The Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Wetland Expansion in Xinjiang
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Location of Study
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Wetland Data
2.2.2. Driver Data
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Wetland Area Dynamics
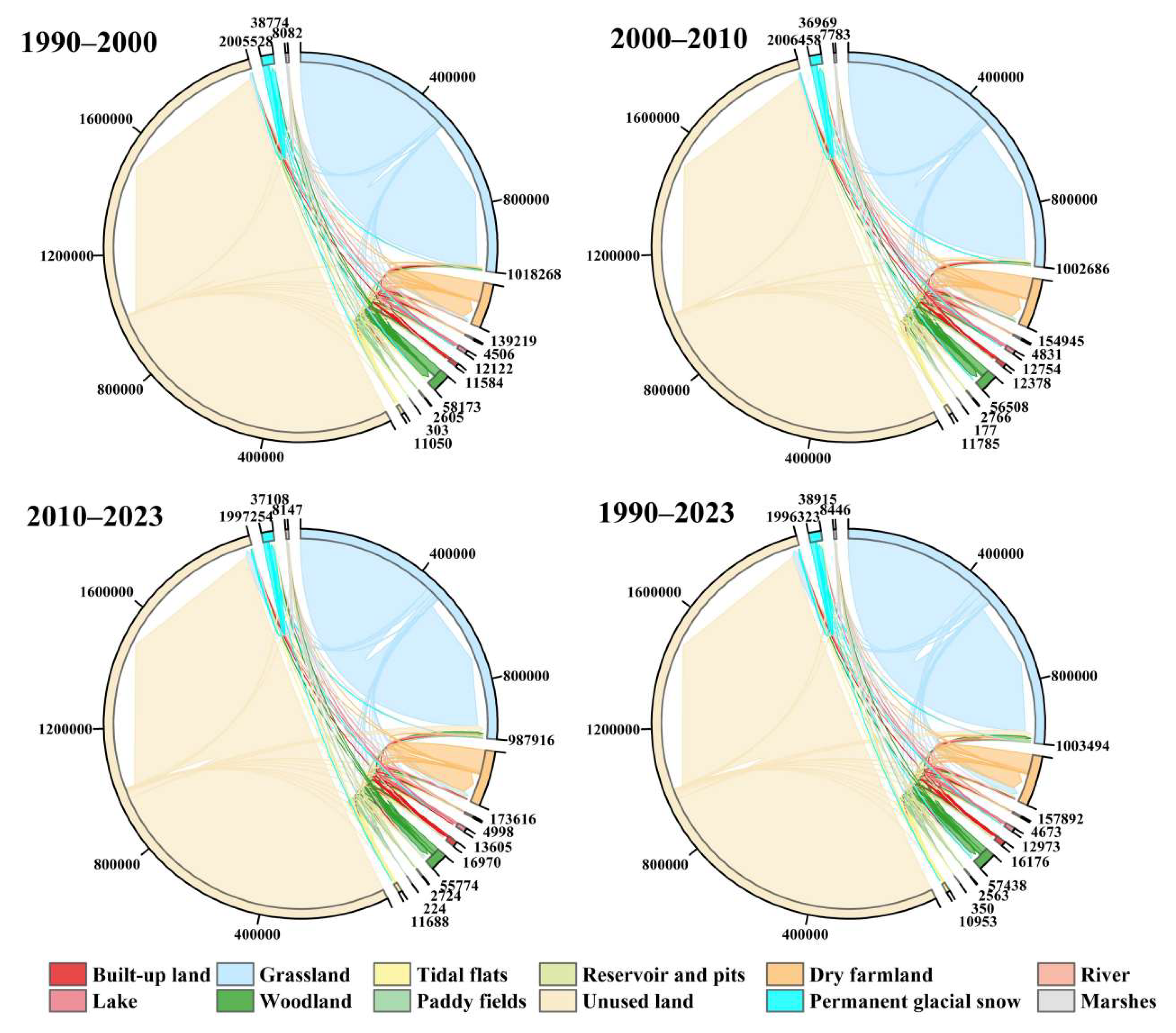
2.3.2. Land Transfer Analysis
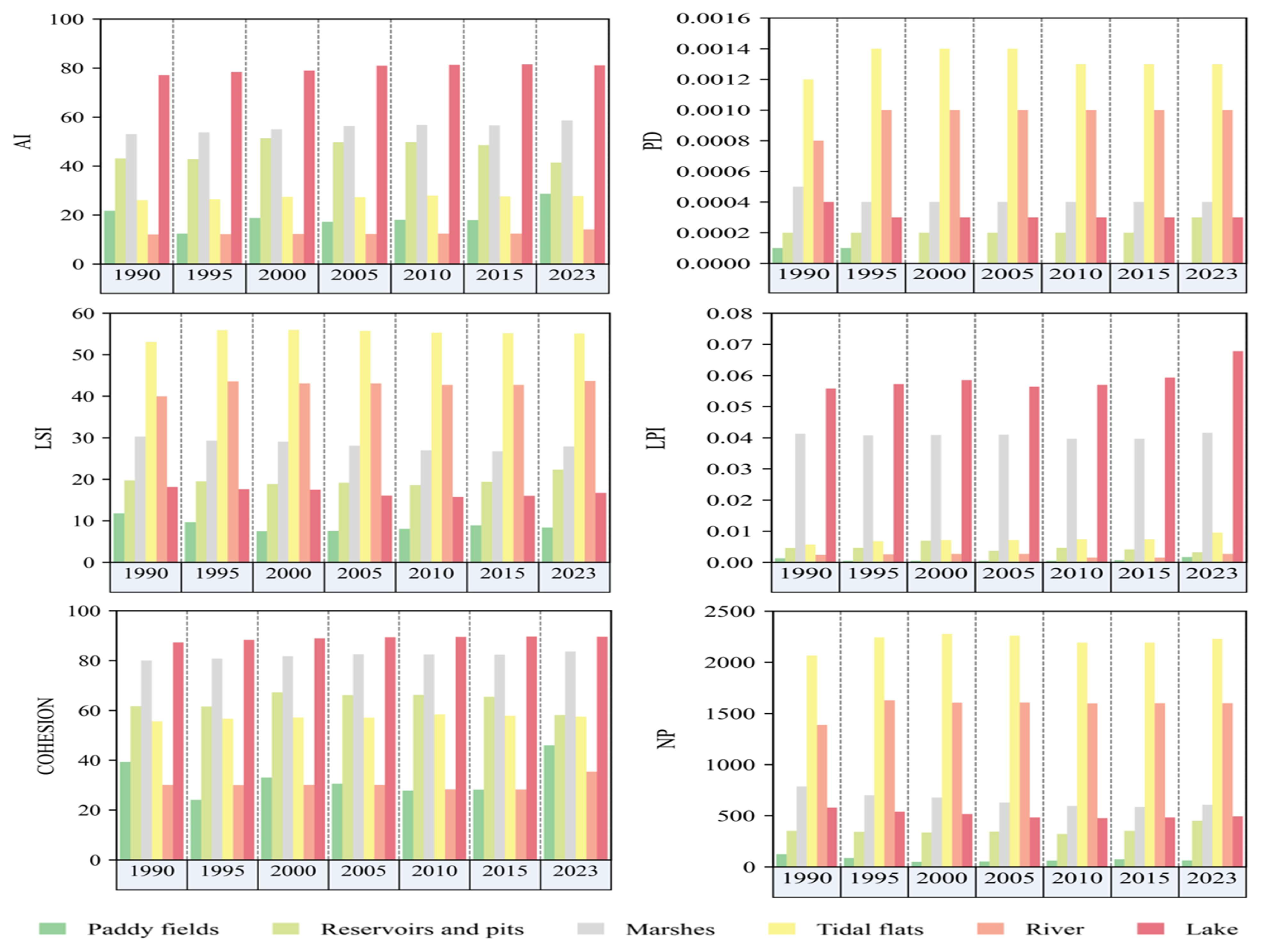
2.3.3. Landscape Pattern Index
2.3.4. InVEST Model
2.3.5. Methodology for Analyzing Drivers of Wetland Change
3. Results
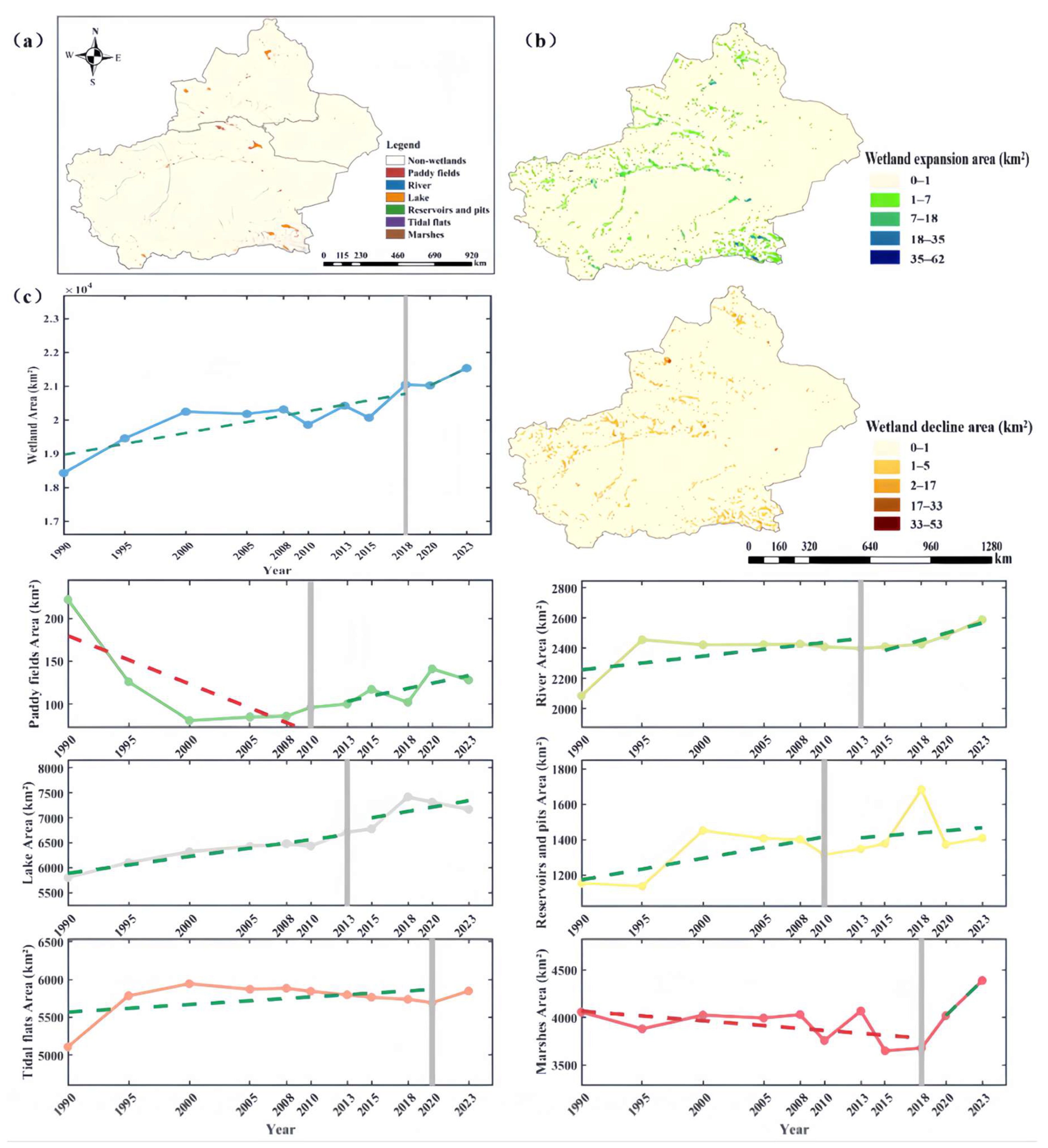
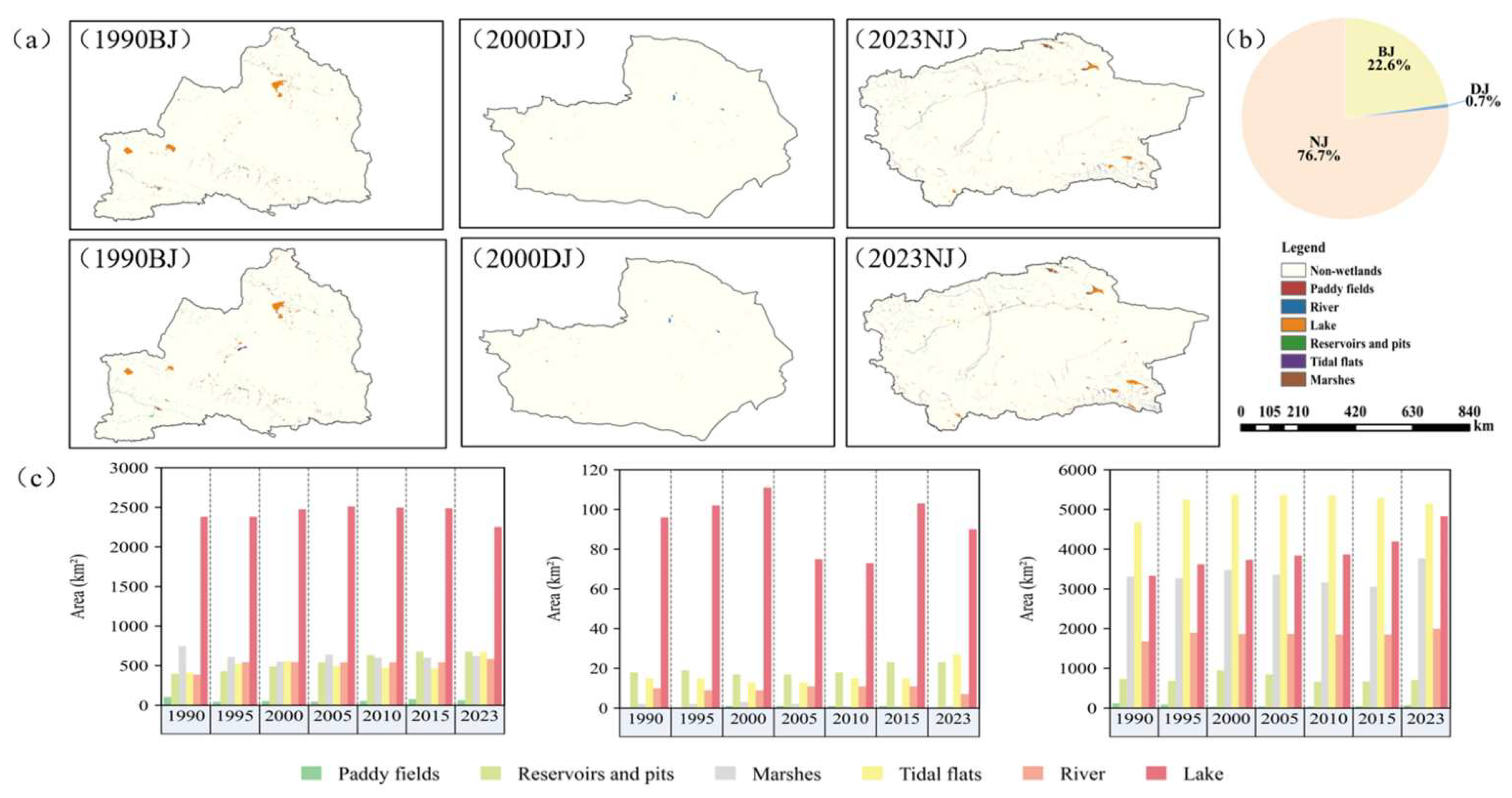
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Wetlands in Xinjian
3.2. Changes in Wetland Landscape Pattern Indices
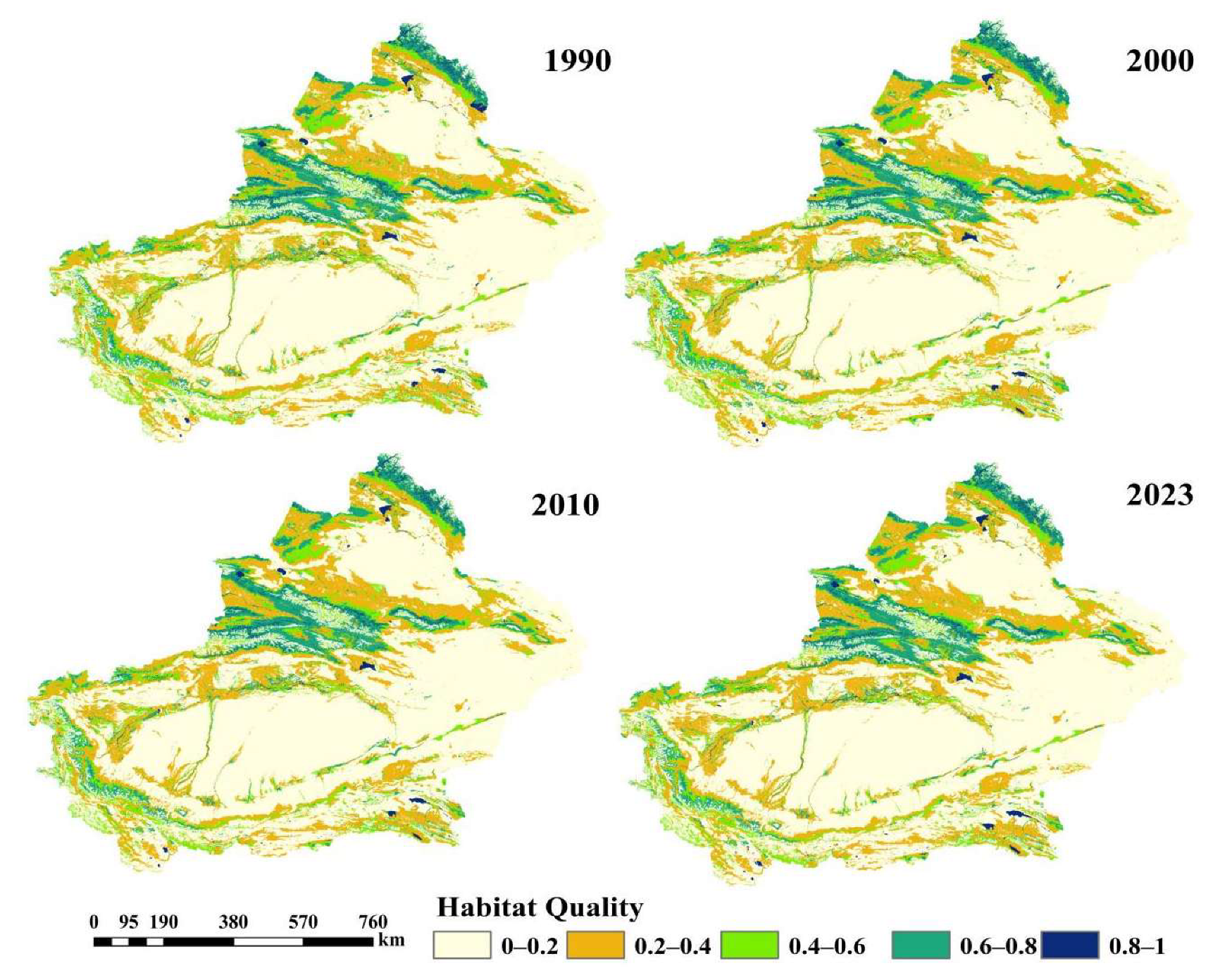
3.3. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Wetland Habitat Quality
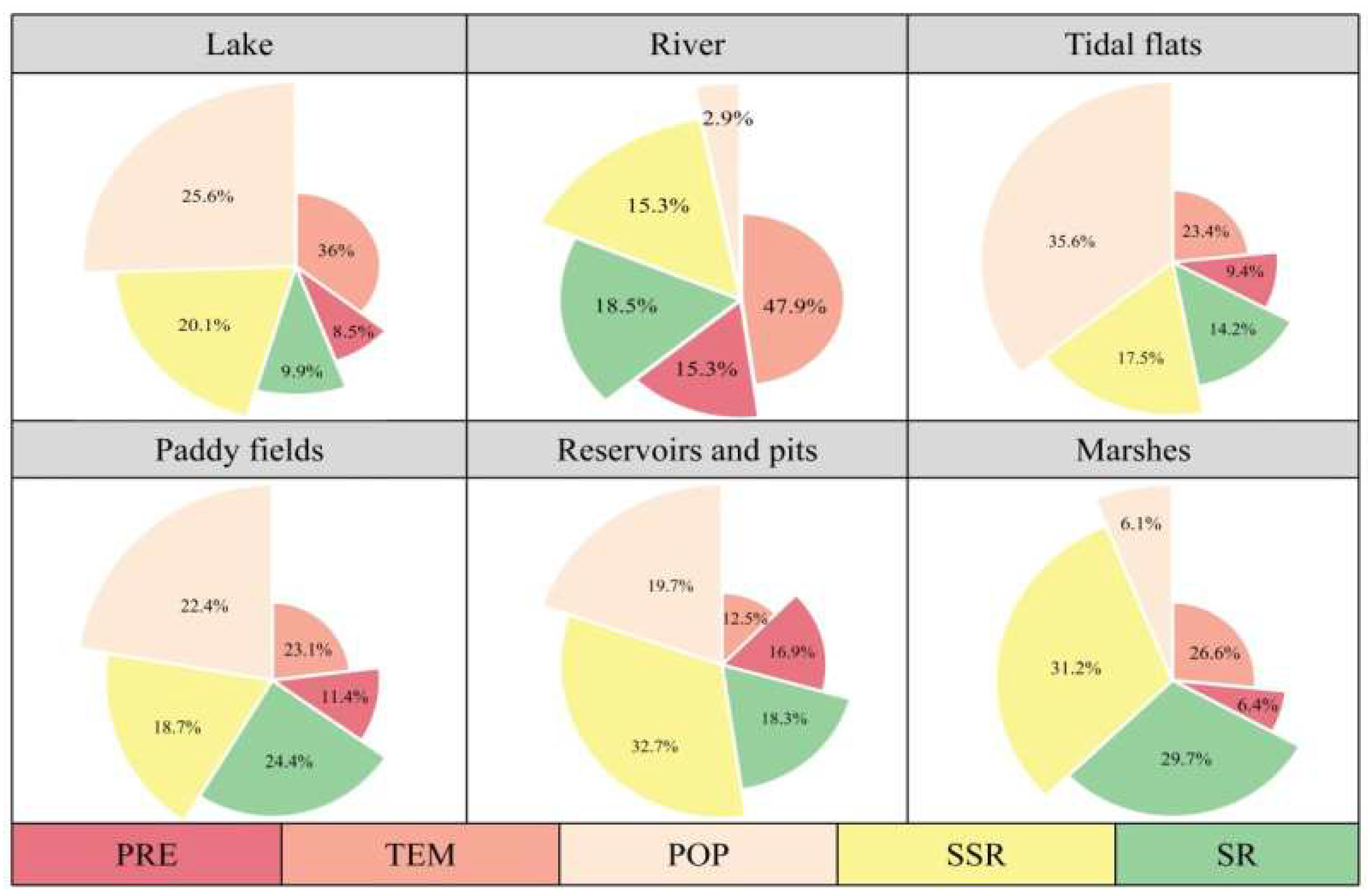
3.4. Analysis of Environmental Factors Affecting the Area of Each Wetland Type
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Wetland Changes in Xinjiang and Their Driving Mechanisms
4.1.1. Wetland Expansion and Regional Differences
4.1.2. Driving Mechanisms of Wetland Changes
4.2. Wetland Conservation Policies and Restoration Measures
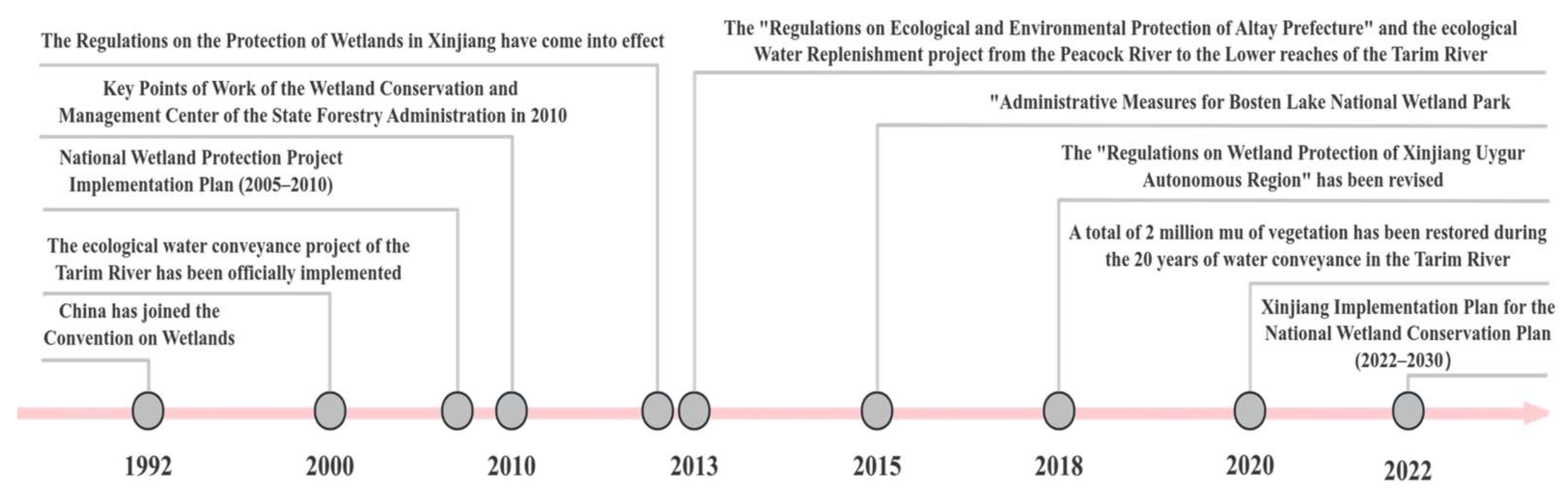
4.2.1. Historical Development of Wetland Conservation Policies
4.2.2. Impact of Ecological Water Diversion Projects
4.2.3. Impact of Agricultural Irrigation and Reservoir Construction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, F.; Su, F.L.; Mi, C.X.; Sun, D. Analysis of driving forces on wetland ecosystem services value change: A case in Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.J.; Niu, Z.G.; Chen, Y.F.; Li, L.F.; Zhang, H.Y. Global wetlands: Potential distribution, wetland loss, and status. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.X.; Chang, Y.; Wang, G.D.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.M.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.H.; Li, B.L.; Zong, M.; Huang, W.T. Planning for the wetland restoration potential based on the viability of the seed bank and the land-use change trajectory in the Sanjiang Plain of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, L.; Malekmohammadi, B.; Yavari, A.R. Assessing and modeling the impacts of wetland land cover changes on water provision and habitat quality ecosystem services. Nat. Resour. Res. 2020, 29, 3701–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.L.; Li, G.S.; Liao, H.J.; Ouyang, N.L.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, D. Remote sensing of coastal wetland degradation using the landscape directional succession model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.S.; Wen, Y.; Fan, W.; Liu, Q.N.; Tarolli, P. Monitoring the coastal wetlands dynamics in Northeast Italy from 1984 to 2016. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adade, R.; Nyarko, B.K.; Aheto, D.W.; Osei, K.N. Fragmentation of wetlands in the south eastern coastal savanna of Ghana. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2017, 12, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Dong, Y.H.; Deng, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, H.D.; Dong, S.K. Forest fragmentation and landscape connectivity change associated with road network extension and city expansion: A case study in the Lancang River Valley. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.W.; Wang, S.X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.L.; Wang, L.T. Spatiotemporal change and landscape pattern variation of eco-environmental quality in Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration from 2001 to 2015. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 125534–125548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, G.K.; Takyi, S.A.; Amponsah, O.; Yeboah, A.S.; Owusu, R.O. Exploring the effects of rapid urbanization on wetlands: Insights from the Greater Accra Metropolitan Area, Ghana. SN Soc. Sci. 2021, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Fan, X.Y.; Ma, J.G.; Pimm, S.L.; Kong, L.Q.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.S.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.G.; et al. Hidden loss of wetlands in China. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3065–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.G.; Deng, Y.; Tang, Z.H.; Lei, X.; Chen, Z. Modeling the potential impacts of urban ecosystem changes on carbon storage under different scenarios by linking the CLUE-S and the InVEST models. Ecol. Model. 2017, 345, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzęciwilk, K.; Grygoruk, M. Restoration is an investment. Comparing restoration costs and ecosystem services in selected European wetlands. J. Water Land Dev. 2025, 64, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Mo, S.; Wu, H.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L. Influence of human activities and climate change on wetland landscape pattern—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleniewska, M.; Mitrowska, D.; Szporak-Wasilewska, S.; Ciężkowski, W.; Berezowski, T. Actual and reference evapotranspiration for a natural, temperate zone fen wetland—Upper Biebrza case study. J. Water Land Dev. 2024, 61, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantyka-Pringle, C.; Leston, L.; Messmer, D.; Asong, E.; Bayne, E.M.; Bortolotti, L.E.; Sekulic, G.; Wheater, H.S.; Howerter, D.W.; Clark, R.G. Antagonistic, synergistic and direct effects of land use and climate on Prairie wetland ecosystems: Ghosts of the past or present? Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 1924–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Q.; Chen, Y.N.; Guan, X.F.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Mao, W.Y. Recent climate and hydrological changes in a mountain-basin system in Xinjiang, China. Earth-Sci. Rev 2022, 226, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiapaer, G.; Liang, S.L.; Yi, Q.X.; Liu, J.P. Vegetation dynamics and responses to recent climate change in Xinjiang using leaf area index as an indicator. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.Q.; He, M.X.; Hu, B.B.; Mo, X.Q.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, B.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Status of wetlands in China: A review of extent, degradation, issues, and recommendations for improvement. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 146, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.N.; Yu, R.; Mao, D.H.; Wen, B.L.; Liu, X.T. Spatiotemporal variations of wetlands in northern Xinjiang with relationship to climate change. Wetlands Ecol. Manag. 2021, 29, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.; Cao, Y.Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Huang, J.H.; Jin, R.; et al. Study on spatiotemporal changes of wetlands based on PLS-SEM and PLUS model: The case of the Sanjiang Plain. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Xia, J.; Hong, M.; Bo, L. The evolution of “three-zone space” in the Yangtze River Economic Belt under major functional zoning strategy from 1980 to 2018. Urban Plan. Forum 2021, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Ma, H.; Yang, D.; Hu, W.; Li, H. The Main Drivers of Wetland Evolution in the Beig-Tian-Hebei Plain. Land 2023, 12, 480. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, W. Spatiotemporal dynamics of wetlands and their driving factors based on PLS-SEM: A case study in Wuhan. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Kuang, W.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Xu, X.L.; Qin, Y.W.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.C.; Zhang, S.W.; Li, R.D.; Yan, C.Z.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, M.H.; Yuan, Q.Z.; Chen, Z.J.; Jiang, S.Z.; Deng, W. Evolution of wetland patterns and key driving forces in China’s drylands. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, F. Evaluation and analysis of upscaling of different land use/land cover products (FROM-GLC30, GLC_FCS30, CCI_LC, MCD12Q1 and CNLUCC): A case study in China. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 17340–17360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yang, X.C.; Jin, Y.X.; Xu, B.; Zhou, Q.B. Remote sensing and evaluation of the wetland ecological degradation process of the Zoige Plateau Wetland in China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Abulizi, A.; Mamitimin, Y.; Mamat, K.; Yuan, L.; Bai, S.J.; Yu, T.T.; Akbar, A.; Zhang, X.F.; Shen, F. Spatiotemporal evolution of habitat quality and scenario modeling prediction in the Tuha region. Land 2024, 13, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhuang, H.L.; Cheng, M.K.; Yang, H.; Wang, W.F.; Ci, H.; Yan, Z.J. Spatial and temporal variations of habitat quality and influencing factors in urban agglomerations on the north slope of Tianshan Mountains, China. Land 2025, 14, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanasopoulos, N.; Singh, A.; Hadjidoukas, P. Machine learning-based modeling, feature importance and Shapley additive explanations analysis of variable-stiffness composite beam structures. Structures 2024, 62, 106206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.J.; Yan, F.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Li, Y.J. Interpretable machine learning models and decision-making mechanisms for landslide hazard assessment under different rainfall conditions. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 270, 126582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.X.; Jin, W.P.; Zhang, H.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M. Analysis of long-term wetland variations in China using land use/land cover dataset derived from Landsat images. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Gu, X.C.; Yang, G.; Yao, J.Q.; Liao, N. Impacts of climate change and human activities on water resources in the Ebinur Lake Basin, Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2021, 13, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.D.; Li, J.L.; Bao, A.M.; Frankl, A.; Wang, H.Y.; Bai, J.; Shen, Z.F.; Li, L.H.; De Maeyer, P.; van de Voorde, T. Ecological restoration trajectory of the Taitema Lake wetland in arid northwest China: A 36-year wetland health assessment using Landsat time series data. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 111956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Li, B.F.; Fan, Y.T.; Sun, C.J.; Fang, G.H. Hydrological and water cycle processes of inland river basins in the arid region of Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2019, 11, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.L.; Xia, Z.L.; Xu, J.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Yang, H.Q.; Li, D.H. Exploring annual lake dynamics in Xinjiang (China): Spatiotemporal features and driving climate factors from 2000 to 199. Clim. Change 2021, 166, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.H.; Wang, Z.M.; Wu, B.F.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, B. Land degradation and restoration in the arid and semiarid zones of China: Quantified evidence and implications from satellites. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3841–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fang, G.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. The Potential Risks and Challenges of Climate Change in the Arid Region of Northwest China. Reg. Sustain. 2021, 2, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Sheng, Y. Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Water Resources in Arid Region of Northwest China. Water 2020, 12, 2543. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Shen, Y. Long-Term Drastic Spatiotemporal Changes of Drainage Areas in Multi-Type Lake Basins in Xinjiang, China. Water 2020, 12, 2092. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.R.; Dube, O.P.; Solecki, W.; Aragón-Durand, F.; Cramer, W.; Humphreys, S.; Kainuma, M.; Kala, J.; Mahowald, N.; Mulugetta, Y.; et al. Framing and Context. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; IPCC Sixth Assessment Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 121–196. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.N.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.T.; Wang, H.J.; Deng, H.J. Progress and prospects of climate change impacts on hydrology in the arid region of northwest China. Environ. Res. 2015, 139, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.X.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.J.; Yuan, R.F.; Gui, J.; Lv, Y.M. Climate background, fact and hydrological effect of multiphase water transformation in cold regions of the Western China: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 33–57. [Google Scholar]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Kraaijenbrink, P.D.A.; Shea, J.M.; Shrestha, A.B.; Pellicciotti, F.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; de Jong, S.M. High-Resolution Monitoring of Snow and Glacier Melt in the Upper Indus Basin Using Remote Sensing. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 359–367. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.S.; Zhou, K.F.; Zuo, Q.T.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, W. Land use/land cover change responses to ecological water conveyance in the lower reaches of Tarim River, China. J. Arid Land 2021, 13, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.D.; Li, J.L.; Bao, A.M.; Warner, T.A.; Li, L.H.; Chang, C.; Bai, J.; Liu, T. Characterizing seasonal and long-term dynamics of a lacustrine wetland in Xinjiang, China, using dense time-series remote sensing imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 5502–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Niu, Z.G.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, K.Y.; Zhou, D.M.; Guo, J.H.; Liang, L.; Wang, X.F.; Li, D.D.; Huang, H.B.; et al. China’s wetland change (1990–2000) determined by remote sensing. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Lu, X.; Cao, J.J. Comparative assessment of the spatiotemporal dynamics and driving forces of natural and constructed wetlands in arid and semiarid areas of northern China. Land 2023, 12, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, A.Y.; Xu, J.; Deng, M.J.; Ling, H.B. How does ecological water conveyance promote the improvement of habitat quality in the lower reaches of inland rivers in arid regions? A ‘past-future’ perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 502, 145374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.Y.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.H.; Chang, Z.Q.; Cao, S.K. Impacts of river recharge on groundwater level and hydrochemistry in the lower reaches of Heihe River Watershed, northwestern China. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhu, C.G.; Wang, Y.; Hao, X.M. Ecohydrological effects of water conveyance in a disconnected river in an arid inland river basin. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.Q.; Chen, Y.N.; Zhang, X.Q.; Ding, J.L.; Lv, G.H. Identifying reservoirs and estimating evaporation losses in a large arid inland basin in Northwestern China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liu, S.H.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, S.C.; Zhang, Y.K.; Feng, T.T.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhao, Y.H.; Lai, Z.Q.; et al. Spatial-temporal patterns of urban expansion by land use/land cover transfer in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, R.; Scholz, M. Adaptation strategy to mitigate the impact of climate change on water resources in arid and semi-arid regions: A case study. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 3557–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data | Time Range | Spatial Resolution | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation (DEM) | 2019 | 30 m | ASTER GDEM (http://www.geodata.cn) (accessed on 22 April 2025) |
| Temperature (TEM), precipitation (PRE) | 1990–2023 | 4 km | Terra Climate Dataset (http://www.climatologylab.org/) (accessed on 30 April 2025) |
| Surface runoff (SR), subsurface runoff (SSR) | 1990–2023 | 0.1° | FLDAS Dataset (https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/) (accessed on 13 May 2025) |
| Population (POP) | 1990–2023 | 1 km | 1990–2000: Resource and Environmental Science Data Center (RESDC), Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/) (accessed on 20 May 2025) 2000–2023: Global Population Distribution Data, LandScan (https://landscan.ornl.gov) (accessed on 20 May 2025) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z. The Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Wetland Expansion in Xinjiang. Land 2025, 14, 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091889
Qian J, Chen Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Li Z, Fang G, Liu C, Wang Y, Wei Z. The Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Wetland Expansion in Xinjiang. Land. 2025; 14(9):1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091889
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Jiaorong, Yaning Chen, Yonghui Wang, Yupeng Li, Zhi Li, Gonghuan Fang, Chuanxiu Liu, Yihan Wang, and Zhixiong Wei. 2025. "The Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Wetland Expansion in Xinjiang" Land 14, no. 9: 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091889
APA StyleQian, J., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Li, Z., Fang, G., Liu, C., Wang, Y., & Wei, Z. (2025). The Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Wetland Expansion in Xinjiang. Land, 14(9), 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091889











