Evaluating the Therapeutic Efficacy of an Anti-BAFF Receptor Antibody Using a Rheumatoid Arthritis Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production of Anti-BAFF-R (BR3) Antibodies
2.2. Evaluation of Anti-BR3 Antibodies’ Binding Abilities Using ELISA and Flow Cytometry
2.3. Evaluation of the Ability of Anti-BR3 Antibodies to Neutralize BAFF-Induced B-Cell Proliferation In Vitro
2.4. Mouse Model of Collagen-Induced Arthritis
2.5. CIA Severity Scoring Method
2.6. Sera Collection
2.7. Immune Phenotyping
2.8. Processing and Evaluation of Joint Histology
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Design, Expression, and Purification of Anti-BR3 Antibodies
3.2. In Vitro Characterization of the Anti-BR3 Antibodies
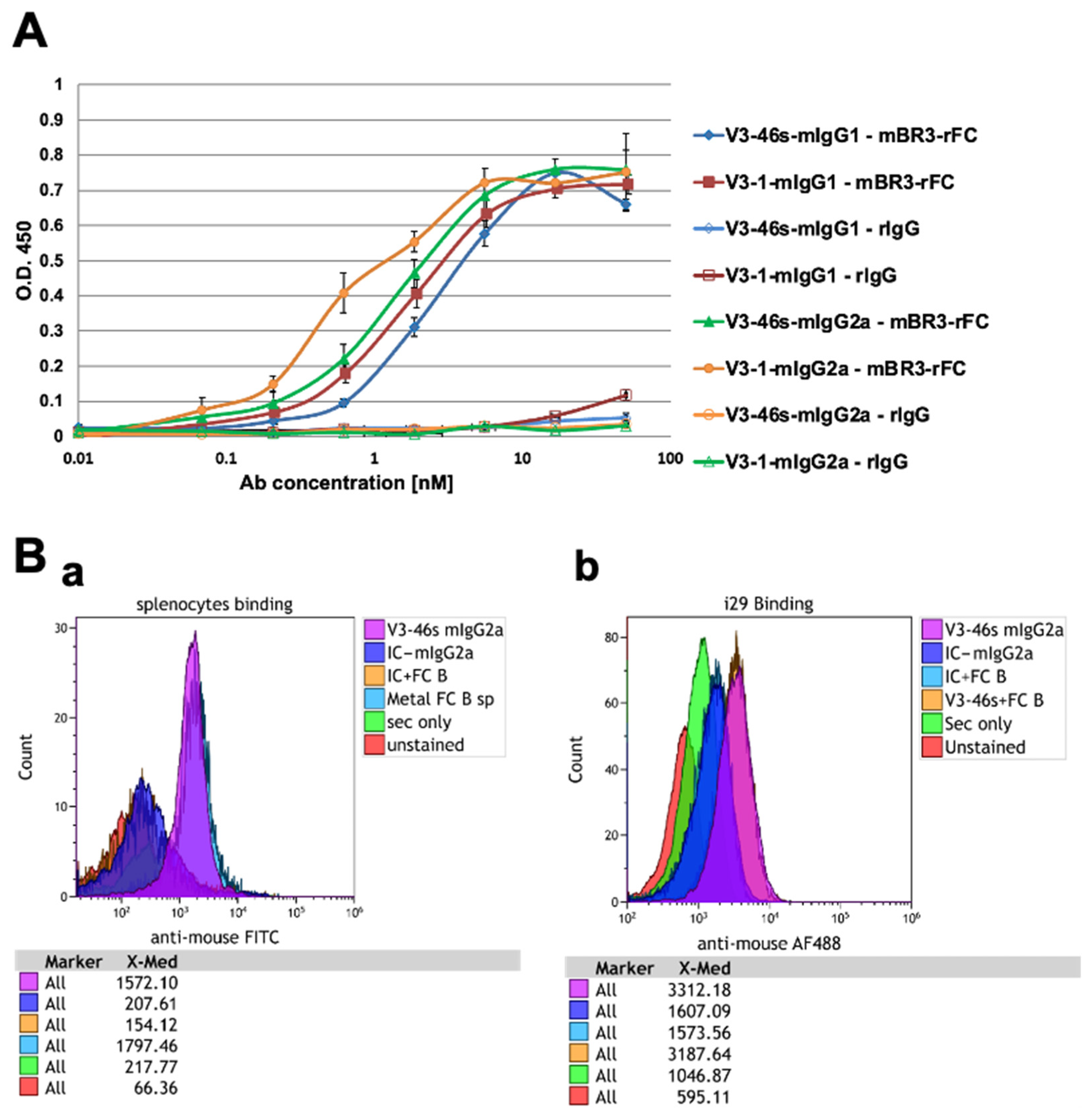
3.2.1. All the Anti-BR3 Antibodies Bind BR3
3.2.2. V3-46s mIgG2a Antibody Bind BR3 on i29 Cells and Splenocytes
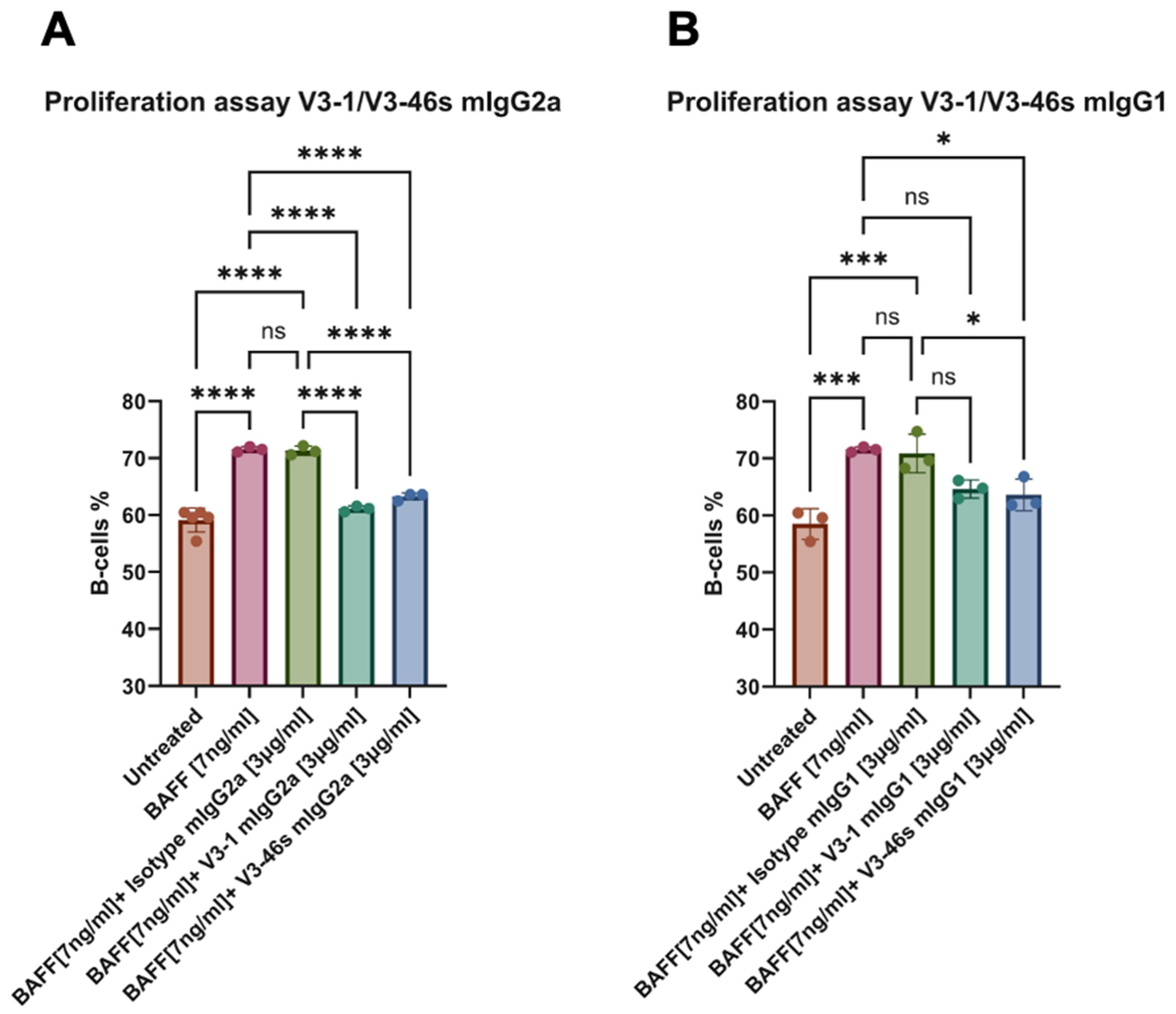
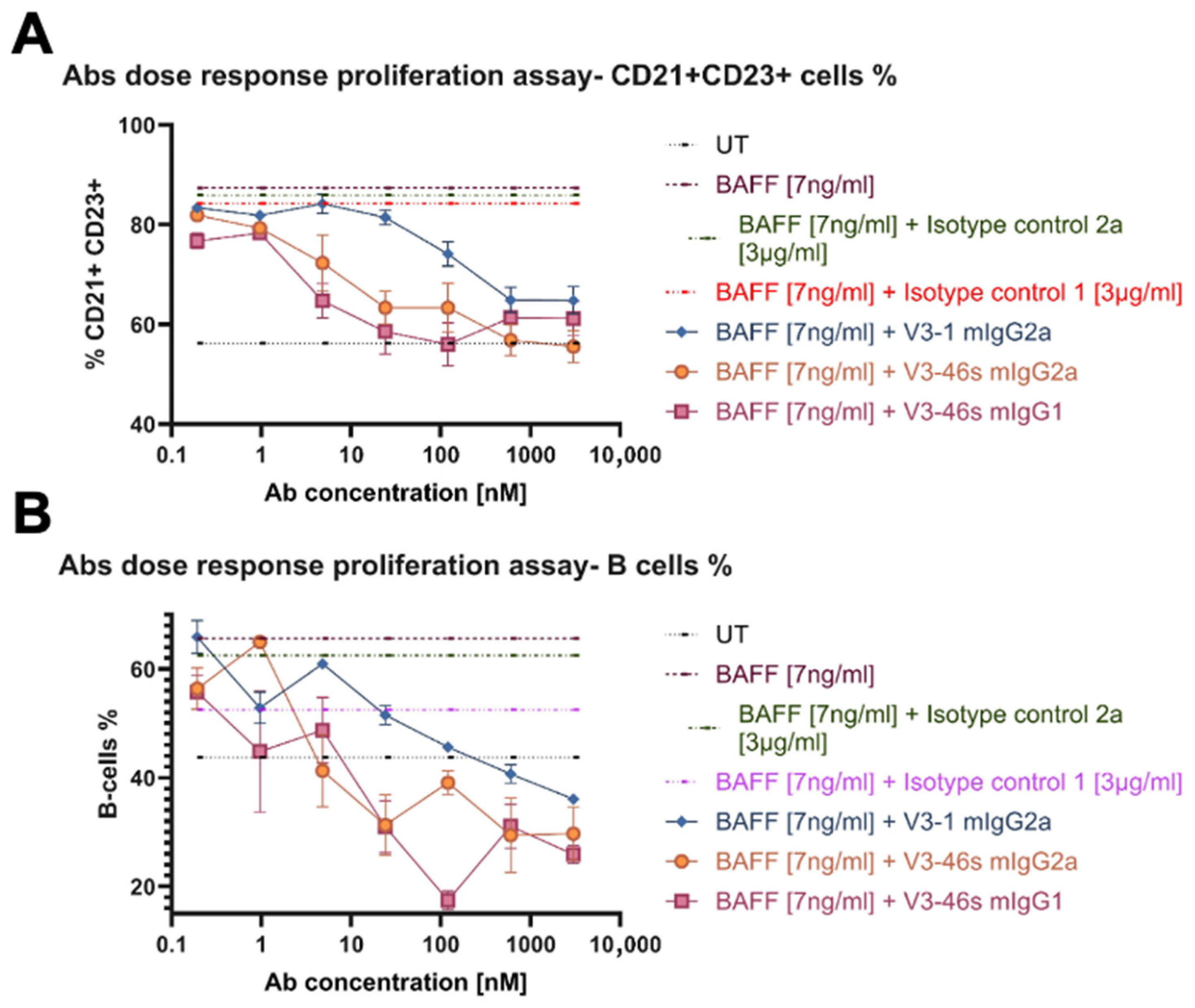
3.3. V3-46s mIgG2a Exhibits Neutralization of BAFF-Induced B-Cell Proliferation In Vitro
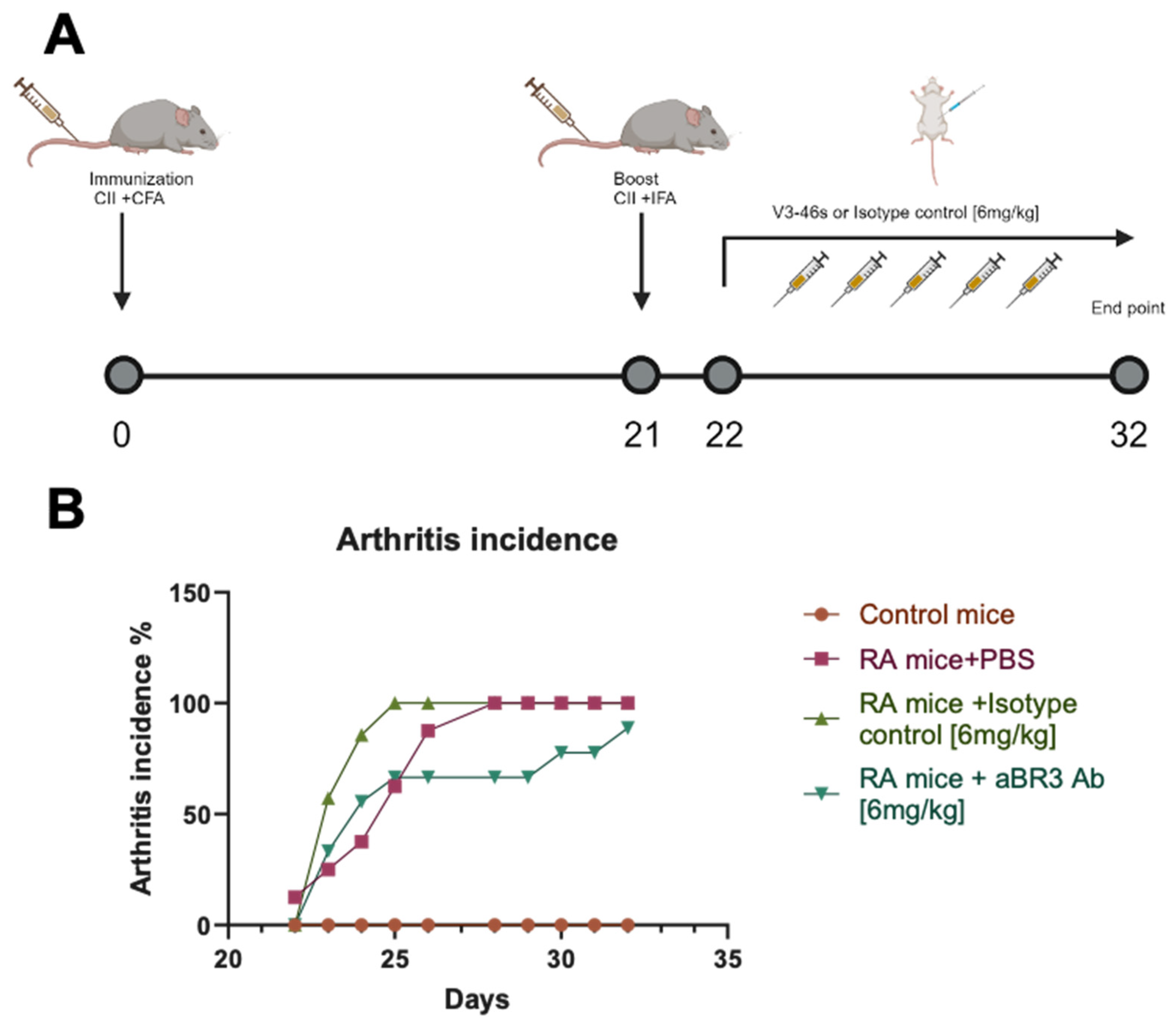
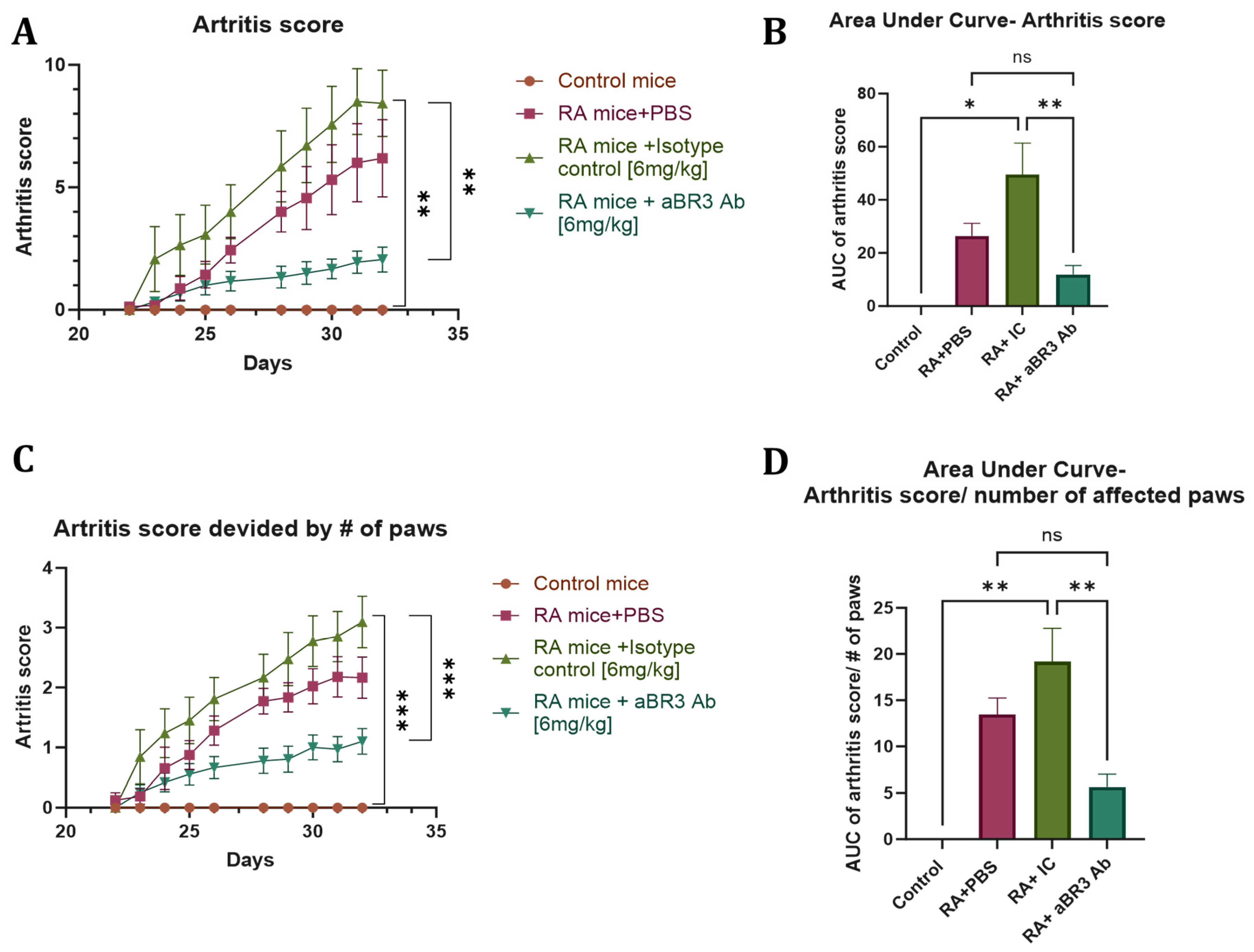
3.4. In Vivo Evaluation of V3-46s mIgG2a mAb Using the CIA Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamanos, Y.; Drosos, A.A. Epidemiology of adult rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2005, 4, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahid, M.; Khan, K.U.; Rehan, U.-H.; Ahmed, R.S. Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Scientific Understanding of the Disease. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 34, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Delft, M.A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J. An overview of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Au, S.; Reddy, S.R.K.; Katsaros, E.; Agrawal, D.K. Factors Underlying Failure of Methotrexate Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Implications in Personalized Care. Arch. Intern Med. Res. 2025, 8, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudu, T.; Oztas, M.; Nikiphorou, E. Contemporary approaches to the management of rheumatoid arthritis: Precision and progress. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2025, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Gao, J.; Kang, J.; Wang, X.; Niu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Treatment Prospects. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 750753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.C. Current role of rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 18, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zha, M.; Liu, Q.; Lai, Z.; Li, L.; Shao, Y.; Sun, J. Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy Based on B Cells. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2025, 19, 7837–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisini, I.; Davidson, A. BAFF: A local and systemic target in autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 158, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, L.M.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Vital, E.M. Evolution and trajectory of B-cell targeted therapies in rheumatic diseases. Lancet Rheumatol. 2025, 7, e355–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.J.; Yoon, B.Y.; Jhun, J.Y.; Oh, H.J.; Min, S.W.; Cho, M.L.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Min, J.K. Regulation of B cell activating factor (BAFF) receptor expression by NF-KappaB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis B cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Chang, Y.; Wei, W. The role of BAFF in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 2015, 76, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, H.; Su, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, C.; Xie, Q.; Xia, X.; He, G.; Yang, L. Therapeutic effects of a novel BAFF blocker on arthritis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, W.; Merrill, J.T.; McKay, J.D.; Lisse, J.R.; Zhong, Z.J.; Freimuth, W.W.; Genovese, M.C. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging Study. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, P.; Reddy, V.; Isenberg, D. Improving B-cell depletion in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitdemange, A.; Blaess, J.; Sibilia, J.; Felten, R.; Arnaud, L. Shared development of targeted therapies among autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: A systematic repurposing analysis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2020, 12, 1759720X20969261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.L.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.J.; Shu, J.L.; Li, Y.; Tai, Y.; Xu, S.Q.; Xu, J.H.; Wei, W. BAFF, involved in B cell activation through the NF-kappaB pathway, is related to disease activity and bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1665–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.R.; Cohen, P.L. Living life without B cells: Is repeated B-cell depletion a safe and effective long-term treatment plan for rheumatoid arthritis? Int. J. Clin. Rheumtol. 2012, 7, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Hu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, R.; Yang, P.; Guo, H.; Nan, G.; Guo, N.; Gou, X. Applicability and implementation of the collagen-induced arthritis mouse model, including protocols (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, D.D.; Latham, K.A.; Rosloniec, E.F. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, C.M.; Balazs, M.; Deforge, L.S.; Dennis, M.S.; Fuh, G.; Hurst, S.D.; Lee, C.V.; Lowman, H.B.; Martin, F.; Nakamura, G.R.; et al. Polypeptide That Binds BR3 and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent 20100280227A1, 4 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim-Perach, R.; Grinberg, Y.; Vaks, L.; Nahary, L.; Benhar, I. Production of Stabilized Antibody Fragments in the E. coli Bacterial Cytoplasm and in Transiently Transfected Mammalian Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1904, 455–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.; Kim, H.S.; Tong, R.K.; Bainbridge, T.W.; Vernes, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Chung, S.; Dennis, M.S.; Zuchero, Y.J.; et al. Effector-attenuating Substitutions That Maintain Antibody Stability and Reduce Toxicity in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 3900–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitia, R.; Rubartelli, A.; Kikutani, H.; Hammerling, U.; Stavnezer, J. The regulation of membrane-bound and secreted alpha-chain biosynthesis during the differentiation of the B cell lymphoma I.29. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 2859–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; He, F. Curcumin protects against collagen-induced arthritis via suppression of BAFF production. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimstein, C.; Choi, Y.K.; Wasserfall, C.H.; Satoh, M.; Atkinson, M.A.; Brantly, M.L.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Song, S. Alpha-1 antitrypsin protein and gene therapies decrease autoimmunity and delay arthritis development in mouse model. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, R.A. When to use the Bonferroni correction. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2014, 34, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, P.; Vetter, T.R. Two-Sample Unpaired t Tests in Medical Research. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.C.; Albittar, A.; Huang, J.J.; Hirayama, A.V.; Kimble, E.L.; Portuguese, A.J.; Chapuis, A.; Shadman, M.; Till, B.G.; Cassaday, R.D.; et al. Factors associated with long-term outcomes of CD19 CAR T-cell therapy for relapsed/refractory CLL. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 6990–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ines, M.; Zeineb, Z.; Selma, B.; Olfa, S.; Leila, R.; Rawdha, T.; Aicha, B.T.; Chadli, D.; Leila, A. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C. Rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: An update. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2013, 8, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehnberg, M.; Amu, S.; Tarkowski, A.; Bokarewa, M.I.; Brisslert, M. Short- and long-term effects of anti-CD20 treatment on B cell ontogeny in bone marrow of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollastro, S.; Klarenbeek, P.L.; Doorenspleet, M.E.; van Schaik, B.D.C.; Esveldt, R.E.E.; Thurlings, R.M.; Boumans, M.J.H.; Gerlag, D.M.; Tak, P.P.; Vos, K.; et al. Non-response to rituximab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with incomplete disruption of the B cell receptor repertoire. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Chen, S.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, H.; Su, X.; Luo, Y.; Yang, L. A novel BAFF antagonist, BAFF-Trap, effectively alleviates the disease progression of systemic lupus erythematosus in MRL/lpr mice. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 129, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Lee, H.T.; Lim, H.; Lee, S.H.; Son, J.Y.; Lee, J.U.; Yoo, K.Y.; Ryu, S.E.; Rhie, J.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. BAFF-neutralizing interaction of belimumab related to its therapeutic efficacy for treating systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.V.; Hymowitz, S.G.; Wallweber, H.J.; Gordon, N.C.; Billeci, K.L.; Tsai, S.P.; Compaan, D.M.; Yin, J.; Gong, Q.; Kelley, R.F.; et al. Synthetic anti-BR3 antibodies that mimic BAFF binding and target both human and murine B cells. Blood 2006, 108, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, D.D.; Reshetylo, S.; Nytes, C.; Goodsett, C.T.; Hematti, P. Blockade of BAFF Receptor BR3 on T Cells Enhances Their Activation and Cytotoxicity. J. Immunother. 2018, 41, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, A.; Varin, M.M.; Le Pottier, L.; Pochard, P.; Bendaoud, B.; Youinou, P.; Pers, J.O. Specific forms of BAFF favor BAFF receptor-mediated epithelial cell survival. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 51, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Seshasayee, D.; Lee, W.P.; Caplazi, P.; McVay, S.; Suto, E.; Nguyen, A.; Lin, Z.; Sun, Y.; DeForge, L.; et al. Dual B cell immunotherapy is superior to individual anti-CD20 depletion or BAFF blockade in murine models of spontaneous or accelerated lupus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, E.; De La Torre, I.; Leandro, M.J.; Cambridge, G. B cell phenotypes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis relapsing after rituximab: Expression of B cell-activating factor-binding receptors on B cell subsets. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 190, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, W.H.; Fiorentino, D.; Chung, L.; Moreland, L.W.; Deodhar, M.; Harler, M.B.; Saulsbery, C.; Kunder, R. Cutting-edge approaches to B-cell depletion in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1454747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

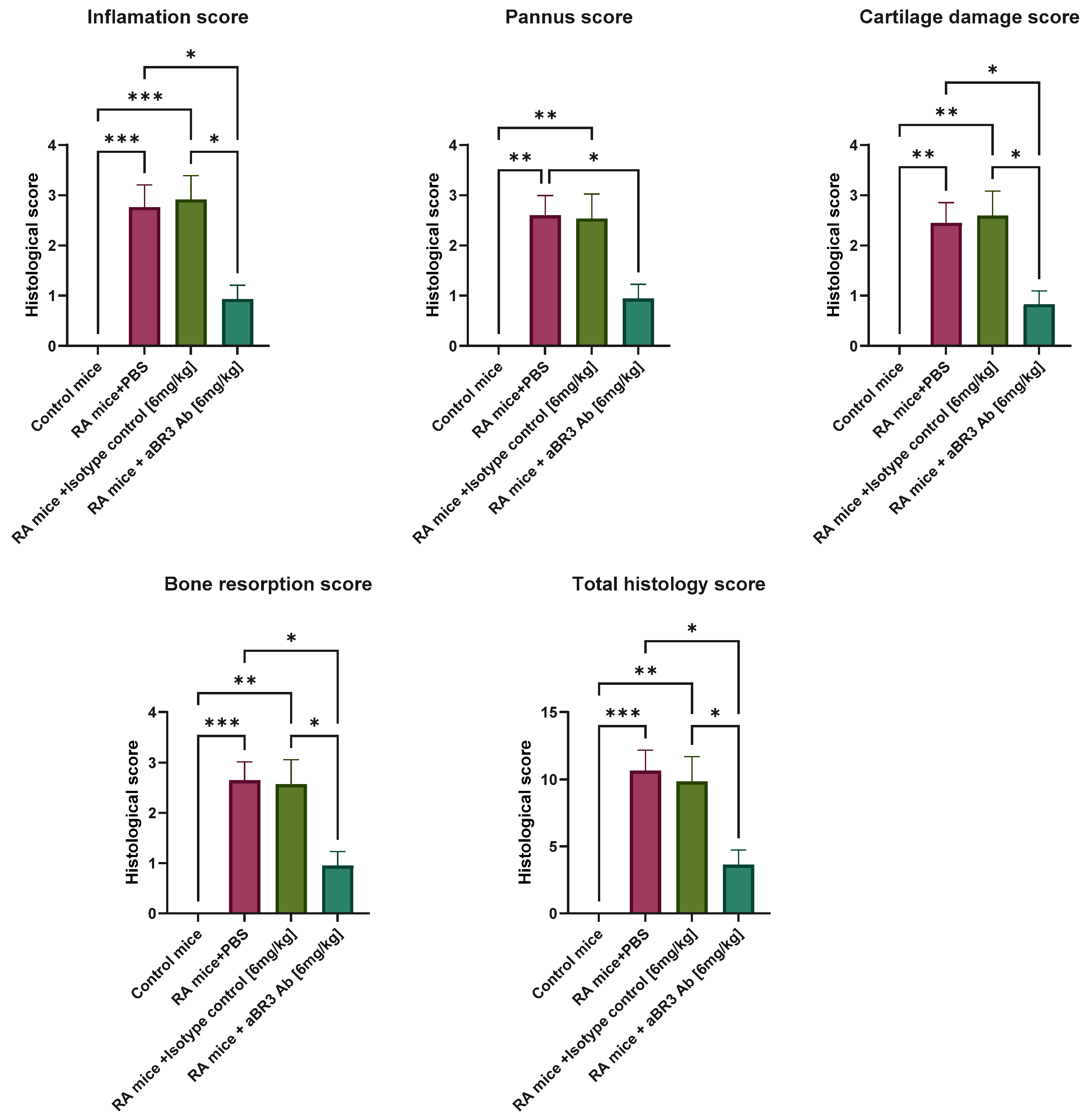
| Paw Score | Clinical Observations |
|---|---|
| 0 | Normal paw. No obvious differences in appearance vs. healthy mice. |
| 1 | One or two toes inflamed and swollen. No apparent swelling of paw or ankle. |
| 2 | Three or more toes inflamed and swollen, but no paw swelling, OR Mild swelling of entire paw. |
| 3 | Swelling of entire paw and some toes. |
| 4 | Severe swelling of entire paw and all toes. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aharon, A.; Birnboim-Perach, R.; Grotto, O.; Amir, A.; Diadko, D.; Beltran, N.; Nahary, L.; Benhar, I. Evaluating the Therapeutic Efficacy of an Anti-BAFF Receptor Antibody Using a Rheumatoid Arthritis Mouse Model. Antibodies 2025, 14, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040090
Aharon A, Birnboim-Perach R, Grotto O, Amir A, Diadko D, Beltran N, Nahary L, Benhar I. Evaluating the Therapeutic Efficacy of an Anti-BAFF Receptor Antibody Using a Rheumatoid Arthritis Mouse Model. Antibodies. 2025; 14(4):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040090
Chicago/Turabian StyleAharon, Adi, Rachel Birnboim-Perach, Omer Grotto, Adi Amir, Daniel Diadko, Nitzan Beltran, Limor Nahary, and Itai Benhar. 2025. "Evaluating the Therapeutic Efficacy of an Anti-BAFF Receptor Antibody Using a Rheumatoid Arthritis Mouse Model" Antibodies 14, no. 4: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040090
APA StyleAharon, A., Birnboim-Perach, R., Grotto, O., Amir, A., Diadko, D., Beltran, N., Nahary, L., & Benhar, I. (2025). Evaluating the Therapeutic Efficacy of an Anti-BAFF Receptor Antibody Using a Rheumatoid Arthritis Mouse Model. Antibodies, 14(4), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040090







