Abstract
Land use efficiency (LUE) serves as a crucial nexus between economic development and sustainable resource management, directly influencing urban production–consumption systems. While economic development stages (EDSs) reflect a region’s environmental carrying capacity and profoundly affect LUE, the specific mechanisms governing this relationship remain unclear. In this study, we combined multi-source data to portray the spatiotemporal patterns of EDSs and LUE in 276 Chinese cities from 1995 to 2020, and we identified the nonlinear effects of EDSs on LUE. Based on the fine-scale LUE, it is confirmed that the older the age of urban land generation, the higher the LUE, laying a theoretical foundation for subsequent research. Simultaneously, the EDS continues to be upgraded, with approximately 70% of cities reaching the post-industrialization stage or higher by 2020. The results of partial dependency plots (PDPs) revealed that the EDS has a positive impact on LUE. From the perspective of different urban scales, the higher the EDSs of supercities, type I large cities, type II large cities, and type II small cities, the greater the positive impact on LUE, whereas the impact patterns at other urban scales follow an inverted U-shape. These findings carry important implications for sustainable spatial development, particularly in optimizing land resource allocation to assist the shift to more efficient production systems and responsible consumption patterns.
1. Introduction
Urbanization is a significant driver of socioeconomic transformation [1]. Global urban land use almost tripled between 1985 and 2015 [2]. Urbanization has contributed to regional integration, economic development [3], and large-scale agricultural production [4]. However, it also has several negative consequences, including global warming [5,6], extreme drought [7], and urban polarization [8]. As urbanization advances, inefficient land use and extensive expansion patterns become increasingly incompatible with the concept of sustainable development, posing significant challenges for the coordinated development of the urban economy, society, and environment. Urban land serves as an important spatial carrier of urban economic development and directly reflects the transformation of land use patterns. Its effective application will assist in adjusting the industrial structure and optimizing the industrial layout, especially in ecologically fragile areas and rapidly urbanized regions [9]. Therefore, strengthening the dynamic supervision and management of urban land use and ensuring the rational allocation and efficient use of land resources are crucial to promoting sustainable urban development, enhancing overall competitiveness, and addressing the challenges brought about by urbanization.
Land use efficiency (LUE), a key indicator of the rational allocation and efficient utilization of land resources and a core factor in measuring urban sustainable development, is essential in promoting urban economic growth and environmental protection [10,11,12,13,14]. Current studies on LUE primarily focus on the following aspects: (1) definition—LUE is defined as the added value of secondary and tertiary industries per unit of urban land, based on the economic benefits of land [15,16,17,18]; (2) measurement methods—based on socioeconomic statistical data from administrative divisions, the LUE of administrative units is calculated using methods such as data envelopment analysis [19], stochastic frontier analysis [20], and the super-efficiency slacks-based measure model [21,22]; (3) research scales—these are primarily based on macro-scales, such as national, regional, provincial, and municipal scales; (4) influencing factors—research focuses on establishing the relationship between LUE and factors such as transportation accessibility [23], industrial structure optimization [24,25], industrial agglomeration [26], urban structure [27], different land use expansion patterns [28,29], and urban land policy [30].
Economic development stages (EDSs), which comprehensively reflect various aspects of a city, directly reflect a city’s level of economic development and are closely related to LUE [31,32]. Therefore, understanding the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of EDSs is crucial in effectively improving LUE. EDS theories primarily include the following: the list stage division (structural changes in major national production sectors), the Kuznets stage division (evolution of industrial structure indicators), the Rostow stage division (evolution of leading industries, manufacturing structure, and human pursuit goals), the Hoffmann theorem (Hoffmann ratio = net output value of consumer goods industry/net output value of capital goods industry), and the Chenery standard model (GDP per capita). On the one hand, the book A Comparative Study of Industrialization and Economic Growth highlights the profound significance of the per capita GDP and its guiding role in the division of the EDSs [33]. On the other hand, only the Chenery standard model clarifies the quantitative association between the per capita GDP and the EDSs [34]. Therefore, the per capita GDP, as a comprehensive representation of a country or region’s economic activity, offers an intuitive and effective way to understand the overall trend of economic development, making it a commonly used metric in the definition of EDSs.
Several limitations in previous research should be noted. First, research to date has primarily relied on socioeconomic statistical data from administrative units to directly calculate LUE. However, the discrepancy between the actual area of urban land and built-up areas leads to rough and inaccurate LUE estimations. Second, research focusing on administrative units has overlooked the spatial heterogeneity of LUE within cities. Finally, while existing research generally notes the strong association between LUE and the EDSs, it has not thoroughly explored how the EDS influences LUE. Given the unprecedented speed and scale of China’s urbanization process and industrial structure transformation within a global context, along with the limitations mentioned above, this study selected 276 Chinese cities as its research subjects. The LitPop method provides an innovative solution to overcome the above limitations by integrating multi-source data. This method can accurately and precisely depict the spatial pattern of LUE at a fine scale, revealing the spatial heterogeneity within cities, which was previously difficult to detect due to administrative boundary limitations. It establishes a new paradigm for the monitoring of LUE and bridges the gap between macro-scale policy planning and micro-scale land management. This study aimed to classify cities into different EDS categories based on the per capita GDP and investigate the nonlinear impact of the EDSs on LUE using a partial dependence plot (PDP), in order to establish a scientific foundation for the rational allocation of land resources and urban sustainability.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Based on data acquisition limitations, 276 cities in China were ultimately selected as the focus of this study (Figure 1). These included 7 supercities, 14 megacities, 14 type I large cities, 68 type II large cities, 109 medium-sized cities, 63 type I small cities, and one type II small city. These cities, distributed across diverse geographical regions and characterized by varying degrees of urbanization and economic development levels, provide an ideal research context for examining EDSs’ impacts on LUE, thereby enhancing the representativeness and generalizability of this study.
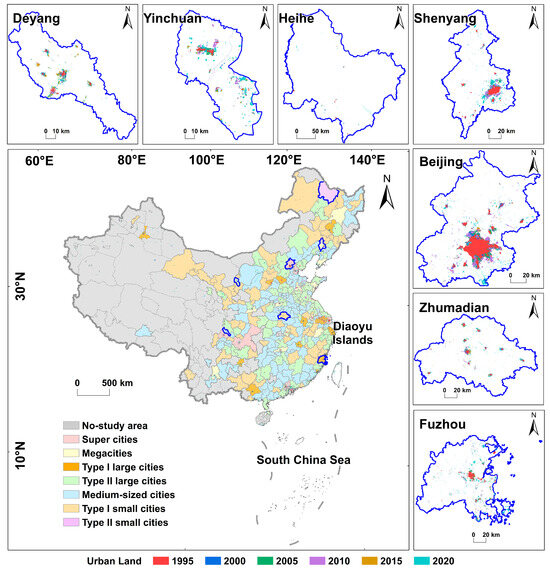
Figure 1.
Geographical location of the study area and urban land expansion process from 1995 to 2020 (supercity: Beijing; megacity: Shenyang; type I large city: Fuzhou; type II large city: Yinchuan; medium-sized city: Deyang; type I small city: Zhumadian; and type II small city: Heihe).
2.2. Modeling Framework and Data Processing
Based on previous research, which demonstrates that LUE is related to EDSs but where the specific impact remains unclear [31], we developed a model to clearly describe the specific impact of EDSs on LUE (Figure 2). We used multi-source data fusion and the LitPop approach to identify the fine-scale LUE, divided EDSs by the deflated per capita GDP, and obtained the spatiotemporal patterns of the LUE and EDSs. Taking the above spatiotemporal patterns as input, after normalization, splitting training and test sets, selecting the best model, and finally using PDPs for visualization, the specific impact patterns of the EDSs on LUE were discovered. Furthermore, the mechanism was investigated from the direct and indirect impacts of EDSs on LUE, as well as the differences in patterns across urban scales.
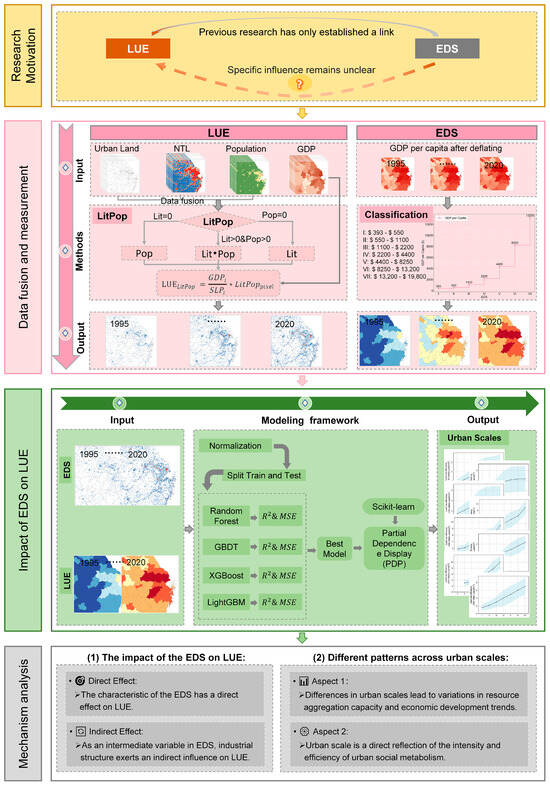
Figure 2.
Modeling framework of this study (research motivation, data fusion and measurement, impact of EDSs on LUE, and mechanism analysis).
This study used data from multiple sources, including land use data, nighttime light images, and the China Urban Statistical Yearbook. The data are presented in Table 1. Data preprocessing included the following. (1) Identification of urban land: Based on urban land data in the CNLUCC, the dataset was preprocessed (e.g., projection and clipping) and verified using CLCD and Sentinel data to create a high-precision urban land dataset for the years 1995 to 2020. (2) Correction of nighttime light data: The nighttime light images included DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS data. DMSP/OLS requires mutual and saturation correction, whereas NPP/VIIRS data require background noise removal and adjustment for extreme brightness values. Additionally, the continuity of the two nighttime light datasets was corrected to generate a stable nighttime light dataset for the years 1995 to 2020. (3) Correction of population data: To ensure accuracy and consistency, this study used the population spatial distribution grid dataset from the Resource and Environmental Science and Data Platform of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Population census data from each city served as a benchmark for correction, resulting in the creation of a population grid dataset for the years 1995 to 2020. (4) GDP of secondary and tertiary industries: To account for price changes affecting real GDP growth, this study selected 1995 as the base year and used officially released secondary and tertiary GDP indices to deflate the nominal GDP from 2000 to 2020, thereby eliminating price factor interference and obtaining the real GDP of secondary and tertiary industries for each city. (5) Per capita GDP: Using 1995 as the base year, it is essential to eliminate the impact of price changes by applying the per capita GDP index for deflation, followed by conversion using the exchange rate from CNY to USD in that year to obtain the per capita GDP data for each city in USD from 1995 to 2020.

Table 1.
Data sources and descriptions.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Measurement of LUE
Nighttime light data have been frequently utilized to map urbanization progress [35,36,37,38], estimate GDP and populations [39,40], analyze electricity consumption [41], and monitor disasters [42]. Previously, the spatialization of socioeconomic data has principally utilized nighttime light data to decompose data proportionally to each pixel. However, the application of this proportional relationship leads to overallocation in suburban areas and underallocation in urban areas [43]. To alleviate this phenomenon, Zhao et al. [44] proposed the LitPop method with higher accuracy, which combines nighttime light data with population data to generate lighted population images and then decomposes them proportionally. Eberenz et al. [43] further enhanced the LitPop method, leading to its widespread application [45,46]. Building on the research foundation outlined above, this study proposes a process for measuring LUE based on the improved LitPop method (Equation (1)) to generate light population images from 1995 to 2020. We then constructed a mapping relationship between the total GDP of each city’s secondary and tertiary industries and the light population images. Finally, based on the mapping relationships (Equation (2)), the total GDP of each city’s secondary and tertiary industries was distributed across a smaller regular grid (1 km × 1 km) to measure LUE in Chinese cities. The formula is as follows:
where is the pixel value of the nighttime light images, is the pixel value of the population grid data, is the pixel value of the images, is the sum of the pixels in the nighttime light population image of each city, is the sum of the GDP of the secondary and tertiary industries in each city, and is the LUE for each pixel.
2.3.2. Division of EDSs
The per capita GDP can effectively and objectively reflect the overall patterns of urban economic development and is the most widely used indicator in evaluating EDSs. This study incorporates the temporality of the classification criteria and dynamic changes in the CNY-USD exchange rate, drawing upon the classification criteria developed by Qi et al. [34], which have been widely applied in other studies [47,48]. The EDSs are divided into seven categories based on the per capita GDP data of each city in US dollars from 1995 to 2020: primary production stage I (USD $393–$550), primary production stage II (USD $550–$1100), initial industrialization (USD $1100–$2200), intermediate industrialization (USD $2200–$4400), post-industrialization (USD $4400–$8250), initial developed economy (USD $8250–$13,200), and developed economy era (USD $13,200–$19,800).
2.3.3. Emerging Hotspot Analysis
Emerging hotspot analysis, which enables an in-depth exploration of the potential trends and patterns in data, has been widely used in various fields, including urban expansion [49], urban heat islands [50], urban transportation [51], and epidemics [52]. Compared to traditional hotspot analysis, emerging hotspot analysis can more effectively identify the dynamic changes in data across both temporal and spatial dimensions, allowing for the identification of potential future trends. Additionally, it can identify the entire process of hotspot formation, strengthening, or weakening, providing valuable insights into prospective locations and attributes.
The emerging hotspot analysis process in this study was as follows. (1) A spatiotemporal cube (in NetCDF format) was constructed from each year’s LUE to intuitively reflect the temporal, spatial, and attribute characteristics of LUE. (2) The spatial and temporal patterns of LUE were analyzed using the ArcGIS Pro emerging hotspot analysis tool. Input from a spatiotemporal cube, set the number of spatial neighbors to 8, and set the neighbor time step to 1, followed by Mann–Kendall trend analysis and significance testing. (3) The spatiotemporal patterns of LUE were classified based on the spatial patterns of LUE in each city, along with the Mann–Kendall trend analysis and significance test results. There were 17 developing hotspot analysis patterns, including eight hotspots (new, consecutive, intensifying, persistent, diminishing, sporadic, oscillating, and historical), eight cold spots (new, consecutive, intensifying, persistent, diminishing, sporadic, oscillating, and historical), and no pattern detected.
2.3.4. Identification of Marginal Effects
A partial dependence plot (PDP) depicts the marginal effects of feature variables on a machine learning model’s prediction outcomes and shows whether the target variable and feature have a linear or nonlinear relationship. When other factors remain constant, the PDP illustrates the average impact of a single variable on the model prediction results [53,54]. In this study, the PDP was shown to accurately identify the nonlinear trend in the impact of the EDSs on LUE, helping to understand how changes in the EDS affect LUE. To ensure that the PDP diagram accurately represented the impacts of the EDSs on LUE, this study evaluated the four models of random forest, GBDT, XGBoost, and LightGBM to determine the best regression model. The R2 results (Figure 3a) showed that XGBoost > LightGBM > random forest > GBDT, and the XGBoost model had the lowest MSE (Figure 3b). To provide a more intuitive comparison of the model effects, the mean R2 and MSE of each model were calculated (Figure 3c). The results revealed that XGBoost delivered the best performance. Furthermore, because there are clear differences in the EDSs and LUE at different urban scales, this study selected the XGBoost regression model from the perspective of different urban scales and used the scikit-learn toolkit’s Partial Dependence Display function to map a PDP diagram of the impact of the EDS on LUE to identify its marginal effect.
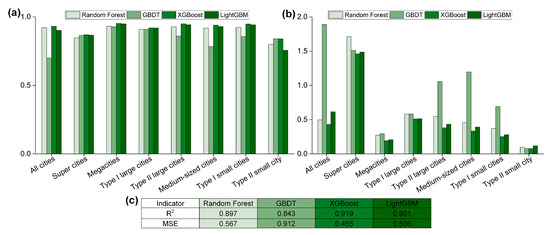
Figure 3.
R2 and MSE of random forest, GBDT, XGBoost, and LightGBM: (a) R2 for different urban scales, (b) MSE for different urban scales, and (c) average R2 and MSE.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of LUE
Temporal evolution trends and spatial heterogeneity in LUE: China’s LUE has increased annually, with the average value rising from 164 million CNY/km2 in 1995 to 501 million CNY/km2 in 2020, representing an average annual increase of 13 million CNY/km2. The spatial heterogeneity of LUE is primarily evident in three key aspects. First, based on the spatial heterogeneity of LUE within the city, regardless of the urban scale, the LUE is highest in the city center and gradually diminishes toward the peripheral areas (Figure 4a), a trend that aligns with the process of urban land expansion. Second, there were noticeable differences in LUE across various urban scales (Figure 4b). In 1995, the LUE decreased in the order of the urban scale. However, as the economy gradually developed, the LUE in different urban scales increased to varying extents. By 2020, the ranking of LUE was, in descending order, as follows: supercities, type I large cities, megacities, type II large cities, medium-sized cities, type I small cities, and type II small cities. Regarding the proportion of LUE at different urban scales (Figure 4c), the proportion of higher LUE increased annually. By 2020, with the continuous expansion of the urban scale, the proportion of LUE of less than 100 million CNY/km2 gradually decreased, while the proportion of LUE greater than 2 billion CNY/km2 steadily increased. Finally, the Getis–Ord Gi statistic was used to identify specific clusters of high and low LUE. Chinese cities exhibit a three-segmented distribution: predominantly cold spots in the north, not significant in the center, and predominantly hotspots in the south (Figure 4d). Emerging hotspot analysis was used to effectively capture the clustering trends of LUE across time and space. Regarding hotspots, oscillating hotspots were primarily concentrated in Central and Southern China, as well as in some cities in Northeast China, while consecutive hotspots were mainly concentrated in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration and Chengdu–Chongqing urban agglomeration, which are closely related to the high level of economic development and national policy support caused by the industrial agglomeration effect. The rapid development of the Chengdu–Chongqing urban agglomeration is also consistent with current national policy-guided strategic planning [55,56]. Cold spots include diminishing, sporadic, and historical cold spots, which are mainly located in the northwest regions, such as Shanxi Province, the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region.
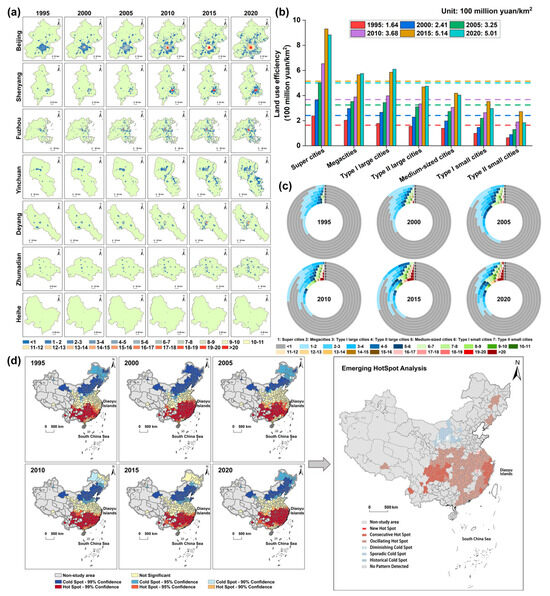
Figure 4.
Characteristics of LUE: (a) spatial distribution characteristics of LUE (with the urban scale decreasing from top to bottom), (b) average LUE in different urban scales, (c) proportion of LUE at different urban scales, and (d) hot and cold spot analysis.
Land maturation and efficiency enhancement process: The term “age” is introduced to reveal the land maturation and efficiency enhancement process and is defined as the difference between 2020 and the year in which urban land is generated. As urban land ages, the continuous improvement in LUE reflects the process of land maturation and efficiency enhancement. This concept is essentially different from the general term “land development” and emphasizes the dynamic evolution of functional optimization and efficiency accumulation during the use of urban land. Figure 5a–f compare the differences in land maturation and efficiency enhancement processes across various urban scales at different ages. From the perspective of the differently colored polygons, it is clear that, as urban land matures, LUE gradually increases, confirming the land maturation and efficiency enhancement processes. Using urban land in 1995 as an example, the LUE of all cities increased from 164 million CNY/km2 at age 0 to 826 million CNY/km2 at age 25. However, the LUE at different ages does not always follow a pattern whereby older land consistently shows higher LUE. For example, megacities have lower LUE at age 25 (1.08 billion CNY/km2) than at age 20 (1.11 billion CNY/km2). The land maturation and efficiency enhancement process provides a theoretical foundation for subsequent research on the impact of EDSs on LUE.
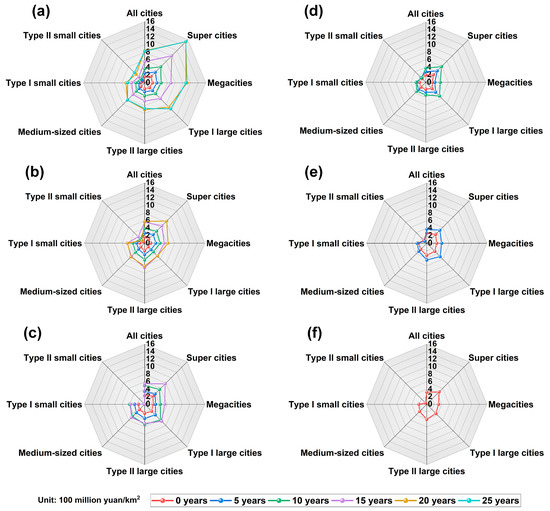
Figure 5.
Urban land maturation and efficiency improvement processes. Polygons of different colors represent LUE at various ages. The red polygon represents LUE at age 0. (a) Urban land in 1995, (b) urban land in 2000, (c) urban land in 2005, (d) urban land in 2010, (e) urban land in 2015, and (f) urban land in 2020.
3.2. Characteristics of EDSs
Temporal evolution trends of EDSs: From 1995 to 2020, the EDSs of Chinese cities continued to upgrade; by 2020, approximately 70% of cities had entered the post-industrialization stage or a more advanced stage. Figure 6a illustrates the temporal evolution trend of the percentage at different EDSs from 1995 to 2020. In 1995, 87.32% and 12.31% of cities were in the primary production and industrialization stages, respectively; only Shenzhen had entered the stage of an initial developed economy. By 2000, most Chinese cities remained in the primary production stage, but the number of cities in primary production stage II had increased significantly, accounting for 50.36%. The percentage of cities in the industrialization stage increased to 31.52% and Shenzhen entered the developed economy era. In 2005, the proportion of cities in the primary production stage decreased to 31.16%, with most cities basically in primary production stage II. Meanwhile, the percentage of cities in the industrialization stage increased significantly, reaching 68.12%. Shenzhen maintained its position in the developed economy era, while Zhuhai entered the initial developed economy stage. In 2010, only 2.17% of cities were in the primary production stage, while 91.30% were in the industrialization stage, with the initial, intermediate, and post-industrialization stages accounting for 27.90%, 45.29%, and 18.12%, respectively. A total of 6.52% of the cities in the initial developed economy and developed economy eras were located in the Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta urban agglomerations. By 2015, for the first time, all cities had moved out of the primary production stage. A significantly higher number of cities entered the initial developed economy and developed economy eras, accounting for nearly 20% of the total, with provincial capitals mostly entering the initial developed economy stage. In 2020, the combined percentage of cities in intermediate industrialization and post-industrialization reached 71.01%, with post-industrialization accounting for an even greater share at 42.03%. The number of cities that had advanced to the initial developed economy and developed economy era increased significantly, reaching 76, accounting for 27.54% of the total.
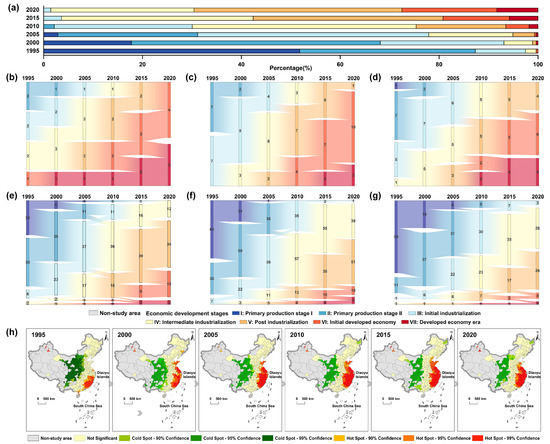
Figure 6.
Division of the EDSs: (a) the percentages of the EDSs in different years; (b–g) show the transition processes of the EDSs in different urban scales and (h) shows the identification of hot and cold spots in the EDSs from 1995 to 2020.
Spatial differences and identification of hot and cold spots in EDSs at various urban scales: There is a correlation between the EDS and the urban scale—the larger the urban scale, the later the EDS (Figure 6b–g). In 1995, cities at all urban scales were mainly in the primary production stage. By 2020, supercities and megacities had entered the initial developed economy or even the developed economy era. Type I large cities were in post-industrialization or higher, while type II large cities, medium-sized cities, and type I small cities were primarily in the intermediate industrialization stage or in higher stages of industrialization. Type II small cities were developing slowly and were still in the intermediate industrialization stage. From the identification of hot and cold spots using the EDSs (Figure 6h), the hotspots were mainly concentrated in the southeast in 1995 and then gradually expanded northward. By 2005, a spatial pattern emerged with the eastern coastal areas serving as hotspots, a trend that has persisted to the present. The expansion areas of these hotspots were basically in non-significant regions. Cold spots were primarily concentrated in the central and western regions, and their extent has remained largely unaltered.
3.3. LUE Characteristics Varying Throughout EDSs
Figure 7 shows a bubble heat map that depicts the various characteristics of LUE in different EDSs. The LUE increased as the bubble was enlarged and the color darkened and vice versa. For all cities (Figure 7a), from a vertical perspective, taking 2010 as an example, the LUE increased from 233 million CNY/km2 in primary production stage II to 582 million CNY/km2 in the developed economy era, indicating that, as the EDS advanced, the LUE increased. From a horizontal perspective, taking the developed economy era as an example, the LUE increased from 290 million CNY/km2 in 2000 to 870 million CNY/km2 in 2020, indicating that the later the EDS, the higher the LUE. Different urban scales also followed the same patterns, with varying growth speeds and magnitudes (Figure 7b–h). As the EDS advances, the LUE of supercities and type II large cities increases at a faster rate and that of megacities and type I large cities increases at a moderate rate. In contrast, the LUE of medium-sized cities and small cities increases relatively slowly, which may be closely linked to factors such as the urbanization level, land use structure, industrial structure, and policy support [30,57,58].
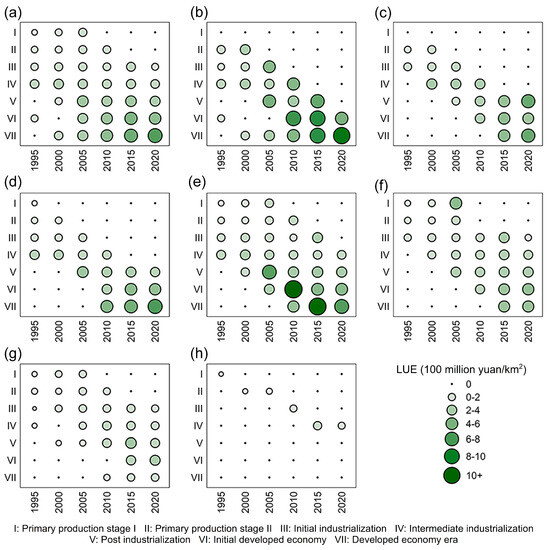
Figure 7.
Differences in LUE at different EDSs: (a) all cities, (b) supercities, (c) megacities, (d) type I large cities, (e) type II large cities, (f) medium-sized cities, (g) type I small cities, and (h) type II small cities.
3.4. Impact of EDSs on LUE
Theoretical basis: The above findings indicate a positive association between the EDS and LUE; as the EDS advances, the LUE gradually increases. At the same time, the spatial differences in the EDSs and LUE exhibit some consistency across urban scales and hot and cold spot areas. In summary, these two aspects provide an important theoretical basis for further research on the specific mechanism of the impact of the EDSs on LUE.
Impact of EDSs on LUE: The EDS has a significant impact on the quality of life and consumption structure, but it also directly reflects the vitality and development potential of the economy of a city. Exploring the impact of the EDSs on LUE will help to optimize industrial structures and promote sustainable urban development. The PDP was used to investigate the average influence of the EDSs on LUE by visualizing the marginal effects of the feature points. As illustrated in Figure 8a–h, regardless of the urban scale, the EDS has a positive impact on LUE, indicating that LUE gradually increases as the EDS advances. The impact of the EDS on LUE varies depending on the urban scale. By 2020, the impact of the EDS on LUE had decreased in the following order: supercities, type II large cities, type I large cities, megacities, medium-sized cities, type I small cities, and type II small cities.
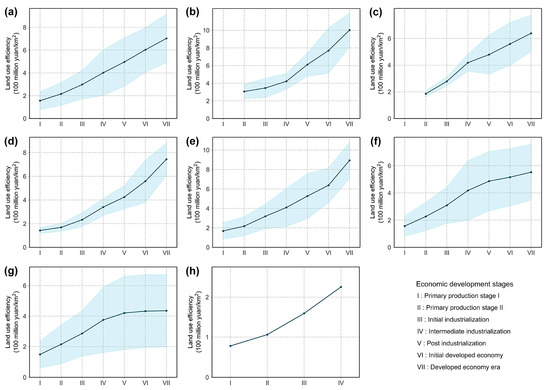
Figure 8.
Impact of EDSs on LUE at different urban scales (X-axis, EDS; Y-axis, LUE; the blue-shaded part is one standard deviation): (a) all cities, (b) supercities, (c) megacities, (d) type I large cities, (e) type II large cities, (f) medium-sized cities, (g) type I small cities, and (h) type II small cities.
Figure 9 demonstrates that the growth in LUE at different urban scales progressed from one EDS to the next. For all cities, when the economic development stage transitioned from stage I to II, stage II to III, stage III to IV, stage IV to V, stage V to VI, and stage VI to VII, the LUE increased by 59 million CNY/km2, 82 million CNY/km2, 104 million CNY/km2, 94 million CNY/km2, 107 million CNY/km2, and 100 million CNY/km2, respectively. This confirms the trend whereby the later the EDS, the greater the impact on LUE. The impact of LUE evolution from one EDS to the next varied across different urban scales. According to the average growth in LUE, supercities, megacities, type I large cities, type II large cities, medium-sized cities, type I small cities, and type II small cities exhibited values of 139 million CNY/km2, 91 million CNY/km2, 100 million CNY/km2, 121 million CNY/km2, 66 million CNY/km2, 48 million CNY/km2, and 49 million CNY/km2 respectively. Combined with the growth trend in the impact of the EDS on LUE between 1995 and 2020, with the evolution of the EDS, the growth rate of LUE in supercities, type I large cities, type II large cities, and type II small cities gradually increased. This indicates that the later the EDSs of these cities, the greater the impact on LUE. With the advancement of the EDS, the growth rate of the LUE for megacities, medium-sized cities, and type I small cities was the highest during the transition from initial to intermediate industrialization, at 140 million CNY/km2, 109 million CNY/km2, and 89 million CNY/km2, respectively. This implies that the impact of the EDSs of these cities on LUE follows an inverted U-shaped pattern, with the LUE growing faster at larger urban scales.
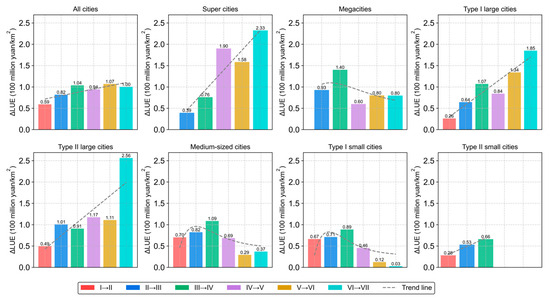
Figure 9.
The growth in LUE at different urban scales from the previous stage to the next stage (I: primary production stage I, II: primary production stage II, III: initial industrialization, IV: intermediate industrialization, V: post-industrialization, VI: initial developed economy, VII: developed economy era).
4. Discussion
4.1. Typicality of Chinese Cities as Research Objects
Two notable typologies emerge when exploring the impact of the EDSs on LUE in Chinese cities. On the one hand, the speed and scale of China’s urbanization process are globally unprecedented. The urbanization rate of the resident population increased from 29.04% in 1995 to 63.89% in 2020, reflecting not only the massive migration of the population from rural areas to urban but also China’s profound and rapid urbanization process. On the other hand, with this rapid urbanization, China’s industrial structure underwent a significant and rapid transformation, from an agriculture-dominated economy to an industry- and service-dominated economy. This transformation not only altered the economic structure but also influenced urbanization trends. Therefore, the combination of these two aspects has led to clear spatial differentiation in economic development across various urban scales.
China’s urbanization process is characterized by a rapid pace of development, large-scale expansion [59], and significant changes in land use patterns. These characteristics provide typical cases and valuable insights into global urbanization. The expansion of urban land is not only an important feature of the urbanization process but also a major indicator of its progress. The amount of urban land in Chinese cities has been steadily increasing year by year, from 27,314.87 km2 in 1995 to 107,779.32 km2 in 2020, with an average annual increase of 3218.58 km2 (Figure 10a). There is a disparity in urban land areas of different urban scales. By 2020, the urban land area, in descending order, was distributed as follows: type II large cities, medium-sized cities, megacities, type I small cities, supercities, type I large cities, and type II small cities. While experiencing rapid urbanization, China has also experienced a rapid transformation in its industrial structure. China’s transformation from an agriculture-based economic structure to one dominated by industry, manufacturing, and services has resulted in geospatial imbalances and distinct patterns of economic development across different regions and urban scales. As shown in Figure 10b, China’s industrial structure has transformed from 19.6%, 46.7%, and 33.7% in 1995 to 7.7%, 37.8%, and 54.5% in 2020, respectively. During this period, the proportions of primary and secondary industries gradually decreased, whereas the proportion of tertiary industries continued to increase. On the one hand, this indicates that the tertiary industry has become the main driving force behind China’s economic growth. On the other hand, it reflects the fact that the rationalization and upgrading of the industrial structure are constantly improving, signaling that the transformation of China’s economic structure has reached a critical stage. In summary, against the background of uneven development in China’s urban geographical space, this study aims to offer a scientific basis for urban land use planning and policy formulation.
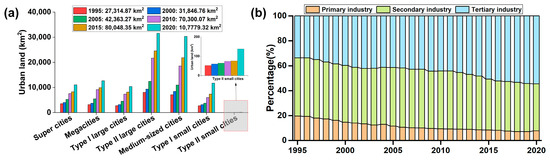
Figure 10.
Expansion characteristics of urban land and the percentage of the industrial structure in China from 1995 to 2020: (a) quantitative characteristics of urban land expansion and (b) the percentages of the three industrial structures.
4.2. In-Depth Analysis of Mechanism of Impact of EDSs on LUE
The dynamic impact of the characteristics of different EDSs on LUE is mainly reflected in two key dimensions: (1) the EDSs have a direct effect on LUE, and, by combining the variations in each EDS’s characteristics, we can demonstrate its direct impact on LUE; (2) the industrial structure, as an intermediate variable of the EDS, has an indirect impact on LUE [60]. The optimization and upgrading of the industrial structure is an important driving force for the urbanization process and also a core factor sustaining urban development, reflecting the evolution of the EDSs. Considering these two aspects, this study thoroughly analyzes the mechanism by which different EDSs influence LUE.
The characteristics of different EDSs have a significant impact on LUE. Specifically, primary production stage I was dominated by agriculture, during which urban land was used more often for residential purposes and the LUE was the lowest. In primary production stage II, the proportion of the primary industry remained large, and the proportion of the secondary industry began to rise. During this phase, part of the urban land was used for industrial purposes, but the overall level of LUE remained low. In the initial industrialization stage, the traditional structure dominated by agriculture gradually shifted to an industrialized structure dominated by modern industry. With the rapid rise and dominance of the secondary industry, the LUE increased, although it was still limited by factors such as the technological level and workforce quality. In the stage of intermediate industrialization, the secondary industry continued to dominate, while the proportion of tertiary industries began to rise rapidly. With technological advancements and the optimization and upgrading of the industrial structure, the functions of urban land became more diversified, leading to further improvements in LUE. In post-industrialization, the tertiary industry began to shift from steady to rapid growth and gradually became the main force for regional economic growth. During this stage, the use of urban land tended to be more commercial, and the LUE improved considerably. When the EDS entered the initial developed economy and developed economy eras, the tertiary industry continued to dominate. With the deepening development of urbanization and industrialization, the structure and function of urban land become more rational. At the same time, relevant urban departments enhanced the protection and management of land resources, leading to higher and more stable LUE.
This study found that the impact of the EDSs on LUE varied across urban scales. There are two important aspects to this result. Firstly, urban scale disparities affect resource aggregation capabilities and economic growth patterns [61], and urban land expansion is positively correlated with the administrative hierarchy—that is, cities with stronger administrative hierarchies tend to experience faster expansion processes while controlling for other economic and demographic drivers of urban expansion [62]. This means that larger cities will have stronger resource-aggregating capabilities and more advantageous economic development trends, resulting in a continuous improvement in the LUE as the EDS advances in larger cities. However, owing to the lack of resources and policy support, medium-sized and small cities may be able to promote improvements in LUE in the early EDSs, but they cannot always maintain a large growth rate, thus forming an inverted U-shaped effect. These results also reflect the essence of the urban economic growth pole theory, which highlights the unbalanced development of the economy in geographical space. Secondly, the urban scale is a direct reflection of the intensity and efficiency of urban social metabolism [63,64]. Compared to medium-sized and small cities, large cities have a more rational industrial structure, more comprehensive infrastructure, and greater advantages in optimizing the allocation of land resources or urban governance capabilities. These advantages often effectively promote the maximization of the economic value of land resources, resulting in higher LUE. In contrast, medium-sized and small cities have relatively low LUE due to these limitations. Notably, the economic growth rates of megacities were significantly lower than those of urban land, leading to a decline in LUE in the later part of the study period.
4.3. Recommendations for Sustainable Spatial Development
LUE serves as a core regulatory variable in urban social metabolism systems [65]. Enhancing LUE can effectively strengthen the urban metabolic intensity and efficiency, thereby promoting sustainable urban development. Based on this theoretical framework, this study proposes an integrated policy system across three dimensions—dynamic monitoring and assessment, differentiated management, and urban renewal—to establish a comprehensive governance mechanism for LUE enhancement.
First, an intelligent dynamic monitoring and assessment system should be established by integrating multi-source geospatial big data. This would involve creating a national urban multi-dimensional information database and real-time monitoring platform to enable the dynamic diagnosis of LUE and the precise identification of EDSs. The system would provide data-driven support for policymaking, effectively addressing issues of policy lags and arbitrary decision making. Second, a classified and tiered land management policy system should be implemented. Research reveals significant heterogeneity in how EDSs affect LUE across urban scales, necessitating differentiated policy approaches. Specifically, for land-scarce regions including supercities, type I large cities, type II large cities, and type II small cities, an efficiency-oriented refined management approach should be adopted, featuring minimum floor area ratio standards for industrial land and incentive mechanisms for urban redevelopment. Secondly, other urban scales should implement stricter urban growth boundaries and adopt land supply mechanisms that are dynamically aligned with their EDSs. Crucially, regional coordination mechanisms must be established throughout policy implementation to prevent negative spillover effects from unbalanced resource flows. Implementing sequential and partitioned governance modes can effectively support China in achieving sustainable land use and advancing its carbon neutrality goals [66]. Third, a LUE-oriented urban renewal model should be developed as a strategic approach for efficiency enhancement. Key strategies include functional upgrading and spatial restructuring in older urban areas; promoting intensive renewal models based on mixed-use and three-dimensional development; and establishing an evaluation mechanism that connects renewal outcomes to LUE improvements.
This study innovatively reveals the significant scale differences in the nonlinear relationship between EDSs and LUE, providing an important theoretical basis for sustainable urban development. The discovery of the differential impact patterns on LUE in different urban scales at different EDSs has broken through the traditional assumption of homogeneity in research and deepened our understanding of the relationship between urban development and sustainable land use. The research results provide a scientific basis for the formulation of differentiated policies for the sustainable development of national land space, and they have important guiding significance for the coordinated promotion of high-quality urban development and ecological civilization construction.
4.4. Limitations
This study confirms the feasibility of measuring LUE using multi-source data from the perspective of spatial heterogeneity within cities [67,68]. Furthermore, this study included 276 Chinese cities with various urban scales and levels of economic development. Based on earlier research on the relationship between the EDSs and LUE, this study explored the specific impacts of the EDSs on LUE. Our findings provide a scientific theoretical basis for the formulation of more effective and scientifically based land management policies tailored to different urban scales and various EDSs. The use of per capita GDP indicators to characterize EDSs has certain limitations, mainly reflected in the failure to fully capture the multi-dimensional characteristics of economic development. Of note, the relationship between factors such as land use development patterns, policy support, and LUE has not been previously examined [28,69]. Future research should fully consider the comprehensive impact of natural and human factors on LUE. Furthermore, incorporating the impact patterns of EDSs on LUE as constraints into land resource optimization and simulation modeling will significantly contribute to standardizing urban land use practices and mitigating the intensifying “human–land conflict” [70,71,72].
5. Conclusions
In this study, we selected 276 Chinese cities as research objects and comprehensively measured the LUE at a fine scale based on multi-source data, such as nighttime light images, land use, and socioeconomic data. We also divided the EDSs using the per capita GDP and a PDP to further illustrate the nonlinear impacts of the EDSs on LUE. Furthermore, the mechanism underlying the impacts of the EDSs on LUE was examined from two perspectives: the characteristics of different EDSs and the disparities observed across various urban scales.
This study has the following significant findings. First, China’s LUE has increased annually, with the average value rising from 164 million CNY/km2 in 1995 to 501 million CNY/km2 in 2020. This confirms the processes of land maturation and efficiency enhancement, which provide a theoretical foundation for exploring the impacts of the EDSs on LUE. Second, the EDSs of Chinese cities continue to upgrade, with the share of late industrialization and higher stages approaching 70% by 2020. There is a positive correlation between the urban scale and the EDS, with larger urban scales corresponding to later EDSs. Finally, the LUE characteristics varied throughout the EDSs, confirming that the EDSs had a positive impact on LUE. An obvious difference in the impact of the EDSs on LUE was observed across urban scales. As of 2020, the later the EDSs of supercities, type I large cities, type II large cities, and type II small cities, the more significant the impact on LUE. Conversely, megacities, medium-sized cities, and type I small cities exhibited an inverted U-shaped impact pattern.
In conclusion, this study provides a comprehensive analysis of the impacts of EDSs on LUE, expanding the ideas for the promotion of the efficient use of land resources and the healthy development of the urban economy. It also provides valuable insights for the formulation of land policies that align with the EDSs. Furthermore, comparative studies across different urban scales will help to develop targeted guiding strategies and approaches for land planning and management at each scale, thereby contributing to the optimization and adjustment of land policies and promoting sustainable urban development.
Author Contributions
X.L.: Data curation, methodology, software, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. W.L.: Conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, writing—review and editing. Q.L.: Writing—review and editing. Z.L.: Writing—review and editing. Z.S.: Writing—review and editing. G.C.: Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42030409).
Data Availability Statement
Our data were derived from the following resources available in the public domain: CNLUCC and Population—https://www.resdc.cn/ (25 February 2025); CLCD—https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5816591 (25 February 2025); Sentinel—https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/ (25 February 2025); DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS—https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/ (25 February 2025); China City Statistical Yearbook—http://www.stats.gov.cn/ (25 February 2025). The collection and preprocessing of the data are described in Section 2.2.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sethi, S.S.; Vinoj, V. Urbanization and regional climate change–linked warming of Indian cities. Nat. Cities 2024, 1, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.C.; Venter, Z.S.; Demuzere, M.; Zhan, W.; Gao, J.; Zhao, L.; Qian, Y. Large disagreements in estimates of urban land across scales and their implications. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Tang, M.; Wu, Y.; Bao, S.; Wu, Q. Government–led regional integration and economic growth: Evidence from a quasi–natural experiment of urban agglomeration development planning policies in China. Cities 2025, 156, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Zhang, X.; Reis, S.; Chen, D.; Xu, J.; Gu, B. Urbanization can benefit agricultural production with large–scale farming in China. Nat. Food. 2021, 2, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Sciusco, P.; Jiao, T.; Feron, S.; Lei, C.; Li, F.; John, R.; Fan, P.; Li, X.; Williams, C.A.; et al. Albedo changes caused by future urbanization contribute to global warming. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, G.; Zwiers, F.W.; Hu, T. Contribution of urbanization to warming in China. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, S.; Gan, Y.; Wang, C.; Horton, D.E.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Niyogi, D.; Xia, J.; Chen, N. Widespread global exacerbation of extreme drought induced by urbanization. Nat. Cities 2024, 1, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.N.; Connor, D.S.; Stuhlmacher, M.; Peng, J.; Turner, B.L., II. More urbanization, more polarization: Evidence from two decades of urban expansion in China. npj Urban Sustain. 2024, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Huang, Y.; Chen, D. Analysis of the expansion characteristics of rural settlements based on scale growth function in Himalayan Region. Land 2022, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, X.; Kuang, W.; Guo, C. Characteristics of changes in urban land use and efficiency evaluation in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1990 to 2020. Land 2022, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, Z.; Guo, H.; Weng, Q.; Du, W.; Xing, Q.; Cai, G. An assessment of urbanization sustainability in China between 1990 and 2015 using land use efficiency indicators. npj Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroso, N.H.; Lengoiboni, M.; Zevenbergen, J.A. Urbanization and urban land use efficiency: Evidence from regional and Addis Ababa satellite cities, Ethiopia. Habitat. Int. 2021, 117, 102437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, A.; Wang, K.; Bai, J.; Gu, N.; Feng, R. Analyzing sustainable development in Chinese cities: A focus on land use efficiency in production–living–ecological aspects. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 448, 141461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Cao, S.; Du, M.; Lu, L. Distinctive roles of land–use efficiency in sustainable development goals: An investigation of trade–offs and synergies in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 134889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yu, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, J. Exploring the influence of urban form on land—Use efficiency from a spatiotemporal heterogeneity perspective: Evidence from 336 Chinese cities. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shu, B.; Wu, Q. Urban land use efficency in China: Spatial and temporal characteristics, regional difference and influence factors. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Wu, C. Comparative study on urban land use efficiency. Econ. Geogr. 2003, 23, 367–370, 392. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Luan, W. Spatial-temporal patterns of urban land use efficiency in China’s national special economic parks. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 111959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yeung, G.; Zhu, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L. Efficiency of urban land use in China’s resource–based cities, 2000–2018. Land Use Policy 2022, 115, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xiao, W.; Li, L.; Ye, Y.; Song, X. Urban land use efficiency and improvement potential in China: A stochastic frontier analysis. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. Spatial–temporal differences of industrial land use efficiency and its influencing factors for China’s central region: Analyzed by SBM model. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, X.; Huang, H. Exploring the coupling coordination and key factors between urbanization and land use efficiency in ecologically sensitive areas: A case study of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustain. Cities. Soc. 2022, 86, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wei, Y.D.; Huang, X.; Chen, B. Economic transition, spatial development and urban land use efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Habitat. Int. 2017, 63, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y. Study the effect of industrial structure optimization on urban land–use efficiency in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, H.; Liu, H.; Liao, C. Urban development sustainability, industrial structure adjustment, and land use efficiency in China. Sustain. Cities. Soc. 2023, 89, 104338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Pan, L.; Jing, X.; Li, G.; Zhuo, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. The spatiotemporal non-stationary effect of industrial agglomeration on urban land use efficiency: A case study of Yangtze River Delta, China. Land 2022, 11, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Fang, C.; Shu, T.; Ren, Y. Spatiotemporal impacts of urban structure upon urban land–use efficiency: Evidence from 280 cities in China. Habitat. Int. 2023, 131, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Maity, I.; Dadashpoor, H.; Novotnẏ, J.; Banerji, S. Building in or out? Examining urban expansion patterns and land use efficiency across the global sample of 466 cities with million+ inhabitants. Habitat. Int. 2022, 120, 102503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Jia, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, Z.; Hao, Y. Spatial and temporal inequity of urban land use efficiency in China: A perspective of dynamic expansion. Environ. Impact. Asses. 2024, 104, 107357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroso, N.H. Urban land policy and urban land use efficiency: An analysis based on remote sensing and institutional credibility thesis. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Tian, Z. Built-up land efficiency in urban China: Insights from the General Land Use Plan (2006–2020). Habitat. Int. 2016, 51, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Yue, L.; Ahmad, F.; Draz, M.U.; Chandio, A.A.; Ahmad, M.; Amin, W. Empirical investigation of urban land use efficiency and influencing factors of the Yellow River basin Chinese cities. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenery, H.B.; Robinson, S.; Syrquin, M. Industrialization and Growth: A Comparative Study; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jin, F. China’s economic development stage and its spatio—Temporal evolution: A prefectural–level analysis. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 64, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cheng, C. Monitoring fine-scale urban shrinkage space with NPP-VIIRS imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarif, N.; Roy, A.K. Measuring urban shrinkage in India using night-light data from DMSP–OLS and VIIRS–NPP satellite sensors. Cities 2024, 152, 105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi–temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W.D. Using luminosity data as a proxy for economic statistics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8589–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Xin, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Xiang, W. Modeling population density based on nighttime light images and land use data in China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 90, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y. Estimation of regional electricity consumption using National Polar-Orbiting Partnership’s visible infrared imaging radiometer Suite night-time light data with gradient boosting regression trees. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Lian, T.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. NPP-VIIRS DNB daily data in natural disaster assessment: Evidence from selected case studies. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberenz, S.; Stocker, D.; Röösli, T.; Bresch, D.N. Asset exposure data for global physical risk assessment. Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2020, 12, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, Y.; Cao, G.; Samson, E.L.; Zhang, J. Forecasting China’s GDP at the pixel level using nighttime lights time series and population images. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; Jing, W.; Chen, Z. GDP spatial differentiation in the perspective of urban functional zones. Cities 2024, 151, 105126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, F. Global gridded GDP data set consistent with the shared socioeconomic pathways. Sci. Data. 2022, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, B. The evolution process and regulation of China’s regional development pattern. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2437–2454. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Research on regional variability in the evolution of territorial space pattern and its driving factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. China Land Sci. 2022, 36, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, B.; Bhardwaj, A.; Sam, L. Revealing the evolution of spatiotemporal patterns of urban expansion using mathematical modelling and emerging hotspot analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 364, 121477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Gao, F.; Liao, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W. Spatiotemporal evolution patterns of urban heat island and its relationship with urbanization in Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao greater bay area of China from 2000 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Cho, N.; Son, S. Spatiotemporal characteristics of elderly population’s traffic accidents in Seoul using space–time cube and space–time kernel density estimation. PLoS ONE. 2018, 13, e196845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.; Tan, D.; Mai, T.; Bei, C.; Qin, J.; Pang, W.; Zhang, Z. An analysis of spatiotemporal pattern for COIVD-19 in China based on space–time cube. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellan-Garcia, J.; Fernández, J.; Khan, M.I.; Abbas, Y.M.; Carrillo, J. Uniaxial tensile ductility behavior of ultrahigh-performance concrete based on the mixture design–Partial dependence approach. Cement. Concerte. Comp. 2023, 140, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroyama, R.; Yoshimura, C. Assessing bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) habitat suitability using partial dependence function combined with classification approaches. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 35, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Lu, C.; She, J.; Zhou, Y. Spatio-temporal evolution of resilience: The case of the Chengdu–Chongqing urban agglomeration in China. Cities 2024, 153, 105226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, H.; Ao, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, B.; Martek, I. Resilient city construction efficiency and its influencing factors in China’s Chengdu—Chongqing Economic Circle: Considering both construction input and resilience level of the city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 114, 105726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, G.; Liu, H. Does natural resources supervision improve construction land use efficiency: Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Y.D. How does industrial agglomeration affect urban land use efficiency? A spatial analysis of Chinese cities. Land Use Policy 2022, 119, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Realizing China’s urban dream. Nature 2014, 509, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; He, C.; Yeung, G.; Xu, Y. Industrial structure upgrading and urban land use efficiency: Evidence from 115 resource–based cities in China, 2000–2019. Geogr. Res. 2023, 42, 86–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, B. The types of city size distributions and their evolution. Cities 2024, 150, 105045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, Y.D.; Liao, F.H.; Huang, Z. Administrative hierarchy and urban land expansion in transitional China. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 56, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Yao, X. City size and energy efficiency of Chinese manufacturing firms: An empirical study from a city characteristic perspective. Energ. Econ. 2024, 129, 107207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Peng, J.; Wu, Q. Exploring the non–linear effects of city size on urban industrial land use efficiency: A spatial econometric analysis of cities in eastern China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wang, X. Urban land use change and its effect on social metabolism: An empirical study in Shanghai. Habitat. Int. 2015, 49, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. Towards carbon neutrality in China: A systematic identification of China’s sustainable land-use pathways across multiple scales. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 2024, 44, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Lu, Y.; Yue, W.; Xiao, W.; Shen, X.; Shan, Z. A new approach to peri-urban area land use efficiency identification using multi-source datasets: A case study in 36 Chinese metropolitan areas. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 150, 102826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; He, T.; Xiao, W.; Chen, W.; Lu, D.; Liu, S. Measuring the coupling of built–up land intensity and use efficiency: An example of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities. Soc. 2022, 87, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, R.; Chen, J. Does industrial land marketization reform faciliate urban land use efficiency? Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 96, 103609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. Does partition matter? A new approach to modeling land use change. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 106, 102041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Song, W. A land-use spatial optimum allocation model coupling a multi-agent system with the shuffled frog leaping algorithm. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 77, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Ai, T.; Liu, D. A land-use spatial optimization model based on genetic optimization and game theory. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).