Anthropogenic Influences in Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Mediterranean Forest Landscapes in Sicily
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
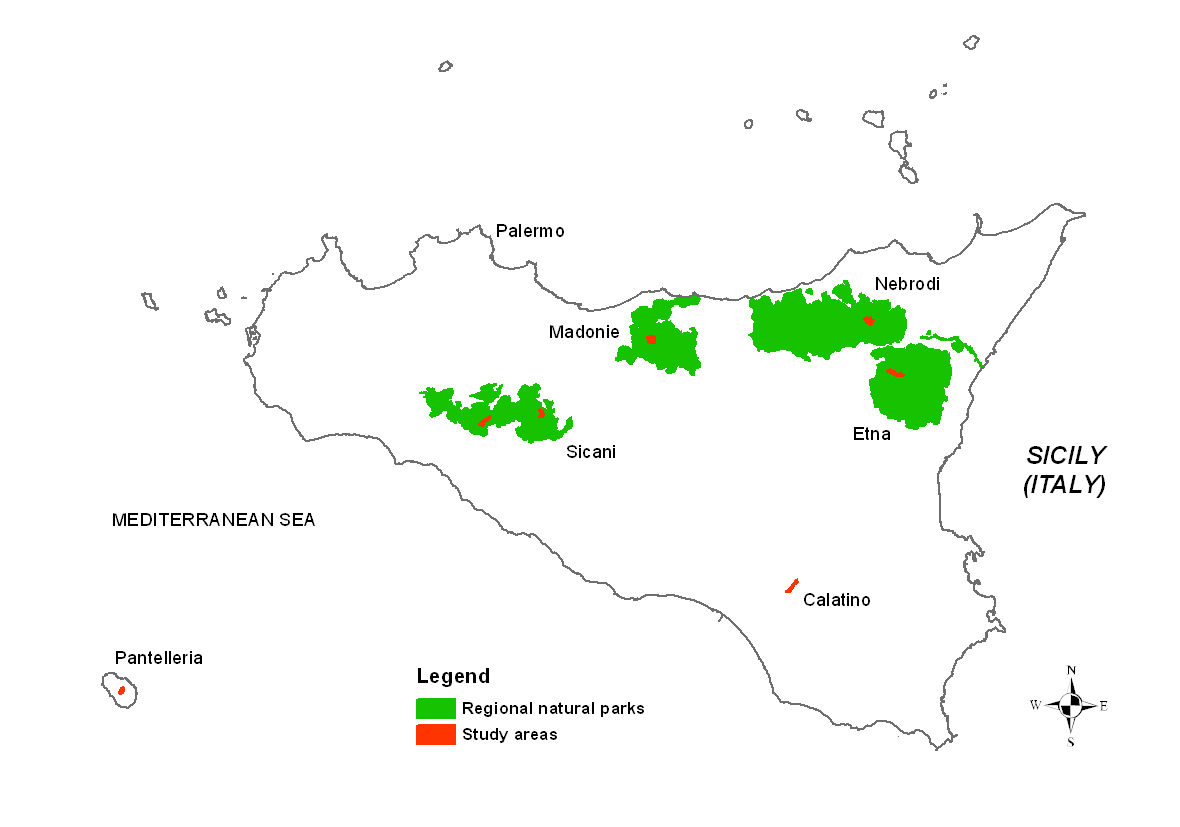
| Study Area | Main Geomorphology/Geography | Name of Municipality | Protected Area/Natura 2000 Site | Surface Area (ha) | Forest Type (Main) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pantelleria | Circum-sicilian volcanic island (Sicilian Channel) | Pantelleria | SCI ITA010019 “Isola di Pantelleria: Montagna grande e Monte Gibele”; Riserva Naturale Orientata “Isola di Pantelleria” | 233.2 | Mediterranean pines (Pinus pinaster, P. halepensis) |
| Calatino | Flatlands and low rolling hills | Caltagirone | SCI ITA070005 “Bosco di S. Pietro” | 421.3 | Plantations (Eucalyptus camaldulensis, E. globulus); cork oak; Mediterranean shrubland (Cistus sp. pl., Phillyrea latifolia, Pistacia lentiscus, Olea europaea var. sylvestris, Daphne laureola, Lonicera implexa, Calicotome infesta, Spartium junceum, Chamaerops humilis) |
| Nebrodi | Mountain range | Tortorici | SCI ITA030043 “Monti Nebrodi”; Nebrodi Regional Park | 436.8 | Beech; turkey oak; supramediterranean shrubland (Crataegus sp. pl., Rubus ulmifolius, Rosa sp. pl., Ilex aquifolium) |
| Madonie | Mountain range | Isnello | SCI ITA020016 “Monte Quacella, Monte Cervi, Pizzo Carbonara, Monte Ferro, Pizzo Otiero”; Madonie Regional Park | 526.8 | Beech; holm oak |
| Etna | Volcanic mountain | Maletto | Etna Regional Park | 421.7 | Corsican pine (Pinus nigra subsp. Laricio); holm oak; downy oak; plantations (Cedrus atlantica, Pinus radiata) |
| Sicani PA | Mountain range | Palazzo Adriano | SCI ITA020025 “Bosco di S. Adriano”; Sicani Regional Park | 317.7 | Plantations (Pinus halepensis, P. pinea, Cupressus sempervirens, Eucalyptus camaldulensis, E. globulus, E. gomphocephala); holm oak; downy oak |
| Sicani CS | Mountain range | Castronovo di Sicilia | SCI ITA020011 “Rocche di Castronovo, Pizzo Lupo, Gorghi di S. Andrea”; Sicani Regional Park | 261.2 | Plantations (Pinus halepensis, Cupressus sempervirens) |
2.2. Data Processing and Analysis
- clipping of the study areas and allocation of land use using the Sicily Regional Forest Map [21];
- labeling the non-woodlands not included in the Sicily Regional Forest Map, following the CORINE Land Cover III lev. legend;
- classifying historical land use (LU) using aerial photo interpretation of the 1955, 1968 and 1988 images and updating it to the 2012 layer;
- quantifying land cover (LC) for 1955, 1968, 1988 and 2012;
- map overlaying for the diachronic analysis of LULC changes for the whole period (1955–2012) and the sub-periods (1955 to 1968, 1968 to 1988, 1988 to 2012).
| Regional Forest Inventory 2010, legend [22] | Corine LC, III-level legend | |
|---|---|---|
| Beech forest | Deciduous forests (311) | |
| Chestnut forest | ||
| Turkey oak forest | ||
| Downy oak forest | ||
| Cork oak forest | ||
| Holm oak forest | ||
| Orno-ostrietum forest | ||
| Riparian vegetation | ||
| Other deciduous forests | ||
| Pioneer vegetation | ||
| Corsican pine forest | Coniferous forests (312) | |
| Mediterranean pine forest | ||
| Supramediterranean shrubland | Shrubland (323) | |
| Mediterranean shrubland | ||
| Plantations | exotic deciduous plantations | Deciduous plantations |
| coniferous plantations | Coniferous plantations | |
| Natural grasslands and pastures | Natural grasslands and pastures (321) | |
 | LC (%) | Number Points |
| <5% | 1 | |
| 5%–10% | 2–3 | |
| 11%–20% | 4–7 | |
| 21%–50% | 8–18 | |
| 51%–80% | 19–28 | |
| 81%–100% | 29–36 |
| Land Use Change | Classes | |
|---|---|---|
| from | to | |
| no change | Unvaried | |
| grassland | shrubland | Evolution |
| shrubland or grassland | deciduous or coniferous forest | |
| shrubland | grassland | Degradation |
| deciduous or coniferous forest | shrubland or grassland | |
| shrubland or grassland | exotic deciduous or coniferous plantations | |
- “unvaried”;
- “less significant,” where the change in observed LC was less than or equal to 20%;
- “increase” or “decrease,” where a progressive or regressive change, respectively, of over 20% was recorded for LC.
| Land Cover Change | Classes |
|---|---|
| no change | Unvaried |
| ≤±20% | Less significant |
| >+20% | Increase |
| >−20% | Decrease |
3. Results
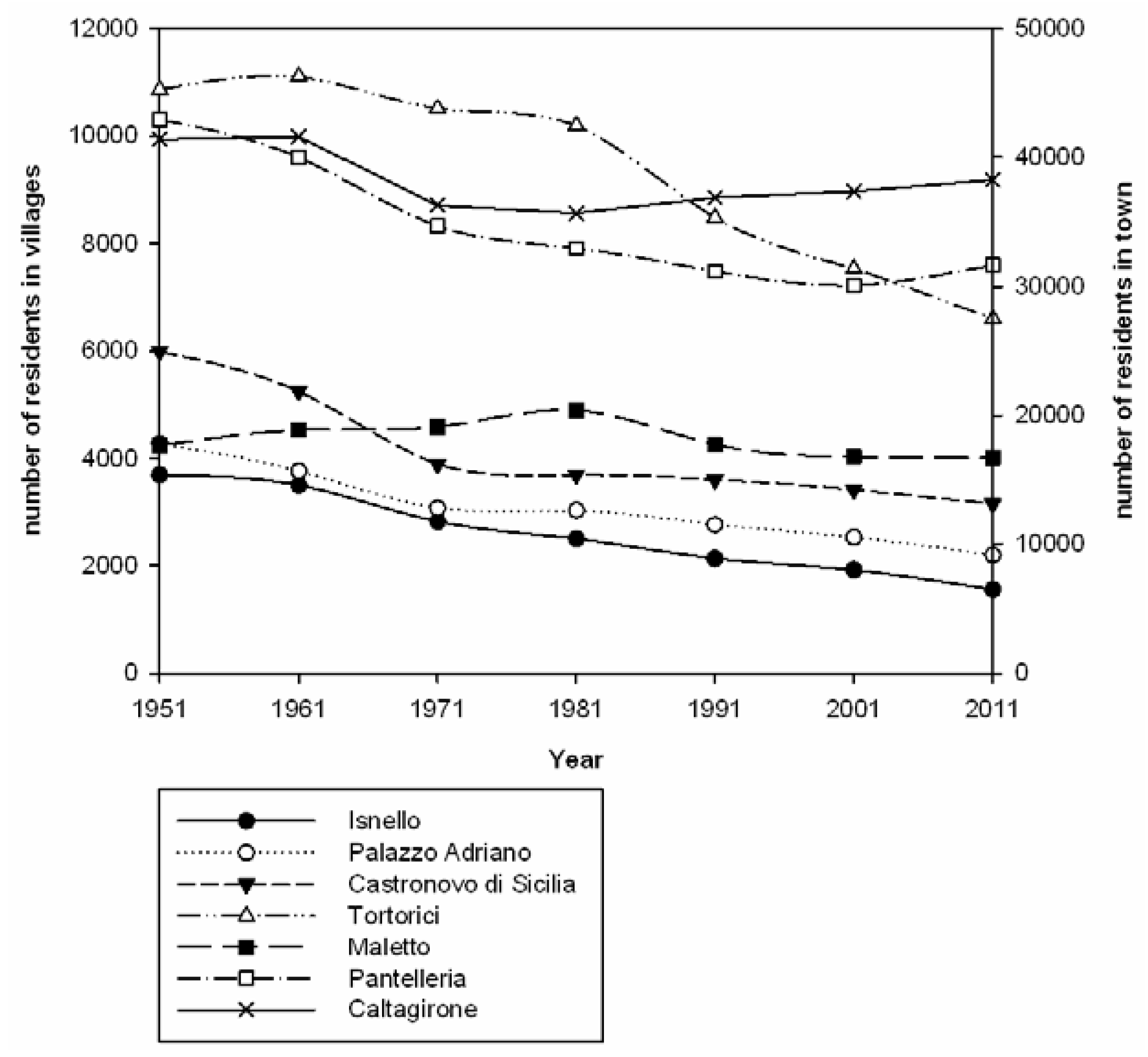
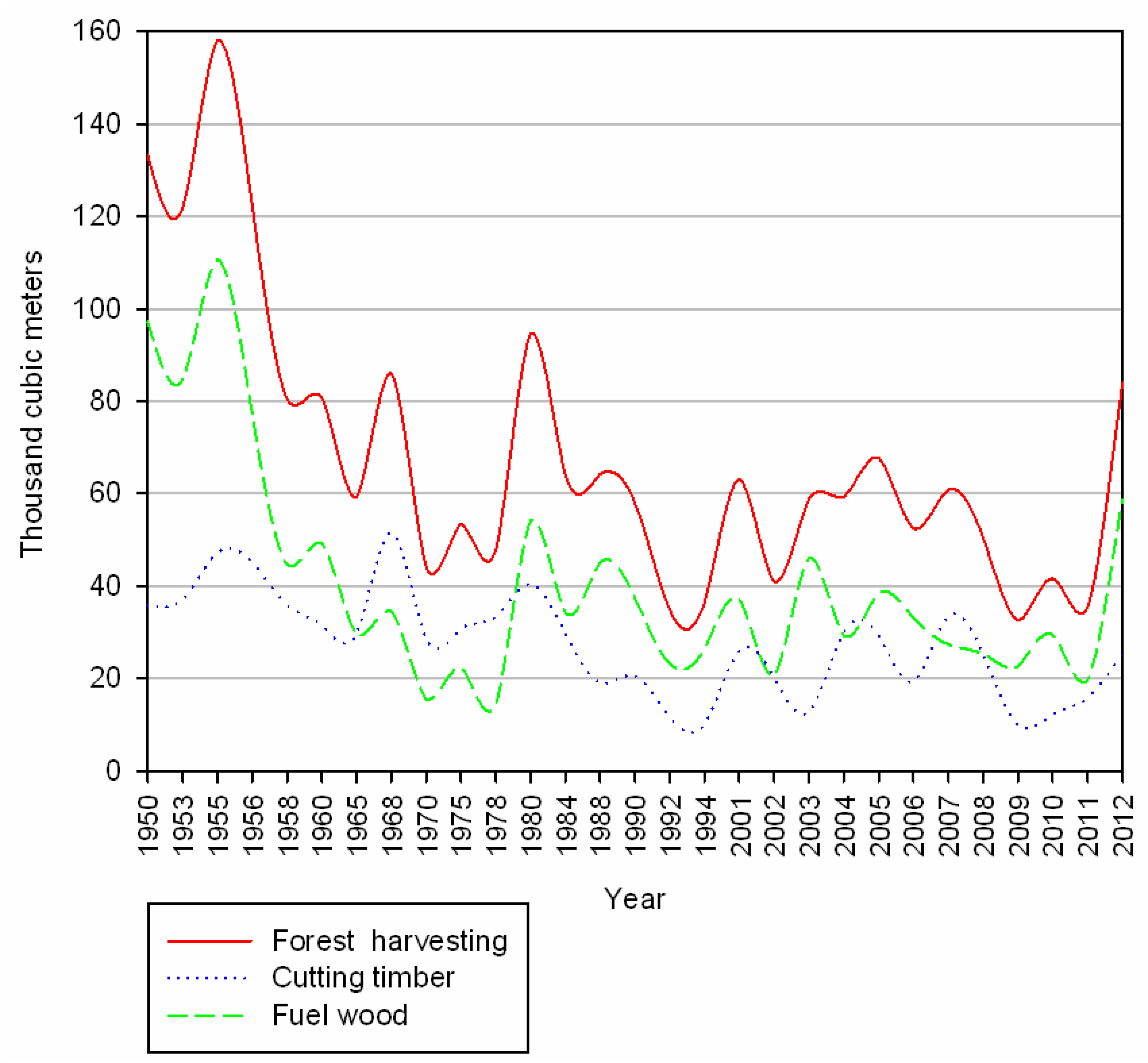
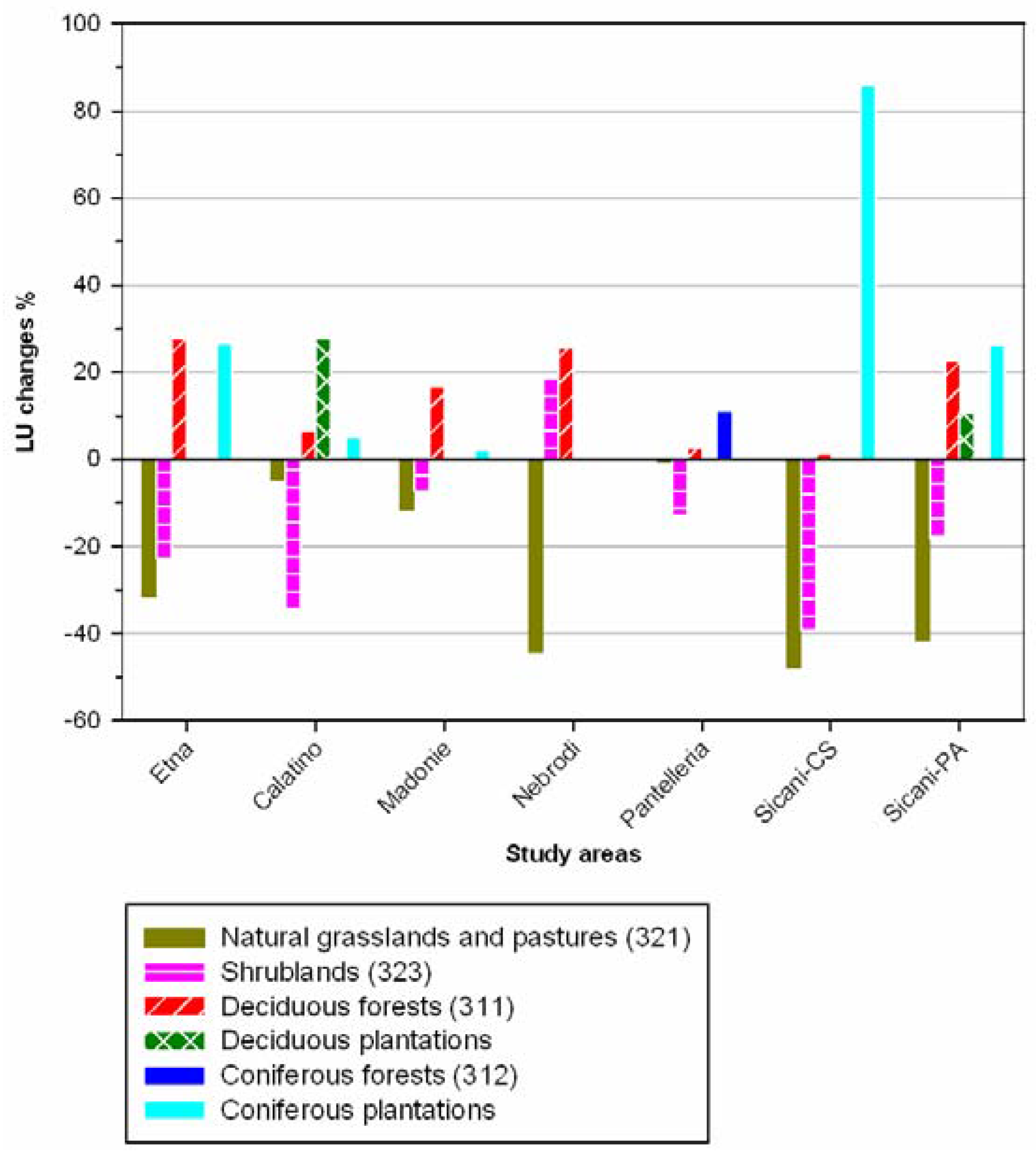
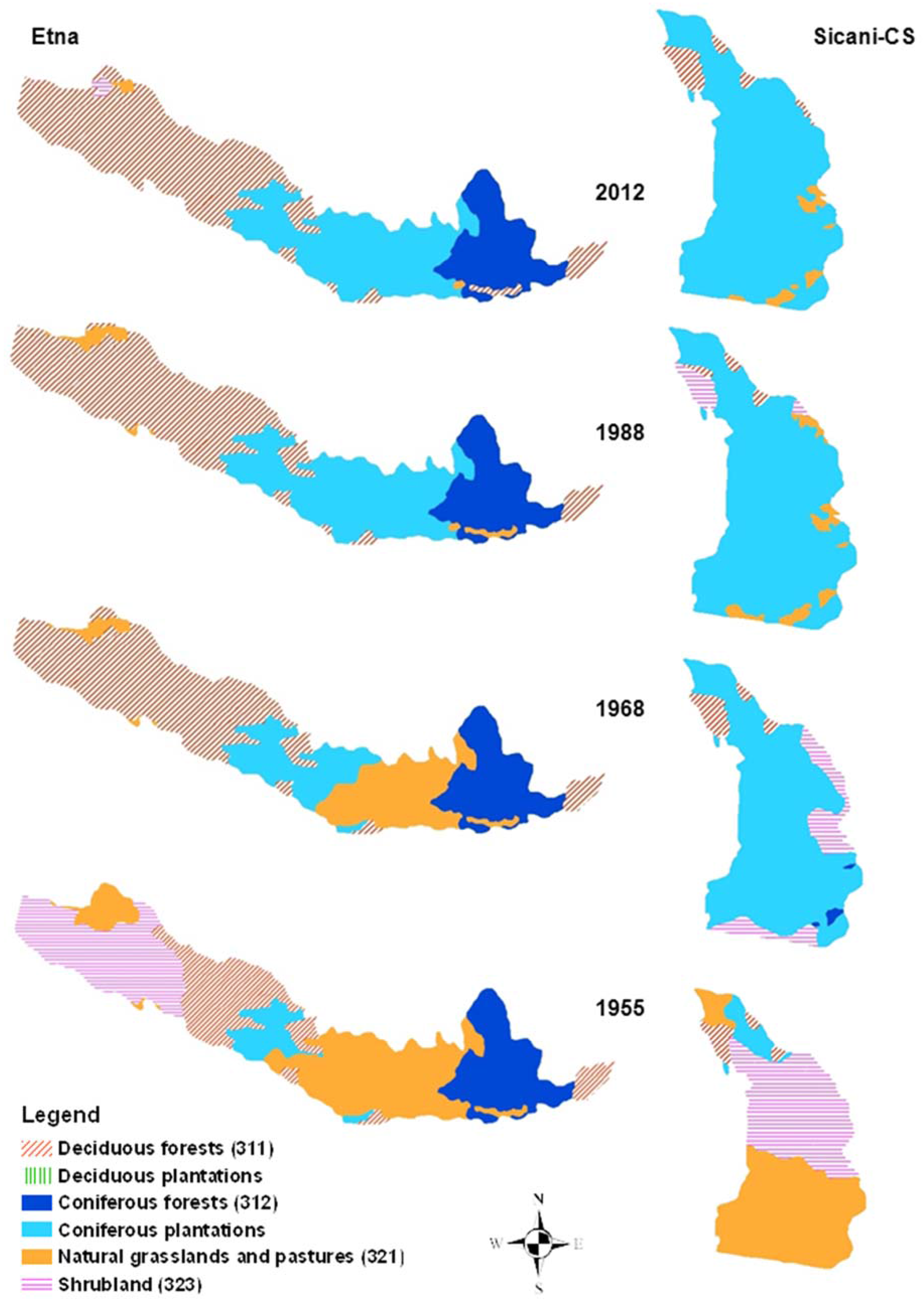
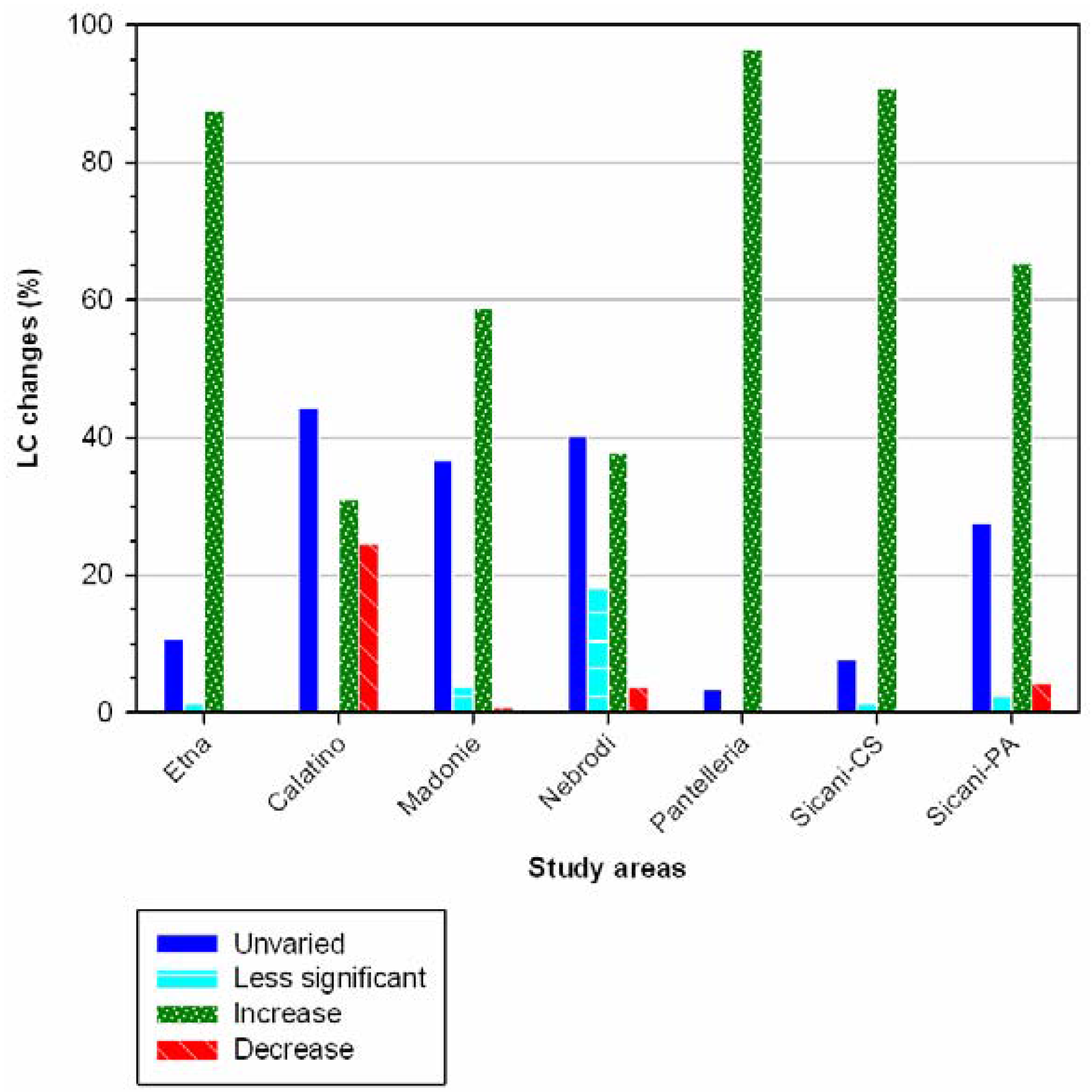

4. Discussion
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbera, G.; Cullotta, S.; Rossi-Doria, I.; Ruhl, J.; Rossi-Doria, B. I paesaggi a Terrazze in Sicilia. Metodologia per l'analisi, la Tutela e la Valorizzazione; Collana Studi e Ricerche dell’ARPA Sicilia: Palermo, Italy, 2010; p. 214. [Google Scholar]
- Grove, A.T.; Rackham, O. The Nature of Mediterranean Europe: An Ecological History; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2001; p. 384. Available online: http://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.475 (accessed on 10 March 2015).
- Feddema, J.J.; Oleson, K.W.; Bonan, G.B.; Mearns, L.O.; Buja, L.E.; Meehl, G.A.; Washington, W.M. The importance of land-cover change in simulating future climates. Science 2005, 310, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueppers, L.M.; Snyder, M.A. Influence of irrigated agriculture on diurnal surface energy and water fluxes, surface climate, and atmospheric circulation in California. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Mitigation of Climate Change: Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change; Metz, B., Davidson, O.R., Bosch, P.R., Dave, R., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 863. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. The contribution of urbanization to recent extreme heat events and a potential mitigation strategy in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan area. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 114, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldemichael, A.T.; Hossain, F.; Pielke, R.; Beltrán-Przekurat, A. Understanding the impact of dam-triggered land use/land cover change on the modification of extreme precipitation. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avetisyan, M.; Baldos, U.; Hertel, T. Development of the GTAP version 7 land use data base. GTAP Res. Memo. 2011, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hertel, T.W.; Rose, S.K.; Tol, R.S.J. Economic Analysis of Land Use in Global Climate Change Policy; Routledge Explorations in Environmental Economics, Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 343. Available online: http://www.routledge.com/books/details/9780415773089/ (accessed on 06 April 2015).
- Barbera, G.; Cullotta, S. The Halaesa landscape (III B.C.) as ancient example of the complex and bio-diverse traditional Mediterranean polycultural landscape. Landsc. Hist. 2014, 35, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braudel, F. Civiltà e imperi del Mediterraneo nell’età di Filippo II; Einaudi: Torino, Italy, 1986; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Barbera, G.; Cullotta, S. An inventory approach to the assessment of main traditional landscapes in Sicily (Central Mediterranean Basin). Landsc. Res. 2012, 37, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, S.; di Pasquale, G.; Mulligan, M.; di Martino, P.; Rego, F. Recent Dinamics of the Mediterranean Vegetation and Landscape; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2004; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhl, J.; Chiavetta, U.; La Mantia, T.; La Mela Veca, D.S.; Pasta, S. Land cover change in the Nature Reserve “Sughereta di Niscemi” (SE Sicily) in the 20th century. In Remote Sensing & GIS for Environmental Studies; Erasmi, S., Cyffka, B., Kappas, M., Eds.; Gottinger Geographische Abhandlungen: Gottingen, Germany, 2005; Volume 113, pp. 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kirtman, B.; Power, S.B.; Adedoyin, J.A.; Boer, G.J.; Bojariu, R.; Camilloni, I.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Fiore, A.M.; Kimoto, M.; Meehl, G.A.; et al. (Eds.) Near-term climate change: Projections and predictability. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 953–1028. Available online: http://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.023 (accessed on 16 September 2014).
- Costantini, E.A.C.; Urbano, F.; Bonati, G.; Nino, P.; Fais, A. Atlante Nazionale Delle aree a Rischio di Desertificazione; INEA: Roma, Italy, 2007; p. 108. [Google Scholar]
- Camerano, P.; Cullotta, S.; Varese, P. Strumenti Conoscitivi per la Gestione delle Risorse Forestali Della Sicilia. Tipi Forestali; Regione Siciliana: Palermo, Italy, 2011; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, D.R.; Motzkin, G.; Slater, B. Land-use history as long-term disturbance: Regional forest dynamics in Central New England. Ecosystems 1998, 1, 96–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, W.; Stortelde, A.H.F. Vanishing Tuscan Landscapes: Landscape Ecology of A Sub-Mediterranean-Montane Area (Solano Basin, Tuscany, Italy), 2nd ed.; Pudoc Scientific Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Regione Siciliana. Carta Delle Categorie Forestali Della Regione Sicilia; Assessorato Territorio e Ambiente, Comando del Corpo Forestale Della Regione Sicilia: Palermo, Italy, 2011; Available online: http://sif.regione.sicilia.it (accessed on 23 September 2013).
- Hofmann, A.; Cibella, R.; Bertani, R.; Miozzo, M.; Fantoni, I.; Luppi, S. Strumenti Conoscitivi per la Gestione Delle Risorse Forestali Della Sicilia. Sistema Informativo Forestale Regionale; Assessorato Territorio e Ambiente, Regione Siciliana: Palermo, Italy, 2011; p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- AA VV. Sistema Informativo Forestale Della Regione Siciliana; Istruzioni per il Rilievo Degli Attributi di Seconda Fase: Palermo, Italy, 2008; p. 261. [Google Scholar]
- Quézel, P.; Médail, F. Ecologie et Biogéographie des Forêts du Bassin Méditerranéen; Elsevier, Collection Environnement: Paris, France, 2003; p. 573. [Google Scholar]
- Regione Siciliana. Carta Della Sensibilità Alla Desertificazione Della Regione Sicilia; Assessorato Territorio e Ambiente: Palermo, Italy, 2011; Available online: http://www.artasicilia.eu/old_site/web/desertificazione (accessed on 23 September 2013).
- ISTAT. Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, Roma. Available online: http://istat.it (accessed on 09 March 2015).
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Assessment. Terms and Definitions; Forest Resources Assessment Programme, Working Paper 144/E; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Mela Veca, D.S.; Cullotta, S.; Sferlazza, S.; Maetzke, F.G. Anthropogenic Influences in Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Mediterranean Forest Landscapes in Sicily. Land 2016, 5, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/land5010003
La Mela Veca DS, Cullotta S, Sferlazza S, Maetzke FG. Anthropogenic Influences in Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Mediterranean Forest Landscapes in Sicily. Land. 2016; 5(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/land5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Mela Veca, Donato S., Sebastiano Cullotta, Sebastiano Sferlazza, and Federico G. Maetzke. 2016. "Anthropogenic Influences in Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Mediterranean Forest Landscapes in Sicily" Land 5, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/land5010003
APA StyleLa Mela Veca, D. S., Cullotta, S., Sferlazza, S., & Maetzke, F. G. (2016). Anthropogenic Influences in Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Mediterranean Forest Landscapes in Sicily. Land, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/land5010003







