A Targeted Integration-Based CHO Cell Platform for Simultaneous Antibody Display and Secretion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
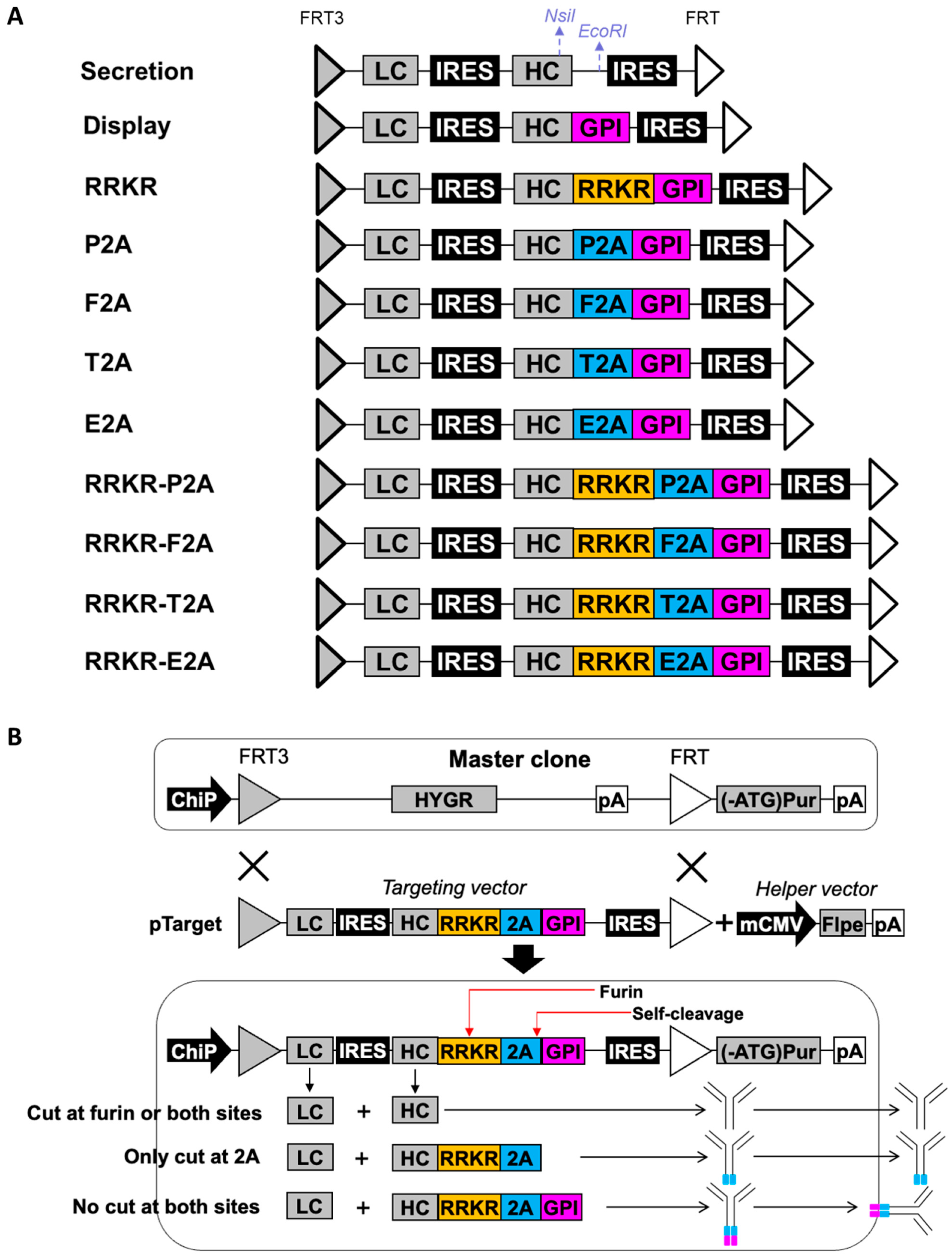
2.1. Construction of Targeting Vectors Expressing Single Antibodies and Antibody Libraries
2.2. Generation and Characterization of Stably Transfected Cell Pools
2.3. Cell Staining, Flow Cytometry Analysis, and FACS Enrichment
2.4. Protein Purification, SDS-PAGE, and Peptide Mapping Analysis
2.5. TOPO Cloning for HC and LC Sequences
3. Results
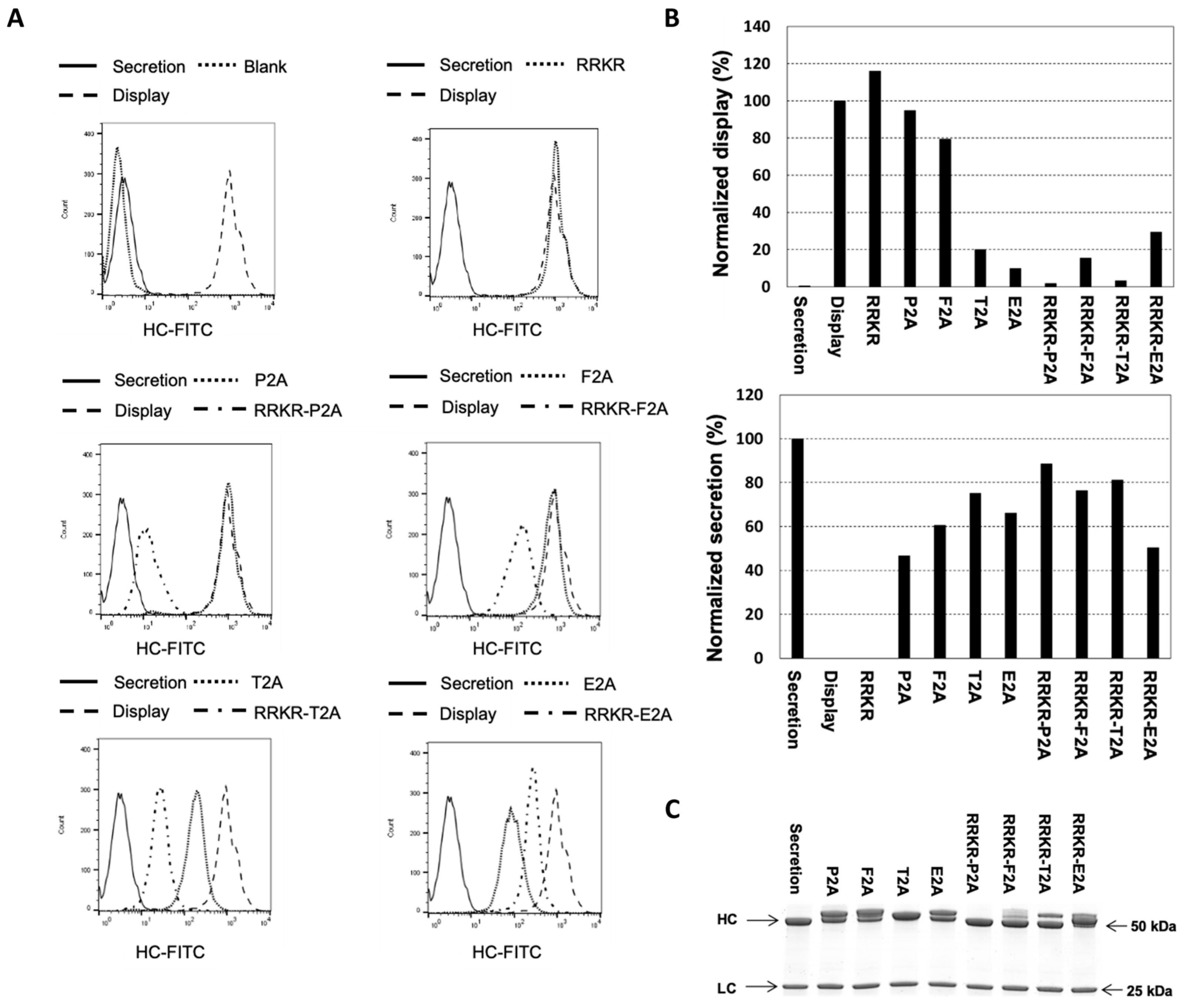
3.1. Evaluation of mFCS, 2A Peptides, and Their Combinations for Simultaneous Display and Secretion of Full-Length IgG Antibody
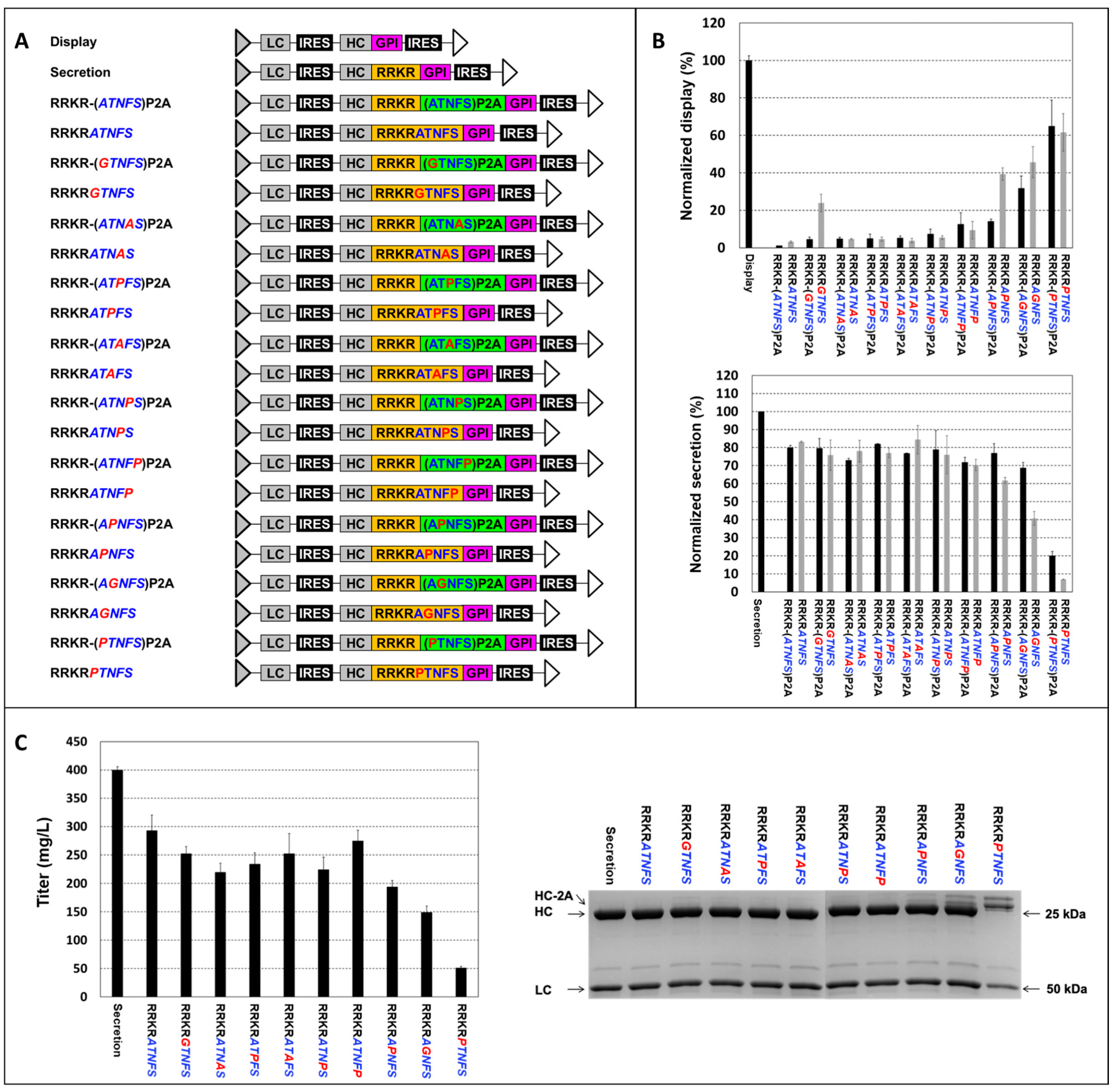
3.2. Point Mutation of P2A in RRKR-P2A for Obtaining Different Display-to-Secretion Ratios
3.3. Engineering Furin Cleavage Sequence (FCS) for Obtaining Different Display-to-Secretion Ratios
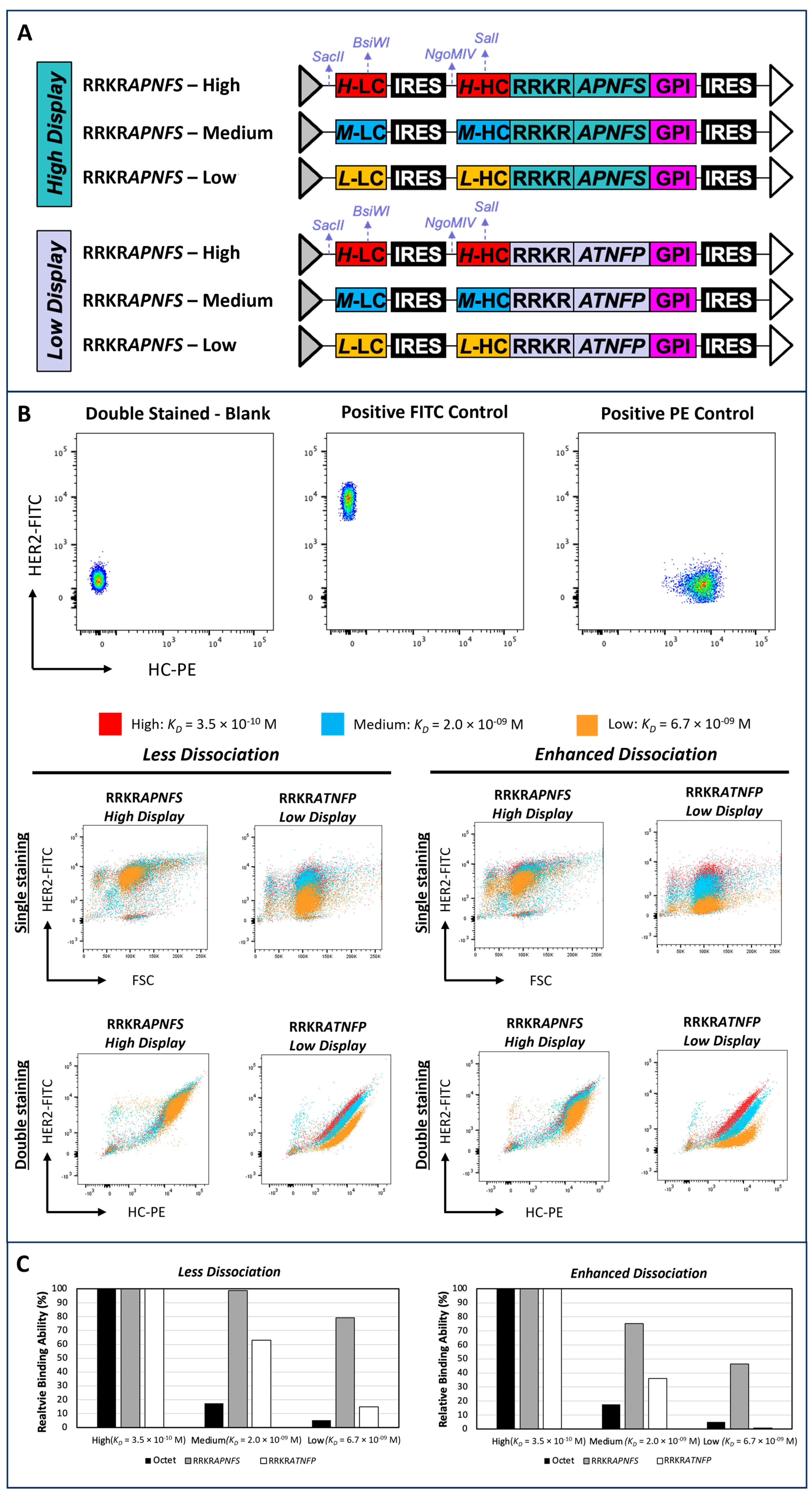
3.4. Comparison of Low- and High-Display-Level Vectors for Discriminating Antibodies with Similar Binding Affinities
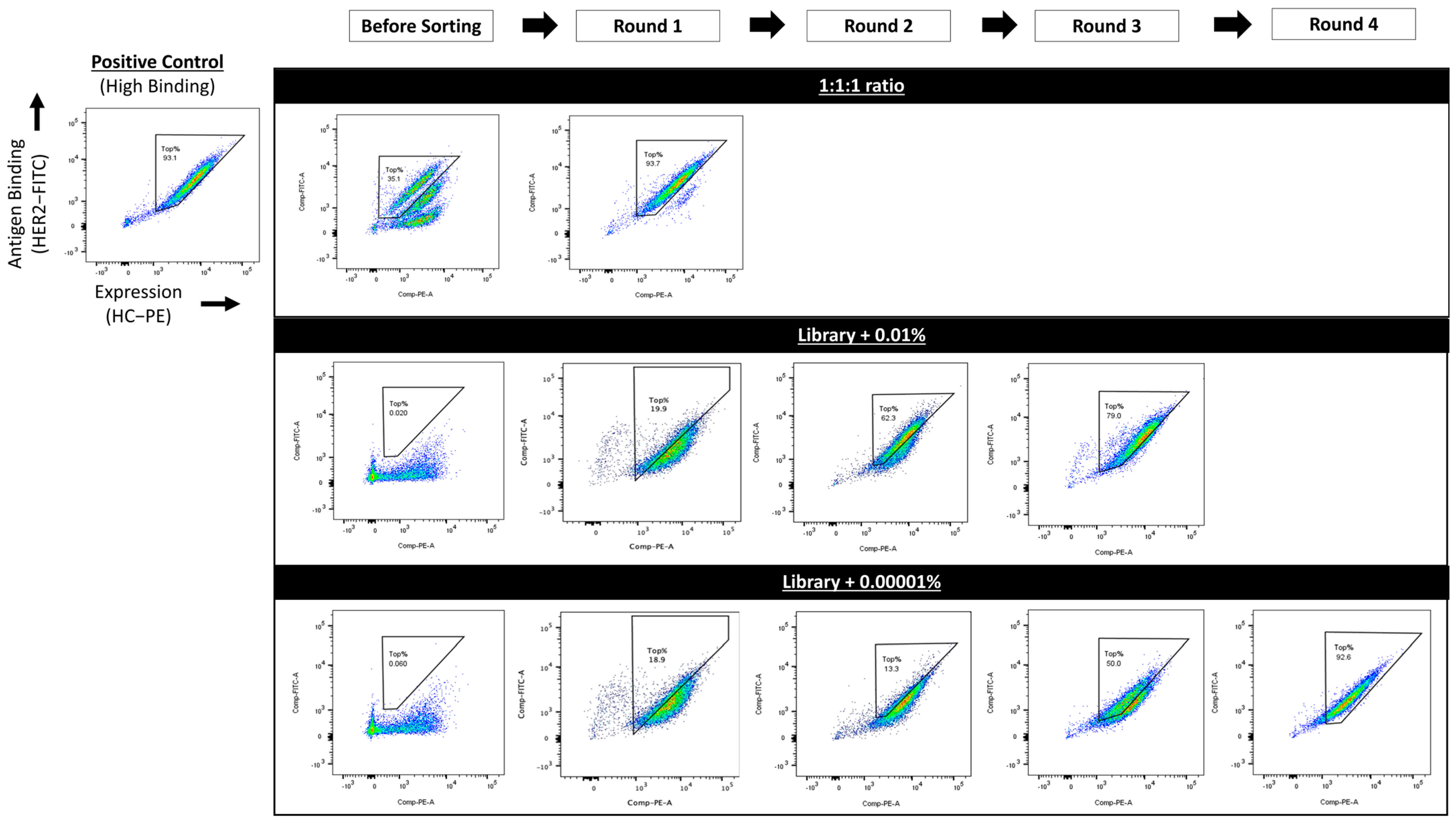
3.5. Evaluation of Simultaneous Display and Secretion Platform for Sorting Sensitivity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CHO | Chinese hamster ovary |
| ZZ-PDGFR | Dual Z-domain with PDGFR transmembrane domain |
| EMCV | Encephalomyocarditis virus |
| ECSTASY | Enzyme-cleavable surface-tethered all-purpose screening system |
| E2A | Equine rhinitis A virus 2A peptide |
| FACS | Fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| Fab | Fragment antigen binding |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| FITC-HC | FITC-conjugated IgG specific to the heavy chain |
| F2A | Foot-and-mouth disease virus 2A peptide |
| GPI | Glycophospholipid |
| HC | Heavy chain |
| HC-PE | F(ab’)2 Fragment Goat Anti-Human IgG, Fc Gamma specific phycoerythrin |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HER2-FITC | HER2-Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| HYGR | Hygromycin resistance |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IVCD | Integrated viable cell density |
| IRES | Internal ribosomal entry site |
| LC | Light chain |
| MFI | Mean fluorescence intensity |
| mFCS | Minimal furin cleavage sequence |
| F3 | Mutated FRT3 |
| PFA | Peptide feature area |
| Pcd | Pg cell−1 day−1 |
| PDGFR | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor |
| pA | Polyadenylation signals |
| P2A | Porcine teschovirus-1 2A peptid |
| RMCE | Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange |
| R-PE | R-phycoerythrin |
| scFv | Single-chain variable fragment |
| qMab | Specific productivity |
| (ATG-)Puro | Start codon-deficient puromycin resistance gene |
| T2A | Thosea asigna virus 2A peptide |
| VH | Variable Heavy |
| VL | Variable Light |
| F | Wild-type FRT |
References
- Lu, R.-M.; Hwang, Y.-C.; Liu, I.J.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, H.-Z.; Li, H.-J.; Wu, H.-C. Development of therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Tomar, P.C. Hybridoma technology; advancements, clinical significance, and future aspects. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valldorf, B.; Hinz, S.C.; Russo, G.; Pekar, L.; Mohr, L.; Klemm, J.; Doerner, A.; Krah, S.; Hust, M.; Zielonka, S. Antibody display technologies: Selecting the cream of the crop. Biol. Chem. 2022, 403, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Mei, J.; Wu, S.; Ying, G.; Yi, Y. Precision engineering of antibodies: A review of modification and design in the Fab region. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 133730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, J.F.; Lim, Y.W.; Carter, K.P.; Wagner, E.K.; Wayham, N.; Adler, A.S.; Johnson, D.S. Affinity maturation of antibodies by combinatorial codon mutagenesis versus error-prone PCR. Mabs 2020, 12, 1803646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavny, P.; Hegde, M.; Doerner, A.; Parthiban, K.; McCafferty, J.; Zielonka, S.; Hoet, R. Advancements in mammalian display technology for therapeutic antibody development and beyond: Current landscape, challenges, and future prospects. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1469329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaa, R.; Mayer, H.M.; Noack, D.; Kumari, K.; Guenther, R.; Tsai, S.-P.; Ji, Q.; Doerner, A. Mammalian display to secretion switchable libraries for antibody preselection and high throughput functional screening. In Mabs; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2023; Volume 15, p. 2251190. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.J.; Bowers, P.M.; Kehry, M.R.; Horlick, R.A. Mammalian cell display and somatic hypermutation in vitro for human antibody discovery. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2014, 11, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Ljungars, A.; Waibl, F.; Greiff, V.; Andersen, J.T.; Gjølberg, T.T.; Jenkins, T.P.; Voldborg, B.G.; Grav, L.M.; Kumar, S.; et al. Assessing developability early in the discovery process for novel biologics. mAbs 2023, 15, 2171248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, W.; Li, S. Construction and applications of mammalian cell-based DNA-encoded peptide/protein libraries. ACS Synth. Biol. 2023, 12, 1874–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Nagata, S.; Pastan, I. Isolation of anti-CD22 Fv with high affinity by Fv display on human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9637–9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerli, R.R.; Bauer, M.; Buser, R.B.; Gwerder, M.; Muntwiler, S.; Maurer, P.; Saudan, P.; Bachmann, M.F. Isolation of human monoclonal antibodies by mammalian cell display. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14336–14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Jacobsen, F.W.; Cai, L.; Chen, Q.; Shen, D. Development of a novel mammalian cell surface antibody display platform. In Mabs; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 508–518. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, P.; Raab, H.; Kohr, W.J.; Caras, I.W. Glycophospholipid membrane anchor attachment. Molecular analysis of the cleavage/attachment site. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, Y.; Pakabunto, K.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tsurushita, N. Whole IgG surface display on mammalian cells: Application to isolation of neutralizing chicken monoclonal anti-IL-12 antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 2007, 327, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medof, M.E.; Walter, E.I.; Roberts, W.L.; Haas, R.; Rosenberry, T.L. Decay accelerating factor of complement is anchored to cells by a C-terminal glycolipid. Biochemistry 1986, 25, 6740–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, M.R.; Masters, E.; Pazeraitis, D.; Perera, R.L.; Syrjanen, J.L.; Surade, S.; Thorsteinson, N.; Parthiban, K.; Jones, P.C.; Sattar, M.; et al. Beyond affinity: Selection of antibody variants with optimal biophysical properties and reduced immunogenicity from mammalian display libraries. Mabs 2020, 12, 1829335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huhtinen, O.; Salbo, R.; Lamminmäki, U.; Prince, S. Selection of biophysically favorable antibody variants using a modified Flp-In CHO mammalian display platform. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1170081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Qu, B.; An, L.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, P.; Hang, H. Simultaneous maturation of single chain antibody stability and affinity by CHO cell display. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, N.; Lopez-Anton, N.; Gurjar, S.A.; Khalique, H.; Khalaf, Z.; Clerkin, S.; Leydon, V.R.; Parker-Manuel, R.; Raeside, A.; Payne, T. Development of a novel mammalian display system for selection of antibodies against membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 18436–18448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yea, K.; Xie, J.; Ruiz, D.; Wilson, I.A.; Lerner, R.A. Selecting agonists from single cells infected with combinatorial antibody libraries. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmeier, L.; Hellmann, I.; Gutknecht, C.K.; Wolter, F.I.; Cook, S.C.; Reddy, S.T.; Grawunder, U.; Beerli, R.R. Transpo-mAb display: Transposition-mediated B cell display and functional screening of full-length IgG antibody libraries. Mabs 2016, 8, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, I.; Waldmeier, L.; Bannwarth-Escher, M.-C.; Maslova, K.; Wolter, F.I.; Grawunder, U.; Beerli, R.R. Novel antibody drug conjugates targeting tumor-associated receptor tyrosine kinase ROR2 by functional screening of fully human antibody libraries using Transpo-mAb display on progenitor B cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, R.; Shen, B.; Li, N.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, M.; Fang, P.; Wang, S. High-throughput functional screening for next-generation cancer immunotherapy using droplet-based microfluidics. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segaliny, A.I.; Jayaraman, J.; Chen, X.; Chong, J.; Luxon, R.; Fung, A.; Fu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Rivera, R.; Ma, X. A high throughput bispecific antibody discovery pipeline. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephides, D.; Davoli, S.; Whitley, W.; Ruis, R.; Salter, R.; Gokkaya, S.; Vallet, M.; Matthews, D.; Benazzi, G.; Shvets, E. Cyto-mine: An integrated, picodroplet system for high-throughput single-cell analysis, sorting, dispensing, and monoclonality assurance. SLAS Technol. Transl. Life Sci. Innov. 2020, 25, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.; Lulla, A.; So, T.Y.; Pereyra-Gerber, P.; Raybould, M.I.J.; Kohler, T.N.; Yam-Puc, J.C.; Kaminski, T.S.; Hughes, R.; Pyeatt, G.L. Rapid discovery of monoclonal antibodies by microfluidics-enabled FACS of single pathogen-specific antibody-secreting cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, A.S.; Mizrahi, R.A.; Spindler, M.J.; Adams, M.S.; Asensio, M.A.; Edgar, R.C.; Leong, J.; Leong, R.; Johnson, D.S. Rare, high-affinity mouse anti-PD-1 antibodies that function in checkpoint blockade, discovered using microfluidics and molecular genomics. Mabs 2017, 9, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, A.; McFadden, K.; Bergen, J.; Landas, J.; Berry, K.A.; Gonzalez, A.; Salimi-Moosavi, H.; Murawsky, C.M.; Tagari, P.; King, C.T. Rapid single B cell antibody discovery using nanopens and structured light. In Mabs; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2019; Volume 11, pp. 1025–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, V.; Manning, B.; O’Donnell, B.; O’Reilly, B.; O’Sullivan, D.; O’Kennedy, R.; Leonard, P. Exploiting highly ordered subnanoliter volume microcapillaries as microtools for the analysis of antibody producing cells. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, L.; Zhuang, L.; Roy, G.; Bowen, M.A.; Dall’Acqua, W.F.; Hawley-Nelson, P.; Marelli, M. Amber suppression coupled with inducible surface display identifies cells with high recombinant protein productivity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, K.H.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chiang, I.S.; Chuang, C.H.; Kao, C.H.; Cheng, T.C.; Wang, Y.T.; Lin, W.W.; Chen, B.M.; Roffler, S.R.; et al. High-throughput sorting of the highest producing cell via a transiently protein-anchored system. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouquin, T.; Rasmussen, P.B.; Bertilsson, P.-A.; Okkels, J.S. Regulated readthrough: A new method for the alternative tagging and targeting of recombinant proteins. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 125, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-P.; Hsieh, Y.-T.; Prijovich, Z.M.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Chen, K.-C.; Lu, W.-C.; Tseng, Q.; Leu, Y.-L.; Cheng, T.-L.; Roffler, S.R. ECSTASY, an adjustable membrane-tethered/soluble protein expression system for the directed evolution of mammalian proteins. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2012, 25, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Wages, J.M.; Larrick, J.W. Antibody-membrane switch (AMS) technology for facile cell line development. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2014, 27, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Breous-Nystrom, E.; Schultze, K.; Meier, M.; Flueck, L.; Holzer, C.; Boll, M.; Seibert, V.; Schuster, A.; Blanusa, M.; Schaefer, V.; et al. Retrocyte Display® technology: Generation and screening of a high diversity cellular antibody library. Methods 2014, 65, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomimatsu, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Tanaka, H.; Yamashita, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Teruya, K.; Kazuno, S.; Kinjo, T.; Hamasaki, T.; Kusumoto, K. A rapid screening and production method using a novel mammalian cell display to isolate human monoclonal antibodies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.W.; Le, K.C.; Maynard, J.A. Identification of high affinity HER2 binding antibodies using CHO Fab surface display. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2018, 31, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horlick, R.A.; Macomber, J.L.; Bowers, P.M.; Neben, T.Y.; Tomlinson, G.L.; Krapf, I.P.; Dalton, J.L.; Verdino, P.; King, D.J. Simultaneous surface display and secretion of proteins from mammalian cells facilitate efficient in vitro selection and maturation of antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19861–19869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, P.M.; Horlick, R.A.; Kehry, M.R.; Neben, T.Y.; Tomlinson, G.L.; Altobell, L.; Zhang, X.; Macomber, J.L.; Krapf, I.P.; Wu, B.F. Mammalian cell display for the discovery and optimization of antibody therapeutics. Methods 2014, 65, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebischer-Gumy, C.; Moretti, P.; Ollier, R.; Ries Fecourt, C.; Rousseau, F.; Bertschinger, M. SPLICELECTTM: An adaptable cell surface display technology based on alternative splicing allowing the qualitative and quantitative prediction of secreted product at a single-cell level. Mabs 2020, 12, 1709333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Drewello, D.; Wichter, J.; Nommay, A.; Wilms, B.; Knopf, H.P.; Jostock, T. Surface display vectors for selective detection and isolation of high level antibody producing cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 2386–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, I.; Lou, H.; Li, C.Z.; Chen, Z.R.; Zhang, Z.H.; Liu, S.; Wu, S.; Tan, W.; et al. Simultaneous expression of displayed and secreted antibodies for antibody screen. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.K.; Aguilar, K.; Tsai, J.; Galimidi, R.; Gnanapragasam, P.; Yang, L.; Baltimore, D. Use of mutated self-cleaving 2A peptides as a molecular rheostat to direct simultaneous formation of membrane and secreted anti-HIV immunoglobulins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izidoro, M.A.; Gouvea, I.E.; Santos, J.A.; Assis, D.M.; Oliveira, V.; Judice, W.A.; Juliano, M.A.; Lindberg, I.; Juliano, L. A study of human furin specificity using synthetic peptides derived from natural substrates, and effects of potassium ions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 487, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, J.E.; Skarzynski, M.; Therres, J.A.; Ostovitz, J.R.; Zhou, H.; Kreitman, R.J.; Pastan, I. Designing the furin-cleavable linker in recombinant immunotoxins based on Pseudomonas exotoxin A. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chng, J.; Wang, T.; Nian, R.; Lau, A.; Hoi, K.M.; Ho, S.C.L.; Gagnon, P.; Bi, X.; Yang, Y. Cleavage efficient 2A peptides for high level monoclonal antibody expression in CHO cells. In Mabs; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2015; Volume 7, pp. 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, K.; Araki, T.; Matsuzaki, O.; Sato, A.; Kanno, K.; Kitaguchi, N.; Ito, H. Cell display library for gene cloning of variable regions of human antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen. J. Immunol. Methods 1997, 202, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.; Pastan, I. Display and selection of scFv antibodies on HEK-293T cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 562, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, M.; Gao, L.; Gao, X.; Xiang, S.; Wu, L.; Fu, J.; Song, H. Mammalian cell display for rapid screening scFv antibody therapy. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, P.M.; Horlick, R.A.; Neben, T.Y.; Toobian, R.M.; Tomlinson, G.L.; Dalton, J.L.; Jones, H.A.; Chen, A.; Altobell, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Coupling mammalian cell surface display with somatic hypermutation for the discovery and maturation of human antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20455–20460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, M.; Esslinger, C.; Seidenberg, J.; Weber, M.; Zingg, A.; Townsend, C.; Eicher, B.; Rutkauskaite, J.; Riese, P.; Guzman, C.A. Fast-Track Discovery of SARS-CoV-2-Neutralizing Antibodies from Human B Cells by Direct Functional Screening. Viruses 2024, 16, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Rader, C.; Peng, H. A mammalian cell display platform based on scFab transposition. Antib. Ther. 2023, 6, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, N.; Zhao, Y.; Hang, H.Y. Coupling recombinase-mediated cassette exchange with somatic hypermutation for antibody affinity maturation in CHO cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yu, D.; Tian, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Lei, C.; Yang, Z. A novel and effective approach to generate germline-like monoclonal antibodies by integration of phage and mammalian cell display platforms. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, D.M.; Weber, C.R.; Parola, C.; Meng, S.M.; Greiff, V.; Kelton, W.J.; Reddy, S.T. High-throughput antibody engineering in mammalian cells by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homology-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 7436–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parola, C.; Neumeier, D.; Friedensohn, S.; Csepregi, L.; Di Tacchio, M.; Mason, D.M.; Reddy, S.T. Antibody discovery and engineering by enhanced CRISPR-Cas9 integration of variable gene cassette libraries in mammalian cells. In Mabs; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2019; Volume 11, pp. 1367–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Parthiban, K.; Perera, R.L.; Sattar, M.; Huang, Y.; Mayle, S.; Masters, E.; Griffiths, D.; Surade, S.; Leah, R.; Dyson, M.R.; et al. A comprehensive search of functional sequence space using large mammalian display libraries created by gene editing. Mabs 2019, 11, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.B.; Lin, J.; Tay, S.J.; Mariati Yeo, J.; Nguyen-Khuong, T.; Yang, Y. Multiplexed engineering glycosyltransferase genes in CHO cells via targeted integration for producing antibodies with diverse complex-type N-glycans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, H.P.; Mahfut FBin Chen, S.W.; Huang, Y.; Huo, J.; Zhang, W.; Lam, K.P.; Xu, S.; Yang, Y. Manufacturability and functionality assessment of different formats of T-cell engaging bispecific antibodies. In Mabs; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2023; Volume 15, p. 2231129. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Acqua, W.F.; Damschroder, M.M.; Zhang, J.; Woods, R.M.; Widjaja, L.; Yu, J.; Wu, H. Antibody humanization by framework shuffling. Methods 2005, 36, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Yan, F.; Doronina, V.A.; Escuin-Ordinas, H.; Ryan, M.D.; Brown, J.D. 2A peptides provide distinct solutions to driving stop-carry on translational recoding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 3143–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, R.W.; Andrew, S.M.; Hogarth, M.P.; Pietersz, G.A.; McKenzie, I.F.C. The effect of temperature on the binding kinetics and equilibrium constants of monoclonal antibodies to cell surface antigens. Mol. Immunol. 1990, 27, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, R.; Chen-Tsai, R.Y.; Kong, L.-J. A system for site-specific integration of transgenes in mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusiak, B.; Jagtap, K.; Gaidukov, L.; Duportet, X.; Bandara, K.; Chu, J.; Zhang, L.; Weiss, R.; Lu, T.K. Comparison of integrases identifies Bxb1-GA mutant as the most efficient site-specific integrase system in mammalian cells. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019, 8, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Gao, X.D.; Krasnow, N.A.; McElroy, A.; Tao, Y.A.; Duby, J.E.; Steinbeck, B.J.; McCreary, J.; Pierce, S.E.; Tolar, J. Efficient site-specific integration of large genes in mammalian cells via continuously evolved recombinases and prime editing. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hew, B.E.; Gupta, S.; Sato, R.; Waller, D.F.; Stoytchev, I.; Short, J.E.; Sharek, L.; Tran, C.T.; Badran, A.H.; Owens, J.B. Directed evolution of hyperactive integrases for site specific insertion of transgenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.C.L.; Bardor, M.; Li, B.; Lee, J.J.; Song, Z.; Tong, Y.W.; Goh, L.-T.; Yang, Y. Comparison of internal ribosome entry site (IRES) and Furin-2A (F2A) for monoclonal antibody expression level and quality in CHO cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, J.P.Z.; Mariati, M.; Bi, J.; Chang, M.W.; Yang, Y. A Targeted Integration-Based CHO Cell Platform for Simultaneous Antibody Display and Secretion. Antibodies 2025, 14, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020038
Ng JPZ, Mariati M, Bi J, Chang MW, Yang Y. A Targeted Integration-Based CHO Cell Platform for Simultaneous Antibody Display and Secretion. Antibodies. 2025; 14(2):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020038
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Jessica P. Z., Mariati Mariati, Jiawu Bi, Matthew Wook Chang, and Yuansheng Yang. 2025. "A Targeted Integration-Based CHO Cell Platform for Simultaneous Antibody Display and Secretion" Antibodies 14, no. 2: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020038
APA StyleNg, J. P. Z., Mariati, M., Bi, J., Chang, M. W., & Yang, Y. (2025). A Targeted Integration-Based CHO Cell Platform for Simultaneous Antibody Display and Secretion. Antibodies, 14(2), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020038








