Cup Plant (Silphium perfoliatum): Agronomy, Uses, and Potential Role for Land Restoration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Plant Description
3. Environmental Requirements
4. Crop Management
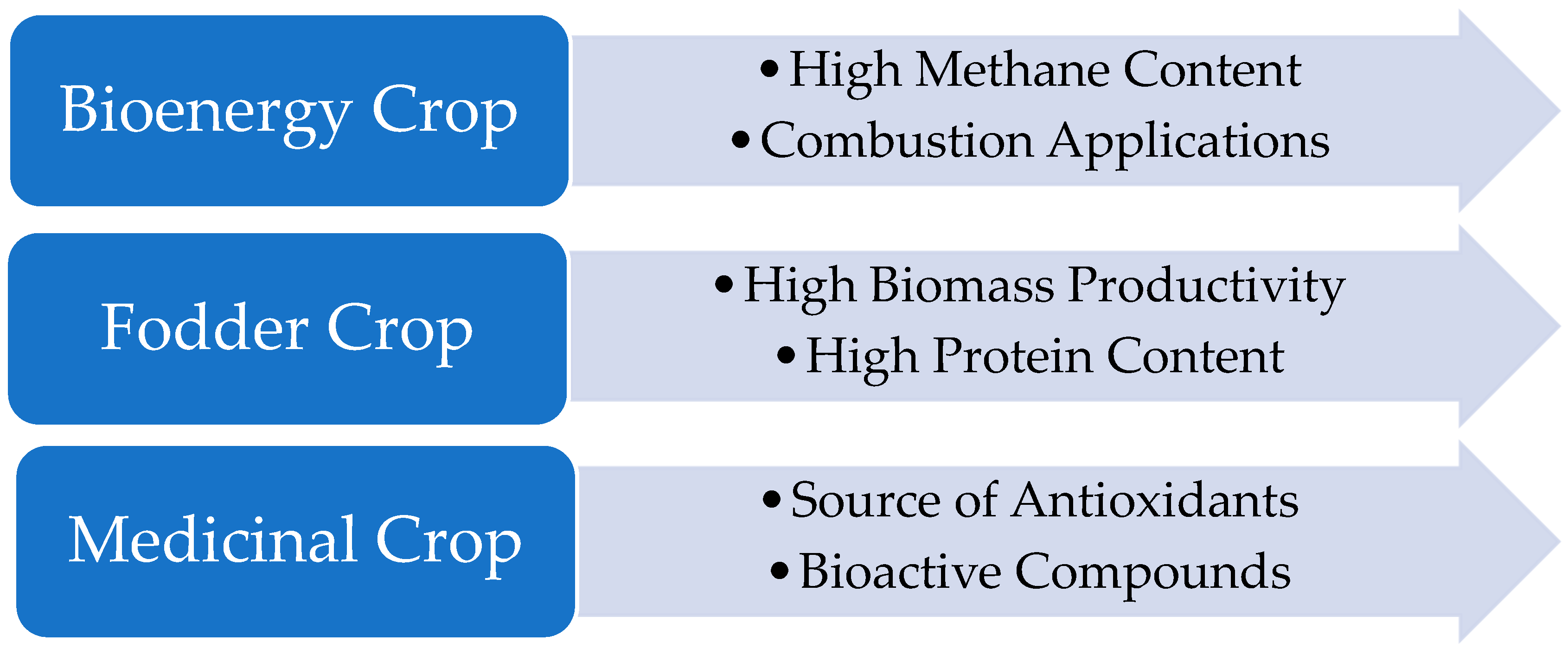
5. Uses
5.1. Bioenergy Crop
5.2. Fodder Crop
5.3. Medicinal Crop
6. Land Restoration
6.1. Phytoremediation
6.2. Restoration of Flood-Prone Areas
6.3. Greenhouse Gas Mitigation
6.4. Enhancement of Soil Organic Carbon
6.5. Prevention of Weed Invasions
6.6. Soil Erosion Control
6.7. Pollinator Support
7. Opportunities and Challenges in Cup Plant Cultivation
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Gomiero, T. Soil degradation, land scarcity and food security: Reviewing a complex challenge. Sustainability 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hammad, A.; Tumeizi, A. Land degradation: Socioeconomic and environmental causes and consequences in the eastern Mediterranean. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, G.S.; Kaur, M.; Kaushik, P. Impact of climate change on agriculture and its mitigation strategies: A review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.I.; Kaufmann, R.K. Anthropogenic and natural causes of climate change. Clim. Change 2014, 122, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, B.; Ganguli, N.; Matthew, R.; VanLoon, G.W.; Hipel, K.W.; Orbinski, J. Climate change-triggered land degradation and planetary health: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4509–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, H. Combating land degradation and desertification: The land-use planning quandary. Land 2019, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Angel, M.; Cerón-Hernández, V.A.; Ospina-Salazar, D.I. Applications and perspectives for land restoration through nature-based solutions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 36, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooke, J.; Sandercock, P. Use of vegetation to combat desertification and land degradation: Recommendations and guidelines for spatial strategies in Mediterranean lands. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 107, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernas, J.; Bernasová, T.; Gerstberger, P.; Moudrý, J.; Konvalina, P.; Moudrý, J., Jr. Cup plant, an alternative to conventional silage from a LCA perspective. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumalan, R.L.; Muntean, C.; Kostov, A.; Kržanović, D.; Jucsor, N.L.; Ciulca, S.I.; Sumalan, R.M.; Gheju, M.; Cernicova-Buca, M. The cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.)–a viable solution for bioremediating soils polluted with heavy metals. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2020, 48, 2095–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumplido-Marin, L.; Burgess, P.J.; Facciotto, G.; Coaloa, D.; Morhart, C.; Bury, M.; Paris, P.; Nahm, M.; Graves, A.R. Comparative economics of Sida hermaphrodita (L.) Rusby and Silphium perfoliatum L. as bioenergy crops in Europe. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peni, D.; Stolarski, M.J.; Bordiean, A.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Dębowski, M. Silphium perfoliatum—A herbaceous crop with increased interest in recent years for multi-purpose use. Agriculture 2020, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwek, H.; Włodarczyk, M.; Możdżer, E.; Bury, M.; Kitczak, T. Chemical composition and biogas formation potential of Sida hermaphrodita and Silphium perfoliatum. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.L.; Biertuempfel, A.; Friedritz, L.; Power, E.F.; Wright, G.A.; Dauber, J. Floral resources provided by the new energy crop, Silphium perfoliatum L. (Asteraceae). J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansberger, M.; Montgomery, L.F.; Liebhard, P. Botanical characteristics, crop management and potential of Silphium perfoliatum L. as a renewable resource for biogas production: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 63, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figas, A.; Rolbiecki, R.; Rolbiecki, S.; Jagosz, B.; Łangowski, A.; Sadan-Ozdemir, H.A.; Atilgan, A. Towards water-efficient irrigation of cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) for energy production: Water requirements and rainfall deficit. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancalion, P.H.; Holl, K.D. Upscaling ecological restoration by integrating with agriculture. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2025, 23, e2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, G.; Baj, T.; Kowalski, R.; Hanif, M.A. Characteristics of selected Silphium species as alternative plants for cultivation and industry with particular emphasis on research conducted in Poland: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoo, B.; Schroetter, S.; Kage, H.; Schittenhelm, S. Root traits of cup plant, maize and lucerne grass grown under different soil and soil moisture conditions. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2017, 203, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ende, L.M.; Hummel, L.; Lauerer, M. Dispersal and persistence of cup plant seeds (Silphium perfoliatum). Plant Ecol. Evol. 2024, 157, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tassel, D.L.; Albrecht, K.A.; Bever, J.D.; Boe, A.A.; Brandvain, Y.; Crews, T.E.; Wever, C. Accelerating Silphium domestication: An opportunity to develop new crop ideotypes and breeding strategies informed by multiple disciplines. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoo, B.; Kage, H.; Schittenhelm, S. Radiation use efficiency, chemical composition, and methane yield of biogas crops under rainfed and irrigated conditions. Europ. J. Agron. 2017, 87, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, D.; Panten, K.; Schwarz, A.; Bischoff, W.A.; Schittenhelm, S. Comparison of maize, permanent cup plant, and a perennial grass mixture with regard to soil and water protection. GCB Bioenergy 2020, 12, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, K.; Uther, H.; Kurbel, V.B.; Wild, A.J.; Lauerer, M.; Pausch, J. Moderate drought constrains crop growth without altering soil organic carbon dynamics in perennial cup-plant and silage maize. GCB Bioenergy 2024, 16, e70007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiaudinis, G.; Jasinskas, A.; Šlepetienė, A.; Karčauskienė, D. The evaluation of biomass and energy productivity of common mugwort (Artemisia vulgaris L.) and cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) in Albeluvisol. Žemdirbystė 2012, 99, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Šiaudinis, G.; Skuodienė, R.; Repšienė, R. The investigation of three potential energy crops: Common mugwort, cup plant, and Virginia mallow on Western Lithuania’s Albeluvisol. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinskas, A.; Simonavičiūtė, R.; Šiaudinis, G.; Liaudanskienė, I.; Antanaitis, Š.; Arak, M.; Olt, J. The assessment of common mugwort (Artemisia vulgaris L.) and cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) productivity and technological preparation for solid biofuel. Zemdirbyste 2014, 101, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, T.; Wu, J.; Albrecht, K.A.; Johnson, P.J.; Boe, A. Genetic variation for biomass and related morphological traits in cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.). Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, T.; Wu, J.; Boe, A. Genetic variation for achene traits in cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.). Open J. Genet. 2015, 5, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarski, M.J.; Śnieg, M.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Tworkowski, J.; Szczukowski, S. Short rotation coppices, grasses and other herbaceous crops: Productivity and yield energy value versus 26 genotypes. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 119, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boe, A.; Albrecht, K.A.; Johnson, P.J.; Wu, J. Biomass production of cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) in response to variation in plant population density in the North Central USA. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, B.; Lemmer, A.; Oechsner, H.; Reinhardt-Hönisch, A.; Claupein, W.; Graeff-Hönninger, S. Methane Yield Potential of Novel Perennial Biogas Crops Influenced by Harvest Date. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 58, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumplido-Marin, L.; Graves, A.R.; Burgess, P.J.; Morhart, C.; Paris, P.; Jablonowski, N.D.; Facciotto, G.; Bury, M.; Martens, R.; Nahm, M. Two novel energy crops: Sida hermaphrodita (L.) Rusby and Silphium perfoliatum L.—State of knowledge. Agronomy 2020, 10, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, R.; Kędzia, B. Antibacterial Activity of Silphium perfoliatum. Extracts. Pharm. Biol. 2007, 45, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.K.; Jokhakar, P.H.; Kalaria, R.K.; Vasava, D.K.; Kachhadiya, R.R. Phytoremediation: A novel and promising approach for the clean-up of heavy metal-contaminated soils associated with microbes. In Microbial Remediation of Azo Dyes with Prokaryotes, 1st ed.; Shah, M.P., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 233–258. [Google Scholar]
- Nescu, V.; Ciulca, S.; Sumalan, R.M.; Berbecea, A.; Velicevici, G.; Negrea, P.; Gaspar, S.; Sumalan, R.L. Physiological aspects of absorption, translocation, and accumulation of heavy metals in Silphium perfoliatum L. plants grown in a mining-contaminated soil. Minerals 2022, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmann, B.; Ruf, T.; Well, R.; Emmerling, C.; Fuß, R. Greenhouse gas emissions from Silphium perfoliatum and silage maize cropping on Stagnosols. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2023, 186, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jia, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Tao, J.; Zhao, X. Caffeoylquinic acids from Silphium perfoliatum L. show hepatoprotective effects on cholestatic mice by regulating enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 337, 118870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopushnyak, V.; Polutrenko, M.; Hrytsulyak, H.; Plevinskis, P.; Tonkha, O.; Pikovska, O.; Voloshin, Y. Accumulation of heavy metals in Silphium perfoliatum L. for the cultivation of oil-contaminated soils. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2022, 23, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y.; Ding, X.; Han, Y. The gene SiPrx from Saussurea involucrata enhances the stress resistance of Silphium perfoliatum L. Plants 2025, 14, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, V.; Koleva, V. Silphium perfoliatum: A promising energy crop for phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Sci. Pap. Ser. E Land R. 2024, 13, 672. Available online: https://landreclamationjournal.usamv.ro/pdf/2024/Art80.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Mockevičienė, I.; Šiaudinis, G.; Karčauskienė, D.; Repšienė, R.; Barčauskaitė, K.; Anne, O. The evaluation of the phytoremediation potential of the energy crops in acid soil by sewage sludge fertilization. Land 2023, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumalan, R.L.; Nescu, V.; Berbecea, A.; Sumalan, R.M.; Crisan, M.; Negrea, P.; Ciulca, S. The impact of heavy metal accumulation on some physiological parameters in Silphium perfoliatum L. plants grown in hydroponic systems. Plants 2023, 12, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmann, B.; Wöhl, L.; Fuß, R.; Schrader, S.; Well, R.; Ruf, T. N2 and N2O mitigation potential of replacing maize with the perennial biomass crop Silphium perfoliatum—An incubation study. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 1649–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, M.; Korte, C.A.C.; Entrup, J.; Altrogge, H.; Bischoff, P.; Elfers, J.; Pude, R. Evaluation of the intra-and interspecific development of different accessions of Silphium perfoliatum L. and Silphium integrifolium Michx. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorpp, Q.; Schrader, S. Earthworm functional groups respond to the perennial energy cropping system of the cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.). Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 87, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazoulis, I.; Antonopoulos, N.; Kanatas, P.; Karavas, N.; Bertoncelj, I.; Travlos, I. Invasive alien plant species—Raising awareness of a threat to biodiversity and ecological connectivity (EC) in the Adriatic-Ionian region. Diversity 2022, 14, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazoulis, I.; Kanatas, P.; Papastylianou, P.; Tataridas, A.; Alexopoulou, E.; Travlos, I. Weed management practices to improve establishment of selected lignocellulosic crops. Energies 2021, 14, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, D.R.; Jones, V.L. Rapid evolution of invasive weeds under climate change: Present evidence and future research needs. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 664034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerswald, K.; Oberneder, A.; Wiesmeier, M.; Ebertseder, F.; Fritz, M. Erosion impact of cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) stands established with and without nurse crop. Soil Use Manag. 2025, 41, e70047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, T.; Aartsma, P.; Deumlich, D.; Chifflard, P.; Panten, K. From field to model: Determining EROSION 3D model parameters for the emerging biomass plant Silphium perfoliatum L. to predict effects on water erosion processes. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaalishvili, V.B.; Dzanagov, S.K.; Bekuzarova, S.A.; Gaplaev, M.S.; Tsagaraeva, E.A.; Kokoev, K.P.; Lazarov, T.K.; Osikina, R.V. Ways to Reduce Water Erosion on Mountainous Slope Lands. In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference “AgroSMART—Smart Solutions for Agriculture”, Tyumen, Russia, 16–19 July 2019; pp. 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cîrlig, N. Entomofaunistic study on the species Silphium perfoliatum L. in the Republic of Moldova. Sci. Papers Ser. A Agron. 2022, 65, 348–353. Available online: https://ibn.idsi.md/sites/default/files/imag_file/348-353_2_2022.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Mueller, A.L.; Berger, C.A.; Schittenhelm, S.; Stever-Schoo, B.; Dauber, J. Water availability affects nectar sugar production and insect visitation of the cup plant Silphium perfoliatum L. (Asteraceae). J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2020, 206, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, J.F.; Kirkegaard, J.A.; Hunt, J.R.; Ryan, M.H.; Ohlander, L.; Peoples, M.B. Break crops and rotations for wheat. Crop Pasture Sci. 2015, 66, 523–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebman, M.; Dyck, E. Crop rotation and intercropping strategies for weed management. Ecol. Appl. 1993, 3, 92–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegada-Lizarazu, W.; Monti, A. Energy crops in rotation. A review. Biomass Βioenergy 2011, 35, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ende, L.M.; Knöllinger, K.; Keil, M.; Fiedler, A.J.; Lauerer, M. Possibly invasive new bioenergy crop Silphium perfoliatum: Growth and reproduction are promoted in moist soil. Agriculture 2021, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors | Year | Journal | Publisher |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peni et al. [12] | 2020 | Agriculture | MDPI |
| Gansberger et al. [15] | 2015 | Industrial Crops and Products | Elsevier |
| Cumplido-Marin et al. [11] | 2020 | Agronomy | MDPI |
| Van Tassel et al. [21] | 2017 | Crop Science | Wiley |
| Authors | Heavy Metal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Cu | Pb | Cr | Cd | Ni | Hg | Co | |
| Nescu et al. [36] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Sumalan et al. [10] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Angelova and Koleva [41] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Mockevičienė et al. [42] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Sumalan et al. [43] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Zhang et al. [38] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Lopushnyak et al. [39] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Ecosystem Services—Ways of Land Restoration | Uses | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Phytoremediation | Bioenergy Crop | Lack of Registered PPP |
| Soil Erosion Control | Fodder Crop | Lack of Equipment |
| Restoration of Flood-Prone Areas | Medicinal Crop | Socio-Economic Barriers |
| Reduction in Nutrient Leaching | Invasive Character | |
| Long-Term Weed Suppression | ||
| GHG * Mitigation | ||
| SOC Increase | ||
| Pollinator Support |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gazoulis, I.; Pyliou, K.; Kokkini, M.; Danaskos, M.; Kanatas, P.; Travlos, I. Cup Plant (Silphium perfoliatum): Agronomy, Uses, and Potential Role for Land Restoration. Land 2025, 14, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061307
Gazoulis I, Pyliou K, Kokkini M, Danaskos M, Kanatas P, Travlos I. Cup Plant (Silphium perfoliatum): Agronomy, Uses, and Potential Role for Land Restoration. Land. 2025; 14(6):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061307
Chicago/Turabian StyleGazoulis, Ioannis, Konstantina Pyliou, Metaxia Kokkini, Marios Danaskos, Panagiotis Kanatas, and Ilias Travlos. 2025. "Cup Plant (Silphium perfoliatum): Agronomy, Uses, and Potential Role for Land Restoration" Land 14, no. 6: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061307
APA StyleGazoulis, I., Pyliou, K., Kokkini, M., Danaskos, M., Kanatas, P., & Travlos, I. (2025). Cup Plant (Silphium perfoliatum): Agronomy, Uses, and Potential Role for Land Restoration. Land, 14(6), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061307







