Abstract
Desert ecosystems play a critical role in global climate regulation. Current research reveals a relative lack of research regarding desert ecosystem service (ES) supply and demand. Therefore, we selected the Ulanbuh desert, one of the eight major deserts in China, as study area. Using specialized models, we quantify the supply and demand of four ES, including water yield (Wy), soil conservation (Sc), windbreak and sand fixation (Ws), and carbon sequestration (Cs), from 1985 to 2020. Univariate linear regression analysis and panel data analysis (PDA) were used to examine trends in desert ES supply–demand ratio (ESDR) and its determinants. The findings indicated that ES supply presented increases in Sc and Cs, and decline in Ws from 1985 to 2020. Demand patterns showed a growth trend for Wy and Cs. ESDR revealed that Sc, Ws, and Cs show an excess of supply over demand and are in a decreasing trend, while Wy displays a supply deficit relative to demand with no significant change. The comprehensive ESDR decreased over the study period, with a supply-deficit status emerging in the southwestern area. Natural factors (NDVI and precipitation) and socio-economic factors (GDP and population density) served as the main factors affecting the comprehensive ESDR. This research provides a novel perspective for desert ecosystems management and conservation, emphasizing the necessity of incorporating the ES supply and demand balance into regional development policies to achieve sustainable development in arid regions.
1. Introduction
Serving as a vital mediator between environment and human welfare [1,2], ecosystem services (ES) are indispensable for sustainable management in preserving global ecological stability and anthropogenic advancement. A comprehensive understanding of ES necessitates systematic evaluation of both supply and demand [3,4]. ES supply denotes ecological processes generating tangible benefits for human livelihoods, while the desired level of service that humans aspire to achieve defines ES demand [5,6]. At present, the dual pressures of global climate change and anthropogenic interventions have significantly impacted the ES supply and demand [7]. Environmental stressors and human activities degrade ecosystem structures, altering the capacity to deliver products and services [8,9]. Meanwhile, population growth and economic activities amplify societal ES demand [10].
The ES supply and demand serve as critical indicators for assessing the transfer from nature to human society, offering insights into the potential for sustainable nature–human symbiosis [11,12]. However, when demand exceeds supply, it can lead to the degradation of ES quality and increased regional risk [13]. Recently, investigating the ES supply and demand has emerged as a focal area in the field of sustainable ecology [14]. Scholars have introduced the concept of the ecosystem services supply–demand ratio (ESDR) to capture the spatial variability in supply and demand scenarios, which provides a nuanced view for spatial mismatch analysis [15,16,17,18]. Current research endeavors on ESDR have largely centered on quantifying balance under static conditions and mapping spatial distributions [16,19]. Different scholars have utilized ESDR to investigate the spatial distribution of supply and demand across diverse regions, including metropolitan clusters (Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area), provincial territories (Shandong Province), and arid zones (the Bairin Left Banner) [20,21,22]. This research indicates spatial heterogeneity in the mismatch of ES supply and demand, with climate and socio-economic elements being pinpointed as crucial causes [23,24,25].
The desert ecosystem constitutes a vital component of terrestrial ecosystems [26], providing essential ES, such as windbreak and soil fixation (Ws) and carbon sequestration (Cs), to the maintenance of global ecological balance and climate conditions [27]. Deserts support unique biodiversity [28], including specialized terrestrial vertebrate species and endemic biota adapted to extreme environmental conditions [29]. Meanwhile, approximately 6% of the global population relies on desert-specific resources to meet cultural and subsistence needs [30]. Notably, the slow recovery rates of desert ecosystems amplify uncertainties regarding vegetation degradation and the deficit in ES supply and demand caused by desertification [31,32]. Although many initiatives have been made globally for desertification control, existing studies still mainly focus on high productivity regions, such as forests and grasslands [33,34,35], and the quantification of ES in desert ecosystems remains critically understudied. Therefore, analyzing the ESDR and its determinations in desert ecosystems is not only critical to optimizing desert land use and resource management, but also the theoretical basis for improving policies for global desertification control.
The Ulanbuh Desert is one of the eight major deserts in China and is located in the core area of the northern windbreak and sand fixation belt [36]. It is a key node for the ecological barrier of northwest China and the ecological security of the Yellow River Basin, and the study of its ES supply and demand has irreplaceable strategic value. It plays a significant role in consolidating the Northern Ecological Security Barrier. Based on the above research context, this study selected Ulanbuh Desert as an example, aiming to achieve the following: (1) Quantify the spatial and temporal dynamics of supply and demand for four ES, Wy, Sc, Ws and Cs, and ESDR for the period 1985–2020. (2) Identify the main determinants affecting the ESDRC. The findings establish an empirical foundation for desert ecosystem management and sustainable regional transitions, offering critical insights to strengthen the Northern Sand Prevention Belt and enhance ecological security in North China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Ulanbuh Desert is located in the northwest region of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in northern China, extending across the Alshan League and Bayan Nur of Inner Mongolia (39°17′–40°46′ N, 105°24′–107°01′ E), with an area of about 1.3 × 106 hm2 (Figure 1). The terrain of the area is marked by a low middle and high surroundings, with elevations ranging from 980–1499 m. The region is predominantly defined by a temperate arid climate with low precipitation (110–160 mm) and high evapotranspiration (2380 mm). The Yellow River serves as the principal water source for the region. And its mean annual temperature is 8.6 °C with a large diurnal temperature difference [37]. The natural vegetation is dominated by hyper-arid and arid types of desert vegetation and halophytic vegetation [38].
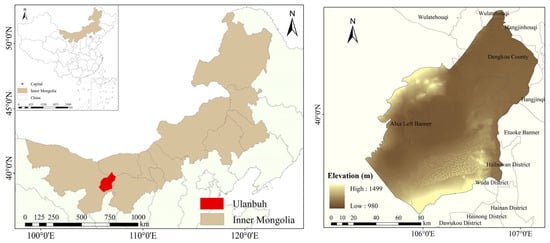
Figure 1.
Location and topographic subregions of Ulanbuh Desert.
2.2. Data Sources
The natural and socio-economic data collected specifically include eight periods of time: 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, with a uniform spatial resolution of 1 km. Meteorological data from the region and its neighboring meteorological stations were obtained by Kriging interpolation to obtain meteorological raster data. The water consumption data in the Inner Mongolia Water Resources Bulletin includes water used for livestock and fishery, forestry, irrigation, industry, urban and rural life, and ecological environment, and the relevant missing data were found by reviewing literature. Potential evapotranspiration (PET) in the study area was calculated using the Modified-Hargreaves method [39]. The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) was calculated by using python’s gma library. The NDVI data were obtained using Landsat 5/7/8, using the GEE platform, after de-clouding and filtered processing. The data sources used in this study are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
The data sources of this study.
2.3. ES Supply
2.3.1. Water Yield (Wy) Supply
The Wy is the capability of ecosystems to capture and store water from rainfall or surface runoff through natural processes [36]. The Wy supply of Ulanbuh Desert in this study was quantified by the “water yield” of the InVEST 3.14 model.
2.3.2. Soil Conservation (Sc) Supply
The mitigation of soil erosion by leveraging the structures and processes of ecosystem is regarded as Sc [40]. The Sc supply was assessed by the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model [41].
2.3.3. Windbreak and Soil Fixation (Ws) Supply
The Ws denotes the function as wind speed reduction and sand and storm suppression [42]. In terms of the difference between the potential soil wind erosion under vegetation cover and the actual soil wind erosion under bare soil conditions [43], the revised wind erosion equation (RWEQ) model can quantify the Ws supply [44].
2.3.4. Carbon Sequestration (Cs) Supply
The Cs is the process by which vegetation converts atmospheric CO2 into organic matter through photosynthesis and then fixes it into the soil [45,46]. This study quantified the net primary productivity of Ulanbuh Desert by the net primary productivity (NPP) calculation model which was developed by Zhu based on the Carnegie–Ames–Stanford approach (CASA) model [47], and then the Cs was calculated by the carbon conversion factor [46,48].
2.4. ES Demand
2.4.1. Wy Demand
This study adopted actual human water consumption as an indicator to represent the demand for Wy. Given the difficulty in obtaining water usage data from the counties and banners within the Ulanbuh Desert, this study selects the per-capita water consumption calculated based on the water usage and population data from the Water Resources Bulletin of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region [49]. Finally, the product of per-capita water used and population density is used as the demand for Wy.
2.4.2. Sc Demand
The severity of soil erosion is directly proportional to the demand for soil management which humans expect [50]. The demand for Sc represents the societal need to mitigate the negative impacts of soil erosion. We operationalize this demand as the potential soil loss that society aims to prevent. Consequently, the actual amount of soil erosion was adopted as the Sc demand [51].
2.4.3. Ws Demand
Analogous to Sc demand, the demand for Ws signifies the societal need to reduce the detrimental effects of wind-driven soil loss. The actual wind erosion was considered as a problem that people hope to solve, leading us to hypothesize that it corresponds to the demand for Ws [52]. Therefore, the actual soil wind erosion was regarded as Ws demand.
2.4.4. Cs Demand
The demand for Cs is characterized as the anthropogenic pressure on ecosystems to offset carbon dioxide emissions. Therefore, the Cs demand is characterized based on per-capita carbon emissions in this study [53]. Considering the availability of data, this study obtained carbon emission data for China from 1985 to 2020 by consulting the China Emission Accounts and Datasets (CEADs), and used population data to calculate the per-capita carbon emissions [54]. Finally, the product of per-capita carbon emissions and raster data on population density is used to find the demand for Cs.
2.5. Supply and Demand for ES and Driving Factors
2.5.1. Supply and Demand
This ESDR introduced to characterize the balance state between the ES supply and demand in this study [55]. The detailed formula is presented below:
where S represents the actual amount of ES supply, while D signifies the ES demand. Smax denotes the maximum values of ES supply, and Dmax denotes the maximum values of ES demand. When ESDR > 0, it denotes a surplus condition where the service supply outstrips demand. When ESDR = 0 it signifies equilibrium between supply and demand. Conversely, when ESDR < 0, it implies a deficit scenario where supply falls short of demand.
The ESDRC was employed to characterize the ES supply and demand in the research area. The formula is outlined below:
where n implies the number of types of ES (n = 4, including Wy, Sc, Ws, and Cs, in this study). ESDRi signifies the supply–demand ratio of the ith ES, which include Wy supply and demand ratio (ESDRWy), Sc supply and demand ratio (ESDRSc), Ws supply and demand ratio (ESDRWs), and Cs supply and demand ratio (ESDRCs).
2.5.2. Analysis of Driving Factors
Panel data analysis (PDA) is a commonly used regression analysis method in econometrics that considers both time and cross-sectional dimensions simultaneously. In this study, different points represented different cross-sections, while different years reflect the time series nature of the data. To enhance the precision of our findings, we chose annual data spanning from 1985 to 2020 for the driving factors analysis. Considering the actual situation and data availability, we selected twelve indicators as drivers from the three dimensions of nature, land use, and socio-economics by combining the existing relevant studies [38,56,57] on arid zones and the unique geographic characteristics of the Ulanbuh Desert (Table 2). With the aid of Stata 18 software, a panel data model was constructed using the selected driving factors as independents and ESDRC as the dependent. Common models include mixed-, random-, and fixed-effects models [58].

Table 2.
The driving factors to effect on supply-demand ratio.
Considering the potential interactions among the independent variables, performing a multicollinearity test on the independent variable data is crucial. The variance inflation factor (VIF) served as a standard measure to assess multicollinearity within the dataset, where a VIF score exceeding 10 suggests the existence of multicollinearity [59]. Upon examination, the VIF of all factors were found to be less than 10. Therefore, this study sequentially utilized both the fixed- and random-effects models for regression analysis (Table 3 and Table 4). Following this, the Hausman test was administered to ascertain the appropriate model. Consequently, adopting the fixed effects model is deemed more appropriate [58].

Table 3.
Results of random-effects model.

Table 4.
Results of fixed-effects model.
2.6. The Univariate Linear Regression Trend Test
To explore multiyear trends in supply, demand, and ESDR dynamics across the Ulanbuh Desert from 1985-2020, a univariate linear regression analysis was employed. This study determined the significance level of the trend test by comparing the p-value with 0.05, and the annual rate of change by the slope of the univariate linear regression equation. The results were categorized into five categories based on the magnitude of the slope and p-value: insignificant increase (slope > 0 and p ≥ 0.05), significant increase (slope > 0 and p < 0.05), insignificant change (slope = 0), insignificant decrease (slope < 0 and p ≥ 0.05), and significant decrease (slope < 0 and p < 0.05). The specific calculation formula for the slope is
where slope represents the coefficient of the regression equation. n is the number of years (n = 8, in this study). Yi refers to the supply/demand value in the ith year.
3. Results
3.1. Changes in ES Supply
From 1985 to 2020, there were obvious spatial distributional differences in Wy supply variability within the study area (Figure 2). Specifically, the central region exhibited mainly insignificantly changed in Wy supply, the northeastern part was insignificantly decreased, and the eastern and western parts were insignificantly increased. There were not distinct spatial differences in the overall changes in Sc, Ws, and Cs supply. The Sc and Cs exhibited an overall insignificant increasing trend, and Ws showed an overall insignificantly decrease.
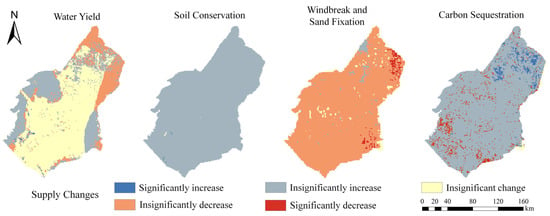
Figure 2.
Trend of supply of Wy, Sc, Ws, and Cs in the Ulanbuh Desert from 1985 to 2020.
3.2. Changes in ES Demand
From 1985 to 2020, there have been notable spatial distribution differences in the changes in demand for both Sc and Ws, whereas the changes in demand for Wy and Cs have exhibited no significant spatial distribution variations (Figure 3). Specifically, Sc and Ws demonstrated a decreasing trend in the northeastern part of the study area, accompanied by an increasing trend in the central and southwestern areas. Both Wy and Cs showed an overall upward trend.
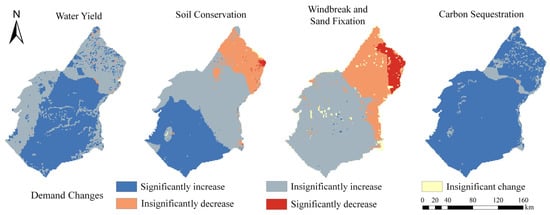
Figure 3.
Trend of demand of Wy, Sc, Ws, and Cs in the Ulanbuh Desert from 1985 to 2020.
3.3. Changes in Supply-Demand Ratio for ES
All ESDR exhibited similar spatial distributions, consistently demonstrating a spatial mismatch between supply and demand from 1985 to 2020 (Figure A1). Therefore, only the spatial distribution for 2020 is presented (Figure 4). Overall, ESDRSc, ESDRWs, ESDRCs, and ESDRC displayed a surplus status. However, it observed localized deficits in the southwestern region for ESDRSc, ESDRWs, and ESDRC, as well as in the northeastern region for ESDRCs. ESDRWy exhibited an overall deficit status, while a notable surplus was identified in the eastern Yellow River coastal area.
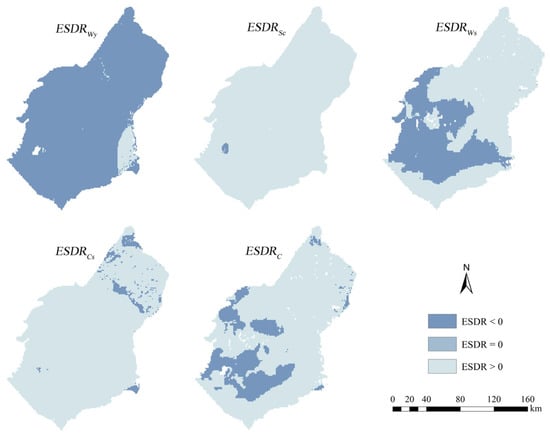
Figure 4.
The spatial distribution ESDRWy, ESDRSc, ESDRWs, ESDRCs, and ESDRC in the Ulanbuh Desert in 2020.
The overall trend from 1985 to 2020 showed an insignificant change in ESDRWy and decreasing trends in ESDRSc, ESDRWs, ESDRCs, and ESDRC. However, there was spatial differentiation in the supply–demand ratio for each service. Specifically, there was an insignificant upward trend of ESDRC in the northeastern region, while the remaining regions showed an insignificant downward trend (Figure 5). The ESDRWs followed the same trend as ESDRC. However, the ESDRWy showed insignificant change in its spatial distribution, the ESDRCs demonstrated an insignificant downward trend. The ESDRSc increases slightly in the northeastern and southern regions, and decreases slightly in other areas.
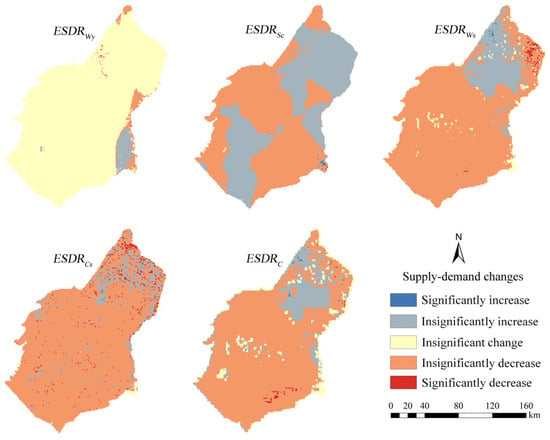
Figure 5.
Trend of supply–demand of ESDRWy, ESDRSc, ESDRWs, ESDRCs, and ESDRC in the Ulanbuh Desert from 1985 to 2020.
3.4. Driving Factors
The random-effects model results indicate that PET and SR were not statistically significant (Table 3). In the fixed-effects model, MAT failed to achieve statistical significance (Table 4). The Hausman test, where the null hypothesis posits that the random effects model is appropriate, yielded a result of Prob > chi2 = 0.0000, which is significantly less than 0.05 (Table 5). Consequently, we reject the null hypothesis, indicating that the fixed-effects model is more appropriate. At the same time, the size of the final impact factor is determined based on the test results of the fixed-effects model.

Table 5.
Results of Hausman test.
In the analysis of driving factors of ESDRC, MAT was not tested for significance. Among the factors that passed the significance test, NDVI, AP, and SPEI are the main natural factors (Figure 6a), and GDP and PD are the primary socio-economic factors (Figure 6b). Regrading land use factors, it is found that CsP has the strongest explanatory power, which has a negative influence on ESDRC (Figure 6c). This study revealed that policy factors have a minor and negative impact on ESDRC (Figure 6b).
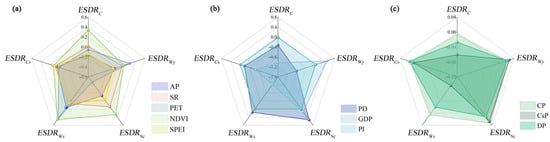
Figure 6.
The influence of natural factors (a), land use factors (b), and socio-economic factors (c).
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Supply–Demand Balance
This study revealed significant spatial heterogeneity in ESDRWy and ESDRWs across the Ulanbuh Desert, aligning with established patterns of ESDR distribution in arid ecosystems [60,61]. Notably, the overall ESDRWy in the study area shows a deficit status, which contrasts with the surplus reported in the upper Ganjiang River basin [6]. This discrepancy may be due to distinct driving mechanisms. Desert ecosystems exhibit ESDRWy, primarily regulated by precipitation fluctuations [52,62,63]. The high permeability of its sandy soils facilitates rapid infiltration, resulting in substantial subsurface runoff [64,65], leading to insufficient Wy supply. Conversely, ESDRWy in the upper Ganjiang River basin shows greater sensitivity to land use changes [6], highlighting the unique water–energy contradictions in arid regions. ESDRWy surpluses occurred in the eastern Ulanbuh Desert, correlating with enhanced surface water recharge from ecological water diversion projects and aligns with the implementation of Yellow River Basin ecological security strategies [66]. ESDRWs in the southwestern part of the study area showed deficits, which is mainly due to the high distribution of mobile dunes, semi-fixed dunes, and fixed dunes [36]. Meanwhile the northeastern part showed a surplus status, attributed to the vegetation restoration that significantly decrease sediment transport demand through effective sand fixation [67]. Enhancing Ws and Sc effectively reduces wind and water erosion, improves soil environmental stability, and thereby contributes to the enhancement of Cs.
The trends of ESDR in the Ulanbuh showed significant spatial differentiation, corroborating previous arid region studies [68,69]. ESDRSc, ESDRWs, and ESDRCs all exhibit an increasing trend in the northeastern of Ulanbuh, potentially driven by the synergistic photovoltaic–agropastoral systems that enhanced ecological functions and sustainable productivity [70]. Firstly, the sand-control function of photovoltaic components and the cultivation of suitable plants can effectively reduce wind erosion [71,72,73]. Additionally, planting elevates regional vegetation coverage by approximately 75%, substantially enhancing carbon sequestration capacity [70]. Furthermore, root system development in eco-agropastoral systems reinforces soil structure, improving soil aggregate stability and erosion resistance [74,75], leading to an increase in ESDRSc. These observed changes in the ecosystem service supply–demand relationships have profound implications for the Ulanbuh Desert ecosystem and its surrounding environment. The surplus status and increasing ESDR for Ws, Sc, and Cs in the northeast indicate that enhanced vegetation cover reduces water and wind erosion while increasing carbon storage. Research has shown that the deficit status of Wy exacerbates water stress on natural vegetation, limits ecological restoration potential, and may create feedback loops that further degrade ecosystem resilience [67]. The surplus of Ws and the increase in the ESDR reduced sediment input to the Yellow River, reflecting a significant improvement in the effectiveness of regional Ws [76].
4.2. Multiple Factors Drive the ESDR
This research identified both natural and socio-economic factors as significant contributors to the overall supply–demand balance, aligning with the conclusions of existing research [6,77]. From the perspective of natural factors, NDVI emerged as the most influential positive factor affecting the ESDRC, primarily through its regulatory effects on ESDRSc, ESDRWs, and ESDRCs. Vegetation roots enhance soil stability, thereby improving erosion resistance and reducing the amount of soil erosion [78]. Meanwhile, vegetation is identified as a primary force against windbreak and sand fixation, mitigating the demand for Ws by attenuating near-surface wind speeds through canopy structure modification [36,42,79]. Furthermore, vegetation enhances Cs supply by effectively capturing atmospheric CO2 and storing it as organic matter in soils [80].
Desert ecosystems, located in arid and semi-arid regions, are particularly sensitive to climatic conditions, with the availability of water resources being a key factor affecting the balance of ES. Our study revealed that precipitation is a significant negative climatic factor impacting the ESDRC in the study, predominantly influencing the ESDRWy, ESDRSc, and ESDRCs. Insufficient precipitation coupled with high evapotranspiration rates are identified as the primary causes of regional drought [81]. Although regional precipitation has exhibited a fluctuating upward trend, the evapotranspiration rate demonstrates a more pronounced increase. Furthermore, precipitation remains relatively low, while evapotranspiration levels are substantially high. (Figure 7). The slight rise in precipitation proves insufficient to compensate for water loss caused by high evapotranspiration rates [82], consequently exacerbating the deficit in ESDRWy. Scholars have found that due to cyanobacterial crusts, carbon emissions from crusted soils in the Ulanbuh Desert increase with rising precipitation, thereby reducing the carbon sequestration capacity in the desert [83]. Moreover, intense rainfall leads to increased actual soil erosion, which in turn leads to a substantial rise in the Sc demand [84].
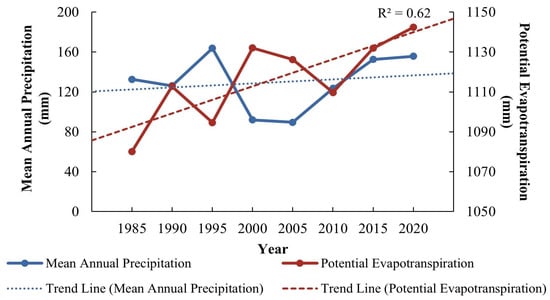
Figure 7.
Mean annual precipitation and potential evapotranspiration and their trends in the Ulanbuh Desert from 1985 to 2020.
Socio-economic factors also cannot be ignored. The research analysis identified GDP and population density as negative influences to the ESDRC. These factors jointly reflect human activities intensity. Enhanced human interventions elevate ES demand, thereby disrupting the balance between supply and demand [85]. GDP escalation often correlates with higher energy consumption, particularly from the combustion of fossil fuels, which elevates CO2 emissions. This process simultaneously rises Cs demand and lowers the supply–demand ratio [86,87]. Population density primarily affects the ESDRC through its impact on Wy and Cs demand. Increased population density leads to heightened water consumption for both production and domestic purposes, resulting in greater exploitation and depletion of water resources and, consequently, an augmented demand for Wy [88]. Furthermore, higher population density is linked to increased carbon emissions, which in turn amplifies the Cs demand [14].
4.3. Ecological Conservation Strategies in Response to Declining ESDR
The study revealed significant supply and demand declining in Sc, Ws, and Cs, with the NDVI identified as the primary natural factor. Therefore, enhancing vegetation coverage can effectively alleviate mitigate the rate of decline in the ESDRSc, ESDRWs, and ESDRCs. In arid regions, this is primarily achieved by planting drought-tolerant vegetation to mitigate soil erosion and sand mobility, while enhancing carbon sequestration via root biomass accumulation and litter decomposition. Furthermore, leveraging the abundant solar and wind energy resources of desert ecosystems [54], the expanded deployment of renewable energy infrastructure (photovoltaic power stations) can stabilize sand movement and fix soil carbon [89,90]. However, Wy falls short of demand in this region, and vegetation restoration may also increase water demand. Therefore, vegetation restoration in these areas must account for water resource constraints to prevent exacerbating the deficit. On one hand, regional GDP growth should drive the adoption of water-saving irrigation technologies, reducing water consumption per unit of GDP and improving water use efficiency through optimized vegetation spatial patterns. On the other hand, the geographical advantage of the Ulanbuh Desert near the Yellow River should be utilized to implement ecological water diversion projects, replenishing regional water resources. These integrated strategies promote synergistic energy–industry–ecological development, supporting the sustainable governance of desert ecosystems.
4.4. Limitation and Prospect
This research evaluated the ES of desert ecosystems by examining both supply and demand aspects and analyzed the driving factors affecting ESDRC, providing a basis for the ecological protection and restoration of desert ecosystems. However, there are still some limitations in our research. Firstly, the four selected services do not fully represent the ES of the region. Future studies could consider a broader range of ES, such as biodiversity and tourism. Additionally, when calculating the composite supply–demand ratio, we employed an equal-weighting method without objectively quantifying the weights among the supply–demand ratios of various indicators. Future research can explore and apply more objective weighting methods, such as the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) incorporating expert knowledge, principal component analysis (PCA), or entropy weighting based on indicator variability, to better reflect the relative importance of different ES in the desert context. Secondly, a more comprehensive set of socio-economic factors, such as the effect of livestock density and urbanization rate on ES, should be considered in the future. Lastly, future research should prioritize utilizing higher-resolution data sources (e.g., Sentinel-2 at 10–20 m, or Landsat at 30 m) and adapting models capable of effectively integrating and processing such finer-scale data to capture the heterogeneity of desert ecosystems more accurately.
5. Conclusions
Through the analysis of ES (Wy, Sc, Ws, and Cs) supply and demand dynamics in the Ulanbuh Desert from 1985 to 2020, this study delineated the driving factors influencing them. Specifically, the ESDRWy showed insignificant change, while the overall trend for ESDRCs was downward. The areas showing an increasing trend in ESDRSc are concentrated in the northeastern and southwestern portions of the study area. The ESDRWs shows an increasing trend in the northeastern area. The ESDRC also exhibited a downward trend, with a supply–deficit status emerging in the southwestern sector. The multifactorial analysis identified NDVI, solar radiation, and precipitation as dominant natural regulators, coupled with GDP and population density as primary anthropogenic driving factors. Addressing the issue of regional supply and demand deficit necessitates the rational planning of land use structure and layout tailored to each region, as well as the formulation of policies that align with regional ecological characteristics, thereby ensuring harmonious development between ecology and socio-economy. It is crucial to incorporate policy implementation and more granular changes over time into our future research endeavors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.C. and X.W.; methodology, W.C. and X.Z.; software, W.C., H.L. (Huan Liu) and X.Z.; formal analysis, X.W.; investigation, Q.Y.; data curation, H.L. (Huan Liu); writing—original draft preparation, W.C.; writing—review and editing, Q.Y., G.J., L.W. (Lixin Wang), L.W. (Lu Wen) and X.Z.; visualization, H.L. (Huamin Liu); supervision, L.W. (Lu Wen); funding acquisition, L.W. (Lixin Wang) and L.W. (Lu Wen). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Science & Technology Infrastructure Resources Survey Program (Grant Nos.2023FY100702-03), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 32460288, 32160279).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all the producers of the datasets used in this study. We are also grateful to the reviewers for their helpful comments on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ES | Ecosystem services |
| Wy | Water yield |
| Sc | Soil conservation |
| Ws | Windbreak and sand fixation |
| Cs | Carbon sequestration |
| PDA | Panel data analysis |
| ESDR | ES supply–demand ratio |
| ESDRWy | Wy supply and demand ratio |
| ESDRSc | Sc supply and demand ratio |
| ESDRWs | Ws supply and demand ratio |
| ESDRCs | Cs supply and demand ratio |
| NDVI | Normalized difference vegetation index |
| GDP | Gross domestic product |
| SPEI | Standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index |
Appendix A
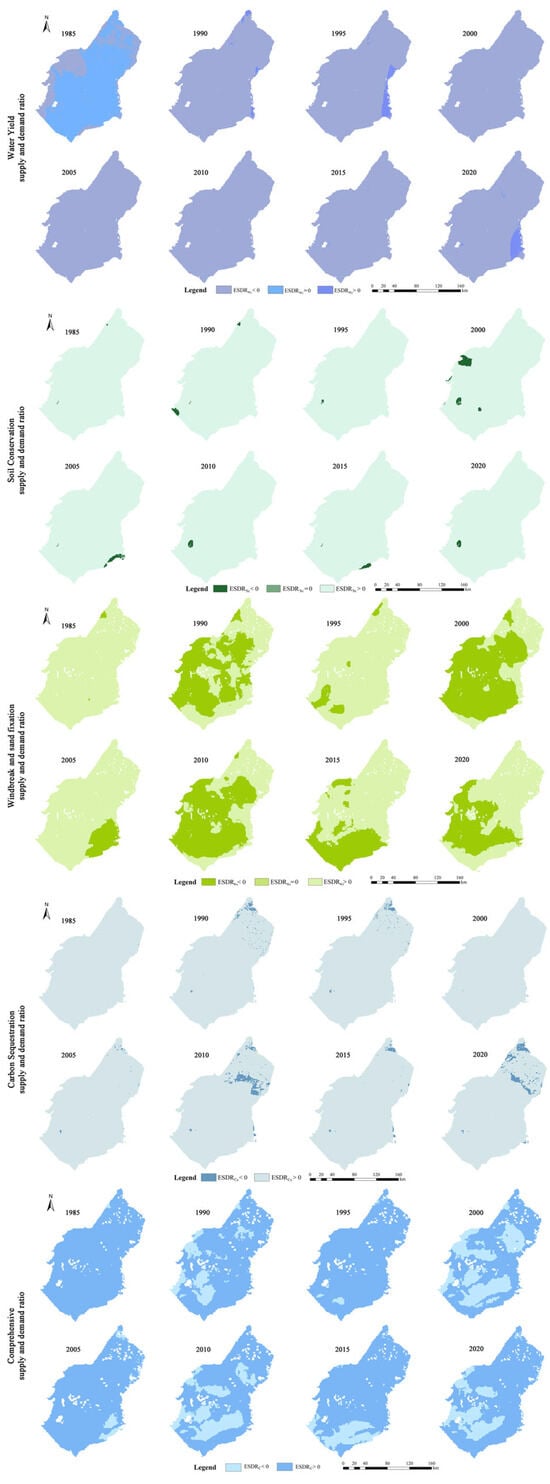
Figure A1.
Spatial and temporal distribution of ESDRWy, soil conservation ESDRSc, ESDRWs, ESDRCs, and ESDRC in Ulanbuh Desert from 1985 to 2020.
References
- Brauman, K.A.; Daily, G.C.; Duarte, T.K.; Mooney, H.A. The Nature and Value of Ecosystem Services: An Overview Highlighting Hydrologic Services. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2007, 32, 67–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, R.; Reyers, B.; Biggs, R.; Spierenburg, M.; Duriappah, A. Multi-Scale and Cross-Scale Assessments of Social–Ecological Systems and Their Ecosystem Services. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Eguskitza, N.; Martín-López, B.; Onaindia, M. A Comprehensive Assessment of Ecosystem Services: Integrating Supply, Demand and Interest in the Urdaibai Biosphere Reserve. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xie, G.; Lu, C.; Xu, J. Involvement of ecosystem service flows in human wellbeing based on the relationship between supply and demand. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, S.; Schulp, C.J.E.; Verburg, P.H. Mapping Ecosystem Services Demand: A Review of Current Research and Future Perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 55, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, J.; Han, Y.; Zhong, L.; Liu, S. Threshold Effects and Supply-Demand Ratios Should Be Considered in the Mechanisms Driving Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Ochuodho, T.O.; Yang, J. Impact of Land Use and Climate Change on Water-Related Ecosystem Services in Kentucky, USA. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhong, J. Guiding and Constraining Reclamation for Coastal Zone through Identification of Response Thresholds for Ecosystem Services Supply–Demand Relationships. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 1804–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, B. Integrating Ecosystem Service Supply and Demand into Ecological Risk Assessment: A Comprehensive Framework and Case Study. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2977–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, J. Spatially Heterogeneity Response of Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand to Urbanization in China. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 169, 106303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, J. Identifying the Spatial Relationships and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Supply–Demand Matching: A Case of Yiluo River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, H.; Peng, J.; Wu, J. A review of ecosystem services supply and demand. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Chang, M.; Ma, Z. Research on the Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Supply–Demand Risks of Ecosystem Services in the Yellow River Basin Integrating the Hierarchy of Needs Theory. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Wang, J.; Jin, Z.; Qi, Y.; Fang, Y.; Liu, J. Did Improvements of Ecosystem Services Supply-Demand Imbalance Change Environmental Spatial Injustices? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Jin, G. Scale Effects on the Supply–Demand Mismatches of Ecosystem Services in Hubei Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorilla, R.S.; Kalogirou, S.; Poirazidis, K.; Kefalas, G. Identifying Spatial Mismatches between the Supply and Demand of Ecosystem Services to Achieve a Sustainable Management Regime in the Ionian Islands (Western Greece). Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Y. Nonlinear Relationship and Threshold-Based Zones between Ecosystem Service Supply-Demand Ratio and Land Use Intensity: A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 481, 144148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yao, L. A Study on Matching Supply and Demand of Ecosystem Services in the Hexi Region of China Based on Multi-Source Data. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Hou, X.; Xu, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, G. Quantification and Driving Force Analysis of Ecosystem Services Supply, Demand and Balance in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Understanding the Spatial Relationships and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Supply-Demand Mismatches towards Spatially-Targeted Management of Social-Ecological System. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 136882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Shan, R.; Wang, B. Mapping and Assessing Supply–Demand Matching of Recreational Ecosystem Services in Shandong Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Xue, L.; Chen, J.; Tarolli, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Qian, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X. Understanding Driving Mechanisms behind the Supply-Demand Pattern of Ecosystem Services for Land-Use Administration: Insights from a Spatially Explicit Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 427, 139239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, B.; Kroll, F.; Müller, F.; Windhorst, W. Landscapes’ Capacities to Provide Ecosystem Services—A Concept for Land-Cover Based Assessments. Landsc. Online 2009, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y. Responses of the Water-Yield Ecosystem Service to Climate and Land Use Change in Sancha River Basin, China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2017, 101, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, N.; Dong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ya, X.; Zhao, Y. Integrating Supply and Social Demand in Ecosystem Services Assessment: A Review. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 25, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y. An Evaluation of Topsoil Carbon Storage in Chinese Deserts. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.T.; Davis, K.M.; Abad, H.; McClung, M.R.; Moran, M.D. Ecosystem Services of the Big Bend Region of the Chihuahuan Desert. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 27, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauer, R.H.; Riskind, D.H. Transactions of the Symposium on the Biological Resources of the Chihuahuan Desert Region, United States and Mexico, Sul Ross State University, Alpine, Texas, 17–18 October 1974; US Department of the Interior, National Park Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Safriel, U.; Adeel, Z.; Niemeijer, D.; Puigdefabregas, J.; White, R.; Lal, R.; Winslow, M.; Ziedler, J.; Prince, S.; Archer, E.; et al. Dryland systems. In Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: Current State and Trends Assessment; El-Kassas, M., Ezcurra, E., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 623–662. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Costanza, R. Valuation and Management of Desert Ecosystems and Their Services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 66, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Odorico, P.; Bhattachan, A.; Davis, K.F.; Ravi, S.; Runyan, C.W. Global Desertification: Drivers and Feedbacks. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic Shifts in Ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, J.; Bullock, J.M.; Egoh, B.; Everson, C.; Everson, T.; O’Connor, T.; O’Farrell, P.J.; Smith, H.G.; Lindborg, R. Grasslands—More Important for Ecosystem Services than You Might Think. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.; Futter, M.N.; Bishop, K. On the Forest Cover–Water Yield Debate: From Demand- to Supply-Side Thinking. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 806–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morri, E.; Pruscini, F.; Scolozzi, R.; Santolini, R. A Forest Ecosystem Services Evaluation at the River Basin Scale: Supply and Demand between Coastal Areas and Upstream Lands (Italy). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 37, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wen, L.; Wang, F.; Li, K.; Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem service value in Ulan Buh Desert. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Wu, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lu, Y. Effects of Groundwater Depth on Vegetation Coverage in the Ulan Buh Desert in a Recent 20-Year Period. Water 2023, 15, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, F.; Li, L.; Yang, Z.; Tang, P.; Yang, L.; Tian, T. Interplay of Environmental Shifts and Anthropogenic Factors with Vegetation Dynamics in the Ulan Buh Desert over the Past Three Decades. Forests 2024, 15, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droogers, P.; Allen, R. Estimating reference evapotranspiration under inaccurate data conditions. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2002, 16, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, E.; Ouyang, Z.; Yu, X.; Xiao, Y. Spatial Patterns and Impacts of Soil Conservation Service in China. Geomorphology 2014, 207, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Porter, J.P. RUSLE: Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Wang, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, K. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecosystem Services and Its Potential Drivers in Coalfields of Shanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Liu, J.; Shao, Q. Effects of Vegetation Coverage Change on Soil Conservation Service of Typical Steppe in Inner Mongolia. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2014, 16, 426–434. [Google Scholar]
- Fryrear, D.W.; Bilbro, J.D.; Saleh, A.; Schomberg, H.; Stout, J.E.; Zobeck, T.M. RWEQ: Improved Wind Erosion Technology. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 55, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Kong, L.; Huang, B.; Xu, W.; Ouyang, Z. Mapping Ecosystem Services Bundles to Detect High- and Low-Value Ecosystem Services Areas for Land Use Management. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jing, P.; Sun, P.; Ren, H.; Ai, Z. The Non-Significant Correlation between Landscape Ecological Risk and Ecosystem Services in Xi’an Metropolitan Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W. Remote Sensing Estimation of Vegetation Net Primary Productivity of Terrestrial Ecosystems in China and Its Relationship with Climate Change. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Jia, G.; Yang, Q.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Svenning, J.-C.; Wen, L. Construction of Ecological Network and Its Temporal and Spatial Evolution Characteristics: A Case Study of Ulanqab. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Shi, J.; Gong, J. Spatiotemporal Changes in the Watershed Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand Relationships in the Eastern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Diversity 2023, 15, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y. Investigating the Trade-Offs between the Supply and Demand for Ecosystem Services for Regional Spatial Management. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; Feng, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Fu, X. Analysis on supply and demand balance of soil conservation service and its driving factors on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 2722–2733. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2031.Q.20220812.1539.002 (accessed on 24 June 2025). (In Chinese).
- Gong, J.; Shi, J.; Zhu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y. Accounting for Land Use in an Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand in a Desert Steppe of Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M. The Correlation Between Urban Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand and Residents’ Well-Being in the Arid Regions of Northwest China. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, T.; Chang, M.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, L. Exploring the Changes and Driving Mechanisms in the Production-Transport-Consumption Process of Ecosystem Services Flow in the Yellow River Basin under the Background of Policy Changes. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Bai, Y.; Alatalo, J.M.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, G.; Xu, J. Indicators for Spatial–Temporal Comparisons of Ecosystem Service Status between Regions: A Case Study of the Taihu River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Cao, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wen, L. Evaluation and Driving Factors of Ecological Integrity in the Alxa League from 1990 to 2020. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1266736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, J.; Han, F. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Mountainous Ecosystem Services in an Arid Region and Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study of the Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang. Land 2022, 11, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfikar, R. Estimation Model and Selection Method of Panel Data Regression: An Overview of Common Effect, Fixed Effect, and Random Effect Model. JEMA: Jur. Ilm. Bid. Akuntansi. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, W.; Mayberry, R.; Bae, S.; Singh, K.; He, Q.P.; Lillard, J.W., Jr. A Study of Effects of MultiCollinearity in the Multivariable Analysis. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Halik, Ü.; Mamat, Z.; Aishan, T.; Welp, M. Identifying Mismatches of Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand under Semi-arid Conditions: The Case of the Oasis City Urumqi, China. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, H.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, H. Evaluating the Ecological Benefits of Plantations in Arid Areas from the Perspective of Ecosystem Service Supply and Demand-Based on Emergy Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxman, T.E.; Snyder, K.A.; Tissue, D.; Leffler, A.J.; Ogle, K.; Pockman, W.T.; Sandquist, D.R.; Potts, D.L.; Schwinning, S. Precipitation Pulses and Carbon Fluxes in Semiarid and Arid Ecosystems. Oecologia 2004, 141, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Du, B.; Pang, S. Will Vegetation Restoration Affect the Supply-Demand Relationship of Water Yield in an Arid and Semi-Arid Watershed? Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 959, 178292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidron, G.J. Analysis of Dew Precipitation in Three Habitats within a Small Arid Drainage Basin, Negev Highlands, Israel. Atmos. Res. 2000, 55, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tang, Q.; Lei, J.; Xu, X.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y. An Overview of Non-Conventional Water Resource Utilization Technologies for Biological Sand Control in Xinjiang, Northwest China. Env. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, M. Evaluating the Inter-Annual Surplus/Deficit Dynamic of Water Retention Service in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Bourque, C.P.-A.; Zhang, J.; Qin, S.; Wu, B. Relating Historical Vegetation Cover to Aridity Patterns in the Greater Desert Region of Northern China: Implications to Planned and Existing Restoration Projects. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Halike, A.; Luo, J.; Yao, K.; Yao, L.; Tang, H.; Tuheti, B. Multi-Scale Supply and Demand Relationships of Ecosystem Services Under Multiple Scenarios and Ecological Zoning to Promote Sustainable Urban Ecological Development in Arid Regions of China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, T. Spatiotemporal Changes in the Supply and Demand of Ecosystem Services in the Kaidu-Kongque River Basin, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jia, L.; Jia, T.; Hao, Z. An Carbon Neutrality Industrial Chain of “Desert-Photovoltaic Power Generation-Ecological Agriculture”: Practice from the Ulan Buh Desert, Dengkou, Inner Mongolia. China Geol. 2022, 5, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhou, H.; Cong, S. Near-Ground Impurity-Free Wind and Wind-Driven Sand of Photovoltaic Power Stations in a Desert Area. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 179, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Zhao, M.; Hu, X. Experimental Study on the Effect of Sand and Dust on the Performance of Photovoltaic Modules in Desert Areas. Energies 2024, 17, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Mu, R.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; An, J.; Li, X. Effects of Two Ecological Governance Measures for Photovoltaic Power Stations on Plant Growth and Soil Nutrients. Plants 2025, 14, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, A.; Ahmadi, H.; Soufi, M.; Motamedvaziri, B.; Moeini, A. Assessment of the Potential of Semi-Arid Plants to Reduce Soil Erosion in the Konartakhteh Watershed, Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, Z.; Parhizkar, M.; Zomorodian, M.; Shamsi, R.; mirmohammadmeygooni, S.; Shabanpour, M. The Role of Extracellular Polysaccharide Produced by Bradyrhizobium strain in Root Growth, Improvement of Soil Aggregate Stability and Reduction of Soil Detachment Capacity. Rhizosphere 2023, 27, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Xue, X.; Wang, T. Estimation of the quantity of aeolian saltation sediments blown into the Yellow River from the Ulanbuh Desert, China. J. of. Arid. Land 2018, 6, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Shao, Y.; Bai, Y. Identifying Ecosystem Service Supply-Demand Imbalance for Sustainable Land Management in China’s Loess Plateau. Land Use Policy 2022, 123, 106423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, R.; Yang, Q. Research Advances of Vegetation Effect on Soil and Water Conservation in China. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 2002, 26, 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Chen, X.; Hu, Z.; Zan, C.; Liu, T.; De Maeyer, P.; Sun, Y. Deciphering the Impact of Wind Erosion on Ecosystem Services: An Integrated Framework for Assessment and Spatiotemporal Analysis in Arid Regions. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, K. Identification of Ecosystem Service Bundles and Driving Factors in Beijing and Its Surrounding Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.; Ishida, K.; Kavvas, M.; Ercan, A.; Carr, K. Assessment of 21st Century Drought Conditions at Shasta Dam Based on Dynamically Projected Water Supply Conditions by a Regional Climate Model Coupled with a Physically-Based Hydrology Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashizi, A.K.; Sharafatmandrad, M. Investigating Tradeoffs between Supply, Use and Demand of Ecosystem Services and Their Effective Drivers for Sustainable Environmental Management. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Cao, X.; Lu, W. Carbon Dioxide Fluxes of Cyanobacterial Crusts and Underlying Soil under Different Precipitation Patterns in the Ulan Buh Desert, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 930961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashizi, A.K.; Sharafatmandrad, M. Water Regulation and Soil Retention Services in Semiarid Ecosystems of Southeastern Iran, 2018–2020. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3979–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, Z.; Ren, J.; Lu, N.; Fan, W.; Zhang, P.; Dong, X. Linking Ecosystem Services Supply, Social Demand and Human Well-Being in a Typical Mountain–Oasis–Desert Area, Xinjiang, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, B.; Bai, Y.; Xu, X.; Alatalo, J.M. Quantifying Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand Shortfalls and Mismatches for Management Optimisation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Lowe, D. A Fast Method for Updating Global Fossil Fuel Carbon Dioxide Emissions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 034012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafatmandrad, M.; Mashizi, A.K. Temporal and Spatial Assessment of Supply and Demand of the Water-Yield Ecosystem Service for Water Scarcity Management in Arid to Semi-Arid Ecosystems. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasner, N.Z.; Fox, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ave, K.; Carvalho, F.; Li, Y.; Walston, L.J.; Ricketts, M.P.; Jordaan, S.M.; Abou Najm, M.; et al. Impacts of Photovoltaic Solar Energy on Soil Carbon: A Global Systematic Review and Framework. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 208, 115032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Meng, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H.; Ren, Y.; Guo, L. The Role of Typical Low Vertical Lattice Sand Barriers in Regulating the Airflow Field on Wind-Eroded Surfaces of Photovoltaic Power Plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1521144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).