Development of Fully Human Antibodies Targeting SIRPα and PLA2G7 for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Recombinant Human PLA2G7
2.2. ICAT5 Fab and ICAT6 VH Libraries Panning Against SIRPα and PLA2G7
2.3. Purification of Fab, VH and IgG
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Biolayer Interferometry (BLI)
2.6. Cell Lines
2.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.8. PLA2G7 Activity Assay
2.9. Phagocytosis Assay
2.10. Cell Migration Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
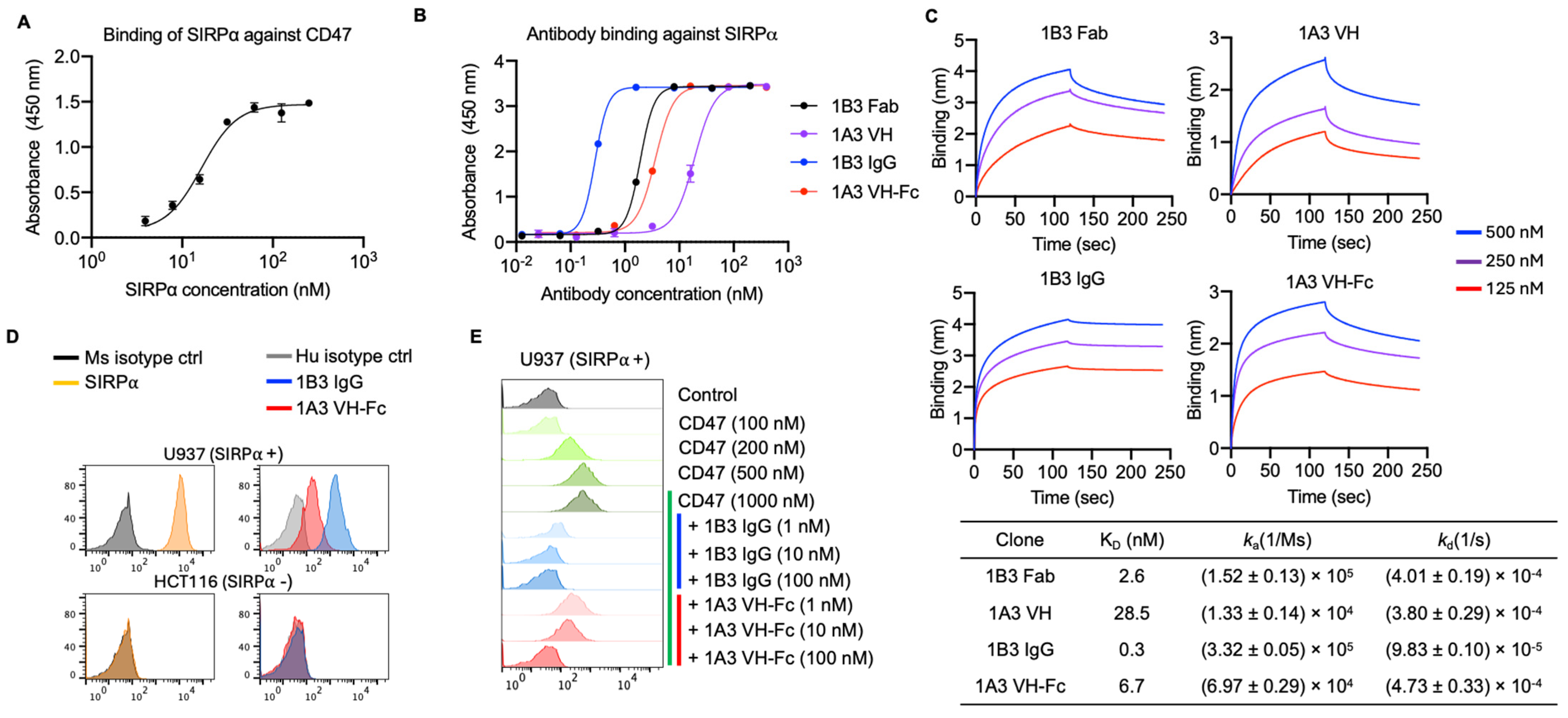
3.1. Generation of Anti-SIRPα Antibodies with Competitive Epitopes to CD47
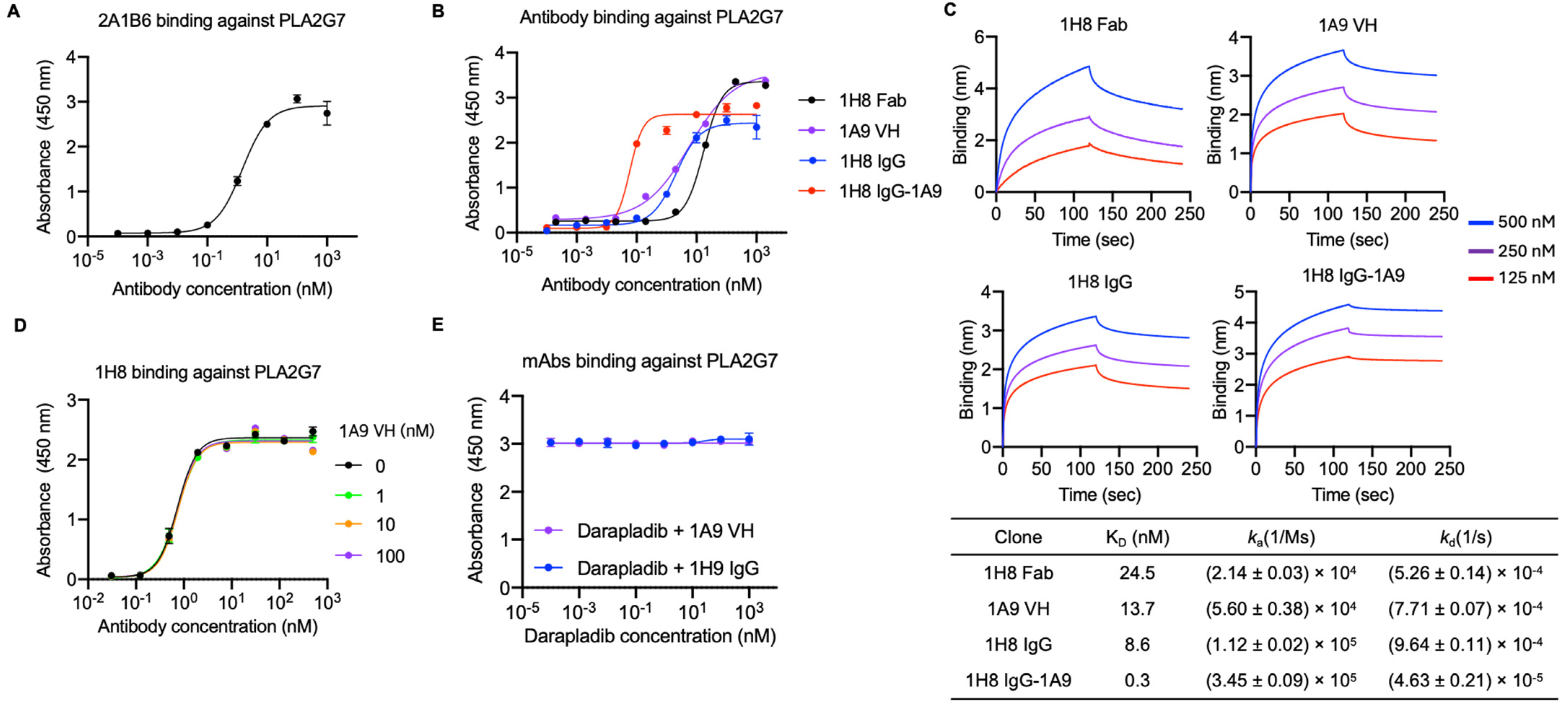
3.2. Identification of Two Anti-PLA2G7 Antibodies with Non-Overlapping Epitopes and Engineering a Bispecific Antibody
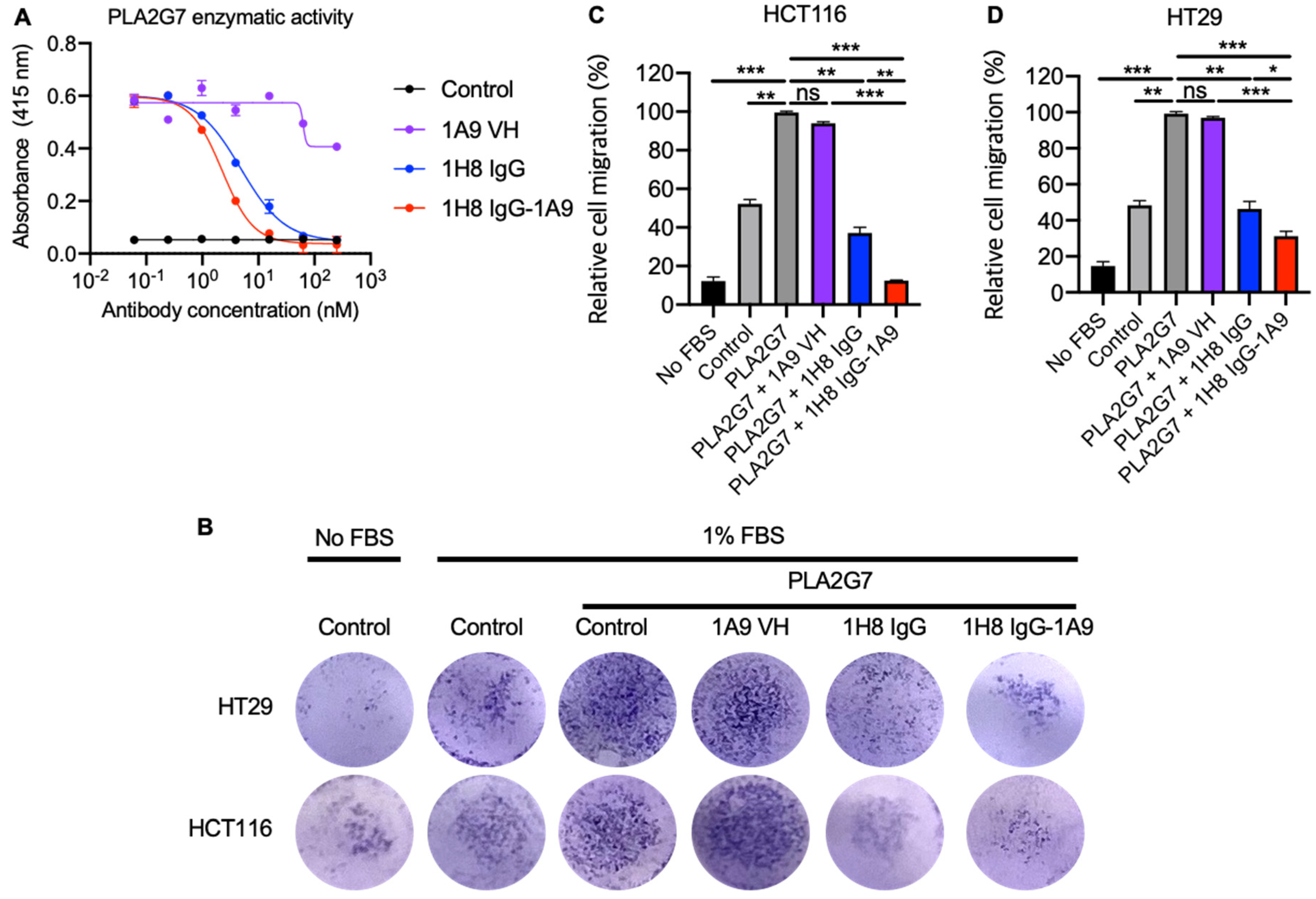
3.3. Anti-SIRPα Antibodies Enhanced Macrophage Phagocytic Activity Against Cancer Cells When Combined with Tumor Opsonizing IgG1
3.4. Mono and Bispecific Antibodies Inhibited the PLA2G7 Enzymatic Activity and Blocked PLA2G7- Mediated Tumor Cell Migration
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, S.; van der Laan, L.J.; Vernon-Wilson, E.; Renardel de Lavalette, C.; Döpp, E.A.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Simmons, D.L.; van den Berg, T.K. Signal-regulatory protein is selectively expressed by myeloid and neuronal cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, A.N.; Van den Berg, T.K. The interaction between signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) and CD47: Structure, function, and therapeutic target. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Z.; Tian, W.; Cang, S.; Yu, J. Targeting the CD47/SIRPalpha pathway in malignancies: Recent progress, difficulties and future perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1378647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Jamieson, C.H.; Pang, W.W.; Park, C.Y.; Chao, M.P.; Majeti, R.; Traver, D.; van Rooijen, N.; Weissman, I.L. CD47 is upregulated on circulating hematopoietic stem cells and leukemia cells to avoid phagocytosis. Cell 2009, 138, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeti, R.; Chao, M.P.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Pang, W.W.; Jaiswal, S.; Gibbs, K.D., Jr.; van Rooijen, N.; Weissman, I.L. CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and therapeutic antibody target on human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cell 2009, 138, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uger, R.; Johnson, L. Blockade of the CD47-SIRPalpha axis: A promising approach for cancer immunotherapy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advani, R.; Flinn, I.; Popplewell, L.; Forero, A.; Bartlett, N.L.; Ghosh, N.; Kline, J.; Roschewski, M.; LaCasce, A.; Collins, G.P.; et al. CD47 Blockade by Hu5F9-G4 and Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.; Trout, C.V.; Mikolon, D.; Adams, P.; Guzman, R.; Mavrommatis, K.; Abbasian, M.; Hadjivassiliou, H.; Dearth, L.; Fox, B.A.; et al. Discovery and Preclinical Activity of BMS-986351, an Antibody to SIRPalpha That Enhances Macrophage-mediated Tumor Phagocytosis When Combined with Opsonizing Antibodies. Cancer Res. Commun. 2024, 4, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, N.G.; Herndler-Brandstetter, D.; Weiskopf, K.; Shan, L.; Volkmer, J.P.; George, B.M.; Lietzenmayer, M.; McKenna, K.M.; Naik, T.J.; McCarty, A.; et al. Anti-SIRPalpha antibody immunotherapy enhances neutrophil and macrophage antitumor activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E10578–E10585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Yoon, M.S.; Hustinx, H.; Sim, J.; Wan, H.I.; Kim, H. Assessing and mitigating the interference of ALX148, a novel CD47 blocking agent, in pretransfusion compatibility testing. Transfusion 2020, 60, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjoelker, L.W.; Wilder, C.; Eberhardt, C.; Stafforini, D.M.; Dietsch, G.; Schimpf, B.; Hooper, S.; Le Trong, H.; Cousens, L.S.; Zimmerman, G.A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of a platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Nature 1995, 374, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Wang, K.; Shen, J. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2: The story continues. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 79–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Maguire, C.T.; Wolfert, R.; Burns, A.R.; Reardon, M.; Geis, R.; Holvoet, P.; Morrisett, J.D. Relationship of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and oxidized low density lipoprotein in carotid atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewski, A.; Macphee, C. Role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis: Biology, epidemiology, and possible therapeutic target. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaro, O.; Youm, Y.; Shchukina, I.; Ryu, S.; Sidorov, S.; Ravussin, A.; Nguyen, K.; Aladyeva, E.; Predeus, A.N.; Smith, S.R.; et al. Caloric restriction in humans reveals immunometabolic regulators of health span. Science 2022, 375, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candels, L.S.; Becker, S.; Trautwein, C. PLA2G7: A new player in shaping energy metabolism and lifespan. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.T.; Yu, F.F.; Fan, B.F.; Wu, Y.B.; Zhou, Z.L.; Lin, W.Q.; Yang, Y. Combination of theoretical analysis and experiments: Exploring the role of PLA2G7 in human cancers, including renal cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, S. Identification and molecular modelling of potential drugs targeting the genes involved in the progression of lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Gene Rep. 2024, 37, 102067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, H.B.; Png, C.W.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Wong, S.B.; Zhang, Y. Monocyte-derived factors including PLA2G7 induced by macrophage-nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell interaction promote tumor cell invasiveness. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55473–55490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, W.F.; Meng, F.S.; Jiang, Q.Y.; Tang, W.Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; Lin, X.H.; Xue, R.Y.; Zhang, S.; Dong, L. Inhibiting PLA2G7 reverses the immunosuppressive function of intratumoral macrophages and augments immunotherapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, D.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Vergara, S.; Conard, A.; Adams, C.; Calero, G.; Ishima, R.; Mellors, J.W.; Dimitrov, D.S. A highly-specific fully-human antibody and CAR-T cells targeting CD66e/CEACAM5 are cytotoxic for CD66e-expressing cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2022, 525, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Schafer, A.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Liu, X.; Martinez, D.R.; Chen, C.; Sun, Z.; Leist, S.R.; Drelich, A.; Zhang, L.; et al. High Potency of a Bivalent Human V(H) Domain in SARS-CoV-2 Animal Models. Cell 2020, 183, 429–441.e416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.L.; Zeng, Z.F.; Gan, W.Q.; Wang, W.Q.; Li, T.G.; Hou, Y.F.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, R.X.; Yang, M. Lp-PLA2 inhibition prevents Ang II-induced cardiac inflammation and fibrosis by blocking macrophage NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 2016–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, J.P.; Ninio, E.; Panayiotou, A.; Palmen, J.; Cooper, J.A.; Ricketts, S.L.; Sofat, R.; Nicolaides, A.N.; Corsetti, J.P.; Fowkes, F.G.; et al. PLA2G7 genotype, lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity, and coronary heart disease risk in 10 494 cases and 15 624 controls of European Ancestry. Circulation 2010, 121, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Parish, C.R.; Coupland, L.A. A Rapid and Accurate Bioluminescence-Based Migration Assay Permitting Analysis of Tumor Cell/Stromal Cell Interactions. Methods Protoc. 2020, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Mine, N.; Kufe, D.W.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Kawabe, T. CBP501 inhibits EGF-dependent cell migration, invasion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of non-small cell lung cancer cells by blocking KRas to calmodulin binding. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 74006–74018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, R.K.; Discher, D.E. Inhibition of “self” engulfment through deactivation of myosin-II at the phagocytic synapse between human cells. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Dang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, X.; Wang, C.; Raoof, M.; Sun, Z.; Yu, J.; et al. Promoting antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis for effective macrophage-based cancer immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oei, H.H.; van der Meer, I.M.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Stijnen, T.; Breteler, M.M.; Witteman, J.C. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity is associated with risk of coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke: The Rotterdam Study. Circulation 2005, 111, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainio, P.; Lehtinen, L.; Mirtti, T.; Hilvo, M.; Seppanen-Laakso, T.; Virtanen, J.; Sankila, A.; Nordling, S.; Lundin, J.; Rannikko, A.; et al. Phospholipase PLA2G7, associated with aggressive prostate cancer, promotes prostate cancer cell migration and invasion and is inhibited by statins. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Cheng, L. The CD47-SIRPalpha axis is a promising target for cancer immunotherapies. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Ying, T.; Wu, Y. Single-domain antibodies as therapeutics for solid tumor treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 2854–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Kong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lei, C.; Li, J.; Ding, L.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. A highly stable human single-domain antibody-drug conjugate exhibits superior penetration and treatment of solid tumors. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 2785–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maute, R.; Xu, J.; Weissman, I.L. CD47-SIRPalpha-targeted therapeutics: Status and prospects. Immuno-Oncol. Technol. 2022, 13, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.A.; Lakhani, N.J.; Eng, C.; Hecht, J.R.; Bendell, J.C.; Philip, P.A.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Johnson, B.; Kardosh, A.; Ippolito, T.M.; et al. A phase Ib/II study of the anti-CD47 antibody magrolimab with cetuximab in solid tumor and colorectal cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallera, D.A.; Oh, F.; Kodal, B.; Hinderlie, P.; Geller, M.A.; Miller, J.S.; Felices, M. A HER2 Tri-Specific NK Cell Engager Mediates Efficient Targeting of Human Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reusing, S.B.; Vallera, D.A.; Manser, A.R.; Vatrin, T.; Bhatia, S.; Felices, M.; Miller, J.S.; Uhrberg, M.; Babor, F. CD16xCD33 Bispecific Killer Cell Engager (BiKE) as potential immunotherapeutic in pediatric patients with AML and biphenotypic ALL. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 3701–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasse, S.; Brockelmann, P.J.; Momotow, J.; Plutschow, A.; Huttmann, A.; Basara, N.; Koenecke, C.; Martin, S.; Bentz, M.; Grosse-Thie, C.; et al. AFM13 in patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: Final results of an open-label, randomized, multicenter phase II trial. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhani, N.J.; Patnaik, A.; Liao, J.B.; Moroney, J.W.; Miller, D.S.; Fleming, G.F.; Axt, M.; Wang, Y.V.; Agoram, B.; Volkmer, J.P.; et al. A phase Ib study of the anti-CD47 antibody magrolimab with the PD-L1 inhibitor avelumab (A) in solid tumor (ST) and ovarian cancer (OC) patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.D.; Gip, P.; McKenna, K.M.; Zhao, F.F.; Mata, O.; Choi, T.S.; Duan, J.Q.; Sompalli, K.; Majeti, R.; Weissman, I.L.; et al. Combination Treatment with 5F9 and Azacitidine Enhances Phagocytic Elimination of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Investigators, S.; White, H.D.; Held, C.; Stewart, R.; Tarka, E.; Brown, R.; Davies, R.Y.; Budaj, A.; Harrington, R.A.; Steg, P.G.; et al. Darapladib for preventing ischemic events in stable coronary heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Tompson, D.; Magee, M.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, H.; Gross, A.S.; Liu, Y. Single and Multiple Dose Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Safety of the Novel Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 Enzyme Inhibitor Darapladib in Healthy Chinese Subjects: An Open Label Phase-1 Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.; Jang, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Jung, Y.; Kim, J.; Seo, J.; Han, T.S.; Jang, E.; Son, H.Y.; et al. The lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 inhibitor Darapladib sensitises cancer cells to ferroptosis by remodelling lipid metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morigny, P.; Kaltenecker, D.; Zuber, J.; Machado, J.; Mehr, L.; Tsokanos, F.F.; Kuzi, H.; Hermann, C.D.; Voelkl, M.; Monogarov, G.; et al. Association of circulating PLA2G7 levels with cancer cachexia and assessment of darapladib as a therapy. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1333–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, S.; Baek, D.-S.; Mellors, J.W.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Li, W. Development of Fully Human Antibodies Targeting SIRPα and PLA2G7 for Cancer Therapy. Antibodies 2025, 14, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14010021
Shin S, Baek D-S, Mellors JW, Dimitrov DS, Li W. Development of Fully Human Antibodies Targeting SIRPα and PLA2G7 for Cancer Therapy. Antibodies. 2025; 14(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Seungmin, Du-San Baek, John W. Mellors, Dimiter S. Dimitrov, and Wei Li. 2025. "Development of Fully Human Antibodies Targeting SIRPα and PLA2G7 for Cancer Therapy" Antibodies 14, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14010021
APA StyleShin, S., Baek, D.-S., Mellors, J. W., Dimitrov, D. S., & Li, W. (2025). Development of Fully Human Antibodies Targeting SIRPα and PLA2G7 for Cancer Therapy. Antibodies, 14(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14010021






