Humanized VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins Targeting the L-HN Fragment of Tetanus Toxin Provided Protection In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Cell Lines, and Animals
2.2. Immunization of the Camel
2.3. Construction of the Phage-Display Nanobody Library
2.4. Biopanning and Isolation of the TL-HN-Specific VHHs
2.5. Construction, Expression, and Purification of VHH-hFc Fusion Protein
2.6. Cross-Reaction and Binding Activity of the VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins
2.7. KD Analysis and Cross-Competitive Binding Assay
2.8. Neutralizing Activity
2.9. Humanization Modification and Activity Evaluation of VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins
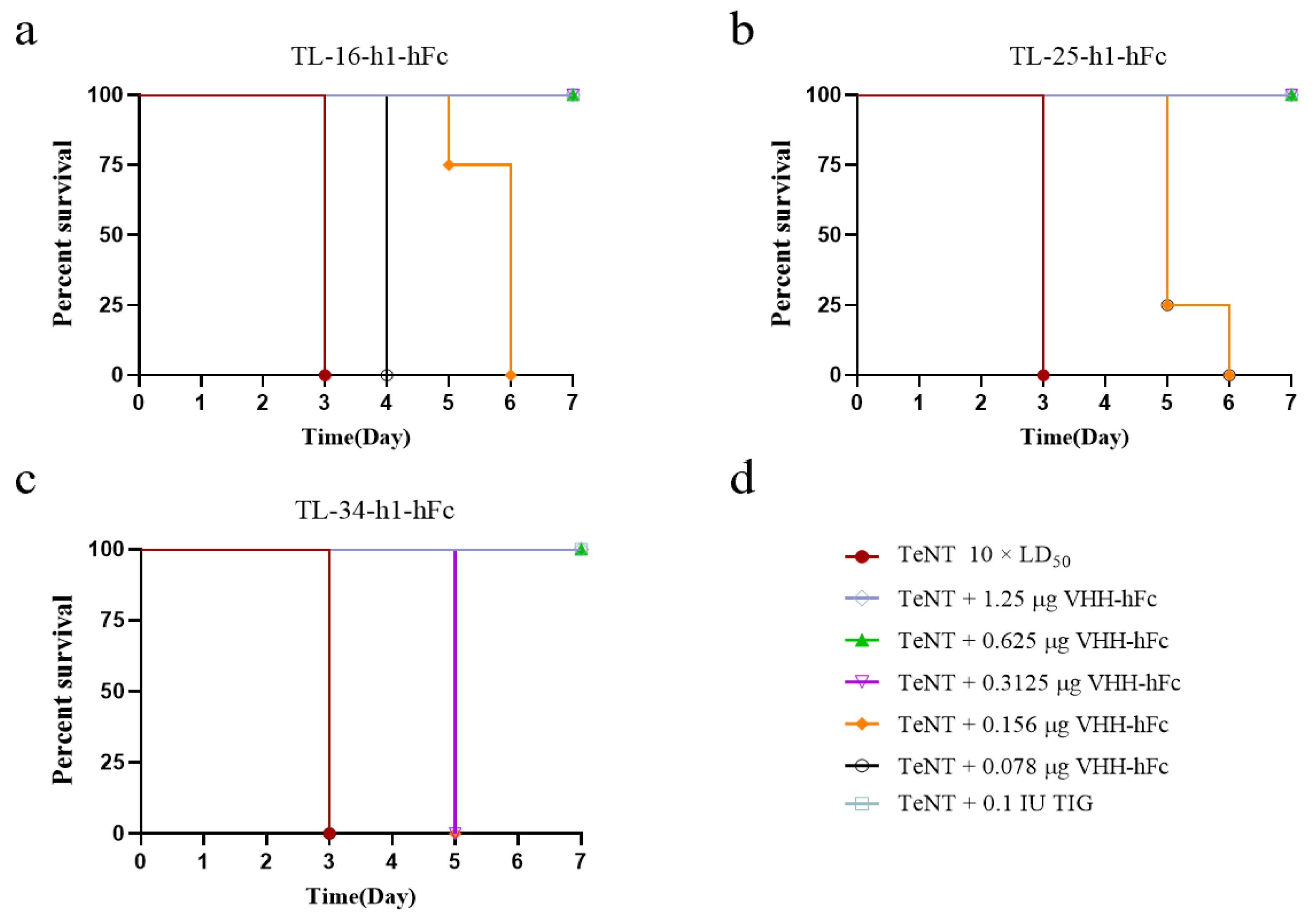
2.10. Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of the Humanized VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins in a Mouse Model
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Construction and Biopanning of the Phage-Display VHH Library
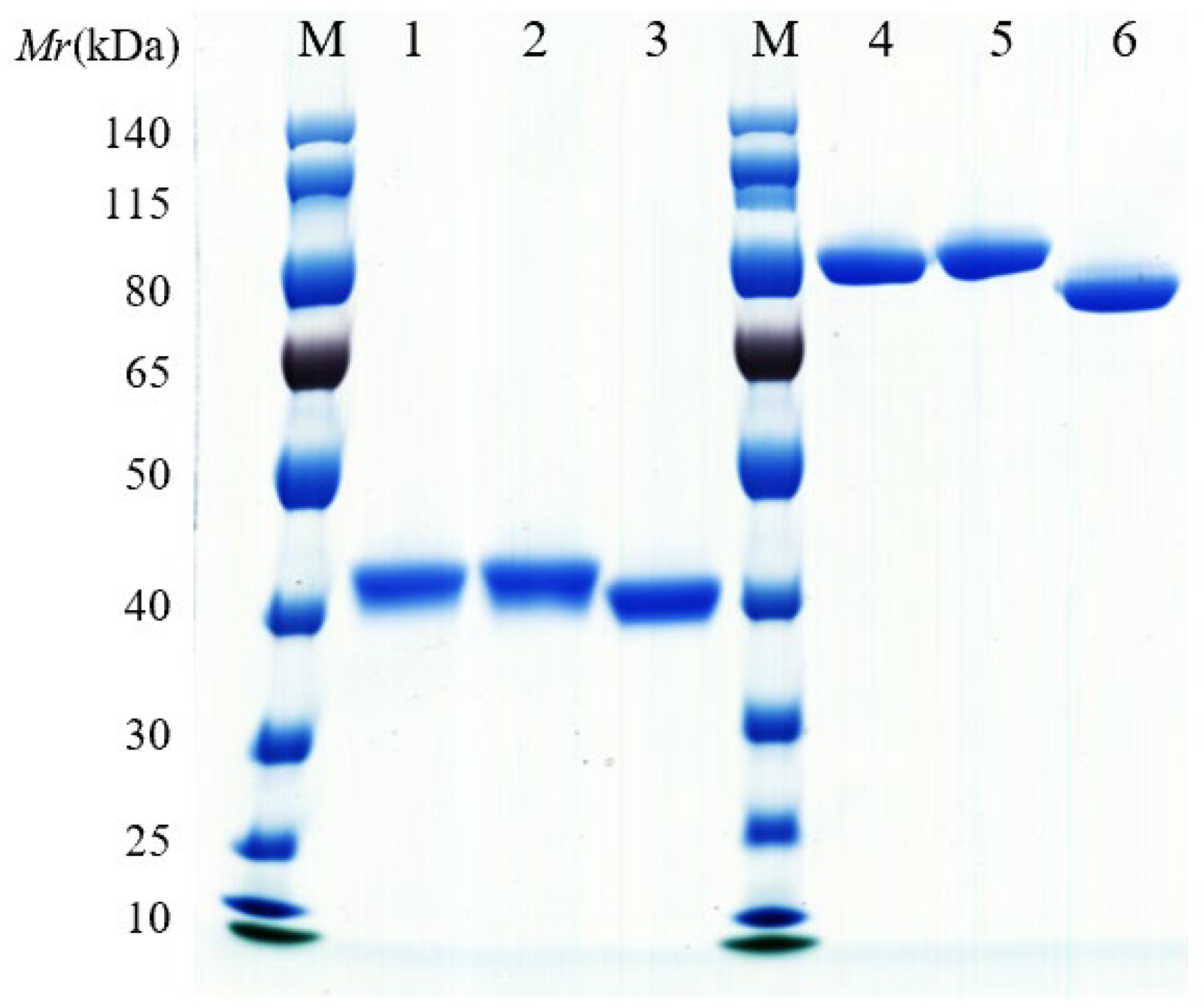
3.2. Expression and Purification of VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins
3.3. Preliminary Screening of VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins with Effective Neutralizing Activity In Vivo
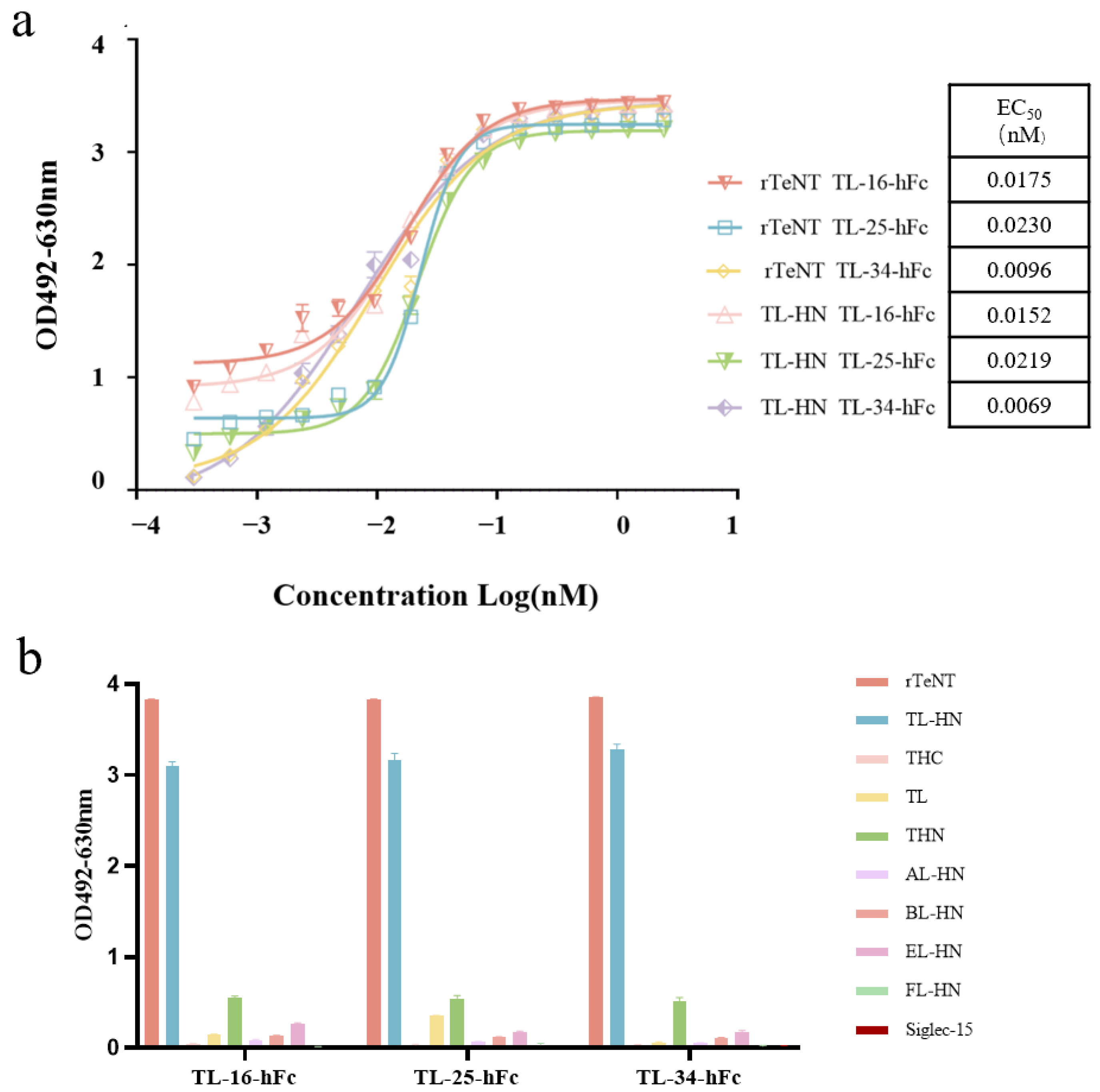
3.4. Binding Activity and Cross-Reactivity of the VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins
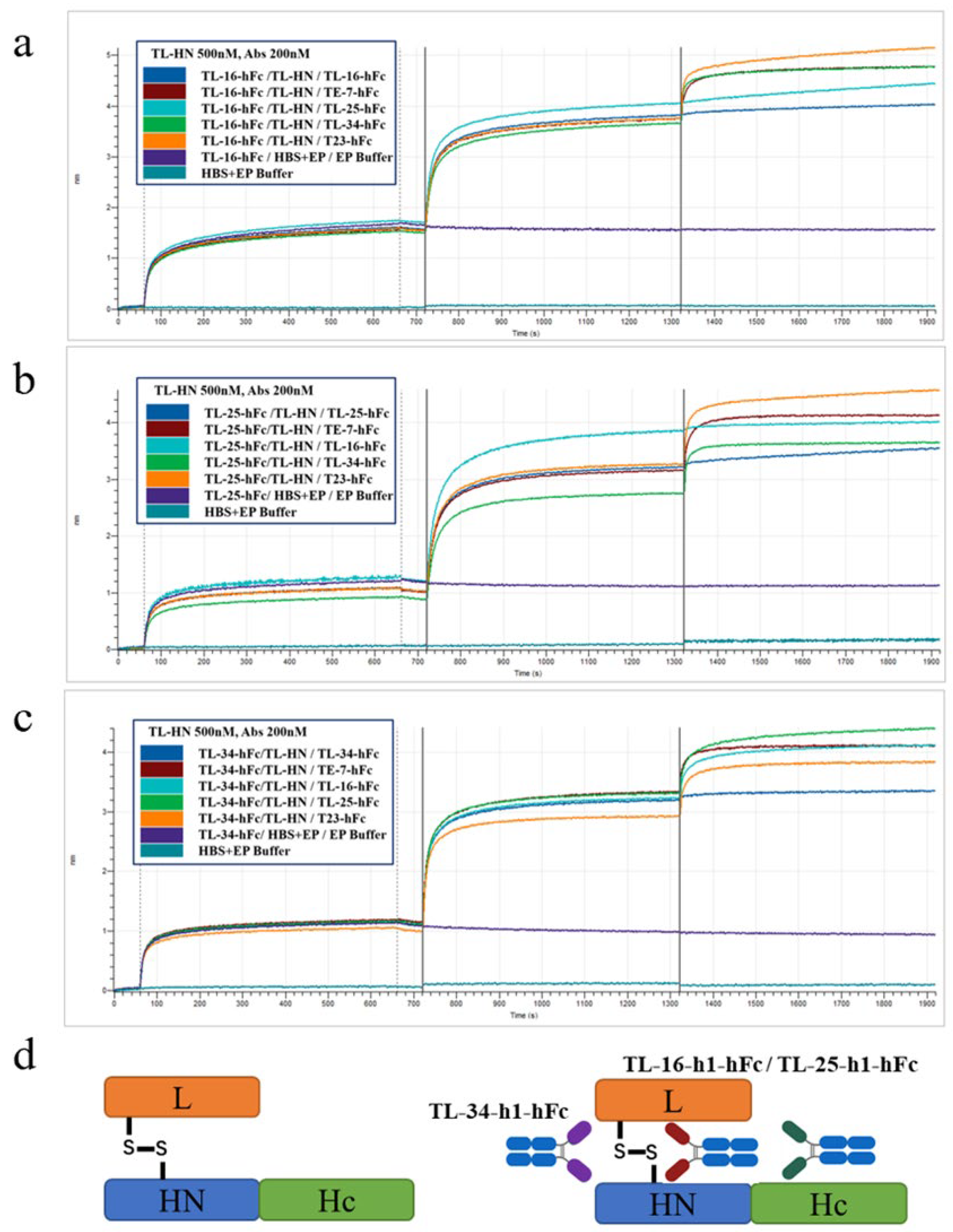
3.5. Affinity and Competitive Binding Activity of the VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins
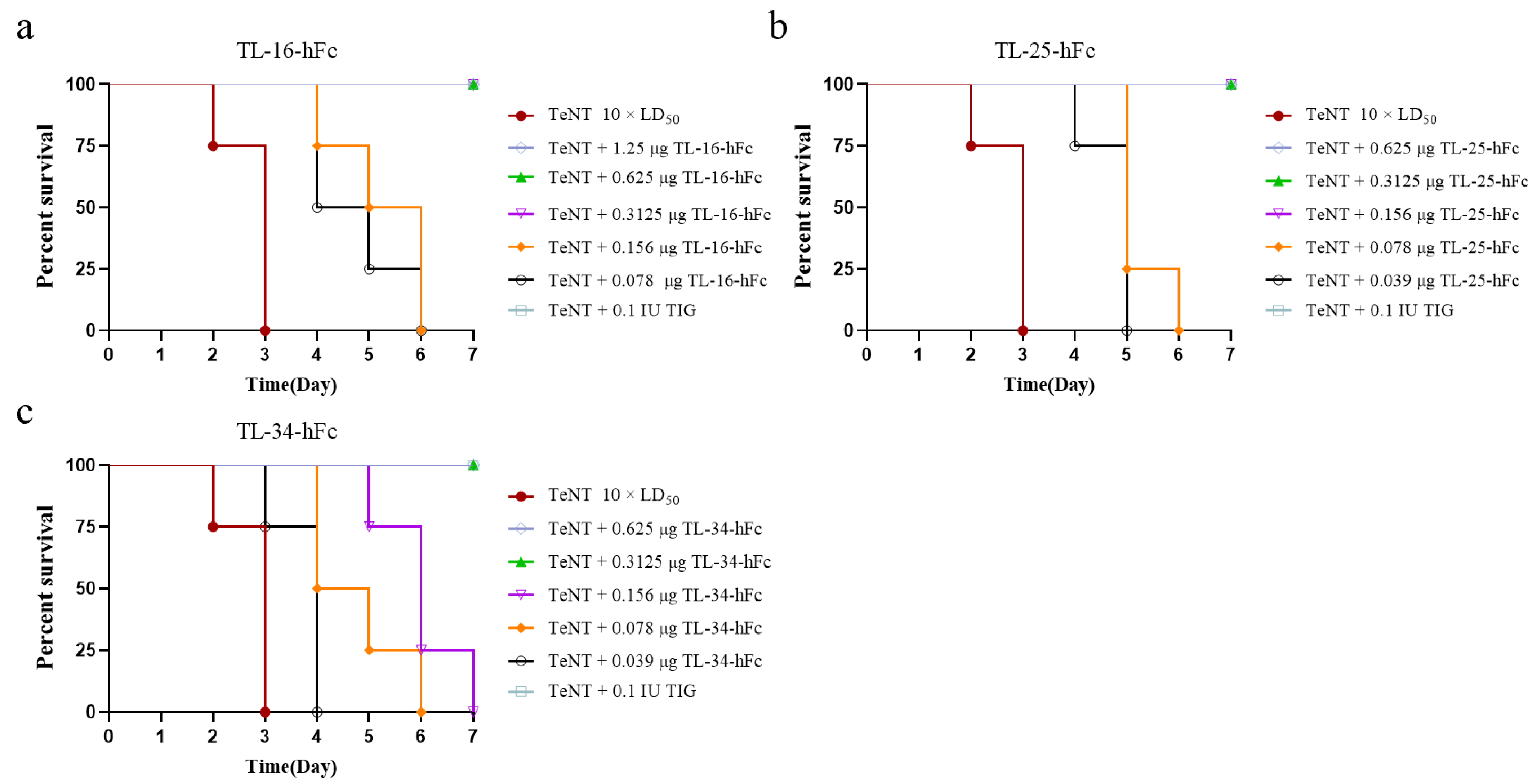
3.6. Neutralizing Activity of VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins at Different Doses
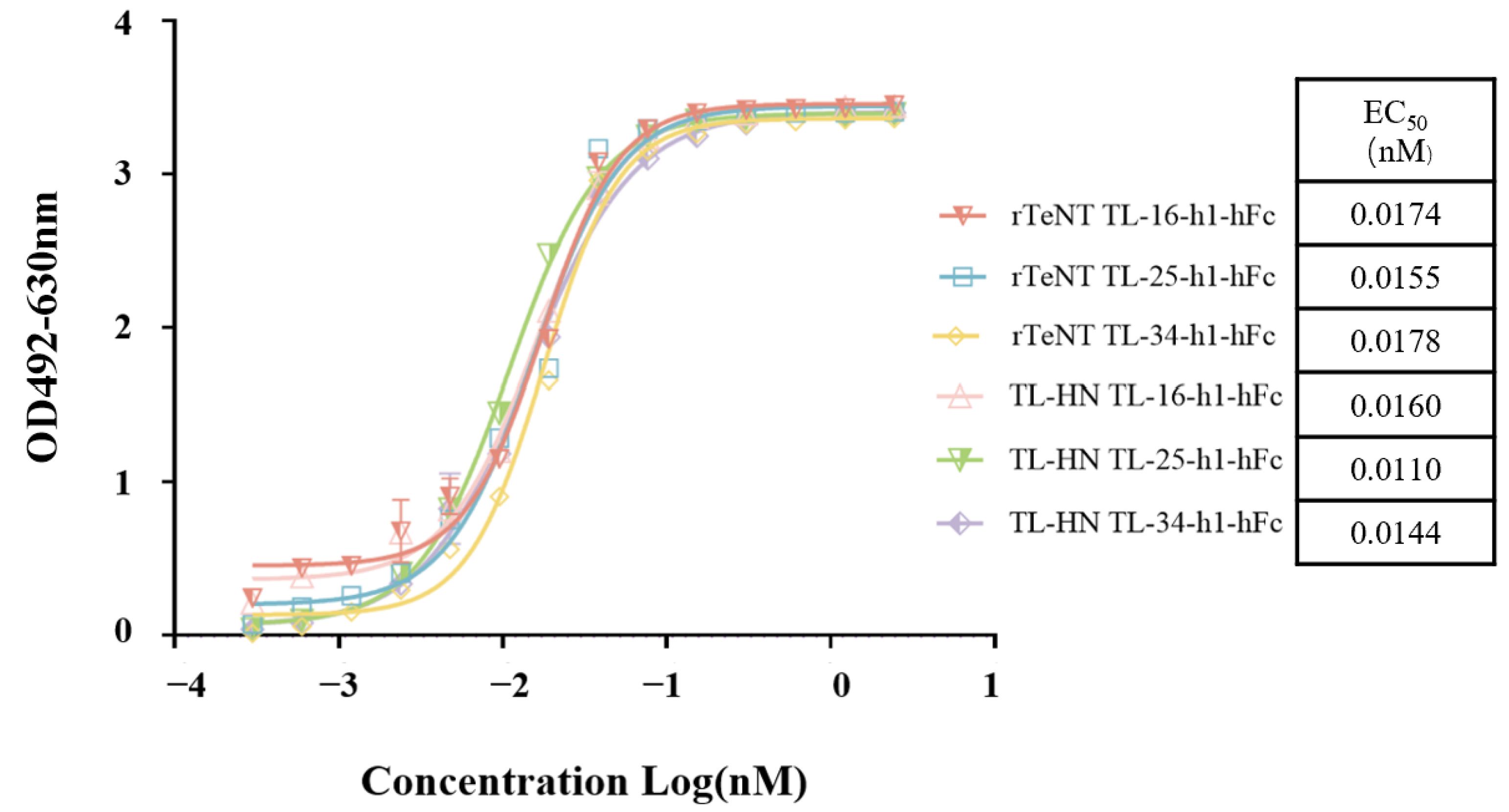
3.7. Humanization and Characterization of the Humanized VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cook, T.M.; Protheroe, R.T.; Handel, J.M. Tetanus: A review of the literature. Br. J. Anaesth. 2001, 87, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, L.M.; Thwaites, C.L. Tetanus. Lancet 2019, 393, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megighian, A.; Pirazzini, M.; Fabris, F.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and tetanus neurotoxin: From peripheral uptake to central nervous tissue targets. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, P.; Teisch, L.; Allen, C.J.; Ruiz, G. Tetanus: A Potential Public Health Threat in Times of Disaster. Prehosp. Disaster Med. 2017, 32, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goonetilleke, A.; Harris, J.B. Clostridial neurotoxins. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75 (Suppl. 3), iii35–iii39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, G.; Papini, E.; Genna, G.; Montecucco, C. An intact interchain disulfide bond is required for the neurotoxicity of tetanus toxin. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 4136–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotinou, C.; Emsley, P.; Black, I.; Ando, H.; Ishida, H.; Kiso, M.; Sinha, K.A.; Fairweather, N.F.; Isaacs, N.W. The crystal structure of tetanus toxin Hc fragment complexed with a synthetic GT1b analogue suggests cross-linking between ganglioside receptors and the toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32274–32281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Baldwin, M.R.; Barbieri, J.T. Molecular basis for tetanus toxin coreceptor interactions. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 7179–7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, A.; Bade, S.; Alves, J.; Bigalke, H.; Binz, T. Two carbohydrate binding sites in the H(CC)-domain of tetanus neurotoxin are required for toxicity. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 326, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, G.; Benfenati, F.; Poulain, B.; Rossetto, O.; Polverino de Laureto, P.; DasGupta, B.R.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature 1992, 359, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.B.; Martin, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Daniels, S.J.; Lavidis, N.A.; Popoff, M.R.; Hadzic, G.; Mariana, A.; Chau, N.; McCluskey, A.; et al. Dynamin inhibition blocks botulinum neurotoxin type A endocytosis in neurons and delays botulism. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35966–35976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Masuyer, G.; Stenmark, P. Botulinum and Tetanus Neurotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 811–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, B.M.; Bodt, S.M.L.; McNutt, P.M. Special Delivery: Potential Mechanisms of Botulinum Neurotoxin Uptake and Trafficking within Motor Nerve Terminals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edupuganti, O.P.; Ovsepian, S.V.; Wang, J.; Zurawski, T.H.; Schmidt, J.J.; Smith, L.; Lawrence, G.W.; Dolly, J.O. Targeted delivery into motor nerve terminals of inhibitors for SNARE-cleaving proteases via liposomes coupled to an atoxic botulinum neurotoxin. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Yu, R.; Chi, X.; Chen, Z.; Hao, M.; Du, P.; Fan, P.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Fang, T.; et al. Tetanus vaccine-induced human neutralizing antibodies provide full protection against neurotoxin challenge in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 91, 107297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwaites, C.L.; Beeching, N.J.; Newton, C.R. Maternal and neonatal tetanus. Lancet 2015, 385, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaji, M.A.; Mustapha, M.G.; Ashir, G.M.; Akuhwa, R.T.; Bello, M.A.; Farouk, A.G. Recurrent generalized tetanus: A case report. Trop. Dr. 2011, 41, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, P.; Nunley, M.K.; Demetriades, D.; Velmahos, G.; Doucet, J.J. Tetanus and trauma: A review and recommendations. J. Trauma. 2005, 58, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylor, C.; Dadachova, E.; Casadevall, A. Monoclonal antibody-based therapies for microbial diseases. Vaccine 2009, 27 (Suppl. 6), G38–G46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Gutiérrez, A.; Díaz-Ramos, P.; Sulleiro-Avendaño, E.; de Miguel-Marañón, M.; Padilla-Gallego, M.E.; Sancho-López, A.; Ruiz-Antúnez, S.; Prieto-Yerro, C. Contribution of the spanish agency for medicines and healthcare products to the European committee for the evaluation of medicinal products for human use. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2015, 215, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Qaisar, I.; Naeem, M.; Mazhar, A.U.; Ashfaq, M. Intrathecal anti-tetanus human immunoglobulin in the treatment of neonatal tetanus. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2011, 21, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gibson, R.B.; Banzhaf, E.J. The Quantitative Changes in the Proteins in the Blood Plasma of Horses in the Course of Immunization. J. Exp. Med. 1910, 12, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Smit, H.; Ackerschott, B.; Tierney, R.; Stickings, P.; Harmsen, M.M. A novel single-domain antibody multimer that potently neutralizes tetanus neurotoxin. Vaccine X 2021, 8, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.K.; Odongo, S.; Radwanska, M.; Magez, S. NANOBODIES®: A Review of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavrtanik, U.; Lukan, J.; Loris, R.; Lah, J.; Hadži, S. Structural Basis of Epitope Recognition by Heavy-Chain Camelid Antibodies. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 4369–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steeland, S.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Libert, C. Nanobodies as therapeutics: Big opportunities for small antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1076–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Gallant, J.; Zheng, J.; Massey, C.; Shi, K.; Tai, W.; Odle, A.; Vickers, M.; Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; et al. The development of Nanosota-1 as anti-SARS-CoV-2 nanobody drug candidates. eLife 2021, 10, e64815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wei, D.K.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, J.S.; Xie, X.M.; Yu, Y.Z.; Pang, X.B. Immunogenicity and immunoprotection of the functional TL-HN fragment derived from tetanus toxin. Vaccine 2023, 41, 6834–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.J.; Shi, D.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, J.S.; Wang, R.; Pang, X.B.; Yang, Z.X.; Yu, Y.Z. Evaluation of a recombinant tetanus toxin subunit vaccine. Toxicon 2020, 187, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.J.; Shi, D.Y.; Mao, Y.Y.; Xiong, X.H.; Lu, J.S.; Pang, X.B.; Dong, X.J.; Yang, Z.X.; Yu, Y.Z. Immunological characterisation and immunoprotective efficacy of functional domain antigens of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Vaccine 2020, 38, 2978–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, J.S.; Liu, S.; Wang, R.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Y.Z.; Yang, Z.X. Recombinant L-HN Fusion Antigen Derived from the L and HN Domains of Botulinum Neurotoxin B Stimulates a Protective Antibody Response Against Active Neurotoxin. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lu, J.; Tan, X.; Wang, R.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Z. Functional EL-HN Fragment as a Potent Candidate Vaccine for the Prevention of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype E. Toxins 2022, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, B.; Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Tan, X.; Wang, R.; Du, P.; Yu, S.; Xu, Q.; Pang, X.; et al. Biological and Immunological Characterization of a Functional L-HN Derivative of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype F. Toxins 2023, 15, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Ji, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, D.; Fang, T.; Jing, Y.; Kwang-Fu Shen, C.; Chen, W. The Immunogenicity of the C Fragment of Tetanus Neurotoxin in Production of Tetanus Antitoxin. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6057348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Lu, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Kang, Q.; et al. Characterization of neutralizing chimeric heavy-chain antibodies against tetanus toxin. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2024, 20, 2366641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, M.; Grinzato, A.; Corti, D.; Barbieri, S.; Leka, O.; Vallese, F.; Tonellato, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Piccoli, L.; Kandiah, E.; et al. Exceptionally potent human monoclonal antibodies are effective for prophylaxis and treatment of tetanus in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e151676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yu, J.; Lin, S.; Liu, T.; Zan, L.; Li, N.; Hong, P.; Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; et al. Structural basis of tetanus toxin neutralization by native human monoclonal antibodies. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, R.; Fang, T.; Yu, T.; Chi, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Fu, L.; Yu, C.; Chen, W. Tetanus Neurotoxin Neutralizing Antibodies Screened from a Human Immune scFv Antibody Phage Display Library. Toxins 2016, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Xue, C.; Xiong, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, H. Preparation and characterization of a neutralizing murine monoclonal antibody against tetanus toxin. J. Immunol. Methods 2023, 513, 113427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, A.B.; Cryz, S.J., Jr.; Schürch, U.; Ganss, M.T.; Bruderer, U. Immunotherapy with human monoclonal antibodies. Fragment A specificity of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies is crucial for full protection against tetanus toxin. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, W.A.; Bizzini, B.; Snyder, R.M.; Bernhard, E.; Wagner, R.R. Neutralization of tetanus toxin by distinct monoclonal antibodies binding to multiple epitopes on the toxin molecule. Infect. Immun. 1984, 45, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Kamei, M.; Sugimoto, N.; Ma, Y.; Hashizume, S. Characteristics of toxin-neutralization by anti-tetanus human monoclonal antibodies directed against the three functional domains [A], [B] and [C] of the tetanus toxin molecule and a reliable method for evaluating the protective effects of monoclonal antibodies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1992, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliprandini, E.; Takata, D.Y.; Lepique, A.; Kalil, J.; Boscardin, S.B.; Moro, A.M. An oligoclonal combination of human monoclonal antibodies able to neutralize tetanus toxin in vivo. Toxicon X 2019, 2, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Montal, M. Molecular dissection of botulinum neurotoxin reveals interdomain chaperone function. Toxicon 2013, 75, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukić, I.; Marinković, E.; Filipović, A.; Krnjaja, O.; Kosanović, D.; Inić-Kanada, A.; Stojanović, M. Key protection factors against tetanus: Anti-tetanus toxin antibody affinity and its ability to prevent tetanus toxin—Ganglioside interaction. Toxicon 2015, 103, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Panning Round | Input | Output | Output/Input Ratio | Enrichment Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | 5.0 × 1011 | 4.2 × 107 | 8.4 × 10−5 | - |
| Second | 1.0 × 1011 | 1.95 × 107 | 1.95 × 10−4 | 2.3 |
| Group a | Dose of TeNT b | Surviving/Total Mice c | Survival (%) | Group a | Dose of TeNT b | Surviving/Total Mice c | Survival (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TL-1-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-19-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-2-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-20-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-3-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-21-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 2/4 | 50 |
| TL-4-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-22-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-5-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-23-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-6-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-24-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-7-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-25-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 |
| TL-8-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-26-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-9-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-27-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-10-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-28-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-11-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-29-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-12-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 2/4 | 50 | TL-30-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 3/4 | 75 |
| TL-13-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-31-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 1/4 | 25 |
| TL-14-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-32-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 2/4 | 50 |
| TL-15-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-33-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-16-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 | TL-34-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 |
| TL-17-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-35-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| TL-18-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | TL-36-hFc | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| Dilution buffer | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| Protein | Kon (104 Ms−1) | Kdis (10−4 s−1) | KD (nM) | χ2 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TL-16-hFc | 2.38 | 2.39 | 10.1 | 0.579 | 0.99 |
| TL-25-hFc | 2.59 | 4.44 | 17.1 | 0.0198 | 0.99 |
| TL-34-hFc | 4.66 | 1.68 | 3.61 | 0.6906 | 0.99 |
| Protein | Kon (104 Ms−1) | Kdis (10−4 s−1) | KD (nM) | χ2 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TL-16-h1-hFc | 2.239 | 0.2036 | 0.9094 | 0.2084 | 0.99 |
| TL-25-h1-hFc | 1.89 | 0.109 | 0.573 | 0.5898 | 0.99 |
| TL-34-h1-hFc | 3.98 | 0.252 | 0.633 | 0.6744 | 0.99 |
| Group | Dose of Protein a (μg) | Dose of TeNT b | Surviving/Total Mice c | Survival (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TL-16-h1-hFc + TL-25-h1-hFc | 0.156 + 0.156 | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 |
| 0.078 + 0.078 | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 | |
| 0.039 + 0.039 | 10 × LD50 | 3/4 | 75 | |
| 0.0195 + 0.0195 | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 | |
| TL-16-h1-hFc + TL-34-h1-hFc | 0.156 + 0.312 | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 |
| 0.078 + 0.156 | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 | |
| 0.039 + 0.078 | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 | |
| 0.0195 + 0.039 | 10 × LD50 | 2/4 | 50 | |
| TL-25-h1-hFc + TL-34-h1-hFc | 0.156 + 0.312 | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 |
| 0.078 + 0.156 | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 | |
| 0.039 + 0.078 | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 | |
| 0.0195 + 0.039 | 10 × LD50 | 3/4 | 75 | |
| TIG | 0.1 IU | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 | 100 |
| Dilution buffer | - | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0 |
| Antibody a | Dose of Protein b | Dose of TeNT c | Number of Survivors/Total Mice per Group | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 h d | 24 h | 48 h | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | 9 d | 12 d | 14 d | |||
| TL-16-h1-hFc | 25 μg/kg | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 2/4 ** | 0/4 ** | 0/4 ** | 0/4 ** | 0/4 ** | 0/4 ** |
| 125 μg/kg | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 3/4 ** | |
| TL-25-h1-hFc | 25 μg/kg | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 3/4 ** | 1/4 ** | 1/4 ** | 0/4 ** | 0/4 ** |
| 125 μg/kg | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 3/4 ** | |
| TL-34-h1-hFc | 50 μg/kg | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 3/4 ** | 2/4 ** | 0/4 ** | 0/4 ** | 0/4 ** | 0/4 * | 0/4 ** |
| 250 μg/kg | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 2/4 ** | 0/4 ** | 0/4 ** | |
| TIG | 0.1 IU | 10 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** |
| B-h3 | 250 μg/kg | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 |
| PBS | - | 10 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 |
| Antibody a | Dose of Protein b | Dose of TeNT c | Number of Survivors/Total Mice per Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h d | 3 h | 6 h | 12 h | 24 h | |||
| TL-16-h1-hFc | 25 μg/kg | 5 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** |
| 125 μg/kg | 5 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | |
| TL-25-h1-hFc | 25 μg/kg | 5 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** |
| 125 μg/kg | 5 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | |
| TL-34-h1-hFc | 50 μg/kg | 5 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** |
| 250 μg/kg | 5 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | |
| TIG | 0.1 IU | 5 × LD50 | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** | 4/4 ** |
| B-h3 | 250 μg/kg | 5 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 |
| PBS | - | 5 × LD50 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Cheng, K.; Guo, J.; Jiang, Y.; Kang, Q.; Wang, R.; Du, P.; Gao, C.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. Humanized VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins Targeting the L-HN Fragment of Tetanus Toxin Provided Protection In Vivo. Antibodies 2025, 14, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020048
Li Y, Cheng K, Guo J, Jiang Y, Kang Q, Wang R, Du P, Gao C, Yu Y, Yang Z, et al. Humanized VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins Targeting the L-HN Fragment of Tetanus Toxin Provided Protection In Vivo. Antibodies. 2025; 14(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yating, Kexuan Cheng, Jiazheng Guo, Yujia Jiang, Qinglin Kang, Rong Wang, Peng Du, Chen Gao, Yunzhou Yu, Zhixin Yang, and et al. 2025. "Humanized VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins Targeting the L-HN Fragment of Tetanus Toxin Provided Protection In Vivo" Antibodies 14, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020048
APA StyleLi, Y., Cheng, K., Guo, J., Jiang, Y., Kang, Q., Wang, R., Du, P., Gao, C., Yu, Y., Yang, Z., Wang, W., & Lu, J. (2025). Humanized VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins Targeting the L-HN Fragment of Tetanus Toxin Provided Protection In Vivo. Antibodies, 14(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020048





