Transformations in the Agricultural and Scenic Landscapes in the Northwest of the Region of Murcia (Spain): Moving towards Long Awaited (Un)Sustainability
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Objective
1.2. Justification and Interest in the Investigation
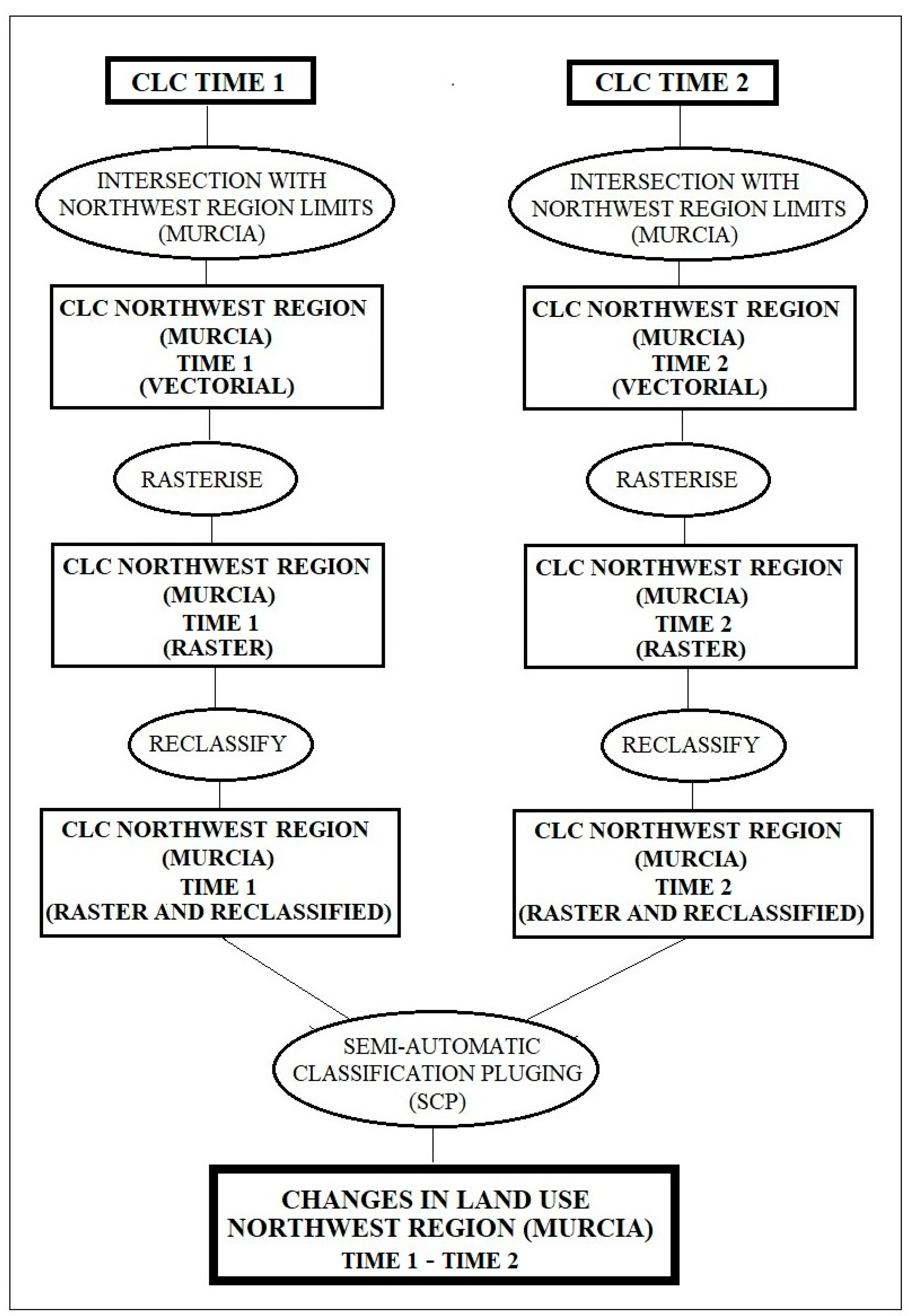
2. Materials and Methods
3. Study Area
4. Results
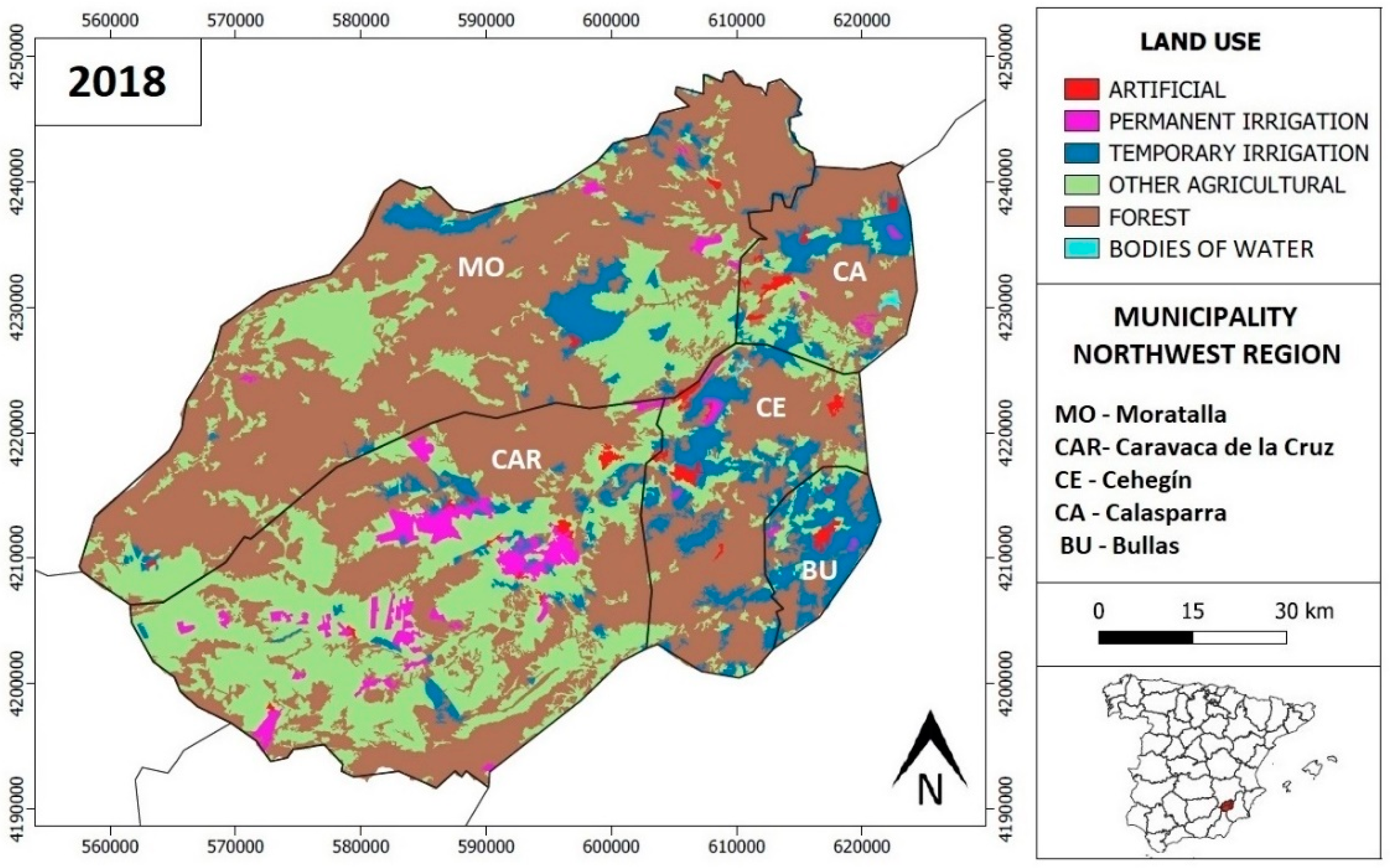
4.1. Recent Evolution of the Coverage and Land Use in the Northwest of the Region of Murcia (1990–2018)
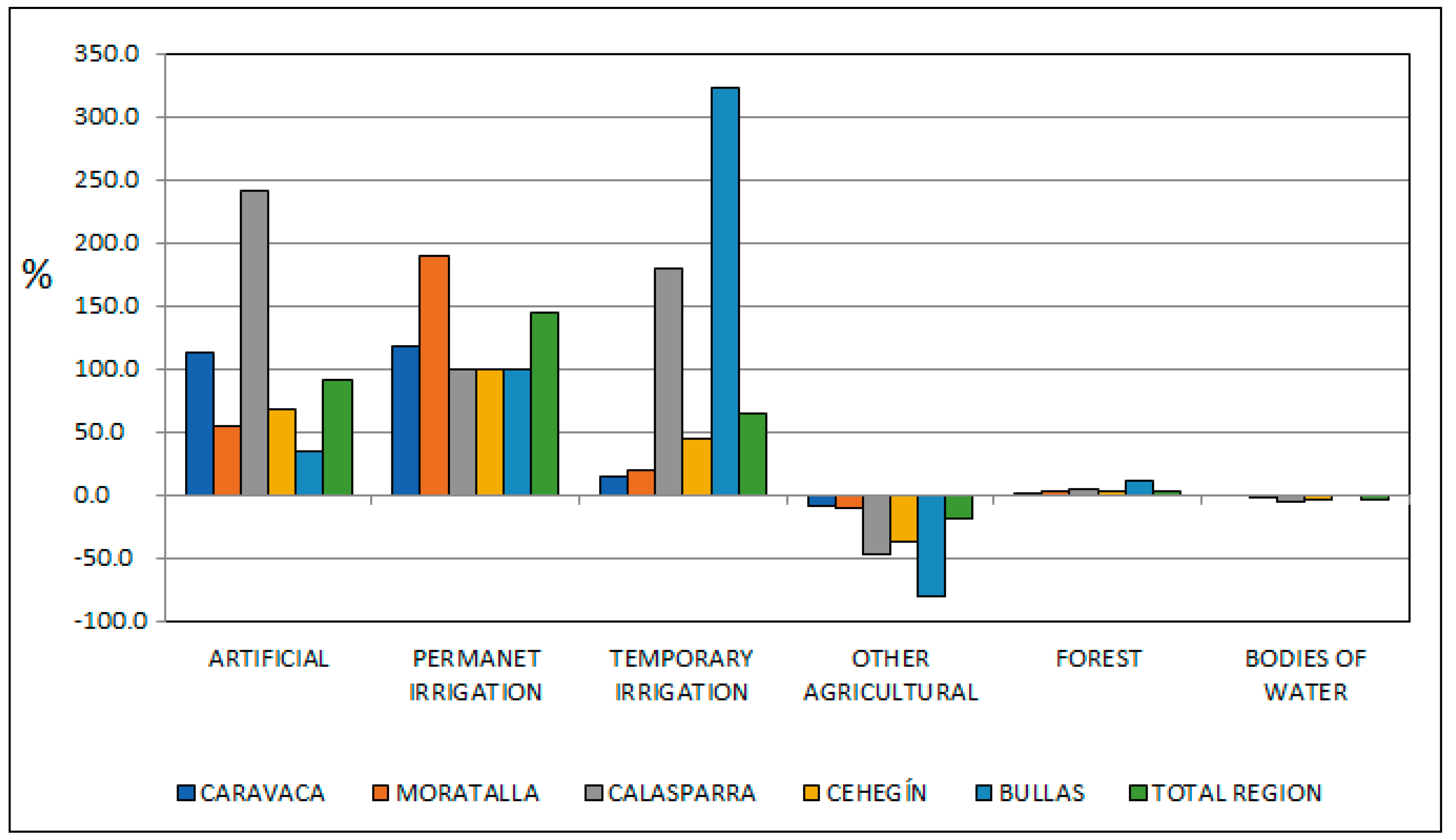
4.2. Transitions and Spatial Dynamics between Coverage and Land Use
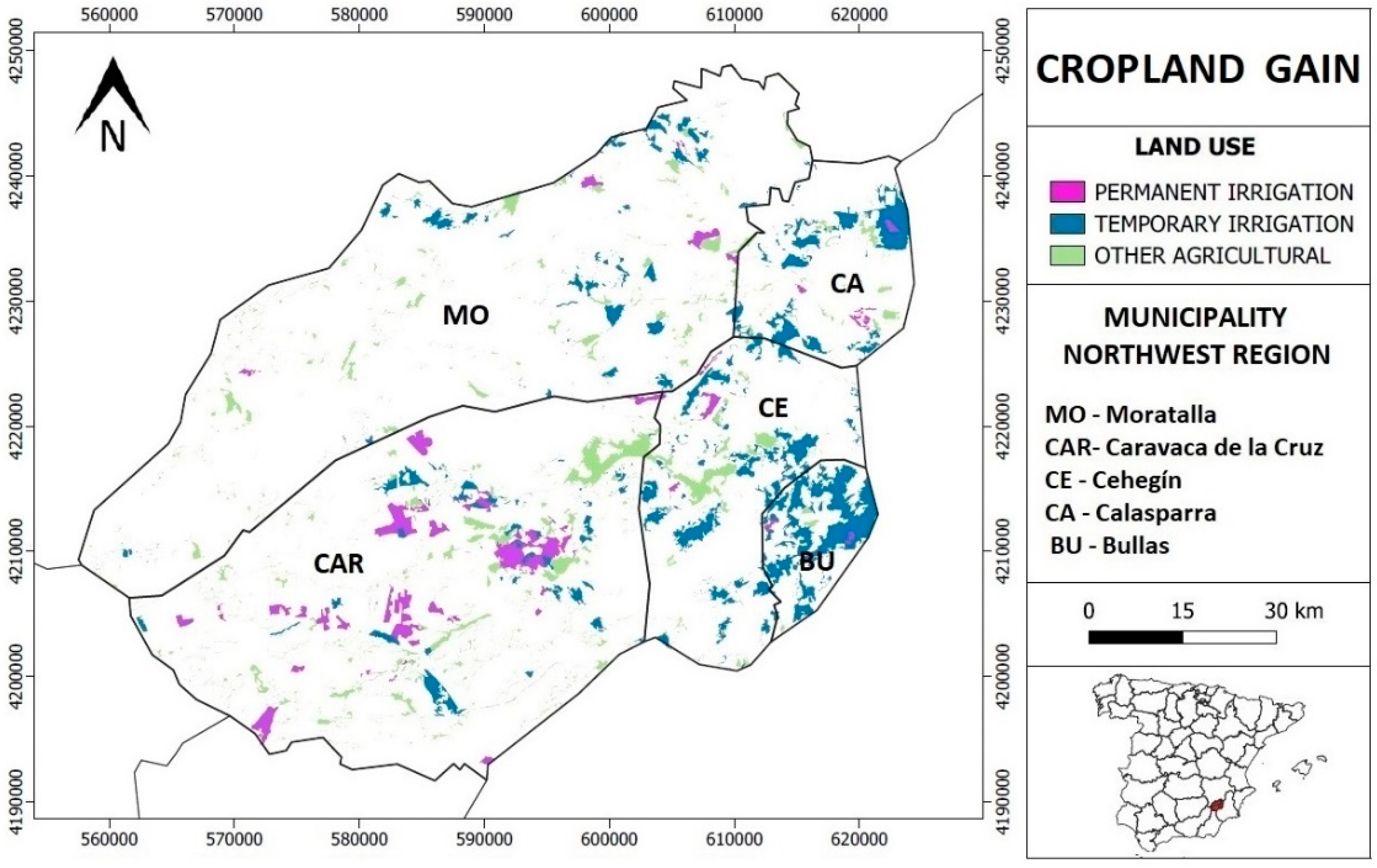
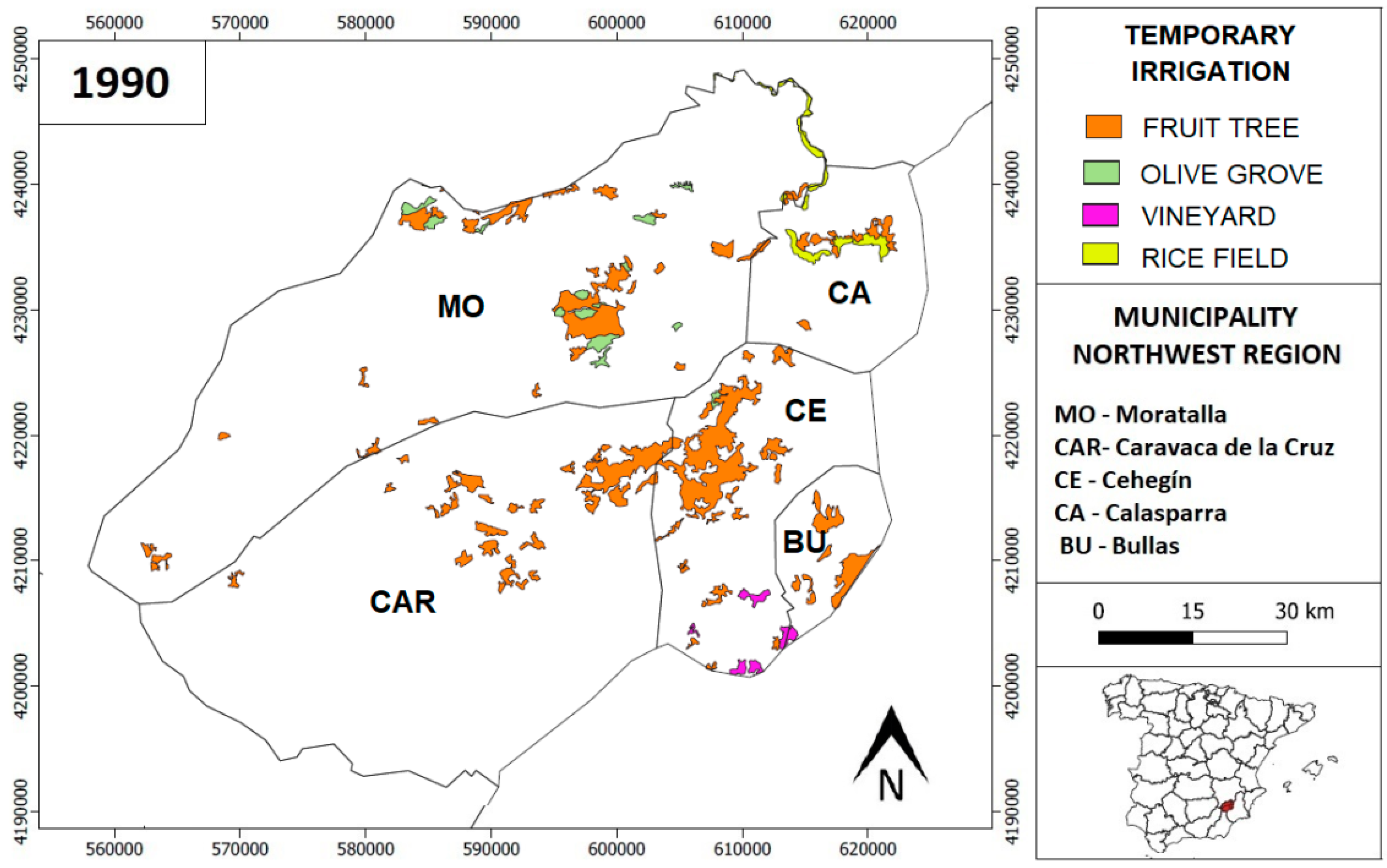
4.3. Evolution of Temporary Irrigation Crops
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Water limitation criteria: we propose applying indicators such as the Water Exploitation Index (WEI)7 and others.
- Profitability criteria: we suggest evaluating the profitability of irrigation after incorporating environmental costs.
- Environmental sustainability criteria: we recommend continuously analysing indicators on the quality status of water bodies, applying the Water Framework Directive. Likewise, we propose constantly examining indicators of circulating flows and even indicators of other impacts related to the energy balance or to the analysis of the life cycle of products.
- Territorial sustainability criteria: we propose identifying irrigation systems located outside their areas of vocation or natural aptitude and to recognise the need to preserve crops with high cultural and environmental values (particularly traditional irrigation systems with a high diversity and mosaic crops). Being located in or not in the territory of the owners of agricultural companies may constitute another factor for the assessment of this territorial dimension.
- The social viability criteria are a more open and complex question. Obviously, it is not easy to precisely define what is considered irrigation for social interest. Therefore, it is perhaps more useful to replace this concept, which may be ambiguous, with more specific operational criteria, such as the impact on local employment, the distribution of costs and benefits, or the identification of irrigated areas with high social conflict. In this sense, irrigation with high environmental costs and a low social profitability (large landowners, little distributed wealth, low-quality temporary employment) would be a candidate for a reduction in the irrigated area.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arahuetes, A.; Hernández, M.; Rico, A.M. Adaptation strategies of the hydrosocial cycles in the Mediterranean region. Water 2018, 10, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, S.; Rico, A.M. Assessing technical and social driving factors of water reuse in agriculture: A review on risks, regulation and the yuck factor. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.; Garrido, A.; Llamas, M.R.; Varela, C. La huella hidrológica de la agricultura española. Ing. Agua 2009, 16, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- WWAP. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2015: Water for a Sustainable World; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2015; ISBN 978-92-3-100071-3. [Google Scholar]
- Caparrós-Martínez, J.L.; Rueda-Lópe, N.; Milán-García, J.; de Pablo Valenciano, J. Public policies for sustainability and water security: The case of Almeria (Spain). Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A. Aspectos Geográficos de la Horticultura de ciclo Manipulado en España; Secretariado de Publicaciones-Universidad de Alicante: Alicante, Spain, 2007; ISBN 978-84-7908-354-0. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, A. Agua y territorio en la Región de Murcia; Fundación Centro de Estudios Históricos e Investigaciones Locales Región de Murcia: Murcia, Spain, 2001; ISBN 84-921128-7-5. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, F. Les paysages de l’horticulture de cycle forcé en Espagne. Enquêtes Rural. 2002, 8, 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, A. Escasez y rentabilidad del agua en el Sureste de España: Agricultura de vanguardia, huertas tradicionales, nuevos regadíos y medio ambiente en el valle del Segura. In Medio Ambiente y Crisis Rural; Fundación Duques de Soria-Universidad de Valladolid: Valladolid, Spain, 1996; pp. 131–157. ISBN 84-7762-657-X. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, A. Agua y agricultura: Transformaciones recientes, problemas medioambientales y socioeconómicos. Geographicalia 1997, 34, 67–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geteches, H.D. Spain’s Ebro River Transfers: Test Case for Water Policy in the European Union. Water Resour. Dev. 2003, 19, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swyngedouw, E. Liquid Power: Contested Hydro-Modernities in Twentieth-First Century Spain; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978026202903213. [Google Scholar]
- López, E. Agua para todos: A new regionalist hydraulic paradigm in Spain. Water Altern. 2009, 2, 370–394. [Google Scholar]
- López, E.; De Stefano, L. Between a rock and a hard place: Re-defining water security, decentralisation and the elusive “Water Pact” in Spain. In Federal Rivers. Managing Water in Multi-Layered Political Systems; Garrick, D.E., Ed.; Eduard Elgal: Northampton, UK, 2015; pp. 158–176. ISBN 1843393158. [Google Scholar]
- Saurí, D.; Del Moral, L. Recent developments in Spanish water policy. Alternatives and conflicts at the end of the hydraulic age. Geoforum 2001, 32, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, A.M. Plan Hidrológico Nacional y Programa A.G.U.A.: Repercusión en las Regiones de Murcia y Valencia. Investig. Geográficas 2010, 51, 235–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swyngedouw, E. Into the sea: Desalination as hydro-social fix in Spain. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2013, 103, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swyngedouw, E.; Williams, J. From Spain’s hydro-deadlock to the desalination fix. Water Int. 2016, 41, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, H.; Saurí, D.; Rico, A.M. The end of scarcity? Water desalination as the new cornucopia for Mediterranean Spain? J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2642–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, R. Nuevos regadíos y cambio territorial: El caso del levante de Almería. In Historia, Clima y Paisaje. Estudios geográficos En memoria del profesor Antonio López Gómez; Universidad de Valencia, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid y Universidad de Alicante: Valencia, Spain, 2005; pp. 513–528. ISBN 84-370-5864-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, J.M.; Gil, E.; García, R. El Antes y Después de la Modernización De Regadíos. la Experiencia de Mula; Editum: Murcia, Spain, 2006; ISBN 978-84-8371-617-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, E.; Gómez, J.M. Los paisajes rurales del Campo de Cartagena- Mar Menor. Del riego itinerante a la factoría bajo cubierta. In Atlas de Los Paisajes Agrarios de España, Ministerio de Agricultura; Alimentación y Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2013; pp. 543–552. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, T. Sobreexplotación de acuíferos y desertificación en el Sureste español. In Aridez, Salinización y agricultura en el Sureste Ibérico; Gil, A., Morales, A., Torres, F.J., Eds.; Fundación Ramón Areces-Instituto Euromediterráneo de Hidrotecnia: Madrid, Spain, 2004; pp. 105–134. ISBN 84-8004-672-4. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, M.C.; Urrestarazu, M.; Valera, D. La contaminación por nitratos en los sistemas agrícolas. Vida Rural 2003, 179, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, E.J. Agricultura, contaminación y protección de acuíferos. In Gestión y Contaminación de recursos hídricos: Problemas y soluciones; Pulido, A., Vallejos, A., Eds.; Servicio de Publicaciones-Universidad de Almería: Almería, Spain, 2003; pp. 277–280. ISBN 84-8240-662-0. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero Pedraza, A.; Romero Díaz, A.; Espinosa Soto, I. Cambios paisajísticos y efectos medioambientales debidos a la agricultura intensiva en la Comarca de Campo de Cartagena-Mar Menor (Murcia). Estud. Geográficos 2015, 76, 473–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, D. The New Imperialism; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-19-926431-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlers, R. Fixing and nixing: The politics of water privatization. Rev. Radic. Political Econ. 2010, 42, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, D. Justice, Nature & the Geography of Difference; Blackwell Publishers: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-1-557-86681-3. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, F.; Ruiz, P.; Martínez, J. Prospectiva 2030 en los cambios de ocupación del suelo en España y sus impactos en el ciclo hidrológico. 2008. Available online: https://www.zaragoza.es/contenidos/medioambiente/cajaAzul/13S5-P2-PRIETO_RUIZ_ACC.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2020).
- Gil Olcina, A. La propiedad del agua en los grandes regadíos deficitarios del sureste peninsular: El ejemplo del Guadalentín. Agric. Y Soc. 1981, 35, 203–231. [Google Scholar]
- Alberola-Romá, A. Propiedad, control y gestión del agua en regadíos deficitarios del Sureste español: La Huerta de Alicante durante la Edad Moderna. Minius 2015, 23, 7–40. [Google Scholar]
- Swyngedouw, E. Accumulation by dispossession: Privatizing H2O. Capital. Nat. Soc. 2005, 16, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subra, P. Geopolitics: A Unique or Multidimensional Concept? Place, Issues and Tools of Local Geopolitics. Hérodote 2012, 3, 45–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mora, N.; Del Moral Ituarte, L.; La-Roca, F.; La Calle, A.; Schmidt, G. Interbasin water transfers in Spain: Interregional conflicts and governance responses. In Globalized Water; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morote, Á.F.; Olcina, J.; Rico, A.M. Challenges and proposals for socio-ecological sustainability of the tagus–segura aqueduct (Spain) under climate change. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morote, A.F.; Hernández, M.; Rico, A.M.; Eslamian, S. Interbasin water transfer conflicts. The case of the Tagus-Segura Aqueduct (Spain). Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 364–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baños, P.; Pérez, I.; Pedreño, A. Aportaciones desde la investigación social al debate sobre agua y regadío. Rev. Cienc. Soc. 2009, 8, 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Calatrava, J.; Martínez-Granados, D. El valor del uso del agua en el regadío de la cuenca del Segura y en las zonas regables del trasvase Tajo-Segura. Econom. Agrari. Y Recur. Nat. 2012, 12, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morote, Á.F.; Olcina, J.; Hernández, M. The use of non-conventional water resources as a means of adaptation to drought and climate change in Semi-Arid Regions: South-Eastern Spain. Water 2019, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Fernández, J.M.; Esteve Selma, M.A.; Baños, I.; Carreño, F.; Moreno, A. Dynamics and sustainability of Mediterranean traditional irrigated lands. In Handbook of Sustainable Development Planning; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2013; pp. 245–274. ISBN 9780857932150. [Google Scholar]
- Alcon, F.; De-Miguel, M.D.; Martínez-Paz, J.M. Assessment of real and perceived cost-effectiveness to inform agricultural diffuse pollution mitigation policies. Land Use Policy 2020, 104561, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colino Sueiras, J.; Martínez Paz, J.M. El agua en la agricultura del sureste español: Productividad, precio y demanda. Mediterr. Económ. 2002, 2, 199–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gil Meseguer, E. La Región de Murcia, un laboratorio de experiencias de ahorro y eficiencia en el uso del agua: La modernización de sus regadíos, entre las políticas agraria y ambiental de la Unión Europea. Papel. Geogr. 2010, 51–52, 131–145. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Fernández, J.; Esteve Selma, M.A. Sequía estructural y algunas externalidades ambientales en los regadíos de la cuenca del Segura. Ing. Agua 2020, 7, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vivo, J.M.; Callejón, J. Análisis de los sectores productivos en la región de Murcia a partir del Valor Añadido Bruto. Cuad. Econ. Murc. 2005, 16, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, F. Sureste español: Regadío, tecnologías hidráulicas y cambios territoriales. Scr. Nova. Rev. Electrónica Geogr. Y Cienc. Soc. 2006, 10, 218. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, E. Los paisajes agrarios de la Región de Murcia. Pap. Geogr. 2006, 43, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- García, R. Transformaciones recientes en las pequeñas huertas del noroeste murciano: Espacios de tradición y de gran valor paisajístico y ambiental. Pap. Geogr. 2010, 51, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, P.; Pedreño, A. La hortofruticultura intensiva de la Región de Murcia: Un modelo productivo diferenciado. In La agricultura española en la era de la globalización; Etxezarreta, Miren (Coordinator); Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación: Madrid, Spain, 2006; pp. 369–422. ISBN 84-491-0748-2. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, C.L. Our visual landscape: Managing the landscape under special consideration of visual aspects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 54, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, J. The Cultural Values Model: An integrated approach to values in landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2008, 84, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, G.; Ponce, M.D. Pareceres sobre la Huerta del Bajo Segura. El Poder de la Identidad y la Cultura en la valoración del Paisaje; Universidad de Alicante: Alicante, Spain, 2016; ISBN 978-84-16724-32-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pedreño, A.; Baños, P. Las aguas subterráneas y la política del desconcierto. In Agricultura familiar en España; Moyano, E., Coord, Eds.; Fundación de Estudios Rurales y Unión de Pequeños Agricultores: Madrid, Spain, 2006; pp. 106–116. [Google Scholar]
- Baños, P.; Pedreño, A.; Pérez, I. Cuando los cultivos de regadío se orientan exitosamente al mercado: Expansión territorial sin límite y efectos ambientales sobre recursos básicos en la Región de Murcia. In VI Congreso Ibérico sobre Gestión y Planificación del Agua; Fundación Nueva Cultura del Agua: Vitoria, Spain, 2008; Available online: https://fnca.eu/biblioteca-del-agua/directorio/file/1060-1306271427-ppt-c0303 (accessed on 4 July 2020).
- Vargas, E.; Pintado, P. The challenge of climate change in Spain. Water resources, agriculture and land. J. Hidrol. 2014, 518, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senent, J.; Pérez, J.; Bielsa, A.M. Assessment of Sustainability in Semiarid Mediterranean Basins: Case Study of the Segura Basin, Spain. Tecnol. Y Cienc. Agua 2016, 7, 67–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, V.; Belmonte, F.; García, R. Analysis of precipitations trends in the Region of Murcia (Southeast Spain) over the period 1956–2015. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Meteorology and Climatology of the Mediterranean, Zagreb, Croatia, 20–22 February 2017; pp. 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Miró, J.J.; Estella, M.J.; Caselles, V.; Gómez, I. Spatial and temporal rainfall changes in the Júcar and Segura basins (1955–2016): Fine-scale trends. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 38, 4699–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senent, J.; Pérez, J.; Carillo, J.; Soto, J. Using SWAT and Fuzzy TOPSIS to assess the impact of climate change in the headwaters of Segura River Basin (SE Spain). Water 2017, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.L.; Senent, M.; Martínez, D.; Aragón, R. La sobreexplotación de acuíferos. In Sobreexplotación de Acuíferos en la Cuenca del Segura. Evaluación y Perspectivas; Senent, M., García, J.L., Eds.; Instituto Euromediterráneo del Agua: Murcia, Spain, 2014; pp. 63–112. ISBN 978-84-92988-22-8. [Google Scholar]
- Stake, R.E. Evaluación Comprensiva y Evaluación Basada en Estándares; Editorial Graó-Colección Crítica y Fundamentos: Barcelona, Spain, 2006; ISBN 84-7827-418-9. [Google Scholar]
- Salkind, N.J. Exploring Research; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0-205-09381-6. [Google Scholar]
- Buzai, G.D.; Baxendale, C. Aportes del análisis geográfico con Sistemas de Información Geográfica como herramienta teórica, metodológica y tecnológica para la práctica del ordenamiento territorial. Pers. Y Soc. 2013, 27, 113–141. [Google Scholar]
- Liverman, D.; Moran, E.F.; Rindfuss, R.R.; Stern, P.C. People and Pixels; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-309-06408-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo, M. Cambios de Usos del Suelo y Simulación de Escenarios en la Comunidad de Madrid; Universidad Complutense: Madrid, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Congedo, L. Semi-automatic classification documentation. Release 2016, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G.; Shusas, E.; McEachern, M. Detecting important categorical land changes while accounting for persistence. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 101, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.; Quiñonero, J.M.; García, R.; Martín de Valmaseda, E.; Sánchez, M.C.; Chocano, C.; Guerrero, F. Fuentes y manantiales de la Cuenca del Segura: Región de Murcia; Instituto Euromediterráneo del Agua and Confederación Hidrográfica del Segura: Murcia, Spain, 2016; ISBN 978-84-92988-24-2. [Google Scholar]
- Espejo, C. El olivar. Un cultivo en retroceso en la Región de Murcia. Pap. Geogr. 1989, 15, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Andrés, J.L. Significado del distrito industrial de la piedra y el mármol en el desarrollo local. In Estudios sobre Desarrollo Regional; Servicio de Publicaciones de la Universidad de Murcia: Murcia, Spain, 2008; pp. 61–94. ISBN 978-84-8371-794-3. [Google Scholar]
- Millán, M. Análisis de la dinámica de un municipio impactado por el turismo rural. El ejemplo de Moratalla. Cuad. Tur. 1998, 1, 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Chocano, C.; Sánchez, C.; López, F. La agroecología como alternativa a la prevención y lucha contra la desertificación en la Región de Murcia: La Comarca del Noroeste. Agroecología 2007, 2, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, C.; Cánovas, F. Identificación de áreas abandonadas en la Región de Murcia. In Abandono de Cultivos en la Región de Murcia: Consecuencias Ecogeomorfológicas; Romero, A., Ed.; Universidad de Murcia: Murcia, Spain, 2016; pp. 63–84. ISBN 978-84-16551-37-8. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, F.; Martínez, C.; Serrato, F.; Fernández, M.A. Principales causas del abandono de cultivos en la Región de Murcia. In Abandono de Cultivos en la Región de Murcia: Consecuencias Ecogeomorfológicas; Romero, A., Ed.; Universidad de Murcia: Murcia, Spain, 2016; pp. 203–226. ISBN 978-84-16551-37-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rupérez-Moreno, C.; Senent-Aparicio, J.; Martínez-Vicente, D.; García-Aróstegui, J.L.; Cabezas Calvo-Rubio, F.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Sustainability of irrigated agriculture with overexploited aquifers: The case of Segura basin (SE, Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 182, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.; Sánchez, M.C. Manantiales de la Comarca del Noroeste de la Región de Murcia: Un patrimonio natural amenazado. Pap. Geogr. 2010, 51–52, 169–188. [Google Scholar]
- Martín de Santa Olalla, F.; Brasa Ramos, A.; Fabeiro Cortes, C.; Fernández González, D.; López Córcoles, H. Improvement of irrigation management towards the sustainable use of groundwater in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecina, S.; Isidoro, D.; Playán, E.; Aragüés, R. Irrigation modernization and water conservation in Spain: The case of Riegos del Alto Aragón. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conan, C.; de Marsily, G.; Bouraoui, F.; Bidoglio, G. A long-term hydrological modelling of the Upper Guadiana river basin (Spain). Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 28, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.F.; De Juan, J.A.; Tarjuelo, J.M. Evaluation of the water cost effect on water resource management: Application to typical crops in a semiarid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 66, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santa Olalla, F.M.; Dominguez, A.; Ortega, F.; Artigao, A.; Fabeiro, C. Bayesian networks in planning a large aquifer in Eastern Mancha, Spain. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Fernández, J.; Esteve Selma, M.A. The dynamics of water scarcity on irrigated landscapes: Mazarrón and Aguilas in south-eastern Spain. System Dynamics Review. J. Syst. Dyn. Soc. 2004, 20, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Legaz, B.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Picón, A.S.; Pugnaire, F.I. Trade-offs between maintenance of ecosystem services and socio-economic development in rural mountainous communities in southern Spain: A dynamic simulation approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | Summary of the manifesto in Diario la Crónica Independiente (22 March 2018). Available at: http://lacronicaindependiente.com/2018/03/segura-transparente-exige-a-la-ministra-de-agricultura-que-ponga-por-fin-orden-en-la-cuenca/. |
| 2 | Caravaca: municipality of the Region of Murcia located in the Northwest region. |
| 3 | |
| 4 | Diario (Newspaper) La Verdad (18 April 2018): http://soydecaravaca.laverdad.es/actualidad/denuncian-transformacion-2000-20180418010843-ntvo.html. |
| 5 | Royal Decree 1/2016 of January 8 (BOE of 19 January 2016), which approved the revision of numerous Hydrological Plans of different river basins, including the river basin zone of the Segura river. More information at: http://www.chsegura.es/chs/planificacionydma/planificacion15-21/. |
| 6 | Most commonly reported as quantitative and qualitative. |
| 7 | The WEI index (Water Exploitation Index) is used as an indicator of the pressure that water extraction exerts on available water resources, and allows identification of the areas most likely to suffer water stress. This indicator is calculated as the quotient between the average annual freshwater withdrawal and the long-term average of the available resource. A result above 20.0% indicates the presence of water stress, and greater than 40.0% a strong competition for water with difficulty in maintaining associated ecosystems. |







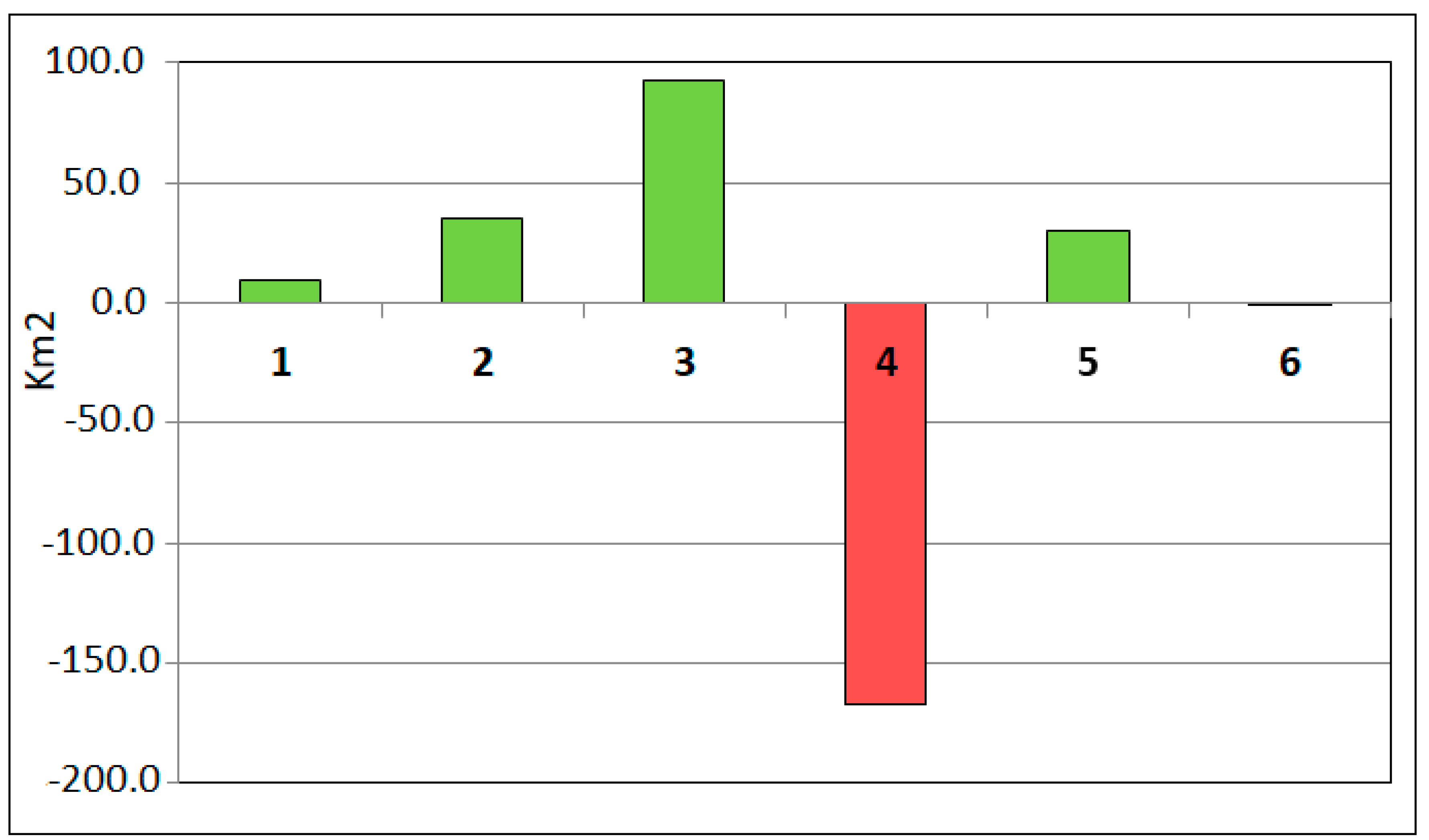

| Time 2 | Total Time 1 | Loss | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category 1 | Category 2 | Category 3 | ||||
| Time 1 | Category 1 | P11 | P12 | P13 | P1+ | P1+–P11 |
| Category 2 | P21 | P22 | P23 | P2+ | P1+–P22 | |
| Category 3 | P31 | P32 | P33 | P3+ | P3+–P33 | |
| Total Time 2 | P + 1 | P + 2 | P + 3 | |||
| Gain | P + 1−P11 | P + 2–P22 | P + 3–P33 | |||
| Surface (Km2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use | 1990 | 2000 | 2012 | 2018 |
| Artificial | 10.5 | 13.7 | 19.3 | 20.1 |
| Permanet Irrigation | 24.4 | 41.7 | 88.4 | 59.4 |
| Temporary Irrigation | 145.3 | 158.4 | 204.9 | 237.9 |
| Other Agricultural | 886.8 | 855.5 | 725.0 | 719.8 |
| Forest | 1308.4 | 1306.2 | 1338.0 | 1338.1 |
| Bodies of Water | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| Total | 2378 | 2378 | 2378 | 2378 |
| Surface 1990 (Km2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use | Caravaca | Moratalla | Calasparra | Cehegín | Bullas | Total |
| Artificial | 2.5 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 3.9 | 1.9 | 10.5 |
| Permanet Irrigation | 23.0 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 24.4 |
| Temporary Irrigation | 29.3 | 47.4 | 13.2 | 44.2 | 11.2 | 145.3 |
| Other Agricultural | 429.5 | 259.3 | 71.8 | 76.9 | 49.3 | 886.8 |
| Forest | 373.1 | 643.7 | 96.9 | 175.1 | 19.5 | 1308.4 |
| Bodies of Water | 0.0 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 2.5 |
| Total | 857.4 | 953.1 | 184.6 | 300.8 | 82.0 | 2378.0 |
| Surface 2018 (Km2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use | Caravaca | Moratalla | Calasparra | Cehegín | Bullas | Total |
| Artificial | 5.3 | 1.4 | 4.3 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 20.1 |
| Permanent Irrigation | 50.0 | 4.2 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 59.6 |
| Temporary Irrigation | 33.7 | 56.3 | 37.0 | 63.7 | 47.2 | 237.9 |
| Other Agricultural | 389.6 | 233.9 | 38.0 | 48.5 | 9.8 | 719.8 |
| Forest | 378.9 | 657.0 | 101.9 | 178.9 | 21.6 | 1338.1 |
| Bodies of Water | 0.0 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 2.4 |
| Total | 857.4 | 953.1 | 184.6 | 300.8 | 82.0 | 2378.0 |
| 2018 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Total | Losses | ||
| 1990 | 1 | 8.5 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 10.5 | 2.0 |
| 2 | 0.2 | 12.7 | 1.0 | 10.1 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 24.4 | 11.7 | |
| 3 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 95.4 | 35.4 | 8.9 | 0.0 | 145.3 | 49.9 | |
| 4 | 5.9 | 41.6 | 124.6 | 614.2 | 100.4 | 0.1 | 886.8 | 272.6 | |
| 5 | 3.5 | 1.7 | 16.1 | 59.4 | 1227.5 | 0.2 | 1308.4 | 80.9 | |
| 6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 0.4 | |
| Total | 20.1 | 59.6 | 237.9 | 719.8 | 1338.1 | 2.4 | 2378.0 | 417.5 | |
| Gains | 11.6 | 46.9 | 142.5 | 105.6 | 110.6 | 0.3 | 417.5 | ||
| Surface Temporary Irrigation 1990–2018 (km2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruit Free | Olive Grove | Vineyard | Rice Field | Total | ||
| Caravaca | 1990 | 29.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 29.3 |
| 2018 | 31.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 33.7 | |
| Moratalla | 1990 | 34.3 | 10.0 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 47.4 |
| 2018 | 50.5 | 3.5 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 56.3 | |
| Calasparra | 1990 | 6.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 7.1 | 13.2 |
| 2018 | 29.2 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 6.1 | 36.9 | |
| Cehegín | 1990 | 39.0 | 0.8 | 4.4 | 0.0 | 44.2 |
| 2018 | 55.9 | 2.7 | 5.2 | 0.0 | 63.7 | |
| Bullas | 1990 | 10.6 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 11.2 |
| 2018 | 44.5 | 0.0 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 47.2 | |
| Total | 1990 | 119.4 | 10.7 | 5.0 | 10.3 | 145.3 |
| 2018 | 211.3 | 9.1 | 9.3 | 8.1 | 237.9 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Marín, R.; Espejo-Marín, C.; Giménez-García, R.; Ruiz-Álvarez, V. Transformations in the Agricultural and Scenic Landscapes in the Northwest of the Region of Murcia (Spain): Moving towards Long Awaited (Un)Sustainability. Land 2020, 9, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9090314
García-Marín R, Espejo-Marín C, Giménez-García R, Ruiz-Álvarez V. Transformations in the Agricultural and Scenic Landscapes in the Northwest of the Region of Murcia (Spain): Moving towards Long Awaited (Un)Sustainability. Land. 2020; 9(9):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9090314
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Marín, Ramón, Cayetano Espejo-Marín, Rubén Giménez-García, and Víctor Ruiz-Álvarez. 2020. "Transformations in the Agricultural and Scenic Landscapes in the Northwest of the Region of Murcia (Spain): Moving towards Long Awaited (Un)Sustainability" Land 9, no. 9: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9090314
APA StyleGarcía-Marín, R., Espejo-Marín, C., Giménez-García, R., & Ruiz-Álvarez, V. (2020). Transformations in the Agricultural and Scenic Landscapes in the Northwest of the Region of Murcia (Spain): Moving towards Long Awaited (Un)Sustainability. Land, 9(9), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9090314






