Industrial Sprawl and Residential Housing: Exploring the Interplay between Local Development and Land-Use Change in the Valencian Community, Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
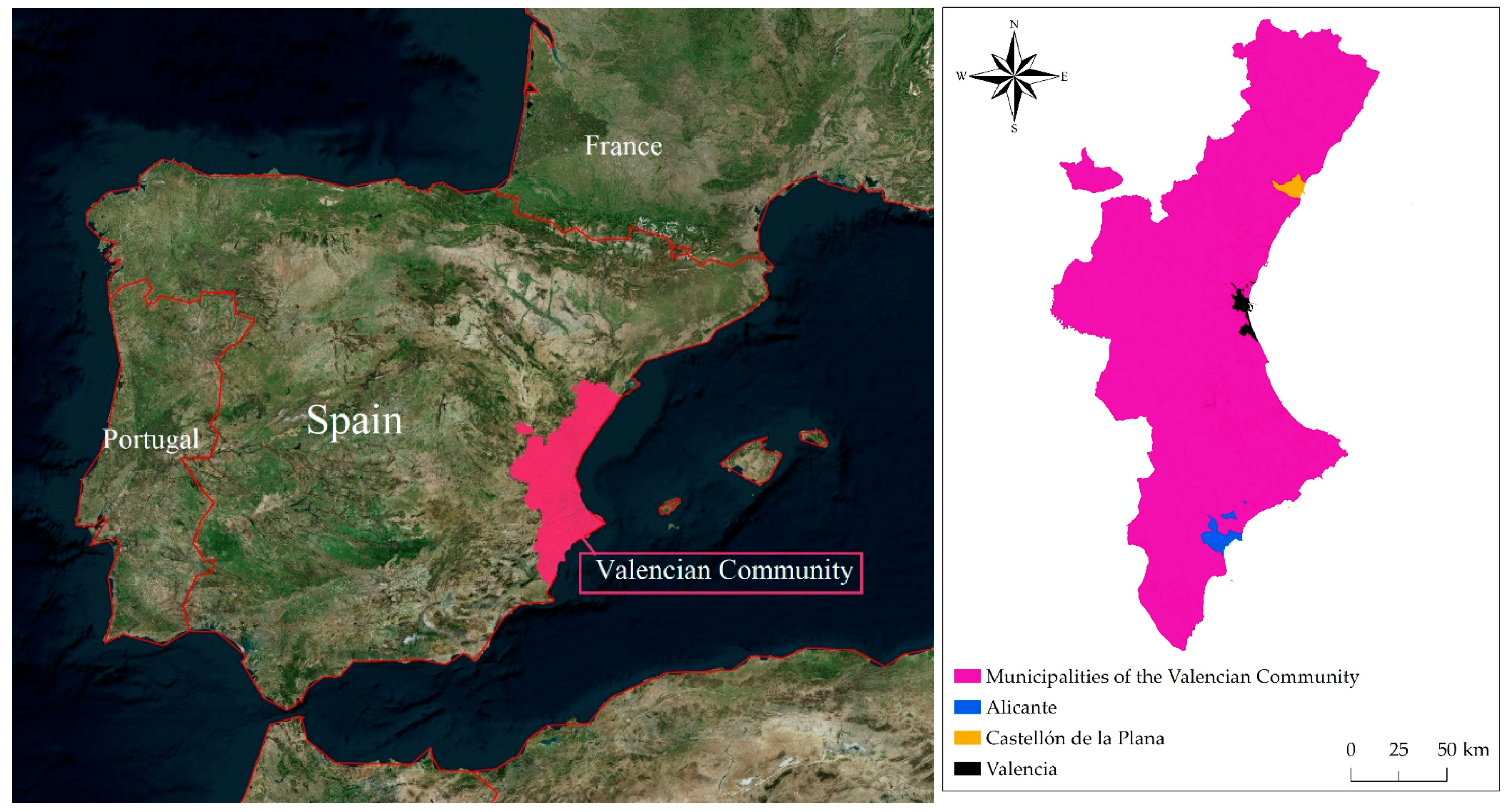
2.1. Case Study
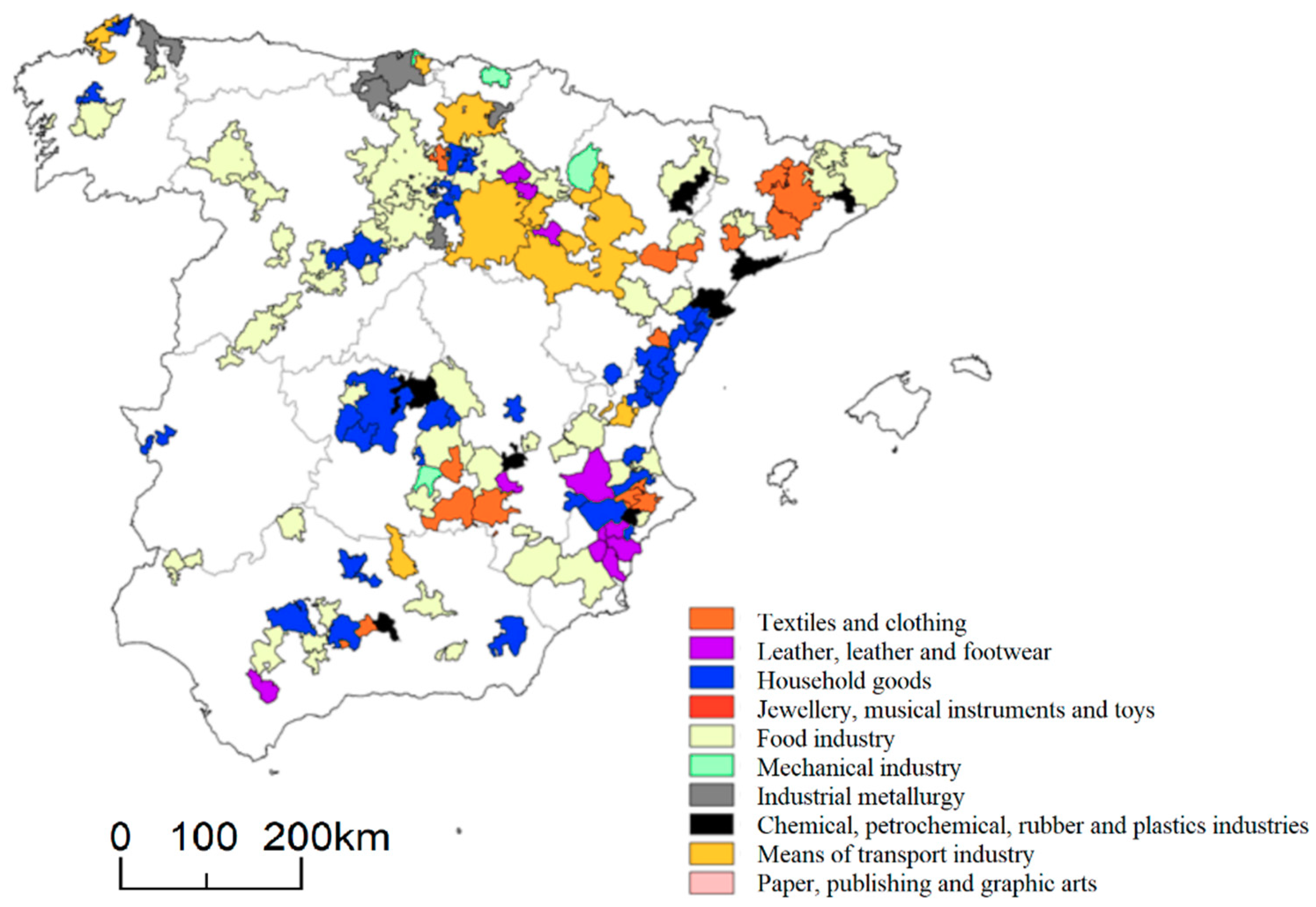
2.2. The Industrial Context
2.3. Indicators
2.4. Cluster Analysis
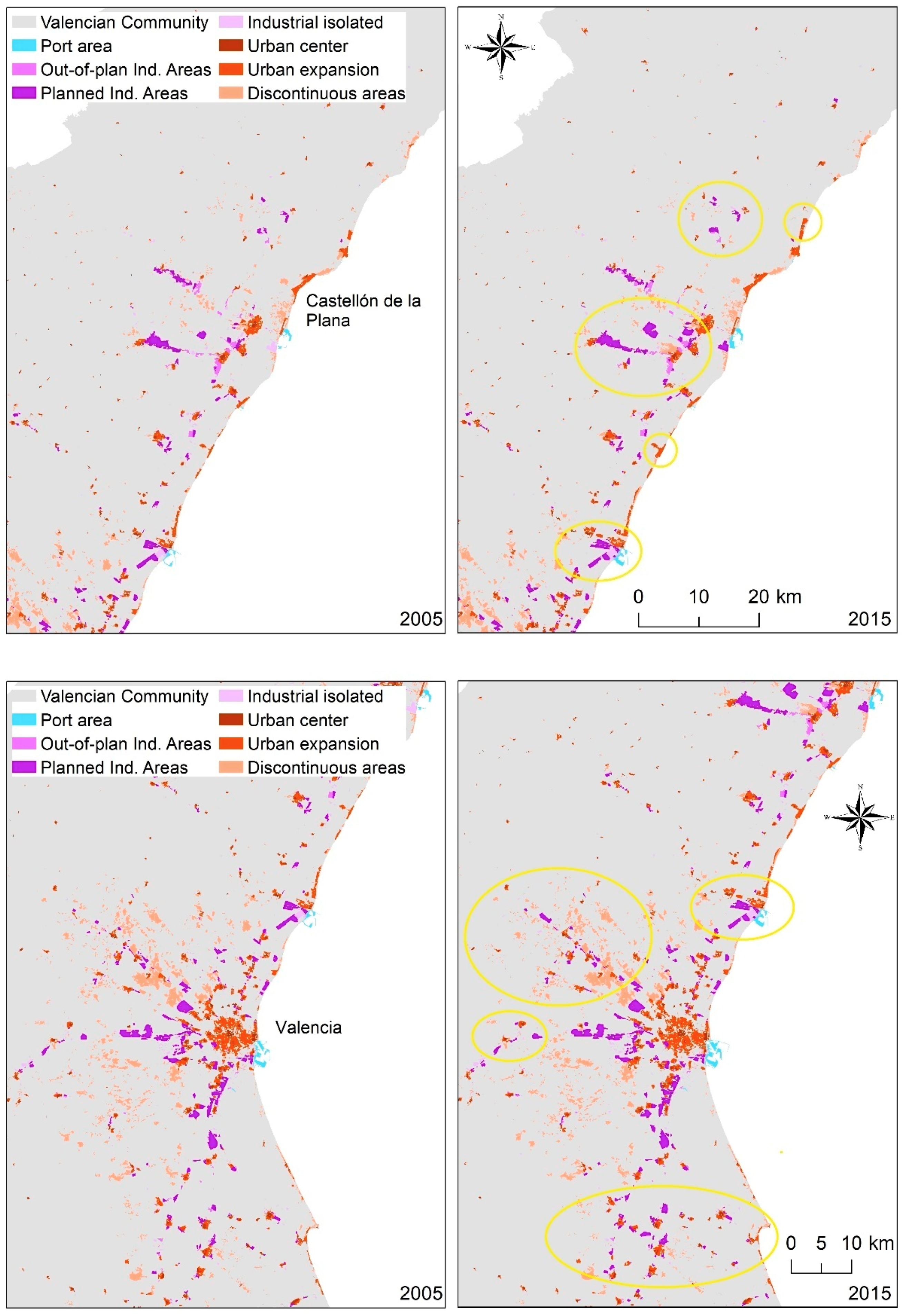
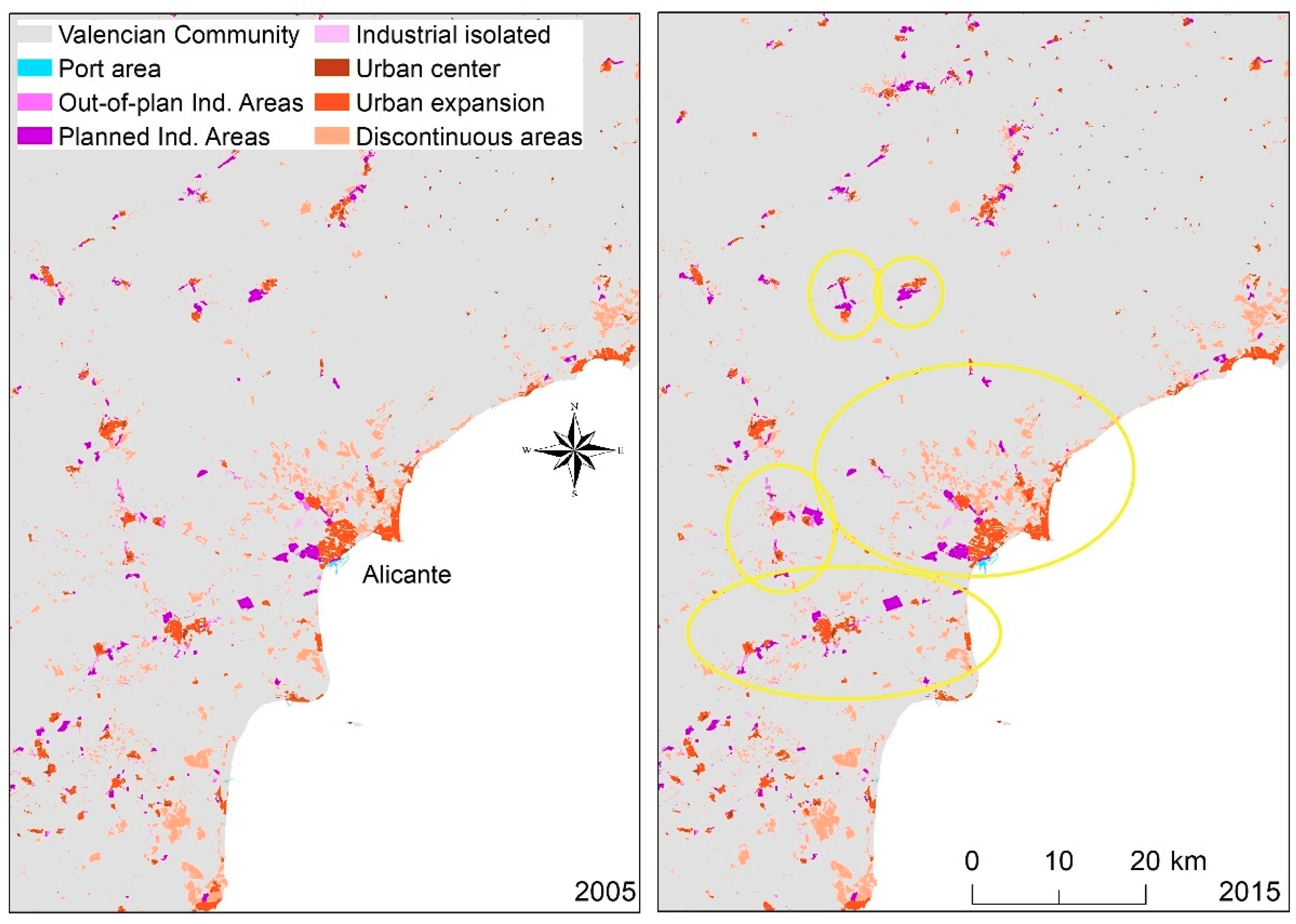
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz-Pacheco, J.; García-Palomares, J.C.; Dí Az-Pacheco, J.; Garcí A-Palomares, J.C. Urban Sprawl in the Mediterranean Urban Regions in Europe and the Crisis Effect on the Urban Land Development: Madrid as Study Case. Urban Stud. Res. 2014, 2014, 807381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Sateriano, A.; Bajocco, S. To grow or to sprawl? Land Cover Relationships in a Mediterranean City Region and implications for land use management. Cities 2013, 30, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, B.; Saurí, D.; Serra, P. Urban sprawl in the Mediterranean? Patterns of growth and change in the Barcelona Metropolitan Region 1993–2000. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2008, 85, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorianopoulos, I.; Pagonis, T.; Koukoulas, S.; Drymoniti, S. Planning, competitiveness and sprawl in the Mediterranean city: The case of Athens. Cities 2010, 27, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.; Petschel-Held, G.; Leontidou, L. Urban sprawl in Europe: Landscape, Land-Use Change and Policy; John and Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hennig, E.I.; Schwick, C.; Soukup, T.; Orlitová, E.; Kienast, F.; Jaeger, J.A. Multi-scale analysis of urban sprawl in Europe: Towards a European de-sprawling strategy. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio, F.A.H. Sprawl and Fragmentation. The case of Medellin Region in Colombia. Tema J. Land-Use Mobil. Environ. 2012, 5, 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zambon, I.; Serra, P.; Saurí, D.; Carlucci, M.; Salvati, L. Beyond the ‘Mediterranean city’: Socioeconomic disparities and urban sprawl in three Southern European cities. Geogr. Ann. Ser. B Hum. Geogr. 2017, 99, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Carlucci, M. Patterns of sprawl: The socioeconomic and territorial profile of dispersed urban areas in Italy. Reg. Stud. 2016, 50, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Morelli, V.G. Unveiling Urban Sprawl in the Mediterranean Region: Towards a Latent Urban Transformation? Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2014, 38, 1935–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorianopoulos, I.; Tsilimigkas, G.; Koukoulas, S.; Balatsos, T. The shift to competitiveness and a new phase of sprawl in the Mediterranean city: Enterprises guiding growth in Messoghia–Athens. Cities 2014, 39, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettel, M.; Friederichsen, N.; Keller, M.; Rosenberg, M. How virtualization, decentralization and network building change the manufacturing landscape: An industry 4.0 perspective. Int. J. Mech. Ind. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hohenberg, P.M. Chapter 67 The historical geography of European cities: An interpretive essay. Handb. Reg. Urban Econ. 2004, 4, 3021–3052. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.C.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Fragkias, M. The New Geography of Contemporary Urbanization and the Environment. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etherington, D.; Jones, M. City-Regions: New Geographies of Uneven Development and Inequality. Reg. Stud. 2009, 43, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounaridis, D.; Chorianopoulos, I.; Koukoulas, S. Exploring prospective urban growth trends under different economic outlooks and land-use planning scenarios: The case of Athens. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 90, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P. Looking Backward, Looking Forward: The City Region of the Mid-21st Century. Reg. Stud. 2009, 43, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, A.E.; Ward, K. Introduction to a Debate on City-Regions: New Geographies of Governance, Democracy and Social Reproduction. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2007, 31, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednar-Friedl, B.; Koland, O.; Steininger, K.W. Urban sprawl and policy responses: A general equilibrium analysis of residential choice. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2011, 54, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombolini, I.; Zambon, I.; Ippolito, A.; Grigoriadis, S.; Serra, P.; Salvati, L. Revisiting “Southern” Sprawl: Urban Growth, Socio-Spatial Structure and the Influence of Local Economic Contexts. Economies 2015, 3, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camagni, R.; Capello, R. Macroeconomic and territorial policies for regional competitiveness: An EU perspective. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2010, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, M. Technopoles of the World: The Making of 21st Century Industrial Complexes; Routledge, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Duvernoy, I.; Zambon, I.; Sateriano, A.; Salvati, L. Pictures from the other side of the fringe: Urban growth and peri-urban agriculture in a post-industrial city (Toulouse, France). J. Rural Stud. 2018, 57, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, K.; Thompson, R.G. Impacts of logistics sprawl on the urban environment and logistics: Taxonomy and review of literature. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 57, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz, A.; Dablanc, L.; Tavasszy, L.A. Logistics sprawl in monocentric and polycentric metropolitan areas: The cases of Paris, France, and the Randstad, the Netherlands. Region 2017, 4, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, B.; Martin, R.; Tyler, P. Does spatial agglomeration increase national growth? some evidence from Europe. J. Econ. Geogr. 2010, 11, 979–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Morales, F.X. The Territorial Agglomerations of Firms: A Social Capital Perspective from the Spanish Tile Industry. Growth Chang. 2005, 36, 74–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviano, G.I.P. ’New’ new economic geography: Firm heterogeneity and agglomeration economies. J. Econ. Geogr. 2010, 11, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becattini, G. The Marshallian industrial district as a socio-economic notion. In Industrial Districts and Inter-Firm Cooperation in Italy; Pyke, F., Becattini, G., Sengenberger, W., Eds.; International Institute for Labor Studies: Geneva, Switzerland, 1990; pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.E. The Competitive Advantage of the Nations; The Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, A.J.; Storper, M. The nature of cities: The scope and limits of urban theory. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2015, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasanko, M.; Barredo, J.I.; Lavalle, C.; McCormick, N.; Demicheli, L.; Sagris, V.; Brezger, A. Are european cities becoming dispersed? A comparative analysis of fifteen European urban areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Carlucci, M.; Grigoriadis, E.; Chelli, F.M. Uneven dispersion or adaptive polycentrism? Urban expansion, population dynamics and employment growth in an ‘ordinary’ city. Rev. Reg. Res. 2018, 38, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Woodcock, C.E. Compact, dispersed, fragmented, extensive? A comparison of urban growth in twenty-five global cities using remotely sensed data, pattern metrics, and census information. Urban Stud. 2008, 45, 659–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turok, I.; Mykhnenko, V. The trajectories of European cities, 1960–2005. Cities 2007, 24, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, M.; Grigoriadis, E.; Rontos, K.; Salvati, L. Revisiting a Hegemonic Concept: Long-term ‘Mediterranean Urbanization’ in Between City Re-polarization and Metropolitan Decline. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2016, 10, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Barlow, J.; Leal, J.; Maloutas, T.; Padovani, L. Housing in Southern Europe; Blackwell: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Claver-Cortés, E.; Molina-Azorin, J.F.; Pereira-Moliner, J. Strategic groups in the hospitality industry: Intergroup and intragroup performance differences in Alicante, Spain. Tour. Manag. 2006, 27, 1101–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D. Tourism and the autonomous communities in Spain. Ann. Tour. Res. 1997, 24, 156–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prytherch, D.L. Urban planning and a Europe transformed: The landscape politics of scale in Valencia. Cities 2003, 20, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prytherch, D.L.; Huntoon, L. Entrepreneurial Regionalist Planning in a Rescaled Spain: The Cases of Bilbao and València. GeoJournal 2005, 62, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prytherch, D.L.; Boira Maiques, J.V.B. City profile: Valencia. Cities 2009, 26, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Morales, F.X.; Martínez-Fernández, M.T. Shared Resources in Industrial Districts: Information, Know-How and Institutions in the Spanish Tile Industry. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2008, 31, 35–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, R.; Sforzi, F.; Galletto, V.L.J. Sistemas locales de trabajo y distritos industriales en España 2001–2011. In XLI Conference on Regional Studies; AECR, Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2015; pp. 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Franciosa, A. La valutazione della qualita’percepita del paesaggio: Il caso studio della regione di valencia. Bdc. Bollettino Del Centro Calza Bini 2013, 13, 119–144. [Google Scholar]
- Albertos Puebla, J.M.; Salom Carrasco, J. Le district industriel de la céramique à Castellón (Espagne): Ancrages locaux et déploiement mondial dans un contexte de crise. Sud-Ouest Eur. Rev. Géographique Pyrénées Sud-Ouest 2016, 41–42, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina Morales, X.; Martínez Fernández, M.T.; Coll Serrano, V. Eficiencia de las empresas del distrito industrial cerámico de Castellón: Un análisis comparativo mediante medidas no radiales. Rev. Estud. Reg. 2011, 90, 155–177. [Google Scholar]
- Salom Carrasco, J.S.; Albertos Puebla, J.M. Delimitation and characterization of new urban spaces in Valencia. BAGE 2014, 64, 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Burriel, E.L. Subversion of land-use plans and the housing bubble in Spain. Urban Res. Pract. 2011, 4, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantecón, A. Tourist modernisation and social legitimation in Spain. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2010, 12, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes, J.F.P.; Rodríguez, A.R.; Jiménez, M.S. Determinants of the Competitive Advantage of Residential Tourism Destinations in Spain. Tour. Econ. 2011, 17, 373–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, M.; Domene, E.; Saurí, D. Changing geographies of water-related consumption: Residential swimming pools in suburban Barcelona. Area 2011, 43, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalitat Valenciana. Documentos de Plan de Acciòn Territorial de Infraestrtuctura Verde y Paisaje de la Comunitat Valenciana. In Documentos de Evaluaciòn Ambiental; Generalitat Valenciana: Valencia, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cuadrado-Ciuraneta, S.; Durà-Guimerà, A.; Salvati, L. Not only tourism: Unravelling suburbanization, second-home expansion and “rural” sprawl in Catalonia, Spain. Urban Geogr. 2017, 38, 66–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, F. Lock living: Urban sprawl in Mediterranean cities. Cities 2003, 20, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, D.M.; Altes, W.K.; Altes, W.K.K. Lessons from Valencia: Separating infrastructure provision from land ownership. Town Plan. Rev. 2007, 78, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrego Caballero, F. Cuarenta meses de aplicación de la Ley Reguladora de la Actividad Urbanística de la Comunicad Valenciana (Forty months of application of the LRAU in the Valencian region). Ciudad Y Territ.-Estud. Territ. 2000, 32, 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gascó Verdier, C.; Muñoz Gielen, D. Valencian recipe for building stagnation. Rooilijn 2003, 6, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Roca Cladera, J.; Burns, M.C. The liberalisation of the land market in Spain: The 1998 reform of urban planning legislation. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2000, 8, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, E.; Riutort-Mayol, G.; Palencia-Jiménez, J.S.; Cantarino, I. An urban sprawl index based on multivariate and Bayesian factor analysis with application at the municipality level in Valencia. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2018, 45, 888–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M. The Breakdown of the Spanish Urban Growth Model: Social and Territorial Effects of the Global Crisis. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2010, 34, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.L.M.; Aguirre, S.D.; Grau, V.J.A. Environmental impact on the Mediterranean Spanish coast produced by the latest process of urban developments. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 155, 379–389. [Google Scholar]
- Ybarra, J.A. Determinación cuantitativa de distritos industriales: La experiencia del País Valenciano. Estud. Territ. 1991, 37, 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ybarra, J.A. Los distritos industriales en el desarrollo local valenciano. Quad. d’Innovació 2006, 1, 6–18. [Google Scholar]
- Molina-Morales, F.X.; Martínez-Fernández, M.T. Does homogeneity exist within industrial districts? A social capital-based approach. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2009, 88, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Morales, F.X.; Tomás-Miquel, J.V.; Expósito-Langa, M. La heterogeneidad dimensional de los distritos industriales. Un estudio longitudinal del caso español. Rev. Estud. Reg. 2012, 93, 43–63. [Google Scholar]
- Salom Carrasco, J.; Fajardo, F. Recent Changes in The Socio-Demographic Spatial Structure of The Metropolitan Area of Valencia (2001–2011). Bol. Asoc. Geógrafos Españoles 2017, 73, 123–147. [Google Scholar]
- Padmore, T.; Gibson, H. Modelling systems of innovation: II. A framework for industrial cluster analysis in regions. Res. Policy 1998, 26, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perroux, F. L’Europe sans Rivages; Presses Universitaires de France: Paris, France, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Expósito-Langa, M.; Molina-Morales, F.X.; Capó-Vicedo, J. New Product Development and Absorptive Capacity in Industrial Districts: A Multidimensional Approach. Reg. Stud. 2011, 45, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apparicio, P.; Gelb, J.; Dubé, A.-S.; Kingham, S.; Gauvin, L.; Robitaille, É. The approaches to measuring the potential spatial access to urban health services revisited: Distance types and aggregation-error issues. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2017, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stępniak, M.; Jacobs-Crisioni, C. Reducing the uncertainty induced by spatial aggregation in accessibility and spatial interaction applications. J. Transp. Geogr. 2017, 61, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, M.J.; Shmulevitz, F.; Körkel, M. Aggregation error effects on the discrete-space p-median model: the case of edmonton, Canada. Can. Geogr. Le Géographe Can. 1997, 41, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, J.Y.; Santa María, M.J. Los distritos industriales en la Comunidad Valenciana. In Un Análisis de su Dinámica Industrial; XXXIV Reunión de Estudios Regionales: Baeza-Jaén, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, F.; Valenzuela, L.M.; Botequilha-Leitão, A.; Aguilera-Benavente, F. Landscape metrics in the analysis of urban land use patterns: A case study in a Spanish metropolitan area. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 99, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, P.; Vera, A.; Tulla, A.F.; Salvati, L. Beyond urban–rural dichotomy: Exploring socioeconomic and land-use processes of change in Spain (1991–2011). Appl. Geogr. 2014, 55, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soja, E.W. Regional urbanization and the end of the metropolis era. In Cities in the 21st Century; Routledge, 2016; pp. 71–89. [Google Scholar]
- Biasi, R.; Colantoni, A.; Ferrara, C.; Ranalli, F.; Salvati, L. In-between sprawl and fires: Long-term forest expansion and settlement dynamics at the wildland–urban interface in Rome, Italy. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2015, 22, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Ferrara, C.; Mavrakis, A.; Colantoni, A. Toward forest “sprawl”: Monitoring and planning a changing landscape for urban sustainability. J. For. Res. 2016, 27, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Rojas, M.; Pereira, P.; Brevik, E.C.; Cerdà, A.; Jordán, A. Soil Mapping and Processes Models for Sustainable Land Management Applied to Modern Challenges. In Soil Mapping and Process Modeling for Sustainable Land Use Management; Elsevier BV, 2017; pp. 151–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zambon, I.; Cerdà, A.; Cudlin, P.; Serra, P.; Pili, S.; Salvati, L. Road Network and the Spatial Distribution of Wildfires in the Valencian Community (1993–2015). Agriculture 2019, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Colantoni, A.; Cecchini, M.; Mosconi, E.M. Rethinking Sustainability within the Viticulture Realities Integrating Economy, Landscape and Energy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Serra, P.; Grigoriadis, E.; Carlucci, M.; Salvati, L. Emerging urban centrality: An entropy-based indicator of polycentric development and economic growth. Land Use Policy 2017, 68, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal-Romero, E.; Lasanta, T.; Cerdà, A. Integrating Extensive Livestock and Soil Conservation Policies in Mediterranean Mountain Areas for Recovery of Abandoned Lands in the Central Spanish Pyrenees. A Long-Term Research Assessment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Colantoni, A.; Carlucci, M.; Morrow, N.; Sateriano, A.; Salvati, L. Land quality, sustainable development and environmental degradation in agricultural districts: A computational approach based on entropy indexes. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 64, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, M.; Zambon, I.; Pontrandolfi, A.; Turco, R.; Colantoni, A.; Mavrakis, A.; Salvati, L. Urban sprawl and the ‘olive’landscape: Sustainable land management for ‘crisis’ cities. GeoJournal 2019, 84, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Colantoni, A. Land use dynamics and soil quality in agro-forest systems: A country-scale assessment in Italy. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2015, 58, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Serra, P. One thing leads to another: Economic polarizations and social disparities in a pre-crisis Mediterranean city. Int. Rev. Appl. Econ. 2019, 33, 353–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Ferrara, A.; Salvia, R.; Mosconi, E.M.; Fici, L.; Turco, R.; Salvati, L. Rural Districts between Urbanization and Land Abandonment: Undermining Long-Term Changes in Mediterranean Landscapes. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Bouma, J.; Wallinga, J.; Tittonell, P.; Smith, P.; Cerdà, A.; Montanarella, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Pachepsky, Y.; Van Der Putten, W.H.; et al. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. SOIL 2016, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Mol, G.; De Leeuw, J.; Okx, J.; Molenaar, C.; De Cleen, M.; Visser, S. Soil-Related Sustainable Development Goals: Four Concepts to Make Land Degradation Neutrality and Restoration Work. Land 2018, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
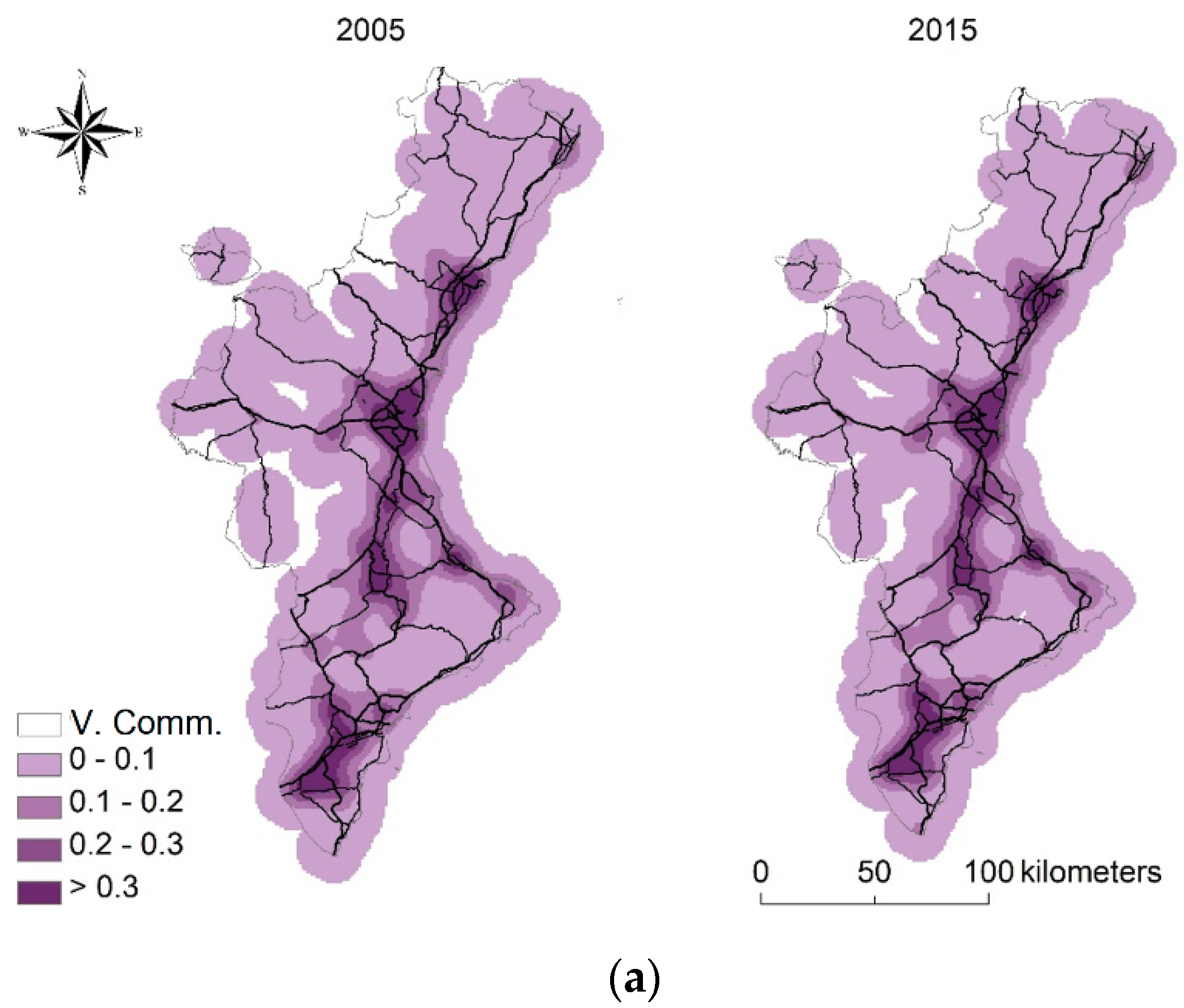
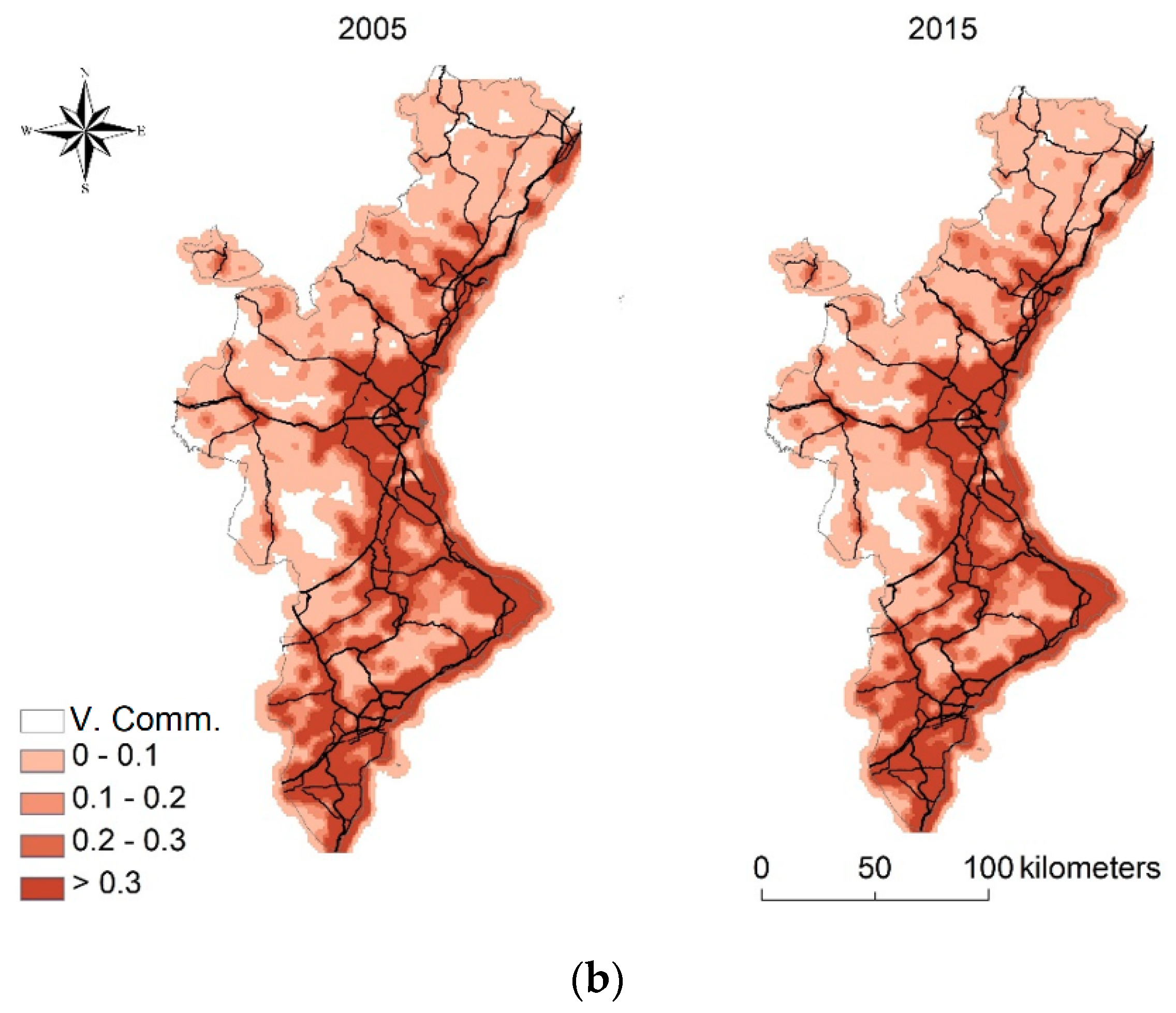
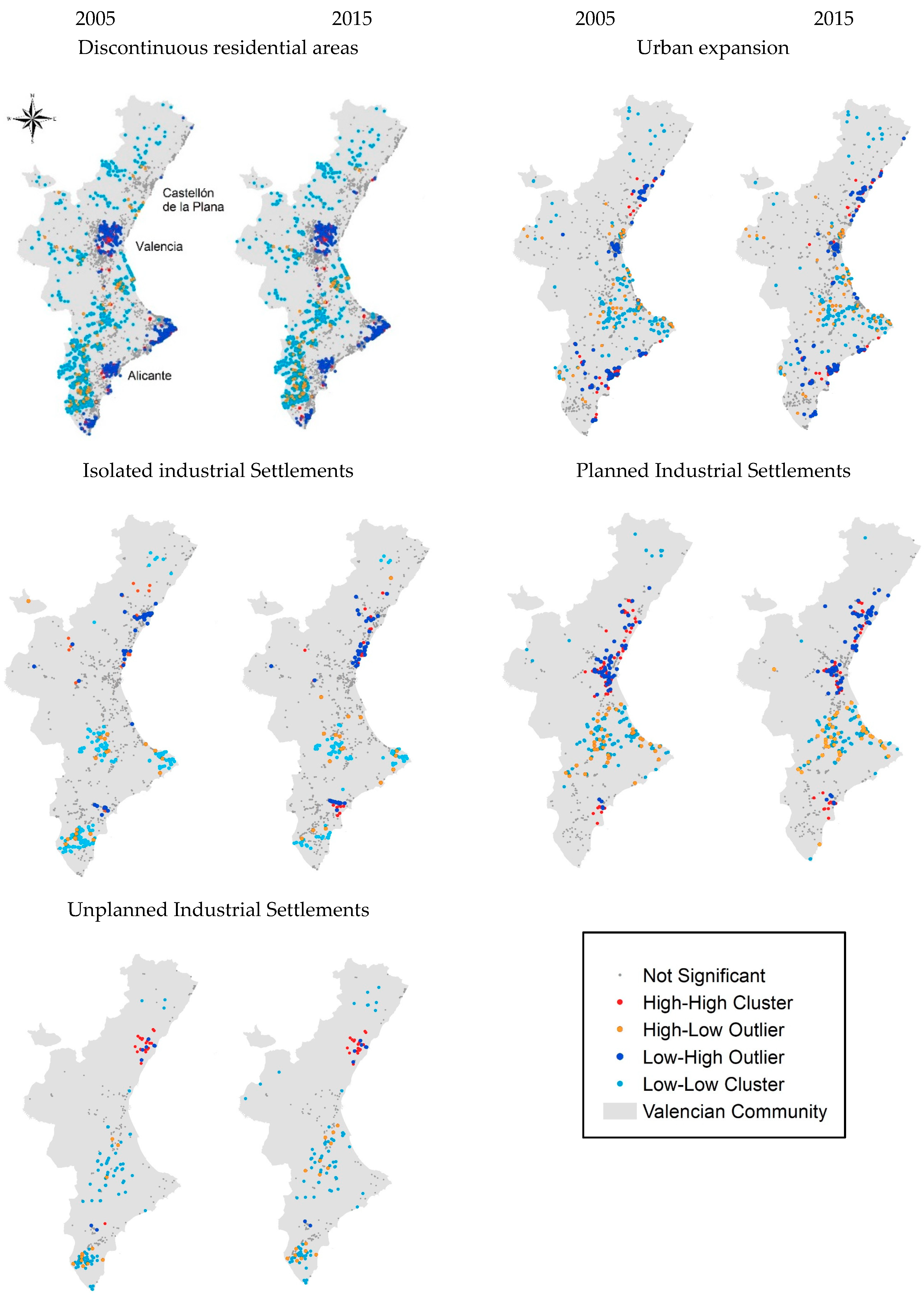
| Acronym | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cooc | Geographic coordinate x of each centroid | |
| Cooy | Geographic coordinate y of each centroid | |
| Cpm | Municipal code | |
| Mun | Municipal name | |
| S_mun | Municipal area | Ha |
| Dtm | Elevation | m |
| Area | Patch area | Ha |
| Per | Patch perimeter | m |
| Area_p | Patch area to perimeter ratio | ha/m |
| D_sea | Distance from the sea | m |
| D_road | Distance (minimum) from the road network | m |
| D_va | Distance from downtown Valencia | m |
| D_al | Distance from downtown Alicante | m |
| D_ca | Distance from downtown Castellon | m |
| A_va | Distance from Valencia airport | m |
| A_al | Distance from Alicante airport | m |
| A_ca | Distance from Castellon Airport | m |
| D_nat | Distance from natural areas | m |
| D_rail | Distance from railway | m |
| Cos | Coastal municipality | Dummy (0: no; 1: yes) |
| Urb | Urban center | Dummy (0: no; 1: yes) |
| Disc | Discontinuous urban areas | |
| Exp | Area with compact urban expansion | |
| I_iso | Isolated industrial area | |
| I_pla | Planned industrial settlement | |
| I_npla | Out-of-plan industrial area |
| 2005 | 2015 | Change (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sup_area (km2) | n_parc | aver_parc (ha) | cv_parc | sup_area | n_parc | aver_parc | cv_parc | Var_sup_1505 | Var_n_1505 | |
| Urban center | 79,754,314 | 732 | 108,954 | 4.1 | 80,440,345 | 742 | 107,829 | 4.1 | 1 | 2 |
| Discontinuous areas | 992,621,479 | 4291 | 231,326 | 7.6 | 1,223,159,368 | 4369 | 277,235 | 11.5 | 23 | 3 |
| Urban expansion | 241,406,968 | 2353 | 102,508 | 1.8 | 268,825,338 | 2535 | 104,764 | 2.4 | 11 | 9 |
| Industrial isolated | 77,794,708 | 976 | 79,708 | 8.1 | 60,698,912 | 965 | 62,383 | 7.2 | −22 | 0 |
| Planned Ind. Areas | 175,128,636 | 691 | 253,442 | 3.4 | 183,157,805 | 770 | 236,944 | 1.9 | 5 | 12 |
| Out-of-plan Ind. Areas | 51,773,908 | 366 | 141,459 | 5.5 | 43,939,408 | 348 | 124,123 | 6.4 | −15 | −3 |
| Total landscape | 57,216,872,486 | 157,687 | 362,066 | 8.2 | 57,162,714,346 | 159,867 | 359,353 | 9.4 | 0 | 1 |
| Land-Use Type | Average | Min | Max | Deviation Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | ||||
| Urban center | 797 | 0 | 7303 | 859 |
| Discontinuous areas | 943 | 0 | 6641 | 869 |
| Urban expansion | 766 | 0 | 6440 | 847 |
| Industrial isolated | 1007 | 8 | 7936 | 874 |
| Ordered industrial estate | 1022 | 0 | 5758 | 970 |
| Unordered industrial estate | 1120 | 3 | 8628 | 1080 |
| 2015 | ||||
| Urban center | 800 | 0.0 | 7303 | 866 |
| Discontinuous areas | 929 | 0.0 | 6641 | 816 |
| Urban expansion | 718 | 0.0 | 5908 | 769 |
| Industrial isolated | 1006 | 8 | 5435 | 798 |
| Ordered industrial estate | 1041 | 22 | 5758 | 954 |
| Unordered industrial estate | 1012 | 3 | 5270 | 843 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zambon, I.; Cerdà, A.; Gambella, F.; Egidi, G.; Salvati, L. Industrial Sprawl and Residential Housing: Exploring the Interplay between Local Development and Land-Use Change in the Valencian Community, Spain. Land 2019, 8, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8100143
Zambon I, Cerdà A, Gambella F, Egidi G, Salvati L. Industrial Sprawl and Residential Housing: Exploring the Interplay between Local Development and Land-Use Change in the Valencian Community, Spain. Land. 2019; 8(10):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8100143
Chicago/Turabian StyleZambon, Ilaria, Artemi Cerdà, Filippo Gambella, Gianluca Egidi, and Luca Salvati. 2019. "Industrial Sprawl and Residential Housing: Exploring the Interplay between Local Development and Land-Use Change in the Valencian Community, Spain" Land 8, no. 10: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8100143
APA StyleZambon, I., Cerdà, A., Gambella, F., Egidi, G., & Salvati, L. (2019). Industrial Sprawl and Residential Housing: Exploring the Interplay between Local Development and Land-Use Change in the Valencian Community, Spain. Land, 8(10), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8100143









