Light Chain Isotype and Antibody-Specificity Impact on Virus Neutralization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of IgG1 Expression Vectors
2.2. Expression and Purification of IgG1 Antibody Isotypes
2.3. N-Glycan Analysis
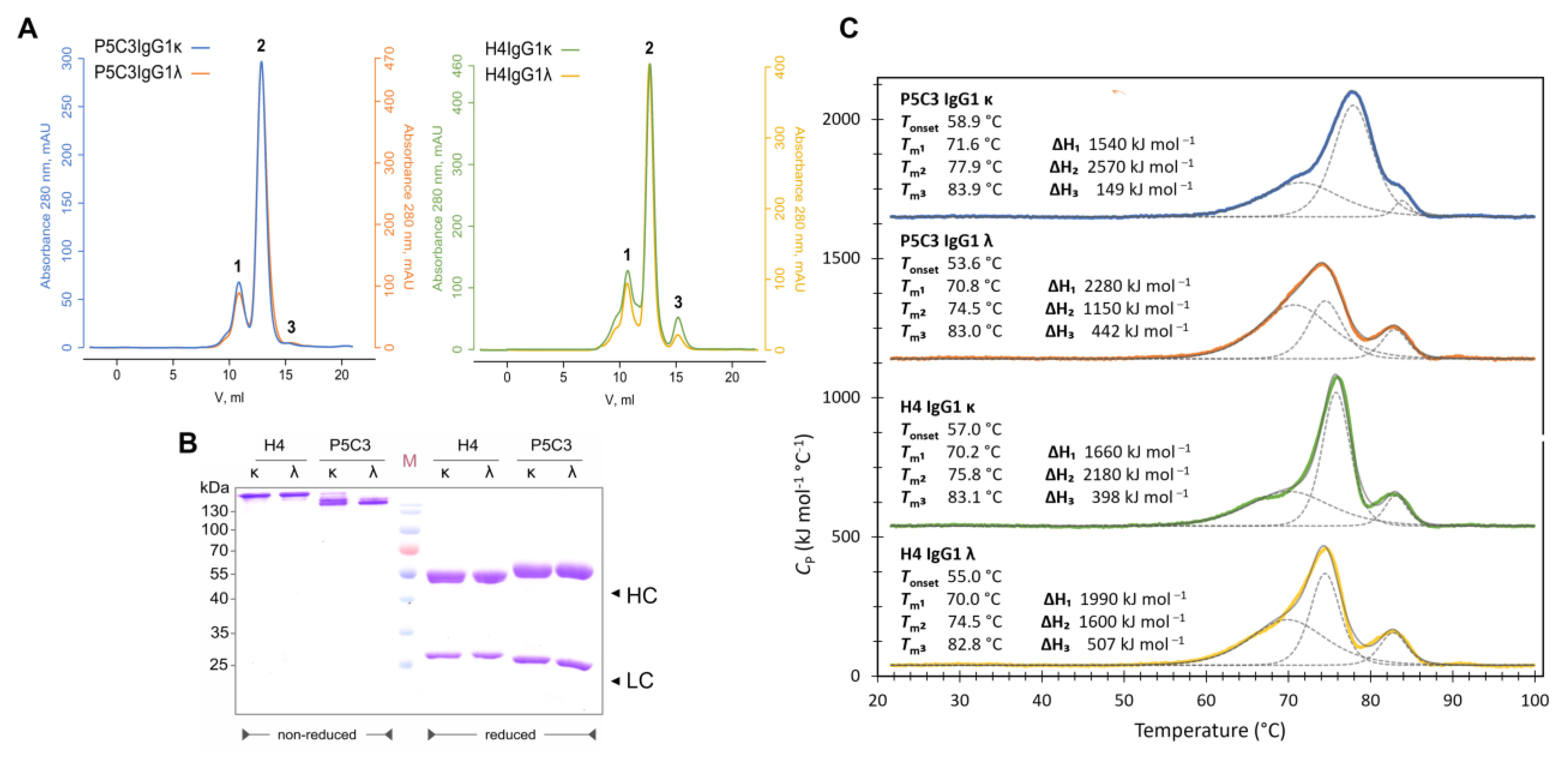
2.4. Thermal Stability of IgG1 Antibody Isotypes
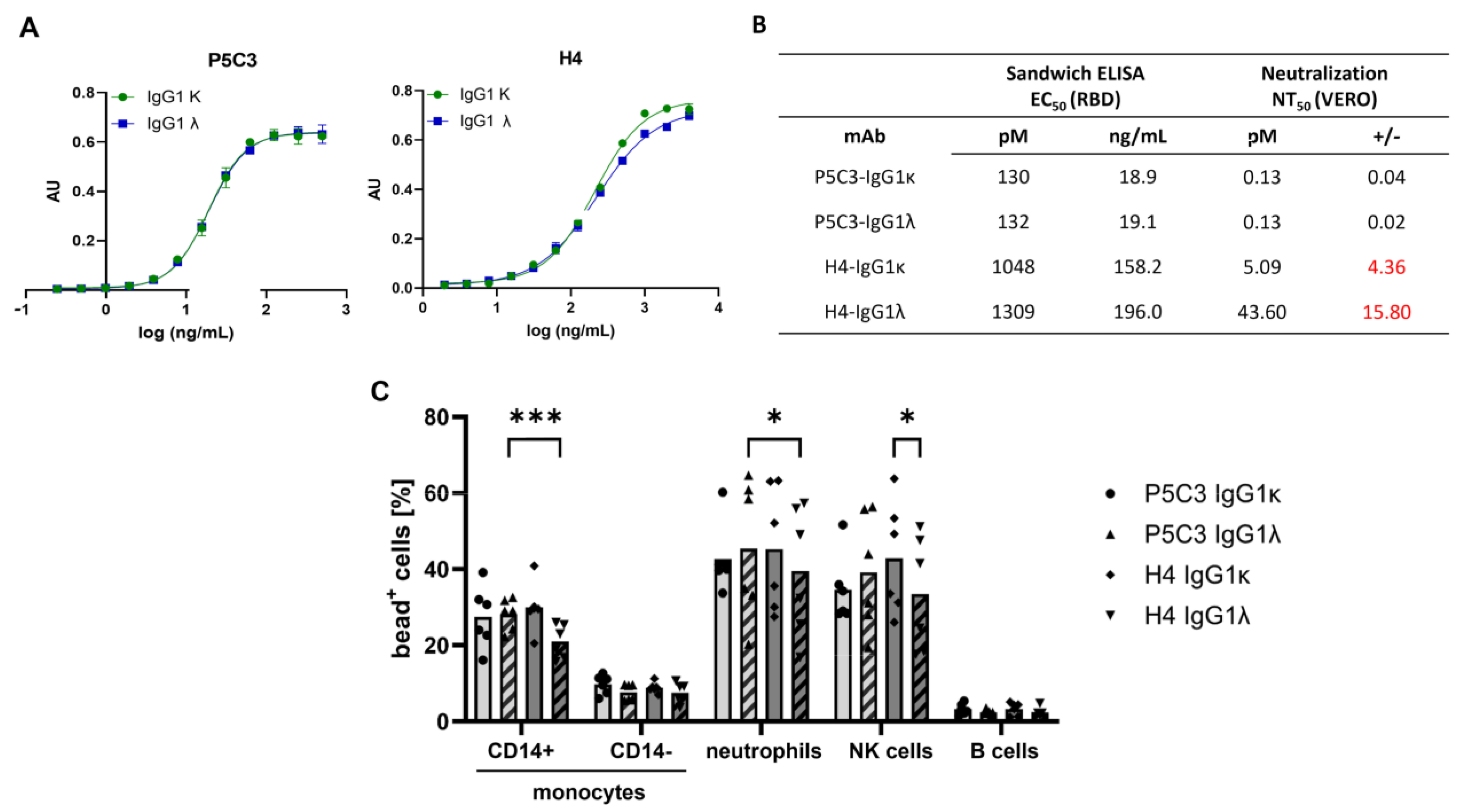
2.5. Direct Sandwich ELISA
2.6. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometric Immune Complex Binding Assay
3. Results
3.1. Expression, Purification, and Biophysical Characterization of Antibody Isotypes
3.2. Antigen-Binding and Virus-Neutralization Activity of Antibody Isotypes
3.3. IgG Immune Complex Binding to Primary Human Leukocytes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hematianlarki, M.; Nimmerjahn, F. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties of immunoglobulin G antibodies. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 328, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferis, R. Recombinant Proteins and Monoclonal Antibodies. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 175, 281–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q. Development of plant-made monoclonal antibodies against viral infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 52, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damelang, T.; Brinkhaus, M.; Van Osch, T.L.J.; Schuurman, J.; Labrijn, A.F.; Rispens, T.; Vidarsson, G. Impact of structural modifications of IgG antibodies on effector functions. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1304365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdani, Y.; Lamamy, J.; Watier, H.; Gouilleux-Gruart, V. Monoclonal Antibody Engineering and Design to Modulate FcRn Activities: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mathieu, M.; Brezski, R.J. IgG Fc engineering to modulate antibody effector functions. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, M.-P.; Lefranc, G. Human Gm, Km, and Am Allotypes: WHO/IMGT Nomenclature and IMGT Unique Numbering for Immunoinformatics and Therapeutical Antibodies. BioMedInformatics 2023, 3, 649–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmann, J.A.; Clark, R.J.; Abraham, R.S.; Bryant, S.; Lymp, J.F.; Bradwell, A.R.; Kyle, R.A. Serum reference intervals and diagnostic ranges for free κ and free λ immunoglobulin light chains: Relative sensitivity for detection of monoclonal light chains. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raybould, M.I.J.; Turnbull, O.M.; Suter, A.; Guloglu, B.; Deane, C.M. Contextualising the developability risk of antibodies with lambda light chains using enhanced therapeutic antibody profiling. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.A.R.; Erasmus, M.F.; D’aNgelo, S.; Naranjo, L.; Ferrara, F.; Leal-Lopes, C.; Durrant, O.; Galmiche, C.; Morelli, A.; Scott-Tucker, A.; et al. Drug-like antibodies with high affinity, diversity and developability directly from next-generation antibody libraries. mAbs 2021, 13, 1980942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larijani, M.; Chen, S.; Cunningham, L.A.; Volpe, J.M.; Cowell, L.G.; Lewis, S.M.; Wu, G.E. The recombination difference between mouse κ and λ segments is mediated by a pair-wise regulation mechanism. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeKosky, B.J.; Lungu, O.I.; Park, D.; Johnson, E.L.; Charab, W.; Chrysostomou, C.; Kuroda, D.; Ellington, A.D.; Ippolito, G.C.; Gray, J.J.; et al. Large-scale sequence and structural comparisons of human naive and antigen-experienced antibody repertoires. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2636–E2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, C.L.; Laffy, J.M.J.; Wu, Y.-C.B.; O’hAre, J.S.; Martin, V.; Kipling, D.; Fraternali, F.; Dunn-Walters, D.K. Significant Differences in Physicochemical Properties of Human Immunoglobulin Kappa and Lambda CDR3 Regions. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.; Shah, H.; Muther, J.J.; Duke, A.L.; Haley, K.; James, J.A. Antigen nature and complexity influence human antibody light chain usage and specificity. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadi, M.M.; Farshidpour, M.; Brown, E.P.; Ouyang, X.; Seaman, M.S.; Pazgier, M.; Ackerman, M.E.; Robinson, H.; Tomaras, G.; Parsons, M.S.; et al. λ Light Chain Bias Associated with Enhanced Binding and Function of Anti-HIV Env Glycoprotein Antibodies. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigaite, R.; Iles, J.K.; Harding, S.; Patel, R.; Wallis, G.; Iles, R.K. Degree of immunoglobulin kappa light chain glycosylation of anti-spike SARS CoV-2 antibodies correlates with COVID-19 severity. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, C.; Turelli, P.; Ni, D.; Perez, L.; Lau, K.; Herate, C.; Marlin, R.; Lana, E.; Pellaton, C.; Raclot, C.; et al. Patient-derived monoclonal antibody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants and confers full protection in monkeys. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1376–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wu, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Chai, Y.; Zheng, A.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, S.; Huang, M.; et al. An updated atlas of antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sub-variants including BQ.1.1 and XBB. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallolimath, S.; Palt, R.; Föderl-Höbenreich, E.; Sun, L.; Chen, Q.; Pruckner, F.; Eidenberger, L.; Strasser, R.; Zatloukal, K.; Steinkellner, H. Glyco engineered pentameric SARS-CoV-2 IgMs show superior activities compared to IgG1 orthologues. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1147960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Kallolimath, S.; Palt, R.; Eminger, F.; Strasser, R.; Steinkellner, H. Codon optimization regulates IgG3 and IgM expression and glycosylation in N. benthamiana. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1320586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, R.; Stadlmann, J.; Schähs, M.; Stiegler, G.; Quendler, H.; Mach, L.; Glössl, J.; Weterings, K.; Pabst, M.; Steinkellner, H. Generation of glyco-engineered Nicotiana benthamiana for the production of monoclonal antibodies with a homogeneous human-like N-glycan structure. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marillonnet, S.; Thoeringer, C.; Kandzia, R.; Klimyuk, V.; Gleba, Y. Systemic Agrobacterium tumefaciens–mediated transfection of viral replicons for efficient transient expression in plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallolimath, S.; Hackl, T.; Gahn, R.; Grünwald-Gruber, C.; Zich, W.; Kogelmann, B.; Lux, A.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Steinkellner, H. Expression Profiling and Glycan Engineering of IgG Subclass 1–4 in Nicotiana benthamiana. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallolimath, S.; Sun, L.; Palt, R.; Stiasny, K.; Mayrhofer, P.; Gruber, C.; Kogelmann, B.; Chen, Q.; Steinkellner, H. Highly active engineered IgG3 antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107249118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, F.; Helm, J.; Pabst, M.; Stadlmann, J. Introduction of a human- and keyboard-friendly N-glycan nomenclature. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-J.; König-Beihammer, J.; Vavra, U.; Schwestka, J.; Kienzl, N.F.; Klausberger, M.; Laurent, E.; Grünwald-Gruber, C.; Vierlinger, K.; Hofner, M.; et al. N-Glycosylation of the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Is Important for Functional Expression in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 689104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, K.R.; Coombes, N.S.; Gagnon, L.; McInroy, L.; Baker, N.; Shaik, I.; St-Jean, J.R.; St-Amant, N.; Buttigieg, K.R.; Humphries, H.E.; et al. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody by wild-type plaque reduction neutralization, microneutralization and pseudotyped virus neutralization assays. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3114–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallolimath, S.; Sun, L.; Palt, R.; Föderl-Höbenreich, E.; Hermle, A.; Voss, L.; Kleim, M.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Gach, J.S.; Hitchcock, L.; et al. IgG1 versus IgG3: Influence of antibody-specificity and allotypic variance on virus neutralization efficacy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1490515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, C.; Turelli, P.; Perez, L.; Pellaton, C.; Esteves-Leuenberger, L.; Farina, A.; Campos, J.; Lana, E.; Fiscalini, F.; Raclot, C.; et al. A highly potent antibody effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, E.; Demarest, S.J. A broad range of Fab stabilities within a host of therapeutic IgGs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 355, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, R.M.; Vlasak, J.; Price, C.; Kirchmeier, M. Contribution of variable domains to the stability of humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibodies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toughiri, R.; Wu, X.; Ruiz, D.; Huang, F.; Crissman, J.W.; Dickey, M.; Froning, K.; Conner, E.M.; Cujec, T.P.; Demarest, S.J. Comparing domain interactions within antibody Fabs with kappa and lambda light chains. mAbs 2016, 8, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.C.; Lux, A.; Biburger, M.; Varghese, P.; Lees, S.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Meyer, A.S. Mixed IgG Fc immune complexes exhibit blended binding profiles and refine FcR affinity estimates. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerntke, C.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Biburger, M. There Is (Scientific) Strength in Numbers: A Comprehensive Quantitation of Fc Gamma Receptor Numbers on Human and Murine Peripheral Blood Leukocytes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kant, R.; Bauer, J.; Karow-Zwick, A.R.; Kube, S.; Garidel, P.; Blech, M.; Rousseau, F.; Schymkowitz, J. Adaption of human antibody λ and κ light chain architectures to CDR repertoires. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2019, 32, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.H.; Patz, E.F., Jr.; Ackerman, M.E. Coming together at the hinges: Therapeutic prospects of IgG3. mAbs 2021, 13, 1882028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournazos, S.; Gazumyan, A.; Seaman, M.S.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Ravetch, J.V. Bispecific Anti-HIV-1 Antibodies with Enhanced Breadth and Potency. Cell 2016, 165, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Oton, J.; Qu, K.; Cortese, M.; Zila, V.; McKeane, L.; Nakane, T.; Zivanov, J.; Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; et al. Structures and distributions of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins on intact virions. Nature 2020, 588, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.E.Z.; Seah, S.G.K.; Chye, D.H.; Massey, S.; Torres, M.; Lim, A.P.C.; Wong, S.K.K.; Neo, J.J.Y.; Wong, P.S.; Lim, J.H.; et al. The Fc-mediated effector functions of a potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody, SC31, isolated from an early convalescent COVID-19 patient, are essential for the optimal therapeutic efficacy of the antibody. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Muecksch, F.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Leist, S.R.; Cipolla, M.; Bournazos, S.; Schmidt, F.; Maison, R.M.; Gazumyan, A.; Martinez, D.R.; et al. Antibody potency, effector function, and combinations in protection and therapy for SARS-CoV-2 infection in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamin, R.; Jones, A.T.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Schäfer, A.; Kao, K.S.; Francis, R.L.; Sheahan, T.P.; Baric, R.S.; Rice, C.M.; Ravetch, J.V.; et al. Fc-engineered antibody therapeutics with improved anti-SARS-CoV-2 efficacy. Nature 2021, 599, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saporiti, S.; Laurenzi, T.; Guerrini, U.; Coppa, C.; Palinsky, W.; Benigno, G.; Palazzolo, L.; Ben Mariem, O.; Montavoci, L.; Rossi, M.; et al. Effect of Fc core fucosylation and light chain isotype on IgG1 flexibility. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bournazos, S.; DiLillo, D.J.; Ravetch, J.V. The role of Fc–FcγR interactions in IgG-mediated microbial neutralization. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravetch, J.V.; Kinet, J.P. Fc Receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1991, 9, 457–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.; Fernaéndez-Fuentes, N.; Fiser, A.; Casadevall, A. The immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region affects kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of antibody variable region interactions with antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13917–13927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Palt, R.; Schütz, G.; Föderl-Höbenreich, E.; Brod, L.; Hermle, A.; Lux, A.; Steinkellner, H.; Kallolimath, S. Light Chain Isotype and Antibody-Specificity Impact on Virus Neutralization. Antibodies 2025, 14, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020050
Sun L, Palt R, Schütz G, Föderl-Höbenreich E, Brod L, Hermle A, Lux A, Steinkellner H, Kallolimath S. Light Chain Isotype and Antibody-Specificity Impact on Virus Neutralization. Antibodies. 2025; 14(2):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020050
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Lin, Roman Palt, Georg Schütz, Esther Föderl-Höbenreich, Laura Brod, Antonia Hermle, Anja Lux, Herta Steinkellner, and Somanath Kallolimath. 2025. "Light Chain Isotype and Antibody-Specificity Impact on Virus Neutralization" Antibodies 14, no. 2: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020050
APA StyleSun, L., Palt, R., Schütz, G., Föderl-Höbenreich, E., Brod, L., Hermle, A., Lux, A., Steinkellner, H., & Kallolimath, S. (2025). Light Chain Isotype and Antibody-Specificity Impact on Virus Neutralization. Antibodies, 14(2), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020050






