Future Technology: Software-Defined Network (SDN) Forensic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Discussing recent articles which investigate the research on network and cloud forensic from the security point of view.
- Providing various categories of network and cloud forensic, their relationship, and their comparison.
- Discussing SDN forensic and providing various approaches.
- Discussing the advantages of using SDN in network and cloud forensic.
- Investigating the challenges and issues of SDN in network and cloud forensic.
- Discussing future research directions of SDN in network and cloud forensic.
2. Backgrounds
2.1. Network Security
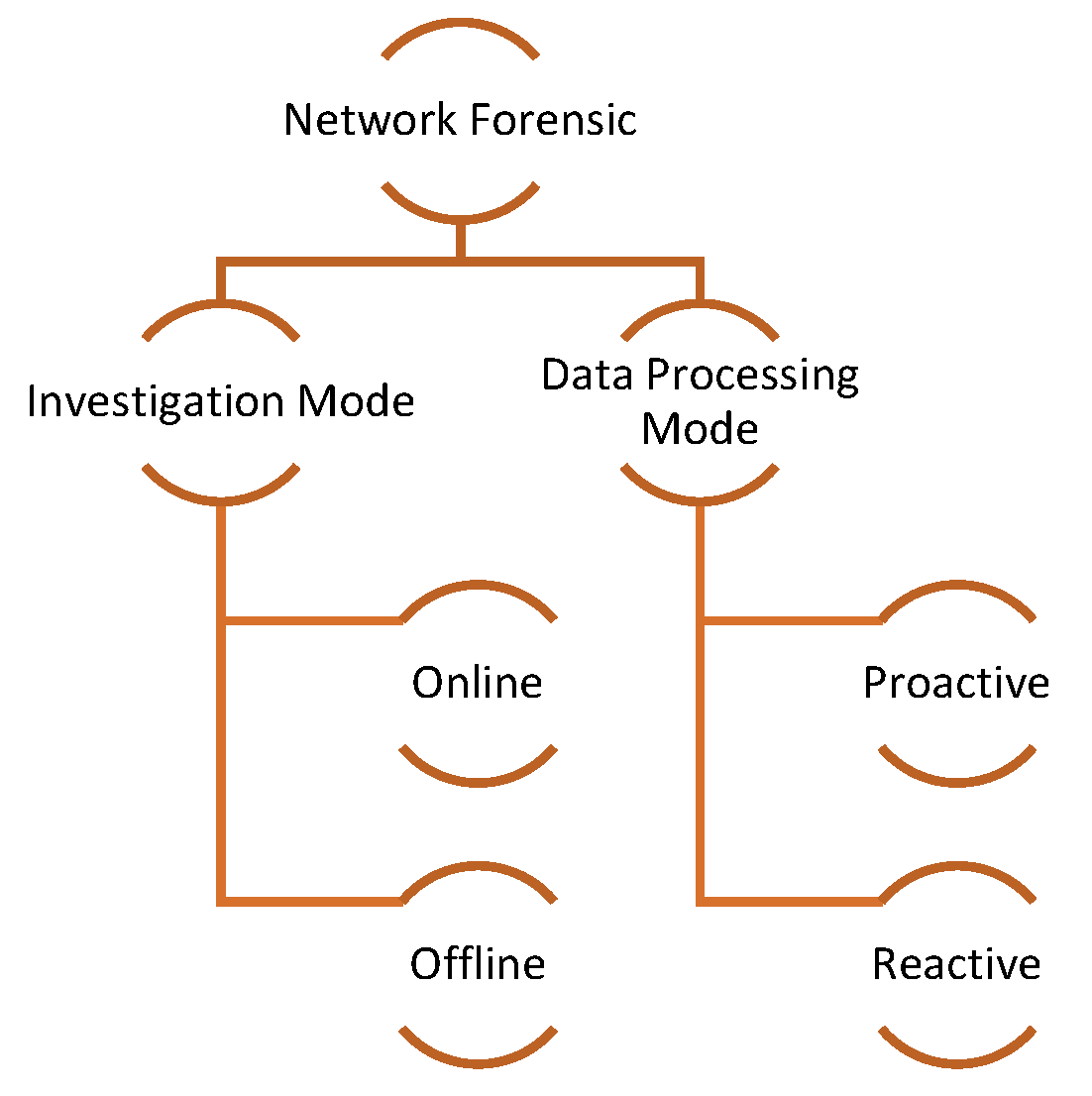
2.1.1. Network Forensics
2.1.2. Categories of Network Forensic
(Investigation Mode and Data Processing Mode Classification)
2.2. Relationship of Network and Cloud Forensic
2.3. Cloud Security
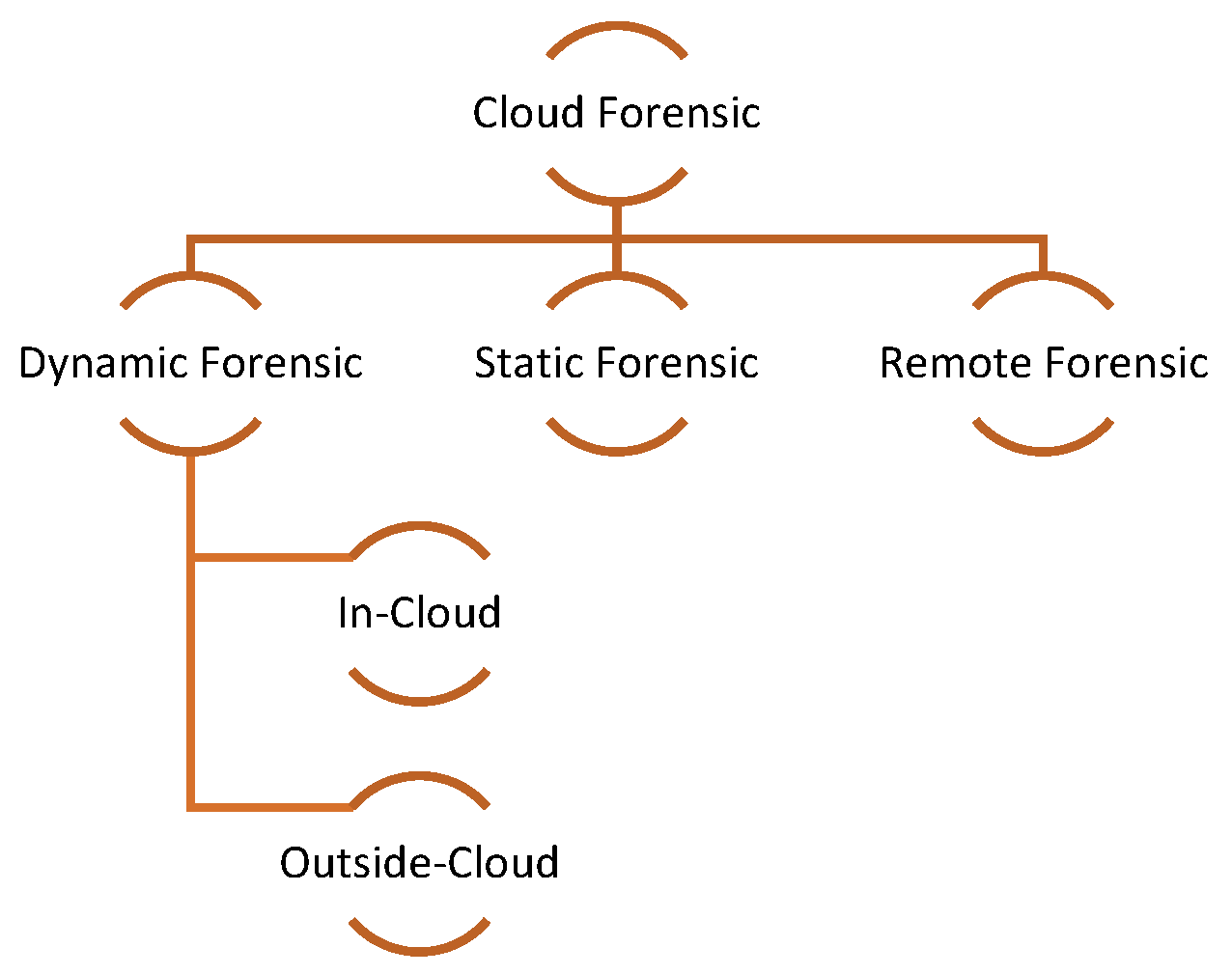
2.3.1. Cloud Forensic
2.3.2. Categories of Cloud Forensic
(Investigation Mode and Cloud Infrastructure Mode Classification)
3. Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
3.1. SDN Forensic
3.2. Security Approaches for SDN
3.2.1. Content Inspection
3.2.2. Traffic Monitoring and Auditing
3.3. Software-Defined Networking (SDN) for Network Forensic
3.3.1. Advantages of Using SDN in Network Forensic
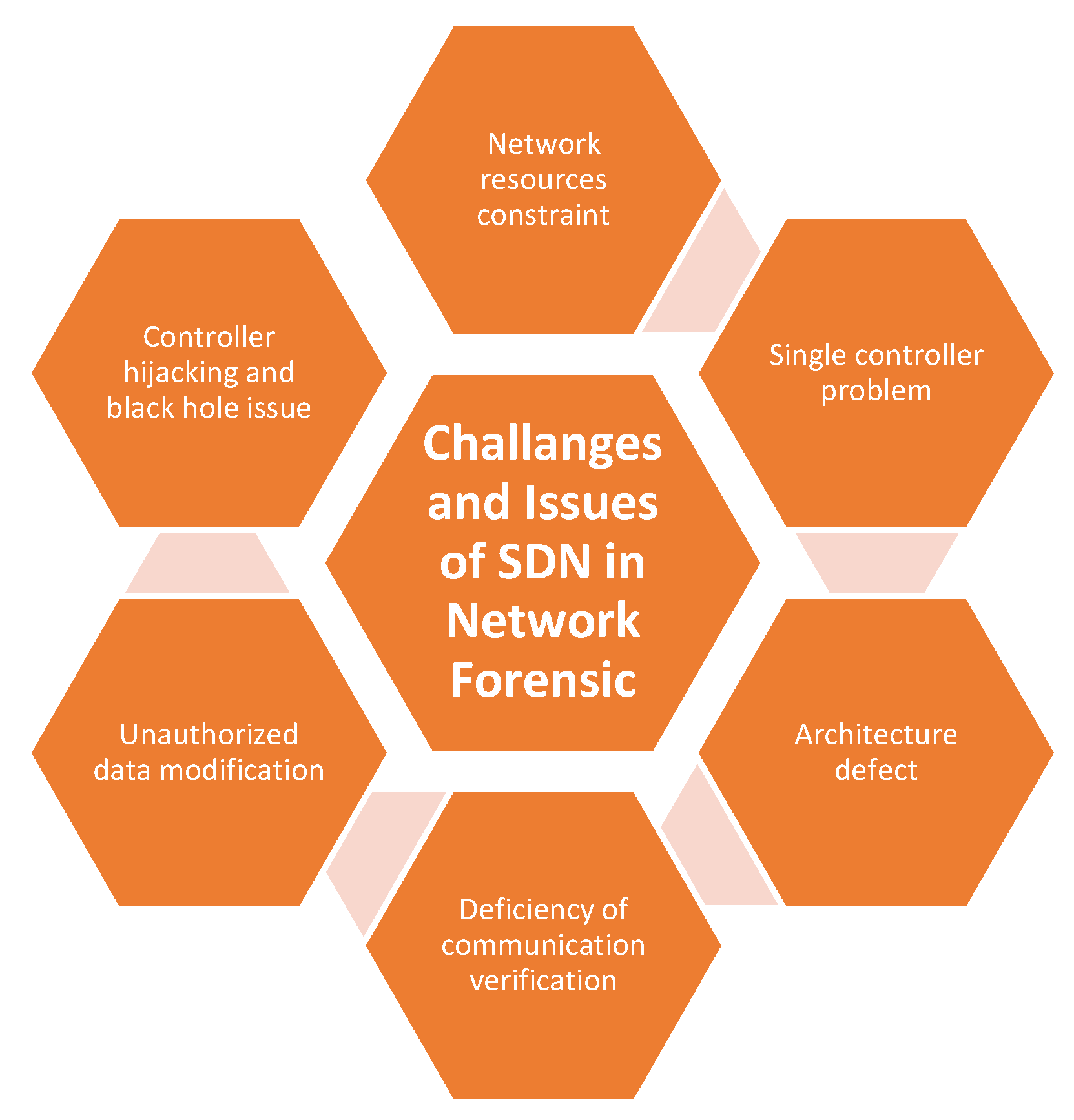
3.3.2. Challenges and Issues of SDN in Network Forensic
3.3.3. Future Research Directions of SDN in Network Forensic
3.4. Software-Defined Networking (SDN) for Cloud Forensic
3.4.1. Advantages of Using SDN in Cloud Forensic
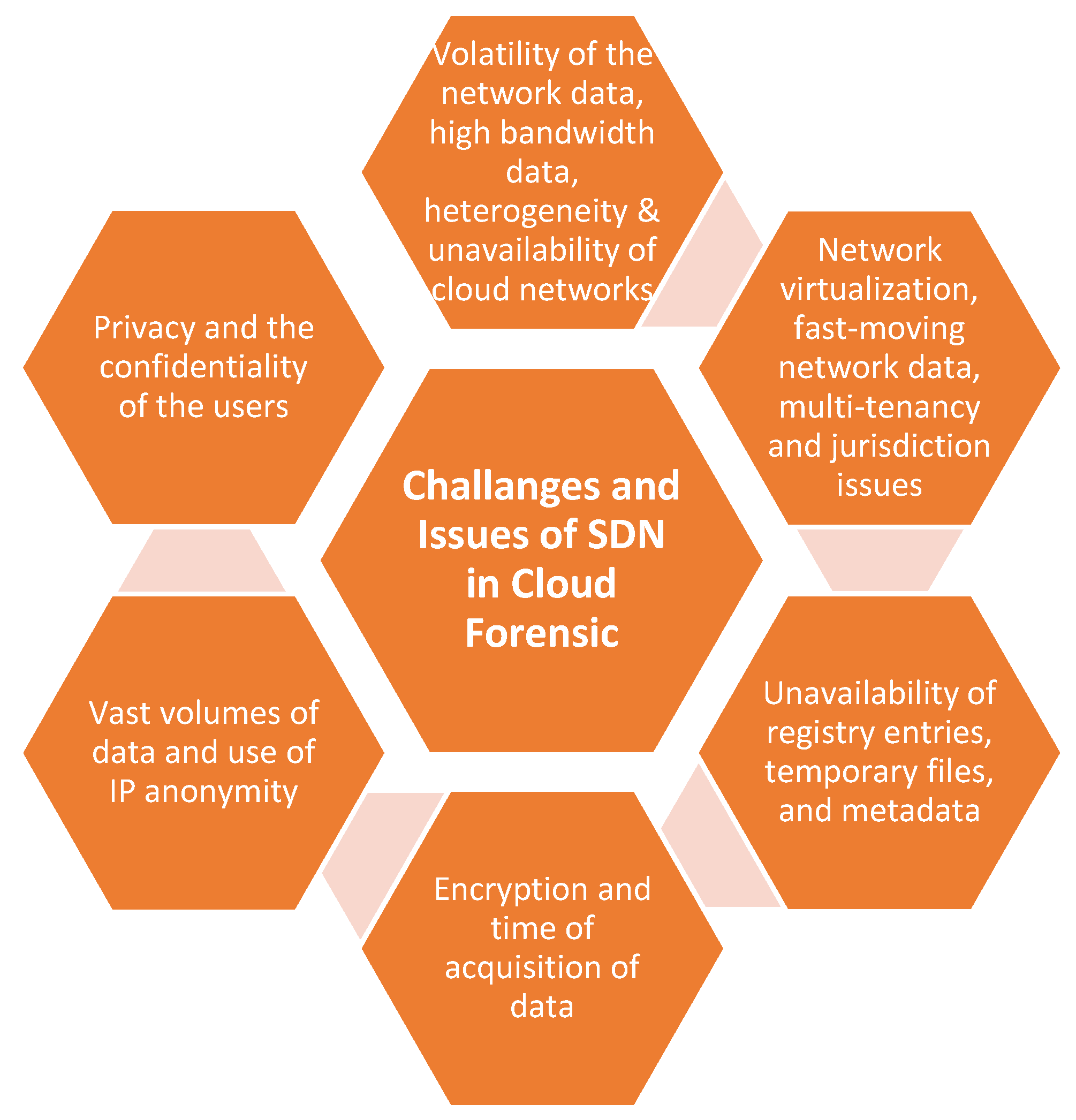
3.4.2. Challenges and Issues of Using SDN in Cloud Forensic
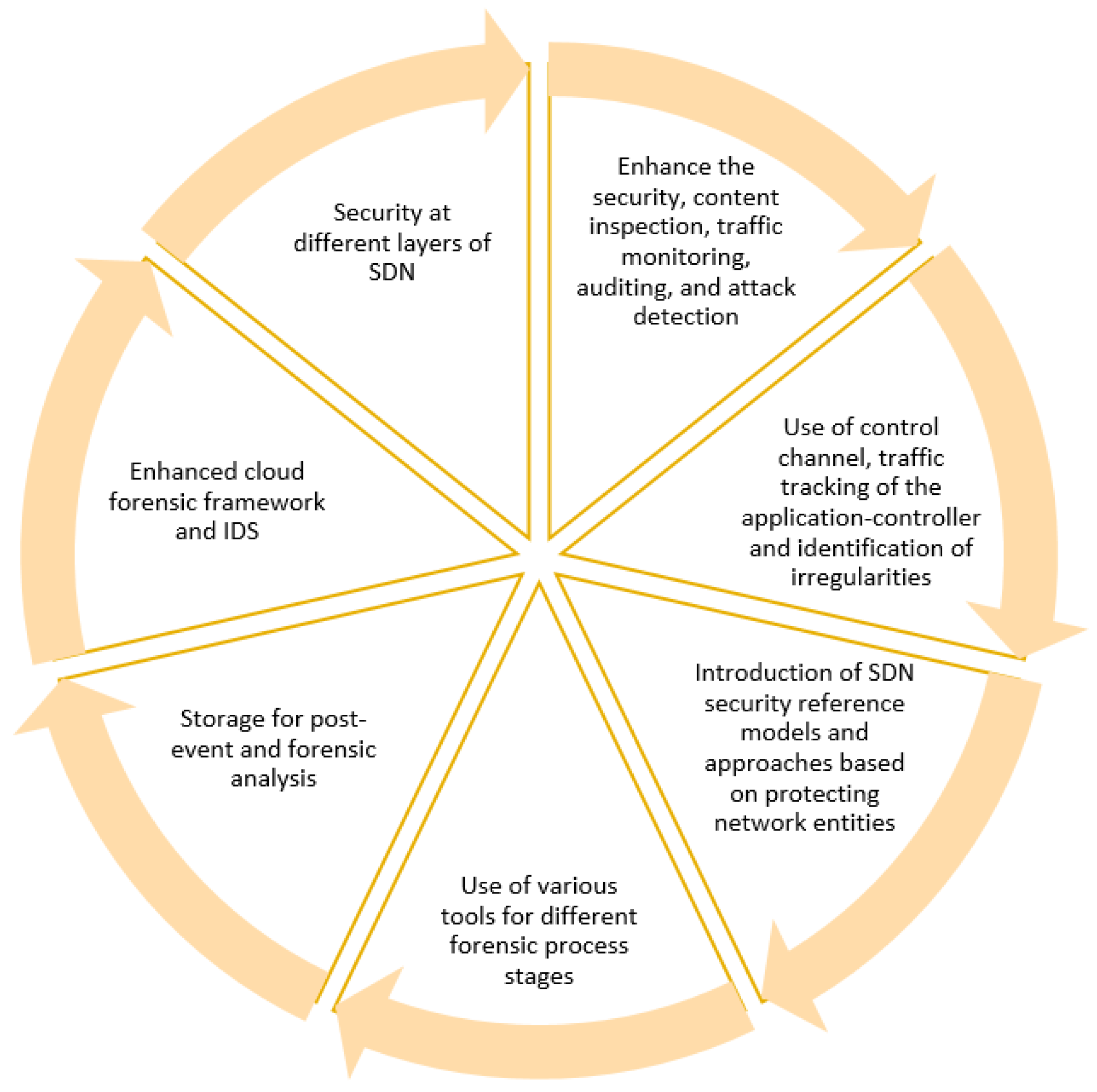
3.4.3. Future Research Directions of Using SDN in Cloud Forensic
3.5. Network Forensic Versus Cloud Forensic
4. Discussion
Recommendations
- To prevent disruption and protection compromises, SDN security reference models and approaches based on protecting network entities should be introduced.
- Using the control channel, traffic tracking of the application-controller and identification of irregularities in particular avenues, such as cloud setups can be implemented.
- Various methods and tools should be implemented to provide strong security in different forensic process stages.
- Different techniques should be used to provide strong security at different layers of SDN.
- It is possible to store and retrieve network/state data for post-event and forensic analysis for efficiency.
- Developing frameworks for the cloud forensic having ease to detect the attacks.
- Enhance the security, content inspection, traffic monitoring, auditing, and attack detection in cloud forensic.
- Creating enhanced Intrusion detection systems and improve their utilization in SDN.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full forms |
| CF | Cloud forensic |
| CS | Cloud security |
| CSP | Cloud service provider |
| DDoS | Distributed denial of service |
| DPI | Deep packet inspection |
| DoS | Denial of service |
| DPI | Deep packet inspection |
| NFI | Network forensics investigator |
| IaaS | Infrastructure as a service |
| ID | Intrusion detection |
| IDS | Intrusion detection systems |
| IPS | Intrusion prevention systems |
| NF | Network forensic |
| NS | Network security |
| PaaS | Platform as a service |
| PS | Protection systems |
| SaaS | Software as a service |
| SDN | Software defined networking |
| SLA | Service level agreement |
| StaaS | Storage as a service |
| QoS | Quality of service |
| VMF | Virtual machine forensics |
References
- Harbawi, M.; Varol, A. An improved digital evidence acquisition model for the Internet of Things forensic I: A theoretical framework. In Proceedings of the 2017 5th International Symposium on Digital Forensic and Security (ISDFS), Tirgu Mures, Romania, 26–28 April 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sree, T.R.; Bhanu, S.M.S. Data Collection Techniques for Forensic Investigation in Cloud. Digit. Forensic Sci. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, M.; Gaivoronski, S. Towards load balancing in SDN-networks during DDoS-attacks. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Science and Technology Conference (Modern Networking Technologies) (MoNeTeC), Moscow, Russia, 28–29 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Celdrán, A.H.; Gil Pérez, M.; Clemente, F.J.G.; Pérez, G.M. Policy-Based Management for Green Mobile Networks through Software-Defined Networking. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2016, 24, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divakaran, D.M.; Fok, K.W.; Nevat, I.; Thing, V.L. Evidence gathering for network security and forensics. Digit. Investig. 2017, 20, S56–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, G. Network forensics: Methodical literature review. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 16–18 March 2016; pp. 2203–2208. [Google Scholar]
- Pilli, E.; Ramesh, S.; Joshi, C.; Niyogi, R. Network forensic frameworks: Survey and research challenges. Digit. Investig. 2010, 7, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manral, B.; Somani, G.; Choo, K.-K.R.; Conti, M.; Gaur, M.S. A Systematic Survey on Cloud Forensics Challenges, Solutions, and Future Directions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 52, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koroniotis, N.; Moustafa, N.; Sitnikova, E. A new network forensic framework based on deep learning for Internet of Things networks: A particle deep framework. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 110, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.; Solanki, M.; Gadhwal, A.; Shah, A.; Patel, P. Challenges and Proposed Solutions for Cloud Forensic. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2015, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt, T.; Reiser, H.P. Network forensics for cloud computing. In IFIP International Conference on Distributed Applications and Interoperable Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Gani, A.; Wahab, A.W.A.; Shiraz, M.; Ahmad, I. Network forensics: Review, taxonomy, and open challenges. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 66, 214–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittinghouse, J.; Ransome, J.F. Cloud Computing: Implementation, Management, And Security; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, D.R.; Sravani, P.L. Challenges of Digital Forensics in Cloud Computing Environment. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farina, J.; Scanlon, M.; Le-Khac, N.-A.; Kechadi, M.T. Overview of the Forensic Investigation of Cloud Services. In Proceedings of the 2015 10th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security, Toulouse, France, 24–27 August 2015; pp. 556–565. [Google Scholar]
- Alex, M.E.; Kishore, R. Forensics framework for cloud computing. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 60, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, K.; Carthy, J.; Kechadi, T.; Baggili, I. Cloud forensics definitions and critical criteria for cloud forensic capability: An overview of survey results. Digit. Investig. 2013, 10, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Gani, A.; Wahab, A.W.A.; Iqbal, S.; Abdelaziz, A.; Mahdi, O.A.; Abdallaahmed, A.I.; Shiraz, M.; Al-Mayouf, Y.R.B.; Khan, Z.; et al. Towards an Applicability of Current Network Forensics for Cloud Networks: A SWOT Analysis. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 9800–9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simou, S.; Simou, S.; Kalloniatis, C.; Kalloniatis, C.; Kavakli, E.; Kavakli, E.; Gritzalis, S.; Gritzalis, S. Cloud forensics: Identifying the major issues and challenges. In International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 271–284. [Google Scholar]
- Mohiddin, S.K.; Yalavarthi, S.B.; Sharmila, S.A. A complete ontological survey of cloud forensic in the area of cloud computing. In Proceedings of Sixth International Conference on Soft Computing for Problem Solving; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Blenk, A.; Basta, A.; Reisslein, M.; Kellerer, W. Survey on Network Virtualization Hypervisors for Software Defined Networking. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2015, 18, 655–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Cai, Z.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Y.; Cheang, C.F. A Survey on Security-Aware Measurement in SDN. Secur. Commun. Networks 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chica, J.C.C.; Imbachi, J.C.; Vega, J.F.B. Security in SDN: A Comprehensive Survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 159, 102595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhunzada, A.; Ahmed, E.; Gani, A.; Khan, M.K.; Imran, M.; Guizani, S. Securing software defined networks: Taxonomy, requirements, and open issues. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Gani, A.; Wahab, A.W.A.; Guizani, M.; Khan, M.K. Topology Discovery in Software Defined Networks: Threats, Taxonomy, and State-of-the-Art. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2017, 19, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Namal, S.; Ylianttila, M.; Gurtov, A. Security in Software Defined Networks: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2015, 17, 2317–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsmadi, I.; Xu, D. Security of Software Defined Networks: A survey. Comput. Secur. 2015, 53, 79–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Gani, A.; Wahab, A.W.A.; Abdelaziz, A.; Ko, K.; Khan, M.K.; Guizani, M. Software-Defined Network Forensics: Motivation, Potential Locations, Requirements, and Challenges. IEEE Netw. 2016, 30, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Mao, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Bian, J. A Compatible OpenFlow Platform for Enabling Security Enhancement in SDN. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakhshi, T. State of the Art and Recent Research Advances in Software Defined Networking. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, Q.; Yu, F.R.; Gong, Q.; Li, J. Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks in Cloud Computing Environments: A Survey, Some Research Issues, and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2016, 18, 602–622. [Google Scholar]
- Lillis, D.; Becker, B.; O’Sullivan, T.; Scanlon, M. Current challenges and future research areas for digital forensic investigation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1604.03850. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1604.03850v1.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Grispos, G.; Storer, T.; Glisson, W.B. Calm before the storm: The challenges of cloud computing in digital forensics. Int. J. Digit. Crime Forensics 2012, 4, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.-H.; Meng, X.-X.; Wang, L.-H. SDNForensics: A comprehensive forensics framework for software defined network. In International Conference on Computer Networks and Communication Technology (CNCT 2016); Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2016; pp. 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Lalb, C.; Contic, M.; Hua, D. LEChain: A blockchain-based lawful evidence management scheme for digital forensics. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 115, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourvahab, M.; Ekbatanifard, G. Digital Forensics Architecture for Evidence Collection and Provenance Preservation in IaaS Cloud Environment Using SDN and Blockchain Technology. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 153349–153364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Park, J.H. Blockchain Security in Cloud Computing: Use Cases, Challenges, and Solutions. Symmetry 2017, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Network Forensic | Cloud Forensic | |
|---|---|---|
| Brief Description | The Forensic Network is a method for finding and detecting network loopholes and preventing further failures. | In a cloud world, cloud forensics is a branch of network forensics and an extension of digital forensic science. |
| Key Features | Network forensics focuses on network traffic monitoring and analysis to track, prevent, and diagnose network security incidents. | Incidents are primarily handled by cloud forensics. This covers cloud computing forensics and its services. |
| Advantages | Security and Enhanced Network Management. | Cloud Security and Cloud protection. |
| Issues | Because of the enormous amount of network traffic and intensive processing needed for forensic analysis, much of which is unrelated to the available data, which creates problems accessing network and cloud architectures. | Forensic investigators face many challenges due to the dispersed nature of the cloud infrastructures, such as contributing to an increase in the time of the investigation, expense, data collection problems and remote analysis of the data. |
| Future Directions | It is possible to incorporate advanced networking intrusion detection/prevention systems. | Sophisticated network virtualization, consumption costs, and on-demand storage capacity can be enforced. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waseem, Q.; Alshamrani, S.S.; Nisar, K.; Wan Din, W.I.S.; Alghamdi, A.S. Future Technology: Software-Defined Network (SDN) Forensic. Symmetry 2021, 13, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050767
Waseem Q, Alshamrani SS, Nisar K, Wan Din WIS, Alghamdi AS. Future Technology: Software-Defined Network (SDN) Forensic. Symmetry. 2021; 13(5):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050767
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaseem, Quadri, Sultan S. Alshamrani, Kashif Nisar, Wan Isni Sofiah Wan Din, and Ahmed Saeed Alghamdi. 2021. "Future Technology: Software-Defined Network (SDN) Forensic" Symmetry 13, no. 5: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050767
APA StyleWaseem, Q., Alshamrani, S. S., Nisar, K., Wan Din, W. I. S., & Alghamdi, A. S. (2021). Future Technology: Software-Defined Network (SDN) Forensic. Symmetry, 13(5), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050767