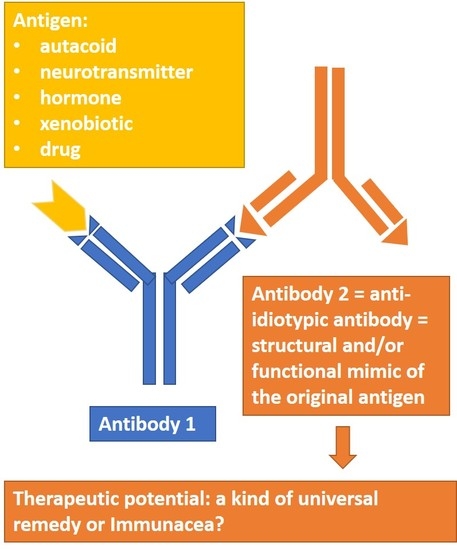
Anti-Idiotypic Agonistic Antibodies: Candidates for the Role of Universal Remedy
Abstract
1. Introduction
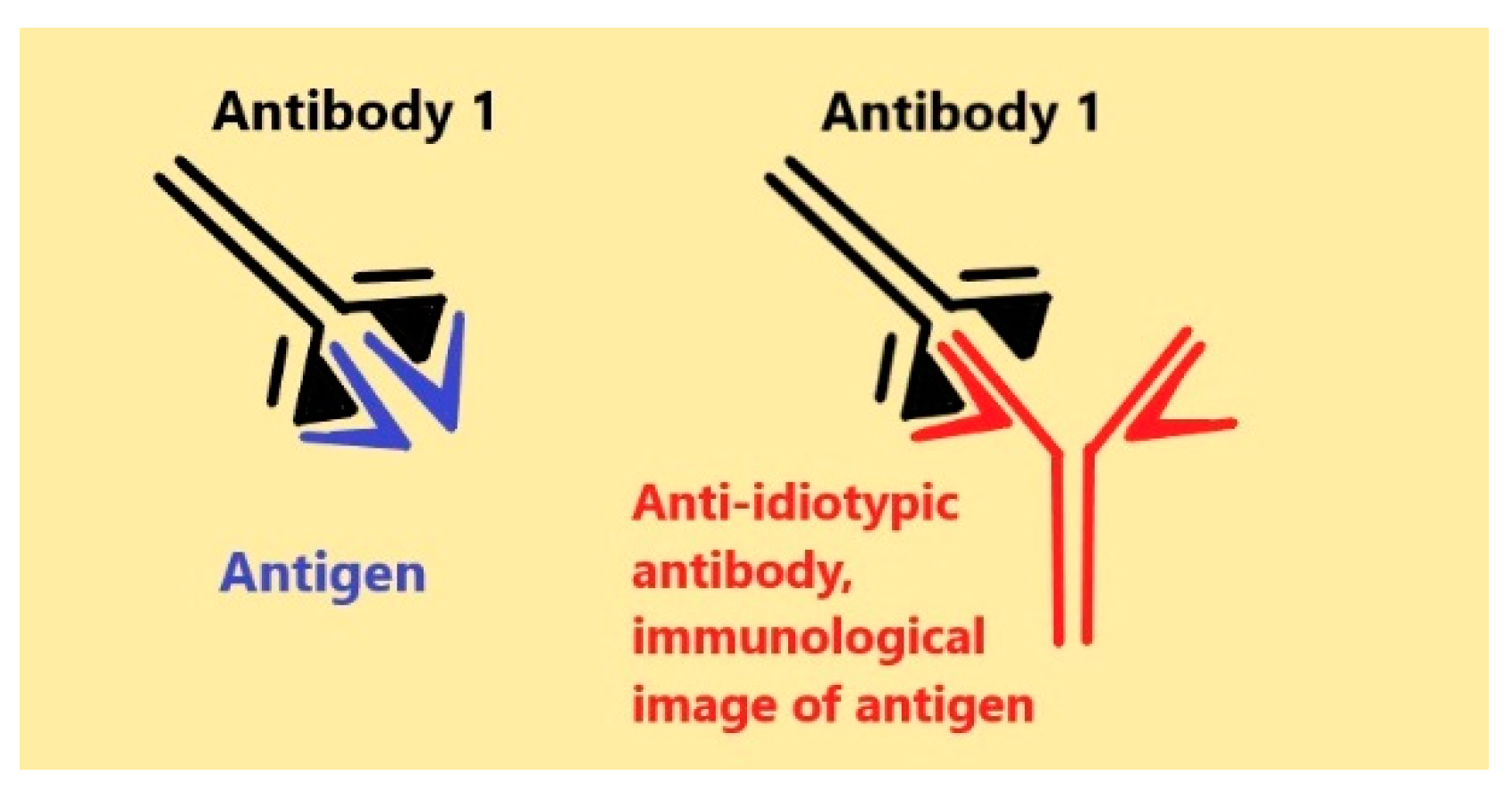
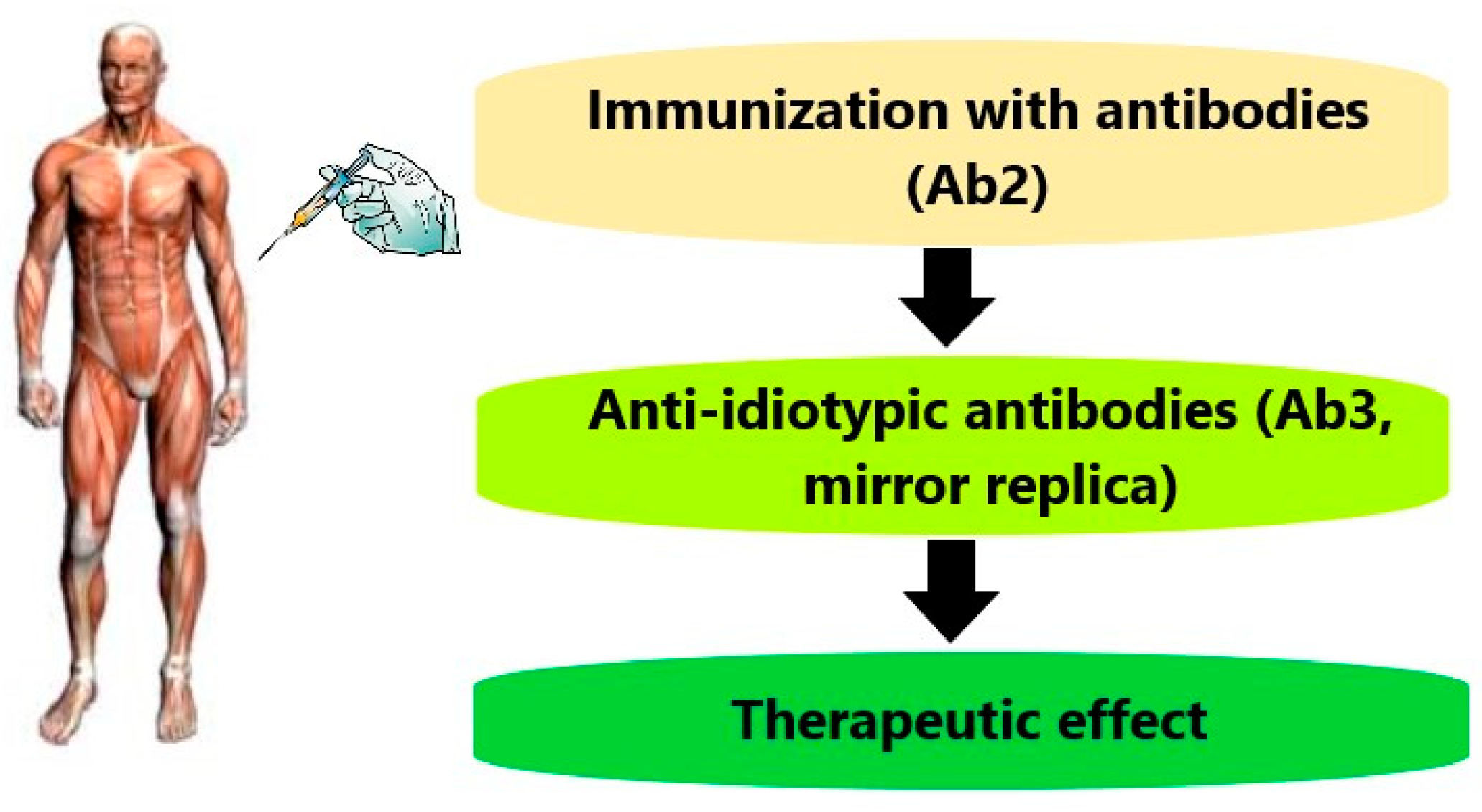
2. Classes of Anti-IDs
3. Autacoid-Like Anti-IDs
4. Neurotransmitter-Like Anti-IDs
5. Hormone-Like Anti-IDs
6. Anti-IDs to Xenobiotics
7. Anti-IDs to Drugs and Treatment of Drug Addiction
8. Anti-IDs in the Pathogenesis of Diseases
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | autoantibody |
| Ab | antibody |
| Anti-IDs | anti-idiotypic antibodies |
| APLS | anti-phospholipid syndrome |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CFS | chronic fatigue syndrome |
| FVIII | antihemophilic globulin, 8th factor of coagulation |
| Ig | immunoglobulin |
| IL | interleukin |
| IVIG | intravenous immunoglobulin |
| ScFv | single chain fragment |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythenatosus |
| T1D | type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| TSH | thyroid stimulating hormone |
| WG | Wegener’s granulomatosis |
References
- Besredka, A. La leucotoxine et son action. Ann. Inst. Pasteur. 1900, 14, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kryzhanovskii, G.N.; Fontalin, L.N.; Pevnickii, L.A. To the question of the formation of anti-antibodies. Vestn. Akad. Med. Nauk. 1960, 15, 18–26. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Oudin, J.; Michel, M. Une nouvelle forme d’allotypie des globulines gamma du sérum de lapin apparemment liée à la fonction et à la spécificité anticorps. CR Acad. Sc. 1963, 257, 805–808. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmann, J. Speculations on idiotypes and homobodies. Ann. Immunol. (Paris) 1973, 124, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jerne, N.K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann. Immunol. (Paris) 1974, 125C, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richter, P.H. A network theory of the immune system. Eur. J. Immunol. 1975, 5, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metchnikoff, E.; Rue, E. L’oeuvre de Paul Ehlrich. Berl. Klin. Wochenschr. 1914, 1, 523–531. [Google Scholar]
- Churilov, L.P.; Stroev, Y.I.; Zaichik, A.S. Autoimmunity vs. autoallergy in immunoneuroendocrine regulation and dysregulation. In Physiologic Autoimmunity and Preventive Medicine; Poletaev, A.B., Ed.; Bentham Science Publishers B.V.: Oak Park, IL, USA; Bussum, The Netherlands; Sharjah, UAE, 2013; pp. 72–166. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, Y.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Maisonneuve, P.; Nydegger, U.E. Anti-idiotypic suppression of autoantibodies to factor VIII (antihaemophilic factor) by high-dose intravenous gammaglobulin. Lancet (London, England) 1984, 2, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, M.; Anafi, L.; Zandman-Goddard, G.; Krause, I.; Goldman, S.; Shalev, E.; Cervera, R.; Font, J.; Fridkin, M.; Thiesen, H.J.; et al. The efficacy of specific IVIG anti-idiotypic antibodies in antiphospholipid syndrome (APS): Trophoblast invasiveness and APS animal model. Int. Immunol. 2007, 19, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoenfeld, Y. Idiotypic induction of autoimmunity: A new aspect of the idiotypic network. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bona, C.; Kohler, H. Anti-idiotypic antibodies and internal images. In Receptor Biochemistry and Methodology Series; Venter, J.C., Fraser, C.M., Linstrom, J., Eds.; Liss: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, G.W.; Muller, S.; Kohler, H. Towards an HIV vaccine based on immune network theory. Сurr. Trends Immunol. 2012, 13, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieber-Emmons, T.; Monzavi-Karbassi, B.; Pashov, A.; Saha, S.; Murali, R.; Kohler, H. The promise of the anti-idiotype concept. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, M.S.; Muller, S.; Kohler, H.; Grant, M.D.; Bernard, N.F. On the benefits of sin: Can greater understanding of the 1F7-idiotypic repertoire freeze enhance HIV vaccine development? Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 9, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, B.A.; Goldbaum, F.A.; Ysern, X.; Poijak, R.J.; Mariuzza, R.A. Molecular basis of antigen mimicry by an anti-idiotope. Nature 1995, 374, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, J.R.; Patawaran, M.; Tosi, M.; Lennon, J.; Pier, G.B. Anti-idiotype-induced, lipopolysaccharide-specific antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Immunol. 1990, 144, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magliani, W.; Polonelli, L.; Conti, S.; Salati, A.; Rocca, P.F.; Cusumano, V.; Mancuso, G.; Teti, G. Neonatal mouse immunity against group B streptococcal infection by maternal vaccination with recombinant anti-idiotypes. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabri, M.R.; Cacciavillano, W.; Chantada, G.L.; Alonso, D.F. Racotumomab for treating lung cancer and pediatric refractory malignancies. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekemeier, H. Inflammation—A Short Survey of Some Terms; Wiss Beitr M-Luther-Univ.: Halle, Germany, 1984; pp. 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Depraetere, H.; Depla, E.; Haelewyn, J.; De Ley, M. An anti-idiotypic antibody with an internal image of human interferon-gamma and human interferon-gamma-like antiviral activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 2260–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuberi, R.I.; Katz, D.H.; Zanetti, M. Production of IL-1-mimicking anti-idiotypic antibodies in rabbits in response to IL-1 immunization. J. Autoimmun. 1988, 1, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couraud, P.O. Anti-angiotensin II anti-idiotypic antibodies bind to angiotensin II receptor. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Zhou, C.C.; Ramin, S.M.; Kellems, R.E. Angiotensin Receptors, Autoimmunity, and Preeclampsia. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 3391–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geha, R.S.; Comunale, M. Regulation of immunoglobulin E antibody synthesis in man by antiidiotypic antibodies. J. Clin. Investig. 1983, 71, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecheri, S.; Mourad, W.; Lapeyre, J.; Jobin, M.; David, B.; Hébert, J. Demonstration of idiotypes expressed on basophil-bound IgE antibodies by using anti-idiotype-induced histamine release in grass pollen-allergic patients. Immunology 1988, 64, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Elazar, Z.; Kanety, H.; Schreiber, M.; Fuchs, S. Anti-idiotypes against a monoclonal anti-haloperidol antibody bind to dopamine receptor. Life Sci. 1988, 42, 1987–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mons, N.; Dubourg, P.; Messier, C.; Chiavaroli, C.; Calas, A.; Geffard, M. Polyclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies as internal images of dopamine. Applications for biochemical and morphological studies of DA receptors in the rat brain. J. Hirnforsch. 1991, 32, 617–625. [Google Scholar]
- Eng, H.; Lefvert, A. Isolation of an antiidiotypic antibody with acetylcholine-receptor-like binding properties from myasthenia gravis patients. Ann. l’Institut Pasteur Immunol. 1988, 139, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamir, H.; Liu, K.P.; Hsiung, S.C.; Yu, P.Y.; Kirchgessner, A.L.; Gershon, M.D. Identification of serotonin receptors recognized by anti-idiotypic antibodies. J. Neurochem. 1991, 57, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Marques, O.; Marques, A.; Giil, L.M.; De Vito, R.; Rademacher, J.; Günther, J.; Lange, T.; Humrich, J.Y.; Klapa, S.; Schinke, S.; et al. GPCR-specific autoantibody signatures are associated with physiological and pathological immune homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Müller, N.; Müller, U.A. Agonistic autoantibodies against B2-adrenergic receptors correlating with macrovascular disease in longstanding diabetes type 2. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jünemann, A.; Hohberger, B.; Rech, J.; Sheriff, A.; Fu, Q.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; Voll, R.E.; Bartel, S.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoebeke, J.; et al. Agonistic autoantibodies to the β2-adrenergic receptor involved in the pathogenesis of open-angle glaucoma. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornholz, B.; Roggenbuck, D.; Jahns, R.; Boege, F. Diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of β1-adrenergic receptor autoantibodies in human heart disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, P.; Hempel, P.; Bimmler, M. Role of alpha1-adrenergic receptor antibodies in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar]
- Loebel, M.; Grabowski, P.; Heidecke, H.; Bauer, S.; Hanitsch, L.G.; Wittke, K.; Meisel, C.; Reinke, P.; Volk, H.D.; Fluge, Ø.; et al. Antibodies to β adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors in patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 52, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sege, K.; Peterson, P.A. Use of anti-idiotypic antibodies as cell-surface receptor probes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 2443–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, G.; Amir-Zaltsman, Y.; Barnard, G.; Kohen, F. Characterization of an antiidiotypic antibody mimicking the actions of estradiol and its interaction with estrogen receptors. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 3633–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, H.N.; Jiang, H.L.; Li, W.; Wu, T.C.; Hong, P.; Li, Y.M.; Zhang, H.; Cui, H.Z.; Zheng, X. Development and characterization of a novel anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody to growth hormone, which can mimic physiological functions of growth hormone in primary porcine hepatocytes. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Feng, Z.; Shang, W.; Maziarz, M.; Radtke, J.; Hampe, C.S. Anti-idiotypic antibody specific to GAD65 autoantibody prevents type 1 diabetes in the NOD mouse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, D.; Cohen, I.R.; Shechter, Y.; Spirer, Z.; Golander, A. Antibodies to insulin receptor followed by anti-idiotype: Antibodies to insulin in child with hypoglycemia. Diabetes 1987, 36, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.I.; Barbetti, F.; Accili, D.; Roth, J.; Gorden, P. Syndromes of autoimmunity and hypoglycemia. Autoantibodies directed against insulin and its receptor. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 1989, 18, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, A.Y.; Gorden, P. Lessons from patients with anti-insulin receptor autoantibodies. In Immunoendocrinology: Scientific and Clinical Aspects; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 369–383. [Google Scholar]
- Uchigata, Y.; Hirata, Y. Insulin autoimmune syndrome (Hirata disease). In Immunoendocrinology: Scientific and Clinical Aspects; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 343–367. [Google Scholar]
- Moller, D.E.; Ratner, R.E.; Borenstein, D.G.; Taylor, S.I. Autoantibodies to the insulin receptor as a cause of autoimmune hypoglycemia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Med. 1988, 84, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Ichiki, Y.; Kitajima, Y. A case of systemic lupus erythematosus presenting as hypoglycemia due to anti-insulin receptor antibodies. Rheumatol. Int. 2008, 29, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, Y.; Zhou, J.-G.; Yuan, G. Systemic lupus erythematosus presenting as hypoglycaemia with insulin receptor antibodies and insulin autoantibodies. Lupus 2009, 18, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, D.; Maron, R.; Cohen, I.R.; Schechter, Y. Mouse antibodies to the insulin receptor developing spontaneously as anti-idiotypes. II. Effects on glucose homeostasis and the insulin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 6416–6419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Djiane, J.; Houdebine, L.M.; Kelly, P.A. Prolactin-like activity of anti-prolactin receptor antibodies on casein and DNA synthesis in the mammary gland. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 7445–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.A.M.; Djiane, J.; Houdebine, L.M.; Kelly, P.A. Stimulatory effects of prolactin and anti-prolactin receptor serum on prolactin binding sites in rat liver cells in suspension culture. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1982, 106, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusanter-Fourt, I.; Djiane, J.; Houdebine, L.M.; Kelly, P.A. In vivo lactogenic effects of anti prolactin receptor antibodies in pseudopregnant rabbits. Life Sci. 1983, 32, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edery, M.; Djiane, J.; Houdebine, L.M.; Kelly, P.A. Prolactin-like activity of antiprolactin receptor antibodies in rat mammary tumor explants. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 3170–3174. [Google Scholar]
- Borba, V.V.; Zandman-Goddard, G.; Shoenfeld, Y. Prolactin and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, S.W.W.; Knight, A.; Adams, D.D. The thyrotrophin receptor. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 1982, 5, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, K.; Hannover Larsen, J.; Mølholm Hansen, J.; Nerup, J. Yersinia enterocolitica infection and thyroid disorders. Lancet 1974, 304, 951–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkman, L.; Bottone, E.J. Antibodies to Yersinia enterocolitica in thyroid disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 1976, 85, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyma, P.; Harrison, L.C.; Robins-Browne, R. Thyrotrophin (TSH) binding sites on Yersinia enterocolitica recognized by immunoglobulins from humans with Graves’ disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1986, 64, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farid, N.R.; Brioñes-Urbina, R.; Nazrul-Islam, M. Biologic activity of anti-thyrotropin anti-idiotypic antibody. J. Cell. Biochem 1982, 19, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farid, N.R. Anti-hormone anti-idiotypes are probes for receptor structure and function. Immunol. Lett. 1985, 9, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Pepper, B.M.; Briones-Urbina, R.; Farid, N.R. Biological activity of anti-thyrotropin anti-idiotypic antibody. Eur. J. Immunol. 1983, 13, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, N.R.; Briones-Urbina, R.; Bear, J.C. Graves’ disease-the thyroid stimulating antibody and immunological networks. Mol. Aspects Med. 1983, 6, 355–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, C.; Chen, H. The monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies mimic HEC toxin produced by Aeromonas hyarophilia. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 1994, 17, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, W.T.; Harvey, D.; Sutherland, P.W.; Reynolds, P.H.S. Food and agricultural immunology production of anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibodies that mimic the phytotoxin dothistromin production of anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibodies that mimic the phytotoxin Dothistromin. Food Agric. Immunol. 1998, 10, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliani, W.; Conti, S.; De Bernardis, F.; Gerloni, M.; Bertolotti, D.; Mozzoni, P.; Cassone, A.; Polonelli, L. Therapeutic potential of antiidiotypic single chain antibodies with yeast killer toxin activity. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantusch, B.; Knittelfelder, R.; Wallmann, J.; Krieger, S.; Szalai, K.; Untersmayr, E.; Vogel, M.; Stadler, B.M.; Scheiner, O.; Boltz-Nitulescu, G.; et al. Internal images: Human anti-idiotypic Fab antibodies mimic the IgE epitopes of grass pollen allergen Phl p 5a. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 2180–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallmann, J.; Epstein, M.M.; Singh, P.; Brunner, R.; Szalai, K.; El-Housseiny, L.; Pali-Schöll, I.; Jensen-Jarolim, E. Mimotope vaccination for therapy of allergic asthma: Anti-inflammatory effects in a mouse model. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2010, 40, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, A.B.; Couraud, P.O.; Andre, C.; Vray, B.; Strosberg, A.D. Anti-alprenolol anti-idiotypic antibodies bind to beta-adrenergic receptors and modulate catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7385–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberland, A.; Wallukat, G.; Schimke, I. Aptamer binding and neutralization of β1-adrenoceptor autoantibodies: Basics and a vision of its future in cardiomyopathy treatment. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2011, 21, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, D.S.; Isom, G.E. Binding of antimorphine anti-idiotypic antibodies to opiate receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1984, 102, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasel, J.A.; Pelosi, L.A. Morphine-mimetic anti-paratypic antibodies: Cross-reactive properties. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 136, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramsch, C.; Schulz, R.; Kosin, S.; Herz, A. Monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies to opioid receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 5853–5859. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, B.F.; Bowen, W.D.; Frazier, J.S.; Rose, J.W.; McFarland, H.F.; McFarlin, D.E.; Murphy, D.L.; Morihisa, J.M. Human antiidiotypic antibody against opiate receptors. Ann. Neurol. 1988, 24, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, P.; Chen, H.; Adelman, M.K.; Schluter, S.F. Autoantibodies to the delta-opioid receptor function as opioid agonists and display immunomodulatory activity. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 217, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Segre, M. Inhibition of cocaine binding to the human dopamine transporter by a single chain anti-idiotypic antibody: Its cloning, expression, and functional properties. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2003, 1638, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolnick, P. Introduction: Biologics to Treat Substance Use Disorders: Vaccines, Monoclonal Antibodies, and Enzymes. Available online: https://books.google.ru/books?id=5Vk-CwAAQBAJ&pg=PA3&lpg=PA3&dq=Nonetheless,+despite+multiple+immunizations,+none+of+the+vaccines+developed+to+date+resulted+in+high+titers+of+high+affinity+anti-drug+antibodies+in+a+majority+of+patients&source=bl&ots=snVRBHl8kC&sig=ACfU3U1WWVb2VMNQhaTtYe_KvZ3lmydXoQ&hl=ru&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwiKt4jzlszpAhUj06YKHYlDBXIQ6AEwAHoECAoQAQ#v=onepage&q=Nonetheless%2Cdespitemultipleimmunizations%2Cnoneofthevaccinesdevelopedtodateresultedinhightitersofhighaffinityanti-drugantibodiesinamajorityofpatients&f=false (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Schabacker, D.S.; Kirschbaum, K.S.; Segre, M. Exploring the feasibility of an anti-idiotypic cocaine vaccine: Analysis of the specificity of anticocaine antibodies (Ab1) capable of inducing Ab2β anti-idiotypic antibodies. Immunology 2000, 100, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, A.V.; Ischenko, A.M.; Rak, A.Y.; Sergeeva, V.E.; Simbirtsev, A.S.; Gamaleya, N.B. Preparation and properties of murine anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibodies recognizing primary rabbit polyclonal antibodies against morphine derivatives. Med. Immunol. 2019, 21, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, B.L.; Bost, K.L. A monoclonal anti-peptide antibody mimics adrenocorticotropic hormone activity. Immunol. Lett. 1991, 28, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaichik, A.S.; Churilov, L.P.; Utekhin, V.J. Autoimmune regulation of genetically determined cell functions in health and disease. Pathophysiology 2008, 15, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüddens, H.; Havsteen, B. Characterization of the porcine ACTH receptor with the aid of a monoclonal antibody. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1986, 367, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spertini, F.; Leimgruber, A.; Morel, B.; Khazaeli, M.B.; Yamamoto, K.; Dayer, J.M.; Weisbart, R.H.; Lee, M.L. Idiotypic vaccination with a murine anti-dsDNA antibody: Phase I study in patients with nonactive systemic lupus erythematosus with nephritis. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 2602–2608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Hosono, O.; Koide, J.; Homma, M.; Abe, T. Suppression of rheumatoid factor synthesis by antiidiotypic antibody in rheumatoid arthritis patients with cross-reactive idiotypes. Arthritis Rheum. 1985, 28, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.R.; Bogdani, M.; LeBoeuf, R.C.; Kirk, E.A.; Maziarz, M.; Banga, J.P.; Oak, S.; Pennington, C.A.; Hampe, C.S. Modulation of diabetes in NOD mice by GAD65-specific monoclonal antibodies is epitope specific and accompanied by anti-idiotypic antibodies. Immunology 2008, 123, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oak, S.; Gilliam, L.K.; Landin-Olsson, M.; Törn, C.; Kockum, I.; Pennington, C.R.; Rowley, M.J.; Christie, M.R.; Banga, J.P.; Hampe, C.S. The lack of anti-idiotypic antibodies, not the presence of the corresponding autoantibodies to glutamate decarboxylase, defines type 1 diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5471–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, D.S.; Bradley, R.J.; Urquhart, C.K.; Kearney, J.F. Naturally occurring anti-idiotypic antibodies in myasthenia gravis patients. Nature 1983, 301, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Brettschneider, K.; Kahle, J.; Orlowski, A.; Becker-Peters, K.; Stichel, D.; Schulze, J.; Braner, M.; Tampé, R.; Schwabe, D.; et al. Neutralisation of factor VIII inhibitors by anti-idiotypes isolated from phage-displayed libraries. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 116, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, D.; Esser, K.; Sher, A. Immunization of mice against African trypanosomiasis using anti-idiotypic antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 1982, 155, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, K.E.; Söderström, T. Neonatal administration of idiotype or antiidiotype primes for protection against Escherichia coli K13 infection in mice. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, M.K.; Ward, R.E.; Kohler, H. Monoclonal idiotope vaccine against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. Science 1984, 226, 1325–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, S.; Ngampasutadol, J.; Yamasaki, R.; McQuillen, D.P.; Rice, P.A. Strategies for mimicking Neisserial saccharide epitopes as vaccines. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 20, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittum-Hudson, J.A.; Rudy, D.; Gerard, H.; Vora, G.; Davis, E.; Haller, P.K.; Prattis, S.M.; Hudson, A.P.; Saltzman, W.M.; Stuart, E.S. The anti-idiotypic antibody to chlamydial glycolipid exoantigen (GLXA) protects mice against genital infection with a human biovar of Chlamydia trachomatis. Vaccine 2001, 19, 4061–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Requena, A.; Burrone, O.R.; Cesco-Gaspere, M. Idiotypes as immunogens: Facing the challenge of inducing strong therapeutic immune responses against the variable region of immunoglobulins. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, H.; Pashov, A.; Kieber-Emmons, T. The Promise of Anti-idiotype Revisited. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, M.M.; De Haard, H.J. Properties, production, and applications of camelid single-domain antibody fragments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillib, S.V.; Ivanova, T.I.; Vasilev, L.A.; Rutovskaya, M.V.; Saakyan, S.A.; Gribova, I.Y.; Tutykhina, I.L.; Sedova, E.S.; Lysenko, A.A.; Shmarov, M.M.; et al. Formatted single-domain antibodies can protect mice against infection with influenza virus (H5N2). Antiviral Res. 2013, 97, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletaev, A.B.; Churilov, L.P.; Stroev, Y.I.; Agapov, M.M. Immunophysiology versus immunopathology: Natural autoimmunity in human health and disease. Pathophysiology 2012, 19, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabibov, A.G.; Ponomarenko, N.A.; Tretyak, E.B.; Paltsev, M.A.; Suchkov, S.V. Catalytic autoantibodies in clinical autoimmunity and modern medicine. Autoimmun. Rev. 2006, 5, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurkova, I.N.; Smirnov, I.V.; Belogurov, A.A.; Ponomarenko, N.A.; Gabibov, A.G. Creation of catalytic antibodies metabolizing organophosphate compounds. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2012, 77, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Anti-ID Bearing Internal Image of … | Biological Effects of Anti-ID | Authors |
|---|---|---|
| Human interferon-γ (IFN-γ) | Binding to the receptor of HuIFN-γ and reproduces antiviral activity | Depraetere et al. [21] |
| Interleukin-1 (IL-1) | Enhancing proliferation of thymocytes | Zuberi et al. [22] |
| Angiotensin | Binding to angiotensin receptors | Couraud et al. [23] |
| Basophil-bound idiotype | Altering histamine release from basophils | Mecheri et al. [26] |
| Haloperidol | Binding to D-2 dopamine receptors | Elazar et al. [27] |
| Dopamine | Inhibiting binding of dopamine to rat brain membranes | Mons et al. [28] |
| Acethylcholine-receptors | Similar binding abilities for cholinergic ligands | Eng et al. [29] |
| Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) | Recognizing 5-HT1B, 5-HT1C and 5-HT2 receptor subtypes | Tamir et al. [30] |
| β2-adrenergic receptor | Agonistic activity | Werner et al. [32] Junemann et al. [33] |
| β1-adrenergic receptor | Agonistic activity | Bornholz et al. [34] |
| α1-adrenergic receptor | Agonistic activity | Karczewski et al. [35] |
| Insulin | Binding to insulin receptors on thymocytes | Sege et al. [37] Elias et al. [41] Taylor et al. [42] Chong et al. [43] |
| Estradiol | Recognizing of estrogen receptor | Mor et al. [38] |
| Growth hormone | Binding to growth hormone receptors, stimulation of porcine hepatocytes to secrete insulin-like growth factor-1 | Lan et al. [39] |
| Prolactin | Prolactin-like activity on casein gene expression and DNA synthesis | Djiane et al. [49] Dusanter-Fourt et al. [51] |
| Thyrotropin | Inhibition biding of thyroid stimulating hormone to thyroid plasma membranes and stimulating their adenylate cyclase activity | Farid et al. [58,59,60,61] |
| ACTH | Stimulation of isolated adrenal cells to secrete corticosterone, inhibition of mitotic activity in adrenal cells. | Clarke et al. [78] |
| HEC toxin of Aeromonas hydrophila | Induction of specific immune reactivity to natural microbial antigen | Chen et al. [62] |
| Mycotoxin of dothistromin | Binding to dothistromin-protein conjugates | Jones et al. [63] |
| Killer toxin (KT) of Pichia anomala | Reaction with KT receptors, therapeutic activity in experimental rat model of vaginal thrush | Magliani et al. [64] |
| Phleum pretense grass pollen allergen | Therapeutic effect on experimental mice model of acute allergic asthma | Hantusch et al. [65] |
| Alprenalol | Binding to β-adrenergic receptors, stimulating of basal adenylate cyclase activity, modulation of catecholamine signal transmission | Schreiber et al. [67] |
| Naloxone | Binding to opiate receptors | Ng et al. [69] |
| Morphine | Inhibition of the morphine binding to opiate receptors | Glasel et al. [70] |
| β-endorphin | Opiate antagonistic activity | Gramsch et al. [71] Roy et al. [72] |
| Cocaine | Binding to hDAT | Ho et al. [74] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanova, A.K.; Ryabkova, V.A.; Tillib, S.V.; Utekhin, V.J.; Churilov, L.P.; Shoenfeld, Y. Anti-Idiotypic Agonistic Antibodies: Candidates for the Role of Universal Remedy. Antibodies 2020, 9, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9020019
Stanova AK, Ryabkova VA, Tillib SV, Utekhin VJ, Churilov LP, Shoenfeld Y. Anti-Idiotypic Agonistic Antibodies: Candidates for the Role of Universal Remedy. Antibodies. 2020; 9(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanova, Aliya K., Varvara A. Ryabkova, Sergei V. Tillib, Vladimir J. Utekhin, Leonid P. Churilov, and Yehuda Shoenfeld. 2020. "Anti-Idiotypic Agonistic Antibodies: Candidates for the Role of Universal Remedy" Antibodies 9, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9020019
APA StyleStanova, A. K., Ryabkova, V. A., Tillib, S. V., Utekhin, V. J., Churilov, L. P., & Shoenfeld, Y. (2020). Anti-Idiotypic Agonistic Antibodies: Candidates for the Role of Universal Remedy. Antibodies, 9(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9020019