Rapidly Progressive Pauci-Immune Glomerulonephritis with Aberrant Fibrinoid Necrosis Associated with Atezolizumab, an Immune Check Point Inhibitor: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
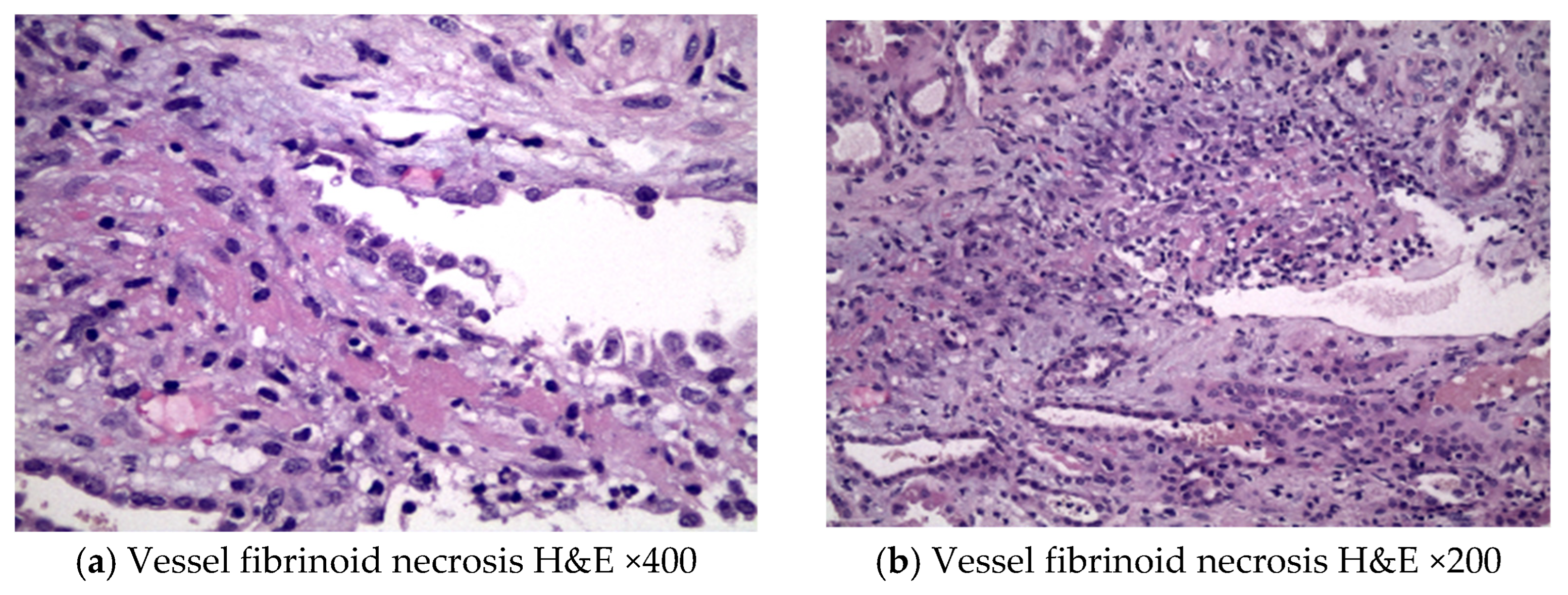
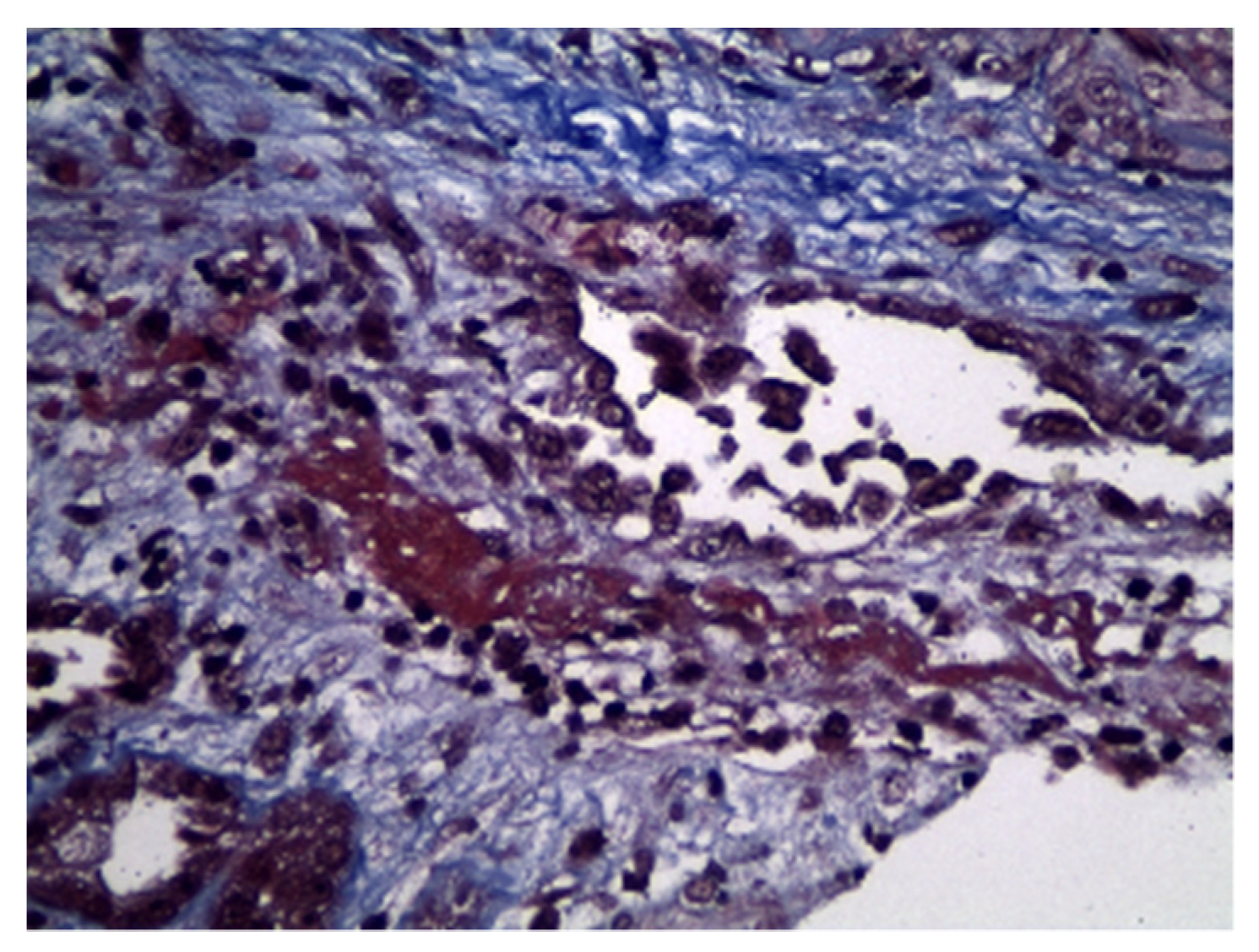
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weber, J.; Mandalà, M.; Del Vecchio, M.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.M.; Cowey, C.L.; Dalle, S.; Schenker, M.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Marquez-Rodas, I.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab versus Ipilimumab in Resected Stage III or IV Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; De Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dine, J.; Gordon, R.; Shames, Y.; Kasler, M.K.; Barton-Burke, M. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: An innovation in immunotherapy for the treatment and management of patients with cancer. Asia Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2017, 4, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, O.; Fouad, M. Risk of pneumonitis in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A me-ta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2016, 10, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xipell, M.; Victoria, I.; Hoffmann, V.; Villarreal, J.; Garcia-Herrera, A.; Reig, O.; Rodas, L.; Blasco, M.; Poch, E.; Mellado, B.; et al. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with atezolizumab, an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (pd-l1) antibody therapy. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1445952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanen, J.B.A.G.; Carbonnel, F.; Robert, C.; Kerr, K.M.; Peters, S.; Larkin, J.; Jordan, K. Management of toxicities from Immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28 (Suppl. S4), i119–i142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, B.A.; Longo, T.A.; Ramalingam, S.; Harrison, M.R. Atezolizumab: A PD-L1–Blocking Antibody for Bladder Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1886–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Bumbaca, D.; Pastuskovas, C.V.; Boswell, C.A.; West, D.; Cowan, K.J.; Chiu, H.; McBride, J.; Johnson, C.; Xin, Y.; et al. Preclinical pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, tissue distribution, and tu-mor penetration of anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody, an immune checkpoint inhibitor. MAbs 2016, 8, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.W.; Gill, D.M.; Agarwal, N.; Maughan, B.L. PD-1 checkpoint inhibition: Toxicities and management. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2017, 35, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerty, D.T.; Allen, P.M. Processing and presentation of self and foreign antigens by the renal proximal tubule. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke, J.; Lucas, J.A.; Zeller, G.C.; Keir, M.E.; Huang, X.R.; Tsuboi, N.; Mayadas, T.N.; Lan, H.Y.; Sharpe, A.H.; Kelley, V.R. Programmed Death 1 Ligand (PD-L) 1 and PD-L2 Limit Autoimmune Kidney Disease: Distinct Roles. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7466–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, A.; Watanabe, M.; Nawata, A.; Ikari, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Shigemoto, K.; Hisano, S.; Nakashima, H. Tubulointerstitial nephritis as adverse effect of programmed cell death 1 inhibitor, nivolumab, showed distinct histological findings. CEN Case Rep. 2017, 6, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzedine, H.; Mateus, C.; Boutros, C.; Robert, C.; Rouvier, P.; Amoura, Z.; Mathian, A. Renal effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Marrone, K.A.; Troxell, M.L.; Ralto, K.M.; Hoenig, M.P.; Brahmer, J.R.; Le, D.T.; Lipson, E.J.; Glezerman, I.G.; Wolchok, J.; et al. Clinicopathological features of acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxi, S.; Yang, A.; Gennarelli, R.L.; Khan, N.; Wang, Z.; Boyce, L.; Korenstein, D. Immune-related adverse events for anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 drugs: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2018, 360, k793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.F.; Chen, Y.; Song, S.Y.; Wang, T.J.; Ji, W.J.; Li, S.W.; Liu, N.; Yan, C.X. Immune-related adverse events associated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment for malignan-cies: A meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamlouk, O.; Selamet, U.; Machado, S.; Abdelrahim, M.; Glass, W.F.; Tchakarov, A.; Gaber, L.; Lahoti, A.; Workeneh, B.; Chen, S. Nephrotoxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors beyond tubulointerstitial nephritis: Single-center experience. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, M.; Jin, J. Nephrotoxicity in patients with solid tumors treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Investig. New Drugs 2021, 39, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallan, A.J.; Alexander, E.; Reid, P.; Kutuby, F.; Chang, A.; Henriksen, K.J. Renal Vasculitis and Pauci-immune Glomerulonephritis Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Kim, H.S.; Ku, B.M.; Choi, Y.-L.; Cristescu, R.; Han, J.; Sun, J.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Patients With Refractory or Relapsed Thymic Epithelial Tumor: An Open-Label Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoine, M.; Dilly, B.; Curie, A.; Hébert, V.; Laurent, C.; Hanoy, M.; Grangé, S.; Guerrot, D.; François, A.; Bertrand, D. Ipilimumab-induced renal granulomatous arteritis: A case report. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person, F.; Chahoud-Schriefer, T.; Fehrle, W.; Janneck, M.; Huber, T.B.; Wiech, T. Severe acute kidney injury due to nivolumab/ipilimumab-induced granulo-matosis and fibrinoid vascular necrosis. J. Immunother. 2020, 43, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, M.H.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, H.; Ahn, M.-J. Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Rapid Progressive Glomerulonephritis after Pembrolizumab Treatment in Thymic Epithelial Tumor: A Case Report. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, e103–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchlu, A.; Jhaveri, K.D.; Wadhwani, S.; Deshpande, P.; Harel, Z.; Kishibe, T.; Henriksen, K.; Wanchoo, R. A systematic review of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated glomerular disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 6, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Cortazar, F.B.; Riella, L.V.; Leaf, D.E. Immune checkpoint inhibitor nephrotoxicity: Update 2020. Kidney360 2020, 1, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Short, S.A.P.; Sise, M.E.; Prosek, J.M.; Madhavan, S.M.; Soler, M.J.; Ostermann, M.; Herrmann, S.M.; Abudayyeh, A.; Anand, S.; et al. ICPi-AKI Consortium Investigators: Acute kidney injury in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.D.; Seethapathy, H.; Strohbehn, I.A.; Zhao, S.H.; Boland, G.M.; Fadden, R.; Sullivan, R.; Reynolds, K.L.; Sise, M.E. Rapid corticosteroid taper versus standard of care for immune checkpoint inhibitor induced nephritis: A single-center retrospective cohort study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference, Year | Immune Check Point Received | ANCA Serology | Initial Corticosteroid Therapy | Other Immunosuppressive Treatment | AKI Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortazar et al. [15], 2020 | Nivolumab | Negative | Corticosteroid, NOS | Rituximab | Full |
| Mamlouk et al. [18], 2019 | Nivolumab | Negative | Prednisone 1 mg/kg | Rituximab | Complete |
| Mamlouk et al. [18], 2019 | Ipilimumab plus nivolumab | Negative | Prednisone 1 mg/kg | Rituximab | Complete |
| Mamlouk et al. [18], 2019 | Tremelimumab | NA | Methyl-prednisolone 2 mg/kg | Rituximab | Partial |
| Gallan et al. [20], 2019 | Pembrolizumab | Negative | Pulse steroid, high-dose oral steroid | None | NA |
| Gallan et al. [20], 2019 | Nivolumab | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Gallan et al. [20], 2019 | Nivolumab | Negative | Corticosteroid, NOS | None | Partial |
| Gallan et al. [20], 2019 | Nivolumab | Negative | Pulse steroid, then oral steroid | IMCgp100 | Complete |
| Cho et al. [21], 2018 | Pembrolizumab | Positive | Corticosteroid, NOS | Cyclophosphamide | Partial |
| Lemoine et al. [22], 2019 | Ipilimumab | Negative | Prednisone 1 mg/kg ×1 month, tapered over 4 weeks | None | Partial |
| Person et al. [23], 2020 | Ipilimumab plus nivolumab | Negative | Methyl-prednisolone 200 mg IV daily | MMF | ESKD |
| Heo et al. [24], 2017 | Pembrolizumab | Positive | Methyl-prednisolone 500 mg IV daily × 3 days, p.o taper | Cyclophosphamide | Partial |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolopoulos, P.; Liapis, G.; Giannakopoulos, P.; Kotsantis, I.; Drouzas, K.; Lionaki, S. Rapidly Progressive Pauci-Immune Glomerulonephritis with Aberrant Fibrinoid Necrosis Associated with Atezolizumab, an Immune Check Point Inhibitor: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Antibodies 2023, 12, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12010010
Nikolopoulos P, Liapis G, Giannakopoulos P, Kotsantis I, Drouzas K, Lionaki S. Rapidly Progressive Pauci-Immune Glomerulonephritis with Aberrant Fibrinoid Necrosis Associated with Atezolizumab, an Immune Check Point Inhibitor: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Antibodies. 2023; 12(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolopoulos, Petros, George Liapis, Panagiotis Giannakopoulos, Ioannis Kotsantis, Konstantinos Drouzas, and Sophia Lionaki. 2023. "Rapidly Progressive Pauci-Immune Glomerulonephritis with Aberrant Fibrinoid Necrosis Associated with Atezolizumab, an Immune Check Point Inhibitor: A Case Report and Review of Literature" Antibodies 12, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12010010
APA StyleNikolopoulos, P., Liapis, G., Giannakopoulos, P., Kotsantis, I., Drouzas, K., & Lionaki, S. (2023). Rapidly Progressive Pauci-Immune Glomerulonephritis with Aberrant Fibrinoid Necrosis Associated with Atezolizumab, an Immune Check Point Inhibitor: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Antibodies, 12(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12010010






