C1q Is Recognized as a Soluble Autoantigen by Anti-C1q Antibodies of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth Media
2.2. Buffers
2.3. Patients
2.4. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins in E. coli
2.5. Biotin Labelling
2.6. ELISA Assays
2.6.1. ELISA Assay for the Recognition of Soluble C1q and Its Globular Head Fragments ghA, ghB, and ghC by Immobilized IgG Autoantibodies from Sera of Patients with LN
2.6.2. Competitive ELISA
2.6.3. ELISA Assay for the Recognition of C1q, ghA, ghB, and ghC by Sera from SLE Patients
2.7. Fluorescent Spectroscopy
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Evaluation of Patients
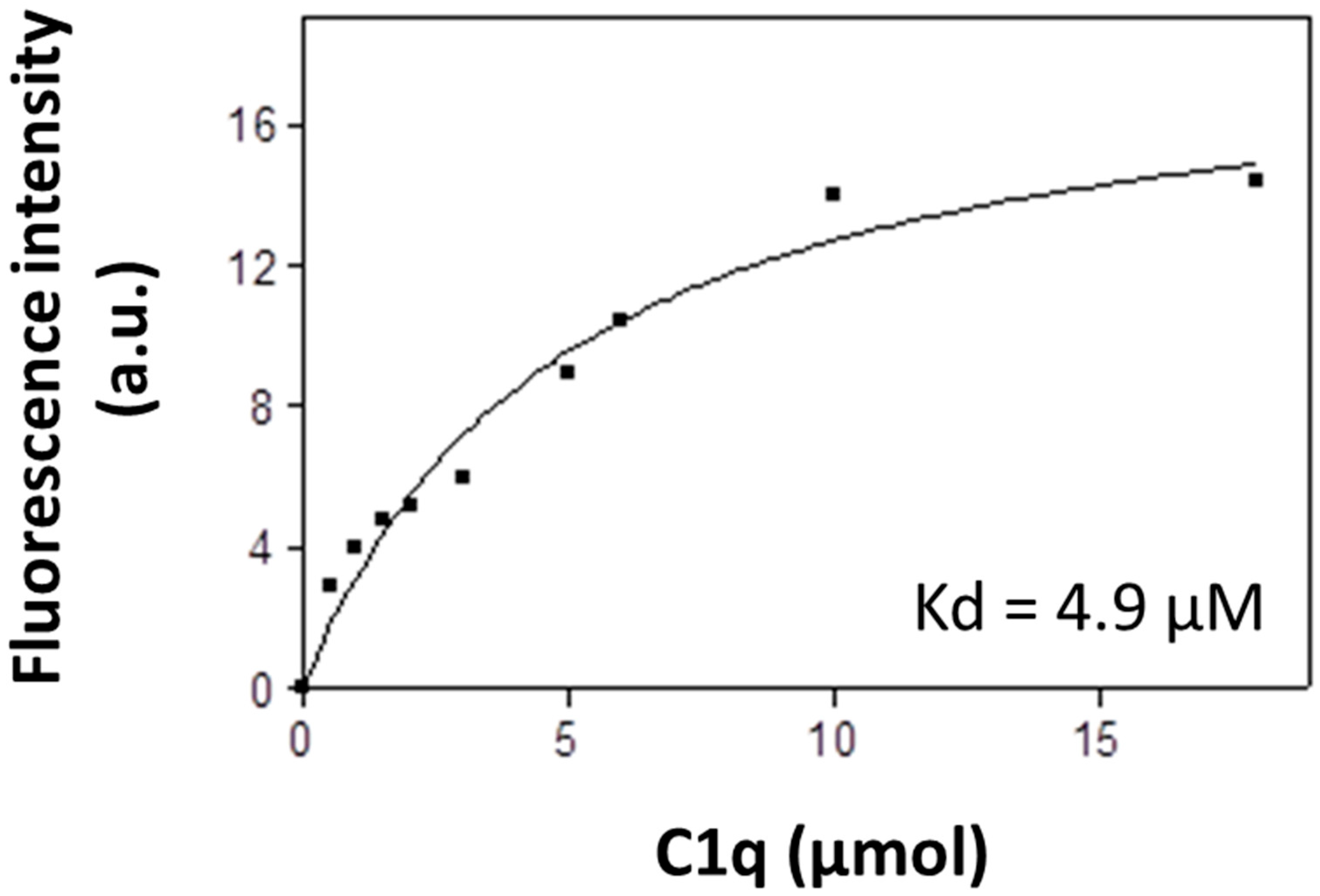
3.2. Fluorescent Analysis
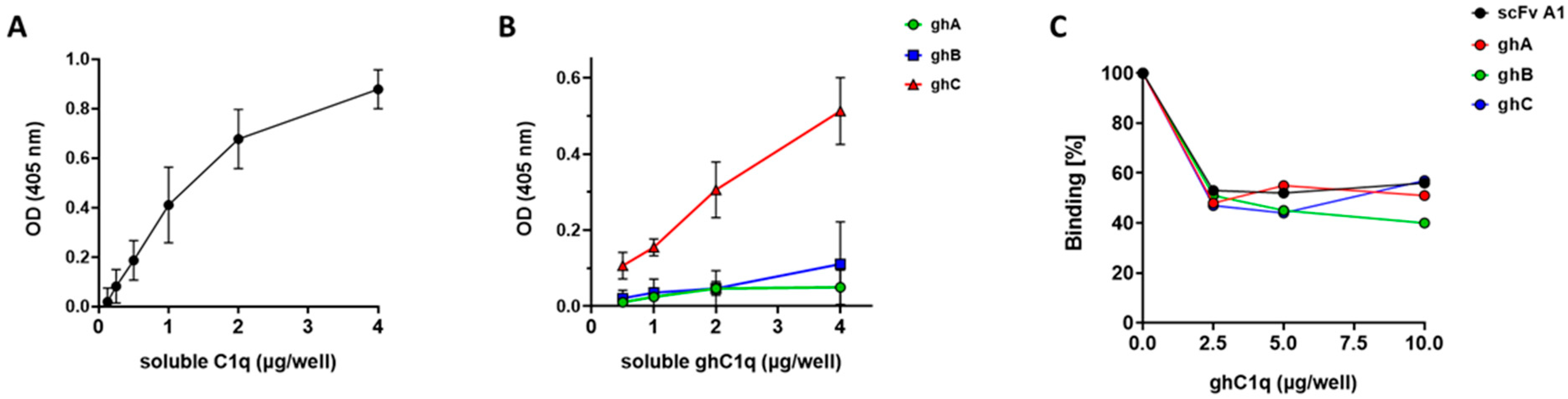
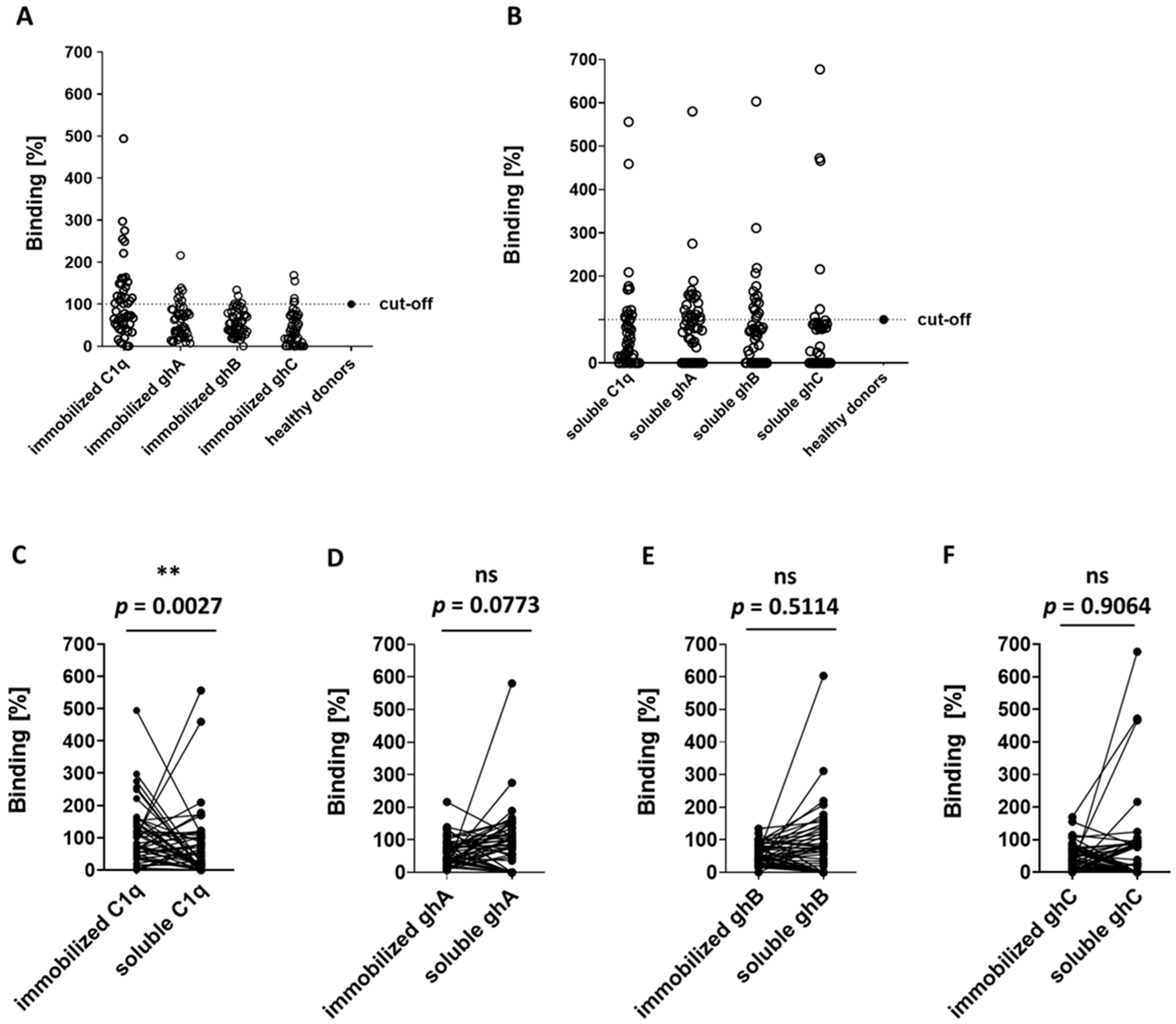
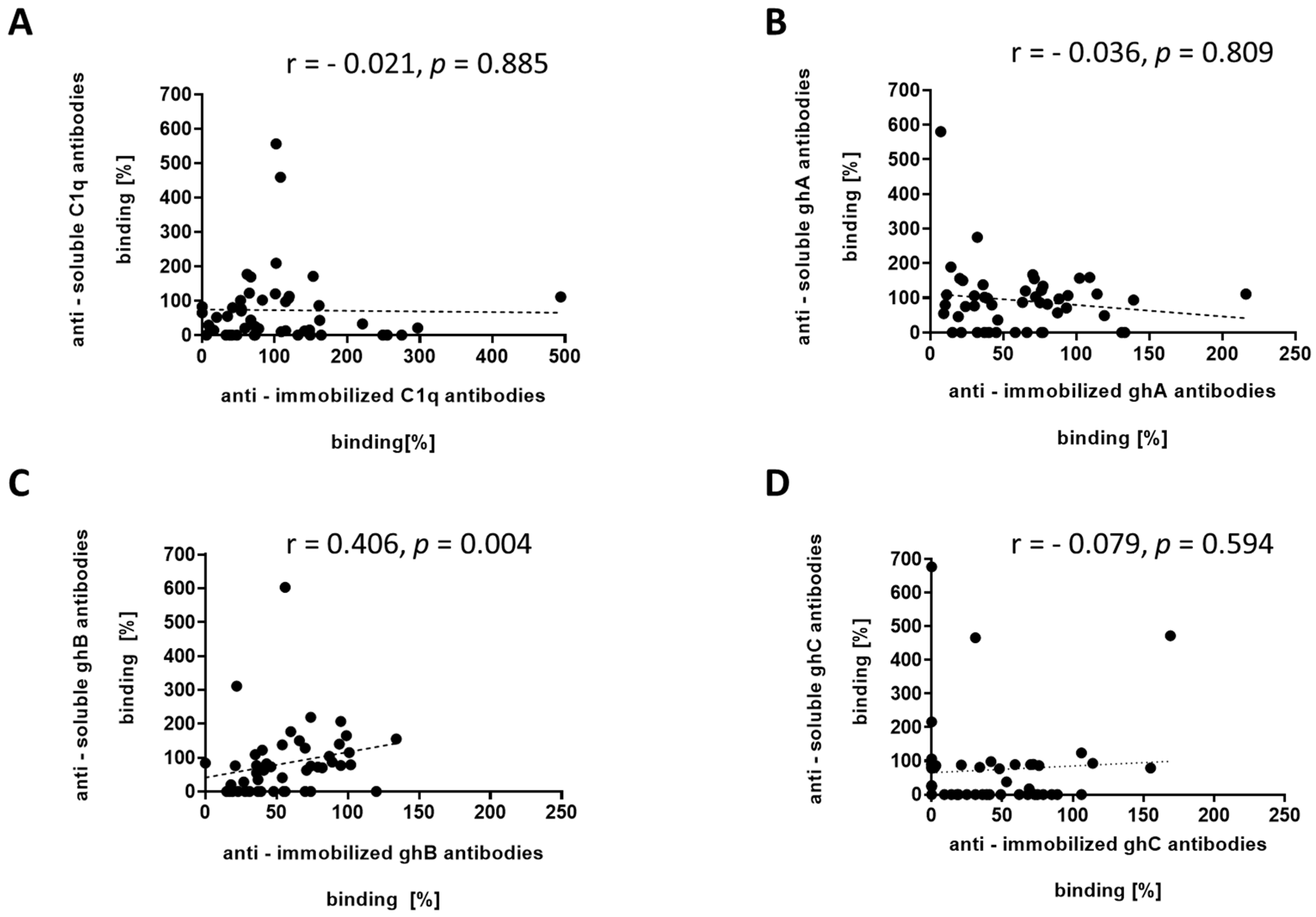
3.3. ELISA Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thielens, N.M.; Tedesco, F.; Bohlson, S.S.; Gaboriaud, C.; Tenner, A.J. C1q: A fresh look upon an old molecule. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 89, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Hosszu, K.K.; Valentino, A.; Peerschke, E.I.B. The C1q family of proteins: Insights into the emerging non-traditional functions. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboriaud, C.; Frachet, P.; Thielens, N.M.; Arlaud, G.J. The human C1q globular domain: Structure and recognition of non-immune self-ligands. Front. Immunol. 2012, 2, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, D.J.; van de Bovenkamp, F.S.; Abendstein, L.; Zuijderduijn, R.; Pool, J.; Kramer, C.S.M.; Slot, L.M.; Drijfhout, J.W.; de Vor, L.; Gelderman, K.A.; et al. Human anti-C1q autoantibodies bind specifically to solid-phase C1q and enhance phagocytosis but not complement activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2310666120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouser, L.; Madhukaran, S.P.; Shastri, A.; Saraon, A.; Ferluga, J.; Al-Mozaini, M.; Kishore, U. Emerging and Novel Functions of Complement Protein C1q. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvan, M.D.; Greenlee-Wacker, M.C.; Bohlson, S.S. C1q and phagocytosis: The perfect complement to a good meal. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulla, R.; Agostinis, C.; Bossi, F.; Rizzi, L.; Debeus, A.; Tripodo, C.; Radillo, O.; De Seta, F.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Tedesco, F. Decidual endothelial cells express surface-bound C1q as a molecular bridge between endovascular trophoblast and decidual endothelium. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2629–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, G.; Bulla, R.; Salmon, J.E.; Tedesco, F. The complement system in the pathophysiology of pregnancy. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis, C.; Bulla, R.; Tripodo, C.; Gismondi, A.; Stabile, H.; Bossi, F.; Guarnotta, C.; Garlanda, C.; De Seta, F.; Spessotto, P.; et al. An alternative role of C1q in cell migration and tissue remodeling: Contribution to trophoblast invasion and placental development. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4420–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.A.; Laust, A.K.; Nelson, E.L.; Tenner, A.J. C1q differentially modulates phagocytosis and cytokine responses during ingestion of apoptotic cells by human monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6175–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, M.E.; Clarke, E.V.; Morgado, P.; Fraser, D.A.; Tenner, A.J. Complement protein C1q directs macrophage polarization and limits inflammasome activity during the uptake of apoptotic cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5682–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, E.V.; Weist, B.M.; Walsh, C.M.; Tenner, A.J. Complement protein C1q bound to apoptotic cells suppresses human macrophage and dendritic cell-mediated Th17 and Th1 T cell subset proliferation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trendelenburg, M. Autoantibodies against complement component C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mahler, M.; Schaarenburg, R.; Trouw, L. Anti-C1q autoantibodies, novel tests, and clinical consequences. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wener, M.H.; Uwatoko, S.; Mannik, M. Antibodies to the collagen-like region of C1q in sera of patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1989, 32, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, M.D.; Burger, R.; Loos, M. Conformational changes in C1q after binding to immune complexes: Detection of neoantigens with monoclonal antibodies. J. Immunol. 1982, 129, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, V.; Bogoeva, V.; Petrova, L.; Tchorbadjieva, M.; Petrova, S.; Georgieva, V.; Georgiev, G.; Deliyska, B.; Vasilev, V.; Tsacheva, I. Autoantigenicity of human C1q is associated with increased hydrophobicity due to conformational transitions in the globular heads. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, P.; Ukoumunne, O.C.; Cottrell, I.; Khan, A.; Maqsood, S.; Thornes, J.; Perry, E.; Isenberg, D. Autoantibodies against C1q as a diagnostic measure of lupus nephritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, M.C.; Botto, M. Are anti-C1q antibodies different from other SLE autoantibodies? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigler, C.; Schaller, M.; Perahud, I.; Osthoff, M.; Trendelenburg, M. Autoantibodies against Complement C1q Specifically Target C1q Bound on Early Apoptotic Cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3512–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yu, F.; Fang, Q.; Yang, H.-Z.; Zhao, M.-H. Detection of anti-C1q antibodies and anti-C1q globular head domain antibodies in sera from Chinese patients with lupus nephritis. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2178–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanova, V.; Tchorbadjieva, M.; Deliyska, B.; Vasilev, V.; Tsacheva, I. Biochemical analysis of the epitope specificities of anti-C1q autoantibodies accompanying human Lupus Nephritis reveals them as a dynamic population in the course of the disease. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 148, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, M.; Bigler, C.; Danner, D.; Ditzel, H.J.; Trendelenburg, M. Autoantibodies against C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus are antigen-driven. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 8225–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhecke, D.; Roumenina, L.T.; Wan, H.; Osthoff, M.; Schaller, M.; Trendelenburg, M. Identification of a major linear C1q epitope allows detection of systemic lupus erythematosus anti-C1q antibodies by a specific peptide-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3706–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsacheva, I.; Radanova, M.; Todorova, N.; Argirova, T.; Kishore, U. Detection of autoantibodies against the globular domain of human C1q in the sera of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2147–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, M.R.; McClain, M.T.; Rubertone, M.V.; Scofield, R.H.; Dennis, G.J.; James, J.A.; Harley, J.B. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchin, G.; Son, M.; Kim, S.J.; Ben-Zvi, I.; Zhang, J.; Diamond, B. Anti-DNA antibodies cross-react with C1q. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 44, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorova, N.; Rangelov, M.; Bogoeva, V.; Stoyanova, V.; Yordanova, A.; Nikolova, G.; Georgiev, H.; Dimitrova, D.; Mohedin, S.; Stoyanova, K.; et al. Anti-idiotype scFv localizes an autoepitope in the globular domain of C1q. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, G.; Georgieva, Y.; Atanasova, A.; Radulova, G.; Kapogianni, A.; Tsacheva, I. Autoinduction as means for optimization of the heterologous expression of recombinant single-chain Fv (scFv) antibodies. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboriaud, C.; Juanhuix, J.; Gruez, A.; Lacroix, M.; Darnault, C.; Pignol, D.; Verger, D.; Fontecilla-Camps, J.C.; Arlaud, G.J. The crystal structure of the globular head of complement protein C1q provides a basis for its versatile recognition properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46974–46982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojouharova, M.S.; Gadjeva, M.G.; Tsacheva, I.G.; Zlatarova, A.; Roumenina, L.T.; Tchorbadjieva, M.I.; Atanasov, B.P.; Waters, P.; Urban, B.C.; Sim, R.B.; et al. Mutational analyses of the recombinant globular regions of human C1q A, B, and C chains suggest an essential role for arginine and histidine residues in the C1q-IgG interaction. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4351–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapogianni, A.; Radulova, G.; Donev, V.; Videv, P.; Cholakova, G.; Iliev, S.; Ivanova, A.; Bogoeva, V.; Tsacheva, I. Characterization of the binding of the globular domains of the complement component C1q to phosphatidylserine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 291, 139116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Païdassi, H.; Tacnet-Delorme, P.; Garlatti, V.; Darnault, C.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Gaboriaud, C.; Arlaud, G.J.; Frachet, P. C1q binds phosphatidylserine and likely acts as a multi ligand bridging molecule in apoptotic cell recognition. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, P.J. Defective waste disposal: Does it induce autoantibodies in SLE? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Serum Number | Immobilized | Fluid-Phase | Clinical Symptoms | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1q | ghA | ghB | ghC | C1q | ghA | ghB | ghC | ||
| 1 | + | cutaneous, joint, vascular, cerebrovasculitis | |||||||
| 2 | + | cutaneous, joint, ocular–pulmonary, symptomatic myositis, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | |||||||
| 3 | + | + | cutaneous, joint, renal, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | ||||||
| 4 | + | cutaneous, joint, Lupus Nephritis, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | |||||||
| 5 | + | cutaneous, joint, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | |||||||
| 7 | + | cutaneous, joint, Necrotic vasculitis in Raynaud’s syndrome, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | |||||||
| 8 | + | cutaneous, joint, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | |||||||
| 9 | + | + | + | cutaneous, joint, Lupus Nephritis 3 degree | |||||
| 10 | + | cutaneous, joint, cerebrovasculitis, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | |||||||
| 11 | + | cutaneous, joint, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | |||||||
| 13 | + | cutaneous, joint, vascular, myopathy | |||||||
| 14 | + | cutaneous, joint, cardiovascular with rhythm disorders | |||||||
| 15 | + | + | + | cutaneous, joint, vascular | |||||
| 16 | + | + | + | + | Rheumatoid polyarthritis—affecting joints of the hands and feet, elbow and shoulder joints | ||||
| 17 | + | + | cutaneous, joint, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | ||||||
| 18 | + | seropositive RA with high joint count | |||||||
| 19 | + | + | seropositive RA with high joint count | ||||||
| 21 | + | + | cutaneous, joint, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | ||||||
| 22 | + | seropositive RA affecting small joints of the hands and feet, shoulder, and knee joints | |||||||
| 23 | + | cutaneous, joint, Lupus Nephritis 1 degree | |||||||
| 24 | + | cutaneous, joint, Necrotic vasculitis in Raynaud’s syndrome, central nervous system, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | |||||||
| 25 | + | cutaneous, joint, vascular, Raynaud’s syndrome | |||||||
| 29 | + | + | cutaneous, joint, vascular, cerebrovasculitis | ||||||
| 35 | + | + | cutaneous, joint, vascular, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | ||||||
| 36 | + | + | seropositive RA affecting the joints of the hands, feet, and knees | ||||||
| 37 | + | + | + | cutaneous, joint, vascular, Raynaud’s syndrome | |||||
| 38 | + | + | cutaneous, joint, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | ||||||
| 39 | + | + | + | cutaneous, joint, myopathy, cerebrovasculitis, multifocal encephalopathy | |||||
| 40 | + | + | + | + | cutaneous, joint, cerebral artery aneurysm, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | ||||
| 41 | + | + | + | + | + | + | seropositive RA and secondary Sjögren’s syndrome | ||
| 42 | + | + | + | + | cutaneous, joint, Lupus Nephritis 2 grade | ||||
| 43 | + | cutaneous, joint, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | |||||||
| 45 | + | + | cutaneous, joint, vascular, minimum 1:80 ANA antibodies | ||||||
| 46 | + | + | + | + | seropositive RA with high joint count | ||||
| 47 | + | cutaneous, joint, vascular | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atanasova, A.A.; Cholakova, G.I.; Kapogianni, A.P.; Donev, V.; Ivanova, D.; Yordanova, A.D.; Bogoeva, V.P.; Tsacheva, I.G. C1q Is Recognized as a Soluble Autoantigen by Anti-C1q Antibodies of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Antibodies 2025, 14, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040094
Atanasova AA, Cholakova GI, Kapogianni AP, Donev V, Ivanova D, Yordanova AD, Bogoeva VP, Tsacheva IG. C1q Is Recognized as a Soluble Autoantigen by Anti-C1q Antibodies of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Antibodies. 2025; 14(4):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040094
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtanasova, Alexandra Anatolieva, Ginka Ilieva Cholakova, Alexandra Panagiotis Kapogianni, Vancho Donev, Delina Ivanova, Anna Dimitrova Yordanova, Vanya Petkova Bogoeva, and Ivanka Georgieva Tsacheva. 2025. "C1q Is Recognized as a Soluble Autoantigen by Anti-C1q Antibodies of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Antibodies 14, no. 4: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040094
APA StyleAtanasova, A. A., Cholakova, G. I., Kapogianni, A. P., Donev, V., Ivanova, D., Yordanova, A. D., Bogoeva, V. P., & Tsacheva, I. G. (2025). C1q Is Recognized as a Soluble Autoantigen by Anti-C1q Antibodies of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Antibodies, 14(4), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040094







