Binding of Immunoglobulin G to Protoporphyrin IX and Its Derivatives: Evidence the Fab Domain Recognizes the Protoporphyrin Ring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Antibodies to Bovine Tf
2.3. Preparation of PPIX and PPIX Derivatives
2.4. Biotinylation of PPIX, Hemin, and Zn-PPIX
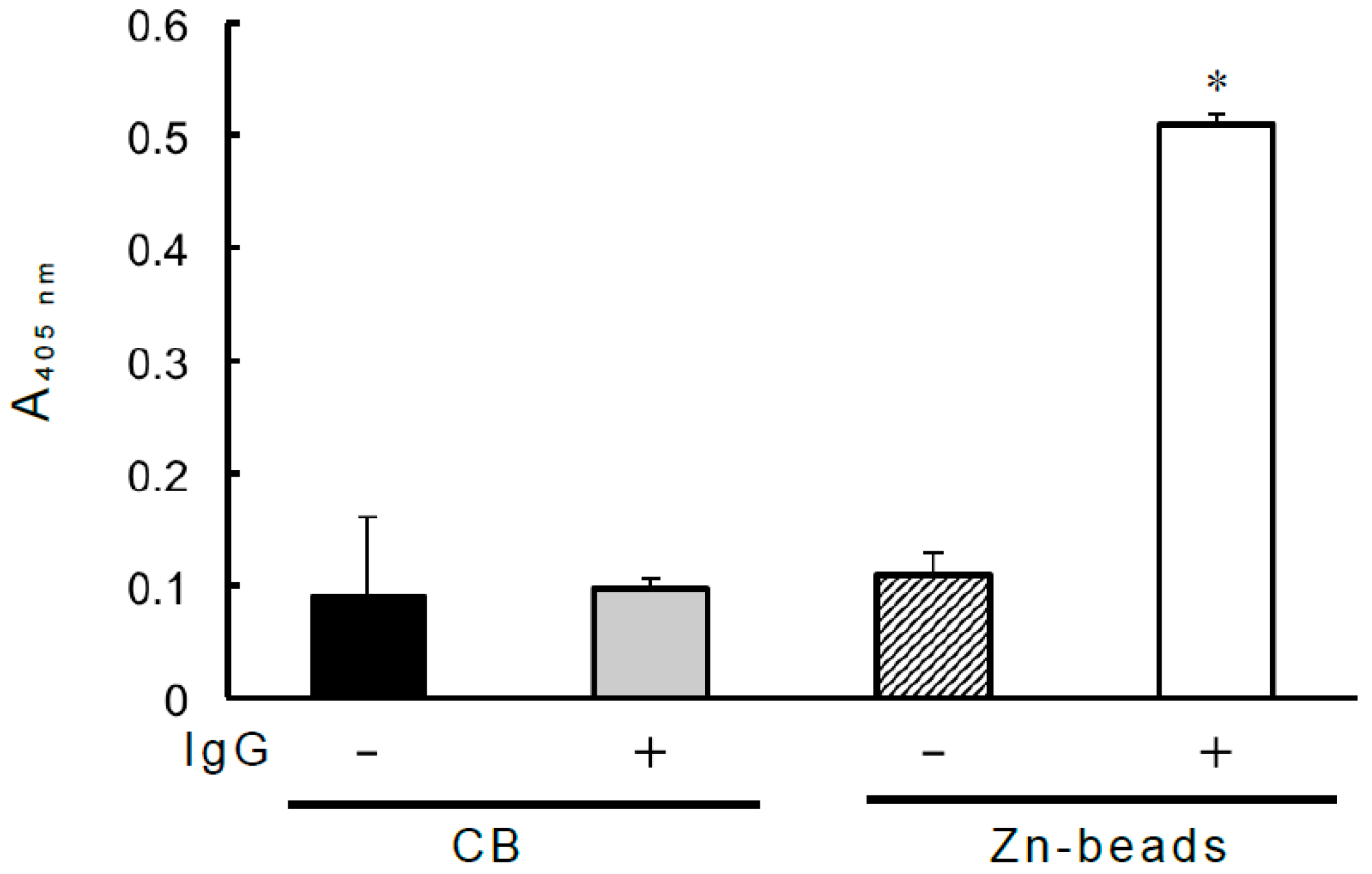
2.5. Binding of Zn-Binding IgG to Biotinylated PPIX
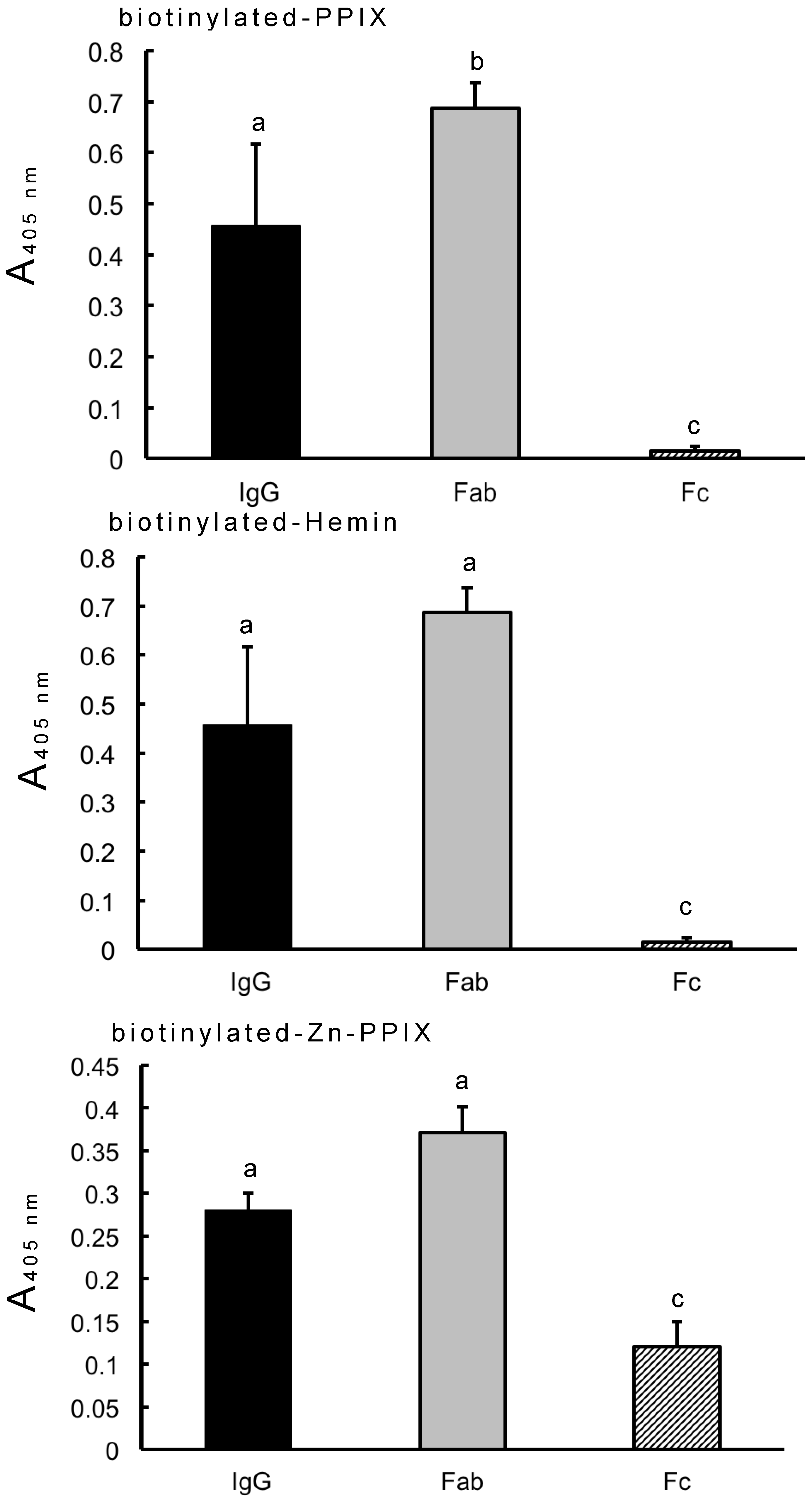
2.6. Binding of Human IgG, Fab and Fc to Biotinylated PPIX, Hemin and Zn-PPIX
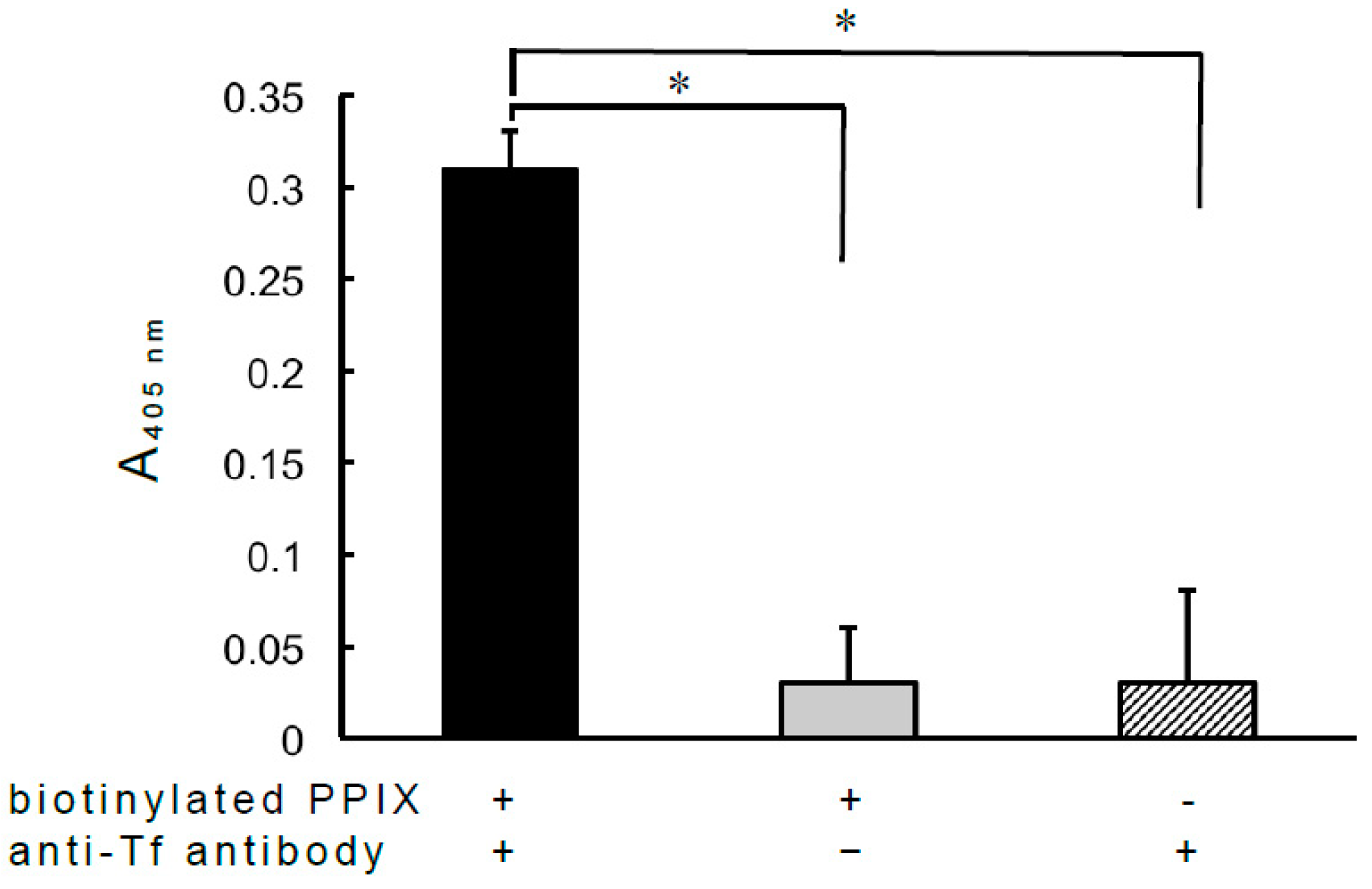
2.7. Effect of the Complex Formed between Antibody and Biotinylated PPIX on the Antibody-Antigen Reaction
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fab-Mediated Binding of IgG to PPIX and Its Derivatives
3.2. Effect of Antibody-PPIX Interactions on Antibody-Antigen Reactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schroeder, H.W.; Cavacini, L.C. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S41–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irani, V.; Guy, A.J.; Andrew, D.; Beeson, J.G.; Ramsland, P.A.; Richards, J.S. Molecular properties of human IgG subclasses and their implications for designing therapeutic monoclonal antibodies against infectious diseases. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koleva, T.; Ensom, M.H.H. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous immuhnoglobulin: a systemic review. Pharmacother. 2006, 26, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, E.E.; Orange, J.S.; Bonilla, F.; Chinen, J.; Chinn, I.K.; Dorsey, M.; EI-Gamal, Y.; Harville, T.O.; Hossny, E.; Mazer, B.; et al. Update of the use of immunoglobulin in human disease: a review of evidence. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, S1–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, W.; Dugannavar, T.A.; Chung, S.J. Fc-binding ligands of immunoglobulin G: An overview of high affinity proteins and ligands. Materials 2016, 9, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, Y.; Matsugano, S.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Orino, K. Binding analysis of human immunoglobulin G as a zinc-binding protein. Antibodies 2016, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaleon, L.; Moseley, H. Effects of photoproducts on the binding properties of protoporhyrin IX to proteins. Biophys. Chem. 2002, 96, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaleon, L.; Magennis, S.M.; Samuel, I.D.W.; Namdas, E.; Lesar, A.; Moseley, H. Characterization of the photoproducts of protoporphyrin IX bound to human serum albumin and immunoglobulin G. Biophys. Chem. 2004, 109, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Sakashita, Y.; Orino, K.; Yamamoto, S. Identification of bovine serum transferrin phenotypes by polyacrylamide gel isoelectric focusing (PAGIEF). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1994, 56, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orino, K.; Saji, M.; Ozaki, Y.; Ohya, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Watanabe, K. Inhibitory effects of horse serum on immunoassay of horse ferritin. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1993, 55, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvat, E.M.; Daltrop, O.; Sobott, F.; Moreau, M.; Barker, P.D.; Stevens, J.M.; Ferguson, S.J. Metal and redox selectivity of protoporphyrin binding to the heme chaperone CcmE. Metallonics 2011, 3, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usami, A.; Tanaka, M.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ohtsuka, H.; Orino, K. Heme-mediated binding of α-casein to ferritin: evidence for preferential α-casein binding to ferrous iron. Biometals 2011, 24, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, C.; Ananthanarayanan, K.; Natarajan, P. Studies on the photophysical charateristics of poly(carboxylic acid)s bound protoporphyrin IX and metal complexes of protoporphyrin IX. Eur. Polymer. J. 2006, 42, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiel, J.E.; Turner, A. The NISTmAb reference material 8671 lifecycle management and quality plan. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2067–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Gao, K.; Song, M.; Liu, Q. The spectroscopy analyses of PpIX by ultrasound irradiation and its sonotoxicity in vitro. Ultrasonics 2013, 53, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orino, K. Physiological implications of mammal ferritin-binding protein interacting with circulating ferritin and a new aspect of ferritin- and zinc-binding proteins. Biometals 2016, 29, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.S. Zinc is an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent: its role in human health. Front. Nutr. 2014, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orino, K. Binding of Immunoglobulin G to Protoporphyrin IX and Its Derivatives: Evidence the Fab Domain Recognizes the Protoporphyrin Ring. Antibodies 2019, 8, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8010006
Orino K. Binding of Immunoglobulin G to Protoporphyrin IX and Its Derivatives: Evidence the Fab Domain Recognizes the Protoporphyrin Ring. Antibodies. 2019; 8(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrino, Koichi. 2019. "Binding of Immunoglobulin G to Protoporphyrin IX and Its Derivatives: Evidence the Fab Domain Recognizes the Protoporphyrin Ring" Antibodies 8, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8010006
APA StyleOrino, K. (2019). Binding of Immunoglobulin G to Protoporphyrin IX and Its Derivatives: Evidence the Fab Domain Recognizes the Protoporphyrin Ring. Antibodies, 8(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8010006



