Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics on Urban Surface Metrics in Semi-Arid Heritage Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) Mapping
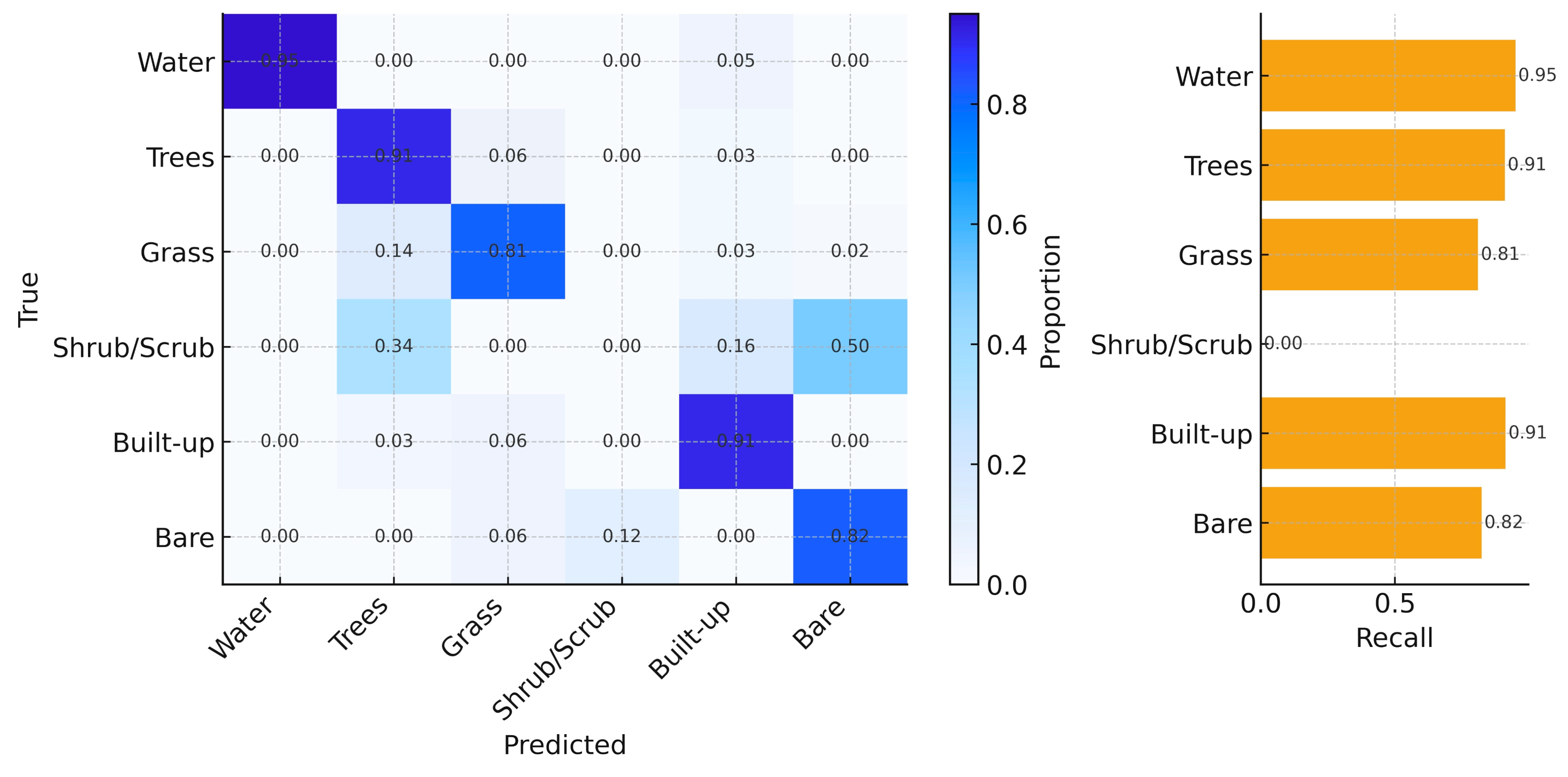
Classification Accuracy and Validation
2.3. Calculation of Spectral Indices
2.3.1. Bare Soil Index
2.3.2. Index-Based Built-Up Index
2.4. LST, SUHI, and UTFVI
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Land Use and Land Cover Transformation in Jaipur, Jodhpur, and Udaipur
3.2. Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics on Urban Build Dynamics
3.3. Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics and Their Influence on Urban Thermal Regimes
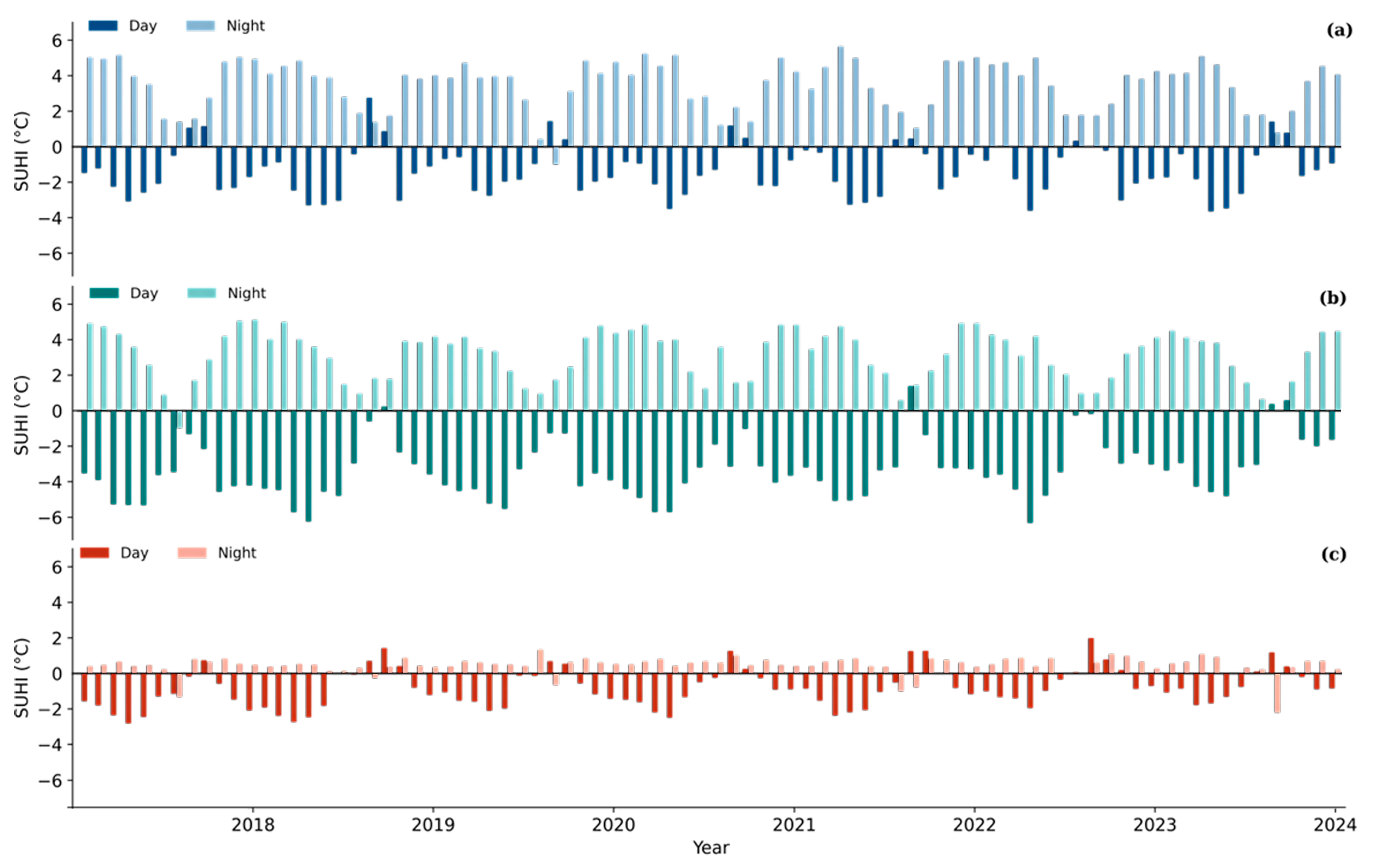
3.3.1. SHUI Dynamics in Semi-Arid Heritage Cities
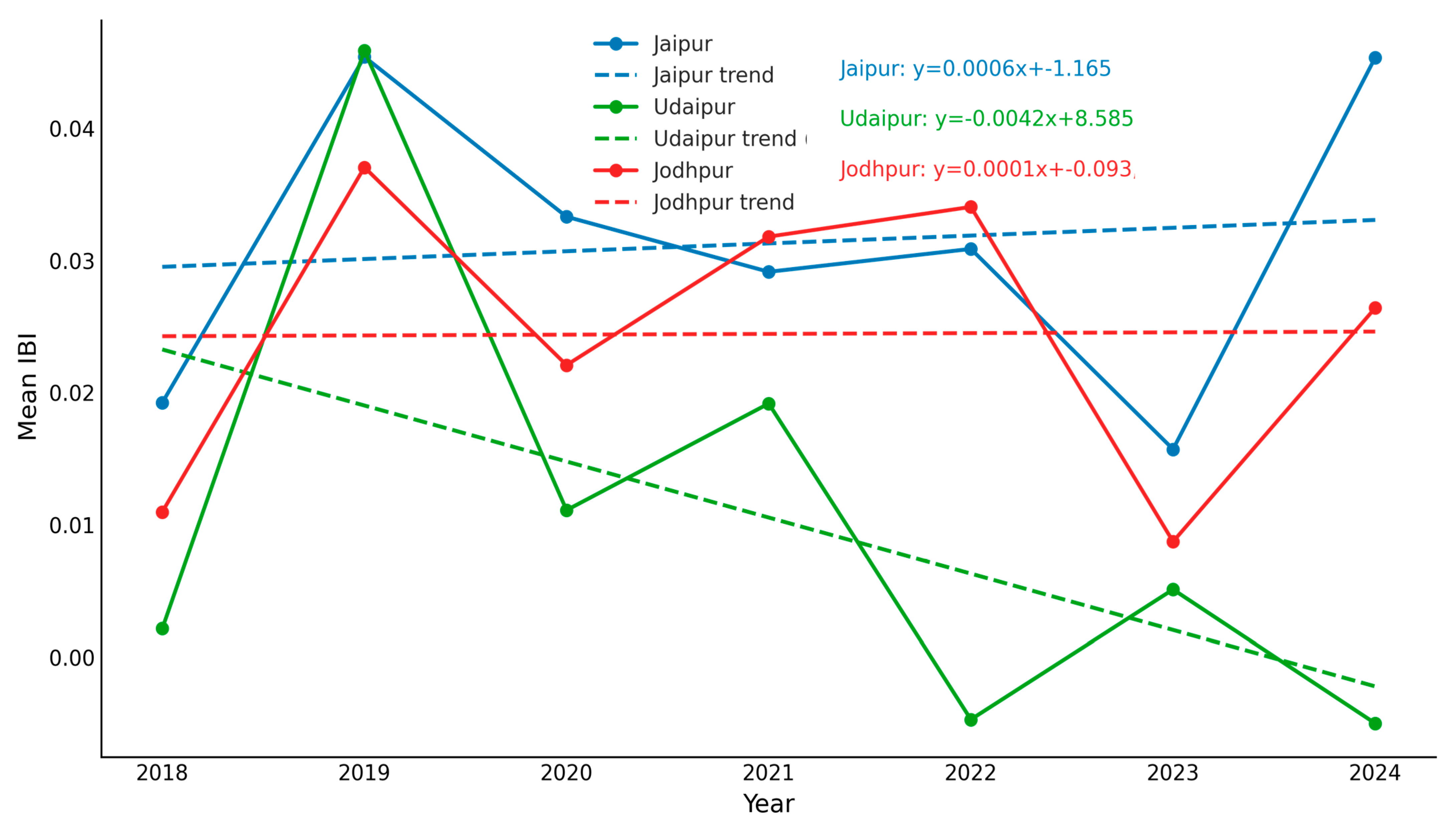
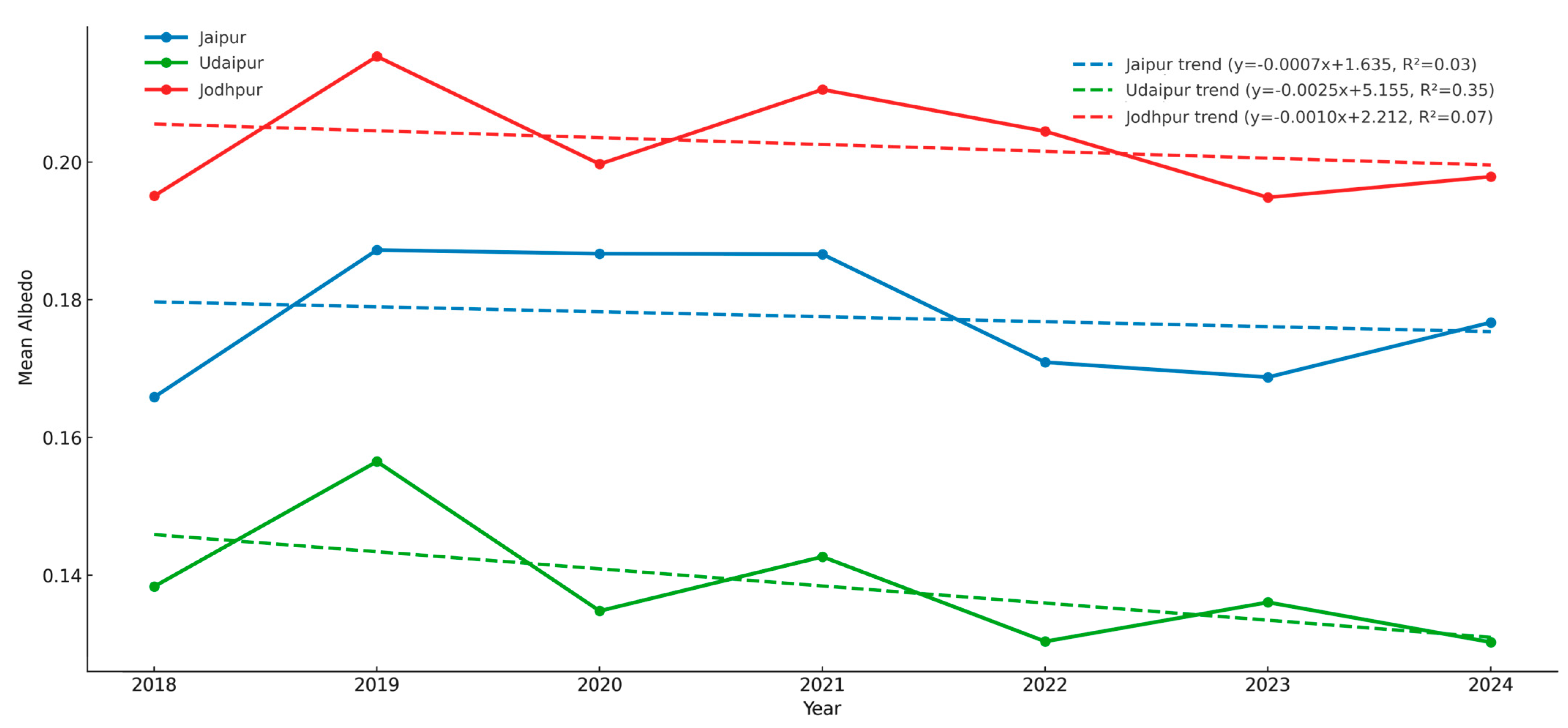
3.3.2. Albedo Dynamics in Semi-Arid Heritage Cities
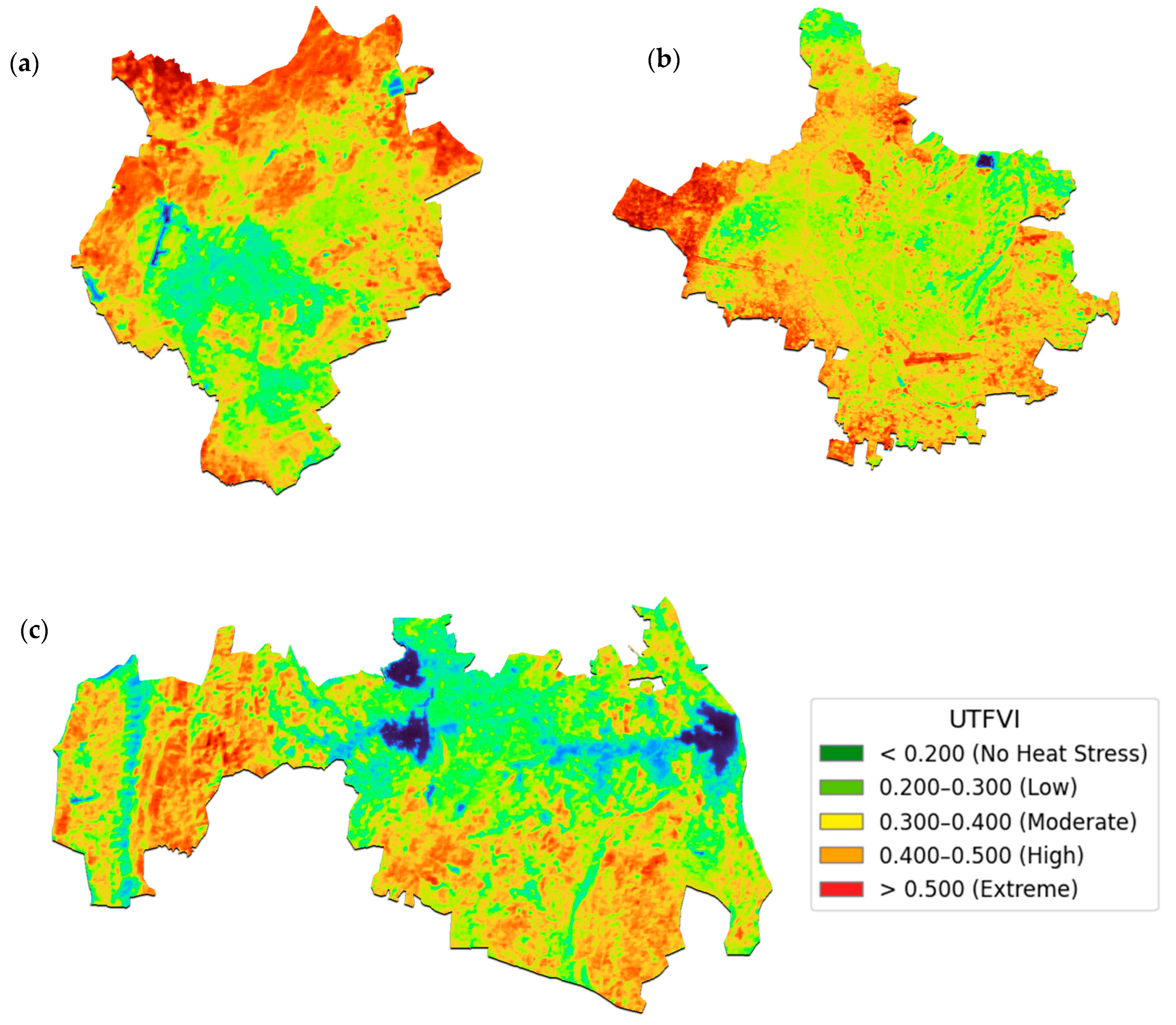
3.3.3. Urban Thermal Field Variance Index (UTFVI) Patterns
3.4. Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics on Bare Soil Exposure and Urban Growth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LULC | Urban Land Use and Land Cover Dynamics |
| IBI | Index-Based Built-up Index |
| SUHI | Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity |
| UTFVI | Urban Thermal Field Variance Index |
| UNESCO | United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization |
| LST | Land Surface Temperature |
| NCR | National Capital Region |
| SUH | Surface Urban Heat |
References
- Gogoi, P.P.; Vinoj, V.; Swain, D.; Roberts, G.; Dash, J.; Tripathy, S. Land use and land cover change effect on surface temperature over Eastern India. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.; Chen, C. Urban expansion and its impacts on local temperature in San Salvador, El Salvador. Urban Clim. 2020, 32, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puplampu, D.A.; Boafo, Y.A. Exploring the impacts of urban expansion on green spaces availability and delivery of ecosystem services in the Accra metropolis. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajizah, S.M.; Altuwaijri, H.A. Assessing the Impact of Urban Expansion on the Urban Environment in Riyadh City (2000–2022) Using Geospatial Techniques. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaidy, A.; Yimer, E.A.; Mogheir, Y.; Huysmans, M.; Villani, L.; van Griensven, A. Groundwater drought and anthropogenic amplifiers: A review of assessment and response strategies in arid and semi-arid areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 978, 179406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, D.P.; Sharma, M.K.; Gaur, K.; Manohar, P.; Malinowski, M.T. Trend Analysis of Temperature and Rainfall of Rajasthan, India. J. Probab. Stat. 2021, 2021, 6296709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, D.; Panda, S.; Dubey, S.K.; Pradhan, R.K. Investigation of temperature and its indices under climate change scenarios over different regions of Rajasthan state in India. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 161, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, D.K. Population Structural Changes and It’s Impact on Economic Growth in Rajasthan. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2022, 9, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Majeed, Y.; Naranjo, G.D.; Gambacorta, E.M. Assessment for crop water stress with infrared thermal imagery in precision agriculture: A review and future prospects for deep learning applications. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 182, 106019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdouri, A.; Wang, R.; Murayama, Y.; Osaragi, T. Understanding the Links between LULC Changes and SUHI in Cities: Insights from Two-Decadal Studies (2001–2020). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Jethoo, A.S.; Varshney, V. Comprehensive diurnal thermal characterization of agro-climatic zones in Rajasthan using remote sensing techniques and time-specific observations. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 16, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Rajasthan: Temperature, Climate Graph, Climate Table for Rajasthan. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/asia/india/rajasthan-739/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Sharma, R. Meteorological Centre Jaipur. Available online: https://epubs.icar.org.in/index.php/JISSS/article/view/128133 (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Jaipur, India Metro Area Population (1950–2025)|MacroTrends’. Available online: https://www.macrotrends.net/global-metrics/cities/21280/jaipur/population?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Maurya, N.K.; Rafi, S.; Shamoo, S. Land use/land cover dynamics study and prediction in jaipur city using CA markov model integrated with road network. GeoJournal 2022, 88, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO World Heritage Centre. The Jantar Mantar, Jaipur. UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1338/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Hill Forts of Rajasthan. UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/247/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Brown, C.F.; Brumby, S.P.; Guzder-Williams, B.; Birch, T.; Hyde, S.B.; Mazzariello, J.; Czerwinski, W.; Pasquarella, V.J.; Haertel, R.; Ilyushchenko, S.; et al. Dynamic World, Near real-time global 10 m land use land cover mapping. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E. Making better use of accuracy data in land change studies: Estimating accuracy and area and quantifying uncertainty using stratified estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Chidthaisong, A.; Diem, P.K.; Huo, L.-Z. A Modified Bare Soil Index to Identify Bare Land Features during Agricultural Fallow-Period in Southeast Asia Using Landsat 8. Land 2021, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ye, R.; Yang, Q.; Hu, T.; Liu, Y.; Chakraborty, T.; Liao, Z. Identification of surface urban heat versus cool islands for arid cities depends on the choice of urban and rural definitions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ottle, C.; Bréon, F.-M.; Nan, H.; Zhou, L.; Myneni, R.B. Surface Urban Heat Island Across 419 Global Big Cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y. The footprint of urban heat island effect in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalan, S.; Sharma, K. Spatio-temporal Assessment of Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics and Urban Heat Island of Jaipur City using Satellite Data. ISPRS-Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, XL-8, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Lu, L.; Fu, P.; Ren, C.; Cai, M.; Li, Q. Exploring the seasonality of surface urban heat islands using enhanced land surface temperature in a semi-arid city. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morini, E.; Touchaei, A.G.; Castellani, B.; Rossi, F.; Cotana, F. The Impact of Albedo Increase to Mitigate the Urban Heat Island in Terni (Italy) Using the WRF Model. Sustainability 2016, 8, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macintyre, H.; Heaviside, C. Potential benefits of cool roofs in reducing heat-related mortality during heatwaves in a European city. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Article-5-vol-34-2-2024-GEOREVIEW. Available online: https://georeview.usv.ro/article-05-vol-34-2-2024/ (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Moisa, M.B.; Gemeda, D.O. Assessment of urban thermal field variance index and thermal comfort level of Addis Ababa metropolitan city, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, S.; Govil, H.; Mukherjee, S. Long-Term Evaluation of Land Surface Temperature with Bare Surface Index and Surface Vegetation Index: A Case Study of a Central Indian City. Pap. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 9, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, A.; Balzter, H.; Ibrahim, G.R.F.; Hameed, H.M.; Wheeler, J.; Adamu, B.; Ibrahim, S.; Najmaddin, P.M. Applying Built-Up and Bare-Soil Indices from Landsat 8 to Cities in Dry Climates. Land 2018, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendy, D.; Tolba, O.; Kamel, T. The impact of increasing urban surface albedo on outdoor air and surface temperatures during summer in newly developed areas. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haashemi, S.; Weng, Q.; Darvishi, A.; Alavipanah, S.K. Seasonal Variations of the Surface Urban Heat Island in a Semi-Arid City. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Sciusco, P.; Jiao, T.; Feron, S.; Lei, C.; Li, F.; John, R.; Fan, P.; Li, X.; Williams, C.A.; et al. Albedo changes caused by future urbanization contribute to global warming. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, B.; Wu, D.; Tang, B. Assessing the Impacts of Urbanization on Albedo in Jing-Jin-Ji Region of China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahfahad; Talukdar, S.; Naikoo, M.W.; Rihan, M.; Mohammad, P.; Rahman, A. Seasonal dynamics of land surface temperature and urban thermal comfort with land use land cover pattern in semi-arid Indian cities: Insights for sustainable Urban Management. Urban Clim. 2024, 57, 102105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayenhoff, E.S.; Voogt, J.A. Impacts of Urban Albedo Increase on Local Air Temperature at Daily–Annual Time Scales: Model Results and Synthesis of Previous Work. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2010, 49, 1634–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large Parks, Reflective Spaces Can Beat Urban Heat: Study|Ahmedabad News-Times of India’. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/ahmedabad/large-parks-reflective-spaces-can-beat-urban-heat-study/articleshow/123173409.cms (accessed on 22 August 2025).
- Hernández, R.C.; Camerin, F. Assessment of ecological capacity for urban planning and improving resilience in the European framework. Cuad. Investig. Geogr. 2023, 49, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
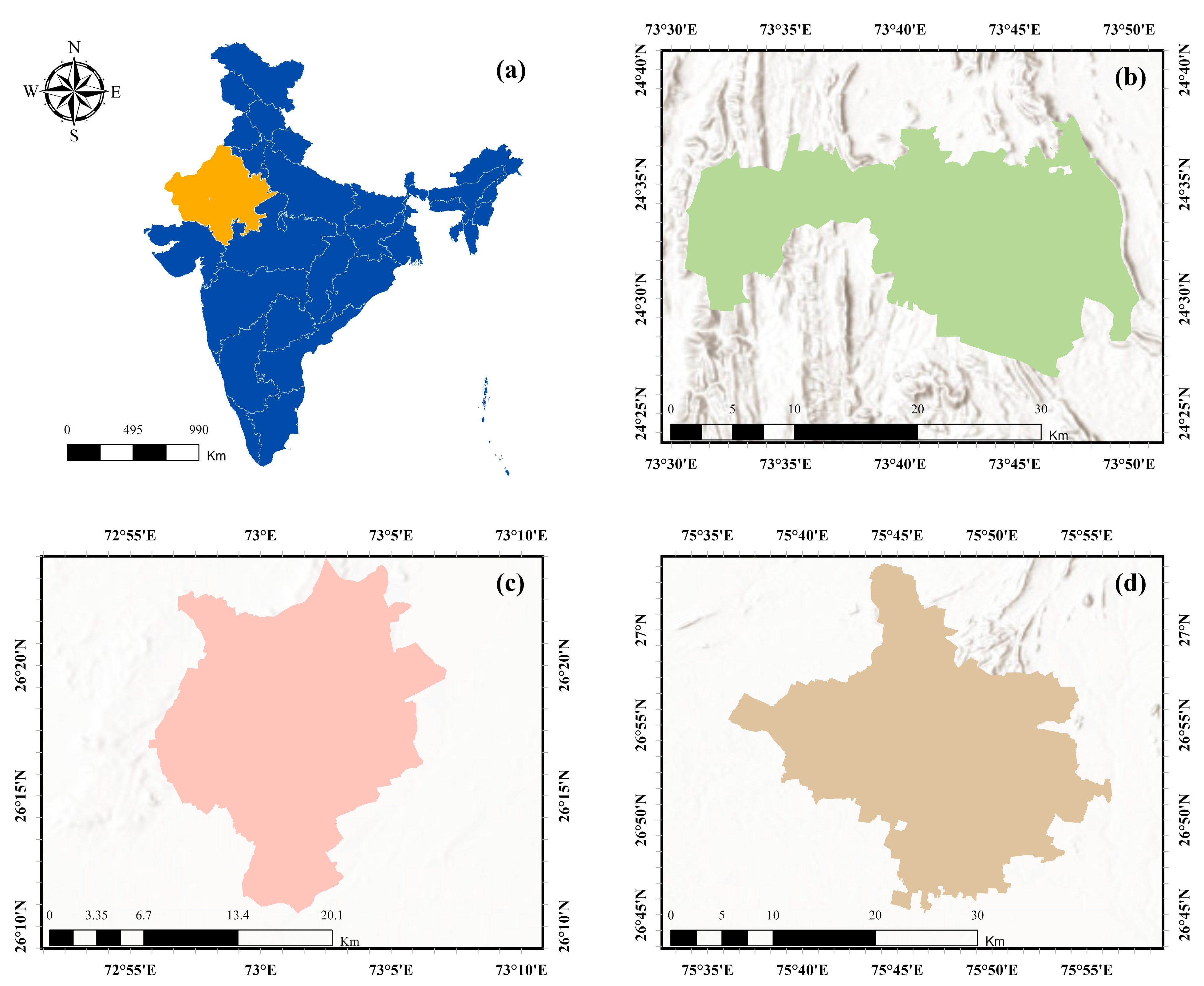





| Dataset/Product | Sensor(s) | Data Source | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic World v1 | Sentinel-2 MSI | Google Earth Engine, World Resources Institute | 10 m | 2018 and 2024 |
| Sentinel-2 MSI | Sentinel-2 MSI | Copernicus/European Space Agency (ESA) | 10–20 m | 2018–2024 |
| Landsat 8/9 C2 Level 2 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS Landsat 9 OLI-2/TIRS-2 | USGS/NASA | 30 m | 2018–2024 |
| City | LULC | Pre | Post | %Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaipur | Bare | 3.59 | 1.85 | −48.47 |
| Jaipur | Built | 346.05 | 383.97 | 10.96 |
| Jaipur | Grass | 93 | 56.08 | −39.7 |
| Jaipur | Shrub/Scrub | 25.15 | 16.18 | −35.67 |
| Jaipur | Trees | 34.99 | 44.49 | 27.15 |
| Jaipur | Water | 1.75 | 1.96 | 12 |
| Jodhpur | Bare | 34.91 | 17.87 | −48.81 |
| Jodhpur | Built | 136.9 | 155.01 | 13.23 |
| Jodhpur | Grass | 48.49 | 50.42 | 3.98 |
| Jodhpur | Shrub/Scrub | 37.25 | 28.87 | −22.5 |
| Jodhpur | Trees | 3.32 | 8.04 | 142.17 |
| Jodhpur | Water | 2.39 | 3.05 | 27.62 |
| Udaipur | Bare | 6.84 | 3.45 | −49.56 |
| Udaipur | Built | 95.97 | 121.48 | 26.58 |
| Udaipur | Grass | 47.43 | 29.84 | −37.09 |
| Udaipur | Shrub/Scrub | 128.95 | 79.18 | −38.6 |
| Udaipur | Trees | 83.21 | 127.13 | 52.78 |
| Udaipur | Water | 13.18 | 14.48 | 9.86 |
| Class Name | Jaipur | Jodhpur | Udaipur |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bare | −48.47 | −48.81 | −49.56 |
| Built | 10.96 | 13.23 | 26.58 |
| Grass | −39.7 | 3.98 | −37.09 |
| Trees | 27.15 | 142.17 | 52.78 |
| Water | 12 | 27.62 | 9.86 |
| City | 2018 Green Area (km2) | 2024 Green Area (km2) | Change (km2) | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaipur | 153.14 | 116.75 | −36.39 | −23.76 |
| Jodhpur | 89.06 | 87.33 | −1.73 | −1.94 |
| Udaipur | 259.59 | 236.15 | −23.44 | −9.03 |
| City | Slope | Intercept | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jaipur | 0.000592 | −1.164527 | 0.0123 |
| Jodhpur | 0.000058 | −0.093250 | 0.0001 |
| Udaipur | −0.004243 | 8.585379 | 0.2655 |
| City SUHI | Series (Day/Night) | Sen’s Slope (°C yr−1) | OLS Slope (°C yr−1) | MK_τ | MK_Z | p (Two-Sided) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaipur | Day | 0.0169 | 0.016 | 0.3333 | 0.901 | 0.3675 |
| Jaipur | Night | −0.0283 | −0.0243 | −0.2381 | −0.601 | 0.548 |
| Jodhpur | Day | 0.1786 | 0.1926 | 0.7143 | 2.103 | 0.0355 |
| Jodhpur | Night | −0.0544 | −0.047 | −0.5238 | −1.502 | 0.1331 |
| Udaipur | Day | 0.0975 | 0.1155 | 0.9048 | 2.703 | 0.0069 |
| Udaipur | Night | −0.0073 | 0.0008 | −0.0476 | 0 | 1 |
| Albedo | Sen’s Slope | OLS Slope | MK_τ | MK_Z | p (Two-Sided) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaipur | −0.00053 | −0.00072 | −0.238 | −0.6 | 0.562 |
| Jodhpur | −0.00162 | −0.00099 | −0.238 | −0.6 | 0.562 |
| Udaipur | −0.00199 | −0.00248 | −0.524 | −1.5 | 0.136 |
| City BSI | Sen’s Slope | OLS Slope | MK_τ | MK_Z | p (Two-Sided) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaipur | 0.001885 | 0.001704 | 0.4286 | 1.2015 | 0.2296 |
| Udaipur | 0.003996 | 0.00395 | 0.7143 | 2.1026 | 0.0355 |
| Jodhpur | 0.004148 | 0.00512 | 0.8095 | 2.403 | 0.0163 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, S.; Avtar, R.; Jain, A.K.; Alkhuraiji, W.S.; Zhran, M. Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics on Urban Surface Metrics in Semi-Arid Heritage Cities. Land 2025, 14, 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091834
Singh S, Avtar R, Jain AK, Alkhuraiji WS, Zhran M. Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics on Urban Surface Metrics in Semi-Arid Heritage Cities. Land. 2025; 14(9):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091834
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Saurabh, Ram Avtar, Ankush Kumar Jain, Wafa Saleh Alkhuraiji, and Mohamed Zhran. 2025. "Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics on Urban Surface Metrics in Semi-Arid Heritage Cities" Land 14, no. 9: 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091834
APA StyleSingh, S., Avtar, R., Jain, A. K., Alkhuraiji, W. S., & Zhran, M. (2025). Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics on Urban Surface Metrics in Semi-Arid Heritage Cities. Land, 14(9), 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091834







