Strategies to Screen Anti-AQP4 Antibodies from Yeast Surface Display Libraries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Media
2.2. Antigens and Antibodies
2.3. Cell Staining
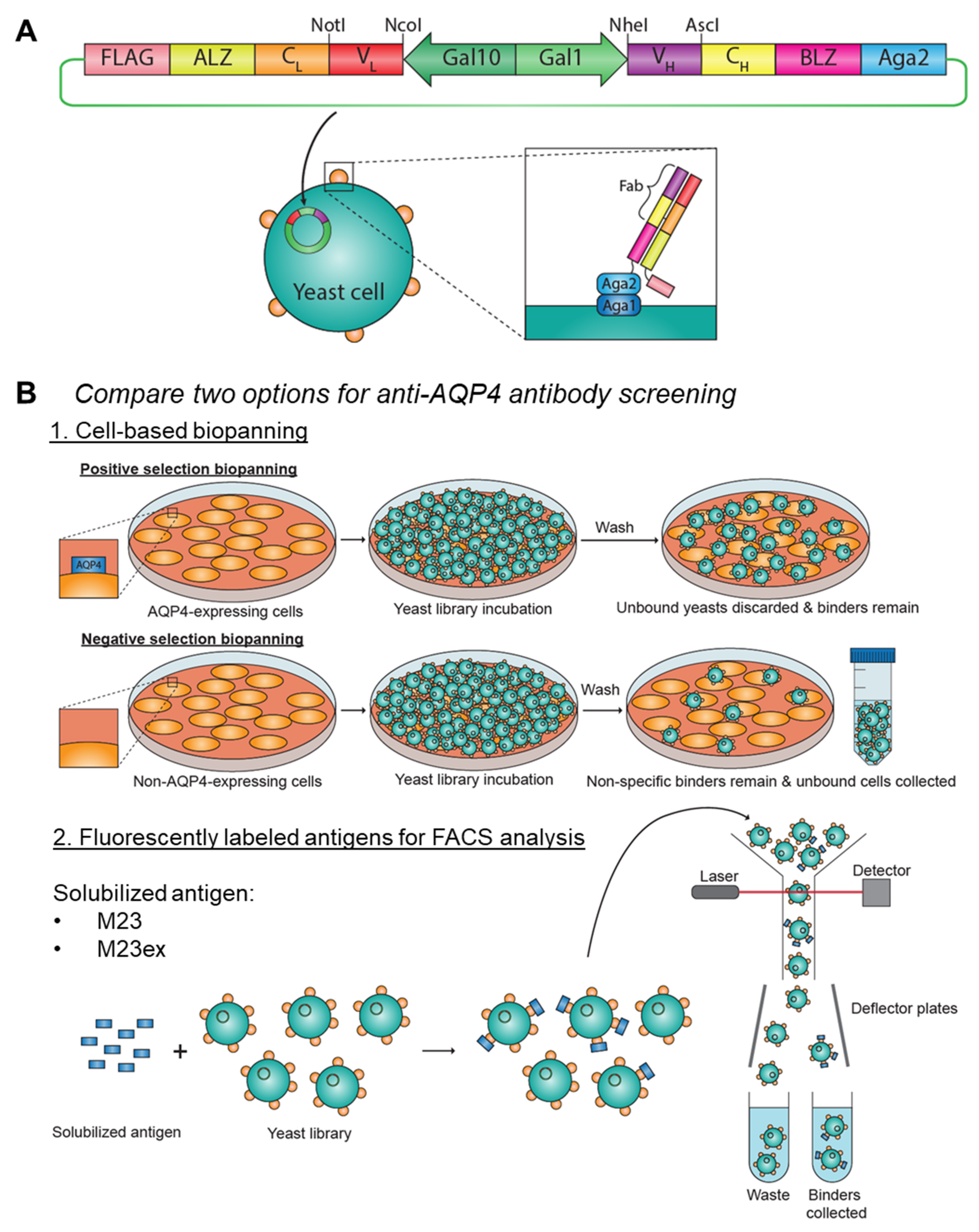
2.4. Yeast Library Construction
2.5. Cell-Based Biopanning
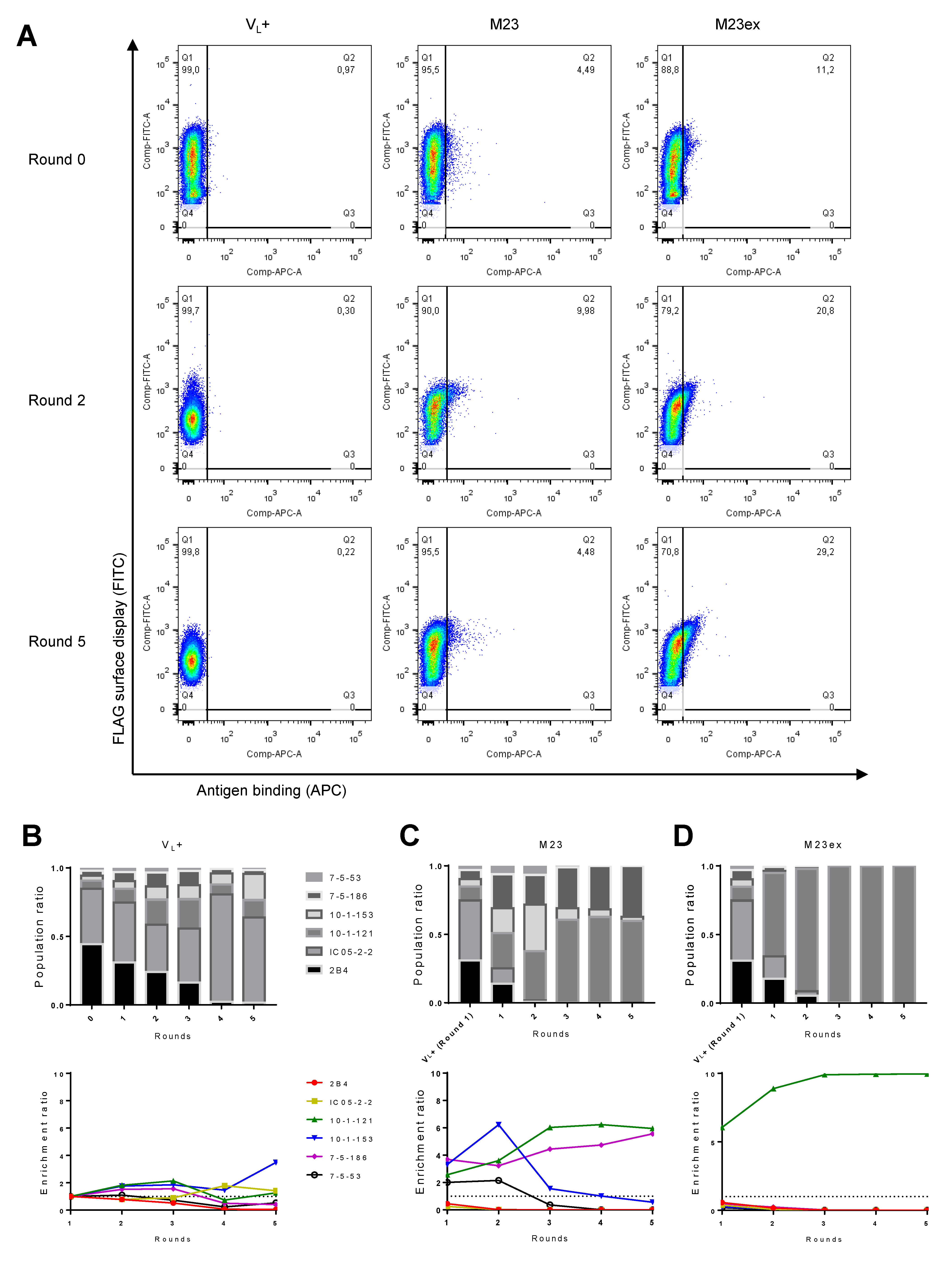
2.6. Flow Cytometry and Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
2.7. NGS Analysis of Sorted Library Composition
3. Results
3.1. Construction of Synthetic Yeast Screening Libraries to Model Anti-AQP4 Antibody Screening
3.2. Monoclonal Anti-AQP4 NMO Antibodies Bind to M23-AQP4 Antigens
3.3. AQP4-Expressing HEK293 as a Target for Cell-Based Biopanning
3.4. Cell-Based Biopanning for Anti-AQP4 Antibody Identification
3.5. FACS Strategy for Anti-AQP4 Clonal Enrichment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, M.L.; Alfaleh, M.A.; Kumble, S.; Zhang, S.; Osborne, G.W.; Yeh, M.; Arora, N.; Hou, J.J.C.; Howard, C.B.; Chin, D.Y.; et al. Targeting Membrane Proteins for Antibody Discovery Using Phage Display. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakheet, T.M.; Doig, A.J. Properties and Identification of Human Protein Drug Targets. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cournia, Z.; Allen, T.W.; Andricioaei, I.; Antonny, B.; Baum, D.; Brannigan, G.; Buchete, N.-V.; Deckman, J.T.; Delemotte, L.; Del Val, C.; et al. Membrane Protein Structure, Function, and Dynamics: A Perspective from Experiments and Theory. J. Membr. Biol. 2015, 248, 611–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dodd, R.B.; Wilkinson, T.; Schofield, D.J. Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies to Complex Membrane Protein Targets: Antigen Generation and Antibody Discovery Strategies. BioDrugs 2018, 32, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M. Autoimmune Responses Are Directed against Self Antigens. In Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease, 5th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 892. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.L.; Lam, C.; Kalluri, S.R.; Saikali, P.; Bautista, K.; Dupree, C.; Glogowska, M.; Case, D.; Antel, J.P.; Owens, G.P.; et al. Intrathecal Pathogenic Anti-Aquaporin-4 Antibodies in Early Neuromyelitis Optica. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trebst, C.; Ayzenberg, I.; Kleiter, I. Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders. In Neuroinflammation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.S.; Phuan, P.-W.; Asavapanumas, N.; Tradtrantip, L. Biology of AQP4 and Anti-AQP4 Antibody: Therapeutic Implications. Brain Pathol. 2013, 23, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crane, J.M.; Verkman, A.S. Determinants of Aquaporin-4 Assembly in Orthogonal Arrays Revealed by Live-Cell Single-Molecule Fluorescence Imaging. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122 Pt 6, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bellis, M.; Pisani, F.; Mola, M.G.; Rosito, S.; Simone, L.; Buccoliero, C.; Trojano, M.; Nicchia, G.P.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. Translational Readthrough Generates New Astrocyte AQP4 Isoforms That Modulate Supramolecular Clustering, Glial Endfeet Localization, and Water Transport. Glia 2017, 65, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, C.; Buccoliero, C.; Mola, M.G.; Abbrescia, P.; Nicchia, G.P.; Trojano, M.; Frigeri, A. AQP4ex Is Crucial for the Anchoring of AQP4 at the Astrocyte End-Feet and for Neuromyelitis Optica Antibody Binding. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.J.; Olsen, M.J.; Cochran, J.R.; Cochran, F.V.; Brown, D.N. Cell Surface Display Systems for Protein Engineering. In Protein Engineering and Design, 23rd ed.; Park, S.J., Cochra, J.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Volume 75, pp. 23–42. ISBN 9780429191633. [Google Scholar]
- Zorniak, M.; Clark, P.A.; Umlauf, B.J.; Cho, Y.; Shusta, E.V.; Kuo, J.S. Yeast Display Biopanning Identifies Human Antibodies Targeting Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tillotson, B.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Shusta, E.V. Cells and Cell Lysates: A Direct Approach for Engineering Antibodies against Membrane Proteins Using Yeast Surface Display. Methods 2013, 60, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisani, F.; Simone, L.; Mola, M.G.; De Bellis, M.; Mastrapasqua, M.; Ruggieri, M.; Trojano, M.; Nicchia, G.P.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. Host-Cell Type Dependent Features of Recombinant Human Aquaporin-4 Orthogonal Arrays of Particles-New Insights for Structural and Functional Studies. Cells 2019, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burgoon, M.P.; Williamson, R.A.; Owens, G.P.; Ghausi, O.; Bastidas, R.B.; Burton, D.R.; Gilden, D.H. Cloning the Antibody Response in Humans with Inflammatory CNS Disease: Isolation of Measles Virus-Specific Antibodies from Phage Display Libraries of a Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis Brain. J. Neuroimmunol. 1999, 94, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.P.; Bennett, J.L.; Lassmann, H.; O’Connor, K.C.; Ritchie, A.M.; Shearer, A.; Lam, C.; Yu, X.; Birlea, M.; DuPree, C.; et al. Antibodies Produced by Clonally Expanded Plasma Cells in Multiple Sclerosis Cerebrospinal Fluid. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soltys, J.; Liu, Y.; Ritchie, A.; Wemlinger, S.; Schaller, K.; Schumann, H.; Owens, G.P.; Bennett, J.L. Membrane Assembly of Aquaporin-4 Autoantibodies Regulates Classical Complement Activation in Neuromyelitis Optica. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2000–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; DeKosky, B.J.; Timm, M.R.; Lee, J.; Normandin, E.; Misasi, J.; Kong, R.; McDaniel, J.R.; Delidakis, G.; Leigh, K.E.; et al. Functional Interrogation and Mining of Natively Paired Human VH:VL Antibody Repertoires. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, T.A.; Chevalier, A.; Song, Y.; Dreyfus, C.; Fleishman, S.J.; De Mattos, C.; Myers, C.A.; Kamisetty, H.; Blair, P.; Wilson, I.A.; et al. Optimization of Affinity, Specificity and Function of Designed Influenza Inhibitors Using Deep Sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banach, B.B.; Cerutti, G.; Fahad, A.S.; Shen, C.-H.; de Souza, M.O.; Katsamba, P.S.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Huang, Y.; et al. Paired Heavy and Light Chain Signatures Contribute to Potent SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization in Public Antibody Responses. bioRxiv 2020. bioRxiv:2020.12.31.424987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, A.S.; Timm, M.R.; Madan, B.; Burgomaster, K.E.; Dowd, K.A.; Normandin, E.; Gutiérrez-González, M.F.; Pennington, J.M.; De Souza, M.O.; Henry, A.R.; et al. Functional Profiling of Antibody Immune Repertoires in Convalescent Zika Virus Disease Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, B.; Zhang, B.; Xu, K.; Chao, C.W.; O’Dell, S.; Wolfe, J.R.; Chuang, G.-Y.; Fahad, A.S.; Geng, H.; Kong, R.; et al. Mutational Fitness Landscapes Reveal Genetic and Structural Improvement Pathways for a Vaccine-Elicited HIV-1 Broadly Neutralizing Antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2011653118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ma, N.; Madden, T.L.; Ostell, J.M. IgBLAST: An Immunoglobulin Variable Domain Sequence Analysis Tool. Nucl. Acids Res. 2013, 41, W34–W40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simone, L.; Pisani, F.; Mola, M.G.; De Bellis, M.; Merla, G.; Micale, L.; Frigeri, A.; Vescovi, A.L.; Svelto, M.; Nicchia, G.P. AQP4 Aggregation State Is a Determinant for Glioma Cell Fate. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2182–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfaleh, M.A.; Jones, M.L.; Howard, C.B.; Mahler, S.M. Strategies for Selecting Membrane Protein-Specific Antibodies Using Phage Display with Cell-Based Panning. Antibodies 2017, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qu, L.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Zou, H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Marks, J.D.; Zhou, Y. High Throughput Identification of Monoclonal Antibodies to Membrane Bound and Secreted Proteins Using Yeast and Phage Display. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valldorf, B.; Hinz, S.C.; Russo, G.; Pekar, L.; Mohr, L.; Klemm, J.; Doerner, A.; Krah, S.; Hust, M.; Zielonka, S. Antibody Display Technologies: Selecting the Cream of the Crop. Biol. Chem. 2021, 403, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gera, N.; Hussain, M.; Rao, B.M. Protein Selection Using Yeast Surface Display. Methods 2013, 60, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bazzi, S.A.; Schmitz, F.; Tanno, H.; McDaniel, J.R.; Lee, C.-H.; Joshi, C.; Kim, J.E.; Monson, N.; Greenberg, B.M.; et al. Molecular Level Characterization of Circulating Aquaporin-4 Antibodies in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowarik, M.C.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Wemlinger, S.; Ritchie, A.M.; Hemmer, B.; Owens, G.P.; Bennett, J.L. The Cerebrospinal Fluid Immunoglobulin Transcriptome and Proteome in Neuromyelitis Optica Reveals Central Nervous System-Specific B Cell Populations. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowarik, M.C.; Astling, D.; Gasperi, C.; Wemlinger, S.; Schumann, H.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Ritchie, A.M.; Hemmer, B.; Owens, G.P.; Bennett, J.L. CNS Aquaporin-4-Specific B Cells Connect with Multiple B-Cell Compartments in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2017, 4, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisani, F.; Mastrototaro, M.; Rossi, A.; Nicchia, G.P.; Tortorella, C.; Ruggieri, M.; Trojano, M.; Frigeri, A.; Svelto, M. Identification of Two Major Conformational Aquaporin-4 Epitopes for Neuromyelitis Optica Autoantibody Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 9216–9224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawlings, A.E. Membrane Proteins: Always an Insoluble Problem? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Majdinasab, E.J.; Fiori, M.C.; Liang, H.; Altenberg, G.A. Polymer-Encased Nanodiscs and Polymer Nanodiscs: New Platforms for Membrane Protein Research and Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.P.; Ritchie, A.; Rossi, A.; Schaller, K.; Wemlinger, S.; Schumann, H.; Shearer, A.; Verkman, A.S.; Bennett, J.L. Mutagenesis of the Aquaporin 4 Extracellular Domains Defines Restricted Binding Patterns of Pathogenic Neuromyelitis Optica IgG. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 12123–12134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krohl, P.J.; Kim, K.B.; Lew, L.; VanDyke, D.; Ludwig, S.D.; Spangler, J.B. A Suspension Cell-Based Interaction Platform for Interrogation of Membrane Proteins. AIChE J. 2020, 66, e16995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lown, P.S.; Hackel, B.J. Magnetic Bead-Immobilized Mammalian Cells Are Effective Targets to Enrich Ligand-Displaying Yeast. ACS Comb. Sci. 2020, 22, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogen, J.P.; Storka, J.; Yanakieva, D.; Fiebig, D.; Grzeschik, J.; Hock, B.; Kolmar, H. Isolation of Common Light Chain Antibodies from Immunized Chickens Using Yeast Biopanning and Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 16, 2000240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Mastrototaro, M.; Rossi, A.; Pisani, F.; Tortorella, C.; Ruggieri, M.; Lia, A.; Trojano, M.; Frigeri, A.; Svelto, M. Aquaporin-4 Orthogonal Arrays of Particles Are the Target for Neuromyelitis Optica Autoantibodies. Glia 2009, 57, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.P.; Abbatemarco, J.R.; Galli, J.J.; Rodenbeck, S.J.; Peterson, L.K.; Haven, T.R.; Street, M.; Rose, J.W.; Greenlee, J.E.; Soldan, M.M.P.; et al. Aquaporin-4 Autoantibody Detection by ELISA: A Retrospective Characterization of a Commonly Used Assay. Mult. Scler. Int. 2021, 2021, 8692328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, A.E.; Shusta, E.V. A Novel High-Throughput Screen Reveals Yeast Genes That Increase Secretion of Heterologous Proteins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.X.; Cho, Y.K.; Shusta, E.V. Mining a Yeast Library for Brain Endothelial Cell-Binding Antibodies. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
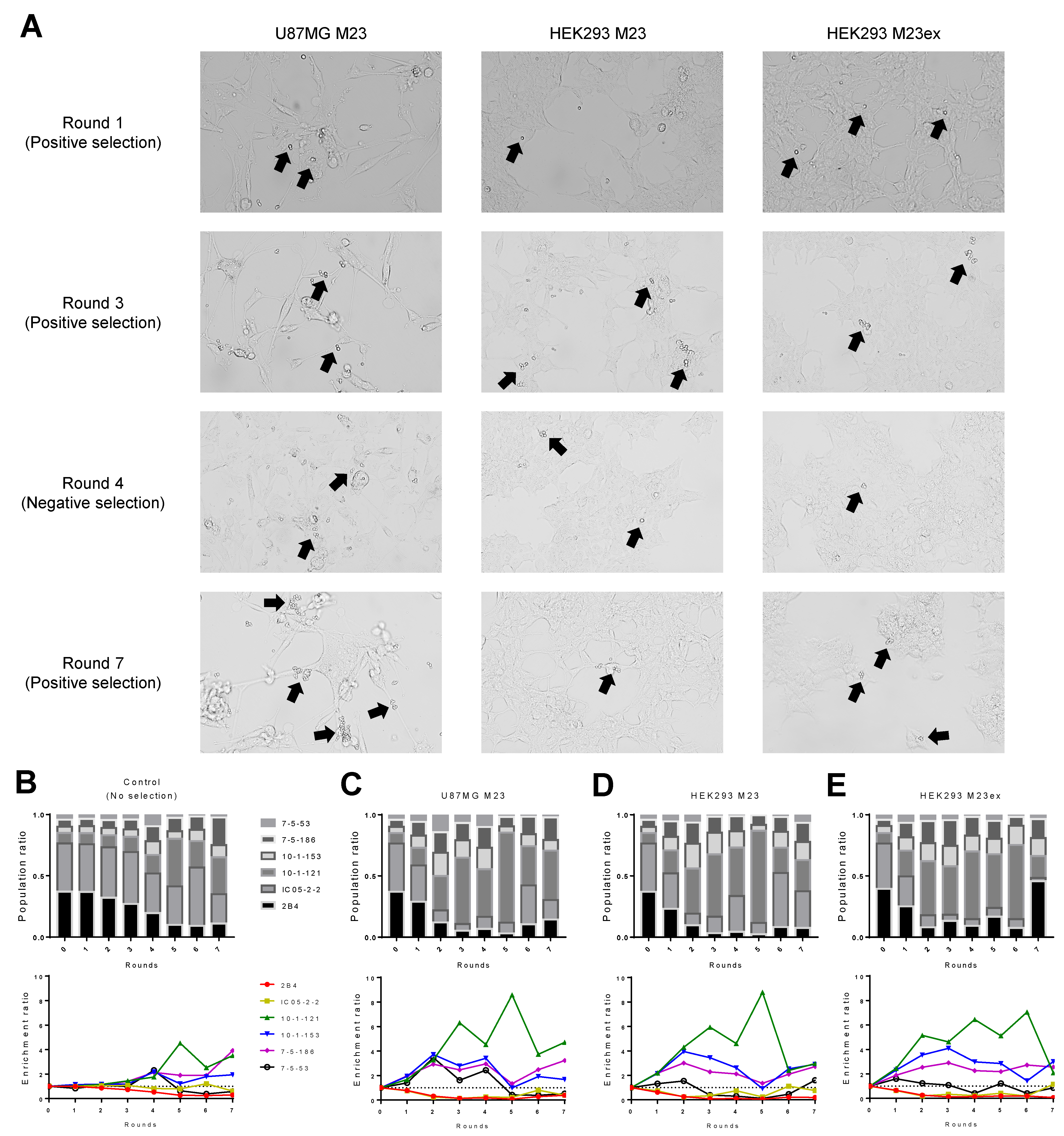
| Cell-Based Biopanning Round | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of yeast applied | 4.8 × 108 | 4.8 × 107 | 2.9 × 107 | 2.9 × 107 | 2.9 × 107 | 2.9 × 107 | 2.9 × 107 | |
| Yeast density (yeast/cm2) | 2.5 × 107 | 5.0 × 106 | 3.0 × 106 | 3.0 × 106 | 3.0 × 106 | 3.0 × 106 | 3.0 × 106 | |
| Surface area (cm2) | 19 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 9.5 | |
| Selection type | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | |
| U87MG M23 | Number of recovered yeast | N.D. | 9.1 × 103 | 3.9 × 104 | 1.4 × 107 | 3.3 × 107 | 8.4 × 104 | 9.0 × 103 |
| Percent recovery (%) | N.D. | 0.019 | 0.14 | 48 | 120 * | 0.30 | 0.032 | |
| HEK293 M23 | Number of recovered yeast | N.D. | 1.7 × 103 | 2.0 × 104 | 1.3 × 107 | 3.8 × 107 | 9.5 × 103 | 3.5 × 103 |
| Percent recovery (%) | N.D. | 0.0035 | 0.070 | 45 | 130 * | 0.033 | 0.012 | |
| HEK293 M23ex | Number of recovered yeast | N.D. | 1.4 × 103 | 1.8 × 104 | 1.4 × 107 | 2.7 × 107 | 1.3 × 104 | 3.0 × 103 |
| Percent recovery (%) | N.D. | 0.0028 | 0.063 | 49 | 93 | 0.044 | 0.011 | |
| Labeled Antigen FACS Round | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection Mode | Yield | Purity | Purity | Purity | Purity | |
| VL+ | Number of yeast applied | 5.0 × 106 | 5.0 × 106 | 5.0 × 106 | 2.5 × 106 | 2.5 × 106 |
| Number of recovered yeast * | 209,914 | 217,913 | 606,383 | 459,926 | 314,037 | |
| Percent recovery (%) | 4.2 | 4.4 | 12 | 18 | 13 | |
| M23 | Number of yeast applied | 5.0 × 107 | 5.0 × 107 | 5.0 × 107 | 5.0 × 107 | 5.0 × 107 |
| Number of recovered yeast * | 8693 | 1321 | 12,410 | 4047 | 1582 | |
| Percent recovery (%) | 0.017 | 0.0026 | 0.025 | 0.0081 | 0.0032 | |
| M23ex | Number of yeast applied | 5.0 × 107 | 5.0 × 107 | 5.0 × 107 | 5.0 × 107 | 5.0 × 107 |
| Number of recovered yeast * | 24,049 | 7576 | 19,967 | 31,089 | 13,227 | |
| Percent recovery (%) | 0.048 | 0.015 | 0.040 | 0.062 | 0.026 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, A.; Jin, W.; Fahad, A.S.; Mussman, B.K.; Nicchia, G.P.; Madan, B.; de Souza, M.O.; Griffin, J.D.; Bennett, J.L.; Frigeri, A.; et al. Strategies to Screen Anti-AQP4 Antibodies from Yeast Surface Display Libraries. Antibodies 2022, 11, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11020039
Huang A, Jin W, Fahad AS, Mussman BK, Nicchia GP, Madan B, de Souza MO, Griffin JD, Bennett JL, Frigeri A, et al. Strategies to Screen Anti-AQP4 Antibodies from Yeast Surface Display Libraries. Antibodies. 2022; 11(2):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11020039
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Aric, Wei Jin, Ahmed S. Fahad, Brooklyn K. Mussman, Grazia Paola Nicchia, Bharat Madan, Matheus Oliveira de Souza, J. Daniel Griffin, Jeffrey L. Bennett, Antonio Frigeri, and et al. 2022. "Strategies to Screen Anti-AQP4 Antibodies from Yeast Surface Display Libraries" Antibodies 11, no. 2: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11020039
APA StyleHuang, A., Jin, W., Fahad, A. S., Mussman, B. K., Nicchia, G. P., Madan, B., de Souza, M. O., Griffin, J. D., Bennett, J. L., Frigeri, A., Berkland, C. J., & DeKosky, B. J. (2022). Strategies to Screen Anti-AQP4 Antibodies from Yeast Surface Display Libraries. Antibodies, 11(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11020039






