Coastal Vulnerability of Archaeological Sites of Southeastern Crete, Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
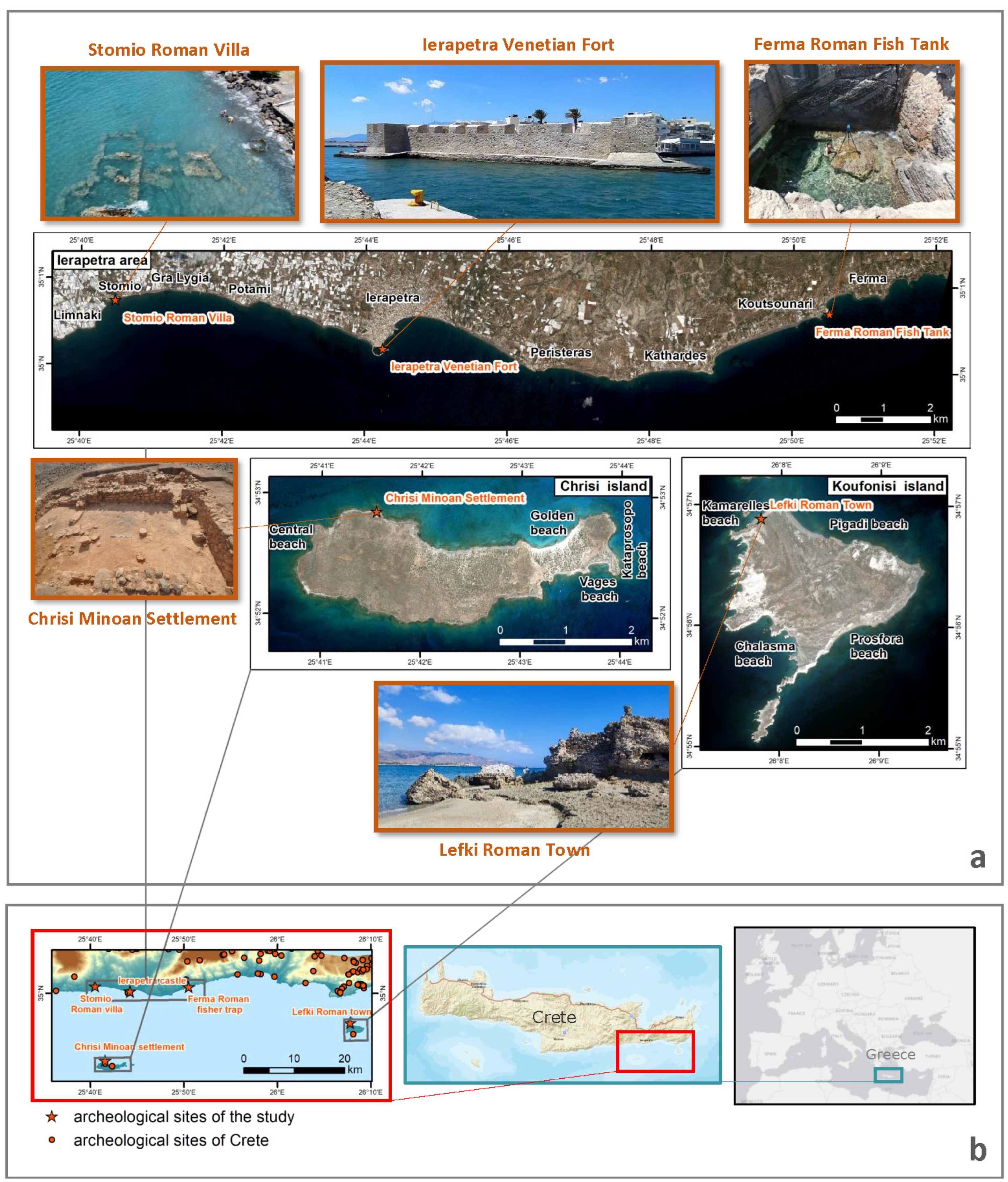
2. The Study Area
2.1. Geology and Tectonic Setting
2.2. Climate and Sea State
2.3. Archaeological Settings
2.4. Coastal Erosion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Analysis of Coastal Vulnerability Factors
3.1.1. Rates of Shoreline Movements
3.1.2. Height of the Cliff/Beach
3.1.3. Coastal Slope
3.1.4. Beach Width
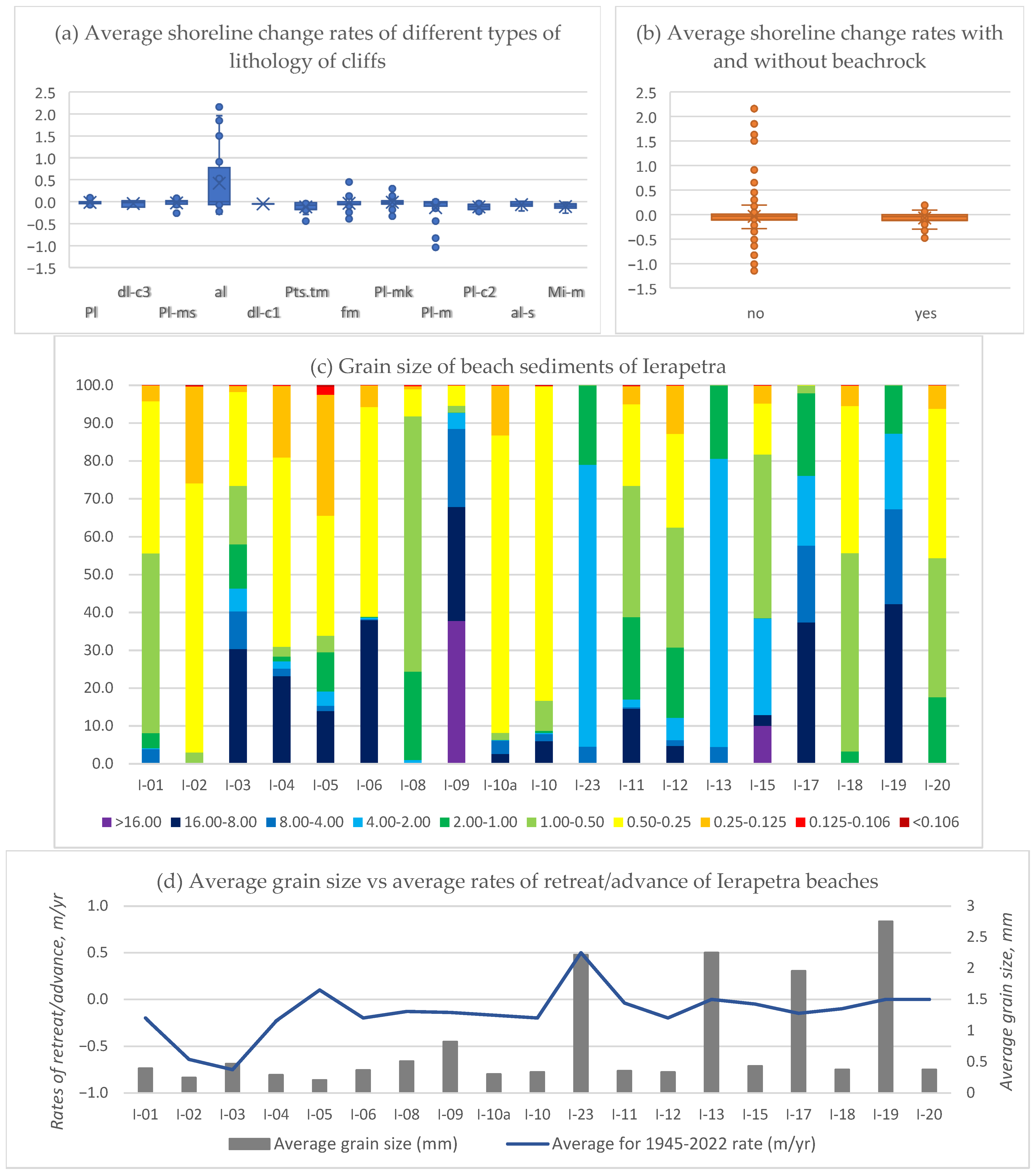
3.1.5. Lithology
3.1.6. Beachrocks
3.1.7. Ground Motions
3.1.8. Average Speed of Winds from Wave-Generating Directions
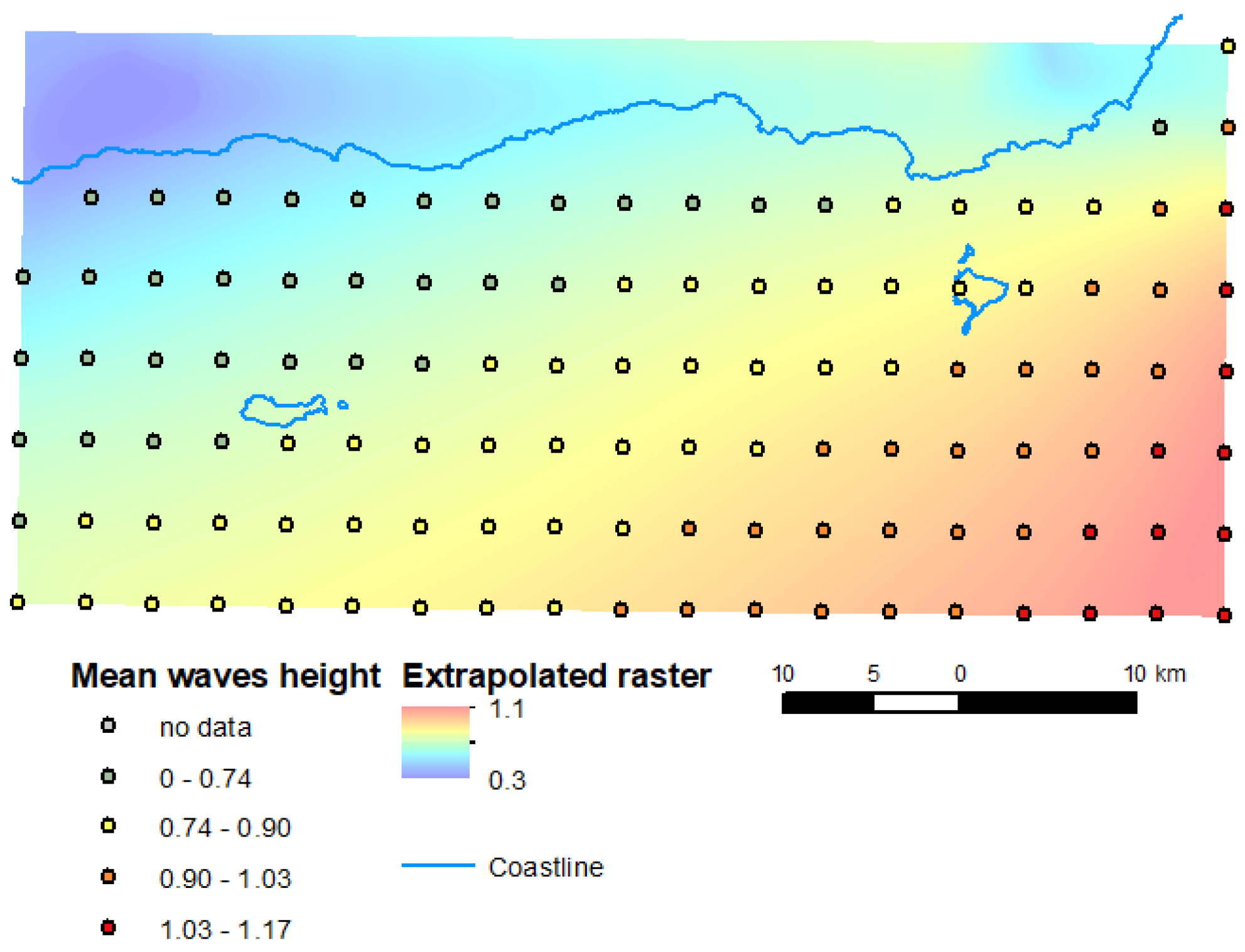
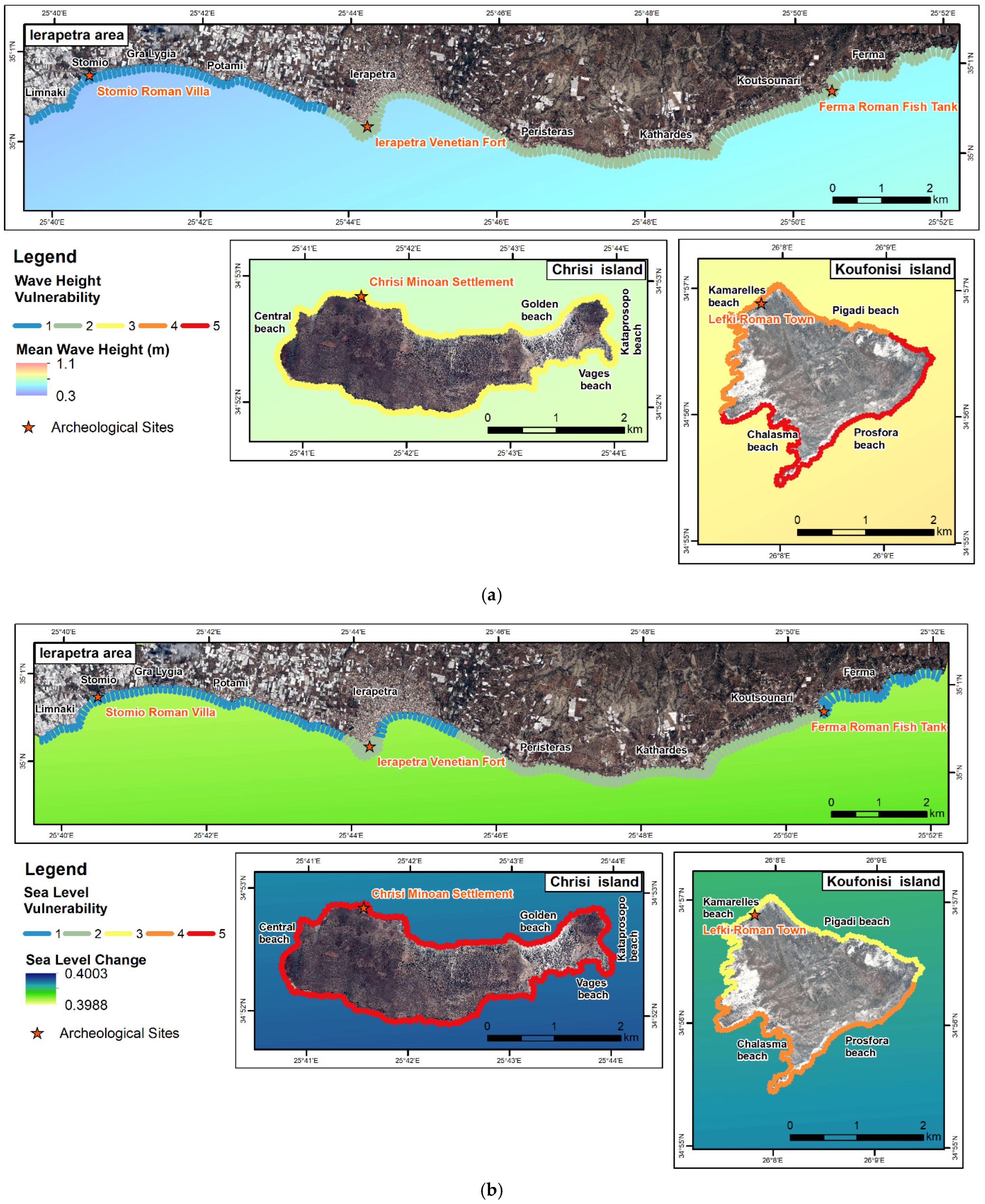
3.1.9. Average Significant Wave Heights
3.1.10. The Average Wind–Wave Effect
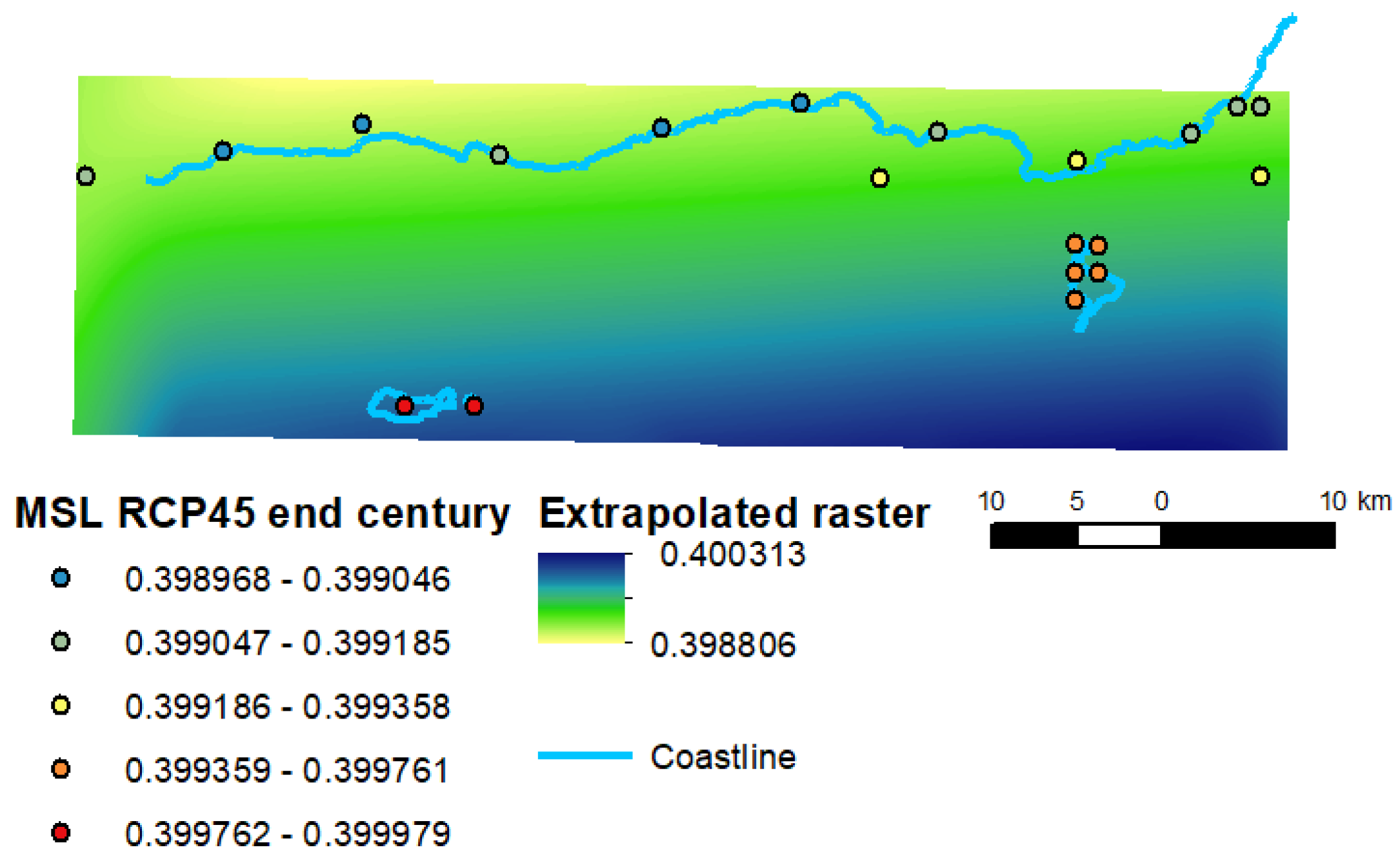
3.1.11. Sea-Level Change
3.2. Uncertainty Assessment
- spatial resolution of the imagery (δs);
- georeferencing to an absolute coordinate system (δa);
- relative georeferencing of two datasets (δr);
- topography-induced horizontal displacement (δt, δot);
- sea-level fluctuations (δf).
3.3. Statistical Analysis
3.4. CVI Calculation
3.5. Analytical Hierarchical Process
4. Results
4.1. Spatial Distribution of Coastal Variables
4.1.1. Shoreline Change
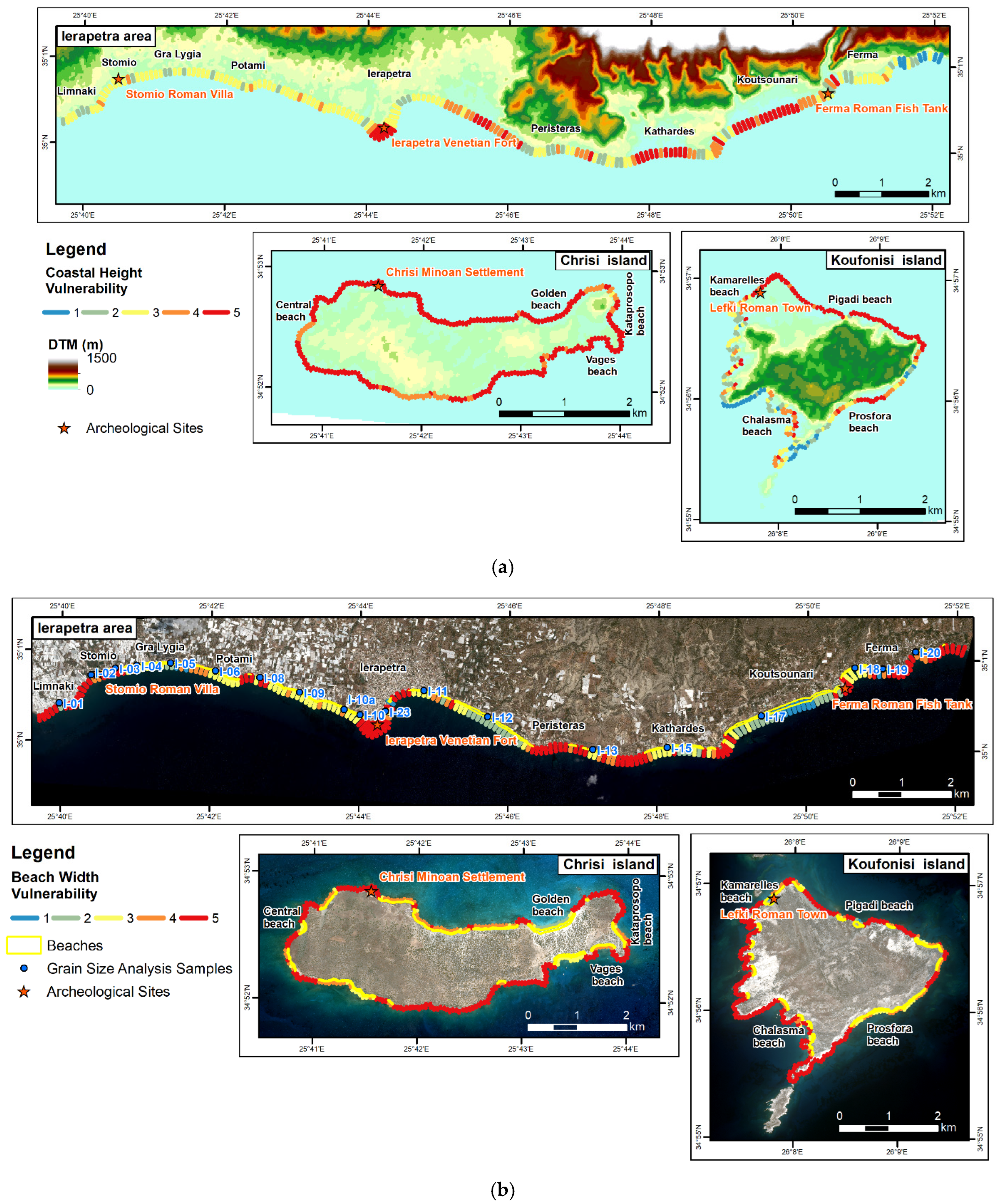
4.1.2. Coastal Height
4.1.3. Coastal Slope
4.1.4. Beach Width
4.1.5. Lithology
4.1.6. Beachrocks
4.1.7. Vertical Ground Motions
4.1.8. Wind Speed
4.1.9. Wave Heights
4.1.10. Wind–Wave Effect
4.1.11. Sea Level
4.2. Relations Between Different Variables and Rates of Shoreline Changes
4.3. Selection, Weighting, and Ranking Variables for CVI Calculation
5. Discussion
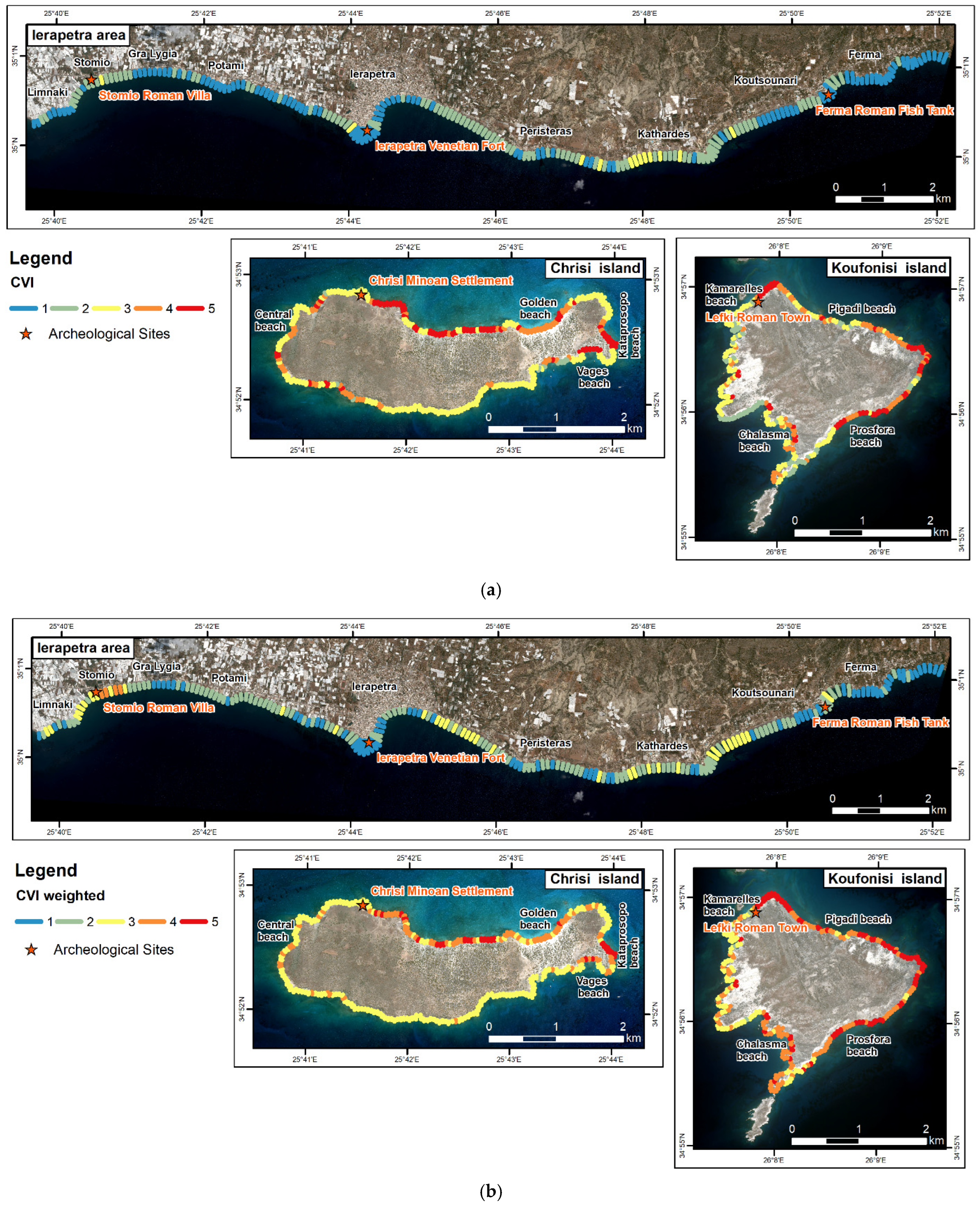
5.1. Coastal Vulnerability Index
5.1.1. CVI
5.1.2. CVI Weighted
5.2. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goumas, S.K.; Kontakos, S.; Mathheaki, A.G.; Xristoforidis, S. Modeling and forecasting of tourist arrivals in Crete using statistical models and models of computational intelligence: A comparative study. Int. J. Oper. Res. Inf. Syst. (IJORIS) 2021, 12, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, A.; Peraki, E.; Chatzoyiannaki, N.; Elvanidou, M.; Kappa, E.; Kakoulaki, G.; Karimali, E.; Katifori, M.; Kouriati, K.; Papadakis, G.; et al. Technology and Methodology for Archaeological Practice: Practical applications for the past reconstruction. In Proceedings of the XVth Congress of the UISPP, Time Drilling Through the Past of the Island of Crete, Colloqium C04, Lisbon, Portugal, 4–9 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, L.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Brown, S.; Hinkel, J.; Tol, R.S.J. Mediterranean UNESCO World Heritage at risk from coastal flooding and erosion due to sea-level rise. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, A.; Lombardo, S.; Doody, P. Living with Coastal Erosion in Europe: Sediment and Space for Sustainability. Part II: Maps and Statistics; Directorate General Environment, European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2004; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrakis, G.; Karditsa, A.; Poulos, S.E.; Ghionis, G.; Kampanis, N.A. Vulnerability assessment for the erosion of the coastal zone due to a potential sea level rise: The case of the Aegean Hellenic Coast. Environ. Syst. 2010, 3, 324. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrakis, G.; Ghionis, G.; Poulos, S.E.; Kampanis, N.A. Greece. In Coastal Erosion and Protection in Europe, 1st ed.; Pranzini, E., Williams, A., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; pp. 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monioudi, I.N.; Karditsa, A.; Chatzipavlis, A.; Alexandrakis, G.; Andreadis, O.P.; Velegrakis, A.F.; Poulos, S.; Ghionis, G.; Petrakis, S.; Sifnioti, D.; et al. Assessment of vulnerability of the eastern Cretan beaches (Greece) to sea level rise. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 16, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosendahl Appelquist, L.; Halsnæs, K. The Coastal Hazard Wheel system for coastal multi-hazard assessment and management in a changing climate. J. Coast. Conserv. 2015, 19, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prémaillon, M.; Regard, V.; Dewez, T.J.; Auda, Y. GlobR2C2 (Global Recession Rates of Coastal Cliffs): A global relational database to investigate coastal rocky cliff erosion rate variations. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2018, 6, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvo, L.M.; Murray, A.B.; Ashton, A. How does underlying geology affect coastline change? An initial modeling investigation. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2006, 111, F2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrakis, G.; Ghionis, G.; Poulos, S. The effect of beach rock formation on the morphological evolution of a beach. The case study of an Eastern Mediterranean beach: Ammoudara, Greece. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 69, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monioudi, I.N.; Velegrakis, A.F.; Chatzipavlis, A.E.; Rigos, A.; Karambas, T.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Hasiotis, T.; Koukourouvli, N.; Peduzzi, P.; Manoutsoglou, E.; et al. Assessment of island beach erosion due to sea level rise: The case of the Aegean archipelago (Eastern Mediterranean). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toimil, A.; Camus, P.; Losada, I.J.; Le Cozannet, G.; Nicholls, R.J.; Idier, D.; Maspataud, A. Climate change-driven coastal erosion modelling in temperate sandy beaches: Methods and uncertainty treatment. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 202, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzoraki, O.; Monioudi, I.N.; Velegrakis, A.F.; Moutafis, N.; Pavlogeorgatos, G.; Kitsiou, D. Resilience of touristic island beaches under sea level rise: A methodological framework. Coast. Manag. 2018, 46, 78–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depountis, N.; Apostolopoulos, D.; Boumpoulis, V.; Christodoulou, D.; Dimas, A.; Fakiris, E.; Leftheriotis, G.; Menegatos, A.; Nikolakopoulos, K.; Papatheodorou, G.; et al. Coastal erosion identification and monitoring in the Patras Gulf (Greece) using multi-discipline approaches. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornitz, V. Global coastal hazards from future sea level rise. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1991, 89, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yin, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.Y. National assessment of coastal vulnerability to sea-level rise for the Chinese coast. J. Coast. Conserv. 2012, 16, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdanavičiūtė, I.; Kelpšaitė, L.; Soomere, T. Multi-criteria evaluation approach to Coastal Vulnerability Index development in micro-tidal low-lying areas. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2015, 104, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder-Myers, L.A. Cultural Heritage at Risk in the Twenty-First Century: A Vulnerability Assessment of Coastal Archaeological Sites in the United States. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2015, 10, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.M.; Maulud, K.N.A. Coastal Vulnerability: A Brief Review on Integrated Assessment in Southeast Asia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrakis, G.; Poulos, S. An holistic approach to beach erosion vulnerability assessment. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Serio, F.; Armenio, E.; Mossa, M.; Petrillo, A.F. How to define priorities in coastal vulnerability assessment. Geosciences 2018, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekovski, I.; Del Río, L.; Armaroli, C. Development of a Coastal Vulnerability Index using analytical hierarchy process and application to Ravenna province (Italy). Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2020, 183, 104982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadis, O.; Chatzipavlis, A.; Hasiotis, T.; Monioudi, I.; Manoutsoglou, E.; Velegrakis, A. Assessment of and adaptation to beach erosion in islands: An integrated approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandarakis, D.; Panagiotopoulos, I.P.; Loukaidi, V.; Hatiris, G.A.; Drakopoulou, P.; Kikaki, A.; Gad, F.K.; Petrakis, S.; Malliouri, D.I.; Chatzinaki, M.; et al. Assessment of the coastal vulnerability to the ongoing sea level rise for the exquisite Rhodes Island (SE Aegean Sea, Greece). Water 2021, 13, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippaki, E.; Tsakalos, E.; Kazantzaki, M.; Bassiakos, Y. Forecasting impacts on vulnerable shorelines, Vulnerability assessment along the coastal zone of Messolonghi area-Western Greece. Climate 2023, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duriyapong, F.; Nakhapakorn, K. Coastal vulnerability assessment: A case study of Samut Sakhon coastal zone. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 33, 469–476. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:54792678 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Boumboulis, V.; Apostolopoulos, D.; Depountis, N.; Nikolakopoulos, K. The importance of geotechnical evaluation and shoreline evolution in Coastal Vulnerability Index calculations. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, M.; del Rio, L.; Plomaritis, T.A.; Benavente, J. Influence of storms on coastal retreat in SW Spain. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 70, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmalavičius, D.; Šmatas, V.; Stankūnavičius, G.; Pupienis, D.; Žilinskas, G. Factors controlling coastal erosion during storm events. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 75, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoni, S.G.; Stavrou, A.; Lawrence, J.A.; Preene, M.; Lawrence, U.L.; Buckley, R. Erosion of the chalk coastal cliffs at Birling Gap, Sussex, UK. Correlation between rate of coastal retreat, geotechnical rocks properties and precipitation. In Proceedings of the Engineering in Chalk 2018 Conference, London, UK, 17–18 September 2018; pp. 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daire, M.Y.; Lopez-Romero, E.; Proust, J.N.; Regnauld, H.; Pian, S.; Shi, B. Coastal Changes and Cultural Heritage (1): Assessment of the Vulnerability of the Coastal Heritage in Western France. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2012, 7, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luccio, D.; Benassai, G.; Di Paola, G.; Rosskopf, C.M.; Mucerino, L.; Montella, R.; Contestabile, P. Monitoring and Modelling Coastal Vulnerability and Mitigation Proposal for an Archaeological Site (Kaulonia, Southern Italy). Sustainability 2018, 10, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, G.; Rizzo, A.; Anfuso, G.; Aucelli, P.P.C.; Gracia, F.J. A tool for evaluating the archaeological heritage vulnerability to coastal processes: The case study of Naples Gulf (southern Italy). Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 179, 104876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO World Heritage: Vulnerability of UNESCO World Heritage Sites to Projected Sea Level Rise in the Mediterranean Sea 2023. Available online: https://stories.ecmwf.int/risks-to-world-heritage-sites-across-the-mediterranean-from-rising-sea-levels-under-climate-change/index.html (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Climate Change 2007: Working Group II: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Available online: https://archive.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/ar4/wg2/en/frontmattersg.html (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Kissel, C.; Laj, C. The Tertiary geodynamical evolution of the Aegean arc: A paleomagnetic reconstruction. Tectonophysics 1988, 146, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Avraham, Z.; Woodside, J.; Lodolo, E.; Gardosh, M.; Grasso, M.; Camerlenghi, A.; Vai, G.B. Eastern Mediterranean basin systems. Geol. Soc. Lond. Mem. 2006, 32, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, J. Geophysical Investigations of the Hellenides; Hamburger Geophys Einzelschriften 34; Wittenborn Söhne: Hamburg, Germany, 1977; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Le Pichon, X.; Angelier, J. The Hellenic arc and trench system: A key to the neotectonic evolution of the eastern Mediterranean area. Tectonophysics 1979, 60, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzoli, P.; Thommeret, J.; Thommeret, Y.; Laborel, J.; Montag-Gioni, L. Crustal block movements from Holocene shorelines: Crete and Antikythira (Greece). Tectonophysics 1982, 86, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, M.; Hetzel, R.; Fassoulas, C.; Kubik, P.W. A long-term rock uplift rate for eastern Crete and geodynamic implications for the Hellenic subduction zone. J. Geodyn. 2014, 78, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.G.; White, N.J.; Shaw, B. An uplift history of Crete, Greece, from inverse modeling of longitudinal river profiles. Geomorphology 2013, 198, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzas, N.; Kolaiti, E.; Anzidei, M. Vertical land movements and sea level changes along the coast of Crete (Greece) since Late Holocene. Quat. Int. 2015, 401, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Veen, J.H.; Postma, G. Neogene tectonics and basin fill patterns in the Hellenic outer-arc (Crete, Greece). Basin Res. 1999, 11, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Lekkas, E.; Katsetsiadou, K.-N.; Rovythakis, E.; Yahav, A. Tsunami Alert Efficiency in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea: The 2 May 2020 Earthquake (Mw6.6) and Near-Field Tsunami South of Crete (Greece). GeoHazards 2020, 1, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, P.; Howell, A.; Jackson, J.; Synolakis, C. Palaeotsunamisand tsunami hazards in the eastern Mediterranean. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 373, 20140374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, I.; Agalos, A.; Samaras, A.G.; Karambas, T.V.; Papadopoulos, G.A. Strong earthquakes and tsunami potentialin the Hellenic subduction zone. J. Geodyn. 2024, 159, 102021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackham, O.; Moody, J. The Making of the Cretan Landscape; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hellenic National Meteorological Service. Available online: http://newportal.hnms.gr/emy/en/climatology/climatology_city?perifereia=Crete&poli=Ierapetra (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; et al. ERA5 Hourly Data on Pressure Levels from 1940 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). 2023. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-era5-pressure-levels?tab=overview (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Shaw, A.G.P. Seasonal sea level extremes in the Mediterranean Sea and at the Atlantic European coasts. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 1457–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkopoulou, T. The Evolution of the Coastal and Maritime Cultural Landscape of South Central and Southeast Crete (Late Final Neolithic to Roman Period). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sassari, Sassari, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, N. ClepsYdra: Translating submerged archaeological remains from shallow water to digital environment with geoinformatics. In Advances in on- and Offshore Archaeological Prospection, Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Archaeological Prospection (ICAP), Kiel, Germany, 28 March–1 April 2023; Kiel University Publishing: Kiel, Germany, 2023; pp. 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofianou, C.; Gallimore, S. Recent Excavations at the Small Theater in Ancient Hierapytna. KENTRO Newsl. INSTAP Study Cent. East Crete 2019, 22, 13–15. Available online: https://instapstudycenter.net/2019/09/01/kentro-volume-22-fall-2019/ (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Coutsinas, N.; Katifori, M.; Roussos, K.; Argyriou, A. The settlement patterns of the Ierapetra isthmus (East Crete) from the Archaic to the Venetian periods, as revealed through the Settle In Eastern Crete Program. J. Greek Archaeol. 2022, 7, 369–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, Ν.P. Ierapetra. In The Nymph of the Libyan Sea. A Guide to Its History, Archaeology, and Culture; [Ιεράπετρα. H νύμφη του Λιβυκού. Oδηγός για την ιστορία, αρχαιολογία και τον πολιτισμό της]; Publication of the Municipality of Ierapetra: Crete, Greece, 1982. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Davaras, C. Carved Fish Tank at Ferma, Ierapetra. [Λαξευτή ιχθυοδεξαμενή στα Φέρμα Ιεράπετρας]; Annual of the Archaiologicon Deltion; Chronika: Sofia, Bulgaria, 1978; Volume B2, pp. 149–154. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Chronaki, D. The Lasithi Prefecture during the Byzantine period. The Lasithi Prefecture and Its History [O νομός Λασιθίου κατά τη Βυζαντινή περίοδο. O νομός Λασιθίου και η ιστορία του]. Aghios Nikolaos Soc. Lett. Arts East. Crete 2016, 1, 285–333. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Theodoulou, T.; Tourtas, A.; Tsimpoukis, G. Underwater Archaeological Survey in the Ierapetra Region. In ClepsYdra. Translating Submerged and Buried Cultural Heritage from Shallow Water to Digital Environment with Geoinformatics; Papadopoulos, N., Ed.; Institute for Mediterranean Studies—Foundation of Research and Technology (IMS-FORTH): Rethymno, Greece, 2024; Available online: https://clepsydra.ims.forth.gr/uploads/book/ClepsYdra_Booklet_2024.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Coutsinas, N.; Guy, M.; Kelly, A. Kouphonisi (Greece): A briefly vibrant Roman harbourage between Crete and Africa. In Géoarchéologie des îles de Méditerranée; Ghilardi, M., Ed.; CNRS: Paris, France, 2016; pp. 333–344. [Google Scholar]
- Papadakis, Ν. Koufonisi: The “Delos” of the Libyan Sea [Κουφονήσι: η “Δήλος” του Λιβυκού]. Archaeol. Arts [Aρχαιολογία και Τέχνες] 1983, 6, 58–65. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Chalikias, K. Living on the Margin: Chryssi Island and the Settlement Patterns of the Ierapetra Area; BAR International Series 2549; British Archaeological Reports Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Donchyts, G.; Baart, F.; Winsemius, H.; Gorelick, N.; Kwadijk, J.; van de Giesen, N. Earth’s surface water change over the past 30 years. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L.; Vargas, L.G. Prediction, Projection, and Forecasting: Applications of the Analytic Hierarchy Process in Economics, Finance, Politics, Games, and Sport; Springer Science+Business Media BV: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, R.; Macwan, J.E.M.; Bhatt, D.; Patel, V. Analytic hierarchy process approach for criteria ranking of sustainable building assessment: A case study. World Appl. Sci. J. 2010, 8, 881–888. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:16009856 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Phukon, P.; Chetia, D.; Das, P. Landslide susceptibility assessment in the Guwahati city, Assam using analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and geographic information system (GIS). Int. J. Comput. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2012, 2, 1–6. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:15967952 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Argyriou, A.V.; Teeuw, R.M.; Rust, D.; Sarris, A. GIS multi-criteria decision analysis for assessment and mapping of neotectonic landscape deformation: A case study from Crete. Geomorphology 2016, 253, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cozannet, G.L.; Garcin, M.; Bulteau, T.; Mirgon, C.; Yates, M.L.; Méndez, M.; Baills, A.; Idier, D.; Oliveros, C. An AHP-derived method for mapping the physical vulnerability of coastal areas at regional scales. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1209–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop-Taylor, R.; Sagar, S.; Lymburner, L.; Alam, I.; Sixsmith, J. Sub-pixel waterline extraction: Characterising accuracy and sensitivity to indices and spectra. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaras, E.; Falchi, U.; Parente, C.; Vallario, A. Accuracy evaluation for coastline extraction from Pléiades imagery based on NDWI and IHS pan-sharpening application. Appl. Geomat. 2022, 15, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelstoss, E.A.; Henderson, R.E.; Kratzmann, M.G.; Farris, A.S. Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) Version 5.1. гser Guide; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report No 2021–1091; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2021; 104p. [CrossRef]
- Geospatial Data INSPIRE Geoportal of the “Hellenic Cadastre”. Available online: https://www.ktimanet.gr/geoportal/catalog/main/home.page;jsessionid=8C59F8A2883C690CBDB247920E300741 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- European Marine Observation and Data Network (EMODnet). Available online: https://emodnet.ec.europa.eu/en (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Lassak, D.; Novikova, A.; Argyriou, A.; Papadopoulos, N. Satellite-Derived Bathymetry for the Islands of South-Eastern Crete. In Proceedings of the IMEKO TC4 International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage, Rome, Italy, 19–21 October 2023; Available online: https://www.imeko.org/index.php/proceedings/9348-satellite-derived-bathymetry-for-the-islands-of-south-eastern-crete (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Sunamura, T. Geomorphology of Rocky Coasts; J. Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992; 302p. [Google Scholar]
- Boye, C.B.; Fiadonu, E.B. Lithological effects on rocky coastline stability. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, G.I. Grain Size Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Geoarchaeology. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Gilbert, A.S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, C.K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousdoukas, M.I.; Velegrakis, A.F.; Plomaritis, T.A. Beachrock occurrence, characteristics, formation mechanisms and impacts. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2007, 85, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.G. Beachrock. In Geomorphology. Encyclopedia of Earth Science; Charles, W., Finkl, C.V., Fairbridge, R.W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Ground Motion Service. Available online: https://egms.land.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- ERA5: How to Calculate Wind Speed and Wind Direction from u and v Components of the Wind? Available online: https://confluence.ecmwf.int/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=133262398 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Mediterranean Sea Waves Reanalysis. Available online: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/MEDSEA_MULTIYEAR_WAV_006_012/description (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Popov, B.A.; Sovershaev, V. A Some features of the coastal dynamics in the Asian Arctic. Probl. Geogr. (Вoпрoсы Геoграфии) 1982, 119, 105–116. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shabanova, N.; Ogorodov, S.; Shabanov, P.; Baranskaya, A. Hydrometeorological forcing of western Russian Arctic coastal dynamics: XX-century history and current state. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 11, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V.; Bezes, A.; Koletsis, I.; Kopania, T.; Lykoudis, S.; Mazarakis, N.; Papagiannaki, K.; Vougioukas, S. The automatic weather stations NOANN network of the National Observatory of Athens: Operation and database. Geosci. Data J. 2017, 4, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Muis, S.; Irazoqui, M.; Verlaan, M. Water Level Change Time Series for the European Coast from 1977 to 2100 Derived from Climate Projections. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/sis-water-level-change-timeseries?tab=overview (accessed on 27 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Sea Level Station Monitoring Facility. Available online: https://www.ioc-sealevelmonitoring.org/station.php?code=iera (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Toutin, T. Geometric processing of remote sensing images: Models, algorithms and methods. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1893–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, F.; Overduin, P.; Sandakov, A.V.; Grosse, G.; Grigoriev, M.N. Short- and long-term thermo-erosion of ice-rich permafrost coasts in the Laptev Sea region. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4297–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, A.; Belova, N.; Baranskaya, A.; Aleksyutina, D.; Maslakov, A.; Zelenin, E.; Shabanova, N.; Ogorodov, S. Dynamics of permafrost coasts of Baydaratskaya Bay (Kara Sea) based on multi-temporal remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramieri, E.; Hartley, A.; Barbanti, A.; Santos, F.D.; Gomes, A.; Hilden, M.; Laihonen, P.; Marinova, N.; Santini, M. Methods for Assessing Coastal Vulnerability to Climate Change. ETC CCA Tech. Pap. 2011, 1, 1–93. Available online: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-cca/products/etc-cca-reports/1 (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Apostolakou, V.; Brogan, T.; Betancourt, P. Bramiana: Salvaging Information from a Destroyed Minoan Settlement in Southeast Crete. 2021, pp. 1–210. Available online: https://www.torrossa.com/it/resources/an/5084270 (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Maanan, M.; Maanan, M.; Rueff, H.; Adouk, N.; Zourarah, B.; Rhinane, H. Assess the human and environmental vulnerability for coastal hazard by using a multi-criteria decision analysis. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 1642–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karymbalis, E.; Chalkias, C.; Chalkias, G.; Grigoropoulou, E.; Manthos, G.; Ferentinou, M. Assessment of the sensitivity of the southern coast of the Gulf of Corinth (Peloponnese, Greece) to sea-level rise. Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 2012, 4, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ružić, I.; Dugonjić Jovančević, S.; Benac, Č.; Krvavica, N. Assessment of the Coastal Vulnerability Index in an Area of Complex Geological Conditions on the Krk Island, Northeast Adriatic Sea. Geosciences 2019, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleri, L.; Abdalla, S.; Benetazzo, A.; Bertotti, L.; Bidlot, J.R.; Breivik, Ø.; Carniel, S.; Jensen, R.E.; Portilla-Yandun, J.; Rogers, W.E.; et al. Wave modelling in coastal and inner seas. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 167, 164–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of the ERA5 significant wave height against NDBC buoy data from 1979 to 2019. Mar. Geod. 2022, 45, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, G.; Franco, L.; Cecioni, C. Regional Downscaling of Copernicus ERA5 Wave Data for Coastal Engineering Activities and Operational Coastal Services. Water 2021, 13, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roome, E.; Christie, D.; Neill, S. Predicting coastal wave conditions: A simple machine learning approach. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2024, 153, 104282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Area | Image | Date | Spatial Resolution, m | RMSE of Referencing, m | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ierapetra | Aerial | 15 July 1945 | 0.7 | 3.0 | Hellenic Military Geographical Service |
| Aerial (partial coverage) | 15 July 1966 | 0.2 | 3.0 | Hellenic Military Geographical Service | |
| Aerial | 12 September 1989 | 0.6 | 1.7 | Hellenic Military Geographical Service | |
| Aerial (partial coverage) | 15 July 2005 | 0.6 | 0.8 | Hellenic Military Geographical Service | |
| Pleiades | 16 June 2022 | 0.5 | 2.8 | Space Agency of France-CNES | |
| Koufonisi | Aerial | 6 August 1992 | 0.2 | 2.1 | Hellenic Military Geographical Service |
| Pleiades | 26 April 2022 | 0.5 | 1.5 | Space Agency of France-CNES | |
| Chrisi | Aerial (partial coverage) | 15 July 1967 | 0.3 | 0.5 | Hellenic Military Geographical Service |
| Aerial | 6 August 1992 | 0.2 | 1.5 | Hellenic Military Geographical Service | |
| Pleiades | 16 June 2022 | 0.5 | - | Space Agency of France-CNES |
| Area | Ierapetra | Koufonisi | Chrisi | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2022 | 2005 | 1989 | 1966 | 1945 | 2022 | 1992 | 2022 | 1992 | 1967 |
| Spatial resolution of the dataset, m (δs) | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Absolute georeferencing, m (δa) | 2.8 | 1.5 | - | |||||||
| Relative georeferencing of two datasets, m (δr) | 0.8 | 1.7 | 3 | 3 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | |||
| Maximum relative height of the area, m (h) | 40 | 45 | 9 | |||||||
| Tilt angle of the spacecraft, ° (α) | 22 | 22 | 22 | |||||||
| Uncertainty of topography-induced horizontal displacement, m (δt) | 16.16 | 18.18 | 3.64 | |||||||
| Accuracy of DEM used for orthorectification, m (z) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Topography-induced horizontal displacement after orthorectification, m (δot) | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | |||||||
| Coastal slope, % (CS) | 8.36 | 43 | 11.85 | |||||||
| Uncertainty of sea-level fluctuations, m (δf) | 2.4 | 0.4 | 1.6 | |||||||
| Uncertainty of shoreline position, m (δx) | 3.73 | 2.60 | 3.00 | 3.85 | 3.91 | 1.68 | 2.15 | 1.72 | 2.24 | 1.75 |
| Uncertainty of rate, m/yr (δr) | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.11 | |||
| Uncertainty of rate for the period between most resent and the oldest years (SH), m/yr (δr) | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |||||||
| Parameter | All Coast | Beaches | Cliffs | Ierapetra | Koufonisi | Chrisi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.0201 | 0.2790 | 0.0902 | 0.1337 | 0.2143 | 0.0882 | ||||||
| Significance F | 0.0146 | 0.00002 | 0.0000001 | 0.00003 | 0.000000000002 | 0.000194 | ||||||
| CH (Coef|p-value) | −0.002 | 0.301 | 0.011 | 0.000 | −0.006 | 0.002 | −0.012 | 0.018 | 0.005 | 0.000 | −0.006 | 0.451 |
| CS (Coef|p-value) | 0.001 | 0.099 | −0.001 | 0.685 | 0.001 | 0.014 | −0.007 | 0.201 | 0.000 | 0.856 | 0.002 | 0.191 |
| BW (Coef|p-value) | 0.001 | 0.073 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.790 | −0.002 | 0.197 | 0.004 | 0.000 | −0.001 | 0.142 |
| WS (Coef|p-value) | −0.043 | 0.050 | −0.004 | 0.828 | −0.078 | 0.000 | −2.422 | 0.000 | −0.016 | 0.332 | 0.001 | 0.917 |
| WH (Coef|p-value) | 0.325 | 0.005 | 0.271 | 0.181 | 0.325 | 0.155 | 20.439 | 0.000 | 0.137 | 0.940 | −4.023 | 0.001 |
| SL (Coef|p-value) | −110.417 | 0.037 | 133.994 | 0.028 | −308.271 | 0.000 | −7313.005 | 0.001 | 573.538 | 0.273 | 1298.300 | 0.000 |
| GM (Coef|p-value) | −0.145 | 0.150 | ||||||||||
| WWE (Coef|p-value) | 0.000 | 0.775 | ||||||||||
| Variables | Shoreline Retreat | Wave Height | Coastal Height | Beach Width | Lithology | Sea Level | Criteria Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoreline retreat | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 0.360 |
| Wave height | 1/2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 0.276 |
| Coastal height | 1/3 | 1/2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 0.167 |
| Beach width | 1/4 | 1/3 | 1/2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0.110 |
| Lithology | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/4 | 1/3 | 1 | 2 | 0.052 |
| Sea level | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/5 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1 | 0.035 |
| Column Total | 2.45 | 4.20 | 6.95 | 10.58 | 18.50 | 24.00 |
| Variables | CVI Ranks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very Low (1) | Low (2) | Moderate (3) | High (4) | Very High (5) | |
| Shoreline changes rates (SH) | >0.9 m/yr | 0.2–0.9 m/yr | −0.1–0.2 m/yr | −0.4–−0.1 m/yr | <−0.4 m/yr |
| Coastal height (CH) | >24 m | 15–24 m | 9–15 m | 4–9 m | <4 m |
| Beach width (BW) | >56 m | 32–56 m | 16–32 m | 0–16 m | 0 m |
| Lithology (L) | Cliffs of: Torrential deposits (dl-c3), Marine marls, clays, sands (Pl), Flysch mélange (fm); Technogenic concrete constructions | Cliffs of: Sandy marls (Pl-ms) White or grey marl (Mi-m) Marls-marly limestones (Pl-mk) Littoral deposits with sand (al-s) Conglomerate in the above marl, pebbles (Pl-c2) | Cliffs of: Alluvial loose sands and clays (al), Marine conglomerates (dl-c1), Marine conglomerates with marls (Plts.tm), Sandy marls (Pl-ms) White marls of Koufonissi (Pl-m) | Beaches mainly of gravel/pebbles | Beaches mainly of sands |
| Waves height (WH) | <0.50 m | 0.50–0.58 m | 0.58–0.74 m | 0.74–0.85 m | >0.85 m |
| Sea-level changes (SL) | <0.39907 m | 0.39907–0.39914 m | 0.39914–0.39970 m | 0.39970–0.39980 m | >0.39980 m |
| Vulnerability Rank | CVI | CVIw | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value Range | % of All Coasts | Value Range | % of All Coasts | |
| Very Low (1) | 1.7–7.3 | 13.7 | 1.6–2.6 | 3.4 |
| Low (2) | 7.3–11.5 | 19.8 | 2.6–3.0 | 11.3 |
| Moderate (3) | 11.5–17.9 | 37.2 | 3.0–3.4 | 28.1 |
| High (4) | 17.9–25.3 | 15.5 | 3.4–3.8 | 39.6 |
| Very High (5) | 25.3–39.5 | 13.7 | 3.8–4.7 | 17.5 |
| Archaeological Site | CVI | CVIw |
|---|---|---|
| Stomio Roman Villa | Low | High |
| Ierapetra Venetian Fort | Very Low | Very Low |
| Ferma Roman Fish Tank | Very Low | Low |
| Lefki Roman Town | Moderate—High—Very High | High—Very High |
| Chrisi Minoan Settlement | Moderate | Moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Novikova, A.V.; Argyriou, A.V.; Andriopoulou, N.C.; Alexandrakis, G.; Papadopoulos, N. Coastal Vulnerability of Archaeological Sites of Southeastern Crete, Greece. Land 2025, 14, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040892
Novikova AV, Argyriou AV, Andriopoulou NC, Alexandrakis G, Papadopoulos N. Coastal Vulnerability of Archaeological Sites of Southeastern Crete, Greece. Land. 2025; 14(4):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040892
Chicago/Turabian StyleNovikova, Anna V., Athanasios V. Argyriou, Nafsika C. Andriopoulou, George Alexandrakis, and Nikos Papadopoulos. 2025. "Coastal Vulnerability of Archaeological Sites of Southeastern Crete, Greece" Land 14, no. 4: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040892
APA StyleNovikova, A. V., Argyriou, A. V., Andriopoulou, N. C., Alexandrakis, G., & Papadopoulos, N. (2025). Coastal Vulnerability of Archaeological Sites of Southeastern Crete, Greece. Land, 14(4), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040892








