Exploring Long-Term Impact of Grazing Management on Land Degradation in the Socio-Ecological System of Asteroussia Mountains, Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil and Land Use Mapping
2.3. Assessing Soil Erosion and Land Desertification
3. Results
3.1. The Evolution of the Asteroussia Pastoral System
- All livestock farms were run by full-time professional stock-breeders, which resided on-site due to the nature of the operation; despite the general ageing of the population these were, and still are, mostly young that responded quickly to the new set of conditions.
- Sheep and goat numbers per farm can be raised very quickly (i.e., within a year) without major investments, simply by slaughtering less female lambs in a particular year or series of years.
3.2. Vegetation Cover Classes Changes and Soil Erosion
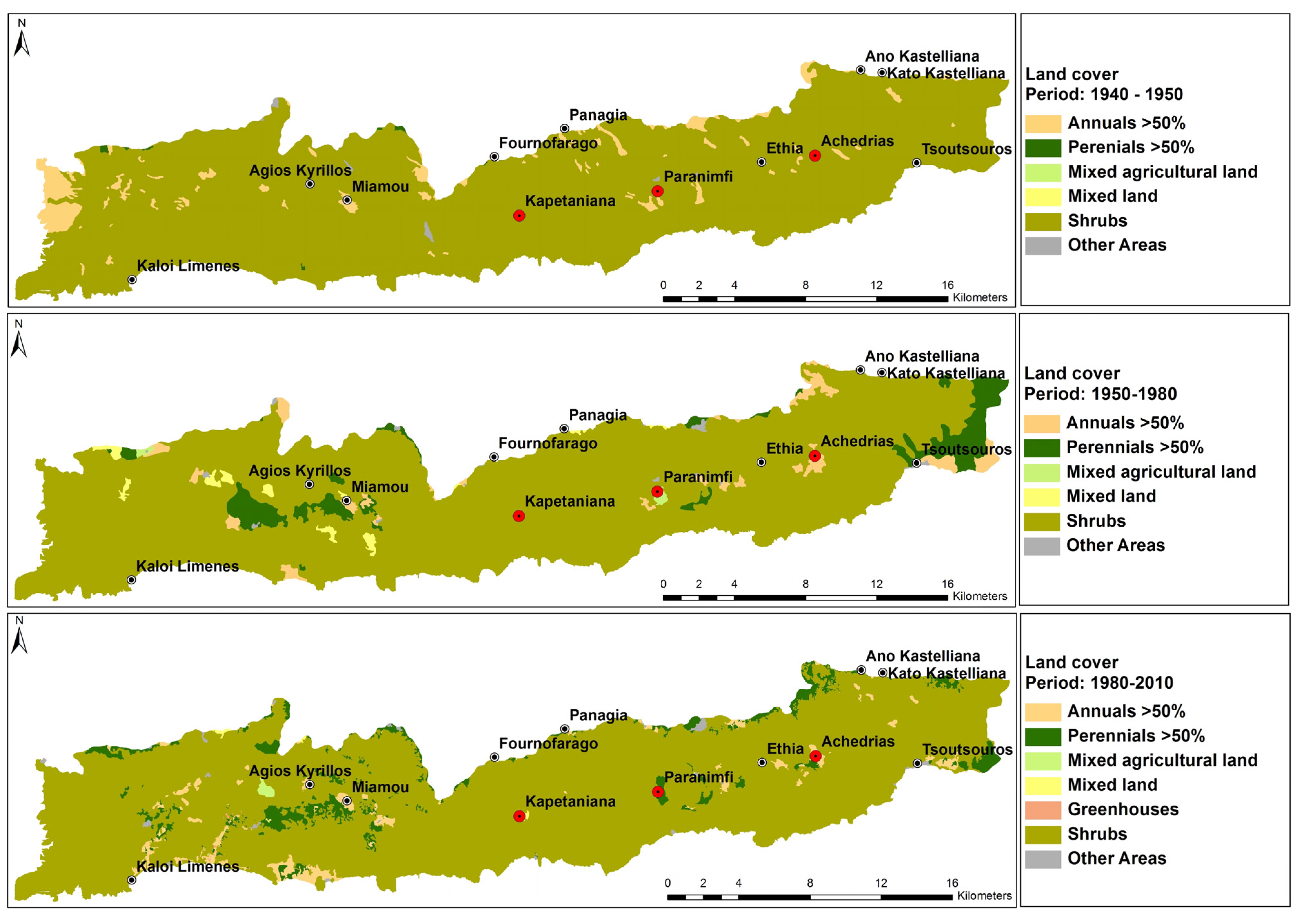
| Land Cover Type | Vegetation Characteristics | Before 1950 | 1950–Mid-1980 | Mid-1980–2010 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | ||
| 211 | Non-irrigated arable land | 1592.9 | 4.1 | 1184.0 | 3.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 221 | Vineyards | 0.0 | 0.0 | 53.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 223 | Olive groves | 53.2 | 0.1 | 2281.6 | 5.9 | 2515.3 | 6.5 |
| 323 | Sclerophyllous, maquis and garrigue | 36,683.4 | 95.5 | 34,672.9 | 90.2 | 33,279.3 | 86.6 |
| 241 | Annual and perennial crops | 0.0 | 0.0 | 77.7 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 242 | Complex cultivation patterns | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1417.9 | 3.7 |
| 243 | Agriculture and natural areas | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1149.9 | 3.0 |
| Other area | 99.2 | 0.3 | 159.3 | 0.4 | 66.4 | 0.2 | |
| TOTAL | 38,428.8 | 100.0 | 38,428.8 | 100.0 | 38,428.8 | 100.0 | |
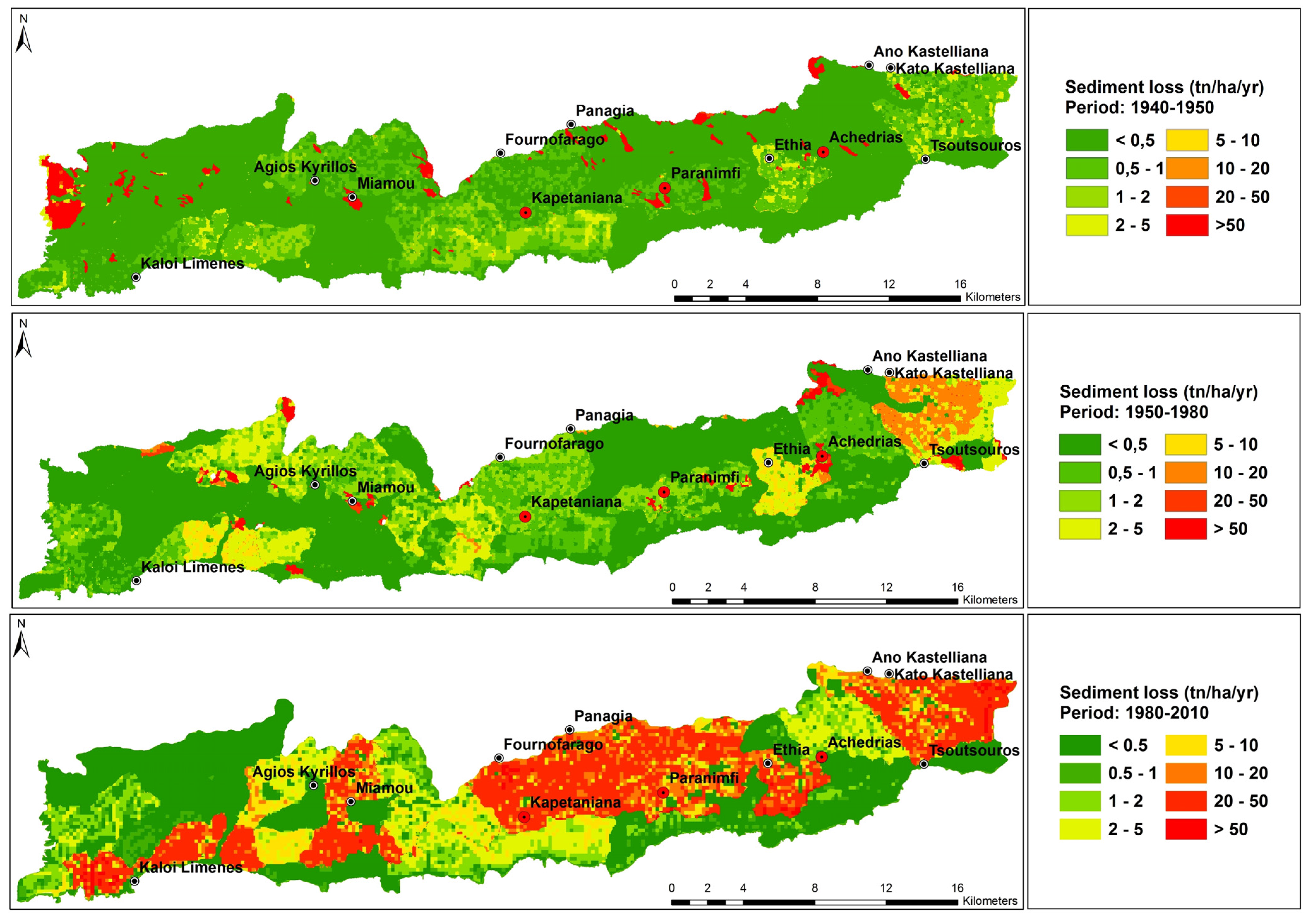
| Sediment Loss (t·ha−1·yr−1) | Before 1950 | 1950–mid-1980 | Mid-1980–2010 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | |
| 0–0.5 | 26311.9 | 68.4 | 20383.3 | 53.0 | 12870.9 | 33.5 |
| 0.5–1 | 7362.1 | 19.2 | 5629.1 | 14.6 | 1929.2 | 5.0 |
| 1–2 | 2198.9 | 5.7 | 4861.5 | 12.7 | 3382.4 | 8.8 |
| 2–5 | 1075.7 | 2.8 | 4211.6 | 11.0 | 4694.0 | 12.2 |
| 5–10 | 78.8 | 0.2 | 1007.8 | 2.6 | 2830.7 | 7.4 |
| 10–20 | 4.1 | 0.0 | 1514.3 | 3.9 | 3228.4 | 8.4 |
| 20–50 | 45.4 | 0.1 | 230.1 | 0.6 | 9167.1 | 23.9 |
| >50 | 1351.8 | 3.5 | 591.1 | 1.5 | 326.0 | 0.8 |
| TOTAL | 38428.8 | 100.0 | 38428.8 | 100.0 | 38428.8 | 100.0 |
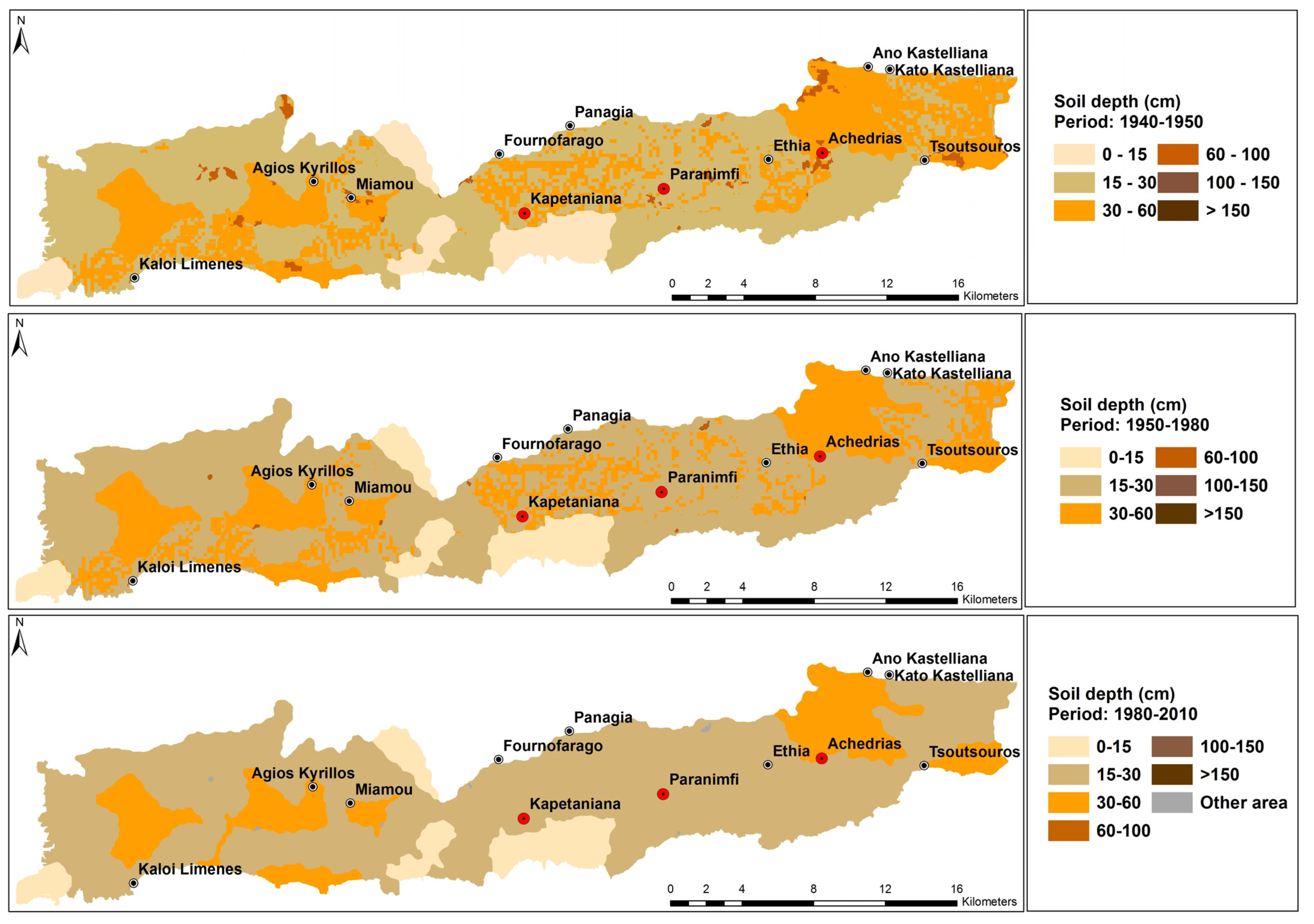
| Soil Depth Class (cm) | Before 1950 | 1950–mid-1980 | Mid 1980–2010 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | |
| 0–15 | 3199.8 | 8.3 | 3200.5 | 8.3 | 3208.8 | 8.3 |
| 15–30 | 21829.9 | 56.8 | 23669.3 | 61.6 | 28504.7 | 74.2 |
| 30–60 | 12764.9 | 33.2 | 11490.5 | 29.9 | 6649.0 | 17.3 |
| 60–100 | 623.4 | 1.6 | 59.5 | 0.2 | 66.4 | 0.2 |
| 100–150 | 10.8 | 0.1 | 8.9 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| >150 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| TOTAL | 38428.8 | 100.0 | 38428.8 | 100.0 | 38428.8 | 100.0 |
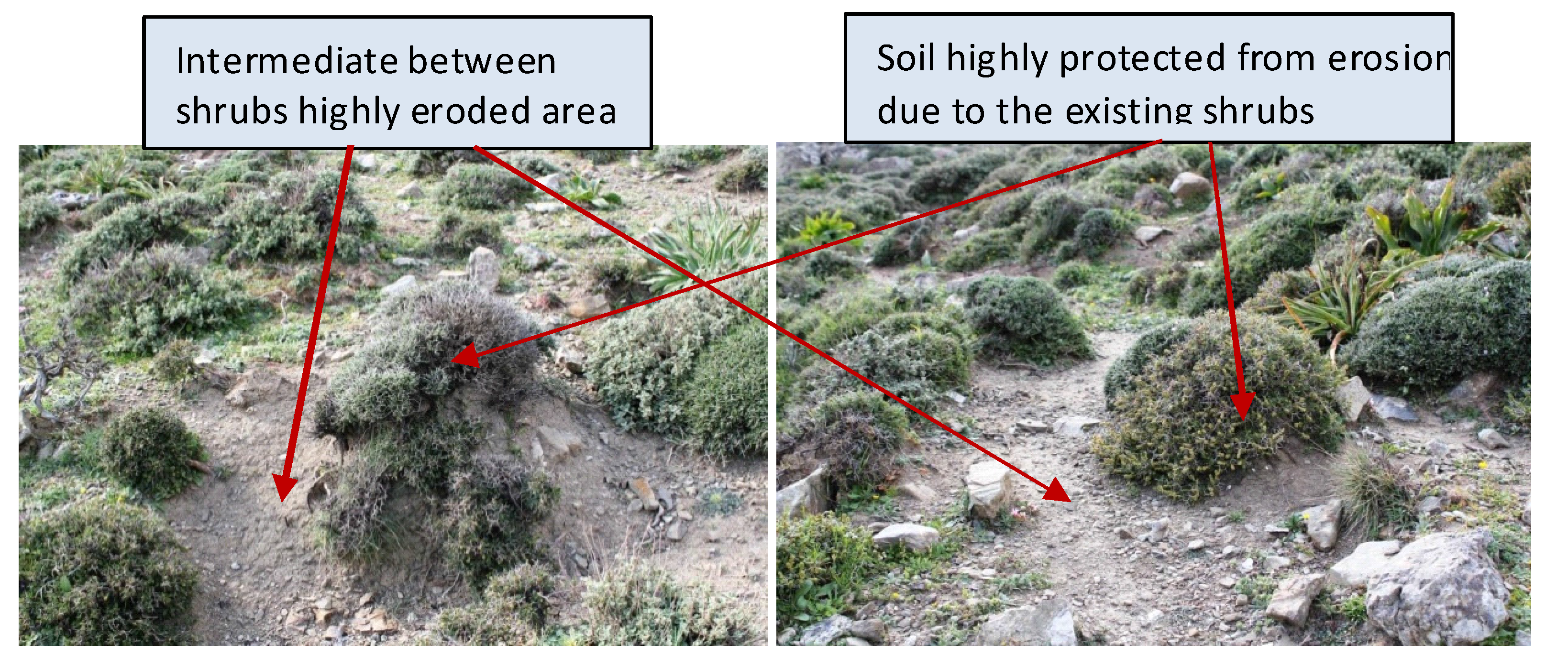
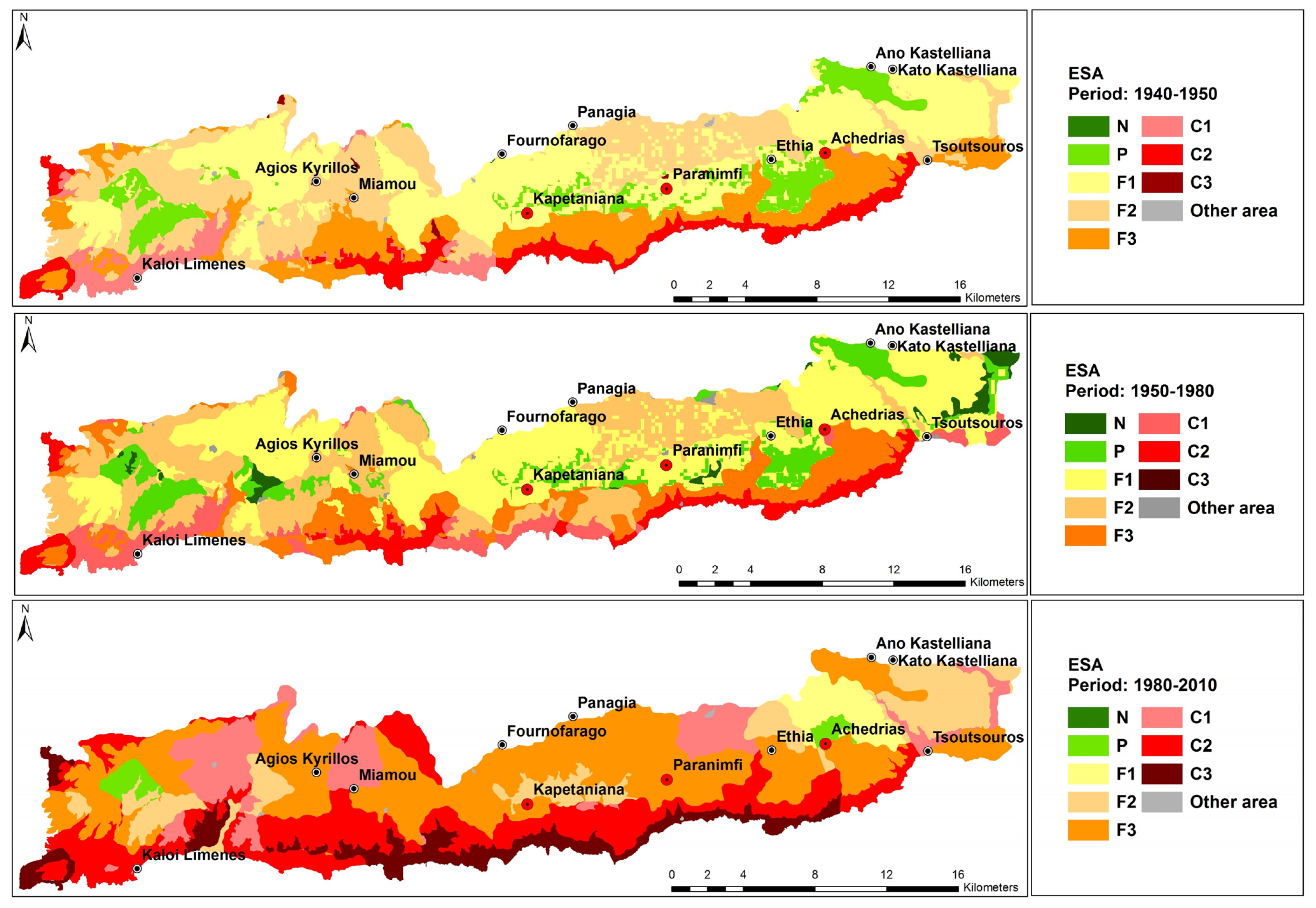
3.3. Regulation of Hydrological Processes and Desertification Risk
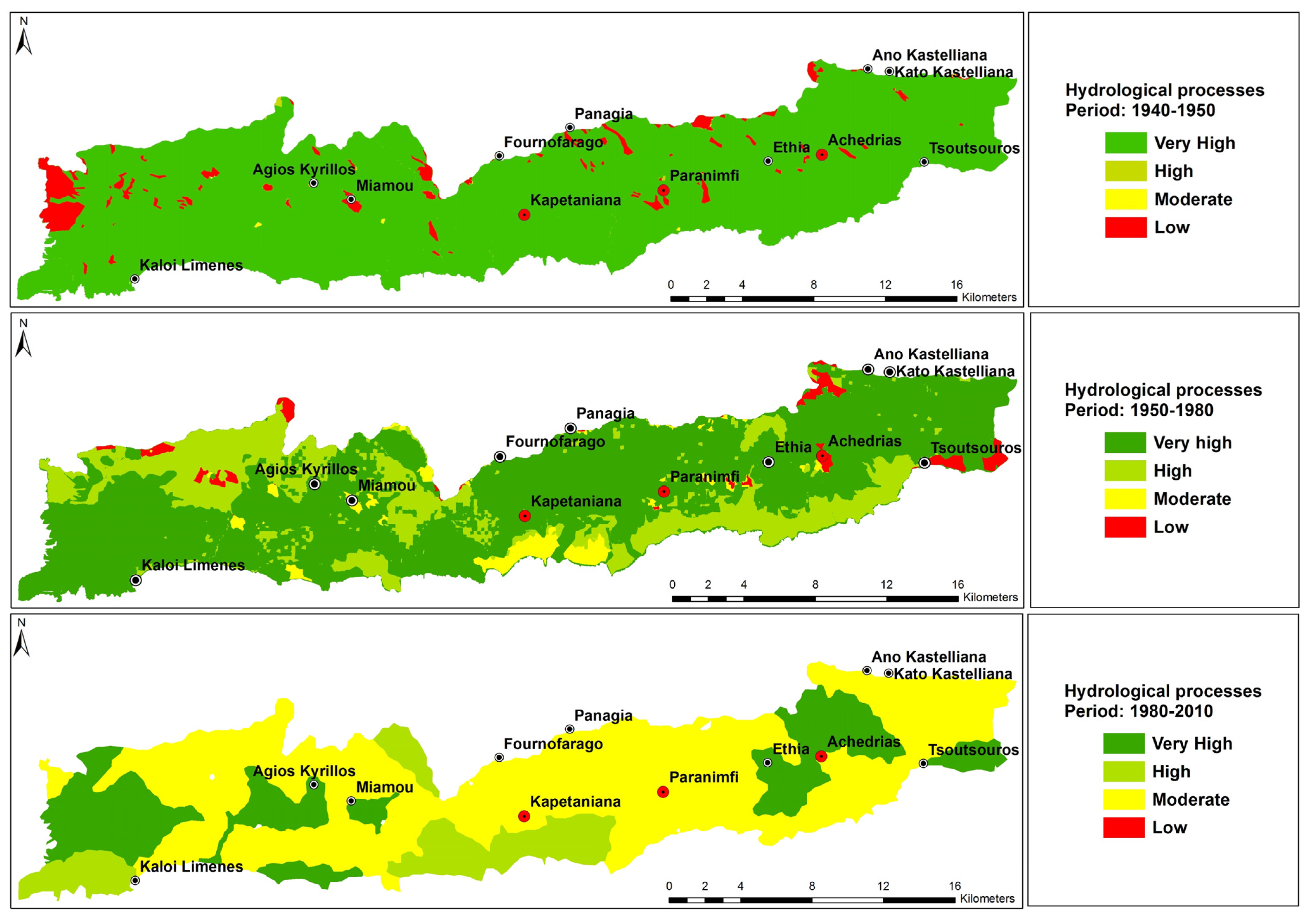
| Type of ESA | Before 1950 | 1950–mid-1980 | Mid-1980–2010 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | |
| Non affected (N) | 2.2 | 0.0 | 713.6 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Potentially(P) | 3239.8 | 8.4 | 3524.2 | 9.2 | 673.0 | 1.8 |
| Fragile (F1) | 13,318.4 | 34.7 | 13,885.4 | 36.1 | 1530.1 | 4.0 |
| Fragile (F2) | 10,109.1 | 26.3 | 9917.9 | 25.8 | 4968.1 | 12.9 |
| Fragile (F3) | 6959.4 | 18.1 | 5332.7 | 13.9 | 14,577.8 | 37.9 |
| Critical (C1) | 1738.4 | 4.5 | 2435.3 | 6.3 | 4661.9 | 12.1 |
| Critical (C2) | 2903.8 | 7.6 | 2436.8 | 6.3 | 8685.5 | 22.6 |
| Critical (C3) | 91.4 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3266.1 | 8.5 |
| Other area | 66.4 | 0.2 | 182.8 | 0.5 | 66.4 | 0.2 |
| TOTAL | 38,428.8 | 100.0 | 38,428.8 | 100.0 | 38,428.8 | 100.0 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibáñez, J.; Martínez, J.; Schnabel, S. Desertification due to overgrazing in a dynamic commercial livestock-grass-soil system. Ecol. Model. 2007, 205, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angassa, A. Effects of grazing intensity and bush encroachment on herbaceous species and rangeland condition in southern Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, K.L.; McKenzie, B.M. Grazing effects on soil physical properties and the consequences for pastures: A review. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2001, 41, 1231–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, B.; Fullen, M.A. Cattle trampling and soil compaction on loamy sands. Soil Use Manag. 1991, 7, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climo, W.J.; Richardson, M.A. Factors affecting the susceptibility of 3 soils in the Manawatu to stock treading. New Zeal. J. Agric. Res. 1984, 27, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, J.J.; Paton, R.J. Effects of sheep treading on soil physical properties and pasture yield of newly sown pastures. New Zeal. J. Agric. Res. 2005, 48, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, K.L.; Macleod, D.; Hutchinson, K.J. Long-term stocking rate effects on soil physical properties. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1997, 37, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C.; Milne, J.; Drewry, J.J.; Smith, N.P.; Hendry, T.; Moore, S.; Reijnen, B. A mechanical hoof for simulating animal treading under controlled conditions. New Zeal. J. Agric. Res. 2001, 44, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Lavee, H. The effect of grazing on soil and water losses under arid and Mediterranean climates. Implications for desertification. Pirineos 1999, 153–154, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiernaux, P.; Bielders, C.L.; Valentine, C.; Bationo, A.; Fernadez-Rivera, S. Effects of livestock grazing on physical and chemical properties of sandy soils in Sahelian rangelands. J. Arid Environ. 1999, 41, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.G.; Navar, J. Processes of desertification by goats heavy grazing in the Tamaulipan thornscrub (matorral) in north-eastern Mexico. J. Arid Environ. 2000, 44, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Ven, T.A.M.; Fryrear, D.W.; Spaan, W.P. Vegetation characteristics and soil loss by wind. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1989, 44, 47–349. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, C.F.; Thornes, J.B. Runoff hydrographs from three Mediterranean vegetation cover types. In Vegetation and Erosion: Processes and Environments; Thornes, J.B., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1990; pp. 363–384. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkby, M.J.; Le Bissonais, Y.; Coulthard, T.J.; Daroussin, J.; McMahon, M.D. The development of land quality indicators for soil degradation by water erosion. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 81, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasis, V.P. Livestock grazing in Mediterranean ecosystems: An historical and policy perspective. In Ecological Basis of Livestock Grazing in Mediterranean Ecosystems, Proceedings of the EU International Workshop, Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–25 October 1997; Papanastasis, V.P., Peter, D., Eds.; European Commission Science, Research and Development: Bruxelles, Belgium, 1998; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel, S.; Lavado, J.F. Erosión del suelo y procesos hidrológicos en dehesas del sur-oeste español. In La Red de Estaciones Experimentales de Seguimiento y Evaluación de la Desertificación (RESEL); Rojo, L., Ed.; Actividades y Resultados 1995–2004; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2008; pp. 34–57. [Google Scholar]
- Papanastasis, V.P. Overgrazing: An issue associated with desertification. In DIS4ME: Desertification Indicators System for Mediterranean Europe. Available online: http://www.kcl.ac.uk/projects/desertlinks/accessdis4me.htm (accessed on 28 May 2015).
- Polyzos, N. Exploitation of rangelands: Actual situation, problems and perspectives. Anim. Sci. Rev. 1991, 7, 154–167. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Zervas, G. Quantifying and optimizing grazing regimes in Greek mountain systems. J. Appl. Ecol. 1998, 35, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiourlis, G.M.; Kasapidis, P.; Parmakelis, A.; Dretakis, M. Effects of grazing on the structure of phryganic ecosystems in the Asterousia mountain of Crete, Greece. In Ecological Basis of Livestock Grazing in Mediterranean Ecosystems, Proceedings of the International Workshop, Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–25 October 1997; Papanastasis, V.P., Peter, D., Eds.; European Commission Science, Research and Development: Bruxelles, Belgium, 1998; pp. 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Volanis, M.; Stefanakis, A.; Hadjigeorgiou, I.; Zoiopoulos, P. Supporting the extensive dairy sheep smallholders of the semi-arid region of Crete through technical intervention. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2007, 39, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjigeorgiou, I.; Vallerand, F.; Tsimpoukas, K.; Zervas, G. The socio-economics of sheep and goat farming in Greece and the implications for future rural development. Opt. Méditerr. Sér. B 2002, 39, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Papanastasis, V.P.; Bautista, S.; Chouvardas, D.; Mantzanas, K.; Papadimitriou, M.; Mayor, A.G.; Koukioumi, P.; Papaioannou, A.; Vallejo, R.V. Comparative assessment of goods and services provided by grazing regulation and reforestation in degraded Mediterranean rangelands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.; Thomas, D. World Atlas of Desertification; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): London, UK, 1997; p. 182. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, J.L.; Bochet, E. Desertification indicators as diagnosis criteria for desertification risk assessment in Europe. J. Arid Environ. 1998, 39, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonakis, A.; Calvo-Cases, E.; Arnau-Rosalen, A. Land use change and land degradation in southeastern Mediterranean Spain. Environ. Manag. 2007, 40, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornes, J.B. Stability and instability in the management of Mediterranean desertification. In Environmental Modelling: Finding Simplicity in Complexity; Wainwright, J., Mulligan, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2004; pp. 303–315. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.R.; El Baroudy, A.A. Use of GIS in mapping the environmental sensitivity to desertification in Wadi El Natrun depression, Egypt. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2008, 2, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Farajzabeh, M.; Egbal, M.N. Evaluation of MEDALUS model for Desertification Hazard Zonation using GIS; study area: Iyzad Khast Plain, Iran. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 2622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Bajocco, S. Land sensitivity to desertification across Italy: Past, present, and future. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.; Kirkby, M.; Geeson, N. Manual on: Key Indicators of Desertification and Mapping Environmentally Sensitive Areas to Desertification; EUR 18882; European Commission-Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development: Brussels, Belgium, 1999; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, F.; Bove, E.; Dumontet, S.; Ferrara, A.; Pisante, M.; Quaranta, G. Evaluating environmental sensitivity at the basin scale through the use of geographic information systems and remotely sensed data: An example covering the Agri basin—Southern Italy. Catena 2000, 40, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J. Desertification Information System to Support National Action Programmes in the Mediterranean (DISMED). In DIS4ME, Desertification Indicator System for Mediterranean Europe; Available online: http://www.unibas.it/desertnet/dis4me/using_dis4me/dismed.htm (accessed on 18 May 2015).
- Brandt, J.; Geeson, N.; Imeson, A. A Desertification Indicator System for Mediterranean Europe. Available online: http://www.kcl.ac.uk/projects/desertlinks/accessdis4me.htm (accessed on 19 May 2015).
- Iosifides, T.; Politidis, T. Socio-economic dynamics, local development and desertification in western Lesvos, Greece. Local Environ. 2005, 10, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys; USDA-SCS Agric. Handbook 436; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; p. 754. [Google Scholar]
- ESRI. ArcMap Version 9.2. User Manual ESRI; ESRI: Redlands, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- CORINE. Available online: http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/COR0-part2 (accessed on 12 November 2010).
- Kirkby, M.J.; Bull, L.J.; Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Vandekerckhove, L. Observed and modelled distributions of channel and gully heads—With examples from S.E. Spain and Belgium. Catena 2003, 50, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, M.J.; Jones, R.J.A.; Irvine, B.; Gobin, A; Govers, G.; Cerdan, O.; van Rompaey, A.J.J.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Daroussin, J.; King, D.; et al. Pan-European Soil Erosion Risk Assessment: The PESERA Map, Version 1 October 2003—Explanation of Special Publication ISPRA 2004 No. 73 (S.P.I.04.73); European Soil Bureau Research Report No. 16, EUR 21176, 18 pp. and 1 Map in ISO B1 Format; Williams, J.R., Sharpley, A.N., Eds.; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmas, C.; Quaranta, G. Assessment Methodologies of Responses to LEDD in Cropland—Case Study-Specific. Deliverable Number Code: 10(D122). Available online Leddra.aegean.gr (accessed on 18 May 2015).
- Tsara, M.; Kosmas, C.; Kirkby, M.; Kosma, D.; Yassoglou, N. An evaluation of the PESERA soil erosion model and its application to a case study in Zakynthos, Greece. Soil Use Manag. 2005, 21, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Requirements; Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Parson, A.; Abrahams, A.D.; Simanton, J.R. Microtopography and soil surface materials on semi-arid piedmont hillslopes, southern Arizona. J. Arid Environ. 1992, 22, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Salvati, L.; Mancino, G.; De Zuliani, E.; Sateriano, A.; Zitti, M.; Ferrara, A. An expert system to evaluate environmental sensitivity: A local-scale approach to desertification risk. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2013, 11, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizos, T.; Detsis, V.; Iosifides, T.; Metaxakis, M. Social capital and social-ecological resilience in the Asteroussia Mountains, southern Crete, Greece. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, 40:1–40:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairis, O.; Karavitis, C.; Kounalaki, A.; Kosmas, C.; Salvati, L. Exploring the impact of overgrazing on soil erosion and land degradation in a dry Mediterranean agro-forest landscape (Crete, Greece). Arid Land Res. Manag. 2015, 29, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizos, T.; Plieninger, T.; Schaich, H. “Instead of 40 Sheep there are 400”: Traditional grazing practices and landscape change in western Lesvos, Greece. Landsc. Res. 2013, 38, 476–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosmas, C.; Detsis, V.; Karamesouti, M.; Kounalaki, K.; Vassiliou, P.; Salvati, L. Exploring Long-Term Impact of Grazing Management on Land Degradation in the Socio-Ecological System of Asteroussia Mountains, Greece. Land 2015, 4, 541-559. https://doi.org/10.3390/land4030541
Kosmas C, Detsis V, Karamesouti M, Kounalaki K, Vassiliou P, Salvati L. Exploring Long-Term Impact of Grazing Management on Land Degradation in the Socio-Ecological System of Asteroussia Mountains, Greece. Land. 2015; 4(3):541-559. https://doi.org/10.3390/land4030541
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosmas, Costas, Vassilis Detsis, Mina Karamesouti, Kate Kounalaki, Penny Vassiliou, and Luca Salvati. 2015. "Exploring Long-Term Impact of Grazing Management on Land Degradation in the Socio-Ecological System of Asteroussia Mountains, Greece" Land 4, no. 3: 541-559. https://doi.org/10.3390/land4030541
APA StyleKosmas, C., Detsis, V., Karamesouti, M., Kounalaki, K., Vassiliou, P., & Salvati, L. (2015). Exploring Long-Term Impact of Grazing Management on Land Degradation in the Socio-Ecological System of Asteroussia Mountains, Greece. Land, 4(3), 541-559. https://doi.org/10.3390/land4030541







