Regenerating Gene Protein as a Novel Autoantigen in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome
3. Regenerating Gene
3.1. General Aspects
3.2. REG, Cytokine, and Chemokine in Salivary Glands of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome
4. Anti-REG Iα Autoantibodies
4.1. Detection of Anti-REG Iα Autoantibodies in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient Sera
4.2. The Role of Anti-REG Iα Autoantibodies in Hyposalivation of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome
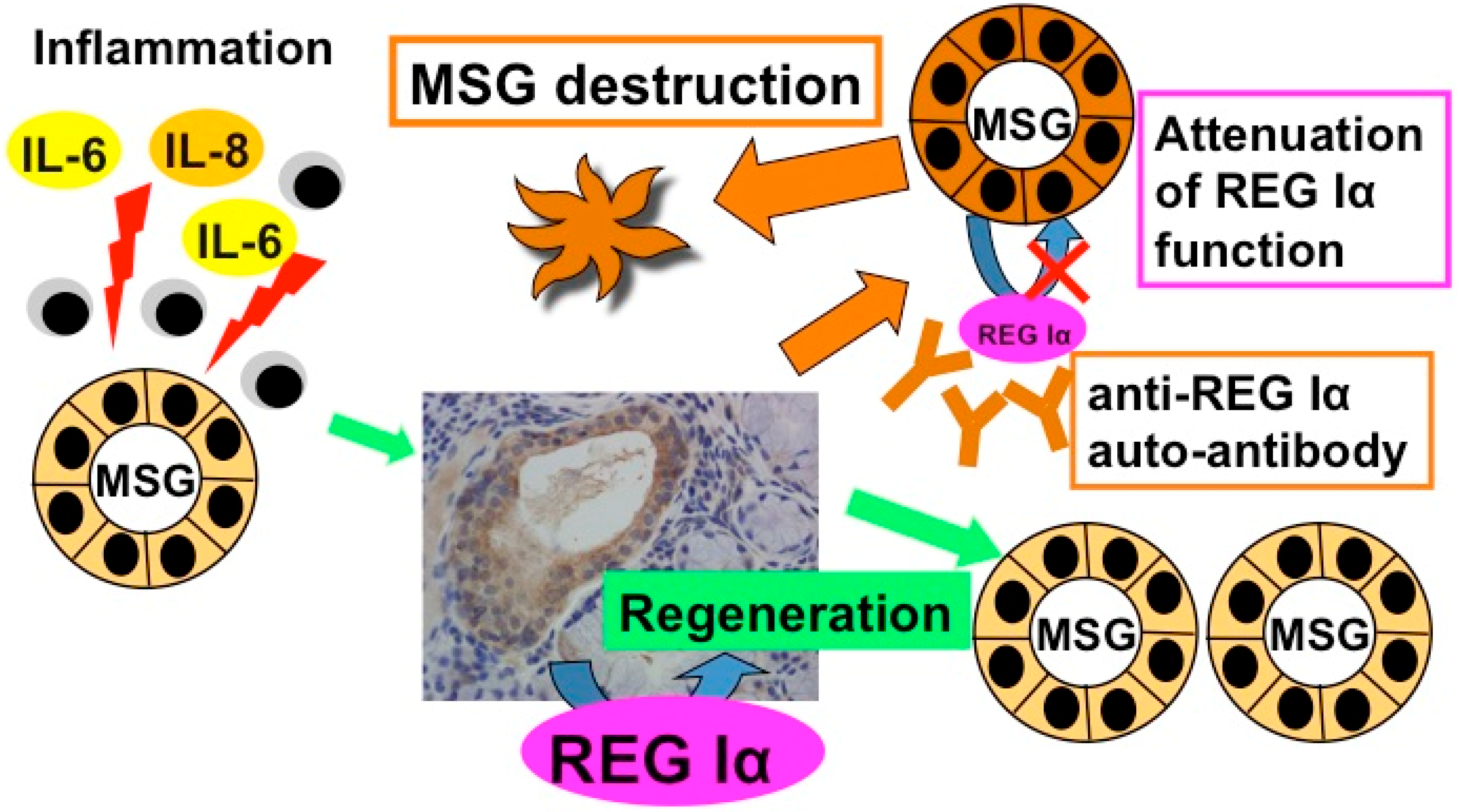
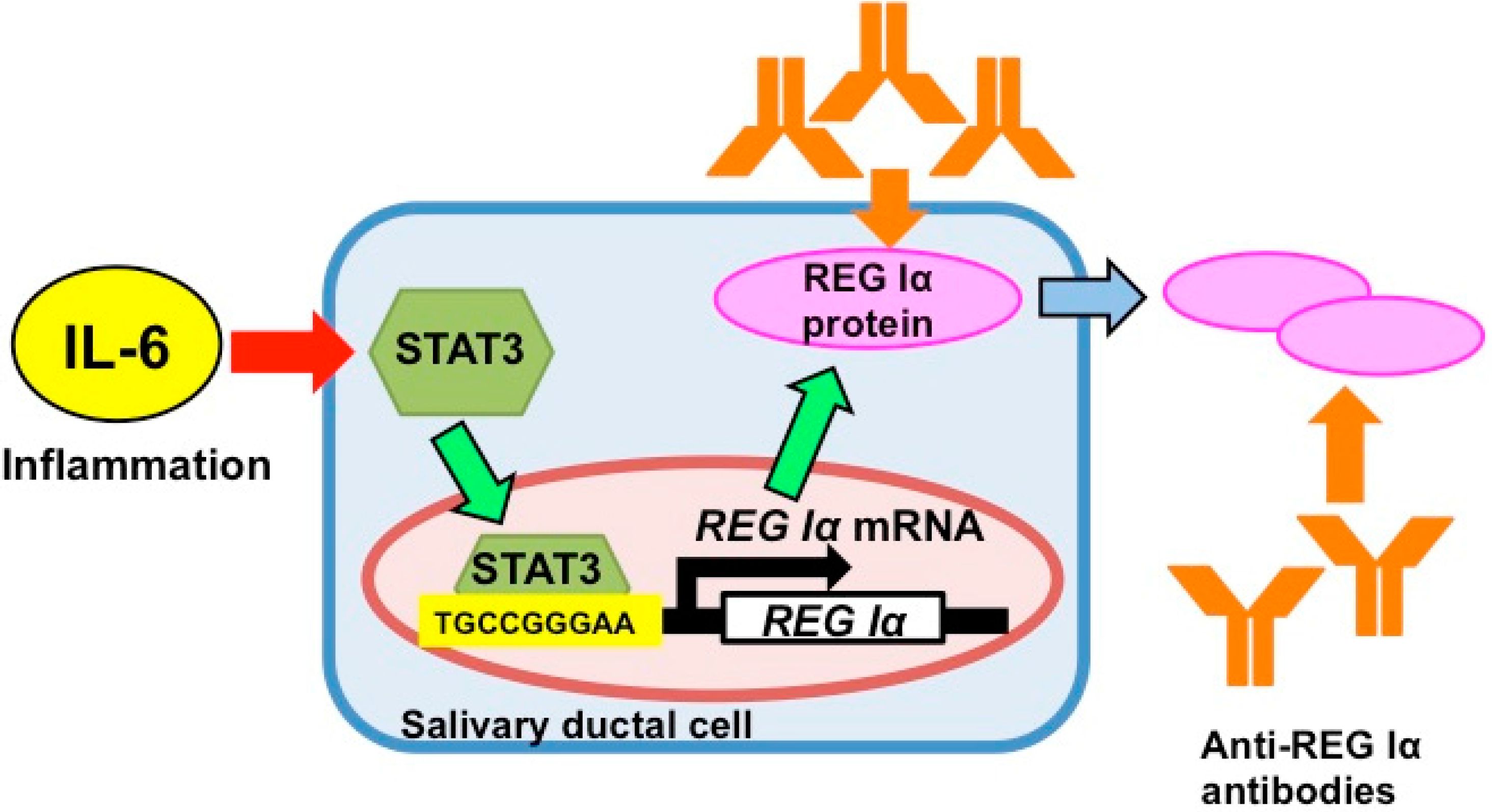
5. Gene Expression of REG Iα as an Auto-Antigen
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anaya, J.M.; Talal, N. Arthritis and Allied Conditions. In A Textbook of Rheumatology, 13th ed.; Koopman, W.J., Ed.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1997; pp. 1561–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Alamanos, Y.; Tsifetaki, N.; Voulgari, P.V.; Venetsanopoulou, A.I.; Siozos, C.; Drosos, A.A. Epidemiology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome in north-west Greece, 1982-2003. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006, 45, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trontzas, P.I.; Andrianakos, A.A. Sjögren’s syndrome: A population based study of prevalence in Greece. The ESOrDIG study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, S.J.; Ibrahim, G.H.; Holmes, G.; Hamburger, J.; Ainsworth, J.R. Estimating the prevalence among Caucasian women of primary Sjögren’s syndrome in two general practices in Birmingham, UK. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 33, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaleu, N.; Jonsson, M.V.; Appel, S.; Jonsson, R. New concepts in the pathogenesis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2008, 34, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venables, P.J. Sjögren’s syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2004, 18, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; De Vita, S.; Zeher, M.; Bosch, J.A.; Toussirot, E.; Medina, F.; Rosas, J.; Anaya, J.M.; Font, J.; SS-HCV Study Group. Sjögren syndrome associated with hepatitis C virus: A multicenter analysis of 137 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 2005, 84, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terazono, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Takasawa, S.; Shiga, K.; Yonemura, Y.; Tochino, Y.; Okamoto, H. A novel gene activated in regenerating islets. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 2111–2114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Takasawa, S. Recent advances in the Okamoto model: The CD38-cyclic ADP-ribose signal system and the regenerating gene protein (Reg)-Reg receptor system in β-cells. Diabetes 2002, 51, S462–S473. [Google Scholar]
- Takasawa, S. Regenerating gene (REG) product and its potential clinical usage. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Ding, L.S.; Lai, M.D. Reg gene family and human diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 2635–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, H.; Takasawa, S.; Yamauchi, M.; Yoshikawa, M.; Tomoda, K.; Kimura, H. Intermittent hypoxia in pancreatic β cells. Pancreat. Diasord. Ther. 2015, S5, 004. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto, K.; Fujimoto, T.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Miyaoka, T.; Sakuramoto-Tsuchida, S.; Yamauchi, A.; Takeda, M.; Kasai, T.; Nakagawara, K.; Nonomura, A.; et al. Involvement of autoimmunity to REG, a regeneration factor, in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 174, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsifis, G.E.; Moutsopoulos, N.M.; Wahl, S.M. T lymphocytes in Sjögren’s syndrome: Contributors to and regulators of pathophysiology. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 32, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoussakis, M.N.; Boiu, S.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Kavantzas, N.; Ziakas, P.; Patsouris, E.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Rates of infiltration by macrophages and dendritic cells and expression of interleukin-18 and interleukin-12 in the chronic inflammatory lesions of Sjögren’s syndrome: correlation with certain features of immune hyperactivity and factors associated with high risk of lymphoma development. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3977–3988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moutsopoulos, H.M. Sjögren’s syndrome: Autoimmune epithelitis. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 72, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, C.; Bombardieri, S.; Jonsson, R.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Alexander, E.L.; Carsons, S.E.; Daniels, T.E.; Fox, P.C.; Fox, R.I.; Kassan, S.S.; et al. Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: A revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavragani, C.P.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. The geoepidemiology of Sjögren’s syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, A305–A310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsias, D.I.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Sjögren’s syndrome: Why autoimmune epithelitis? Oral Dis. 2006, 12, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyfoo, M.S.; Steinfeld, S.; Delporte, C. Usefulness of mouse models to study the pathogenesis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Oral Dis. 2007, 13, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, S.; Peck, A.B.; Humphreys-Beher, M.G. Progress in understanding autoimmune exocrinopathy using the nonobese diabetic mouse: An update. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2002, 13, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, C.P.; Cornelius, J.; Bounous, D.E.; Yamamoto, H.; Humphreys-Beher, M.G.; Peck, A.B. Characterization of the changing lymphocyte populations and cytokine expression in the exocrine tissues of autoimmune NOD mice. Autoimmunity 1998, 27, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys-Beher, M.G.; Brayer, J.; Yamachika, S.; Peck, A.B.; Jonsson, R. An alternative perspective to the immune response in autoimmune exocrinopathy: Induction of functional quiescence rather than destructive autoaggression. Scand. J. Immunol. 1999, 49, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talal, N.; Sylvester, R.A.; Daniels, T.E.; Greenspan, J.S.; Williams, R.C., Jr. T and B lymphocytes in peripheral blood and tissue lesions in Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 1974, 53, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, M.I.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Moutsopoulos, N.M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Foxp3+ T-regulatory cells in Sjogren's syndrome: Correlation with the grade of the autoimmune lesion and certain adverse prognostic factors. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsifis, G.E.; Rekka, S.; Moutsopoulos, N.M.; Pillemer, S.; Wahl, S.M. Systemic and local interleukin-17 and linked cytokines associated with Sjögren’s syndrome immunopathogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, A.; Dardalhon, V.; Brauner, S.; Ambrosi, A.; Higgs, R.; Quintana, F.J.; Sjöstrand, M.; Eloranta, M.L.; Ní Gabhann, J.; Winqvist, O.; et al. Loss of the lupus autoantigen Ro52/Trim21 induces tissue inflammation and systemic autoimmunity by disregulating the IL-23-Th17 pathway. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, A.; Sugawara, Y.; Kuroishi, T.; Sasano, T.; Sugawara, S. Identification of IL-18 and Th17 cells in salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome, and amplification of IL-17-mediated secretion of inflammatory cytokines from salivary gland cells by IL-18. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2898–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.Q.; Hu, M.H.; Li, Y.; Stewart, C.; Peck, A.B. Salivary gland tissue expression of interleukin-23 and interleukin-17 in Sjögren’s syndrome: Findings in humans and mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, R.I.; Kang, H.I. Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 1992, 18, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haneji, N.; Hamano, H.; Yanagi, K.; Hayashi, Y. A new animal model for primary Sjögren’s syndrome in NFS/sld mutant mice. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 2769–2777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kino-Ohsaki, J.; Nishimori, I.; Morita, M.; Okazaki, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Onishi, S.; Hollingsworth, M.A. Serum antibodies to carbonic anhydrase I and II in patients with idiopathic chronic pancreatitis and Sjögren’s syndrome. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacman, S.R.; Berra, A.; Sterin-Borda, L.; Borda, E.S. Human primary Sjögren’s syndrome autoantibodies as mediators of nitric oxide release coupled to lacrimal gland muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Curr. Eye Res. 1998, 17, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacman, S.; Sterin-Borda, L.; Camusso, J.J.; Arana, R.; Hubscher, O.; Borda, E. Circulating antibodies against rat parotid gland M3 muscarinic receptors in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1996, 104, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnock, M.G.; Goodacre, J.A. Cryptic T-cell epitopes and their role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 36, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Yonemura, Y.; Yonekura, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyashita, H.; Sugiyama, K.; Moriizumi, S.; Unno, M.; Tanaka, O.; Kondo, H.; et al. Pancreatic beta-cell replication and amelioration of surgical diabetes by Reg protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3589–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Yonekura, H.; Terazono, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Okamoto, H. Complete nucleotide sequence of human reg gene and its expression in normal and tumoral tissues. The reg protein, pancreatic stone protein, and pancreatic thread protein are one and the same product of the gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 7432–7439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moriizumi, S.; Watanabe, T.; Unno, M.; Nakagawara, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyashita, H.; Yonekura, H.; Okamoto, H. Isolation, structural determination and expression of a novel reg gene, human reg Iβ. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1217, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nata, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Ikeda, T.; Akiyama, T.; Noguchi, N.; Kawaguchi, S.; Yamauchi, A.; Takahashi, I.; Shervani, N.J.; et al. Molecular cloning, expression and chromosomal localization of a novel human REG family gene, REG III. Gene 2004, 340, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasserre, C.; Christa, L.; Simon, M.T.; Vernier, P.; Bréchot, C. A novel gene (HIP) activated in human primary liver cancer. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 5089–5095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orelle, B.; Keim, V.; Masciotra, L.; Dagorn, J.C.; Iovanna, J.L. Human pancreatitis-associated protein. Messenger RNA cloning and expression in pancreatic diseases. J. Clin. Invest. 1992, 90, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartupee, J.C.; Zhang, H.; Bonaldo, M.F.; Soares, M.B.; Dieckgraefe, B.K. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a novel member of the human regenerating protein family: Reg IV. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1518, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, M.; Yonekura, H.; Nakagawara, K.; Watanabe, T.; Miyashita, H.; Moriizumi, S.; Okamoto, H.; Itoh, T.; Teraoka, H. Structure, chromosomal localization, and expression of mouse reg genes, reg I and reg II. A novel type of reg gene, reg II, exists in the mouse genome. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 15974–15982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Planas, R.; Alba, A.; Carrillo, J.; Puertas, M.C.; Ampudia, R.; Pastor, X.; Okamoto, H.; Takasawa, S.; Gurr, W.; Pujol-Borrell, R.; et al. Reg (regenerating) gene overexpression in islets from non-obese diabetic mice with accelerated diabetes: Role of IFNβ. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livesey, F.J.; O'Brien, J.A.; Li, M.; Smith, A.G.; Murphy, L.J.; Hunt, S.P. A Schwann cell mitogen accompanying regeneration of motor neurons. Nature 1997, 390, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimune, H.; Vasseur, S.; Wiese, S.; Birling, M.C.; Holtmann, B.; Sendtner, M.; Iovanna, J.L.; Henderson, C.E. Reg-2 is a motoneuron neurotrophic factor and a signalling intermediate in the CNTF survival pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Fukui, H.; Sekikawa, A.; Yamagishi, H.; Ichikawa, K.; Tomita, S.; Fujii, S.; Imura, J.; Kawamata, H.; Chiba, T.; et al. Involvement of REG Iα protein in the regeneration of ductal epithelial cells in the minor salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 155, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, T.; Takasawa, S.; Nata, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Abe, M.; Shervani, N.J.; Ikeda, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Unno, M.; Matsuno, S.; et al. Activation of Reg gene, a gene for insulin-producing β-cell regeneration: poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase binds Reg promoter and regulates the transcription by autopoly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kazumori, H.; Ishihara, S.; Hoshino, E.; Kawashima, K.; Moriyama, N.; Suetsugu, H.; Sato, H.; Adachi, K.; Fukuda, R.; Watanabe, M.; et al. Neutrophil chemoattractant 2β regulates expression of the Reg gene in injured gastric mucosa in rats. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, N.; Ishihara, S.; Rumi, M.A.; Ortega-Cava, C.F.; Yuki, T.; Kazumori, H.; Takasawa, S.; Okamoto, H.; Kadowaki, Y.; Kinoshita, Y. Interleukin-8 regulate expression of Reg protein in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Kalantzis, A.; Jackson, C.B.; O’Connor, L.; Murata-Kamiya, N.; Hatakeyama, M.; Judd, L.M.; Giraud, A.S.; Menheniott, T.R. Helicobacter pylori CagA triggers expression of the bactericidal lectin REG3γ via gastric STAT3 activation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekikawa, A.; Fukui, H.; Suzuki, K.; Karibe, T.; Fujii, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Tomita, S.; Imura, J.; Shiratori, K.; Chiba, T.; et al. Involvement of the IL-22/REG Iα axis in ulcerative colitis. Lab. Invest. 2010, 90, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekikawa, A.; Fukui, H.; Fujii, S.; Nanakin, A.; Kanda, N.; Uenoyama, Y.; Sawabu, T.; Hisatsune, H.; Kusaka, T.; Ueno, S.; et al. Possible role of REG Iα protein in ulcerative colitis and colitic cancer. Gut 2005, 54, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roescher, N.; Tak, P.P.; Illei, G.G. Cytokines in Sjögren’s syndrome: Potential therapeutic targets. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Ishihara, K.; Hibi, M. Roles of STAT3 in mediating the cell growth, differentiation and survival signals relayed through the IL-6 family of cytokine receptors. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromberg, J. Stat proteins and oncogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 109, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandis, J.R.; Drenning, S.D.; Zeng, Q.; Watkins, S.C.; Melhem, M.F.; Endo, S.; Johnson, D.E.; Huang, L.; He, Y.; Kim, J.D. Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling abrogates apoptosis in squamous cell carcinogenesis in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4227–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.I.; Grandis, J.R. STAT signaling in head and neck cancer. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2489–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, S.O.; Harbor, P.C.; Chernova, O.; Barnett, G.H.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Haque, S.J. Inhibition of constitutively active Stat3 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8404–8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekikawa, A.; Fukui, H.; Fujii, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Tomita, S.; Imura, J.; Chiba, T.; Fujimori, T. REG Iα protein mediates an anti-apoptotic effect of STAT3 signaling in gastric cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, A.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Sakuramoto-Tsuchida, S.; Takeda, M.; Yoshimoto, K.; Miyaoka, T.; Fujimura, T.; Tsujinaka, H.; Tsuchida, C.; Ota, H.; et al. Synergistic activations of REG Iα and REG Iβ promoters by IL-6 and glucocorticoids through JAK/STAT pathway in human pancreatic β cells. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 173058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shervani, N.J.; Takasawa, S.; Uchigata, Y.; Akiyama, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Noguchi, N.; Takada, H.; Takahashi, I.; Yamauchi, A.; Ikeda, T.; et al. Autoantibodies to REG, a beta-cell regeneration factor, in diabetic patients. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 34, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astorri, E.; Guglielmi, C.; Bombardieri, M.; Alessandri, C.; Buzzetti, R.; Maggi, D.; Velesini, G.; Pitzalis, C.; Pozzilli, P. Circulating Reg1α proteins and autoantibodies to Reg1α proteins as biomarkers of β-cell regeneration and damage in type 1 diabetes. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiji, T.; Dohi, Y.; Nishizaki, K.; Takasawa, S.; Okamoto, H.; Nagasaka, S.; Naito, H.; Yonemasu, K.; Taniguchi, S. Enhancement of cell viability in cryopreserved rat vascular grafts by administration of regenerating gene (Reg) inducers. J. Vasc. Res. 2003, 40, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenilman, M.E.; Magnuson, T.H.; Perfetti, R.; Chen, J.; Shuldiner, A.R. Pancreatic reg gene expression is inhibited during cellular differentiation. Ann. Surg. 1997, 225, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; List, E.O.; Kopchick, J.J. Differentially expressed proteins in the pancreas of diet-induced diabetic mice. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2005, 4, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisius, M.M.; Bermudez, D.K.; Fox, P.C. Salivary and serum interleukin 6 in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Badillo-Almaraz, I.; Avalos-Diaz, E.; Villalobos-Hurtado, R.; Herrera-Esparza, R. FasL and Bax genes are differentially expressed in acinar epithelium and inflammatory cells of primary Sjögren salivary glands. Minerva Med. 2003, 94, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Scofield, R.H.; Hyon, J.Y.; Yun, P.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, E.B.; Song, Y.W. Salivary chemokine levels in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010, 49, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekikawa, A.; Fukui, H.; Fuji, S.; Nanakin, A.; Nakada, N.; Uenoyama, Y.; Sawabu, T.; Hisatsune, H.; Kusaka, T.; Ueno, S.; et al. Possible role of REG Iα protein in ulcerative colitis and colitic cancer. Gut 2005, 54, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikehata, F.; Satoh, J.; Nata, K.; Tohgo, A.; Nakazawa, T.; Kato, I.; Kobayashi, S.; Akiyama, T.; Takasawa, S.; Toyota, T.; et al. Autoantibodies against CD38 (ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase) that impair glucose-induced insulin secretion in noninsulin-dependent diabetes patients. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 102, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pupilli, C.; Giannini, S.; Marchetti, P.; Lupi, R.; Antonelli, A.; Malavasi, F.; Takasawa, S.; Okamoto, H.; Ferrannini, E. Autoantibodies to CD38 (ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase) in Caucasian patients with diabetes: Effects on insulin release from human islets. Diabetes 1999, 48, 2309–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, A.; Fallahi, P.; Nesti, C.; Pupilli, C.; Marchetti, P.; Takasawa, S.; Okamoto, H.; Ferrannini, E. Anti-CD38 autoimmunity in patients with chronic autoimmune thyroiditis or Graves' disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2001, 126, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, P.F.; Winter, M.E. A quantitative test for xerostomia. The Saxon test, an oral equivalent of the Schirmer test. Arthritis Rheum. 1985, 28, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, Y.G.; Ball, W.D.; Marchetti, L.; Hand, A.R. Contributions of intercalated duct cells to the normal parenchyma of submandibular glands of adult rats. Anat. Rec. 2001, 263, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, Y.G.; Ball, W.D.; Culp, D.J.; Hand, A.R.; Moreira, J.E. Persistence of a perinatal cellular phenotype in submandibular glands of adult rat. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1995, 43, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aure, M.H.; Konieczny, S.F.; Ovitt, C.E. Salivary gland homeostasis is maintained through acinar cell self-duplication. Dev. Cell 2015, 33, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, T.; Yoshimoto, K.; Fujimura, T.; Takeda, M.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Takasawa, S. New aspects of mechanism of salivary gland dysfunction in Sjögren’s syndrome. In Sjögren’s Syndrome; Hernandez, E.M., Ed.; Nova Scientific Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 125–158. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, J.C.; Grisius, M.; Massey, W. Salivary hypofunction and xerostomia: Diagnosis and treatment. Dent. Clin. North Am. 2005, 49, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P.C. Salivary enhancement therapies. Caries Res. 2004, 38, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiki, Y.; Ohnishi, H.; Muto, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Direct evidence that hepatocyte growth factor is a hepatotrophic factor for liver regeneration and has a potent antihepatitis effect in vivo. Hepatology 1992, 16, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Hagiya, M.; Seki, T.; Shimonishi, M.; Sugimura, A.; Tashiro, K.; Shimizu, S. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature 1989, 342, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Takasawa, S.; Nata, K.; Yamauchi, A.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Ota, H.; Yoshimoto, K.; Sakuramoto-Tsuchida, S.; Miyaoka, T.; Takeda, M.; et al. Prevention of Reg I-induced β-cell apoptosis by IL-6/dexamethasone through activation of HGF gene regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 2988–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, M.; Sato, M. Morphogenesis of normal human salivary gland cells in vitro. Histol. Histopathol. 1994, 9, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Miyaoka, T.; Yoshimoto, K.; Yamauchi, A.; Sakuramoto-Tsuchida, S.; Kondo, S.; Takeda, M.; Tsujinaka, H.; et al. Interleukin-6/STAT pathway is responsible for the induction of gene expression of REG Iα, a new auto-antigen in Sjögren’s syndrome patients, in salivary duct epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2015, 2, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, A.T.; Liu, X.; Kagami, H.; Swaim, W.D.; Wellner, R.B.; O'Connell, B.C.; Ambudkar, I.S.; Baum, B.J. Construction and function of a recombinant adenovirus encoding a human aquaporin 1-green fluorescent protein fusion product. Cancer Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Baum, B.J. Including the p53 ELAV-like protein-binding site in vector cassettes enhances transgene expression in rat submandibular gland. Oral Dis. 2012, 18, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.; Hanawa, H.; Yoshida, T.; Ito, M.; Isoda, M.; Chang, H.; Toba, K.; Yoshida, K.; Kojima, M.; Otaki, K.; et al. Gene expression profiles of cardiomyocytes in rat autoimmune myocarditis by DNA microarray and increase of regenerating gene family. Transl. Res. 2008, 152, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roescher, N.; Tak, P.P.; Illei, G.G. Cytokines in Sjögren’s syndrome. Oral Dis. 2009, 15, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulkkonen, J.; Pertovaara, M.; Antonen, J.; Pasternack, A.; Hurme, M. Elevated interleukin-6 plasma levels are regulated by the promoter region polymorphism of the IL6 gene in primary Sjögren’s syndrome and correlate with the clinical manifestations of the disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001, 40, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szodoray, P.; Alex, P.; Brun, J.G.; Centola, M.; Jonsson, R. Circulating cytokines in primary Sjögren’s syndrome determined by a multiplex cytokine array system. Scand. J. Immunol. 2004, 59, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, D.J.; Weiss, L.; Reibstein, I.; van den Brand, J.; Okamoto, H.; Clark, A.; Slavin, S. Amelioration of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice with advanced disease by linomide-induced immunoregulation combined with Reg protein treatment. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoreschi, K.; Laurence, A.; O’Shea, J.J. Janus kinases in immune cell signaling. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 228, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Yamaoka, K. JAK inhibitor tofacitinib for treating rheumatoid arthritis: From basic to clinical. Mod. Rheumatol. 2013, 23, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Fleischmann, R.; Cohen, S.; Lee, E.B.; Garcia Meijide, J.A.; Wagner, S.; Forejtova, S.; Zwillich, S.H.; Grubem, D.; Koncz, T.; et al. ORAL Standard Investigators, Tofacitinib or adalimumab versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P.C. Salivary enhancement therapies. Caries Res. 2004, 38, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santavirta, N.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Törnwall, J.; Segerberg, M.; Santavirta, S.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Björvell, H. Neuropeptides of the autonomic nervous system in Sjögren's syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1997, 56, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujimoto, T.; Yoshimoto, K.; Fujimura, T.; Takeda, M.; Yamauchi, A.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Takasawa, S. Regenerating Gene Protein as a Novel Autoantigen in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Antibodies 2015, 4, 409-425. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib4040409
Fujimoto T, Yoshimoto K, Fujimura T, Takeda M, Yamauchi A, Itaya-Hironaka A, Takasawa S. Regenerating Gene Protein as a Novel Autoantigen in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Antibodies. 2015; 4(4):409-425. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib4040409
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujimoto, Takashi, Kiyomi Yoshimoto, Takanori Fujimura, Maiko Takeda, Akiyo Yamauchi, Asako Itaya-Hironaka, and Shin Takasawa. 2015. "Regenerating Gene Protein as a Novel Autoantigen in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome" Antibodies 4, no. 4: 409-425. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib4040409
APA StyleFujimoto, T., Yoshimoto, K., Fujimura, T., Takeda, M., Yamauchi, A., Itaya-Hironaka, A., & Takasawa, S. (2015). Regenerating Gene Protein as a Novel Autoantigen in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Antibodies, 4(4), 409-425. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib4040409






