Lateralized Declarative-Like Memory for Conditional Spatial Information in Domestic Chicks (Gallus gallus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Rearing Conditions
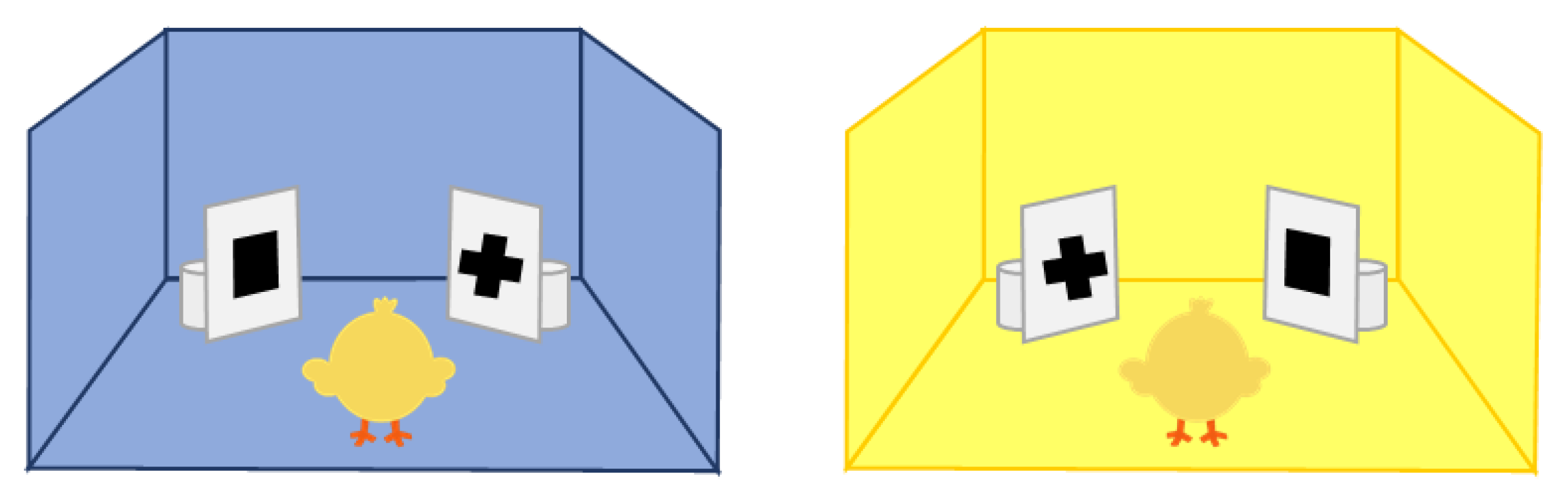
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Exposure Phase
2.4. Eye-Patching
2.5. Test
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Healy, S. Spatial Representation in Animals; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-19-850006-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Newcombe, N.S. Is There a Geometric Module for Spatial Orientation? Squaring Theory and Evidence. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2005, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landau, B.; Lakusta, L. Spatial Representation across Species: Geometry, Language, and Maps. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2009, 19, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulving, E.; Markowitsch, H.J. Episodic and Declarative Memory: Role of the Hippocampus. Hippocampus 1998, 8, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, H. DECLARATIVE MEMORY: Insights from Cognitive Neurobiology. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1997, 48, 547–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manns, J.R.; Eichenbaum, H. Evolution of Declarative Memory. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.; Dickinson, A.; Clayton, N.S. Episodic Memory: What Can Animals Remember about Their Past? Trends Cogn. Sci. (Regul. Ed.) 1999, 3, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillan, D.J.; Premack, D.; Woodruff, G. Reasoning in the Chimpanzee: I. Analogical Reasoning. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 1981, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gaffan, D. Amnesia for Complex Naturalistic Scenes and for Objects Following Fornix Transection in the Rhesus Monkey. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1992, 4, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusek, J.A.; Eichenbaum, H. The Hippocampus and Memory for Orderly Stimulus Relations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7109–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eacott, M.J.; Norman, G. Integrated Memory for Object, Place, and Context in Rats: A Possible Model of Episodic-like Memory? J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1948–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, N.S.; Dickinson, A. Memory for the Content of Caches by Scrub Jays (Aphelocoma Coerulescens). J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 1999, 25, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, N.S.; Dickinson, A. Scrub Jays (Aphelocoma Coerulescens) Remember the Relative Time of Caching as Well as the Location and Content of Their Caches. J. Comp. Psychol. 1999, 113, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forkman, B. Domestic Hens Have Declarative Representations. Anim. Cogn. 2000, 3, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.S.; Evans, L. Representational Signalling in Birds. Biol. Lett. 2007, 3, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, L.R. Declarative and Nondeclarative Memory: Multiple Brain Systems Supporting Learning and Memory. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1992, 4, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckee, R.D.; Squire, L.R. On the Development of Declarative Memory. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1993, 2, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzutti, C.; Vallortigara, G. Hemispheric Memories for the Content and Position of Food Caches in the Domestic Chick. Behav. Neurosci. 2001, 115, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Rogers, L.J. Differential Contributions of the Two Visual Pathways to Functional Lateralization in Chicks. Behav. Brain Res. 1997, 87, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Rogers, L.J. Bilaterally Projecting Neurons in the Two Visual Pathways of Chicks. Brain Res. 1998, 794, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiandetti, C.; Regolin, L.; Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G. Effects of Light Stimulation of Embryos on the Use of Position-Specific and Object-Specific Cues in Binocular and Monocular Domestic Chicks (Gallus gallus). Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 163, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekamp, B.; Prior, H.; Güntürkün, O. Functional Lateralization, Interhemispheric Transfer and Position Bias in Serial Reversal Learning in Pigeons (Columba livia). Anim. Cogn. 1999, 2, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, R.J.; Johnston, A.N.B.; Robins, A.; Rogers, L.J. Light Experience and the Development of Behavioural Lateralisation in Chicks: II. Choice of Familiar versus Unfamiliar Model Social Partner. Behav. Brain Res. 2004, 155, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiandetti, C. Manipulation of Strength of Cerebral Lateralization via Embryonic Light Stimulation in Birds. In Lateralized Brain Functions: Methods in Human and Non-Human Species; Neuromethods; Rogers, L.J., Vallortigara, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 611–631. ISBN 978-1-4939-6725-4. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Rogers, L.J. Social Recognition and Approach in the Chick: Lateralization and Effect of Visual Experience. Anim. Behav. 2002, 63, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugani, R.; Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L. Mapping Number to Space in the Two Hemispheres of the Avian Brain. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2016, 133, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daisley, J.N.; Mascalzoni, E.; Rosa-Salva, O.; Rugani, R.; Regolin, L. Lateralization of Social Cognition in the Domestic Chicken (Gallus gallus). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugani, R.; Regolin, L. Hemispheric Specialization in Spatial versus Ordinal Processing in the Day-Old Domestic Chick (Gallus gallus). Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1477, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolin, C.; Rosa-Salva, O.; Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L. Unsupervised Statistical Learning in Newly Hatched Chicks. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R1218–R1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L.; Marconato, F. Visually Inexperienced Chicks Exhibit Spontaneous Preference for Biological Motion Patterns. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 121533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means; 2018; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Versace, E.; Vallortigara, G. Origins of Knowledge: Insights from Precocial Species. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collie, R.; Hayne, H. Deferred Imitation by 6- and 9-Month-Old Infants: More Evidence for Declarative Memory. Dev. Psychobiol. 1999, 35, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayne, H.; Boniface, J.; Barr, R. The Development of Declarative Memory in Human Infants: Age-Related Changes in Deferred Imitation. Behav. Neurosci. 2000, 114, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daisley, J.N.; Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L. Logic in an Asymmetrical (Social) Brain: Transitive Inference in the Young Domestic Chick. Soc. Neurosci. 2010, 5, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Feruglio, M.; Sovrano, V.A. Reorientation by Geometric and Landmark Information in Environments of Different Size. Dev. Sci. 2005, 8, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugani, R.; Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L. The Use of Proportion by Young Domestic Chicks (Gallus gallus). Anim. Cogn. 2015, 18, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nottelmann, F.; Wohlschläger, A.; Güntürkün, O. Unihemispheric Memory in Pigeons-Knowledge, the Left Hemisphere Is Reluctant to Share. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 133, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisazza, A.; Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G. The Origins of Cerebral Asymmetry: A Review of Evidence of Behavioural and Brain Lateralization in Fishes, Reptiles and Amphibians. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1998, 22, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denenberg, V.H. Hemispheric Laterality in Animals and the Effects of Early Experience. Behav. Brain Sci. 1981, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekamp, B.; Regolin, L.; Güntürkün, O.; Vallortigara, G. A Left-Sided Visuospatial Bias in Birds. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, R372–R373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.J.; Zucca, P.; Vallortigara, G. Advantages of Having a Lateralized Brain. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, S420–S422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallortigara, G.; Rogers, L.J.; Bisazza, A. Possible Evolutionary Origins of Cognitive Brain Lateralization. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 30, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.; Andrew, R.J. Right Hemisphere Advantage for Topographical Orientation in the Domestic Chick. Neuropsychologia 1989, 27, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallortigara, G.; Andrew, R.J. Lateralization of Response by Chicks to Change in a Model Partner. Anim. Behav. 1991, 41, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, G.; Krebs, J.R.; Horn, G. Neural Bases of Recognition Memory Investigated through an Analysis of Imprinting. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1990, 329, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervé, P.-Y.; Zago, L.; Petit, L.; Mazoyer, B.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Revisiting Human Hemispheric Specialization with Neuroimaging. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corballis, M.C.; Manalo, R. Effect of Spatial Attention on Mental Rotation. Neuropsychologia 1993, 31, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapstone, M.; Weintraub, S.; Nowinski, C.; Kaptanoglu, G.; Gitelman, D.R.; Mesulam, M.-M. Cerebral Hemispheric Specialization for Spatial Attention: Spatial Distribution of Search-Related Eye Fixations in the Absence of Neglect. Neuropsychologia 2003, 41, 1396–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; der Haegen, L.V.; Brysbaert, M. Complementary Hemispheric Specialization for Language Production and Visuospatial Attention. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E322–E330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A. Automatic Activation of the Medial Temporal Lobe during Encoding: Lateralized Influences of Meaning and Novelty. Hippocampus 1999, 9, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, E.; Costa, L.D. Hemisphere Differences in the Acquisition and Use of Descriptive Systems. Brain Lang. 1981, 14, 144–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrington, E.K.; Broadbent, D.E.; Weiskrantz, L. Neuropsychological Studies of Object Recognition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1982, 298, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polk, T.A.; Stallcup, M.; Aguirre, G.K.; Alsop, D.C.; D’Esposito, M.; Detre, J.A.; Farah, M.J. Neural Specialization for Letter Recognition. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2002, 14, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellugi, U.; Poizner, H.; Klima, E.S. Language, Modality and the Brain. Trends Neurosci. 1989, 12, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowski, A.; Behrmann, M. Left Hemisphere Specialization for Word Reading Potentially Causes, Rather than Results from, a Left Lateralized Bias for High Spatial Frequency Visual Information. Cortex 2015, 72, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, E.H. Natural Preferences of Chicks and Ducklings for Objects of Different Colors. Psychol. Rep. 1956, 2, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, A.D.; Osorio, D. Colour Preferences and Colour Vision in Poultry Chicks. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L.; Pagni, P. Detour Behaviour, Imprinting and Visual Lateralization in the Domestic Chick. Cogn. Brain Res. 1999, 7, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.J.; Andrew, R.J.; Burne, T.H.J. Light Exposure of the Embryo and Development of Behavioural Lateralisation in Chicks, I: Olfactory Responses. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 97, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.J. Development and Function of Lateralization in the Avian Brain. Brain Res. Bull. 2008, 76, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A.; Conway, M.; Aggleton, J.; Clayton, N.S.; Griffiths, D.P.; Emery, N.J.; Dickinson, A. Elements of Episodic–like Memory in Animals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 356, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loconsole, M.; Mascalzoni, E.; Daisley, J.N.; De Agrò, M.; Vallortigara, G.; Regolin, L. Lateralized Declarative-Like Memory for Conditional Spatial Information in Domestic Chicks (Gallus gallus). Symmetry 2021, 13, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050906
Loconsole M, Mascalzoni E, Daisley JN, De Agrò M, Vallortigara G, Regolin L. Lateralized Declarative-Like Memory for Conditional Spatial Information in Domestic Chicks (Gallus gallus). Symmetry. 2021; 13(5):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050906
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoconsole, Maria, Elena Mascalzoni, Jonathan Niall Daisley, Massimo De Agrò, Giorgio Vallortigara, and Lucia Regolin. 2021. "Lateralized Declarative-Like Memory for Conditional Spatial Information in Domestic Chicks (Gallus gallus)" Symmetry 13, no. 5: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050906
APA StyleLoconsole, M., Mascalzoni, E., Daisley, J. N., De Agrò, M., Vallortigara, G., & Regolin, L. (2021). Lateralized Declarative-Like Memory for Conditional Spatial Information in Domestic Chicks (Gallus gallus). Symmetry, 13(5), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050906






