Detection of Land Subsidence in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal, Using DInSAR Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Relevant Literature
1.3. Scope
1.4. Objective
2. Materials and Methodology
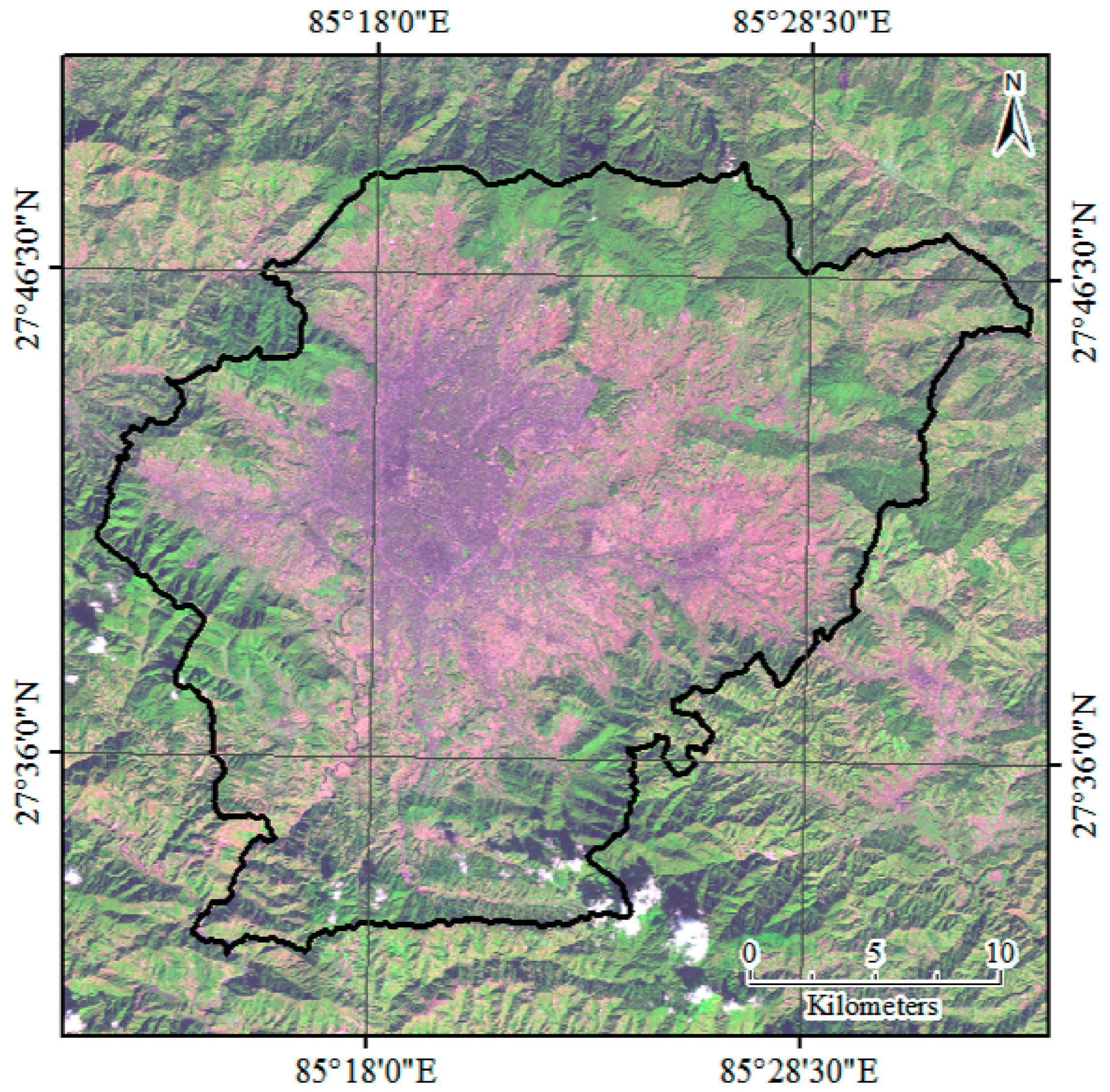
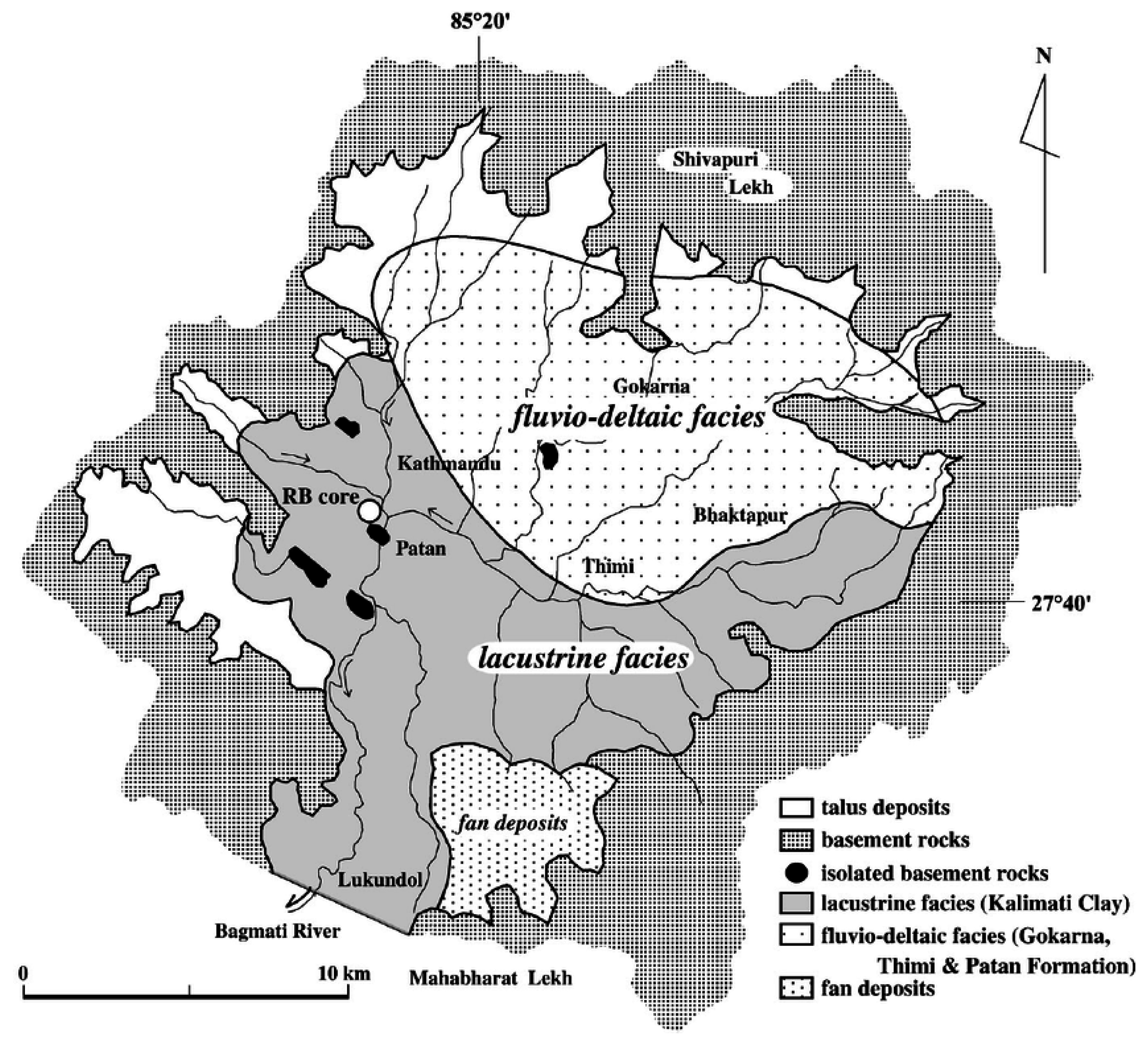
2.1. Study Area
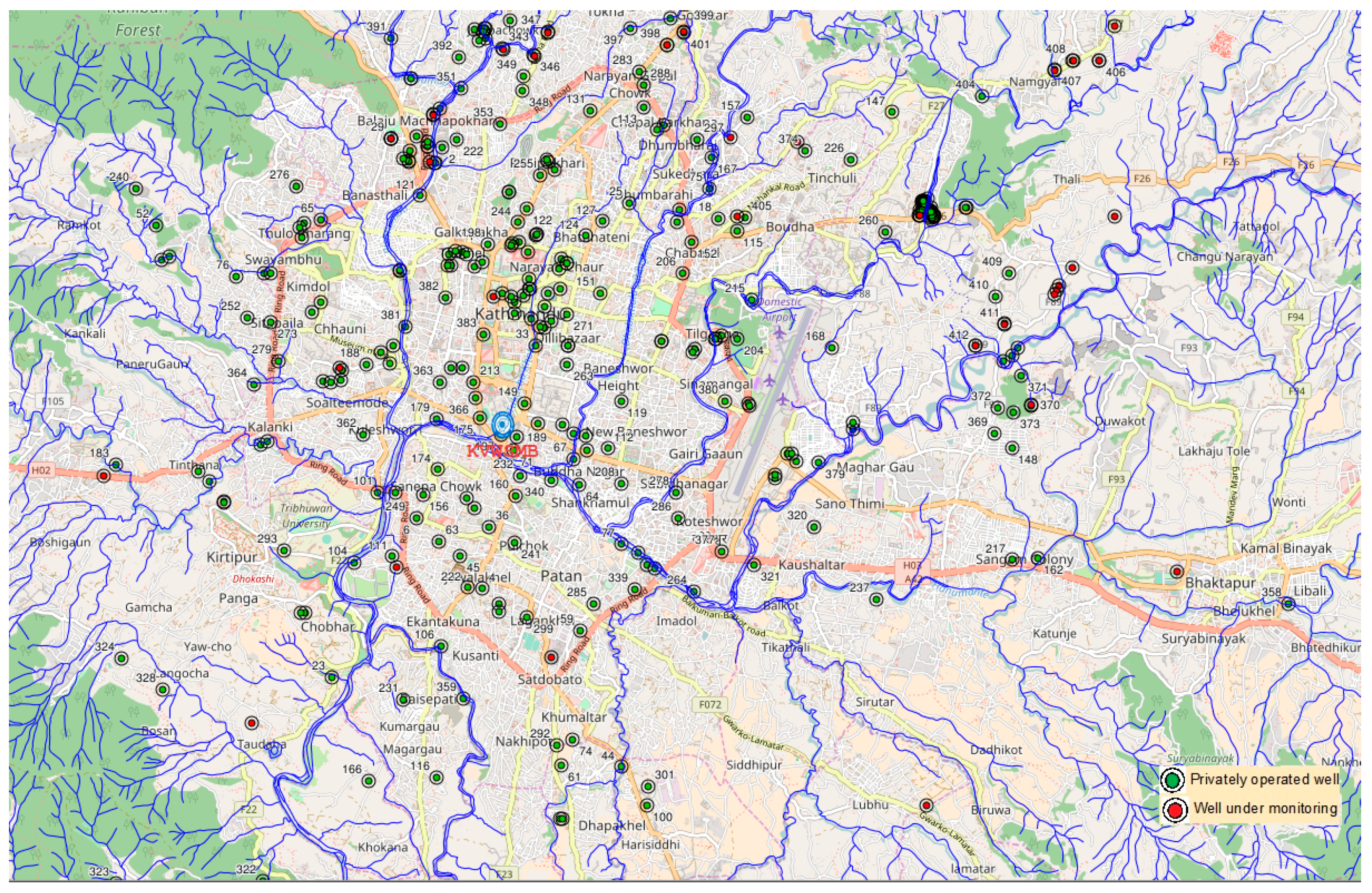
2.2. Data
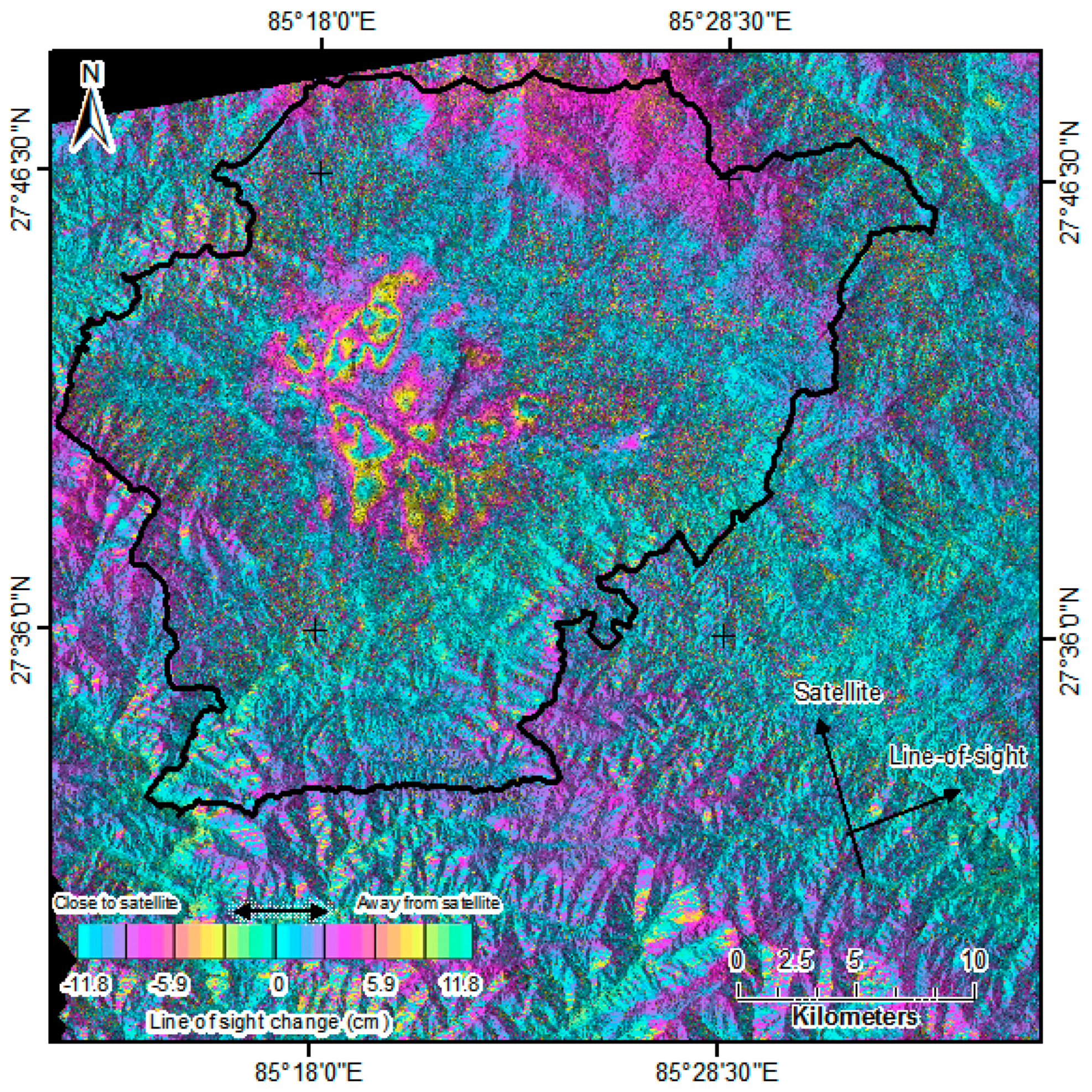
2.3. Methodology
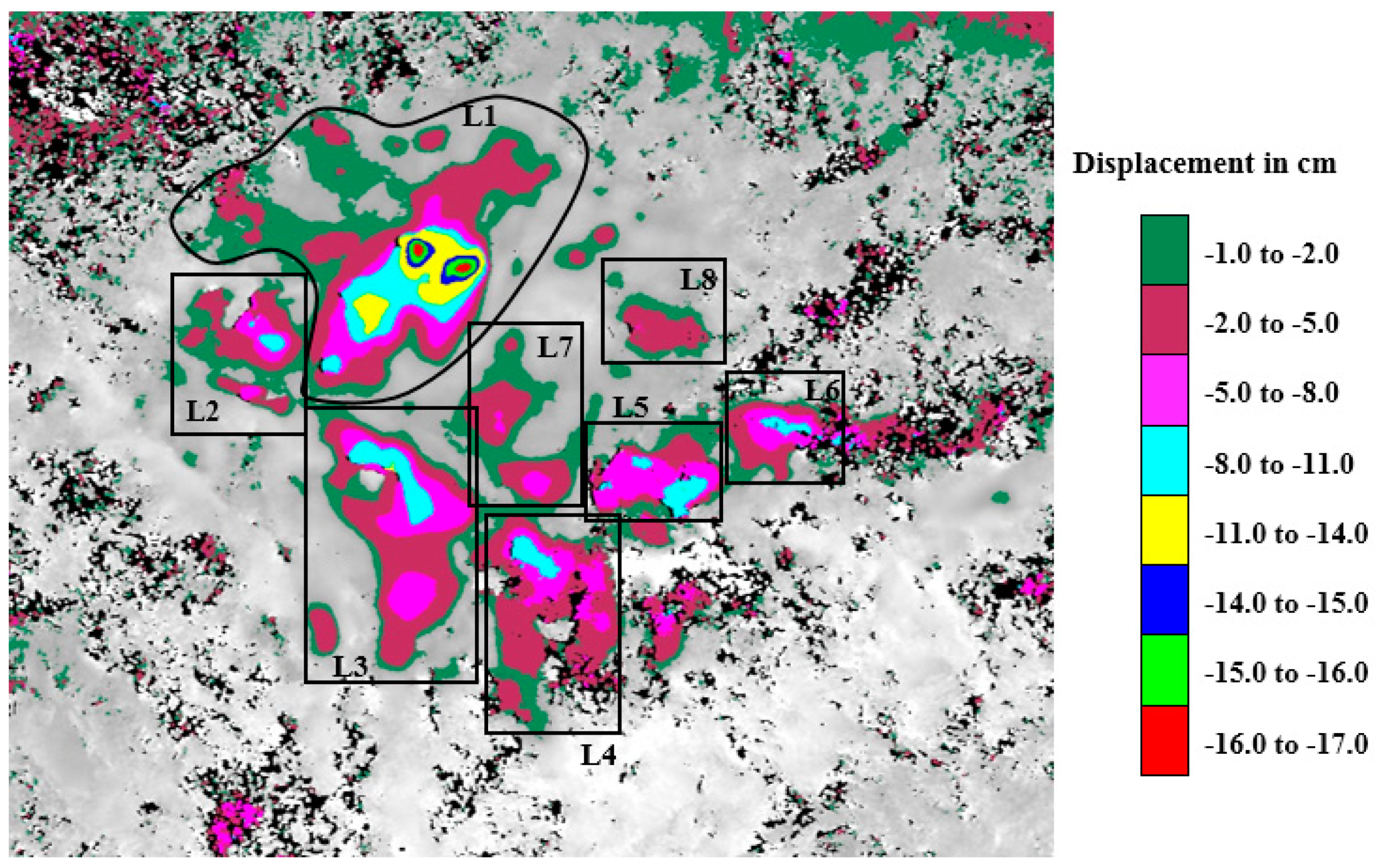
3. Result and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, D.; Xu, S. Risk assessment of land subsidence at Tianjin coastal area in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Wegmuller, U. Land subsidence in Mexico City mapped by ERS differential SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 June–2 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Holzer, T.L.; Galloway, D.L. Impacts of land subsidence caused by withdrawal of underground fluids in the United States. Rev. Eng. Geol. 2005, XVI, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, R. Water level change in the deep well of the University of Tokyo. Bull Earthq. Res. Inst. 1969, 47, 1093–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian, O.G.; Rudolph, L.D.; Cherry, A.J. Analysis of long-term land subsidence near Mexico City: Field investigations and predictive modelling. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3327–3341. [Google Scholar]
- Bankher, K.A.; Al-Harthi, A.A. Earth fissuring and land subsidence in Western Saudi Arabia. Nat. Hazards 1999, 20, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrysch, R.K.; Neighbors, R.J. Land-surface subsidence and its control in the Houston-Galveston region, TX, 1906–1995. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium Land Subsidence, Ravenna, Italy, 2 September 2000; pp. 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Djaja, R.; Darmawan, D.; Hadi, S.; Akbar, A.; Rajiyowiryono, H.; Sudibyo, Y.; Meilano, I.; Kasuma, M.A.; Kahar, J.; et al. Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its geodetic monitoring system. Nat. Hazards 2001, 23, 365–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Ferronato, M.; Gambolati, G.; Bertoni, W.; Gonella, M. A century of land subsidence in Ravenna, Italy. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergado, D.T.; Nutalaya, P.; Balasubramaniam, A.S.; Apaipong, W.; Chang, C.C.; Khaw, L.G. Causes, effects and predictions of land subsidence in AIT campus Chao Phraya Plain, Bangkok, Thailand. Bull Assoc. Eng. Geol. 1987, 25, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phien-wej, N.; Giao, P.H.; Nutalaya, P. Land subsidence in Bangkok, Thailand. Eng. Geol. 2006, 82, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.C.; Chu, H.T.; Hou, C.S.; Lai, T.H.; Chen, R.F.; Nien, P.F. The contribution to tectonic subsidence by groundwater abstraction in the Pingtung area, southwestern Taiwan as determined by GPS measurements. Quat. Int. 2006, 147, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.S.; Shen, S.L.; Cai, Z.Y.; Zhou, G.Y. The state of land subsidence and prediction approaches due to groundwater withdrawal in China. Nat. Hazards 2008, 45, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, T.L. Ground failure induced by ground-water withdrawal from unconsolidated sediments. Geol. Soc. Am. Rev. Eng. Geol. 1984, VI, 67–105. [Google Scholar]
- Budhu, M.; Adiyaman, I.B. Mechanics of land subsidence due to groundwater pumping. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2010, 34, 1459–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.P.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Marín, M.H.; Ortiz-Lozano, J.A.; Zermeño-de-León, M.E. Application of InSAR and gravimetry for land subsidence hazard zoning in Aguascalientes, Mexico. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 17035–17050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, W.E.; Johnson, D.W. Local subsidence of the Goose Creek oil field. J. Geol. 1926, 34, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, J.F.; Davis, G.H. Land subsidence due to withdrawal of fluids. Rev. Eng. Geol. 1969, 2, 187–270. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, F.G.; Cripps, J.C.; Culshaw, M.G. A review of the engineering behavior of soils and rocks with respect to groundwater. Geol. Soc. Eng. Geol. Spec. 1986, 3, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.Q.; Xue, Y.Q.; Ye, S.J.; Wu, J.C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J. Characterization of land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawals in Su-Xi-Chang area, China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, Y.; Abe, I.; Iwasaki, S.; Aoki, S.; Endo, T.; Kaido, R. Review of land subsidence researches in Tokyo. In Proceedings of the Tokyo Symposium in Land Subsidence, Tokyo, Japan, 1 September 1969; pp. 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Perlman, H. United States Geological Survey. Land Subsidence. Available online: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/earthgwlandsubside.html (accessed on 24 February 2017).
- Pandey, V.P.; Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Groundwater in the Kathmandu Valley: Development dynamics, consequences and prospects for sustainable management. Eur. Water 2012, 37, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- 2998-NEP: Urban Water Supply Reforms in the Kathmandu Valley; Inc. Metcalf & Eddy: Houston, TX, USA; CEMAT Consultants Ltd.: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2000; Volume I–II.
- Shrestha, S.; Semkuyu, D.J.; Pandey, V.P. Assessment of groundwater vulnerability and risk to pollution in Kathmandu Valley. Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 556, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, G.; Murray, A.B.; Maharjan, D.R.; Thaku, A.K. Kathmandu Valley Environmental Outlook; International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD): Kathmandu, Nepal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhanang, S.M.; Shrestha, S.D.; Steenhuis, T.S. Comphrensive review of groundwater research in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. In Kathmandu Valley Groundwater Outlook; Shrestha, S., Pradhananga, D., Pandey, V.P., Eds.; Asian Institute of Technology (AIT): Klong Luang, Thailand; Small Earth Nepal (SEN): Kathmandu, Nepal; Center of Research for Environment Energy and Water (CREEW): Kathmandu, Nepal; International Research Center for River Basin Environment-University of Yamanashi: Kofu, Japan, 2012; pp. 6–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T.; Morishita, Y.; Yarai, H. Detailed crustal deformation and fault rupture of 2015 Gorkha earthquake, Nepal, revealed from ScanSAR-based interferograms of ALOS-2. Earth Planets Sp. 2015, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, J.R.; Jolivet, R.; Gonzalez, P.J.; Avouc, J.P.; Hollingswort, J.; Searle, M.P.; Stevens, V.L. Himalayan megathrust geometry and relation to topography revealed by the Gorkha earthquake. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, F.; Walter, T.R.; Motagh, M.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Wang, R.; Samsonov, S.V. The 2015 Gorkha earthquake investigated from radar satellites: Slip and stress modeling along the MHT. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 3, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavé, J.; Yule, D.; Sapkota, S.; Basant, K.; Madden, C.; Attal, M.; Pandey, R. Evidence for a great medieval earthquake (approximate to 1100 AD) in the Central Himalayas. Nepal. Sci. 2005, 307, 1302–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Sapkota, S.N.; Bollinger, L.; Klinger, Y.; Tapponnier, P.; Gaudemer, Y.; Tiwari, D. Primary surface ruptures of the great Himalayan earthquakes in 1934 and 1255. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouac, J.P.; Bollinger, L.; Lave, J.; Cattin, R.; Flouzat, M. Seismic cycle in the Himalayas. C. R. Acad. Sci. II A. 2001, 333, 513–529. [Google Scholar]
- Mugnier, J.L.; Gajurel, A.; Huyghe, P.; Jayangondaperumal, R.; Jouanne, F.; Upreti, B. Structural interpretation of the great earthquakes of the last millennium in the central Himalaya. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 127, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Chen, T. Three Dimensional Surface Displacement Field Associated with the 25 April 2015 Gorkha, Nepal Earthquake: Solution from Integrated InSAR and GPS Measurements with an Extended SISTEM Approach. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Romero, R.; Mulas, J.; Marturia, J.J.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Herrera, G.; Gutierrez, F.; Gonzalez, P. J.; Fernandez, J.; et al. Radar interferometry techniques for the study of ground subsidence phenomena: A review of practical issues through cases in Spain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Hudnut, K.W.; Ingebritsen, S.E.; Phillips, S.P.; Peltzer, G.; Rogez, F.; Rosen, P.A. Detection of aquifer system compaction and land subsidence using interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneed, M.; Ikeheara, M.E.; Galloway, D.L.; Amelung, F. Detection and Measurement of Land Subsidence Using Global Positioning System and Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar, Coachella Valley, California, 1996–98; Water Resources Investigation Report 01-4193; U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY: Sacramento, CA, USA.
- Chatterjee, R.S.; Fruneau, B.; Rudant, J.P.; Roy, P.S.; Frison, P.; Lakhera, R.C.; Dadhwal, V.K.; Saha, R. Subsidence of Kolkata (Calcutta) City, India during the 1990s as observed from space by Differential Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (D-InSAR) technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motagh, M.; Walter, T.R.; Sharifi, M.A.; Fielding, E.; Schenk, A.; Anderssohn, J.; Zschau, J. Land subsidence in Iran caused by widespread water reservoir overexploitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, LI6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayuaji, L.; Josaphat, T.S.S.; Kuze, H. ALOS PALSAR D-InSAR for land subsidence mapping in Jakarta, Indonesia. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonì, R.; Herrera, G.; Meisina, C.; Notti, D.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Zucca, F.; González, P.J.; Palano, M.; Tomás, R.; Fernández, J.; Fernández-Merodo, J.A.; et al. Twenty-year advanced DInSAR analysis of severe land subsidence: The Alto Guadalentín Basin (Spain) case study. Eng. Geol. 2015, 198, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gamal, M.; Djaja, R.; Subarya, C.; Hirose, K.; Maruyama, Y.; Murdohardono, D.; Rajiyowiryono, H. Monitoring land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) using levelling, GPS survey and InSAR techniques. Int. Assoc. Geod. Symp. 2005, 128, 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Cascini, L.; Ferlisi, S.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Peduto, D.; Zeni, G. Subsidence monitoring in Sarno urban area via multi-temporal DInSAR technique. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.; Bignami, C.; Stramondo, S.; Pierdicca, N. Uplift and subsidence due to the 26 December 2004 Indonesian earthquake detected by SAR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3891–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoquinga, Y.; Jingquin, M. DInSAR technique for land subsidence monitoring. Earth Sci. Front. 2008, 15, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Doin, M.P.; Lopez-Quiroz, P.; Tupin, F. Mexico City subsidence measured by InSAR time series: Joint analysis using PS and SBAS approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. App. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, F.; Galloway, D.L.; Bell, J.W.; Zebker, H.A.; Laczniak, R.J. Sensing the ups and downs of Las Vegas: InSAR reveals structural control of land subsidence and aquifer-system deformation. Geology 1999, 27, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calo, F.; Abdikan, S.; Gorum, T.; Pepe, A.; Kilic, H.; Sanli, F.B. The space-borne SBAS-DInSAR technique as a supporting tool for sustainable urban policies: The case of Istanbul Megacity, Turkey. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16519–16536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.R. Ground response of Kathmandu valley on the basis of microtremors. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Auckland, New Zealand, 30 January–4 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Piya, B.K. Generation of a Geological Database for the Liquefaction Hazard Assessment in Kathmandu Valley. Master’s Thesis, International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nautiyal, S.P.; Sharma, P.N. A Geological Report on the Groundwater Investigation of Kathmandu Valley. Unpublished work. 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Moribayashi, S.; Maruo, Y. Basement topography of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: An application of gravitational method to the survey of a tectonic basin in the Himalayas. J. Japan Soci. Eng. Geol. 1980, 21, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocklin, J.; Bhattarai, K.D. Geology of Kathmandu Area and central Mahabharat Range, Nepal Himalaya. HMG/UNDP Mineral Exploration Project, Kathmandu. Unpublished work. 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Masudome, Y.; Paudel, M.R.; Fuji, R.; Hayashi, T.; Mampuku, M.; Sakai, H. Controlling weathering and erosion intensity on the southern slope of the central Himalaya by the Indian summer monsoon during the last glacial. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 71, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiansyah. Tutorial InSAR Menggunakan Sarscape; Department of Geography, University of Indonesia: Depok, Indonesian, Unpublished work; 2013; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Yerro, A.; Corominas, J.; Monells, D.; Mallorqui, J.J. Analysis of the evolution of ground movements in a low densely urban area by means of DInSAR technique. Eng. Geol. 2014, 170, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curlander, J.C.; McDonough, R.N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing; Wiley-Interscience: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Exelis Help Article: Estimating the Appropriate Number of Looks When Multilooking Images in SARscape. Available online: http://www.harrisgeospatial.com/Support/HelpArticles/TabId/185/ArtMID/800/ArticleID/4265/4265.aspx (accessed on 15 September 2014).
- SAR Guidebook. Available online: www.sarmap.ch/pdf/SAR-Guidebook.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2010).
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderssohn, J.; Wetzel, H.U.; Walter, T.R.; Motagh, M.; Djamour, Y.; Kaufmann, H. Land subsidence pattern controlled by old alpine basement faults in the Kashmar Valley, Northeast Iran: Results from InSAR and levelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 174, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrall, G.I. Business Geography and New Real Estate Market Analysis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; p. 216. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.P.; Abe, K.; Ootaki, O. GPS-measured land subsidence in Ojiya City, Niigata Prefecture, Japan. Eng. Geol. 2003, 67, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H. Stratigraphic division and sedimentary facies of the Kathmandu Basin group, Central Nepal. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 2001, 25, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, S.R.; Shah, S. Shallow Aquifer Mapping of Kathmandu Valley. Groundwater Resources Development Board, Babarmahal, Kathmandu. Available online: http://www.academia.edu/27155659/Shallow_Aquifer_Mapping_of_Kathmandu_Valley (accessed on 23 February 2017).
- Pathak, D.R.; Hiratsuka, A. An investigation of nitrate and iron concentrations and their relationship in shallow groundwater systems of Kathmandu. Desalination Water Treat. 2010, 19, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
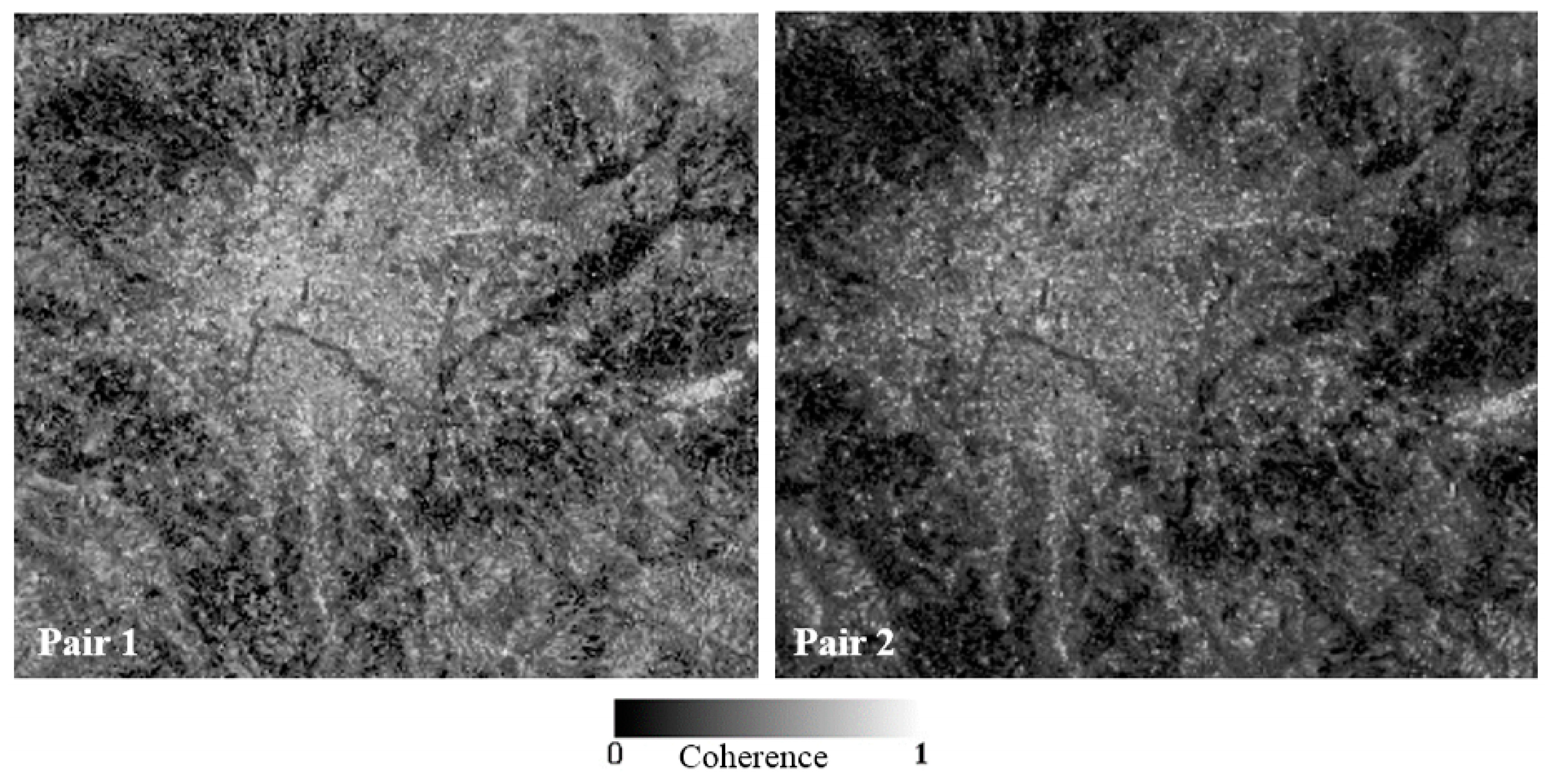




| InSAR Pair | Observation Date | Interval (Days) | Perpendicular Baseline (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pair 1 | 2 November 2007 | 138 | 417 |
| 19 March 2008 | |||
| Pair 2 | 2 November 2007 | 828 | 257 |
| 7 February 2010 |
| Location Point | Location Name | Location Specification | Subsidence Coverage Area (km2) | Maximum Subsidence Depth (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | Central Kathmandu | Mixed-use development | 9.9 | 17 |
| L2 | Chauni | Old Army Camp | 2.5 | 11 |
| L3 | Lalitpur | Mixed-use development | 7.7 | 14 |
| L4 | Imadol | Residential and cropland with few brick kilns | 5.7 | 11 |
| L5 | Thimi | Mixed-use development | 3.0 | 11 |
| L6 | Madhyapur Thimi | Mixed-use development | 2.0 | 11 |
| L7 | New Baneshwor and Koteshwor | Mixed-use development | 2.1 | 8 |
| L8 | Gothatar | Residential and cropland with portion of airport runway | 1.0 | 5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhattarai, R.; Alifu, H.; Maitiniyazi, A.; Kondoh, A. Detection of Land Subsidence in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal, Using DInSAR Technique. Land 2017, 6, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/land6020039
Bhattarai R, Alifu H, Maitiniyazi A, Kondoh A. Detection of Land Subsidence in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal, Using DInSAR Technique. Land. 2017; 6(2):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/land6020039
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhattarai, Richa, Haireti Alifu, Aikebaier Maitiniyazi, and Akihiko Kondoh. 2017. "Detection of Land Subsidence in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal, Using DInSAR Technique" Land 6, no. 2: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/land6020039
APA StyleBhattarai, R., Alifu, H., Maitiniyazi, A., & Kondoh, A. (2017). Detection of Land Subsidence in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal, Using DInSAR Technique. Land, 6(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/land6020039






