The Evolution of Cropland Slope Structure and Its Implications for Fragmentation and Soil Erosion in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Cropland Dataset
2.2.2. Digital Elevation Model and Slope Calculation
2.2.3. Soil Erosion Dataset
2.3. Research Methods
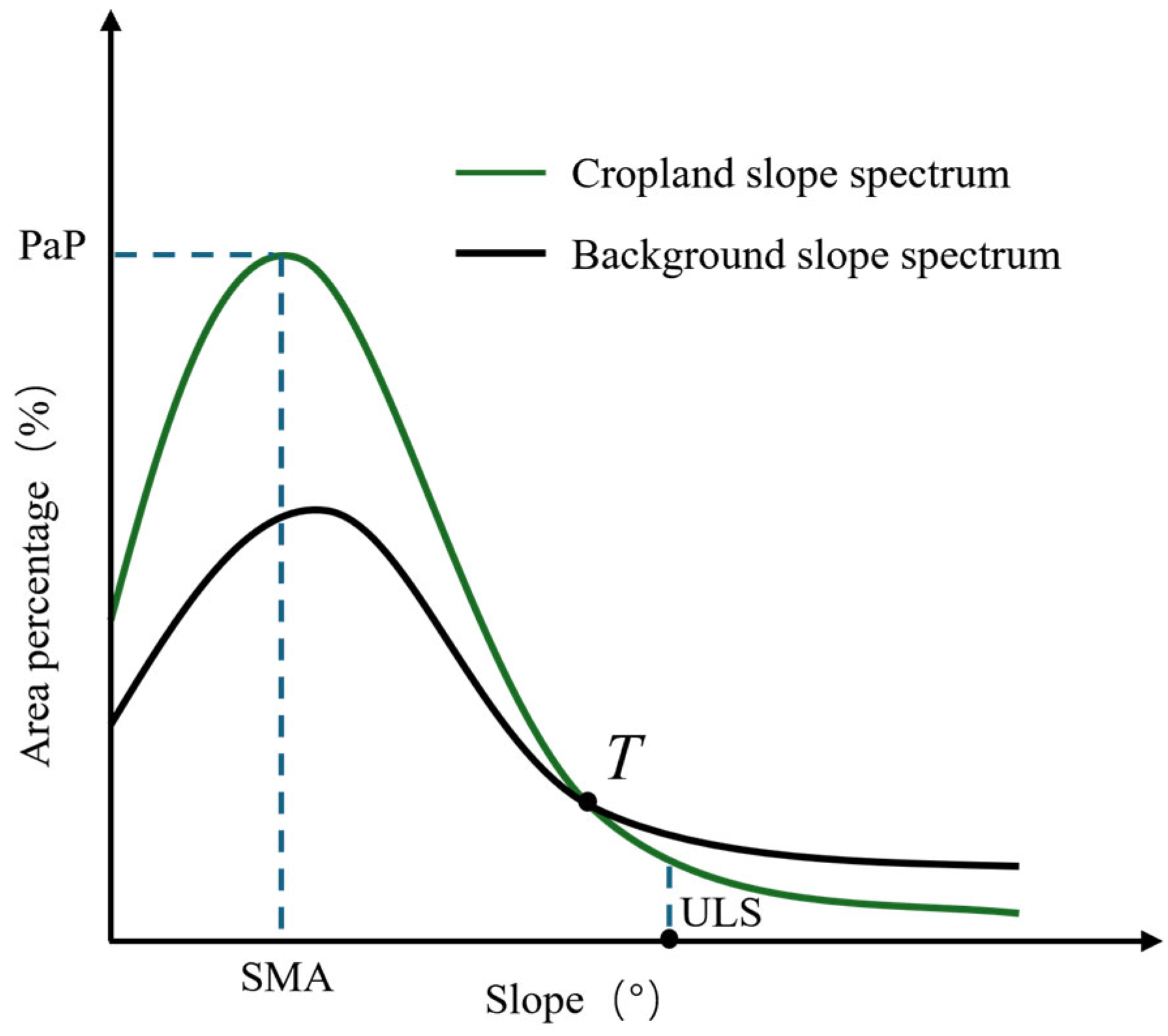
2.3.1. Distribution Characteristics of Cropland Slope
2.3.2. Cropland Slope Change Index
2.3.3. Geographically Weighted Regression
2.3.4. Grid-Based Spatial Partitioning with H3
3. Results
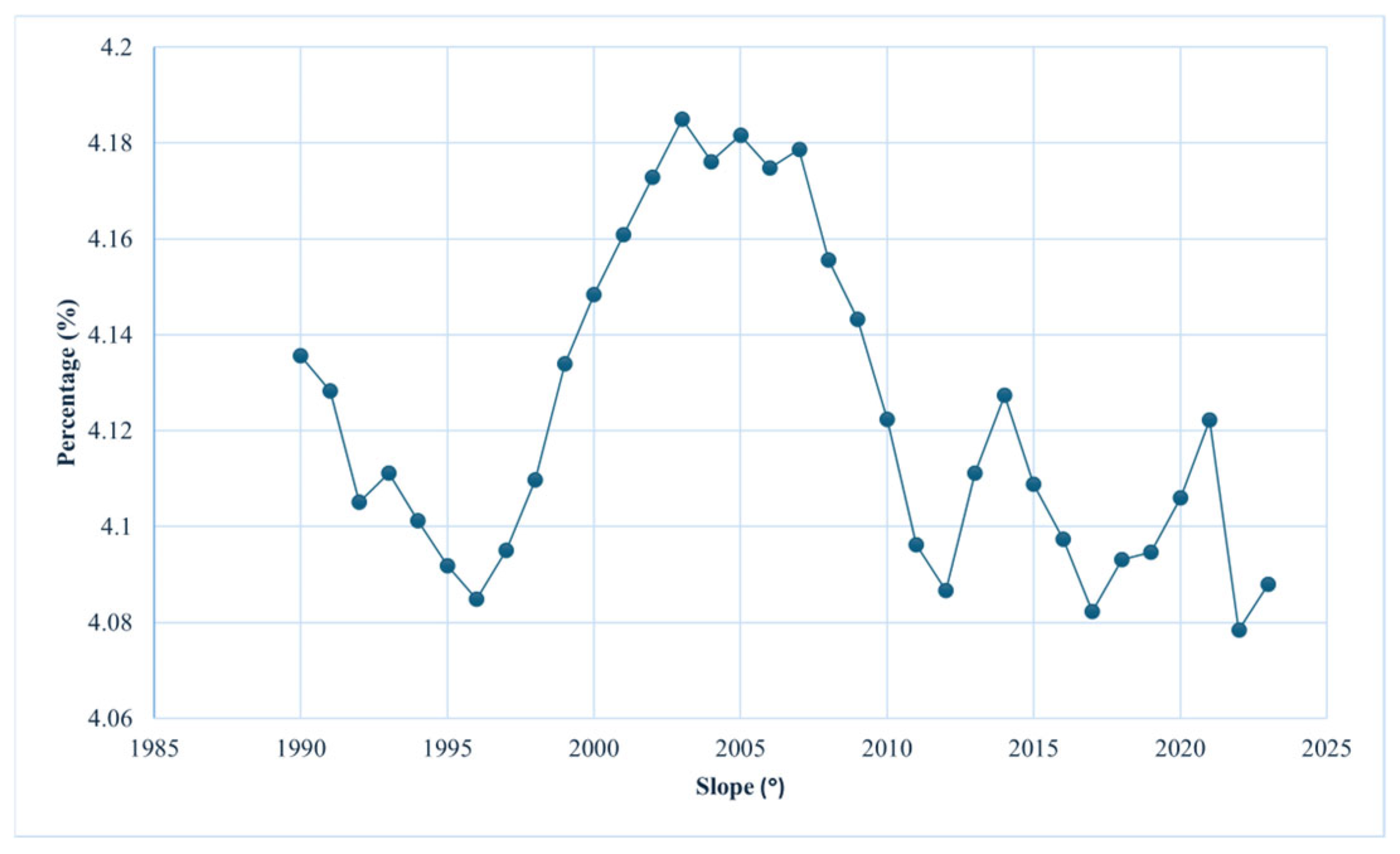
3.1. Nationwide Cropland Slope Structure Variation Characteristics
3.2. Slope Spectrum Changes in Cropland from the Perspective of the H3 Grid
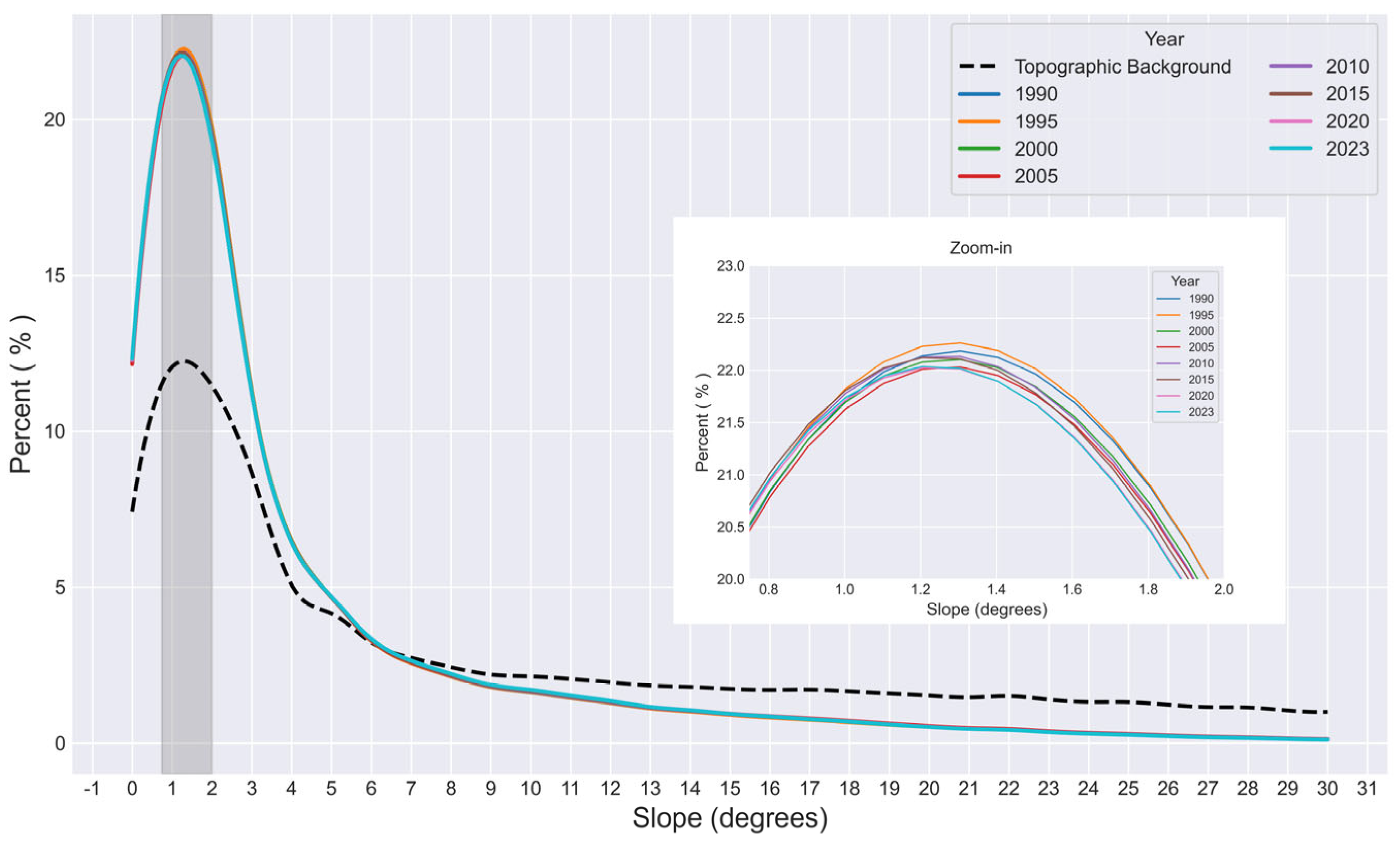
3.2.1. Analysis of Slope Spectrum Characteristics
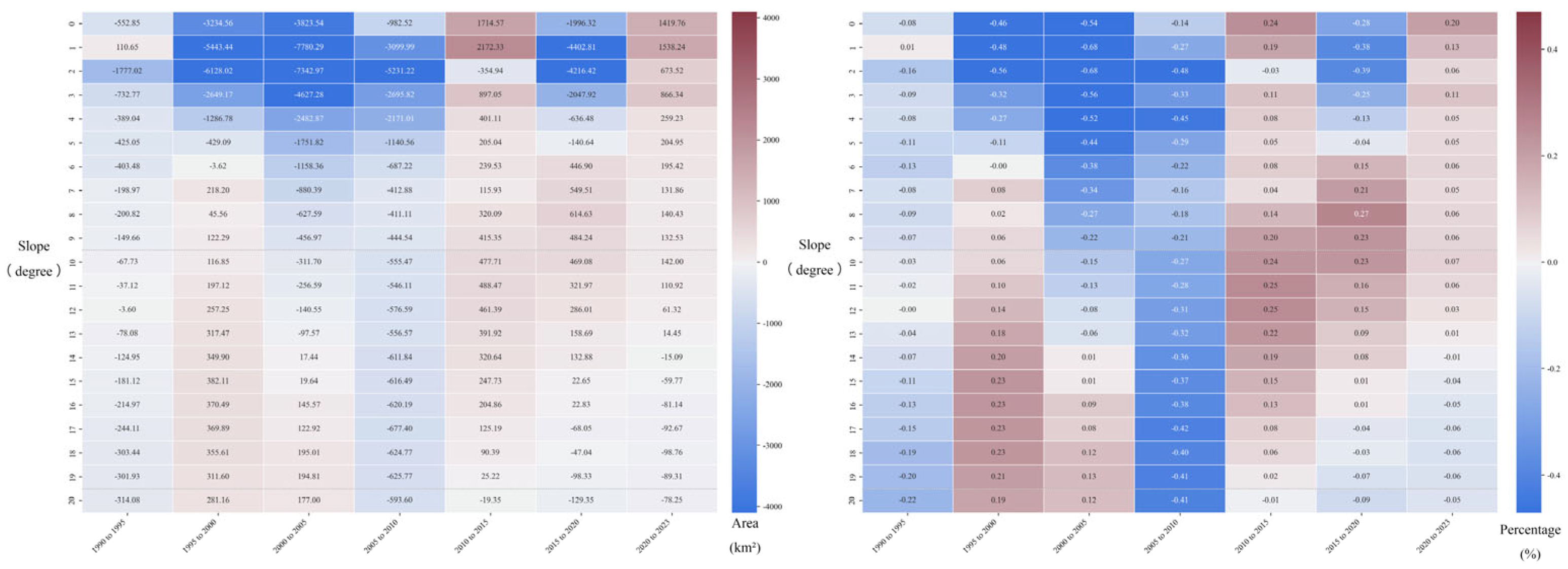
3.2.2. Analysis of Cropland Slope Changes
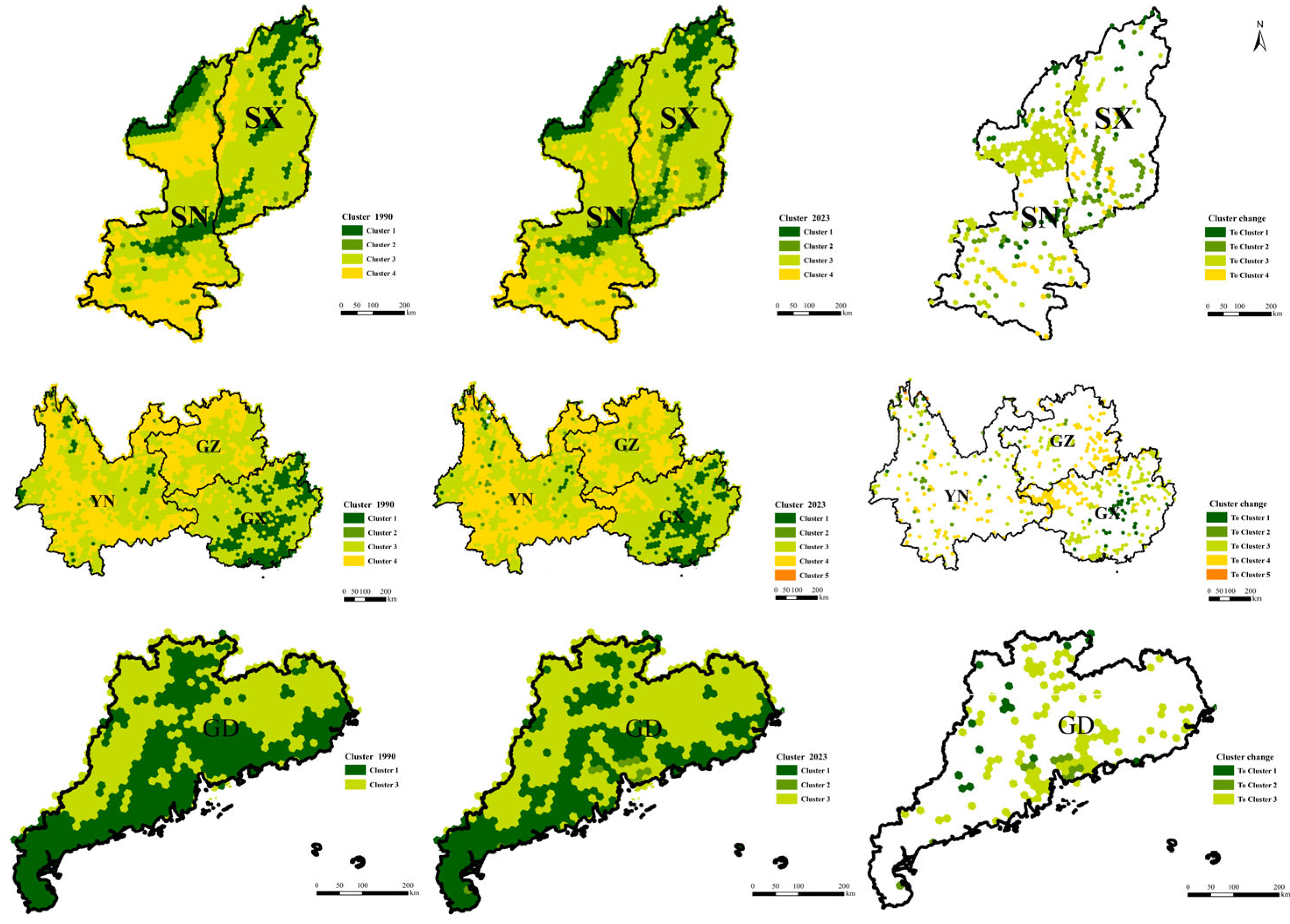
3.2.3. Analysis of Slope Structure Patterns
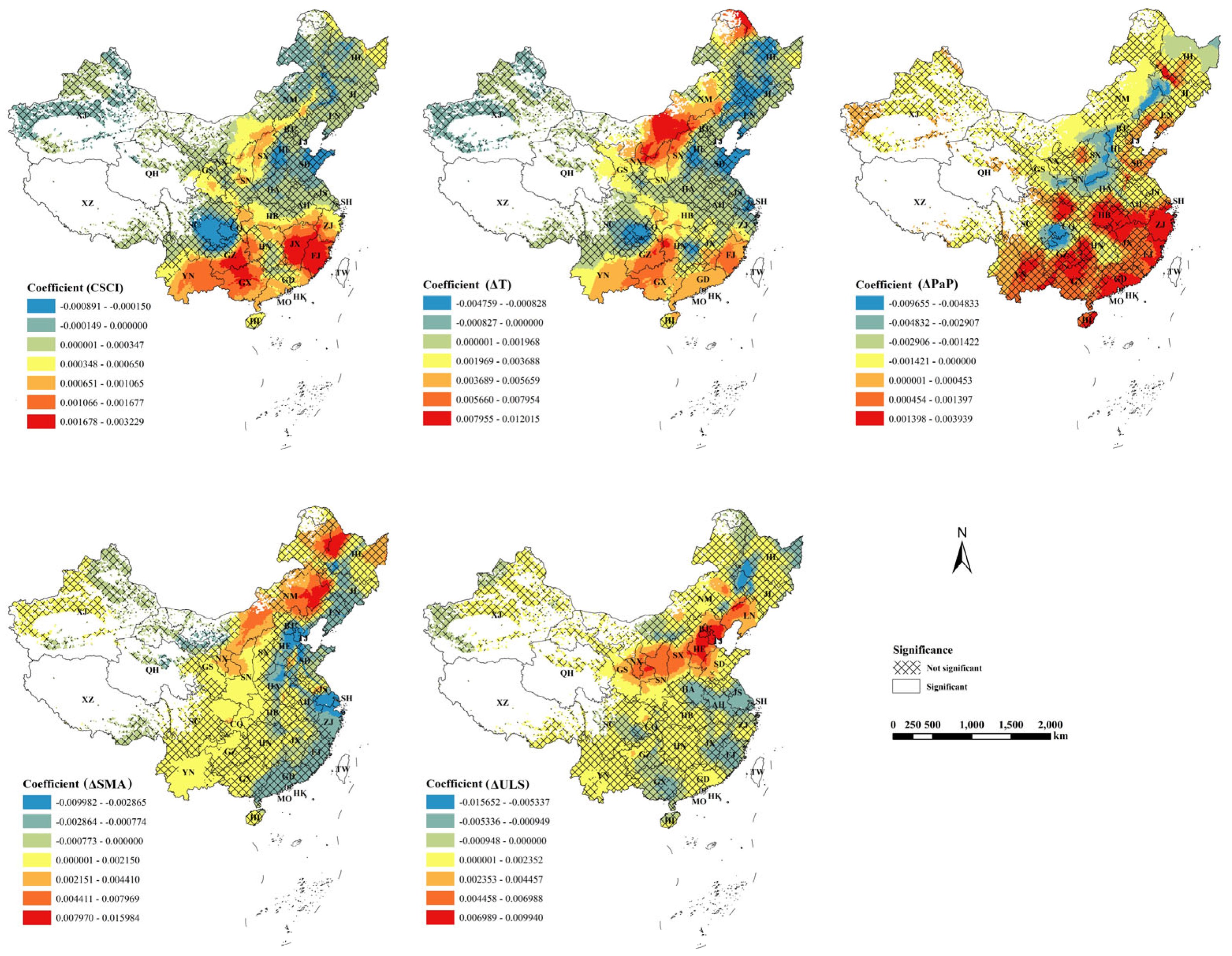
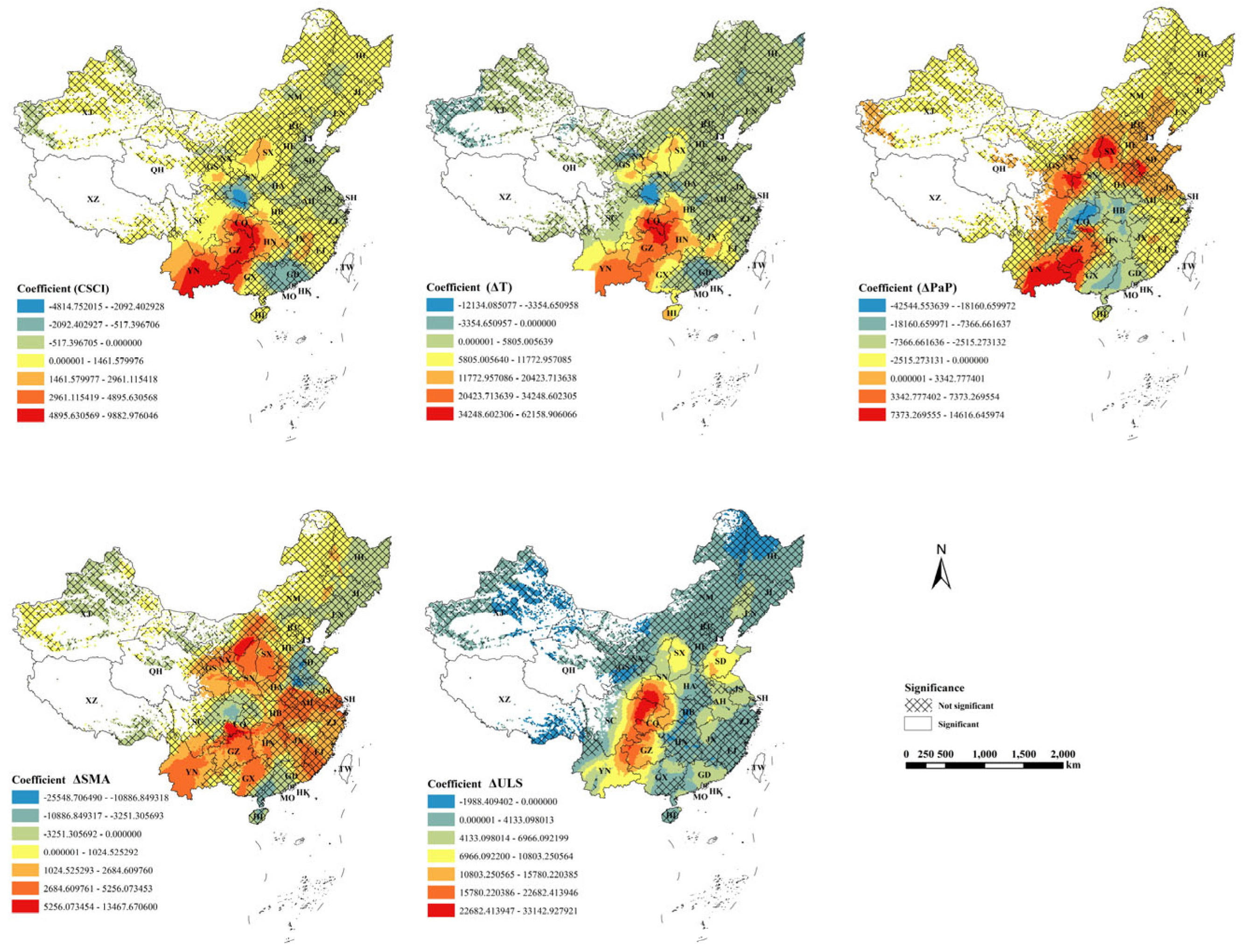
3.3. The Impact of Cropland Slope Structure Changes on Cropland Fragmentation and Soil Erosion
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Heterogeneity of Slope Structure Changes and Its Underlying Causes
4.2. Comparing the Scale Effects of H3 Grids and Administrative Units
4.3. Slope Structure, Cropland Fragmentation, and Soil Erosion Risk
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CLCD | China Land Cover Dataset |
| CSCI | Cropland Slope Change Index |
| GWR | Geographically Weighted Regression |
| ULS | Upper Limit of Slope |
Appendix A
| Full Name | Abbreviation | Full Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing Municipality | BJ | Hunan Province | HN |
| Tianjin Municipality | TJ | Guangdong Province | GD |
| Hebei Province | HE | Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region | GX |
| Shanxi Province | SX | Hainan Province | HI |
| Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region | NM | Chongqing Municipality | CQ |
| Liaoning Province | LN | Sichuan Province | SC |
| Jilin Province | JL | Guizhou Province | GZ |
| Heilongjiang Province | HL | Yunnan Province | YN |
| Shanghai Municipality | SH | Tibet Autonomous Region | XZ |
| Jiangsu Province | JS | Shaanxi Province | SN |
| Zhejiang Province | ZJ | Gansu Province | GS |
| Anhui Province | AH | Qinghai Province | QH |
| Fujian Province | FJ | Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region | NX |
| Jiangxi Province | JX | Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region | XJ |
| Shandong Province | SD | Hong Kong Special Administrative Region | HK |
| Henan Province | HA | Macao Special Administrative Region | MO |
| Hubei Province | HB | Taiwan Province | TW |
References
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Cultivated Land Protection and Rational Use in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Pei, B. Spatial-Temporal Variations of Cultivated Land Compensation and Its Compensation Mechanism in Mainland China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 110, 107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Population Prospects 2024: Summary of Results; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- White, J.C.; Gardea-Torresdey, J. Achieving Food Security through the Very Small. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potapov, P.; Turubanova, S.; Hansen, M.C.; Tyukavina, A.; Zalles, V.; Khan, A.; Song, X.-P.; Pickens, A.; Shen, Q.; Cortez, J. Global Maps of Cropland Extent and Change Show Accelerated Cropland Expansion in the Twenty-First Century. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koiry, S.; Huang, W. Do Ecological Protection Approaches Affect Total Factor Productivity Change of Cropland Production in Sweden? Ecol. Econ. 2023, 209, 107829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.; Xu, W.; Gu, Z.; Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y. A New Framework of Land Use Efficiency for the Coordination among Food, Economy and Ecology in Regional Development. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Peng, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Understanding Land for High-Quality Development. J. Geogr. Sci 2023, 33, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations, U.N. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; Working Paper; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Song, W. Spatial Transformation of Changes in Global Cultivated Land. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Duan, X.; Yun, R. The Impact of Urbanization on Food Security: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province. Land 2023, 12, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Ma, E.; Lin, J.; Liao, L.; Han, Y. Exploring Global Food Security Pattern from the Perspective of Spatio-Temporal Evolution. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Zeng, M.; Luo, K. The Impact of Urbanization on Food Security in China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 93, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Li, Y. Land Space Optimization of Urban-Agriculture-Ecological Functions in the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Chen, B.; Yu, L.; Xin, Q.; Gong, P.; Xu, B. How Does Urban Expansion Interact with Cropland Loss? A Comparison of 14 Chinese Cities from 1980 to 2015. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Liang, J.; Chen, W.; Peng, Y. Uphill or Downhill? Cropland Use Change and Its Drivers from the Perspective of Slope Spectrum. J. Mt. Sci. 2024, 21, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Peng, Q.; Song, Y.; Lyu, L.; Chen, D.; Huang, P.; Peng, F.; Liu, Y. Characteristics and Effects of Global Sloping Land Urbanization from 2000 to 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 937, 173348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Cheng, G. Cultivated Land Loss and Construction Land Expansion in China: Evidence from National Land Surveys in 1996, 2009 and 2019. Land Use Policy 2023, 125, 106496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, T.; Feng, Z.; Wu, K. Identifying the Contradiction between the Cultivated Land Fragmentation and the Construction Land Expansion from the Perspective of Urban-Rural Differences. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 71, 101826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yuan, M.; Han, P.; Wang, D. Assessing Sustainable Urban Development Based on Functional Spatial Differentiation of Urban Agriculture in Wuhan, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 115, 105999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y. Spatial Conflict Identification and Scenario Coordination for Construction-agricultural-ecological Land Use. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 27, 1933–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yin, M. Change of Urban and Rural Construction Land and Driving Factors of Arable Land Occupation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z. Assessing Effects of the Returning Farmland to Forest Program on Vegetation Cover Changes at Multiple Spatial Scales: The Case of Northwest Yunnan, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, G.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, A.; Wu, C. Uphill Cropland and Stability Assessment of Gained Cropland in China over the Preceding 30 Years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 699–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, M.; Nafees, M.; Khan, A.; Yin, H.; Ullah, W.; Rashid, W.; Han, H.; Lashari, A.H. Off-Season Agriculture Encroachment in the Uplands of Northern Pakistan: Need for Sustainable Land Management. Land 2022, 11, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Y.; Tang, Z. Effects of Soil and Water Conservation Management and Rainfall Types on Runoff and Soil Loss for a Sloping Area in North China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2117–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H. Effect of Soil Conservation Measures and Slope on Runoff, Soil, TN, and TP Losses from Cultivated Lands in Northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Qi, Z.; Yin, Z.; Li, A. Soil and Water Conservation Effects of Different Tillage Measures on Phaeozems Sloping Farmland in Northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 1716–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Yu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Fang, N.; Xiao, H.; Wang, L.; Shi, Z. Soil Conservation of Sloping Farmland in China: History, Present, and Future. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 249, 104655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Pattern of the Newly Increased Cultivated Land and Its Vulnerability in Northeast China. Land 2023, 12, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, G.; Xi, Z.; He, P.; Xin, X.; Chen, J.; Yu, H.; Kang, G. Spatiotemporal Changes of Cultivated Land Utilization in Black Soil Region, China Based on Geo-Information Tupu. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Shao, Q.; Ning, J.; Jin, S. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Arable Land and Their Impacts on Grain Output in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 1980 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Song, C.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Cheng, F.; Kong, X.; Feng, Z.; Gao, P. Arable Land Quality in Developing China: An Integrated Exploration from Global Challenges to Localized Solutions. Land 2024, 13, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Gokce, A. Global agricultural losses and their causes. Bull. Biol. Allied Sci. Res. 2024, 2024, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Cheng, C.; Kan, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Wu, X. Impact of Arable Land Abandonment on Crop Production Losses in Ukraine During the Armed Conflict. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmamaw, L.B.; Mohammed, A.A. Effects of Slope Gradient and Changes in Land Use/Cover on Selected Soil Physico-Biochemical Properties of the Gerado Catchment, North-Eastern Ethiopia. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 70, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremew, B.; Tadesse, T.; Bedadi, B.; Gollany, H.T.; Tesfaye, K.; Aschalew, A. Impact of Land Use/Cover Change and Slope Gradient on Soil Organic Carbon Stock in Anjeni Watershed, Northwest Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, W.; Li, G.; Meng, F.; He, T.; Li, X. Urbanization in China Drives Farmland Uphill under the Constraint of the Requisition–Compensation Balance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Long, Y.; Yang, X. Research on the Slope Spectrum of the Loess Plateau. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 2008, 51, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Mu, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, S. Cities Are Going Uphill: Slope Gradient Analysis of Urban Expansion and Its Driving Factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Liu, G.; Zhou, L.; Cui, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y. Satellite Remote Sensing Data Reveal Increased Slope Climbing of Urban Land Expansion Worldwide. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 235, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Cui, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y. Global Urban Land Expansion Tends to Be Slope Climbing: A Remotely Sensed Nighttime Light Approach. Earth’s Future 2023, 11, e2022EF003384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Peng, Q.; Huang, P. Slope Characteristics of Urban Construction Land and Its Correlation with Ground Slope in China. Open Geosci. 2022, 14, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Ren, J.; Hai, W.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; Gao, Y. Research on the Slope Gradient Effect and Driving Factors of Construction Land in Urban Agglomerations in the Upper Yellow River: A Case Study of the Lanzhou–Xining Urban Agglomerations. Land 2023, 12, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zeng, J.; Yang, L.; Gu, T.; Lei, F. Slope-Climbing of Cropland and Its Effects in China. J. Mt. Sci. 2024, 21, 2754–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faostat. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Wen, A.; Tang, Q.; Ouyang, C.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Li, S.; Zhu, W.; Liu, L. Mountain Protection and Mountain Development in China: Review and Prospect. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. (Chin. Version) 2023, 38, 376–384. [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An Assessment of the Global Impact of 21st Century Land Use Change on Soil Erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, S.; Yin, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Z.; et al. The Assessment of Soil Loss by Water Erosion in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinhua News Agency Bulletin of Main Data of the Third National Land Survey. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-08/26/content_5633490.htm (accessed on 10 May 2025). (In Chinese)
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Datasets and Its Dynamics in China from 1985 to 2023. 2024. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/12779975 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Zhang, C.; Dong, J.; Ge, Q. Quantifying the Accuracies of Six 30-m Cropland Datasets over China: A Comparison and Evaluation Analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 197, 106946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fu, M. A Comprehensive Approach for the Spatial Optimization of the Biodiversity Conservation Network in the Qinling Mountains, China. Landsc Ecol 2025, 40, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, S. New Insights of Eco-Environmental Vulnerability in China’s Yellow River Basin: Spatio-Temporal Pattern and Contributor Identification. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Jin, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M. Analysis of Long-Term Wetland Variations in China Using Land Use/Land Cover Dataset Derived from Landsat Images. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippen, R.; Buckley, S.; Agram, P.; Belz, E.; Gurrola, E.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Lavalle, M.; Martin, J.; Neumann, M.; et al. NASADEM global elevation model: Methods and progress. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, XLI-B4, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, J.; He, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, C. New 30-m Resolution Dataset Reveals Declining Soil Erosion with Regional Increases across Chinese Mainland (1990–2022). Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 323, 114681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, J.; He, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, C. The 30 m Annual Soil Water Erosion Dataset in Chinese Mainland from 1990 to 2022. 2024. Available online: https://www.scidb.cn/en/detail?dataSetId=9d14070a664f4d368ca107c5e9d6b746 (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- GDAL/OGR Contributors. GDAL/OGR Geospatial Data Abstraction Software Library; Open Source Geospatial Foundation: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression. In The Sage Handbook of Spatial Analysis; Sage Publishing: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky, I. H3: Uber’s Hexagonal Hierarchical Spatial Index. Available from Uber Engineering Website. Available online: https://eng.uber.com/h3/ (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Zhao, N.; Chen, K.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Cropland Fragmentation Change across China over the Last Two Decades. Agric. Syst. 2024, 218, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.S. The Modifiable Areal Unit Problem (MAUP). In WorldMinds: Geographical Perspectives on 100 Problems: Commemorating the 100th Anniversary of the Association of American Geographers 1904–2004; Janelle, D.G., Warf, B., Hansen, K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 571–575. ISBN 978-1-4020-2352-1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, H.; Xu, B.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Yu, S.; et al. Multiple Perspective Accountings of Cropland Soil Erosion in China Reveal Its Complex Connection with Socioeconomic Activities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 337, 108083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

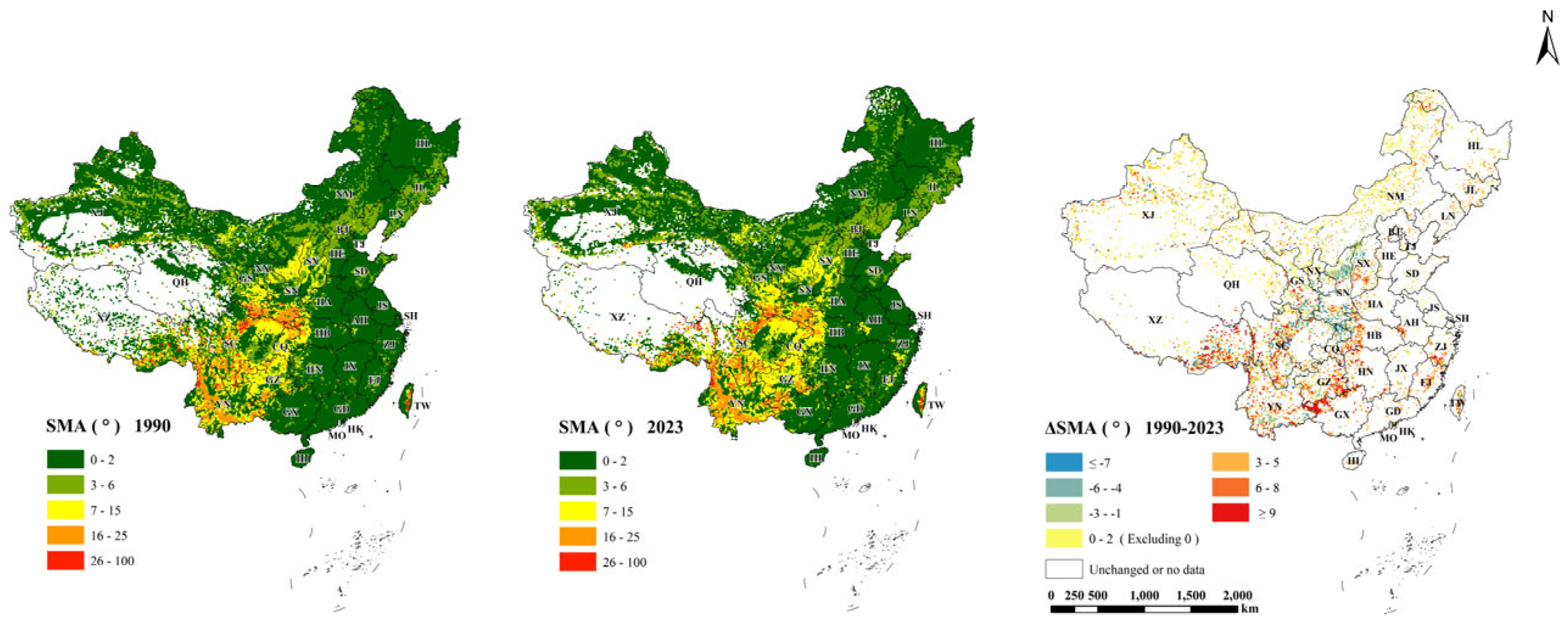
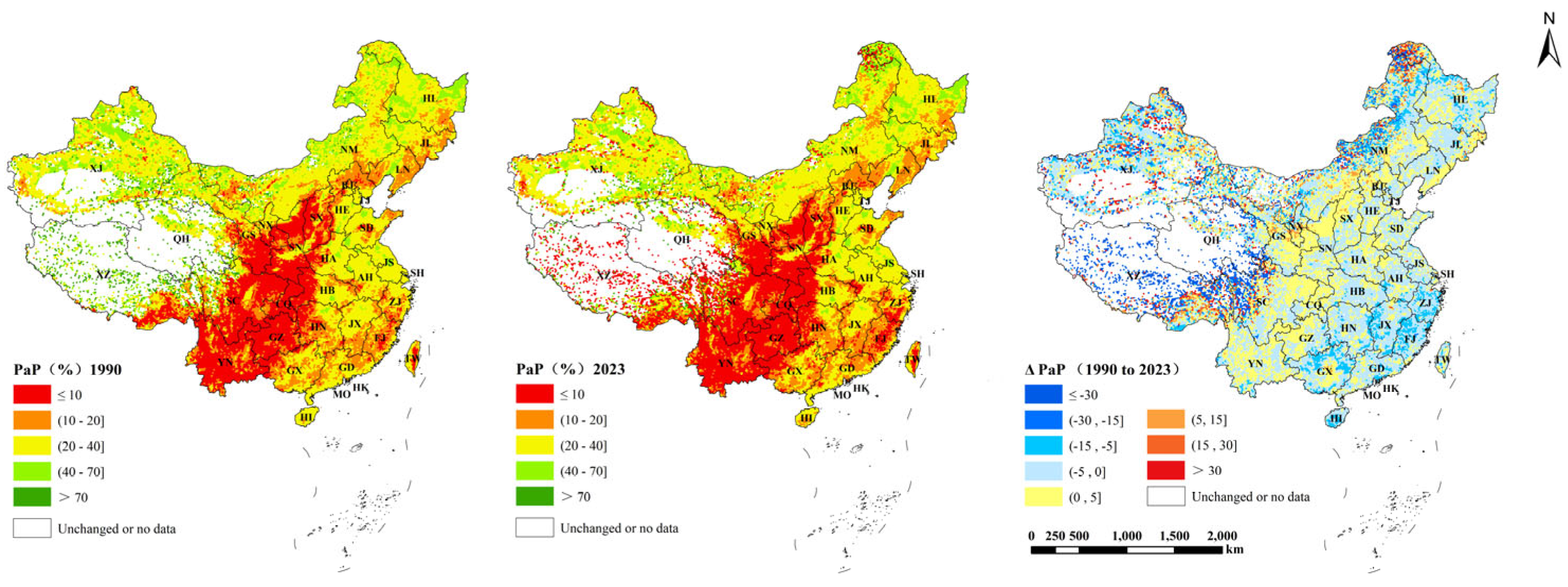
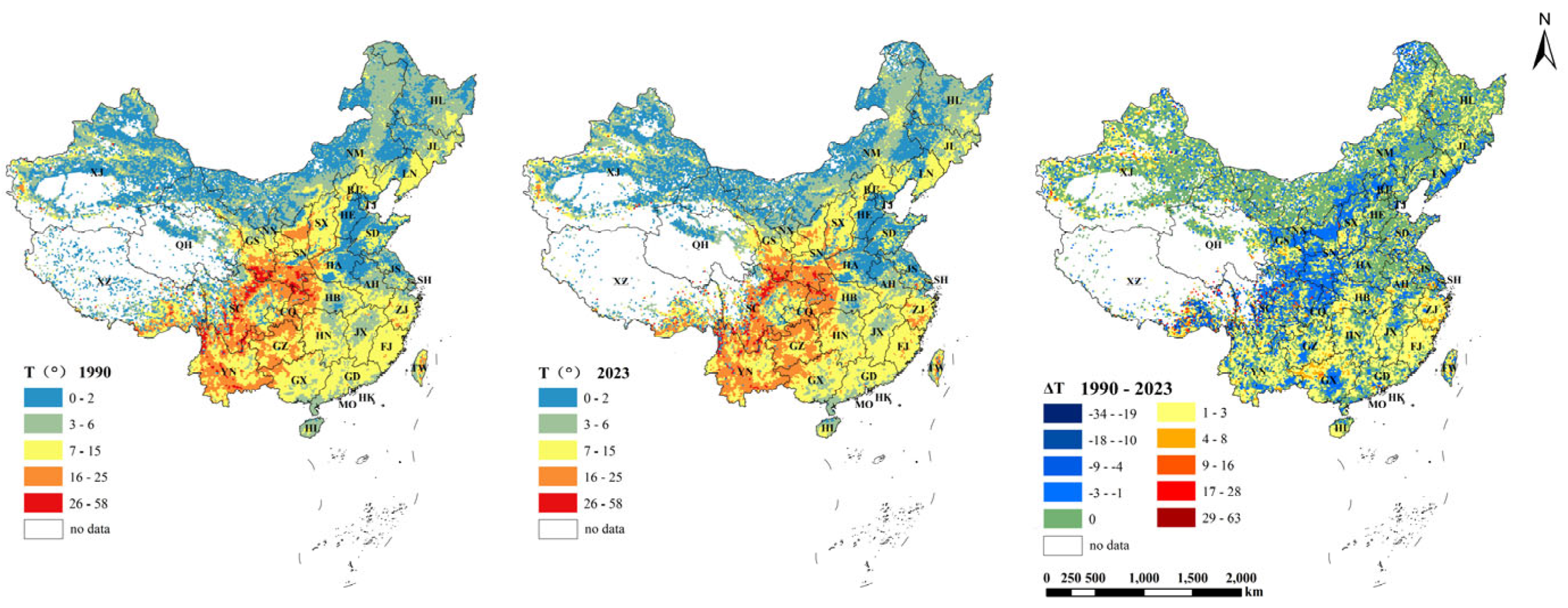
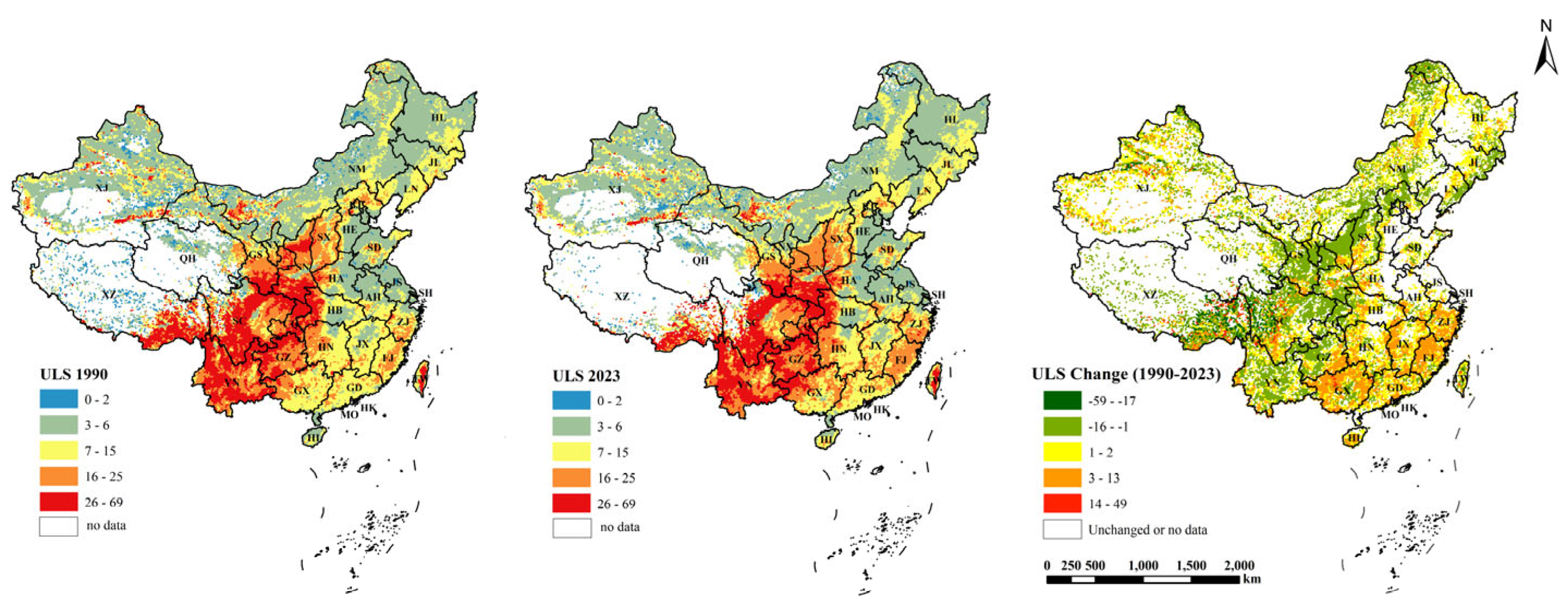
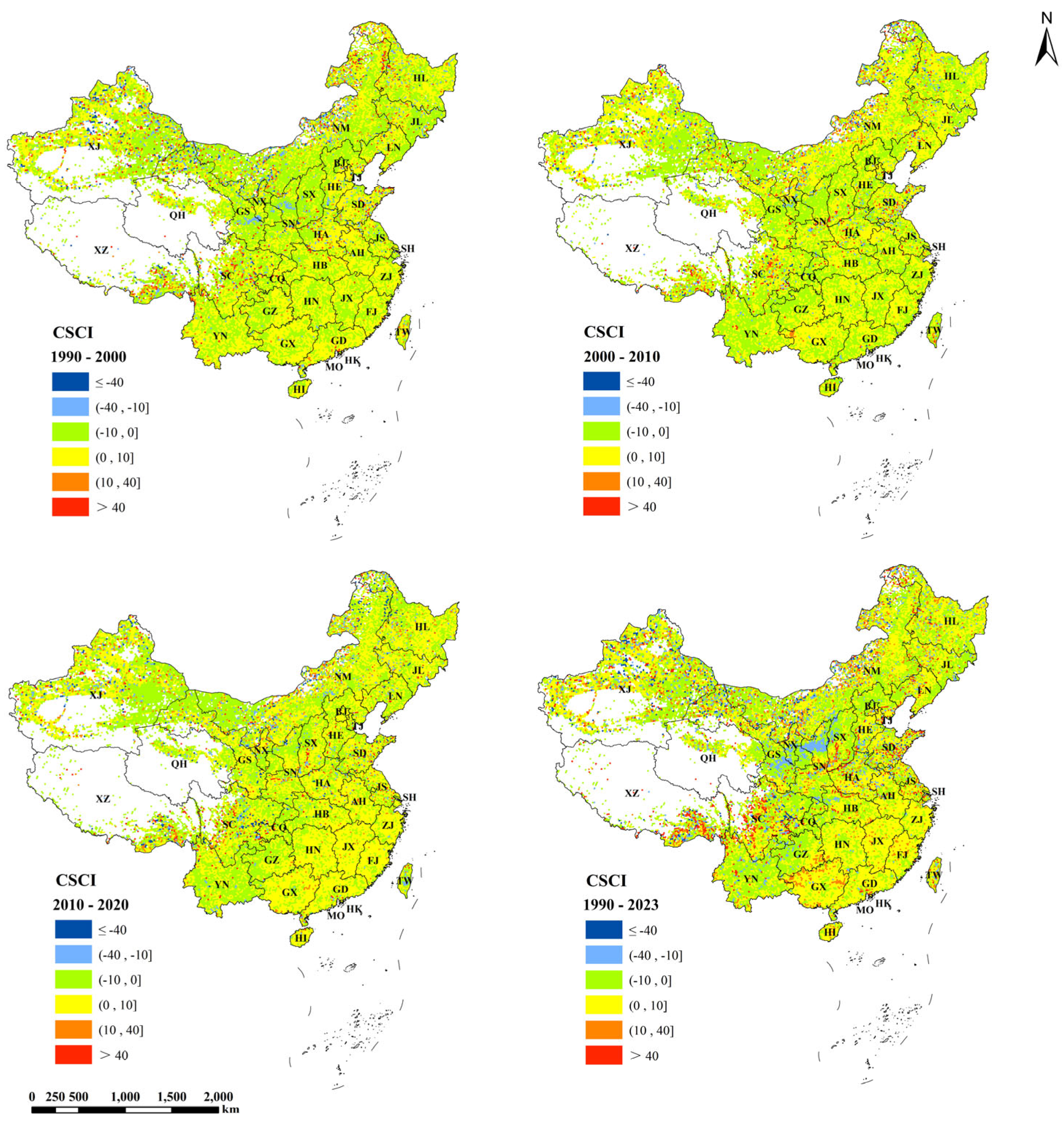
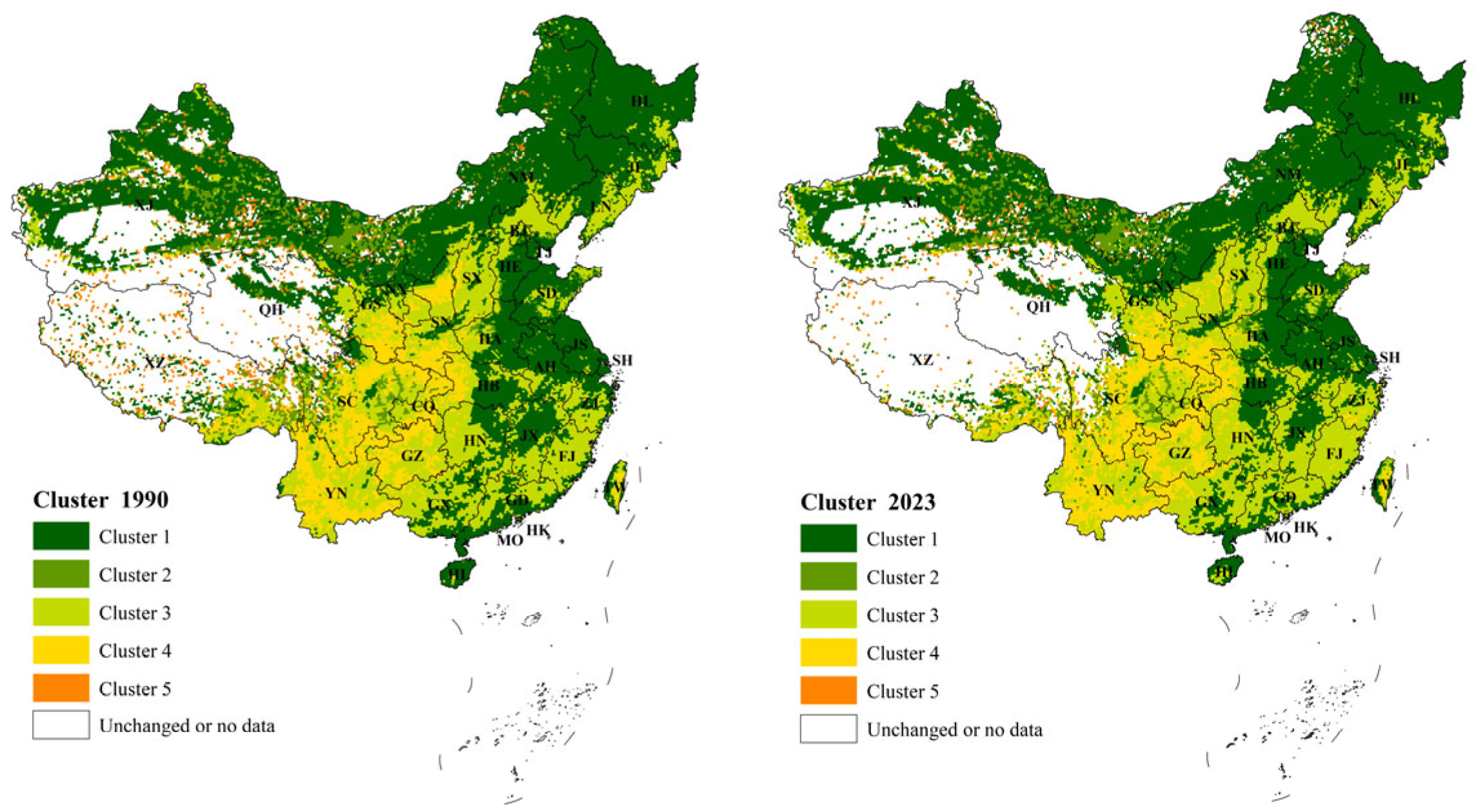
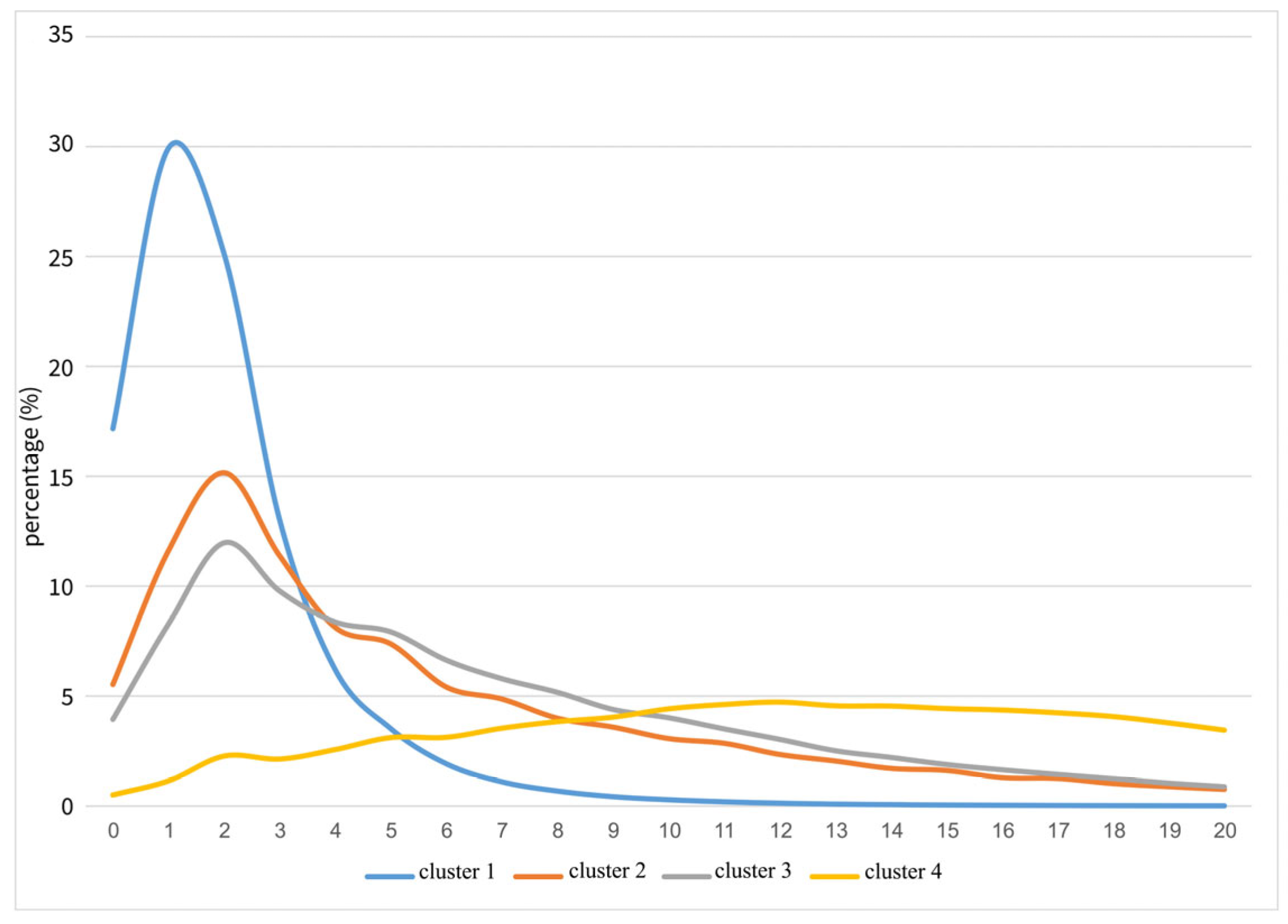
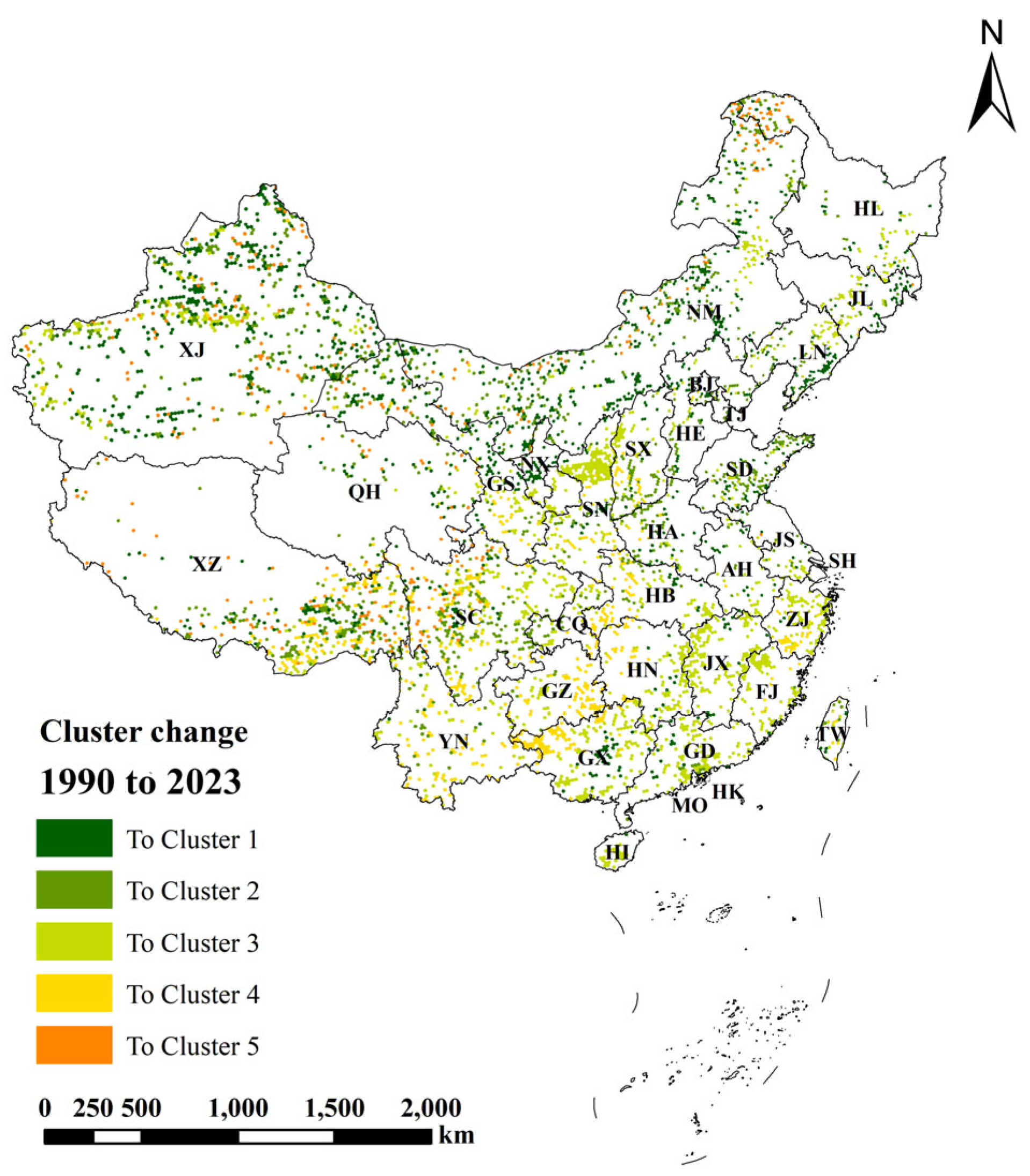
| Indicator | 1990 (R2) | 2023 (R2) | Change Index (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 Cropland Fragmentation Index | 0.5486 | —— | —— |
| 2023 Cropland Fragmentation Index | —— | 0.5650 | —— |
| 1990–2023 Change in Cropland Fragmentation Index | —— | —— | 0.3546 |
| 1990 Soil Erosion Amount | 0.5622 | —— | —— |
| 2023 Soil Erosion Amount | —— | 0.5882 | —— |
| 1990–2023 Change in Soil Erosion Amount | —— | —— | 0.5076 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, G.; Xia, Y.; Bao, L. The Evolution of Cropland Slope Structure and Its Implications for Fragmentation and Soil Erosion in China. Land 2025, 14, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051093
Liu G, Xia Y, Bao L. The Evolution of Cropland Slope Structure and Its Implications for Fragmentation and Soil Erosion in China. Land. 2025; 14(5):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051093
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Guangjie, Yi Xia, and Li Bao. 2025. "The Evolution of Cropland Slope Structure and Its Implications for Fragmentation and Soil Erosion in China" Land 14, no. 5: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051093
APA StyleLiu, G., Xia, Y., & Bao, L. (2025). The Evolution of Cropland Slope Structure and Its Implications for Fragmentation and Soil Erosion in China. Land, 14(5), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051093







