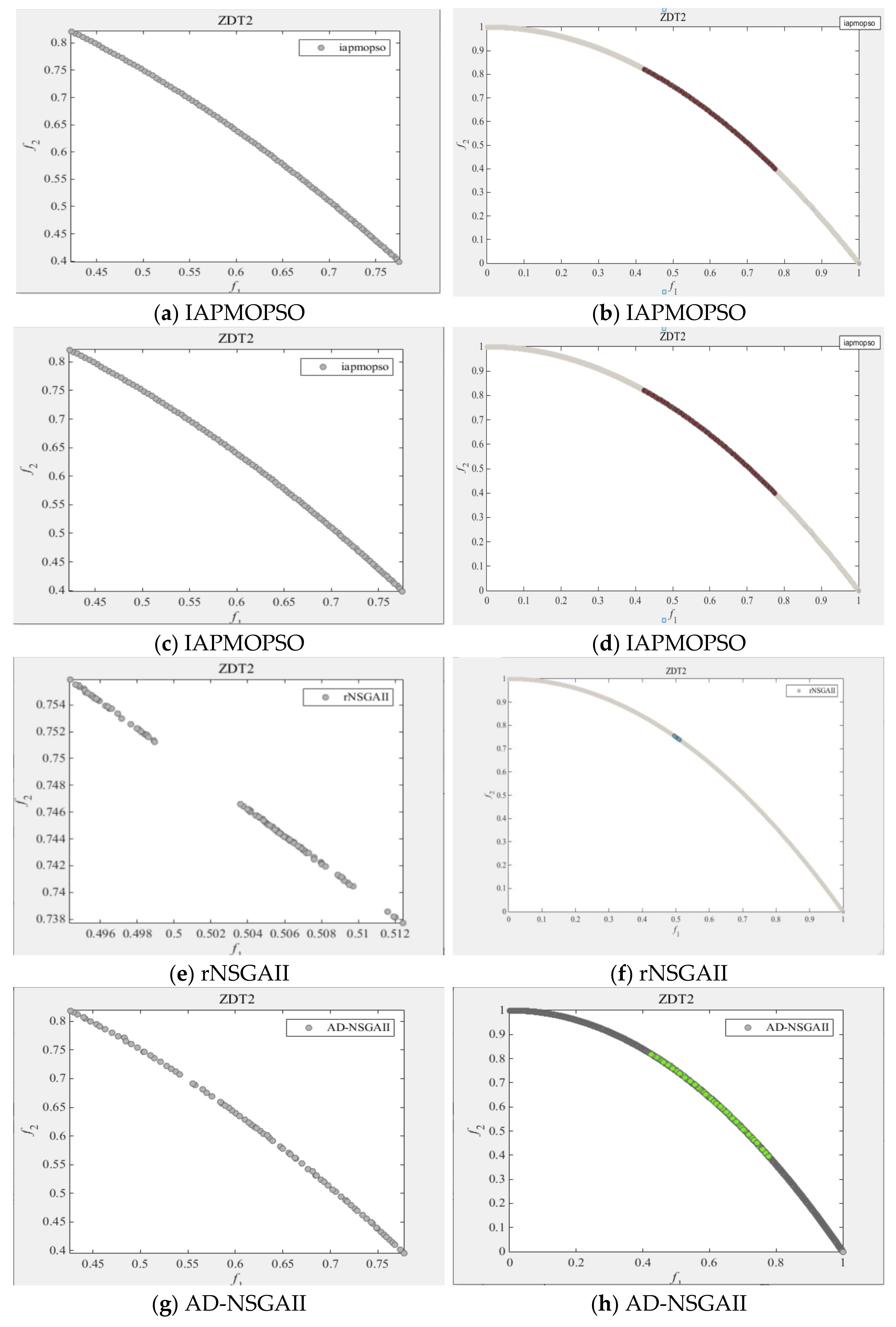
4.1.2. Simulation Results and Discussions
4.2. A Case Study of Portfolio Selection
4.2.1. Stock Dataset and Parameters Setting
4.2.2. Simulation Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, J.; Han, F.; Wang, J.; Ling, Q.H.; Han, H.; Wang, Y. A two-stage evolutionary algorithm for large-scale sparse multi-objective optimization problems. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 72, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zheng, M.P.; Ling, Q.H. An improved multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on tripartite competition mechanism. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 5784–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Feng, Z.; Wu, C.; Lei, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X. Multi-objective optimization of a tubular coreless lpmsm based on adaptive multi-objective black hole algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 53901–53910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 2182–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Jain, H. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference point-based nondominated sorting approach, Part I: Solving problems with box constraints. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2014, 18, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H. MOEA/D: A multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2007, 11, 712–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, E.; Laumanns, M.; Thiele, L. Spea2: Improving the Strength Pareto evolutionary Algorithm; Technical Report 103; Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH): Zurich, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrotas, G. Effective implementation of the ε-constraint method in multi-objective mathematical programming problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009, 213, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.C.; Fonseca, C.M.; Denysiuk, R.; Gaspar-Cunha, A. Methodology to select solutions for multiobjective optimization problems: Weighted stress function method. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 2017, 24, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Martínez, P.; Casado-Ceballos, A.; Sánchez-Oro, J.; Pardo, E.G. Multi-objective grasp for maximizing diversity. Electronics 2021, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, S.; Akbel, M.; Kahraman, H.T. Development of the multi-objective adaptive guided differential evolution and optimization of the MO-ACOPF for wind/PV/tidal energy sources. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 112, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, H.T.; Akbel, M.; Duman, S. Optimization of optimal power flow problem using multi-objective manta ray foraging optimizer. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 116, 108334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, R.; Sanfilippo, A.P.; Voß, S. Fixed set search applied to the multi-objective minimum weighted vertex cover problem. J. Heuristics 2022, 28, 481–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello, C.A.C.; Lechuga, M.S. MOPSO: A proposal for multiple objective particle swarm optimization. Proc. Congr. Evol. Comput. 2002, 2, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.Y.; Meng, X.; Qiao, J.F. A multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on two-archive mechanism. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 119, 108532. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Sierra, M.; Coello, C.C.A. Multi-objective particle swarm optimizers: A survey of the state-of-the-art. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Res. 2006, 2, 287–308. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. Multi/many-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on competition mechanism. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020, 5132803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Qu, B.; Liang, J. A multi-objective particle swarm optimizer using ring topology for solving multimodal multi-objective problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2017, 22, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboud, A.; Rokbani, N.; Fdhila, R.; Qahtani, A.M.; Almutiry, O.; Dhahri, H.; Hussain, A.; Alimi, A.M. DPb-MOPSO: A dynamic pareto bi-level multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 129, 109622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Safavi, H.R. f-MOPSO/Div: An improved extreme-point-based multi-objective PSO algorithm applied to a socio-economic-environmental conjunctive water use problem. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Bai, J.; He, H.; Peng, J.; Tang, D. Ar-moea: A novel preference-based dominance relation for evolutionary multi-objective optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 23, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Liu, Y. Preference-based multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for power network reconfiguration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Wellington, New Zealand, 10–13 June 2019; pp. 845–849. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Han, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, E.S. Preference-based solution selection algorithm for evolutionary multi-objective optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2012, 16, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Jiang, B.; Cai, J.H.; Qiu, F.Y. Multi-objective particle swarm optimization based on bipolar preferences control. Inf. Control 2009, 38, 711–717. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.F.; Zheng, J.H.; Hu, J.J.; Zou, J.; Yu, G. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for adaptive preference radius to divide region. J. Softw. 2017, 28, 2704–2721. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; He, Z.; Qian, Q. Study on multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on preference. Control Decis. 2009, 24, 66–87. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.W.; Wand, J.Q.; Zeng, J.W. Fuzzy preference ranking of multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm. Appl. Res. Comput. 2011, 28, 477–480. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.B. Preference multi-objective optimization algorithm with integrated guidance. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2016, 47, 3072–3078. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.B. Multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm with double thresholds based on preference information. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2016, 42, 492–498. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Huang, T.M.; Chen, S.Y. Multi-objective particle swarm optimization based on angle preference for ε-pareto domination. J. Xihua Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 37, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. Proc. Neural Netw. 1995, 4, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Nagra, A.A.; Han, F.; Ling, Q.H. An improved hybrid self-inertia weight adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm with local search. Eng. Optim. 2019, 51, 1115–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, B.R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Jing, Y.C. A cluster-based competitive particle swarm optimizer with a sparse truncation operator for multi-objective optimization. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 71, 101083. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Cai, T.; Li, K.S.; Pedrycz, W. Constraint handling technique based on Lebesgue measure for constrained multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 227, 107131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Li, H.C. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm using decomposition method and polynomial mutation operator. Microelectron. Comput. 2021, 38, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zitzler, E.; Deb, K.; Thiele, L. Comparison of multi-objective evolutionary algorithms: Empirical results. Evol. Comput. 2000, 8, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, K.; Thiele, L.; Laumanns, M.; Zitzler, E. Scalable multi-objective optimization test problems. Congress on Evolutionary Computation. In Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–17 May 2002; Volume 1, pp. 825–830. [Google Scholar]
- Said, L.B.; Bechikh, S.; Ghédira, K. The r-dominance: A new dominance relation for interactive evolutionary multicriteria decision making. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2010, 14, 801–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.H.; Xie, Z.Z. A study on how to use angle information to include decision maker’s preferences. Acta Electron. Sin. 2014, 42, 2239–2246. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W. Risk-based asset allocation: A new answer to an old question. J. Portf. Manag. 2011, 37, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





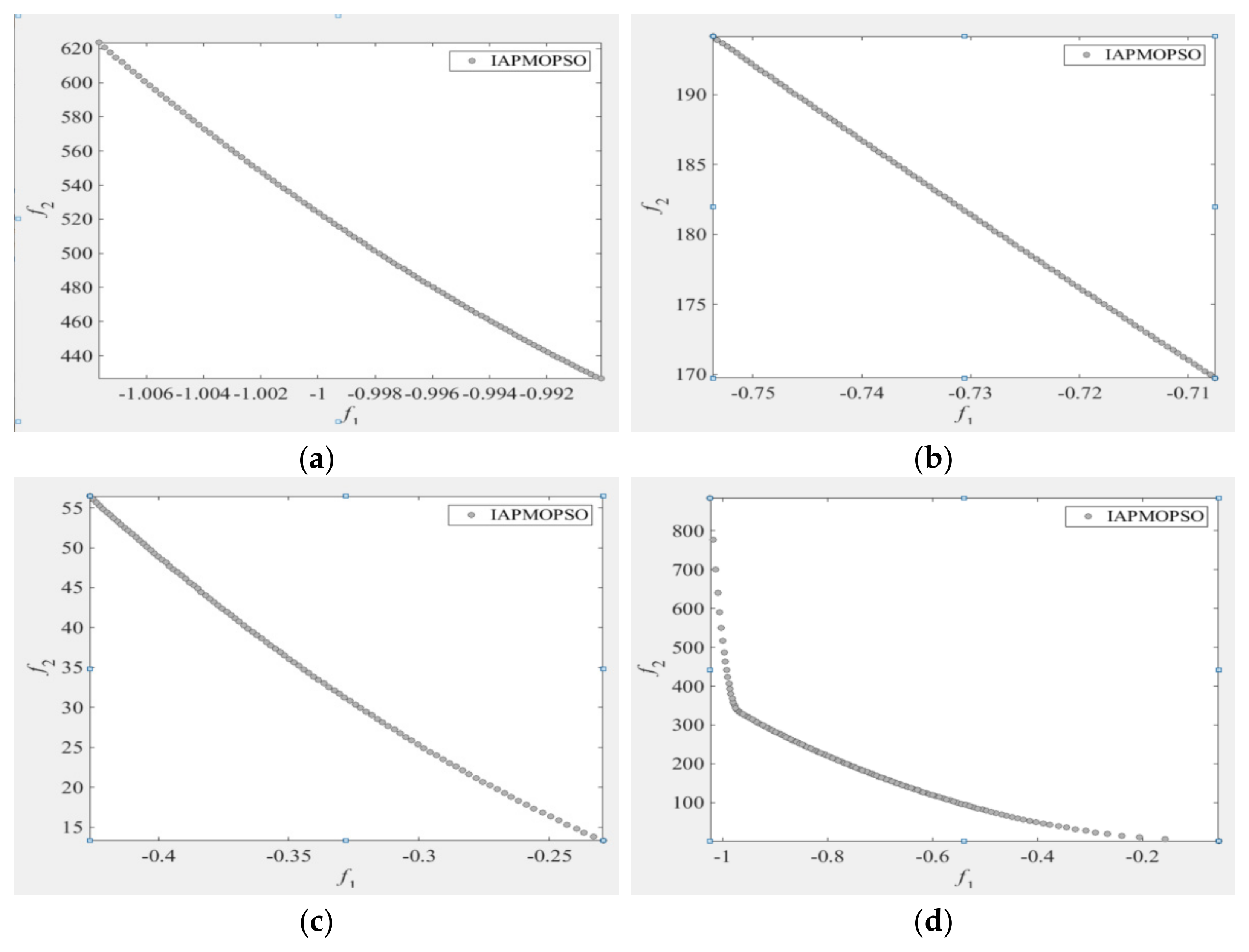
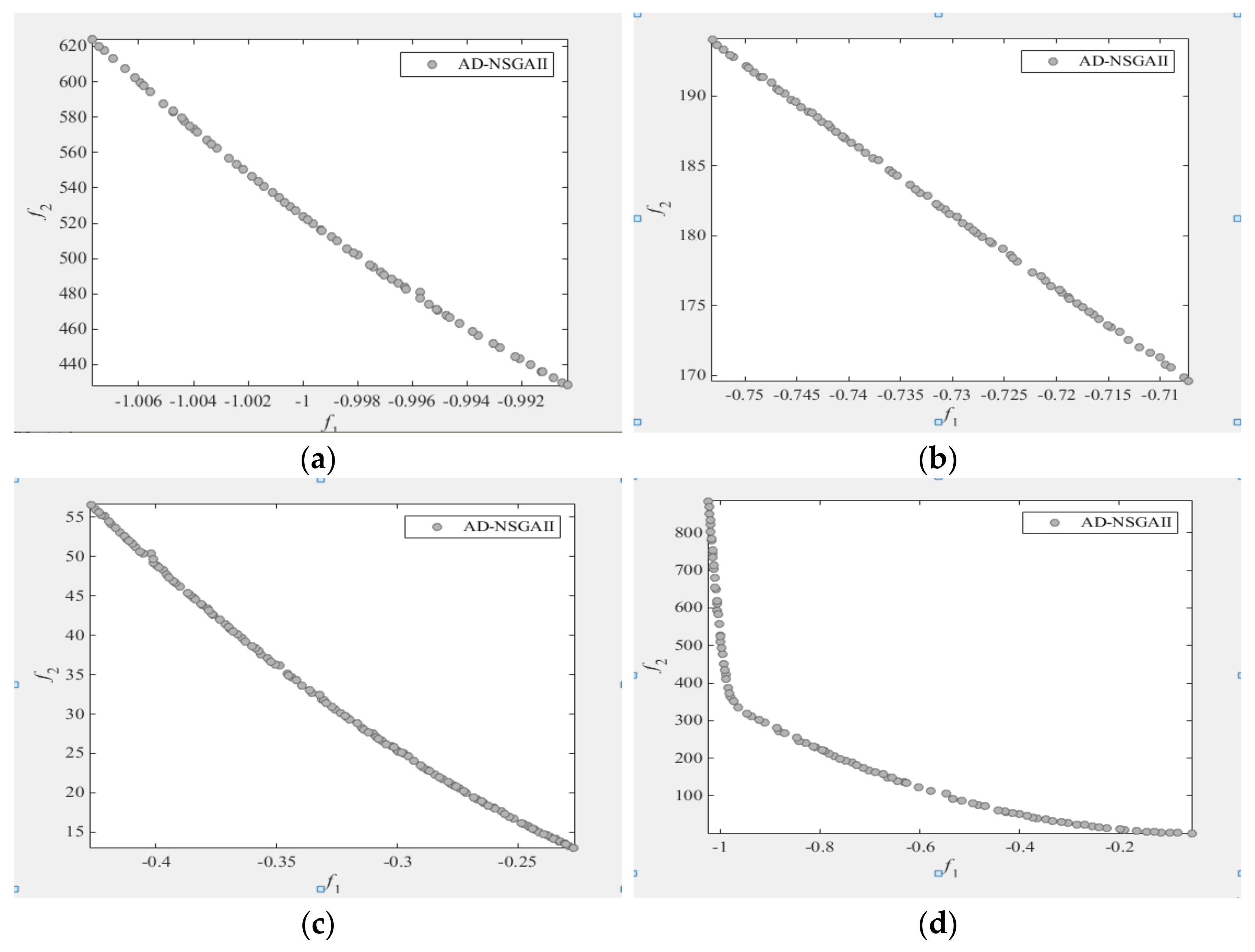
| Parameters | ZDT1 | ZDT2 | ZDT3 | DTLZ2 | DTLZ6 | DTLZ7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | (0.3,0.3) | (0.3,0.3) | (0.3,0.3) | (0.3,0.3,0.3) | (0.3,0.3,0.3) | (1,1,60) |
| α | π/10 | π/10 | π/10 | π/10 | π/10 | π/50 |
| Algorithms | ZDT1 | ZDT2 | ZDT3 | DTLZ2 | DTLZ6 | DTLZ7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAPMOPSO | Mean | 2.2991 × 10−5 | 4.7349 × 10−6 | 2.2991 × 10−5 | 1.5785 × 10−3 | 5.6561 × 10−6 | 1.8570 × 10−3 |
| Std. | 3.15 × 10−5 | 1.76 × 10−5 | 5.95 × 10−5 | 2.66 × 10−3 | 4.62 × 10−3 | 8.27 × 10−4 | |
| TAPMOPSO | Mean | 4.3431 × 10−5 | 6.4199 × 10−6 | 5.1350 × 10−5 | 2.4986 × 10−3 | 5.0829 × 10−6 | 4.4425 × 10−1 |
| Std. | 4.65 × 10−5 | 2.62 × 10−5 | 1.16 × 10−5 | 7.25 × 10−3 | 3.97 × 10−3 | 2.64 × 10−3 | |
| rNSGAII | Mean | 2.4729 × 10−5 | 2.8797 × 10−5 | 2.0818 × 10−5 | 2.042 × 10−3 | 5.2850 × 10−6 | 2.5596 × 10−3 |
| Std. | 9.131 × 10−6 | 1.3885 × 10−5 | 1.9942 × 10−5 | 5.8199 × 10−6 | 5.8142 × 10−6 | 8.2156 × 10−5 | |
| AD-NSGAII | Mean | 1.3089 × 10−4 | 6.0239 × 10−5 | 4.089 × 10−5 | 1.8935 × 10−3 | 9.3850 × 10−6 | 3.2414 × 10−3 |
| Std. | 2.6512 × 10−5 | 6.2153 × 10−6 | 9.2153 × 10−6 | 4.2182 × 10−5 | 3.2156 × 10−5 | 1.2512 × 10−6 | |
| Algorithms | ZDT1 | ZDT2 | ZDT3 | DTLZ2 | DTLZ6 | DTLZ7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAPMOPSO | Mean | 5.5395 × 10−1 | 3.2421 × 10−1 | 5.5395 × 10−1 | 2.8349 × 10−1 | 7.9856 × 10−2 | 2.0227 × 10−1 |
| Std. | 6.23 × 10−5 | 8.27 × 10−4 | 2.38 × 10−4 | 5.51 × 10−3 | 4.83 × 10−3 | 4.73 × 10−2 | |
| TAPMOPSO | Mean | 5.5117 × 10−1 | 3.1480 × 10−1 | 5.0881 × 10−1 | 2.7912 × 10−1 | 9.0344 × 10−2 | 1.9566 × 10−1 |
| Std. | 3.39 × 10−5 | 1.64 × 10−3 | 6.33 × 10−5 | 6.91 × 10−3 | 7.81 × 10−3 | 7.64 × 10−2 | |
| AD−NSGAII | Mean | 5.5072 × 10−1 | 3.2368 × 10−1 | 6.111 × 10−1 | 2.5329 × 10−1 | 9.0095 × 10−2 | 1.9595 × 10−1 |
| Std. | 6.746 × 10−5 | 3.342 × 10−4 | 2.6425 × 10−4 | 2.9543 × 10−4 | 8.5457 × 10−4 | 3.521 × 10−3 | |
| Parameters | Experiment 1 | Experiment 2 | Experiment 3 | Experiment 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | (1,5) | (2,1) | (20,1) | (1,1) |
| α | π/60 | π/60 | π/90 | π |
| Algorithms | Indicator | Experiment 1 | Experiment 2 | Experiment 3 | Experiment 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAPMOPSO | ) | 0.9986 | 0.731 | 0.3435 | 0.7887 |
| 512.78 | 182.04 | 35.81 | 308.53 | ||
| 0.001947 | 0.004016 | 0.009592 | 0.002556 | ||
| AD-NSGAII | 0.9994 | 0.7315 | 0.3271 | 0.7253 | |
| 521.573 | 182.3046 | 32.3651 | 300.2783 | ||
| 0001916 | 0.004013 | 0.010107 | 0.002415 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, Q.-H.; Tang, Z.-H.; Huang, G.; Han, F. An Improved Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Based on Angle Preference. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14122619
Ling Q-H, Tang Z-H, Huang G, Han F. An Improved Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Based on Angle Preference. Symmetry. 2022; 14(12):2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14122619
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Qing-Hua, Zhi-Hao Tang, Gan Huang, and Fei Han. 2022. "An Improved Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Based on Angle Preference" Symmetry 14, no. 12: 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14122619
APA StyleLing, Q.-H., Tang, Z.-H., Huang, G., & Han, F. (2022). An Improved Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Based on Angle Preference. Symmetry, 14(12), 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14122619





