Pairing Alpaca and Llama-Derived Single Domain Antibodies to Enhance Immunoassays for Ricin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
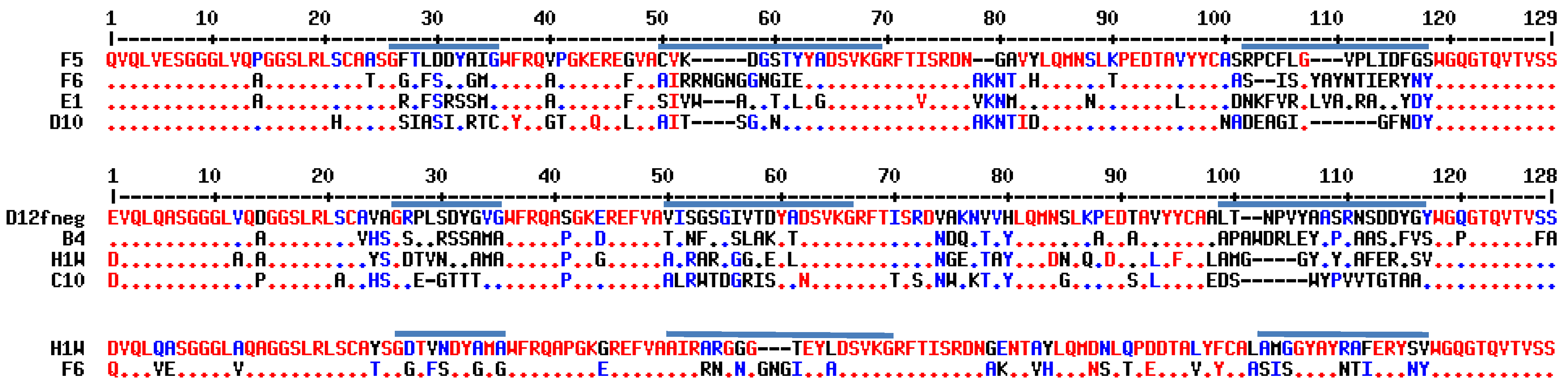
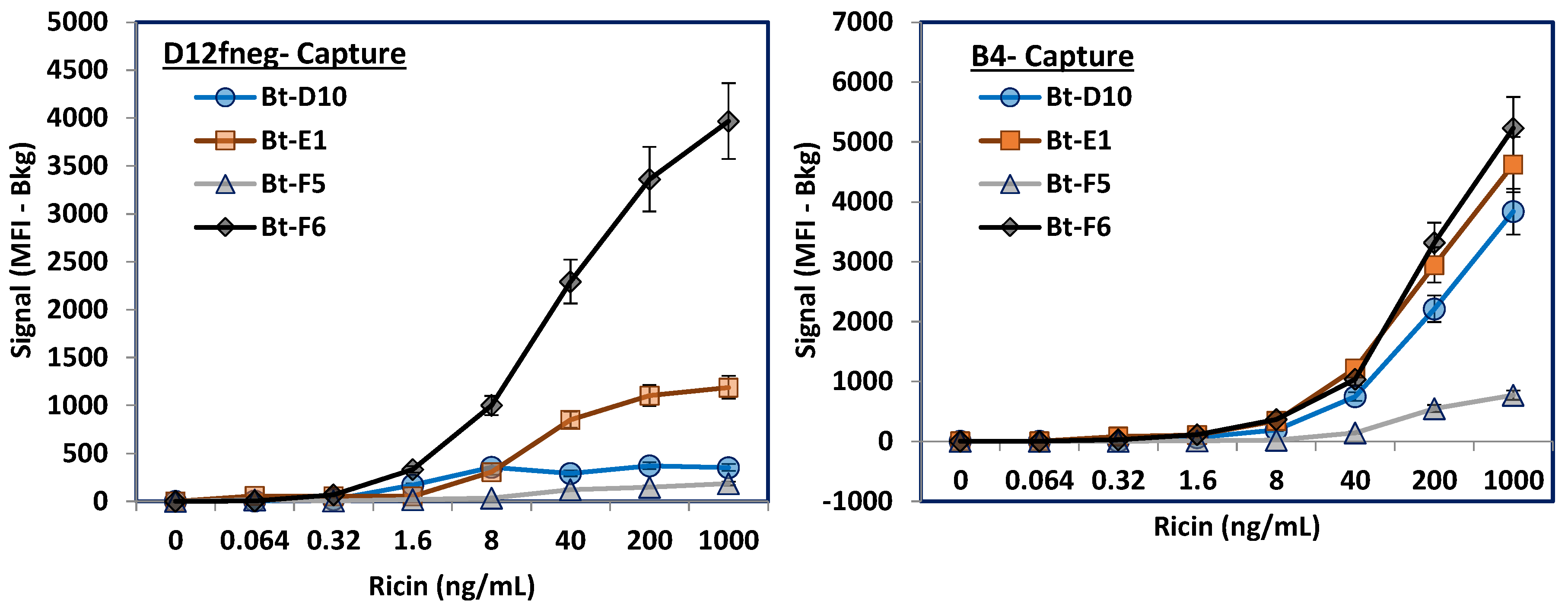
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Protein Preparation
3.3. Circular Dichroism (CD)
3.4. Fluorescence-Based Melting Assay
3.5. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
3.6. MagPlex Sandwich Immunoassays
3.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamers-Casterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hamers, C.; Songa, E.B.; Bendahman, N.; Hamers, R. Naturally-occurring antibodies devoid of light-chains. Nature 1993, 363, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyer, L.H.K. Single-domain antibody fragments derived from heavy-chain antibodies: A review. Vet. Med. 2012, 57, 439–513. [Google Scholar]
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural single-domain antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, A. Biotechnological applications of recombinant single-domain antibody fragments. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, M.D.; Anderson, G.P.; Serrano-Gonzalez, J.; Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Goldman, E.R. Immunodiagnostic reagents using llama single domain antibody-alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walper, S.A.; Lee, P.A.B.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Comparison of single domain antibody immobilization strategies evaluated by surface plasmon resonance. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 388, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Walper, S.A.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Bioconjugates of rhizavidin with single domain antibodies as bifunctional immunoreagents. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 411, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, L.J.; Osborn, L.E.; Carrion, R.; Patterson, J.L.; Hayhurst, A. Rapid assembly of sensitive antigen-capture assays for marburg virus, using in vitro selection of llama single-domain antibodies, at biosafety level 4. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, S213–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wan, D.-B.; Xiong, Y.-H.; He, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-X.; Gee, S.J.; Ryu, D.; Hammock, B.D. Development of a nanobody–alkaline phosphatase fusion protein and its application in a highly sensitive direct competitive fluorescence enzyme immunoassay for detection of ochratoxin a in cereal. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumoulin, M.; Conrath, K.; van Meirhaeghe, A.; Meersman, F.; Heremans, K.; Frenken, L.G.J.; Muyldermans, S.; Wyns, L.; Matagne, A. Single-domain antibody fragments with high conformational stability. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Linden, R.H.J.; Frenken, L.G.J.; de Geus, B.; Harmsen, M.M.; Ruuls, R.C.; Stok, W.; de Ron, L.; Wilson, S.; Davis, P.; Verrips, C.T. Comparison of physical chemical properties of llama V-HH antibody fragments and mouse monoclonal antibodies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1999, 1431, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leski, T.A.; Ansumana, R.; Taitt, C.R.; Lamin, J.M.; Bangura, U.; Lahai, J.; Mbayo, G.; Kanneh, M.B.; Bawo, B.; Bockarie, A.S.; et al. Use of filmarray™ system for detection of Zaire ebolavirus in a small hospital, Bo, Sierra Leone. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leski, T.A.; Ansumana, R.; Malanoski, A.P.; Jimmy, D.H.; Bangura, U.; Barrows, B.R.; Alpha, M.; Koroma, B.M.; Long, N.C.; Sundufu, A.J.; et al. Leapfrog diagnostics: Demonstration of a broad spectrum pathogen identification platform in a resource-limited setting. Health Res. Policy Syst. 2012, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, J.O.; Sherwood, L.J.; Collazo, M.T.; Garza, J.A.; Hayhurst, A. Llama single domain antibodies specific for the 7 botulinum neurotoxin serotypes as heptaplex immunoreagents. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, L.J.; Hayhurst, A. Ebolavirus nucleoprotein C-termini potently attract single domain antibodies enabling monoclonal affinity reagent sandwich assay (MARSA) formulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walper, S.A.; Anderson, G.P.; Lee, P.A.B.; Glaven, R.H.; Liu, J.L.; Bernstein, R.D.; Zabetakis, D.; Johnson, L.; Czarnecki, J.M.; Goldman, E.R. Rugged single domain antibody detection elements for bacillus anthracis spores and vegetative cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walper, S.A.; Lee, P.A.B.; Anderson, G.P.; Goldman, E.R. Selection and characterization of single domain antibodies specific for bacillus anthracis spore proteins. Antibodies 2013, 2, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzogaray, V.; Danquah, W.; Aguirre, A.; Urrutia, M.; Berguer, P.; Vescovi, E.G.; Haag, F.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Goldbaum, F.A. Single-domain llama antibodies as specific intracellular inhibitors of SpvB, the actin ADP-ribosylating toxin of salmonella typhimurium. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, E.; Hirama, T.; Chen, W.X.; Soltyk, A.L.; Brunton, J.; MacKenzie, C.R.; Zhang, J.B. A novel pentamer versus pentarner approach to generating neutralizers of verotoxin 1. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2487–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Thompson, A.A.; Fan, Y.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Ho, M.; Pires-Alves, M.; Wilson, B.A.; Stevens, R.C.; Marks, J.D. A single-domain llama antibody potently inhibits the enzymatic activity of botulinum neurotoxin by binding to the non-catalytic alpha-exosite binding region. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 397, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesolowski, J.; Alzogaray, V.; Reyelt, J.; Unger, M.; Juarez, K.; Urrutia, M.; Cauerhff, A.; Danquah, W.; Rissiek, B.; Scheuplein, F.; et al. Single domain antibodies: Promising experimental and therapeutic tools in infection and immunity. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 198, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.P.; Liu, J.L.; Hale, M.L.; Bernstein, R.D.; Moore, M.; Swain, M.D.; Goldman, E.R. Development of antiricin single domain antibodies toward detection and therapeutic reagents. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9604–9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.P.; Bernstein, R.D.; Swain, M.D.; Zabetakis, D.; Goldman, E.R. Binding kinetics of antiricin single domain antibodies and improved detection using a B chain specific binder. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7202–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, K.B.; Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Lee, A.B.; Anderson, G.P.; Goldman, E.R. Improving the biophysical properties of anti-ricin single-domain antibodies. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 6, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legler, P.M.; Compton, J.R.; Hale, M.L.; Anderson, G.P.; Olson, M.A.; Millard, C.B.; Goldman, E.R. Stability of isolated antibody-antigen complexes as a predictive tool for selecting toxin neutralizing antibodies. mAbs 2017, 9, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.J.; Tremblay, J.M.; Mantis, N.J.; Shoemaker, C.B. Stepwise engineering of heterodimeric single domain camelid vhh antibodies that passively protect mice from ricin toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 36538–36547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuntao, W.; Jiannan, F.; Jianwei, G.; Leiming, G.; Yan, L.; Yingxun, S.; Weisong, Q.; Meiru, H.; Gencheng, H.; Beifen, S. A novel designed single domain antibody on 3-D structure of ricin a chain remarkably blocked ricin-induced cytotoxicity. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walper, S.A.; Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Anderson, G.P.; Goldman, E.R. Development and evaluation of single domain antibodies for vaccinia and the L1 antigen. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Goldman, E.; Zabetakis, D.; Walper, S.; Turner, K.; Shriver-Lake, L.; Anderson, G. Enhanced production of a single domain antibody with an engineered stabilizing extra disulfide bond. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabetakis, D.; Olson, M.A.; Anderson, G.P.; Legler, P.M.; Goldman, E.R. Evaluation of disulfide bond position to enhance the thermal stability of a highly stable single domain antibody. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, C.; Tremblay, J.M.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Mantis, N.J. Mechanisms of ricin toxin neutralization revealed through engineered homodimeric and heterodimeric camelid antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 27880–27889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagihara, Y.; Mine, S.; Uegaki, K. Stabilization of an immunoglobulin fold domain by an engineered disulfide bond at the buried hydrophobic region. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 36489–36495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagihara, Y.; Saerens, D. Engineering disulfide bonds within an antibody. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2014, 1844, 2016–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saerens, D.; Conrath, K.; Govaert, J.; Muyldermans, S. Disulfide bond introduction for general stabilization of immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlapschy, M.; Grimm, S.; Skerra, A. A system for concomitant overexpression of four periplasmic folding catalysts to improve secretory protein production in escherichia coli. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2006, 19, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Goldman, E.R.; Zabetakis, D.; Anderson, G.P. Improved production of single domain antibodies with two disulfide bonds by co-expression of chaperone proteins in the Escherichia coli periplasm. J. Immunol. Methods 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussack, G.; Hirama, T.; Ding, W.; MacKenzie, R.; Tanha, J. Engineered single-domain antibodies with high protease resistance and thermal stability. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corpet, F. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical-clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 10881–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, E.R.; Brozozog-Lee, P.A.; Zabetakis, D.; Turner, K.B.; Walper, S.A.; Liu, J.L.; Anderson, G.P. Negative tail fusions can improve ruggedness of single domain antibodies. Protein Expr. Purif. 2014, 95, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| SdAb | Melting Temperature | Affinity Constants to Ricin A Chain (RTA) by SPR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dye Melt (°C) | CD (°C) (% Refold) | ka (1/Ms) | kd (1/s) | KD (M) | |
| D10 a | 66 | 70 (70%) | 4.0 × 105 | 5.7 × 10−5 | 1.4 × 10−10 |
| E1 a | 65 | 66 (42%) | 1.9 × 105 | 2.4 × 10−4 | 1.3 × 10−9 |
| F5 a | 70 | 71 (77%) | 1.6 × 105 | 2.8 × 10−5 | 1.7 × 10−10 |
| F6 a | 74 | 73 (71%) | 2.0 × 105 | 1.2 × 10−3 | 6.0 × 10−9 |
| D12fneg b | 77 | 79 (100%) | 4.2 × 105 | 9.4 × 10−6 | 2.3 × 10−11 |
| H1W b | 70 | 71 (75%) | 1.7 × 105 | 3.4 × 10−4 | 2.0 × 10−9 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turner, K.B.; Hardy, S.; Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Lee, P.A.B.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Pairing Alpaca and Llama-Derived Single Domain Antibodies to Enhance Immunoassays for Ricin. Antibodies 2017, 6, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6010003
Turner KB, Hardy S, Liu JL, Zabetakis D, Lee PAB, Goldman ER, Anderson GP. Pairing Alpaca and Llama-Derived Single Domain Antibodies to Enhance Immunoassays for Ricin. Antibodies. 2017; 6(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurner, Kendrick B., Sabrina Hardy, Jinny L. Liu, Dan Zabetakis, P. Audrey Brozozog Lee, Ellen R. Goldman, and George P. Anderson. 2017. "Pairing Alpaca and Llama-Derived Single Domain Antibodies to Enhance Immunoassays for Ricin" Antibodies 6, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6010003
APA StyleTurner, K. B., Hardy, S., Liu, J. L., Zabetakis, D., Lee, P. A. B., Goldman, E. R., & Anderson, G. P. (2017). Pairing Alpaca and Llama-Derived Single Domain Antibodies to Enhance Immunoassays for Ricin. Antibodies, 6(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6010003




