Abstract
Engineered Fc-lacking bispecific antibodies have shown an exceptionally high potency for recruiting lymphocyte effector cells and enhancing antitumor activity, which is under evaluation in several clinical trials. However, current treatment regimens raise some issues that should be considered, such as the high cost of clinical-grade bispecific antibodies and the achievement of sustained therapeutic plasma levels. The use of gene transfer methods may circumvent problems related to large-scale production and purification, and result in sustained therapeutic plasma concentrations of the Fc-lacking bispecific antibodies. In fact, terminally differentiated cells and non-terminally differentiated cells can be genetically modified to secrete functionally active bispecific antibodies exerting clear anti-tumor effects. This review highlights the relevance of different promising strategies for in vivo delivery of therapeutic bispecific antibodies.
1. Introduction
Antibody engineering has greatly contributed to the success of antibody-based therapies for cancer, through designing different formats with enhanced effector functions, improved pharmacokinetic properties and decreased immunogenicity [1]. Efforts to further improve the clinical efficacy and safety of antibody-based therapies are ongoing. In this regard, novel antibody-based strategies to redirect immune effector functions represent promising approaches to cancer treatment [2]. These include the genetic engineering of T lymphocytes through the introduction of a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), composed of antibody binding domains connected to T cell activating domains, and the use of bispecific antibodies (bsAbs). Both strategies combine the high specificity of antibody molecules with the efficient trafficking properties and effector functions of T cells [2,3].
BsAbs simultaneously targeting tumor-associated cell surface antigens and effector cell trigger molecules have been developed and shown to redirect cellular cytotoxicity [4,5,6]. Although most bsAbs are in early clinical stage study (phase 1 and phase 2), catumaxomab, an anti-EpCAM x anti-CD3 half mouse/half rat full-length IgG, has been approved by the EMA for intraperitoneal treatment of malignant ascites [7,8]. However, in a phase 1 study for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, it was established that the maximum tolerated dose for multiple intravenous administration of catumaxomab was 5 µg [9]. This is probably a consequence of the tumor cell independent cross-linking of T cells with Fc receptor (FcR)-bearing accessory cells, followed by cytokine release-related symptoms [8].
Furthermore, clinical-grade antibodies for therapeutic use are extremely expensive to produce, and carry non-human glycan epitopes, that can potentially affect immunogenicity and/or therapeutic efficacy, since all patients and healthy controls tested had circulating antibodies against them [10].
For these reasons, it is highly recommended to use engineered Fc-lacking bsAbs such as tandem scFv and diabodies. Tandem scFvs, also known as (scFv)2, consists of two different scFvs connected by a flexible peptide linker on a single protein chain [11]. By reducing the linker length between variable domains (VH and VL) it is possible to force the pairing of domains between two different polypeptides, leading to a compact antibody called diabody [12]. Bispecific diabodies are formed by the association of two VHA-VLB and VHB-VLA fragments expressed in the same cell. This leads to the formation of heterodimers with two different binding sites [13].
Numerous studies have demonstrated the potency of these Fc-lacking bsAbs recruiting lymphocytic effector cells in preclinical studies [14]. Although no bispecific diabodies have been administered to humans, ongoing phase 1 and 2 clinical trials with the anti-CD19 x anti-CD3 tandem scFv blinatumomab revealed impressive clinical results in relapsed B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia [15].
However, these bsAbs lacking in Fc domains present a very short serum half-life and must be administered by continuous intravenous infusion by portable minipumps (Figure 1). Although different strategies have been successfully used to increase the circulation time of recombinant bsAbs: PEGylation, N-glycosylation and fusion to human albumin or albumin-binding domains [16,17], these modifications might also affect bsAb-mediated cytotoxicity and can potentially affect immunogenicity [18].
One way to overcome these limitations would be the use of gene transfer technologies [19]. In vivo secretion of Fc-lacking bsAbs might result in effective and persistent levels of bsAb molecules. This could compensate for the rapid blood-pool clearance and make the bsAbs better tolerated [19].
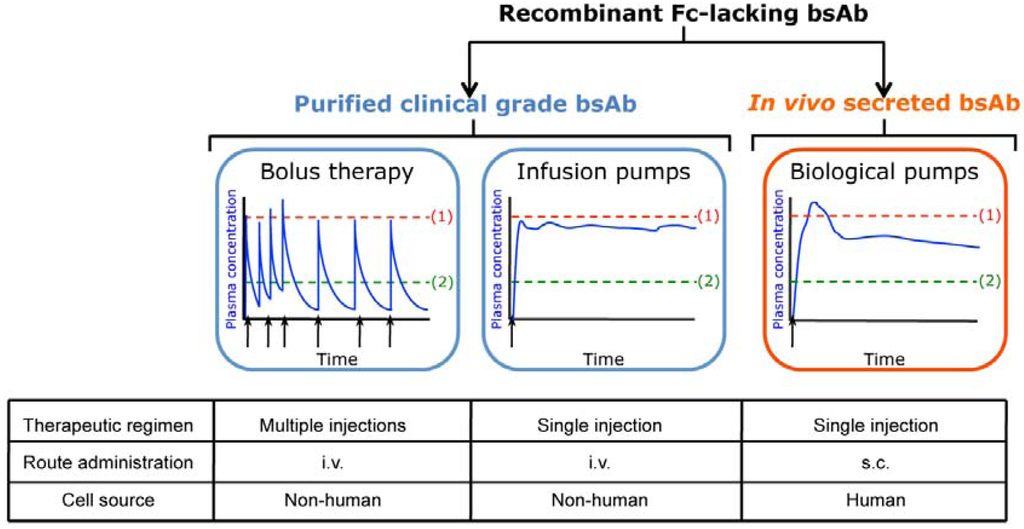
Figure 1.
Schematic chart depicting advantages and limitations associated with the use of systemic administered purified clinical-grade bsAbs (bolus therapy or infusion pumps) and in vivo secreted bsAbs. Simulated pharmacokinetic profile of plasma bsAbs, ranging from subtoxic (1) to subtherapeutic (2).
2. In Vivo Secretion of Fc-lacking Bispecific Antibodies
The feasibility of in vivo secretion of full-length mAbs and engineered antibodies by different cell types has now been demonstrated using different techniques, such as genetic modification of ex vivo expanded terminally differentiated or precursor cells and in vivo gene transfer using viral vectors [20,21,22]. BsAbs have not remained on the margins of these gene therapy strategies, and several papers describing the in vivo secretion of bsAbs have been published (Table 1). In 2003, a seminal work by Blanco et al. [23] demonstrated that non-hematopoietic human cells can be genetically modified to secrete a functionally active bispecific two-chain diabody directed against the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and the CD3ε chain of the TCR/CD3 complex (αCEA x aCD3). Diabody molecules were secreted at high levels and were very efficient at activating human peripheral blood T lymphocytes to proliferate and eliminate human cancer cells expressing CEA in vitro. Furthermore, intratumoral inoculation of diabody producer cells efficiently delayed the growth of human colon carcinoma xenografts.

Table 1.
Different strategies for in vivo production of bispecific antibodies.
| Target antigens | Antibody format | BsAb secreting cells | Effector cells | Disease model | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Vehicle | Transfer Vector | Route of Administration | Cell type | Route of Administration | ||||
| CEA x CD3 | diabody | 293T (h) | plasmid | s.c. co-implant | T cells | i.t. | colon cancer (h) HCT-116 | [23] |
| CEA x CD3 | diabody | T cells (h) | LV | s.c. co-implant | T cells | s.c. co-implant | colon cancer (h) HCT-116 | [26] |
| CEA x CD3 | diabody | MSC (h) | LV | s.c. organoid | T cells | i.v. | colon cancer (h) HCT-116 | [35] |
| HER2 x CD16 | (scFv)2 | MSC-like (m) | RV | i.v. | monocytes | i.p. | breast cancer (h) MDA-MB-453 | [42] |
| CEA x CD3 | diabody | HUVEC | LV | s.c. neovessels | T cells | i.v. | colon cancer (h) HCT-116 | [51] |
Abbreviations: h, human; m, mouse; LV, lentivirus; RV, retrovirus; s.c., subcutaneous; i.v., intravenous; i.t., intratumoral; i.p., intraperitoneal.
Since T lymphocytes have the capacity to home to the tumor deposits [24,25] and are the effector cells of anti-CD3-based bsAbs, a logical strategy was the genetic modification of human T cells with a lentiviral vector encoding the αCEA x αCD3 diabody. Compte et al. [26] demonstrated that functional αCEA x αCD3 diabody was detectable in conditioned medium from lentivirus infected peripheral blood T lymphocytes for several weeks. Furthermore, the concentration of secreted diabody was sufficient to activate primary T cells to proliferate and eliminate CEA+ tumor cells in vitro. Intratumoral secretion of αCEA x αCD3 diabody by gene-modified T lymphocytes improved survival and reduced measurable tumor burden.
This approach would provide: (1) a selective accumulation of gene-modified bsAb-secreting T cells in tumor deposits; (2) the recruitment of both gene-modified and non-modified tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, amplifying the effector immune response; and (3) a highly tumor site-restricted T cell activation, decreasing the toxicity inherent to systemic T-cell activation and enhancing tumoricidal activity (Figure 2a).
However, one of the most important concerns when considering cells as antibody factories is the ability to get sustained antibody plasma levels. The extended life span of stem cells makes them an attractive alternative for the long-term antibody delivery. In several cancer treatment strategies, either neural stem cells (NSC) or mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have been used as delivery vehicles of different therapeutic proteins [27], taking advantage of their inherent tumor-tropic properties [28,29]. In fact, Frank et al. [30] demonstrated that NSC can be engineered to secrete a full-length anti-HER2 human mAb, and can deliver functional antibody to tumor foci in vivo. However, most gene therapy protocols have been focused on the use of MSC, which present certain advantages as therapeutic vehicles: they are readily isolated, easily transduced and exhibit a unique in vitro proliferative capacity using a simple media formulation [29].
Notwithstanding, the use of MSC in cancer-targeting approaches raises concerns, due to their pro-angiogenic properties [31,32,33] and their potential role in tumor progression and metastasis [34,35]. Moreover, the ability of MSC to specifically home to tumors after systemic administration is questionable [22]. As an alternative to systemic administration, MSC can be confined to a specific location, where they will act as biological minipumps avoiding cell dissemination and allowing systemic secretion of therapeutic proteins. Moreover, subcutaneous inoculation of entrapped MSC would provide an easily accessible implant (immunotherapeutic organoid) that could be retrieved once the therapeutic effect is accomplished (Figure 2b). Several works supported the safety, utility and efficacy of this approach to secrete therapeutic proteins that exert a variety of different biological effects in vivo [36,37,38,39,40,41].
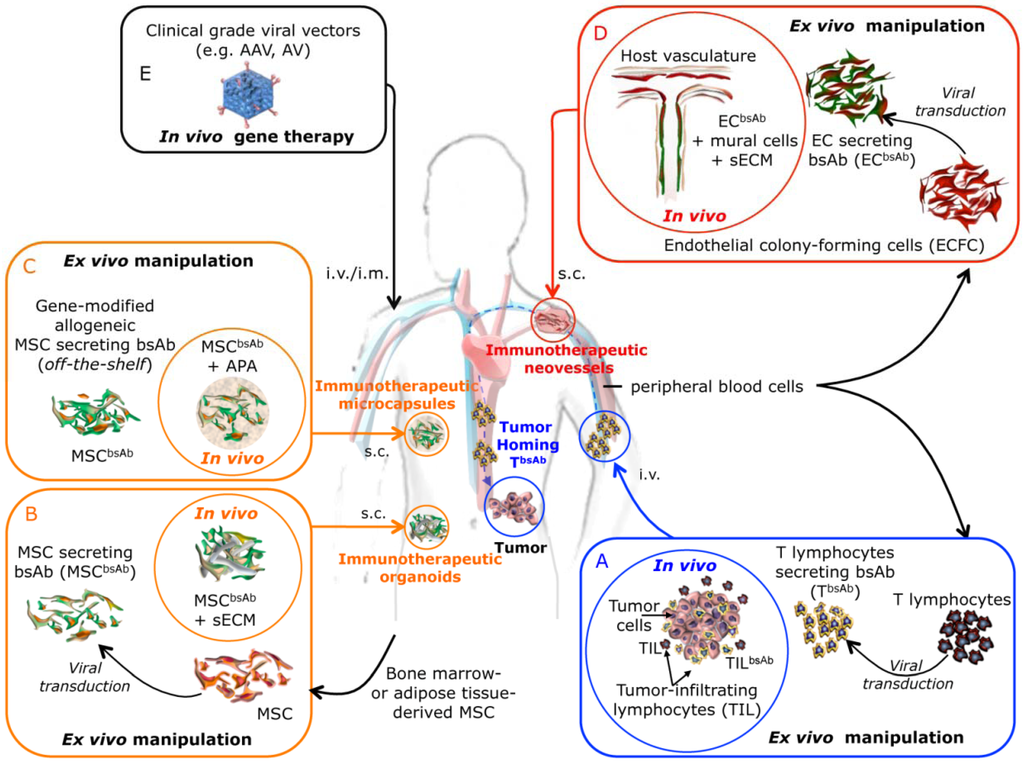
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram illustrating the different strategies for in vivo secretion of bsAbs recruiting lymphocytic effector cells. (A) Ex vivo generation of bsAb-secreting T lymphocytes (TbsAb) for the immunotherapy of cancer. Adoptive transferred TbsAb lymphocytes home to the tumor deposits after reinfusion into the patient, secrete bsAbs and recruit both gene-modified and non-modified tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes. (B) Ex vivo gene-modified autologous MSC secreting bsAbs (MSCbsAb) embedded in a biological synthetic extracelular matrix (sECM) are implanted subcutaneously to generate a immunotherapeutic organoid acting as biological minipumps ensuring the systemic secretion of bsAbs. (C) “Off-the-shelf” stocks of gene-modified allogeneic MSC secreting bsAbs (MSCbsAb). MSCbsAb can be APA (alginate/poly-I-lysine/alginate) microencapsulated and implanted subcutaneously to generate immunotherapeutic microcapsules acting as biological minipumps ensuring the systemic secretion of bsAbs. (D) Autologous endothelial colony forming cells (ECFC) ex vivo transduced for the expression of a bsAbs (ECbsAb), are mixed with autologous mural cells, embedded in a biocompatible scaffold and subcutaneously implanted. In vivo engineered immunotherapeutic neovessels connect with the host vascular bed and allow the release into the bloodstream of the bsAbs. (E) Direct injection of clinical grade viral vectors carrying bsAb genes.
The first demonstration of the use of MSC-based organoids for systemic delivery of engineered antibodies in vivo was a study by Compte et al. [35]. Lentiviral-transduced bone-marrow derived MSC secreting a bispecific αCEA x αCD3 diabody were embedded in a synthetic extracellular matrix and subcutaneously implanted in nude mice, generating a long-lasting functional immunotherapeutic organoid (Table 1). The systemically released αCEA x αCD3 diabody activated passively transferred human T cells to mediate potent and antigen-specific lysis of CEA-expressing tumor in vivo (Figure 2b). This strategy demonstrated for the first time that human MSCs genetically engineered to secrete Fc-lacking bsAbs, seeded in an synthetic ECM scaffold and implanted in a location distant from the primary tumor, are able to induce an effective antitumor response and tumor regression. Later on, Kasuya et al. [42] demonstrated that retrovirally transduced, MSC-like 10T1/2 cells secreted a functional anti-HER2 x anti-CD16 single-chain antibody (Table 1). Furthermore, antibody produced by gene-modified 10T1/2 cells implanted in the perivascular area of pulmonary arteries exhibited antitumor effect against HER-2+ human breast cancer cells implanted intraperitoneally, after inoculation of human T cells.
Another approach for long-lasting bsAbs secretion has focused on endothelial cells. The utility of endothelial cells for gene therapy approaches has been extensively proved in a wide range of different pathologies [43,44,45]. Several works have shown the feasibility to build blood vessel networks in vivo using human endothelial cells and mural cells [33,46,47,48,49]. Given that engineered vessels become eventually anastomosed to the host vascular bed, the secreted protein would be directly released into the blood stream and exert a systemic effect [50].
Taking advantage of the previously developed model of human angiogenesis in vivo, Compte et al. [51] explored the potential of immunotherapeutic neovessels after gene-modifying human vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) for the secretion of a bsAb (Table 1), based on the permissiveness of endothelial cells to be transduced by lentiviral vectors (Figure 2d). As a proof of principle, HUVEC transduced with a lentiviral vector were used for the expression of the αCEA x αCD3 diabody. These endothelial cells, along with MSC as a source of mural cells, were embedded in a solubilized tissue basement membrane matrix (Matrigel) to generate subcutaneous vascular networks capable of systemic bsAbs release in nude mice. Furthermore, the secreted αCEA x αCD3 diabody exerted a therapeutic effect in mice bearing distant CEA+ tumors after inoculation of human T cells. Interestingly, secretion of diabody in mice bearing immunotherapeutic neovessels remained highly stable. Diabody plasma concentration dropped less than 30% relative to the maximum peak, while secretion by MSC-based immunotherapeutic organoids dropped more than 80% during the same lapse of time [35].
In a practical clinical setting, this strategy would require: (1) to establish a suitable source of autologous endothelial cells; and (2) to characterize the most appropriate biological support for the generation of a stable and functional vasculature. Regarding the first point, Melero-Martin et al. [52] have recently demonstrated the vasculogenic potential of endothelial colony-forming cells derived from peripheral blood.
3. Future Prospects
In recent years, the use of gene-modified cells for antibody delivery has shown great potential as a therapeutic tool. Autologous cells seem to be the best choice for cell-based delivery therapies, and the most practical approach might be the use of immunotherapeutic organoids to keep the cells at the implantation site. However, these individualized therapies imply a high economic cost. From a practical point of view, the only realistic approach to apply these strategies to the clinical setting would imply the use of stocks of gene-modified allogeneic cells ready to be used. However, immune responses against allogenic cells represent a major barrier for development in this field. Microencapsulation systems become an interesting alternative to protect gene-modified allogeneic cells from immune system and ensure the systemic release of the antibody for a long period of time (Figure 2c). The feasibility and effectiveness of this approach for the in vivo secretion of therapeutic proteins has been experimentally demonstrated [53,54,55]. Several studies have also demonstrated that stable secretion of antibodies can be reached through in vivo gene therapy methods (Figure 2e). Therapeutic levels of serum antibodies have been reported after intramuscular or intravenous injection of adeno-associated virus, adenovirus or lentivirus [20,21]. These approaches could be applied to cancer immunotherapeutic regimens in which long-term secretion of Fc-lacking bsAbs in vivo is desirable.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Ministerio deEconomía y Competitividad (BIO2011-22738), and the Comunidad de Madrid (S2010/BMD-2312) to L.A-V; and from the Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria/Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI08/90856 and PS09/00227) and Fundación Investigación Biomédica Hospital Puerta de Hierro to L.S.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cuesta, A.M.; Sainz-Pastor, N.; Bonet, J.; Oliva, B.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Multivalent antibodies: When design surpasses evolution. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Vallina, L. Genetic approaches for antigen-selective cell therapy. Curr. Gene Ther. 2001, 1, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontermann, R. Dual targeting strategies with bispecific antibodies. MAbs 2012, 4, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P. Improving the efficacy of antibody-based cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.; Kontermann, R.E. Bispecific antibodies for cancer immunotherapy: Current perspectives. BioDrugs 2010, 24, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; Cuesta, A.M.; Compte, M.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Antibody engineering: Facing new challenges in cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhimolea, E.; Reichert, J.M. World Bispecific Antibody Summit, September 27-28, 2011, Boston, MA. MAbs 2012, 4, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, R.; Klein, A.; Seimetz, D. Catumaxomab: clinical development and future directions. MAbs 2010, 2, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, M.; Passlick, B.; Friccius-Quecke, H.; Jager, M.; Lindhofer, H.; Kanniess, F.; Wiewrodt, R.; Thiel, E.; Buhl, R.; Schmittel, A. Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer patients with the trifunctional monoclonal antibody catumaxomab (anti-EpCAM x anti-CD3): A phase I study. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, D.; Zhang, M.; Hurtado-Ziola, N.; Varki, A. Production platforms for biotherapeutic glycoproteins. Occurrence, impact, and challenges of non-human sialylation. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2012, 28, 147–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.; Riethmuller, G.; Kufer, P. A small bispecific antibody construct expressed as a functional single-chain molecule with high tumor cell cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7021–7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliger, P.; Winter, G. Engineering bispecific antibodies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1993, 4, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliger, P.; Hudson, P.J. Engineered antibody fragments and the rise of single domains. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chames, P.; Baty, D. Bispecific antibodies for cancer therapy: The light at the end of the tunnel? MAbs 2009, 1, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargou, R.; Leo, E.; Zugmaier, G.; Klinger, M.; Goebeler, M.; Knop, S.; Noppeney, R.; Viardot, A.; Hess, G.; Schuler, M.; et al. Tumor regression in cancer patients by very low doses of a T cell-engaging antibody. Science 2008, 321, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.; Karle, A.; Meissburger, B.; Hofig, I.; Stork, R.; Kontermann, R.E. Improved pharmacokinetics of recombinant bispecific antibody molecules by fusion to human serum albumin. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 12650–12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stork, R.; Campigna, E.; Robert, B.; Muller, D.; Kontermann, R.E. Biodistribution of a bispecific single-chain diabody and its half-life extended derivatives. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25612–25619. [Google Scholar]
- Libon, C.; Corvaia, N.; Haeuw, J.F.; Nguyen, T.N.; Stahl, S.; Bonnefoy, J.Y.; Andreoni, C. The serum albumin-binding region of streptococcal protein G (BB) potentiates the immunogenicity of the G130-230 RSV-A protein. Vaccine 1999, 17, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; Blanco, B.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Antibodies and gene therapy: Teaching old 'magic bullets' new tricks. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaranayake, H.; Wirth, T.; Schenkwein, D.; Raty, J.K.; Yla-Herttuala, S. Challenges in monoclonal antibody-based therapies. Ann. Med. 2009, 41, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Martin, D.; Sanz, L.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Engineering human cells for in vivo secretion of antibody and non-antibody therapeutic proteins. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; Compte, M.; Guijarro-Munoz, I.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Non-hematopoietic stem cells as factories for in vivo therapeutic protein production. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, B.; Holliger, P.; Vile, R.G.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Induction of human T lymphocyte cytotoxicity and inhibition of tumor growth by tumor-specific diabody-based molecules secreted from gene-modified bystander cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Restifo, N.P.; Yang, J.C.; Morgan, R.A.; Dudley, M.E. Adoptive cell transfer: a clinical path to effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restifo, N.P.; Dudley, M.E.; Rosenberg, S.A. Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer: Harnessing the T cell response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compte, M.; Blanco, B.; Serrano, F.; Cuesta, A.M.; Sanz, L.; Bernad, A.; Holliger, P.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Inhibition of tumor growth in vivo by in situ secretion of bispecific anti-CEA x anti-CD3 diabodies from lentivirally transduced human lymphocytes. Cancer Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K. Mesenchymal stem cells engineered for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studeny, M.; Marini, F.C.; Dembinski, J.L.; Zompetta, C.; Cabreira-Hansen, M.; Bekele, B.N.; Champlin, R.E.; Andreeff, M. Mesenchymal stem cells: potential precursors for tumor stroma and targeted-delivery vehicles for anticancer agents. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboody, K.S.; Najbauer, J.; Danks, M.K. Stem and progenitor cell-mediated tumor selective gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.T.; Najbauer, J.; Aboody, K.S. Concise review: Stem cells as an emerging platform for antibody therapy of cancer. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 2084–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, R.; Zibert, A.; Laryea, M.; Gobel, U.; Daubener, W.; Dilloo, D. Human bone marrow stromal cells inhibit allogeneic T-cell responses by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated tryptophan degradation. Blood 2004, 103, 4619–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Ozaki, K.; Oh, I.; Meguro, A.; Hatanaka, K.; Nagai, T.; Muroi, K.; Ozawa, K. Nitric oxide plays a critical role in suppression of T-cell proliferation by mesenchymal stem cells. Blood 2007, 109, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; Santos-Valle, P.; Alonso-Camino, V.; Salas, C.; Serrano, A.; Vicario, J.L.; Cuesta, A.M.; Compte, M.; Sanchez-Martin, D.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Long-term in vivo imaging of human angiogenesis: critical role of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the generation of durable blood vessels. Microvasc. Res. 2008, 75, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnoub, A.E.; Dash, A.B.; Vo, A.P.; Sullivan, A.; Brooks, M.W.; Bell, G.W.; Richardson, A.L.; Polyak, K.; Tubo, R.; Weinberg, R.A. Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2007, 449, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compte, M.; Cuesta, A.M.; Sanchez-Martin, D.; onso-Camino, V.; Vicario, J.L.; Sanz, L.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Tumor immunotherapy using gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells loaded into synthetic extracellular matrix scaffolds. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, V.; Blumenfeld, N.; Perricaudet, M.; Beuzard, Y.; Kremer, E.J. Organoids direct systemic expression of erythropoietin in mice. Gene Ther. 1995, 2, 411–417. [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos, N.; Al-Khaldi, A.; Crosato, M.; Lachapelle, K.; Galipeau, J. A neovascularized organoid derived from retrovirally engineered bone marrow stroma leads to prolonged in vivo systemic delivery of erythropoietin in nonmyeloablated, immunocompetent mice. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagg, J.; Lejeune, L.; Paquin, A.; Galipeau, J. Marrow stromal cells for interleukin-2 delivery in cancer immunotherapy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2004, 15, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliopoulos, N.; Francois, M.; Boivin, M.N.; Martineau, D.; Galipeau, J. Neo-organoid of marrow mesenchymal stromal cells secreting interleukin-12 for breast cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4810–4818. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoo, T.; Fukui, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Ohashi, T.; Sado, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Kawamura, T.; Okabe, M.; Hosoya, T.; Kobayashi, E. Generation of a transplantable erythropoietin-producer derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. Transplantation 2008, 85, 1654–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Fallavollita, L.; Nguyen, L.; Burnier, J.; Rafei, M.; Galipeau, J.; Yakar, S.; Brodt, P. Autologous bone marrow stromal cells genetically engineered to secrete an igf-I receptor decoy prevent the growth of liver metastases. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuya, K.; Shimazu, M.; Suzuki, M.; Itoi, T.; Aoki, T.; Tsuchida, A. Bispecific anti-HER2 and CD16 single-chain antibody production prolongs the use of stem cell-like cell transplantation against HER2-overexpressing cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 25, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Squinto, S.P.; Madri, J.A.; Kennedy, S.; Springhorn, J. The ENCEL system: A somatic cell protein delivery system. In Vivo 1994, 8, 771–780. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Wagner, T.E. Long-term expression of human growth hormone (hGH) in mice containing allogeneic yolk sac cell derived neovascular implants expressing hGH. Stem Cells 1996, 14, 232–238. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, H.; Shibata, M.; Brown, B.; Labelle, A.; Hegadorn, C.; Andrews, C.; Hebbel, R.P.; Galipeau, J.; Hough, C.; Lillicrap, D. Ex vivo gene therapy for hemophilia A that enhances safe delivery and sustained in vivo factor VIII expression from lentivirally engineered endothelial progenitors. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, N.; Fukumura, D.; Gralla, O.; Au, P.; Schechner, J.S.; Jain, R.K. Tissue engineering: Creation of long-lasting blood vessels. Nature 2004, 428, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero-Martin, J.M.; Khan, Z.A.; Picard, A.; Wu, X.; Paruchuri, S.; Bischoff, J. In vivo vasculogenic potential of human blood-derived endothelial progenitor cells. Blood 2007, 109, 4761–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero-Martin, J.M.; De Obaldia, M.E.; Kang, S.Y.; Khan, Z.A.; Yuan, L.; Oettgen, P.; Bischoff, J. Engineering robust and functional vascular networks in vivo with human adult and cord blood-derived progenitor cells. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, P.; Tam, J.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells facilitate engineering of long-lasting functional vasculature. Blood 2008, 111, 4551–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Vallina, L.; Sanz, L. The therapeutic potential of engineered human neovessels for cell-based gene therapy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compte, M.; onso-Camino, V.; Santos-Valle, P.; Cuesta, A.M.; Sanchez-Martin, D.; Lopez, M.R.; Vicario, J.L.; Salas, C.; Sanz, L.; Álvarez-Vallina, L. Factory neovessels: Engineered human blood vessels secreting therapeutic proteins as a new drug delivery system. Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.Z.; Dreyzin, A.; Aamodt, K.; Li, D.; Jaminet, S.C.; Dudley, A.C.; Melero-Martin, J.M. Induction of erythropoiesis using human vascular networks genetically engineered for controlled erythropoietin release. Blood 2011, 118, 5420–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, M.; Hoffmeyer, A.; Kroger, J.; Freund, M.; Hain, J.; Holle, A.; Karle, P.; Knofel, W.T.; Liebe, S.; Muller, P.; et al. Microencapsulated cell-mediated treatment of inoperable pancreatic carcinoma. Lancet 2001, 357, 1591–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirone, P.; Bourgeois, J.M.; Chang, P.L. Antiangiogenic cancer therapy with microencapsulated cells. Hum. Gene Ther. 2003, 14, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.; Dahan, N.; Goren, E.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. Encapsulated human mesenchymal stem cells: A unique hypoimmunogenic platform for long-term cellular therapy. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).