Cytokines in the Germinal Center Niche
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Cytokine | Main Producers | Function in the GC | Disease | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-21 | Tfh cells | GC B cell differentiation, affinity maturation, Tfh cell differentiation and function, | XSCID, RA, SLE, T1D | [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] |
| IL-4 | Tfh cells | Ab class switching to IgG1, IgE | XSCID | [17,23] |
| IFN-γ | Tfh cells | Ab class switching to IgG2a | RA, SLE, T1D | [24,25] |
| IL-10 | human Tfh cells, murine Tfr cells | B cell proliferation, plasma cell differentiation, Ab class switching to IgG1 and IgG3 | RA, SLE, Sjogren’s syndrome, Grave’s disease | [26,27,28,29,30,31] |
| IL-6 | FDCs, Plasmablasts | B cell and Tfh cell differentiation | RA, SLE | [32,33,34] |
| IL-27 | unknown | Tfh cell function, IL-21 production | RA, SLE, T1D | [35,36,37] |
| IL-2 | activated Th cells | Treg differentiation, negative regulator for Tfh lineage | EAE, T1D, Atherosclerosis | [38,39,40,41,42] |
| IL-17 | Tfh like cells * | B cell retention in GC, Tfh cell localization to GC LZ | RA, SLE, MS, Sjogren’s syndrome | [43,44,45] |
2. T Follicular Helper Cells, Cytokine Producers in the Germinal Center
2.1. Characterization of T Follicular Helper Cells
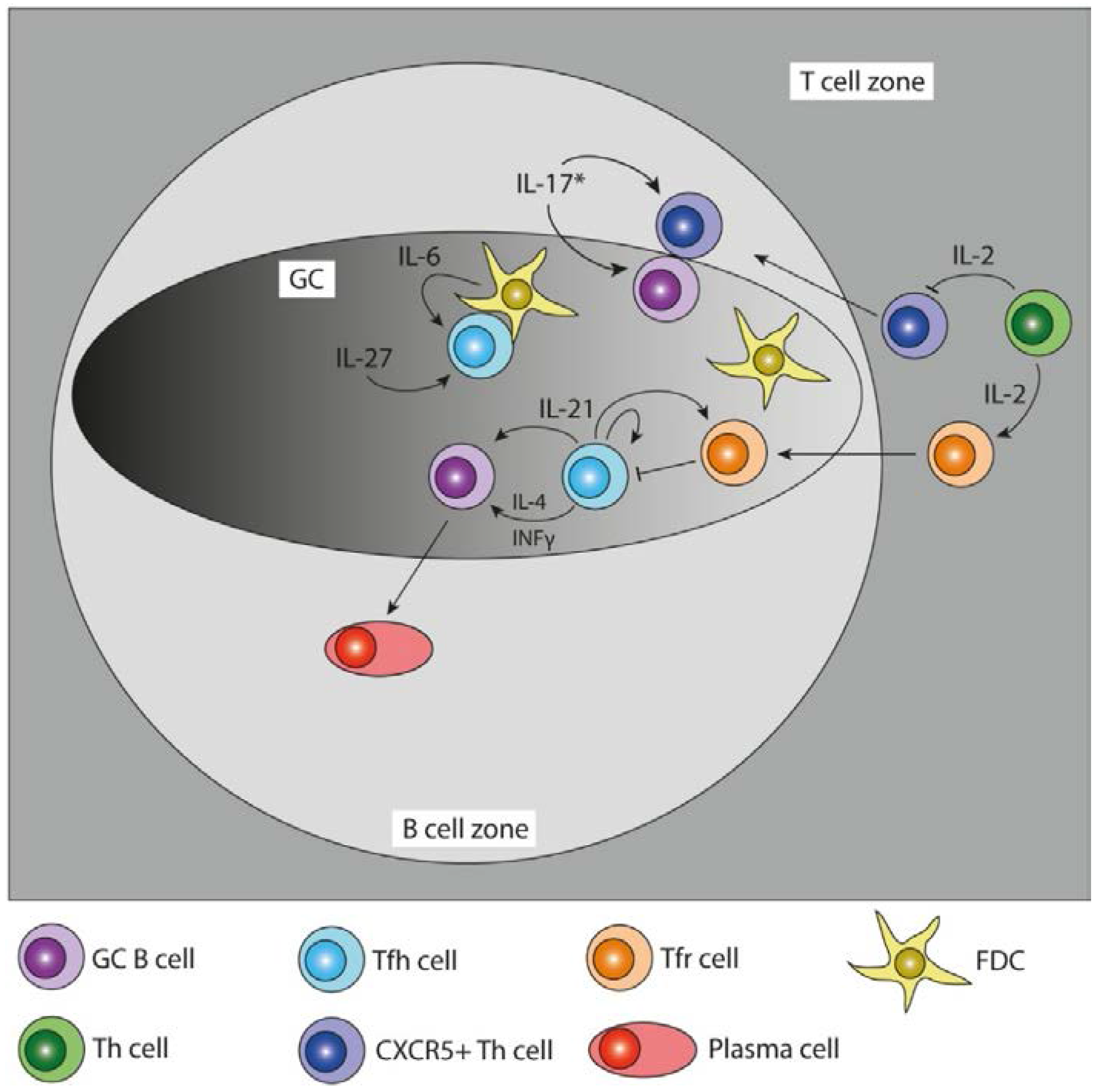
2.2. T Follicular Helper Cell Differentiation
2.3. T Follicular Regulatory Cells
3. Cytokine Signaling within the Germinal Center
3.1. Cytokine Reporter Mice
3.2. IL-21–IL6, Functional Redundancies
3.3. IL-21–IL-2, Antagonizing Functions
3.4. IL-21–IL-4, Collaborative Functions
3.5. Interferon-γ, A Non-Canonical Cytokine Expressed by Tfh Cells
3.6. IL-21–IL-10, Differential Functions in Humans and Mice
3.7. IL-21–IL-17, Complementing Functions in Autoimmune Disease
4. Roles for Germinal Center Cytokine Signaling in Disease
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gershon, R.K.; Kondo, K. Cell interactions in the induction of tolerance: The role of thymic lymphocytes. Immunology 1970, 18, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mier, J.W.; Gallo, R.C. Purification and some characteristics of human T-cell growth factor from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocyte-conditioned media. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 6134–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLennan, I.C.M. Germinal Centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Malisan, F.; de Bouteiller, O.; Guret, C.; Lebecque, S.; Banchereau, J.; Mills, F.C.; Max, E.E.; Martinez-Valdez, H. Within germinal centers, isotype switching of immunoglobulin genes occurs after the onset of somatic mutation. Immunity 1996, 4, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claman, H.N.; Chaperon, E.A.; Triplett, R.F. Thymus-marrow cell combinations. Synergism in antibody production. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. N. Y. N. 1966, 122, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.F.; Mitchell, G.F. Cell to cell interaction in the immune response. I. Hemolysin-forming cells in neonatally thymectomized mice reconstituted with thymus or thoracic duct lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1968, 128, 801–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitfeld, D.; Ohl, L.; Kremmer, E.; Ellwart, J.; Sallusto, F.; Lipp, M.; Förster, R. Follicular B helper T cells express CXC chemokine receptor 5, localize to B cell follicles, and support immunoglobulin production. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaerli, P.; Willimann, K.; Lang, A.B.; Lipp, M.; Loetscher, P.; Moser, B. CXC chemokine receptor 5 expression defines follicular homing T cells with B cell helper function. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Rott, L.S.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Campbell, D.J.; Wu, L.; Butcher, E.C. Subspecialization of CXCR5+ T cells: B helper activity is focused in a germinal center-localized subset of CXCR5+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansel, K.M.; McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; Ngo, V.N.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G.; Cyster, J.G. In vivo-activated CD4 T cells upregulate CXC chemokine receptor 5 and reprogram their response to lymphoid chemokines. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutloff, A.; Dittrich, A.M.; Beier, K.C.; Eljaschewitsch, B.; Kraft, R.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Kroczek, R.A. ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28. Nature 1999, 397, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Kooten, C.; Banchereau, J. CD40-CD40 ligand. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 67, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vogelzang, A.; McGuire, H.M.; Yu, D.; Sprent, J.; Mackay, C.R.; King, C. A fundamental role for interleukin-21 in the generation of T follicular helper cells. Immunity 2008, 29, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurieva, R.I.; Chung, Y.; Hwang, D.; Yang, X.O.; Kang, H.S.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Watowich, S.S.; Jetten, A.M.; Tian, Q.; et al. Generation of T follicular helper cells is mediated by interleukin-21 but independent of T helper 1, 2, or 17 cell lineages. Immunity 2008, 29, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linterman, M.A.; Beaton, L.; Yu, D.; Ramiscal, R.R.; Srivastava, M.; Hogan, J.J.; Verma, N.K.; Smyth, M.J.; Rigby, R.J.; Vinuesa, C.G. IL-21 acts directly on B cells to regulate Bcl-6 expression and germinal center responses. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zotos, D.; Coquet, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Light, A.; D’Costa, K.; Kallies, A.; Corcoran, L.M.; Godfrey, D.I.; Toellner, K.-M.; Smyth, M.J.; et al. IL-21 regulates germinal center B cell differentiation and proliferation through a B cell–intrinsic mechanism. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.; Spolski, R.; Feng, C.G.; Qi, C.-F.; Cheng, J.; Sher, A.; Morse, H.C., 3rd; Liu, C.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Leonard, W.J. A critical role for IL-21 in regulating immunoglobulin production. Science 2002, 298, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chtanova, T.; Tangye, S.G.; Newton, R.; Frank, N.; Hodge, M.R.; Rolph, M.S.; Mackay, C.R. T follicular helper cells express a distinctive transcriptional profile, reflecting their role as non-Th1/Th2 effector cells that provide help for B cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2004, 173, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, W.J. Cytokines and immunodeficiency diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 1, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.D.; Smyth, D.J.; Smiles, A.M.; Plagnol, V.; Walker, N.M.; Allen, J.E.; Downes, K.; Barrett, J.C.; Healy, B.C.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association study data identifies additional type 1 diabetes risk loci. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1399–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.; Kim-Howard, X.; Kelly, J.A.; Kaufman, K.M.; Langefeld, C.D.; Ziegler, J.; Sanchez, E.; Kimberly, R.P.; Edberg, J.C.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; et al. Fine-mapping and transethnic genotyping establish IL2/IL21 genetic association with lupus and localize this genetic effect to IL21. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubier, J.A.; Sproule, T.J.; Foreman, O.; Spolski, R.; Shaffer, D.J.; Morse, H.C.; Leonard, W.J.; Roopenian, D.C. A critical role for IL-21 receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus in BXSB-Yaa mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, R.L.; Liang, H.-E.; Locksley, R.M. Cytokine-secreting follicular T cells shape the antibody repertoire. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotty, S. Follicular helper CD4 T cells (TFH). Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano, G.; Ottum, P.A.; Reyes, L.I.; Burgos, P.I.; Naves, R. Stage-Specific Role of Interferon-Gamma in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, N.F.; Castle, B.E.; Barrett, R.; Kastelein, R.; Dang, W.; Mosmann, T.R.; Moore, K.W.; Howard, M. Interleukin 10, a novel B cell stimulatory factor: Unresponsiveness of X chromosome-linked immunodeficiency B cells. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakkach, A.; Cottrez, F.; Groux, H. Can interleukin-10 be used as a true immunoregulatory cytokine? Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2000, 11, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banchereau, J.; Rousset, F. Human B lymphocytes: Phenotype, proliferation, and differentiation. Adv. Immunol. 1992, 52, 125–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rousset, F.; Garcia, E.; Defrance, T.; Péronne, C.; Vezzio, N.; Hsu, D.H.; Kastelein, R.; Moore, K.W.; Banchereau, J. Interleukin 10 is a potent growth and differentiation factor for activated human B lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1890–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalani, I.; Bhol, K.; Ahmed, A.R. Interleukin-10: Biology, role in inflammation and autoimmunity. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997, 79, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linterman, M.A.; Pierson, W.; Lee, S.K.; Kallies, A.; Kawamoto, S.; Rayner, T.F.; Srivastava, M.; Divekar, D.P.; Beaton, L.; Hogan, J.J.; et al. Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T cells control the germinal center response. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eto, D.; Lao, C.; DiToro, D.; Barnett, B.; Escobar, T.C.; Kageyama, R.; Yusuf, I.; Crotty, S. IL-21 and IL-6 Are Critical for Different Aspects of B Cell Immunity and Redundantly Induce Optimal Follicular Helper CD4 T Cell (Tfh) Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnowski, A.; Chevrier, S.; Belz, G.T.; Mount, A.; Emslie, D.; D’Costa, K.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Kallies, A.; Corcoran, L.M. B and T cells collaborate in antiviral responses via IL-6, IL-21, and transcriptional activator and coactivator, Oct2 and OBF-1. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2049–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T. Interleukin 6 and its Receptor: Ten Years Later. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 249–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meka, R.R.; Venkatesha, S.H.; Dudics, S.; Acharya, B.; Moudgil, K.D. IL-27-induced modulation of autoimmunity and its therapeutic potential. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batten, M.; Ramamoorthi, N.; Kljavin, N.M.; Ma, C.S.; Cox, J.H.; Dengler, H.S.; Danilenko, D.M.; Caplazi, P.; Wong, M.; Fulcher, D.A.; et al. IL-27 supports germinal center function by enhancing IL-21 production and the function of T follicular helper cells. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2895–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batten, M.; Li, J.; Yi, S.; Kljavin, N.M.; Danilenko, D.M.; Lucas, S.; Lee, J.; de Sauvage, F.J.; Ghilardi, N. Interleukin 27 limits autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing the development of interleukin 17-producing T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyman, O.; Kovar, M.; Rubinstein, M.P.; Surh, C.D.; Sprent, J. Selective stimulation of T cell subsets with antibody-cytokine immune complexes. Science 2006, 311, 1924–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, K.E.; Walters, S.; Kohler, R.E.; Mrkvan, T.; Boyman, O.; Surh, C.D.; Grey, S.T.; Sprent, J. In vivo expansion of T reg cells with IL-2-mAb complexes: Induction of resistance to EAE and long-term acceptance of islet allografts without immunosuppression. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setoguchi, R.; Hori, S.; Takahashi, T.; Sakaguchi, S. Homeostatic maintenance of natural Foxp3(+) CD25(+) CD4(+) regulatory T cells by interleukin (IL)-2 and induction of autoimmune disease by IL-2 neutralization. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Fu, S.M.; Ju, S.-T. IL-2: A two-faced master regulator of autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 36, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oestreich, K.J.; Mohn, S.E.; Weinmann, A.S. Molecular mechanisms that control the expression and activity of Bcl-6 in TH1 cells to regulate flexibility with a TFH-like gene profile. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-C.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Myers, R.; Chen, J.; Yi, J.; Guentert, T.; Tousson, A.; Stanus, A.L.; et al. Interleukin 17-producing T helper cells and interleukin 17 orchestrate autoreactive germinal center development in autoimmune BXD2 mice. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graeber, K.E.; Olsen, N.J. Th17 cell cytokine secretion profile in host defense and autoimmunity. Inflamm. Res. Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. Al 2012, 61, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Q.; Yang, P.; Luo, B.; Xie, S.; Druey, K.M.; Zajac, A.J.; Hsu, H.-C.; Mountz, J.D. IL-17RA is essential for optimal localization of follicular Th cells in the germinal center light zone to promote autoantibody-producing B cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2013, 191, 1614–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; He, D.; Zhang, X.; Yue, T.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.Z.; Dong, C.; Chen, G. IL-21 regulates Th17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Hum. Immunol. 2010, 71, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuurman, H.J.; Bell, E.B.; Gärtner, K.; Hedrich, H.J.; Hansen, A.K.; Kruijt, B.C.; de Vrey, P.; Leyten, R.; Maeder, S.J.; Moutier, R. Comparative evaluation of the immune status of congenitally athymic and euthymic rat strains bred and maintained at different institutes: 2. Athymic rats. J. Exp. Anim. Sci. 1992, 35, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dianda, L.; Gulbranson-Judge, A.; Pao, W.; Hayday, A.C.; MacLennan, I.C.; Owen, M.J. Germinal center formation in mice lacking alpha beta T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, R.; Schubel, A.; Breitfeld, D.; Kremmer, E.; Renner-Müller, I.; Wolf, E.; Lipp, M. CCR7 coordinates the primary immune response by establishing functional microenvironments in secondary lymphoid organs. Cell 1999, 99, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardtke, S.; Ohl, L.; Förster, R. Balanced expression of CXCR5 and CCR7 on follicular T helper cells determines their transient positioning to lymph node follicles and is essential for efficient B-cell help. Blood 2005, 106, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, N.M.; Allen, C.D.C.; Lesley, R.; Ansel, K.M.; Killeen, N.; Cyster, J.G. Role of CXCR5 and CCR7 in follicular Th cell positioning and appearance of a programmed cell death gene-1high germinal center-associated subpopulation. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2007, 179, 5099–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, R.; Mattis, A.E.; Kremmer, E.; Wolf, E.; Brem, G.; Lipp, M. A putative chemokine receptor, BLR1, directs B cell migration to defined lymphoid organs and specific anatomic compartments of the spleen. Cell 1996, 87, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.D.C.; Ansel, K.M.; Low, C.; Lesley, R.; Tamamura, H.; Fujii, N.; Cyster, J.G. Germinal center dark and light zone organization is mediated by CXCR4 and CXCR5. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foy, T.M.; Laman, J.D.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Aruffo, A.; Claassen, E.; Noelle, R.J. gp39-CD40 interactions are essential for germinal center formation and the development of B cell memory. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renshaw, B.R.; Fanslow, W.C.; Armitage, R.J.; Campbell, K.A.; Liggitt, D.; Wright, B.; Davison, B.L.; Maliszewski, C.R. Humoral immune responses in CD40 ligand-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Hathcock, K.; Zheng, B.; Kepler, T.B.; Hodes, R.; Kelsoe, G. Cellular interaction in germinal centers. Roles of CD40 ligand and B7-2 in established germinal centers. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 1995, 155, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Essen, D.; Kikutani, H.; Gray, D. CD40 ligand-transduced co-stimulation of T cells in the development of helper function. Nature 1995, 378, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Lim, H.W.; Kim, J.R.; Rott, L.; Hillsamer, P.; Butcher, E.C. Unique gene expression program of human germinal center T helper cells. Blood 2004, 104, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafuri, A.; Shahinian, A.; Bladt, F.; Yoshinaga, S.K.; Jordana, M.; Wakeham, A.; Boucher, L.M.; Bouchard, D.; Chan, V.S.; Duncan, G.; et al. ICOS is essential for effective T-helper-cell responses. Nature 2001, 409, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, R.; Sims, G.P.; Fairhurst, A.-M.; Robbins, R.; da Silva, Y.S.; Spolski, R.; Leonard, W.J.; Lipsky, P.E. IL-21 induces differentiation of human naive and memory B cells into antibody-secreting plasma cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2005, 175, 7867–7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, V.L.; Ma, C.S.; Avery, D.T.; Li, Y.; Good, K.L.; Corcoran, L.M.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Tangye, S.G. Cytokine-mediated regulation of human B cell differentiation into Ig-secreting cells: Predominant role of IL-21 produced by CXCR5+ T follicular helper cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2007, 179, 8180–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinuesa, C.G.; Cook, M.C.; Angelucci, C.; Athanasopoulos, V.; Rui, L.; Hill, K.M.; Yu, D.; Domaschenz, H.; Whittle, B.; Lambe, T.; et al. A RING-type ubiquitin ligase family member required to repress follicular helper T cells and autoimmunity. Nature 2005, 435, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, A.-U.; Rahn, H.-P.; Sallusto, F.; Lipp, M.; Müller, G. Follicular B helper T cell activity is confined to CXCR5(hi)ICOS(hi) CD4 T cells and is independent of CD57 expression. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1892–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, R.; Schmitt, N.; Bentebibel, S.-E.; Ranganathan, R.; Bourdery, L.; Zurawski, G.; Foucat, E.; Dullaers, M.; Oh, S.; Sabzghabaei, N.; et al. Human blood CXCR5+ CD4+ T cells are counterparts of T follicular cells and contain specific subsets that differentially support antibody secretion. Immunity 2011, 34, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sage, P.T.; Francisco, L.M.; Carman, C.V.; Sharpe, A.H. The receptor PD-1 controls follicular regulatory T cells in the lymph nodes and blood. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLeod, M.K.L.; David, A.; McKee, A.S.; Crawford, F.; Kappler, J.W.; Marrack, P. Memory CD4 T cells that express CXCR5 provide accelerated help to B cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2011, 186, 2889–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.P.; Fuhrmann, F.; Hutloff, A. T-follicular helper cells survive as long-term memory cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1981–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, J.S.; Youngblood, B.; Latner, D.R.; Mohammed, A.U.R.; Ye, L.; Akondy, R.S.; Wu, T.; Iyer, S.S.; Ahmed, R. Distinct memory CD4+ T cells with commitment to T follicular helper- and T helper 1-cell lineages are generated after acute viral infection. Immunity 2013, 38, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurieva, R.I.; Chung, Y.; Martinez, G.J.; Yang, X.O.; Tanaka, S.; Matskevitch, T.D.; Wang, Y.-H.; Dong, C. Bcl6 mediates the development of T follicular helper cells. Science 2009, 325, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Rao, S.; Tsai, L.M.; Lee, S.K.; He, Y.; Sutcliffe, E.L.; Srivastava, M.; Linterman, M.; Zheng, L.; Simpson, N.; et al. The transcriptional repressor Bcl-6 directs T follicular helper cell lineage commitment. Immunity 2009, 31, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazilleau, N.; McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; Rosen, H.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G. The function of follicular helper T cells is regulated by the strength of T cell antigen receptor binding. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junt, T.; Fink, K.; Förster, R.; Senn, B.; Lipp, M.; Muramatsu, M.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Ludewig, B.; Hengartner, H. CXCR5-dependent seeding of follicular niches by B and Th cells augments antiviral B cell responses. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2005, 175, 7109–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poholek, A.C.; Hansen, K.; Hernandez, S.G.; Eto, D.; Chandele, A.; Weinstein, J.S.; Dong, X.; Odegard, J.M.; Kaech, S.M.; Dent, A.L.; et al. In vivo regulation of Bcl6 and T follicular helper cell development. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2010, 185, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kageyama, R.; Eto, D.; Escobar, T.C.; Johnston, R.J.; Monticelli, L.; Lao, C.; Crotty, S. ICOS receptor instructs T follicular helper cell versus effector cell differentiation via induction of the transcriptional repressor Bcl6. Immunity 2011, 34, 932–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerfoot, S.M.; Yaari, G.; Patel, J.R.; Johnson, K.L.; Gonzalez, D.G.; Kleinstein, S.H.; Haberman, A.M. Germinal center B cell and T follicular helper cell development initiates in the interfollicular zone. Immunity 2011, 34, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, M.; Moriyama, S.; Ando, Y.; Hikida, M.; Mori, Y.; Kurosaki, T.; Okada, T. Bcl6 protein expression shapes pre-germinal center B cell dynamics and follicular helper T cell heterogeneity. Immunity 2011, 34, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celli, S.; Lemaître, F.; Bousso, P. Real-time manipulation of T cell-dendritic cell interactions in vivo reveals the importance of prolonged contacts for CD4+ T cell activation. Immunity 2007, 27, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.; Tangye, S.G.; Mackay, C.R. T follicular helper (TFH) cells in normal and dysregulated immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deenick, E.K.; Chan, A.; Ma, C.S.; Gatto, D.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Brink, R.; Tangye, S.G. Follicular helper T cell differentiation requires continuous antigen presentation that is independent of unique B cell signaling. Immunity 2010, 33, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, Y.; Sprent, J. T cell priming in vivo: A major role for B cells in presenting antigen to T cells in lymph nodes. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 1987, 138, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baumjohann, D.; Okada, T.; Ansel, K.M. Cutting Edge: Distinct waves of BCL6 expression during T follicular helper cell development. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2011, 187, 2089–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannons, J.L.; Qi, H.; Lu, K.T.; Dutta, M.; Gomez-Rodriguez, J.; Cheng, J.; Wakeland, E.K.; Germain, R.N.; Schwartzberg, P.L. Optimal germinal center responses require a multistage T cell:B cell adhesion process involving integrins, SLAM-associated protein, and CD84. Immunity 2010, 32, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Cannons, J.L.; Klauschen, F.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Germain, R.N. SAP-controlled T-B cell interactions underlie germinal centre formation. Nature 2008, 455, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Hou, S.; Peng, L.; Xu, C.; Liu, W.; et al. Follicular T-helper cell recruitment governed by bystander B cells and ICOS-driven motility. Nature 2013, 496, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.J.; Poholek, A.C.; DiToro, D.; Yusuf, I.; Eto, D.; Barnett, B.; Dent, A.L.; Craft, J.; Crotty, S. Bcl6 and Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular helper cell differentiation. Science 2009, 325, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Eto, D.; Yang, J.A.; Lao, C.; Crotty, S. Cutting edge: STAT1 is required for IL-6-mediated Bcl6 induction for early follicular helper cell differentiation. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2013, 190, 3049–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroenke, M.A.; Eto, D.; Locci, M.; Cho, M.; Davidson, T.; Haddad, E.K.; Crotty, S. Bcl6 and Maf cooperate to instruct human follicular helper CD4 T cell differentiation. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2012, 188, 3734–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, U.; Dalla-Favera, R. Germinal centres: Role in B-cell physiology and malignancy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, G.; Calame, K. Regulation and functions of Blimp-1 in T and B lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 133–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauquet, A.T.; Jin, H.; Paterson, A.M.; Mitsdoerffer, M.; Ho, I.-C.; Sharpe, A.H.; Kuchroo, V.K. The costimulatory molecule ICOS regulates the expression of c-Maf and IL-21 in the development of follicular T helper cells and TH-17 cells. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, Y.; Suto, A.; Kashiwakuma, D.; Kanari, H.; Kagami, S.; Ikeda, K.; Hirose, K.; Watanabe, N.; Grusby, M.J.; Iwamoto, I.; et al. c-Maf activates the promoter and enhancer of the IL-21 gene, and TGF-beta inhibits c-Maf-induced IL-21 production in CD4+ T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Thierry-Mieg, D.; Thierry-Mieg, J.; Kim, H.-P.; Oh, J.; Tunyaplin, C.; Carotta, S.; Donovan, C.E.; Goldman, M.L.; Tailor, P.; et al. Analysis of interleukin-21-induced Prdm1 gene regulation reveals functional cooperation of STAT3 and IRF4 transcription factors. Immunity 2009, 31, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollig, N.; Brüstle, A.; Kellner, K.; Ackermann, W.; Abass, E.; Raifer, H.; Camara, B.; Brendel, C.; Giel, G.; Bothur, E.; et al. Transcription factor IRF4 determines germinal center formation through follicular T-helper cell differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8664–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohoff, M.; Mittrücker, H.-W.; Prechtl, S.; Bischof, S.; Sommer, F.; Kock, S.; Ferrick, D.A.; Duncan, G.S.; Gessner, A.; Mak, T.W. Dysregulated T helper cell differentiation in the absence of interferon regulatory factor 4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11808–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüstle, A.; Heink, S.; Huber, M.; Rosenplänter, C.; Stadelmann, C.; Yu, P.; Arpaia, E.; Mak, T.W.; Kamradt, T.; Lohoff, M. The development of inflammatory T(H)-17 cells requires interferon-regulatory factor 4. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudt, V.; Bothur, E.; Klein, M.; Lingnau, K.; Reuter, S.; Grebe, N.; Gerlitzki, B.; Hoffmann, M.; Ulges, A.; Taube, C.; et al. Interferon-regulatory factor 4 is essential for the developmental program of T helper 9 cells. Immunity 2010, 33, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serre, K.; Mohr, E.; Bénézech, C.; Bird, R.; Khan, M.; Caamaño, J.H.; Cunningham, A.F.; Maclennan, I.C.M. Selective effects of NF-κB1 deficiency in CD4+ T cells on Th2 and TFh induction by alum-precipitated protein vaccines. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auderset, F.; Schuster, S.; Fasnacht, N.; Coutaz, M.; Charmoy, M.; Koch, U.; Favre, S.; Wilson, A.; Trottein, F.; Alexander, J.; et al. Notch signaling regulates follicular helper T cell differentiation. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2013, 191, 2344–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhong, B.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Chu, F.; Nurieva, R.I.; Yan, X.; Chen, P.; van der Flier, L.G.; et al. Transcription factor achaete-scute homologue 2 initiates follicular T-helper-cell development. Nature 2014, 507, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevach, E.M. Regulatory T Cells in Autoimmmunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 423–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.W.; Hillsamer, P.; Banham, A.H.; Kim, C.H. Cutting edge: Direct suppression of B cells by CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2005, 175, 4180–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.W.; Hillsamer, P.; Kim, C.H. Regulatory T cells can migrate to follicles upon T cell activation and suppress GC-Th cells and GC-Th cell-driven B cell responses. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Chu, F.; Nurieva, R.I.; Martinez, G.J.; Rawal, S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Lim, H.; Reynolds, J.M.; Zhou, X.; et al. Follicular regulatory T cells expressing Foxp3 and Bcl-6 suppress germinal center reactions. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollenberg, I.; Agua-Doce, A.; Hernández, A.; Almeida, C.; Oliveira, V.G.; Faro, J.; Graca, L. Regulation of the germinal center reaction by Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2011, 187, 4553–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrat, F.J.; Cua, D.J.; Boonstra, A.; Richards, D.F.; Crain, C.; Savelkoul, H.F.; de Waal-Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; Hawrylowicz, C.M.; O’Garra, A. In vitro generation of interleukin 10-producing regulatory CD4(+) T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by T helper type 1 (Th1)- and Th2-inducing cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, D.A.; Zheng, S.G.; Gray, J.D. Natural and TGF-β–induced Foxp3+CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells are not mirror images of each other. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, C.-M.; Tygrett, L.T.; Boyden, A.W.; Wolniak, K.L.; Legge, K.L.; Waldschmidt, T.J. T regulatory cells participate in the control of germinal centre reactions. Immunology 2011, 133, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josefowicz, S.Z.; Niec, R.E.; Kim, H.Y.; Treuting, P.; Chinen, T.; Zheng, Y.; Umetsu, D.T.; Rudensky, A.Y. Extrathymically generated regulatory T cells control mucosal TH2 inflammation. Nature 2012, 482, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sage, P.T.; Sharpe, A.H. T follicular regulatory cells in the regulation of B cell responses. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros-Tato, A.; León, B.; Graf, B.A.; Moquin, A.; Adams, P.S.; Lund, F.E.; Randall, T.D. Interleukin-2 inhibits germinal center formation by limiting T follicular helper cell differentiation. Immunity 2012, 36, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peuchmaur, M.; Emilie, D.; Crevon, M.C.; Brousse, N.; Gaulard, P.; D’Agay, M.F.; Galanaud, P.; Solal-Celigny, P. Interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma production in follicular lymphomas. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 95, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vyth-Dreese, F.A.; Boot, H.; Dellemijn, T.A.; Majoor, D.M.; Oomen, L.C.; Laman, J.D.; Van Meurs, M.; De Weger, R.A.; De Jong, D. Localization in situ of costimulatory molecules and cytokines in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Immunology 1998, 94, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emilie, D.; Peuchmaur, M.; Maillot, M.C.; Crevon, M.C.; Brousse, N.; Delfraissy, J.F.; Dormont, J.; Galanaud, P. Production of interleukins in human immunodeficiency virus-1-replicating lymph nodes. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinen, E. In Vivo Immunology: Regulatory Processes During Lymphopoiesis and Immunopoiesis; Proceedings of the International Conference on Lymphatic Tissues and Germinal Centers in Immune Reactions 1993: Liege, B.; In Series Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 355. [Google Scholar]
- Bogen, S.A.; Fogelman, I.; Abbas, A.K. Analysis of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-gamma-producing cells in situ during immune responses to protein antigens. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 1993, 150, 4197–4205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butch, A.W.; Chung, G.H.; Hoffmann, J.W.; Nahm, M.H. Cytokine expression by germinal center cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 1993, 150, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toellner, K.M.; Scheel-Toellner, D.; Sprenger, R.; Duchrow, M.; Trümper, L.H.; Ernst, M.; Flad, H.D.; Gerdes, J. The human germinal centre cells, follicular dendritic cells and germinal centre T cells produce B cell-stimulating cytokines. Cytokine 1995, 7, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, I.L.; Mohrs, M. IL-4-producing CD4+ T cells in reactive lymph nodes during helminth infection are T follicular helper cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaretsky, A.G.; Taylor, J.J.; King, I.L.; Marshall, F.A.; Mohrs, M.; Pearce, E.J. T follicular helper cells differentiate from Th2 cells in response to helminth antigens. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazilleau, N.; Eisenbraun, M.D.; Malherbe, L.; Ebright, J.N.; Pogue-Caley, R.R.; McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G. Lymphoid reservoirs of antigen-specific memory T helper cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüthje, K.; Kallies, A.; Shimohakamada, Y.; Belz, G.T.; Light, A.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Nutt, S.L. The development and fate of follicular helper T cells defined by an IL-21 reporter mouse. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, M.; Komatsu, N.; Kawamoto, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kanagawa, O.; Honjo, T.; Hori, S.; Fagarasan, S. Preferential generation of follicular B helper T cells from Foxp3+ T cells in gut Peyer’s patches. Science 2009, 323, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopf, M.; Herren, S.; Wiles, M.V.; Pepys, M.B.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.H. Interleukin 6 influences germinal center development and antibody production via a contribution of C3 complement component. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, H.M.; Vogelzang, A.; Warren, J.; Loetsch, C.; Natividad, K.D.; Chan, T.D.; Brink, R.; Batten, M.; King, C. IL-21 and IL-4 Collaborate To Shape T-Dependent Antibody Responses. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 5123–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavele, K.-M.; Merry, E.; Ehrenstein, M.R. Cutting edge: Circulating plasmablasts induce the differentiation of human T follicular helper cells via IL-6 production. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2015, 194, 2482–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; El Shikh, M.E.M.; El Sayed, R.M.; Best, A.M.; Szakal, A.K.; Tew, J.G. IL-6 produced by immune complex-activated follicular dendritic cells promotes germinal center reactions, IgG responses and somatic hypermutation. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.; Kikly, K.; Michalovich, D.; Young, P.R.; Leonard, W.J. Cloning of a type I cytokine receptor most related to the IL-2 receptor beta chain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11439–11444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaian, M.T.; Whitters, M.J.; Carter, L.L.; Lowe, L.D.; Jussif, J.M.; Deng, B.; Johnson, K.A.; Witek, J.S.; Senices, M.; Konz, R.F.; et al. IL-21 limits NK cell responses and promotes antigen-specific T cell activation: A mediator of the transition from innate to adaptive immunity. Immunity 2002, 16, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, D.T.; Deenick, E.K.; Ma, C.S.; Suryani, S.; Simpson, N.; Chew, G.Y.; Chan, T.D.; Palendira, U.; Bustamante, J.; Boisson-Dupuis, S.; et al. B cell–intrinsic signaling through IL-21 receptor and STAT3 is required for establishing long-lived antibody responses in humans. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, R.; Spolski, R.; Casas, E.; Zhu, W.; Levy, D.E.; Leonard, W.J. The molecular basis of IL-21-mediated proliferation. Blood 2007, 109, 4135–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asao, H.; Okuyama, C.; Kumaki, S.; Ishii, N.; Tsuchiya, S.; Foster, D.; Sugamura, K. Cutting edge: The common gamma-chain is an indispensable subunit of the IL-21 receptor complex. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2001, 167, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgoffe, G.M.; Vignali, D.A.A. STAT heterodimers in immunity: A mixed message or a unique signal? JAK-STAT 2013, 2, e23060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F.; Graeve, L. Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem. J. 1998, 334 (Pt 2), 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddahri, F.; Denanglaire, S.; Bureau, F.; Spolski, R.; Leonard, W.J.; Leo, O.; Andris, F. Interleukin-6/STAT3 signaling regulates the ability of naive T cells to acquire B-cell help capacities. Blood 2009, 113, 2426–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornek, J.L.; Tygrett, L.T.; Waldschmidt, T.J.; Poli, V.; Rickert, R.C.; Kansas, G.S. Critical role for Stat3 in T-dependent terminal differentiation of IgG B cells. Blood 2006, 107, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.; Spolski, R.; Ettinger, R.; Kim, H.-P.; Wang, G.; Qi, C.-F.; Hwu, P.; Shaffer, D.J.; Akilesh, S.; Roopenian, D.C.; et al. Regulation of B cell differentiation and plasma cell generation by IL-21, a novel inducer of Blimp-1 and Bcl-6. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2004, 173, 5361–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Rigby, R.J.; Zotos, D.; Tsai, L.M.; Kawamoto, S.; Marshall, J.L.; Ramiscal, R.R.; Chan, T.D.; Gatto, D.; Brink, R.; et al. B cell priming for extrafollicular antibody responses requires Bcl-6 expression by T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dienz, O.; Eaton, S.M.; Bond, J.P.; Neveu, W.; Moquin, D.; Noubade, R.; Briso, E.M.; Charland, C.; Leonard, W.J.; Ciliberto, G.; et al. The induction of antibody production by IL-6 is indirectly mediated by IL-21 produced by CD4+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batten, M.; Ghilardi, N. The biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin 27. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 85, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, D.C.; Harmon, D.L.; Nunez, F.; Whitehead, A.S. The evolution of haematopoietic cytokine/receptor complexes. Cytokine 1995, 7, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontenot, J.D.; Rasmussen, J.P.; Gavin, M.A.; Rudensky, A.Y. A function for interleukin 2 in Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willerford, D.M.; Chen, J.; Ferry, J.A.; Davidson, L.; Ma, A.; Alt, F.W. Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain regulates the size and content of the peripheral lymphoid compartment. Immunity 1995, 3, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attridge, K.; Wang, C.J.; Wardzinski, L.; Kenefeck, R.; Chamberlain, J.L.; Manzotti, C.; Kopf, M.; Walker, L.S.K. IL-21 inhibits T cell IL-2 production and impairs Treg homeostasis. Blood 2012, 119, 4656–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, I.; Schneider, C.; Fröhlich, A.; Frebel, H.; Christ, D.; Leonard, W.J.; Sparwasser, T.; Oxenius, A.; Freigang, S.; Kopf, M. IL-21 restricts virus-driven Treg cell expansion in chronic LCMV infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.L.; Ochs, H.D. IPEX is a unique X-linked syndrome characterized by immune dysfunction, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, and a variety of autoimmune phenomena. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2001, 13, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsdell, F.; Ziegler, S.F. FOXP3 and scurfy: How it all began. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurieva, R.; Yang, X.O.; Martinez, G.; Zhang, Y.; Panopoulos, A.D.; Ma, L.; Schluns, K.; Tian, Q.; Watowich, S.S.; Jetten, A.M.; et al. Essential autocrine regulation by IL-21 in the generation of inflammatory T cells. Nature 2007, 448, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, T.; Bettelli, E.; Gao, W.; Awasthi, A.; Jäger, A.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-21 initiates an alternative pathway to induce proinflammatory T(H)17 cells. Nature 2007, 448, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelzang, A.; McGuire, H.M.; Liu, S.M.; Gloss, B.; Mercado, K.; Earls, P.; Dinger, M.E.; Batten, M.; Sprent, J.; King, C. IL-21 contributes to fatal inflammatory disease in the absence of Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2014, 192, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clough, L.E.; Wang, C.J.; Schmidt, E.M.; Booth, G.; Hou, T.Z.; Ryan, G.A.; Walker, L.S.K. Release from regulatory T cell-mediated suppression during the onset of tissue-specific autoimmunity is associated with elevated IL-21. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2008, 180, 5393–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yee, C. IL-21 mediated Foxp3 suppression leads to enhanced generation of antigen-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Blood 2008, 111, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, W.-H.; Jee, Y.H.; Liu, R.L.; Coons, S.W.; Kala, M.; Collins, M.; Young, D.A.; Campagnolo, D.I.; Vollmer, T.L.; Bai, X.-F.; et al. IL-21 modulates CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T-cell homeostasis in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2008, 67, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Diamond, J.A.; Yang, J.A.; Crotty, S. STAT5 is a potent negative regulator of TFH cell differentiation. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurieva, R.I.; Podd, A.; Chen, Y.; Alekseev, A.M.; Yu, M.; Qi, X.; Huang, H.; Wen, R.; Wang, J.; Li, H.S.; et al. STAT5 protein negatively regulates T follicular helper (Tfh) cell generation and function. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11234–11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Luo, B.; Wu, Q.; Zajac, A.J.; Wildner, O.; Hsu, H.-C.; Mountz, J.D. Interleukin-21 Promotes Germinal Center Reaction by Skewing the Follicular Regulatory T Cell to Follicular Helper T Cell Balance in Autoimmune BXD2 Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2601–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, A.; Alekseev, A.; Tanaka, K.; Obertas, L.; Lerman, B.; Haymaker, C.; Clise-Dwyer, K.; McMurray, J.S.; Nurieva, R. Batf is important for IL-4 expression in T follicular helper cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betz, B.C.; Jordan-Williams, K.L.; Wang, C.; Kang, S.G.; Liao, J.; Logan, M.R.; Kim, C.H.; Taparowsky, E.J. Batf coordinates multiple aspects of B and T cell function required for normal antibody responses. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ise, W.; Kohyama, M.; Schraml, B.U.; Zhang, T.; Schwer, B.; Basu, U.; Alt, F.W.; Tang, J.; Oltz, E.M.; Murphy, T.L.; et al. Batf controls the global regulators of class switch recombination in both B and T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pène, J.; Gauchat, J.-F.; Lécart, S.; Drouet, E.; Guglielmi, P.; Boulay, V.; Delwail, A.; Foster, D.; Lecron, J.-C.; Yssel, H. Cutting edge: IL-21 is a switch factor for the production of IgG1 and IgG3 by human B cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2004, 172, 5154–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pène, J.; Guglielmi, L.; Gauchat, J.-F.; Harrer, N.; Woisetschläger, M.; Boulay, V.; Fabre, J.-M.; Demoly, P.; Yssel, H. IFN-gamma-mediated inhibition of human IgE synthesis by IL-21 is associated with a polymorphism in the IL-21R gene. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2006, 177, 5006–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlarz, D.; Ziętara, N.; Uzel, G.; Weidemann, T.; Braun, C.J.; Diestelhorst, J.; Krawitz, P.M.; Robinson, P.N.; Hecht, J.; Puchałka, J.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the IL-21 receptor gene cause a primary immunodeficiency syndrome. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suto, A.; Nakajima, H.; Hirose, K.; Suzuki, K.; Kagami, S.; Seto, Y.; Hoshimoto, A.; Saito, Y.; Foster, D.C.; Iwamoto, I. Interleukin 21 prevents antigen-induced IgE production by inhibiting germ line C(epsilon) transcription of IL-4-stimulated B cells. Blood 2002, 100, 4565–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitayama, D.; Sakamoto, A.; Arima, M.; Hatano, M.; Miyazaki, M.; Tokuhisa, T. A role for Bcl6 in sequential class switch recombination to IgE in B cells stimulated with IL-4 and IL-21. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.S.; Suryani, S.; Avery, D.T.; Chan, A.; Nanan, R.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Deenick, E.K.; Tangye, S.G. Early commitment of naïve human CD4+ T cells to the T follicular helper (TFH) cell lineage is induced by IL-12. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2009, 87, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, I.; Kageyama, R.; Monticelli, L.; Johnston, R.J.; Ditoro, D.; Hansen, K.; Barnett, B.; Crotty, S. Germinal center T follicular helper cell IL-4 production is dependent on signaling lymphocytic activation molecule receptor (CD150). J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2010, 185, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Silva, D.G.; Martin, J.L.; Pratama, A.; Hu, X.; Chang, P.-P.; Walters, G.; Vinuesa, C.G. Interferon-γ Excess Leads to Pathogenic Accumulation of Follicular Helper T Cells and Germinal Centers. Immunity 2012, 37, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Kempuraj, D.; Kandere, K.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Barbacane, R.C.; Castellani, M.L.; Felaco, M.; Boucher, W.; Letourneau, R.; Theoharides, T.C. IL-10, an inflammatory/inhibitory cytokine, but not always. Immunol. Lett. 2003, 86, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, L.M.; Horn, M.P.; Lang, A.B.; Moser, B. B cells alter the phenotype and function of follicular-homing CXCR5+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 3562–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löhning, M.; Hutloff, A.; Kallinich, T.; Mages, H.W.; Bonhagen, K.; Radbruch, A.; Hamelmann, E.; Kroczek, R.A. Expression of ICOS in vivo defines CD4+ effector T cells with high inflammatory potential and a strong bias for secretion of interleukin 10. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpin, C.; Déchanet, J.; Van Kooten, C.; Merville, P.; Grouard, G.; Brière, F.; Banchereau, J.; Liu, Y.J. Generation of memory B cells and plasma cells in vitro. Science 1995, 268, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasa, B.; Van Gunst, K.; Jung, N.; Balakrishna, D.; Santamaria, P.; Hanafusa, T.; Itoh, N.; Sarvetnick, N. Islet-specific expression of IL-10 promotes diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice independent of Fas, perforin, TNF receptor-1, and TNF receptor-2 molecules. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2000, 165, 2841–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Nie, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, B.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, C.; Shen, Q. A Regulatory Role for IL-10 Receptor Signaling in Development and B Cell Help of T Follicular Helper Cells in Mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Y.; Quintana, F.J.; Weiner, H.L. Nasal anti-CD3 antibody ameliorates lupus by inducing an IL-10-secreting CD4+CD25−LAP+ regulatory T cell and is associated with down-regulation of IL-17+CD4+ICOS+CXCR5+ follicular helper T cells. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2008, 181, 6038–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangye, S.G.; Ma, C.S.; Brink, R.; Deenick, E.K. The good, the bad and the ugly—TFH cells in human health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moudgil, K.D.; Choubey, D. Cytokines in autoimmunity: Role in induction, regulation, and treatment. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, R.A.; Lee, S.K.; Vinuesa, C.G. Developing connections amongst key cytokines and dysregulated germinal centers in autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.-X.; Harrison, K.; Wilson, G.L.; Moratz, C.; Kehrl, J.H. RGS13 regulates germinal center B lymphocytes responsiveness to CXC chemokine ligand (CXCL)12 and CXCL13. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2002, 169, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-I.; Huang, N.-N.; Kim, D.-U.; Kehrl, J.H. RGS1 and RGS13 mRNA silencing in a human B lymphoma line enhances responsiveness to chemoattractants and impairs desensitization. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, T.; Bettelli, E.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 485–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsdoerffer, M.; Lee, Y.; Jäger, A.; Kim, H.-J.; Korn, T.; Kolls, J.K.; Cantor, H.; Bettelli, E.; Kuchroo, V.K. Proinflammatory T helper type 17 cells are effective B-cell helpers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14292–14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, K.; Turner, J.-E.; Villa, M.; Duarte, J.H.; Demengeot, J.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Stockinger, B. Plasticity of Th17 cells in Peyer’s patches is responsible for the induction of T cell-dependent IgA responses. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichner, K.; Stauss, D.; Kampfrath, B.; Krüger, K.; Müller, G.; Rehm, A.; Lipp, M.; Höpken, U.E. Dysregulated development of IL-17-and IL-21-expressing follicular helper T cells and increased germinal center formation in the absence of RORγt. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, M.; Yi, H.; Rosenblatt, H.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Adelstein, S.; Modi, W.S.; McBride, O.W.; Leonard, W.J. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell 1993, 73, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, R.H.; Schiff, R.I.; Schiff, S.E.; Markert, M.L.; Williams, L.W.; Harville, T.O.; Roberts, J.L.; Puck, J.M. Human severe combined immunodeficiency: Genetic, phenotypic, and functional diversity in one hundred eight infants. J. Pediatr. 1997, 130, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaesser, H.; Sauer, K.; Brooks, D.G. IL-21 is required to control chronic viral infection. Science 2009, 324, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spolski, R.; Leonard, W.J. Interleukin-21: Basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.S.; Du, M.; Zajac, A.J. A vital role for interleukin-21 in the control of a chronic viral infection. Science 2009, 324, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlarz, D.; Ziętara, N.; Milner, J.D.; Klein, C. Human IL-21 and IL-21R deficiencies: Two novel entities of primary immunodeficiency. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2014, 26, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzer, E.; Kansu, A.; Sic, H.; Májek, P.; Ikincioğullari, A.; Dogu, F.E.; Prengemann, N.K.; Santos-Valente, E.; Pickl, W.F.; Bilic, I.; et al. Early-onset inflammatory bowel disease and common variable immunodeficiency-like disease caused by IL-21 deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1651–1659.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márquez, A.; Orozco, G.; Martínez, A.; Palomino-Morales, R.; Fernández-Arquero, M.; Mendoza, J.L.; Taxonera, C.; Díaz-Rubio, M.; Gómez-García, M.; Nieto, A.; et al. Novel association of the interleukin 2-interleukin 21 region with inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1968–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Heel, D.A.; Franke, L.; Hunt, K.A.; Gwilliam, R.; Zhernakova, A.; Inouye, M.; Wapenaar, M.C.; Barnardo, M.C.N.M.; Bethel, G.; Holmes, G.K.T.; et al. A genome-wide association study for celiac disease identifies risk variants in the region harboring IL2 and IL21. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Helms, C.; Liao, W.; Zaba, L.C.; Duan, S.; Gardner, J.; Wise, C.; Miner, A.; Malloy, M.J.; Pullinger, C.R.; et al. A genome-wide association study of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis identifies new disease loci. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, N.; Gatenby, P.A.; Wilson, A.; Malik, S.; Fulcher, D.A.; Tangye, S.G.; Manku, H.; Vyse, T.J.; Roncador, G.; Huttley, G.A.; et al. Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhee, C.G.; Bubier, J.A.; Sproule, T.J.; Park, G.; Steinbuck, M.P.; Schott, W.H.; Christianson, G.J.; Morse, H.C.; Roopenian, D.C. IL-21 is a double-edged sword in the systemic lupus erythematosus-like disease of BXSB.Yaa mice. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2013, 191, 4581–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izui, S.; Ibnou-Zekri, N.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Iwamoto, M. Lessons from BXSB and related mouse models. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 19, 447–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herber, D.; Brown, T.P.; Liang, S.; Young, D.A.; Collins, M.; Dunussi-Joannopoulos, K. IL-21 has a pathogenic role in a lupus-prone mouse model and its blockade with IL-21R.Fc reduces disease progression. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2007, 178, 3822–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, H.M.; Walters, S.; Vogelzang, A.; Lee, C.M.Y.; Webster, K.E.; Sprent, J.; Christ, D.; Grey, S.; King, C. Interleukin-21 is critically required in autoimmune and allogeneic responses to islet tissue in murine models. Diabetes 2011, 60, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, S.-K.; Cho, M.-L.; Park, M.-K.; Oh, H.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Her, Y.-M.; Lee, S.-Y.; Youn, J.; Ju, J.H.; Park, K.S.; et al. Interleukin-21 promotes osteoclastogenesis in humans with rheumatoid arthritis and in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, K.J.; Rüger, B.; von Brevern, M.; Ryffel, B.; Schimpl, A.; Rivett, K. Constitutive expression of interleukin (IL)-4 in vivo causes autoimmune-type disorders in mice. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.R. IL-4 and many roads to lupuslike autoimmunity. Clin. Immunol. Orlando Fla 2003, 108, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, C.; Ma, B.; Tian, J.; Baidoo, S.E.; Mao, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Tong, J.; Yang, M.; et al. Increased frequency of circulating follicular helper T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 827480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivojinovic, S.; Pejnovic, N.; Sefik-Bukilica, M.; Kovacevic, L.; Soldatovic, I.; Bugarski, D.; Mojsilovic, S.; Damjanov, N. Effects of TNF inhibitor on innate inflammatory and Th17 cytokines in stimulated whole blood from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Inflammopharmacology 2012, 20, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.; Cho, S.-H.; Park, H.; Paik, D.-J.; Kim, J.M.; Youn, J. A positive feedback loop of IL-21 signaling provoked by homeostatic CD4+CD25− T cell expansion is essential for the development of arthritis in autoimmune K/BxN mice. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2009, 182, 4649–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, N.; Kishimoto, T. Inhibition of IL-6 for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jandl, C.; King, C. Cytokines in the Germinal Center Niche. Antibodies 2016, 5, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib5010005
Jandl C, King C. Cytokines in the Germinal Center Niche. Antibodies. 2016; 5(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib5010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleJandl, Christoph, and Cecile King. 2016. "Cytokines in the Germinal Center Niche" Antibodies 5, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib5010005
APA StyleJandl, C., & King, C. (2016). Cytokines in the Germinal Center Niche. Antibodies, 5(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib5010005







