ILRA: Novelty Detection in Face-Based Intervener Re-Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We present a contextualization of open world re-identification problems.
- We propose a feature vector based on Isometric LogRatio (ILR) transformation of a posteriori probabilities of belonging to a known intervener, applying a previous descriptor calculated only over the intervener face.
- A threshold-less approach is used to solve the novelty detection problem in an open world scenario. Thus, there is not a need for any user defined threshold.
2. Related Work
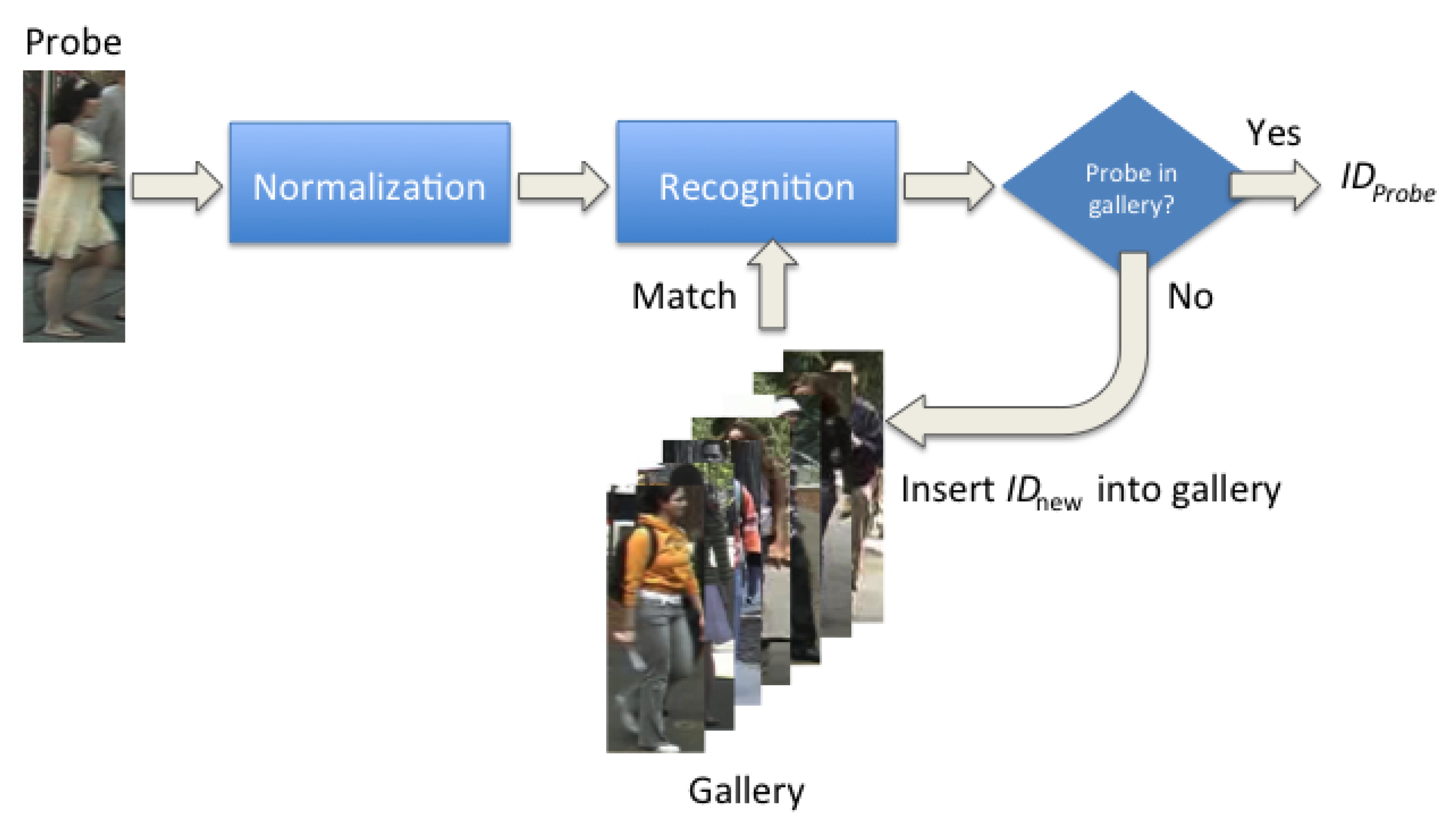
3. Method
3.1. Video Pre-Processing
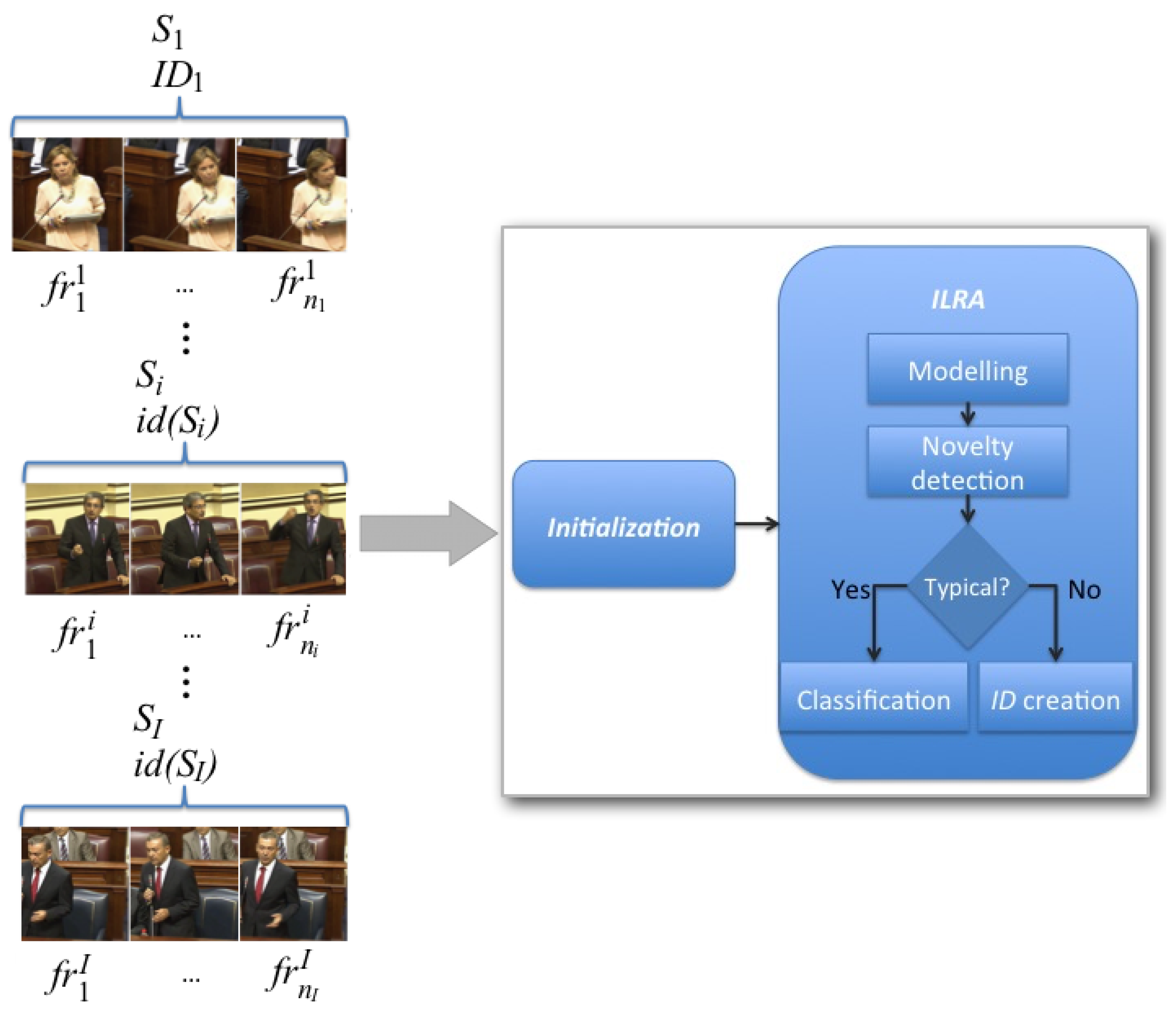
3.2. Initialization Stage
3.3. ILRA Stage
3.4. ILRA Time Complexity
4. Experimental Evaluation and Results
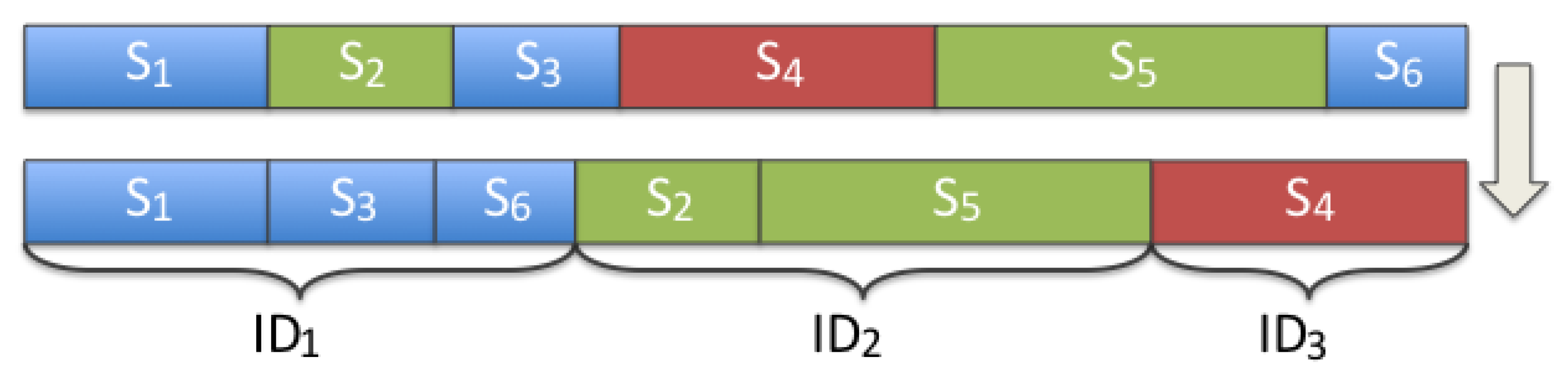
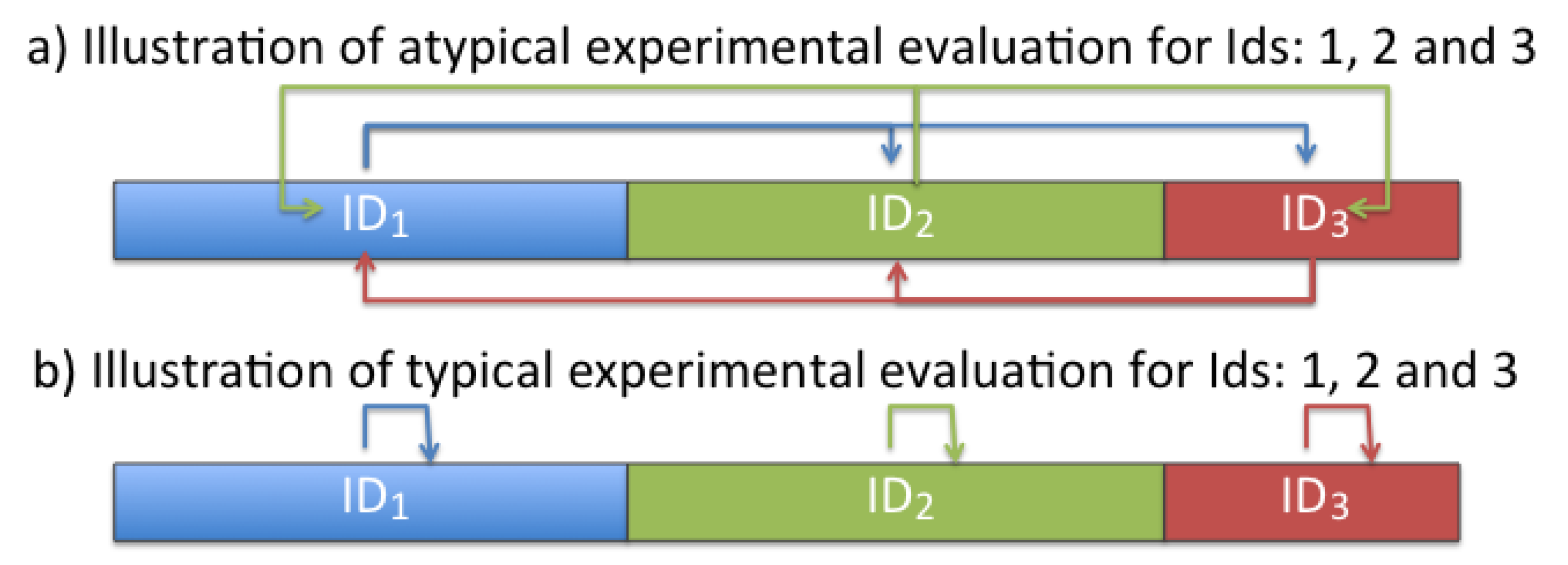
4.1. Evaluation of Novelty Detection in the Initialization Stage
4.2. Evaluation of Novelty Detection in the ILRA Stage
4.3. Evaluation of Intervener Classification in the ILRA Stage
4.4. Evaluation of the Proposed Online System
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gheissari, N.; Sebastian, T.B.; Hartley, R. Person Reidentification Using Spatiotemporal Appearance. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; Volume 2, pp. 1528–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Vezzani, R.; Baltieri, D.; Cucchiara, R. People reidentification in surveillance and forensics: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2013, 46, 29:1–29:37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, B.; Zheng, W.S.; Gong, S.; Xiang, T. Person Re-Identification by Support Vector Ranking. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Aberystwyth, UK, 31 August–3 September 2010; pp. 21.1–21.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, P.M.; Hirzer, M.; Köstinger, M.; Beleznai, C.; Bischof, H. Mahalanobis distance learning for person re-identification. In Person Re-Identification; Gong, S., Cristani, M., Yan, S., Loy, C.C., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 247–267. [Google Scholar]
- Bedagkar-Gala, A.; Shah, S.K. A survey of approaches and trends in person re-identification. Image Vis. Comput. 2014, 32, 270–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, S.Z. Person Re-Identification by Local Maximal Occurrence Representation and Metric Learning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2197–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Markou, M.; Singh, S. Novelty detection: a review-part 1: Statistical approaches. Signal Process. 2003, 83, 2481–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandola, V.; Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2009, 41, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.A.; Clifton, D.A.; Clifton, L.; Tarassenko, L. A review of novelty detection. Signal Process. 2014, 99, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguera, X.; Bozonnet, S.; Evans, N.; Fredouille, C.; Friedland, G.; Vinyals, O. Speaker diarization: A review of recent research. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2012, 20, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoury, E.; Sénac, C.; Joly, P. Audiovisual diarization of people in video content. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2014, 68, 747–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, J.H.; Chang, K.M. A Study of Facial Features of American and Japanese Cartoon Characters. Symmetry 2019, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamachi, M.G.; Chiba, T.; Kurosumi, M.; Mizukoshi, K. Perception of Human Age from Faces: Symmetric Versus Asymmetric Movement. Symmetry 2019, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredin, H.; Gelly, G. Improving Speaker Diarization of TV Series Using Talking-Face Detection and Clustering. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACMMM), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 15–19 October 2016; pp. 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Gebru, I.; Ba, S.; Li, X.; Horaud, R. Audio-visual speaker diarization based on spatiotemporal bayesian fusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39. in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.; Wu, D.; Meignier, S.; Odobez, J.M. EUMSSI Team at the Mediaeval Person Discovery Challenge. In Proceedings of the Working Notes Proceedings of the MediaEval 2015 Workshop, Wurzen, Germany, 14–15 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Friedland, G.; Hung, H.; Yeo, C. Multi-Modal Speaker Diarization of Real-World Meetings Using Compressed-Domain Video Features. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 4069–4072. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzani, L.; Cristani, M.; Murino, V. Symmetry driven accumulation of local features for human characterization and re-identification. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2013, 117, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Guo, Y.; Song, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Tang, Y.Y. Person re-identification by dual-regularized kiss metric learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 2726–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.X.; Wu, A.; Zheng, W.S. Cross-View Asymmetric Metric Learning for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ustinova, E.; Ganin, Y.; Lempitsky, V. Multi-Region Bilinear Convolutional Neural Networks for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Lecce, Italy, 29 August–1 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y. A Discriminatively Learned CNN Embedding for Person Reidentification. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2017, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.P.; Deng, J.D.; Purvis, M.K. Novelty detection in wildlife scenes through semantic context modelling. Pattern Recognit. 2012, 45, 3439–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, D.A.; Clifton, L.; Hugueny, S.; Wong, D.; Tarassenko, L. An extreme function theory for novelty detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2013, 7, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irigoien, I.; Arenas, C. INCA: New statistic for estimating the number of clusters and identifying atypical units. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 2948–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucenna, S.; Cohen, D.; Meltzoff, A.N.; Gaussier, P.; Chetouani, M. Robots learn to recognize individuals from imitative encounters with people and avatars. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, K.; Nakamura, S. Improved Novelty Detection for Online GMM Based Speaker Diarization. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Brisbane, Australia, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.S.; Gong, S.; Xiang, T. Transfer Re-Identification: From Person to Set-Based Verification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2650–2657. [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Lang, S.; Pham, Q.C.; Achard, C. Closed and Open-World Person Re-Identification and Verification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Sydney, Australia, 29 November–1 December 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, B.; Huang, D.; Zheng, W.S. Fast open-world person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2286–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zheng, L.; Ye, Q.; Kang, G.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, J. Image-Image Domain Adaptation with Preserved Self-Similarity and Domain-dissimilarity for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 994–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation Using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, A.; Zheng, W.S. Adversarial Open-World Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 280–296. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.S.; Madden, M.G. One-class classification: Taxonomy of study and review of techniques. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2014, 29, 345–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillón-Santana, M.; Lorenzo-Navarro, J.; Ramón-Balmaseda, E. Descriptors and regions of interest fusion for in- and cross-database gender classification in the wild. Image Vis. Comput. 2017, 57, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillón-Santana, M.; Lorenzo-Navarro, J.; Travieso-González, C.M.; Freire-Obregón, D.; Alonso-Hernández, J.B. Evaluation of local descriptors and CNNs for non-adult detection in visual content. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egozcue, J.J.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Mateu-Figueras, G.; Barceló-Vidal, C. Isometric logratio transformations for compositional data analysis. Math. Geol. 2003, 35, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Canarias, P. Web Site of Canary Islands Parliament. 2018. Available online: http://www.parcan.es/ (accessed on 7 June 2018).
- Marín-Reyes, P.A. ILRA Source Code. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/foumacray/ILRA (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Kazemi, V.; Sullivan, J. One Millisecond Face Alignment with an Ensemble of Regression Trees. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1867–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Human Detection. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikainen, M.; Harwood, D. Performance Evaluation of Texture Measures with Classification Based on Kullback Discrimination of Distributions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Jerusalem, Israel, 9–13 October 1994; Volume 1, pp. 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikainen, M.; Maenpaa, T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, L.; Long, Y.; Kuang, G.; Fieguth, P. Extended local binary patterns for texture classification. Image Vis. Comput. 2012, 30, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shan, S.; He, C.; Zhao, G.; Pietikainen, M.; Chen, X.; Gao, W. WLD: A robust local image descriptor. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 1705–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, Inception-resnet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; He, X.; Gao, J. Ms-celeb-1m: A Dataset and Benchmark for Large-Scale Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, D.N.T.; Khoudour, L.; Achard, C.; Meurie, C.; Lezoray, O. People re-identification by spectral classification of silhouettes. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 2362–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Nielsen, E.; Chávez-Gutiérrez, F.; Lorenzo-Navarro, J.; Castrillón-Santana, M. A multimedia system to produce and deliver video fragments on demand on parliamentary websites. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2016, 76, 6281–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Loh, H.T.; Sun, A. Imbalanced text classification: A term weighting approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sadaoui, S.; Mouhoub, M. An empirical analysis of imbalanced data classification. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2015, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhuang, L.; Dai, H. Parameter Estimation of One-Class SVM on Imbalance Text Classification. In Proceedings of the Conference of the Canadian Society for Computational Studies of Intelligence, Québec City, QC, Canada, 7–9 June 2006; pp. 538–549. [Google Scholar]
- de Deus, J.L.; Neves, J.C.L.; Corrêa, M.C.d.M.; Parent, S.É.; Natale, W.; Parent, L.E. Balance design for robust foliar nutrient diagnosis of “Prata” banana (Musa spp.). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
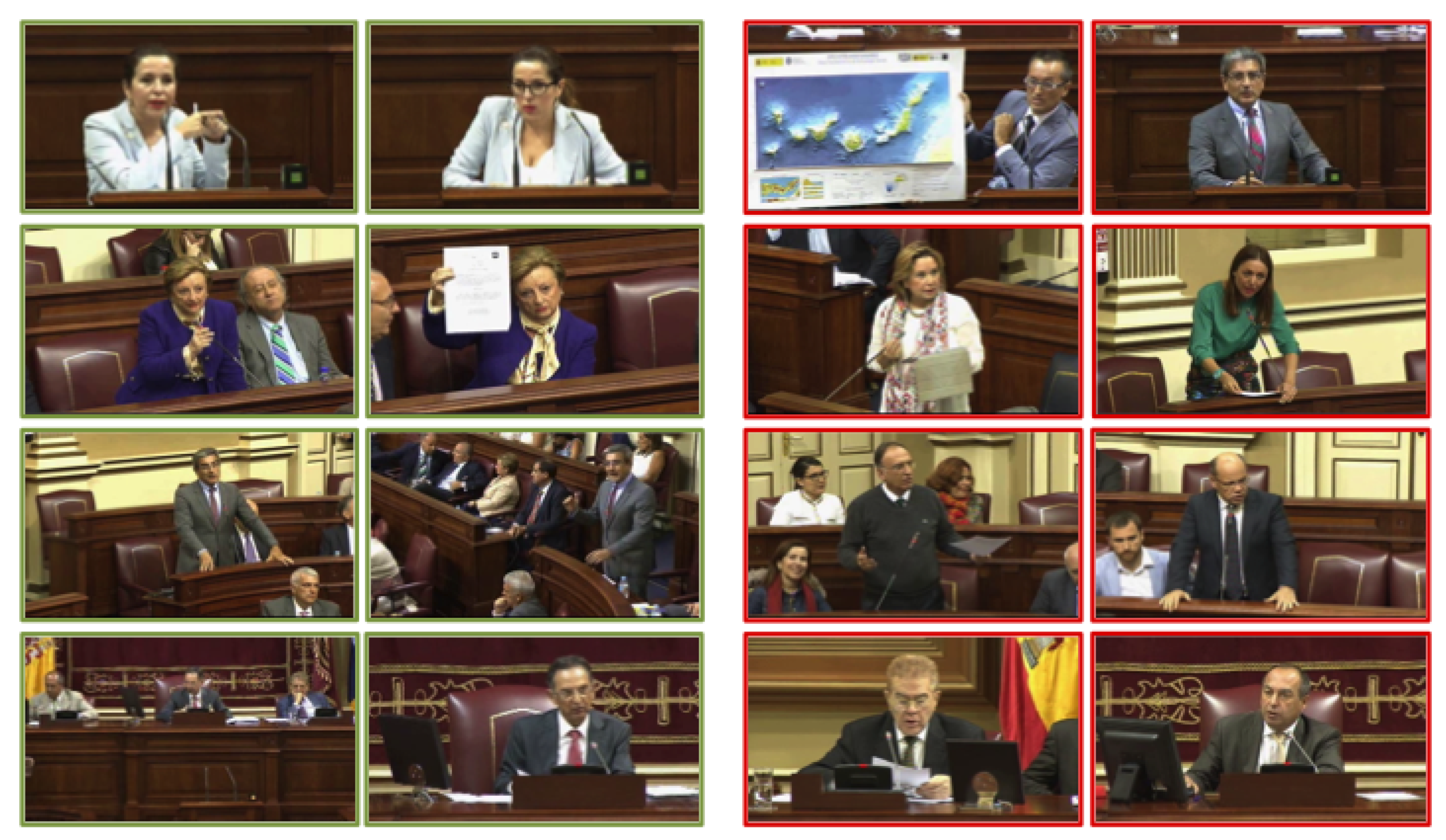

| Video Identifier | Interveners | Shots | Frames | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2771 | 5 | 13 | 2440 | 0:33:23 |
| 2918 | 7 | 33 | 7142 | 1:21:23 |
| 3015 | 8 | 52 | 22,088 | 3:02:44 |
| 2792 | 11 | 55 | 13,956 | 1:48:00 |
| 2907 | 12 | 57 | 9542 | 2:20:20 |
| 3011 | 21 | 73 | 6525 | 2:01:42 |
| Video Features | Descriptor | Novelty Detection in | Novelty Detection in | Intervener Classification in | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initialization Stage | ILRA Stage | ILRA Stage | ||||||||
| Id | K | Typical | Atypical | F | Typical | Atypical | F | MAP Acc. | SVM Acc. | |
| 2771 | 5 | HOG | 100.0 | 90.00 | 94.74 | 80.00 | 60.00 | 68.57 | 96.52 | 96.92 |
| LBP | 80.00 | 90.00 | 84.71 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 48.00 | 62.15 | 64.07 | ||
| LBPu2 | 80.00 | 90.00 | 84.71 | 80.00 | 60.00 | 68.57 | 96.72 | 96.89 | ||
| NILBP | 100.0 | 90.00 | 94.74 | 20.00 | 80.00 | 32.00 | 72.45 | 81.13 | ||
| Resnet | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 60.00 | 80.00 | 68.57 | 98.51 | 98.05 | ||
| WLD | 80.00 | 100.0 | 88.89 | 40.00 | 80.00 | 53.33 | 94.17 | 94.17 | ||
| 2918 | 7 | HOG | 85.71 | 52.38 | 65.02 | 100.0 | 85.71 | 92.31 | 92.15 | 91.12 |
| LBP | 85.71 | 85.71 | 85.71 | 85.71 | 57.14 | 68.57 | 44.34 | 47.57 | ||
| LBPu2 | 85.71 | 90.48 | 88.03 | 28.57 | 100.0 | 44.44 | 98.63 | 98.03 | ||
| NILBP | 100.0 | 85.71 | 92.31 | 100.0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 41.05 | 50.20 | ||
| Resnet | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 29.57 | 86.71 | 42.86 | 97.49 | 97.16 | ||
| WLD | 85.71 | 80.95 | 83.27 | 42.85 | 85.71 | 57.14 | 92.89 | 92.99 | ||
| 3015 | 8 | HOG | 100.0 | 85.71 | 92.31 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 95.30 | 94.24 |
| LBP | 87.50 | 100.0 | 93.33 | 25.00 | 37.50 | 30.00 | 54.92 | 56.47 | ||
| LBPu2 | 87.50 | 100.0 | 93.33 | 50.00 | 100.0 | 66.67 | 97.93 | 98.01 | ||
| NILBP | 100.0 | 96.43 | 98.18 | 87.50 | 12.50 | 21.88 | 63.00 | 67.58 | ||
| Resnet | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 27.27 | 100.0 | 42.85 | 97.78 | 97.52 | ||
| WLD | 100.0 | 96.43 | 98.18 | 87.50 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 63.57 | 68.68 | ||
| 2792 | 11 | HOG | 81.82 | 89.09 | 85.30 | 90.91 | 100.0 | 95.24 | 92.60 | 91.26 |
| LBP | 90.91 | 98.18 | 94.41 | 18.18 | 72.72 | 29.09 | 51.84 | 53.42 | ||
| LBPu2 | 81.82 | 96.36 | 88.50 | 45.45 | 90.91 | 60.61 | 97.12 | 96.84 | ||
| NILBP | 81.82 | 96.36 | 88.50 | 100.0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 45.16 | 55.76 | ||
| Resnet | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 36.00 | 100.0 | 52.94 | 97.94 | 97.83 | ||
| WLD | 81.82 | 98.18 | 89.26 | 9.09 | 90.91 | 16.53 | 85.13 | 85.31 | ||
| 2907 | 12 | HOG | 75.00 | 90.91 | 82.19 | 41.66 | 83.33 | 55.56 | 96.42 | 96.02 |
| LBP | 75.00 | 96.97 | 84.58 | 66.67 | 75.00 | 70.59 | 64.30 | 64.47 | ||
| LBPu2 | 66.67 | 98.48 | 79.51 | 25.00 | 83.33 | 38.46 | 98.11 | 98.19 | ||
| NILBP | 83.33 | 100.0 | 90.91 | 50.00 | 25.00 | 33.33 | 76.19 | 79.07 | ||
| Resnet | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 41.67 | 100.0 | 58.83 | 98.90 | 98.98 | ||
| WLD | 58.33 | 100.0 | 73.68 | 75.00 | 91.67 | 82.50 | 92.25 | 91.87 | ||
| 3011 | 21 | HOG | 52.38 | 94.76 | 67.47 | 47.62 | 71.43 | 57.14 | 41.29 | 96.55 |
| LBP | 42.86 | 97.14 | 59.48 | 61.90 | 61.90 | 61.90 | 20.18 | 49.65 | ||
| LBPu2 | 42.86 | 96.19 | 59.30 | 42.86 | 76.19 | 54.86 | 40.85 | 94.92 | ||
| NILBP | 57.14 | 96.19 | 71.69 | 61.90 | 52.38 | 56.75 | 36.98 | 84.26 | ||
| Resnet | 76.19 | 98.57 | 85.95 | 23.81 | 90.48 | 37.70 | 41.49 | 94.64 | ||
| WLD | 28.57 | 99.05 | 44.35 | 85.71 | 80.95 | 83.27 | 36.70 | 86.09 | ||
| Mean | HOG | 82.49 | 83.81 | 81.17 | 76.70 | 83.41 | 78.14 | 85.71 | 94.35 | |
| LBP | 77.00 | 94.67 | 83.70 | 49.58 | 60.71 | 51.36 | 49.62 | 55.94 | ||
| LBPu2 | 74.09 | 95.25 | 82.23 | 45.31 | 85.07 | 55.60 | 88.23 | 97.15 | ||
| NILBP | 87.05 | 94.12 | 89.39 | 69.90 | 28.31 | 23.99 | 55.81 | 69.67 | ||
| Resnet | 96.03 | 99.76 | 97.66 | 36.22 | 92.70 | 50.62 | 88.69 | 97.36 | ||
| WLD | 63.51 | 95.77 | 79.60 | 56.69 | 71.54 | 48.80 | 77.45 | 86.52 | ||
| Video ID | Descriptor | TRR | TDR | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOG | 83.33 | 74.07 | 78.43 | |
| LBP | 25.00 | 94.44 | 39.53 | |
| 2771 | LBPu2 | 16.67 | 96.30 | 28.42 |
| NILBP | 16.67 | 88.89 | 28.07 | |
| Resnet | 58.33 | 90.74 | 71.01 | |
| WLD | 8.33 | 96.30 | 15.34 | |
| HOG | 38.50 | 99.08 | 55.45 | |
| LBP | 95.72 | 11.63 | 20.75 | |
| 2918 | LBPu2 | 40.11 | 83.28 | 54.14 |
| NILBP | 56.68 | 76.89 | 65.26 | |
| Resnet | 59.15 | 97.65 | 73.68 | |
| WLD | 31.55 | 93.76 | 47.21 | |
| HOG | 71.05 | 95.96 | 81.65 | |
| LBP | 29.47 | 75.76 | 42.44 | |
| 3015 | LBPu2 | 34.21 | 96.80 | 50.55 |
| NILBP | 40.53 | 88.89 | 55.67 | |
| Resnet | 56.83 | 99.58 | 72.37 | |
| WLD | 36.84 | 96.46 | 53.32 | |
| HOG | 71.83 | 69.18 | 70.48 | |
| LBP | 28.17 | 85.18 | 42.34 | |
| 2792 | LBPu2 | 70.42 | 94.12 | 80.56 |
| NILBP | 59.15 | 83.76 | 69.34 | |
| Resnet | 47.59 | 97.69 | 64.00 | |
| WLD | 54.93 | 82.82 | 66.05 | |
| HOG | 52.27 | 48.49 | 50.31 | |
| LBP | 15.91 | 87.09 | 26.90 | |
| 2907 | LBPu2 | 31.82 | 95.12 | 47.69 |
| NILBP | 27.27 | 92.54 | 42.13 | |
| Resnet | 65.79 | 91.41 | 76.51 | |
| WLD | 40.91 | 74.75 | 52.88 | |
| HOG | 82.08 | 95.43 | 88.25 | |
| LBP | 55.66 | 91.34 | 69.17 | |
| 3011 | LBPu2 | 49.06 | 99.69 | 65.75 |
| NILBP | 73.58 | 65.98 | 69.58 | |
| Resnet | 54.68 | 97.85 | 70.15 | |
| WLD | 71.70 | 89.29 | 79.53 | |
| HOG | 66.51 | 80.37 | 70.76 | |
| LBP | 41.66 | 74.24 | 40.19 | |
| Mean | LBPu2 | 40.38 | 94.22 | 54.52 |
| NILBP | 45.65 | 82.83 | 55.01 | |
| Resnet | 57.06 | 95.82 | 71.29 | |
| WLD | 40.71 | 88.90 | 52.39 |
| Video ID | Descriptor | TRR | TDR | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] | 58.33 | 61.11 | 59.69 | |
| [43] | 41.67 | 70.37 | 52.34 | |
| [44] | 41.67 | 70.37 | 52.34 | |
| 2771 | [45] | 33.33 | 79.63 | 46.99 |
| [48] | 79.33 | 64.52 | 71.16 | |
| [46] | 41.67 | 70.37 | 52.34 | |
| [51] | 53.91 | 75.36 | 62.86 | |
| Ours (Resnet) | 58.33 | 90.74 | 71.01 | |
| [42] | 49.41 | 79.85 | 61.05 | |
| [43] | 42.35 | 95.82 | 58.74 | |
| [44] | 48.82 | 97.18 | 64.99 | |
| [45] | 57.65 | 85.07 | 68.72 | |
| 2918 | [48] | 96.00 | 44.71 | 61.01 |
| [46] | 43.53 | 94.78 | 59.66 | |
| [51] | 50.59 | 75.16 | 60.47 | |
| Ours (Resnet) | 59.15 | 97.65 | 73.68 | |
| [42] | 85.81 | 12.56 | 21.91 | |
| [43] | 43.02 | 58.85 | 49.71 | |
| [44] | 45.49 | 57.84 | 50.93 | |
| 3015 | [45] | 48.18 | 51.49 | 49.78 |
| [48] | 80.17 | 47.98 | 60.03 | |
| [46] | 69.52 | 38.58 | 49.62 | |
| [51] | 85.93 | 9.96 | 17.85 | |
| Ours (Resnet) | 56.83 | 99.58 | 72.37 | |
| [42] | 20.33 | 96.28 | 33.57 | |
| [43] | 31.17 | 94.87 | 46.92 | |
| [44] | 31.05 | 95.64 | 46.88 | |
| 2792 | [45] | 48.18 | 51.49 | 49.78 |
| [48] | 89.05 | 58.17 | 70.37 | |
| [46] | 31.17 | 91.56 | 57.27 | |
| [51] | 23.85 | 93.58 | 38.01 | |
| Ours (Resnet) | 47.59 | 97.69 | 64.00 | |
| [42] | 23.49 | 88.23 | 37.10 | |
| [43] | 33.73 | 87.79 | 48.74 | |
| [44] | 28.31 | 89.67 | 43.03 | |
| 2907 | [45] | 26.20 | 88.58 | 40.44 |
| [48] | 91.26 | 88.68 | 89.95 | |
| [46] | 34.94 | 82.92 | 49.16 | |
| [51] | 21.99 | 84.91 | 34.93 | |
| Ours (Resnet) | 65.79 | 91.41 | 76.51 | |
| [42] | 57.61 | 77.38 | 66.05 | |
| [43] | 51.78 | 70.62 | 59.75 | |
| [44] | 53.41 | 70.55 | 60.80 | |
| 3011 | [45] | 58.38 | 73.59 | 65.11 |
| [48] | 66.45 | 70.61 | 68.47 | |
| [46] | 50.76 | 78.68 | 61.71 | |
| [51] | 58.12 | 79.36 | 67.10 | |
| Ours (Resnet) | 54.68 | 97.85 | 70.15 | |
| [42] | 49.16 | 69.24 | 46.56 | |
| [43] | 40.62 | 79.72 | 52.70 | |
| [44] | 41.46 | 80.21 | 53.16 | |
| Mean | [45] | 45.32 | 71.64 | 53.47 |
| [48] | 83.71 | 62.44 | 70.17 | |
| [46] | 45.27 | 76.15 | 54.96 | |
| [51] | 49.07 | 69.72 | 46.87 | |
| Ours (Resnet) | 57.06 | 95.82 | 71.29 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marín-Reyes, P.A.; Irigoien, I.; Sierra, B.; Lorenzo-Navarro, J.; Castrillón-Santana, M.; Arenas, C. ILRA: Novelty Detection in Face-Based Intervener Re-Identification. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091154
Marín-Reyes PA, Irigoien I, Sierra B, Lorenzo-Navarro J, Castrillón-Santana M, Arenas C. ILRA: Novelty Detection in Face-Based Intervener Re-Identification. Symmetry. 2019; 11(9):1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091154
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarín-Reyes, Pedro A., Itziar Irigoien, Basilio Sierra, Javier Lorenzo-Navarro, Modesto Castrillón-Santana, and Concepción Arenas. 2019. "ILRA: Novelty Detection in Face-Based Intervener Re-Identification" Symmetry 11, no. 9: 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091154
APA StyleMarín-Reyes, P. A., Irigoien, I., Sierra, B., Lorenzo-Navarro, J., Castrillón-Santana, M., & Arenas, C. (2019). ILRA: Novelty Detection in Face-Based Intervener Re-Identification. Symmetry, 11(9), 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091154






