Monitoring of Soil Salinization and Analysis of Driving Factors in the Oasis Zone of South Xinjiang
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
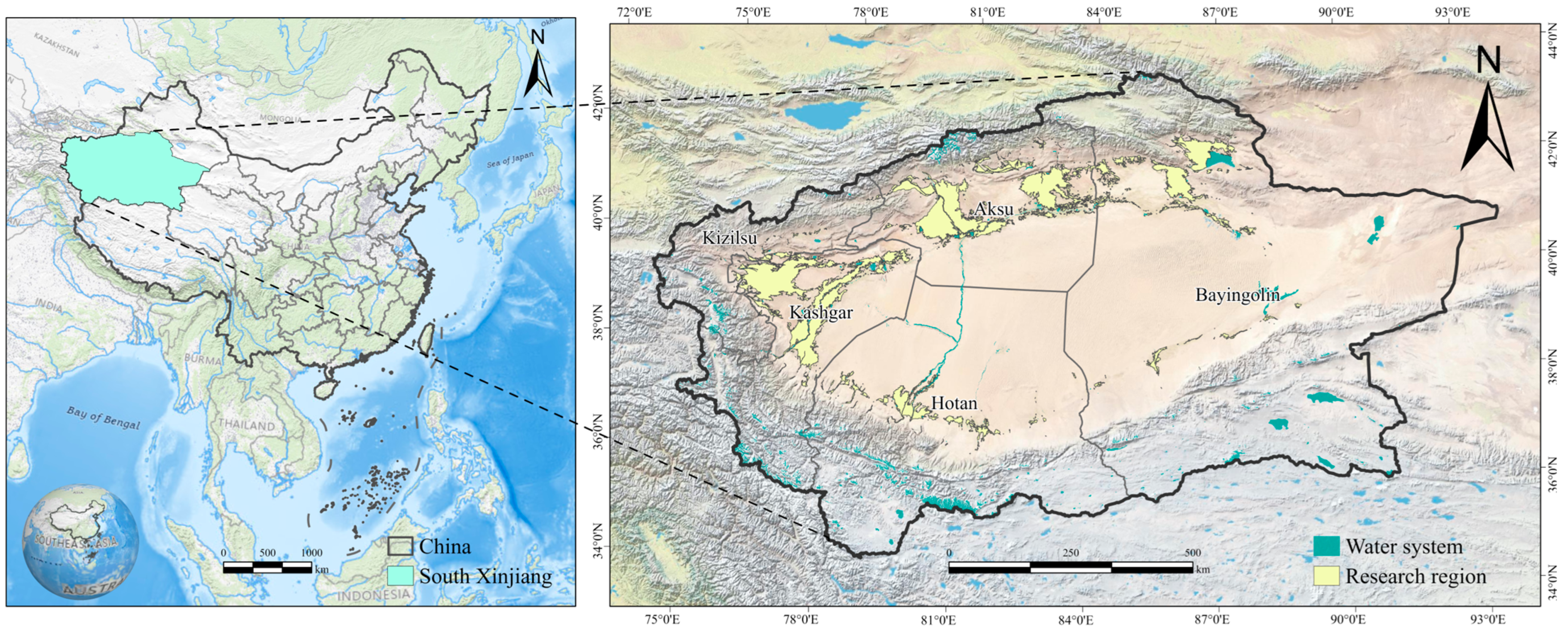
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
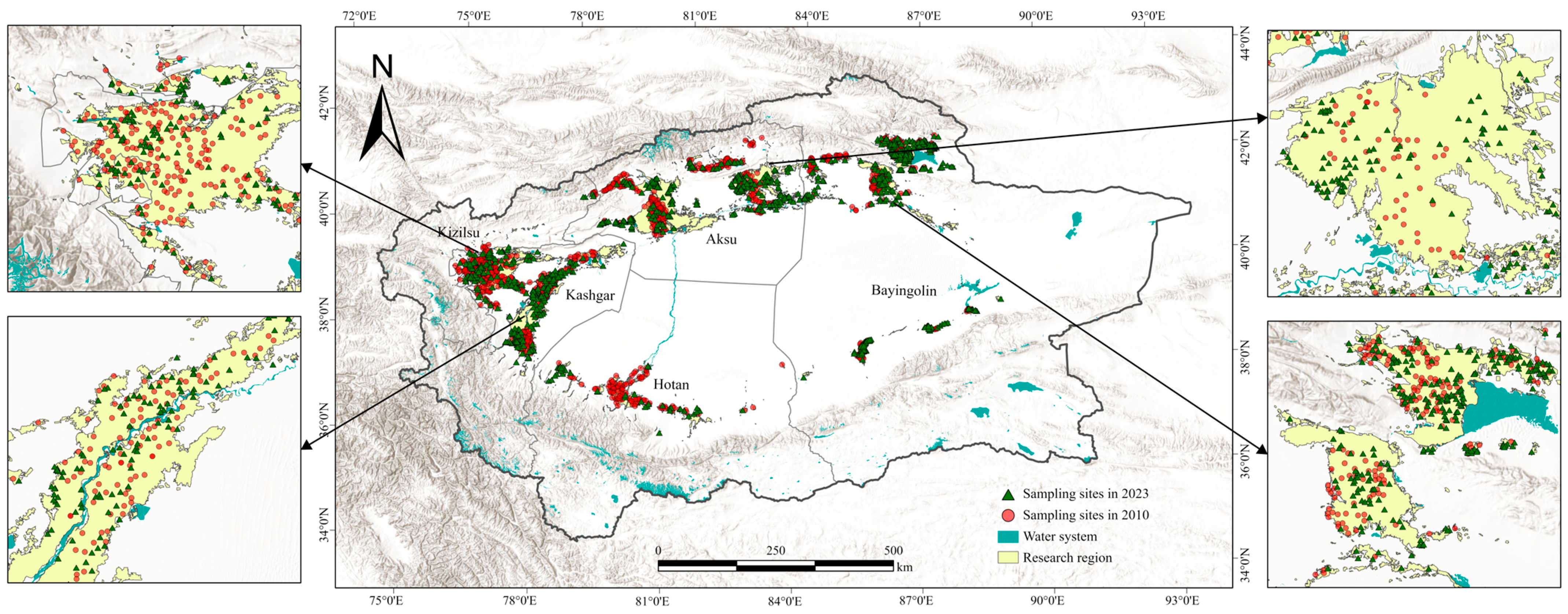
2.2.1. Measured Data
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.3. Geospatial Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Inversion Models
2.3.2. Model Accuracy Evaluation
2.3.3. Piecewise Structural Equation Modeling
3. Results
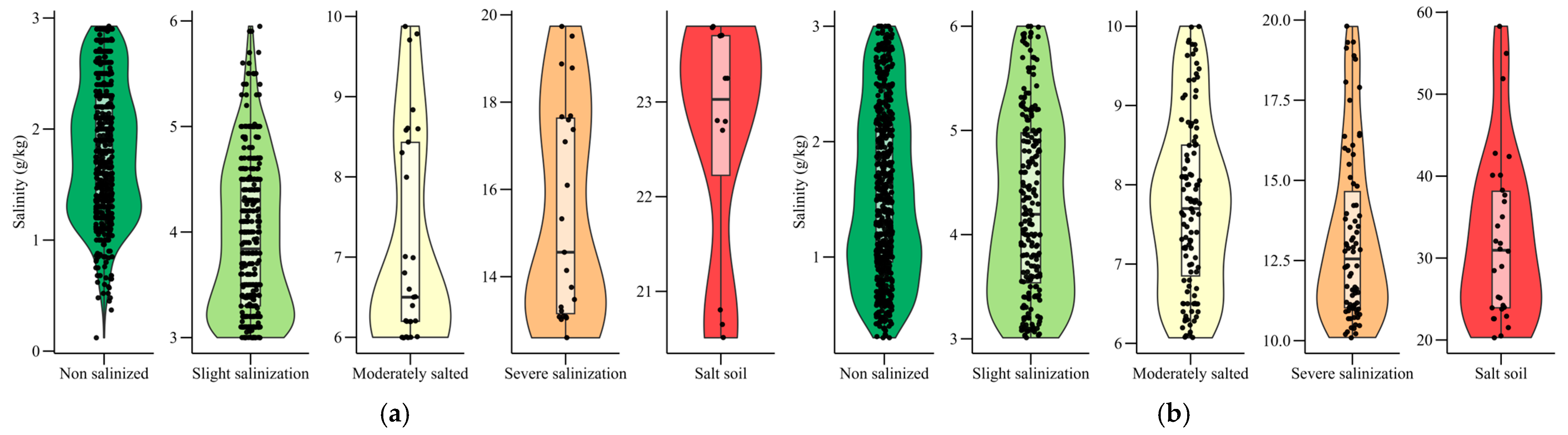
3.1. Statistical Analysis of Measured Data
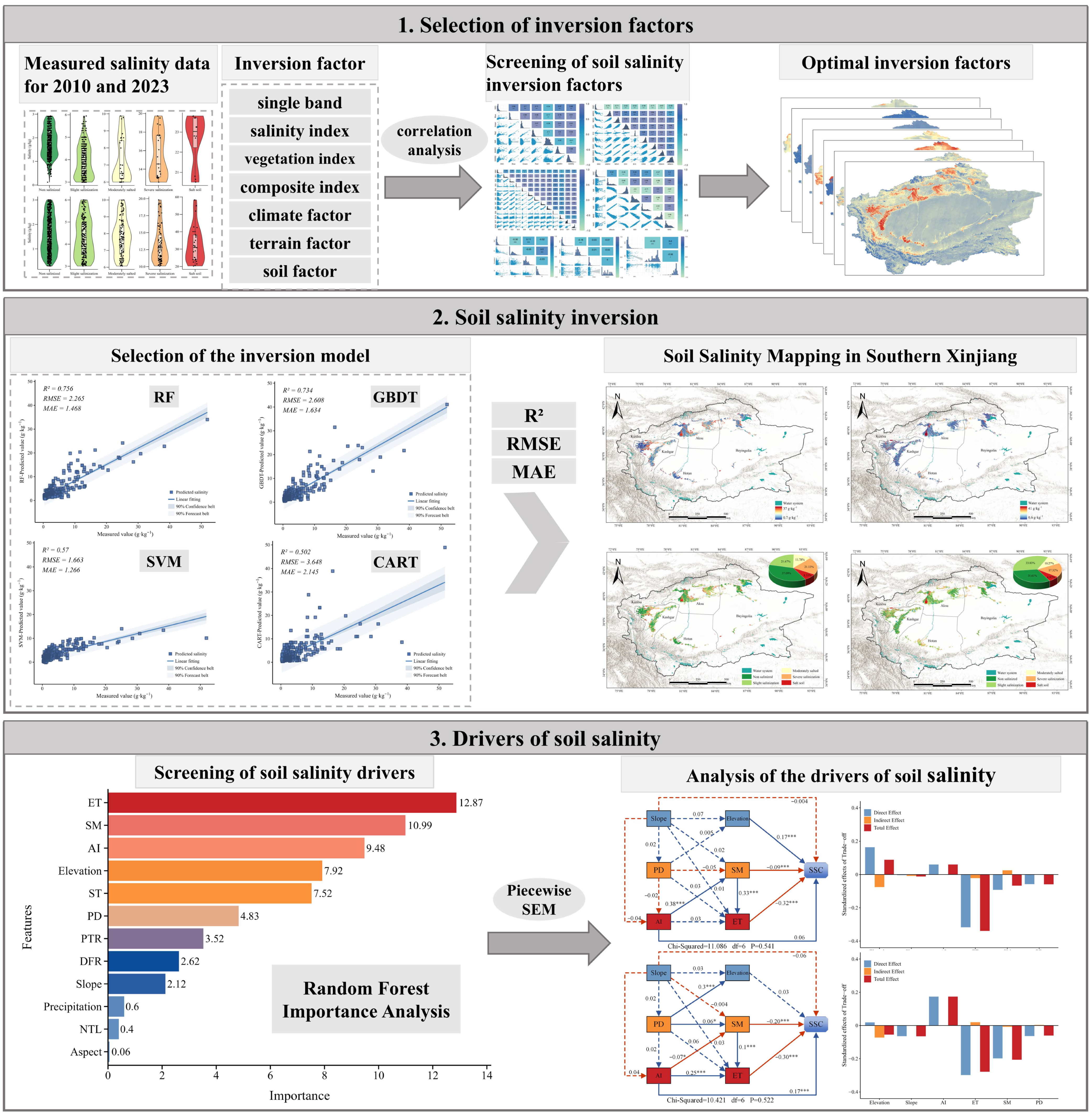
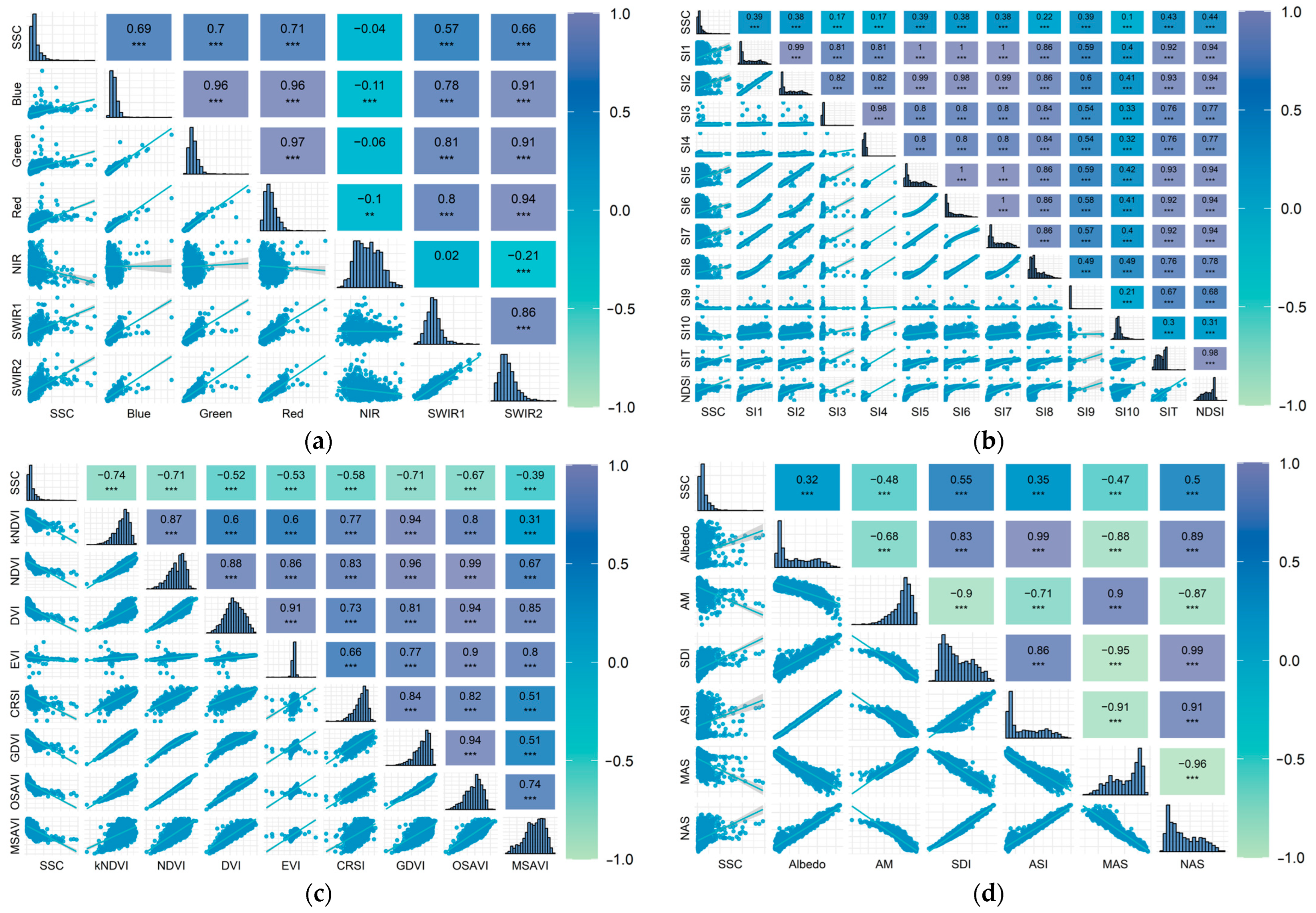
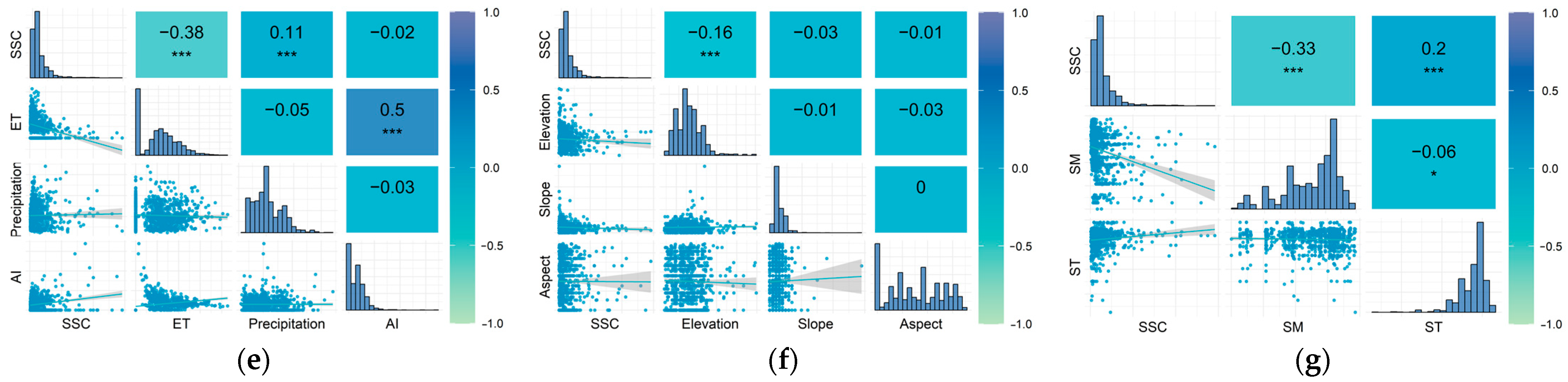
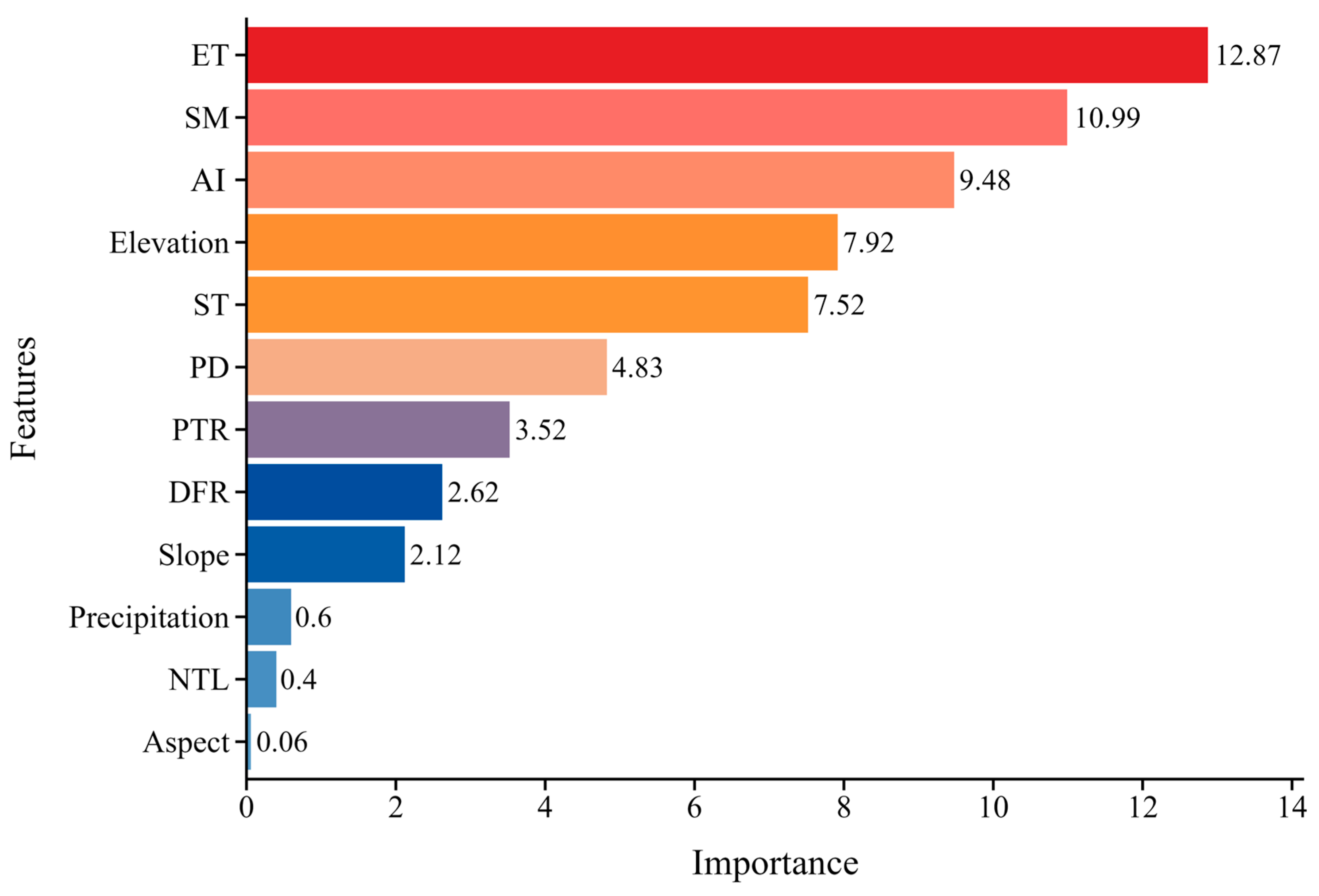
3.2. Screening of Inversion Factors for Soil Salinization
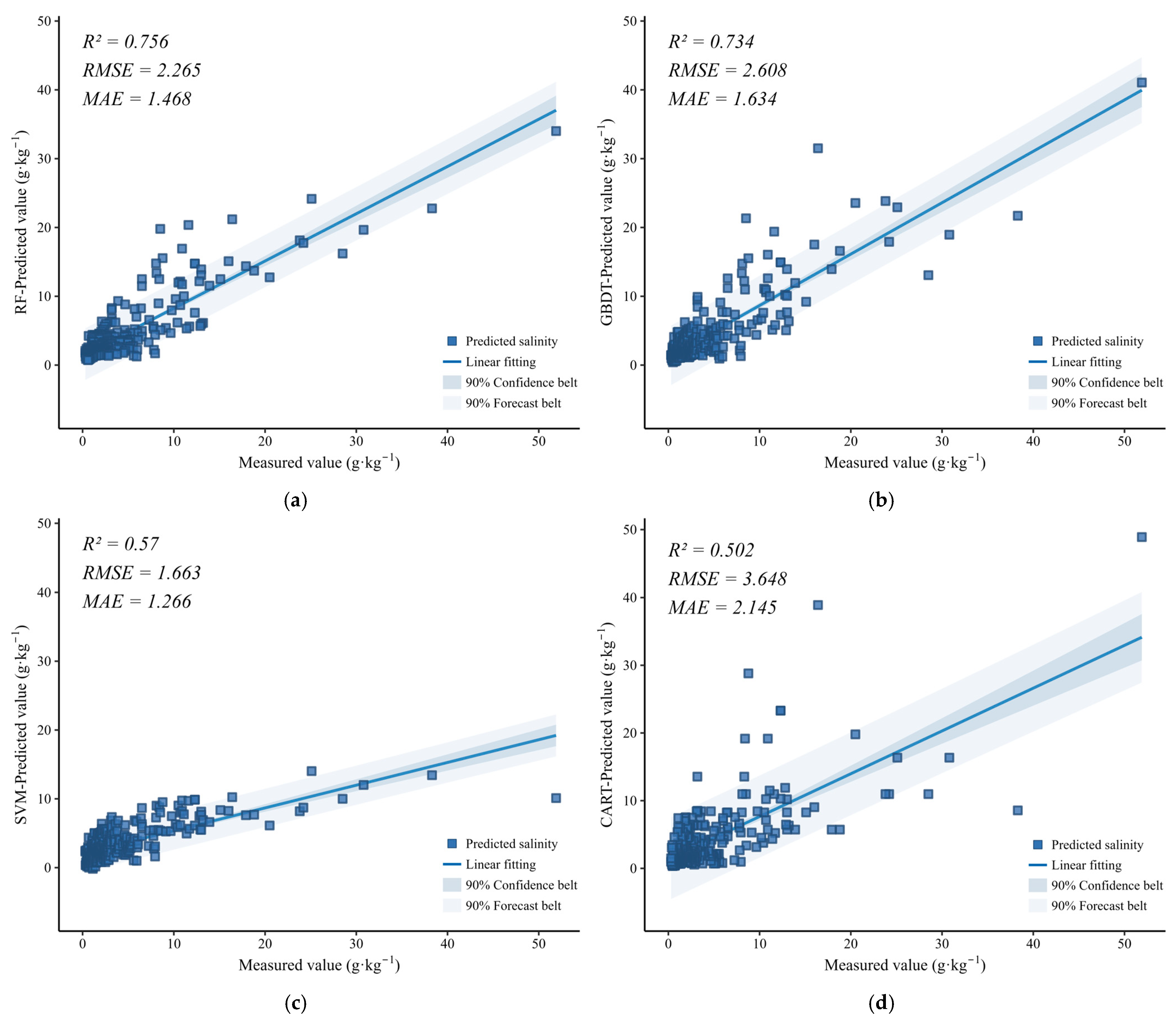
3.3. Model Accuracy Validation and Selection
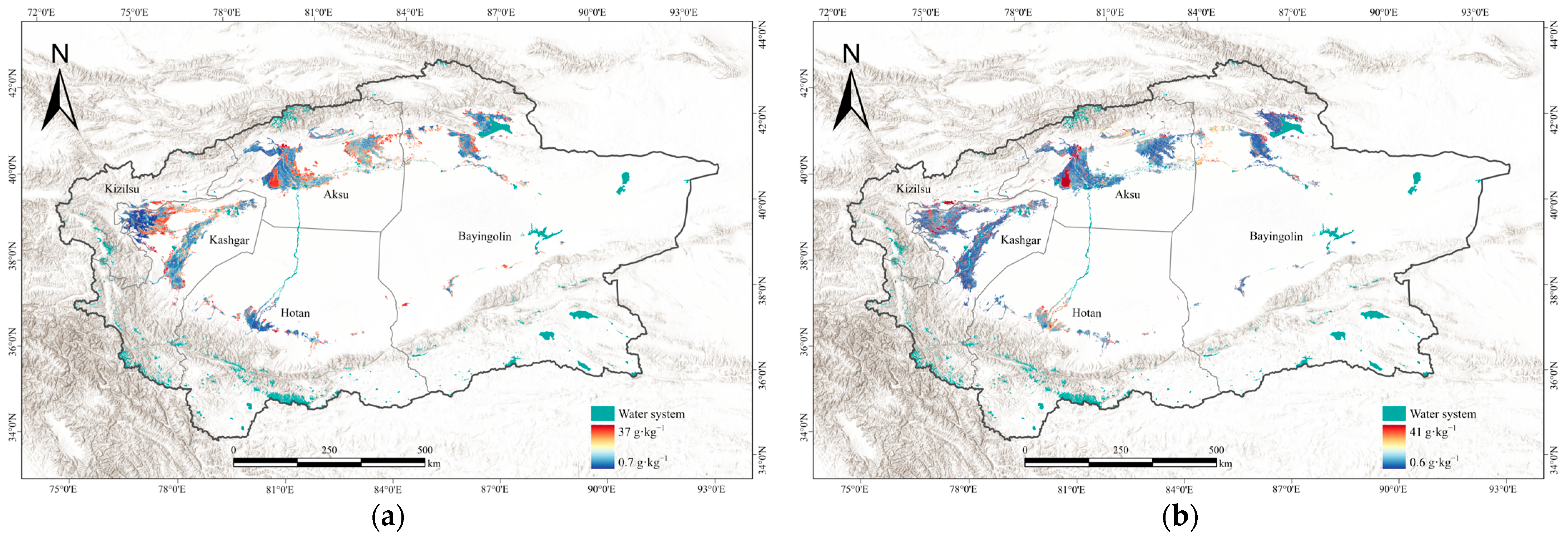
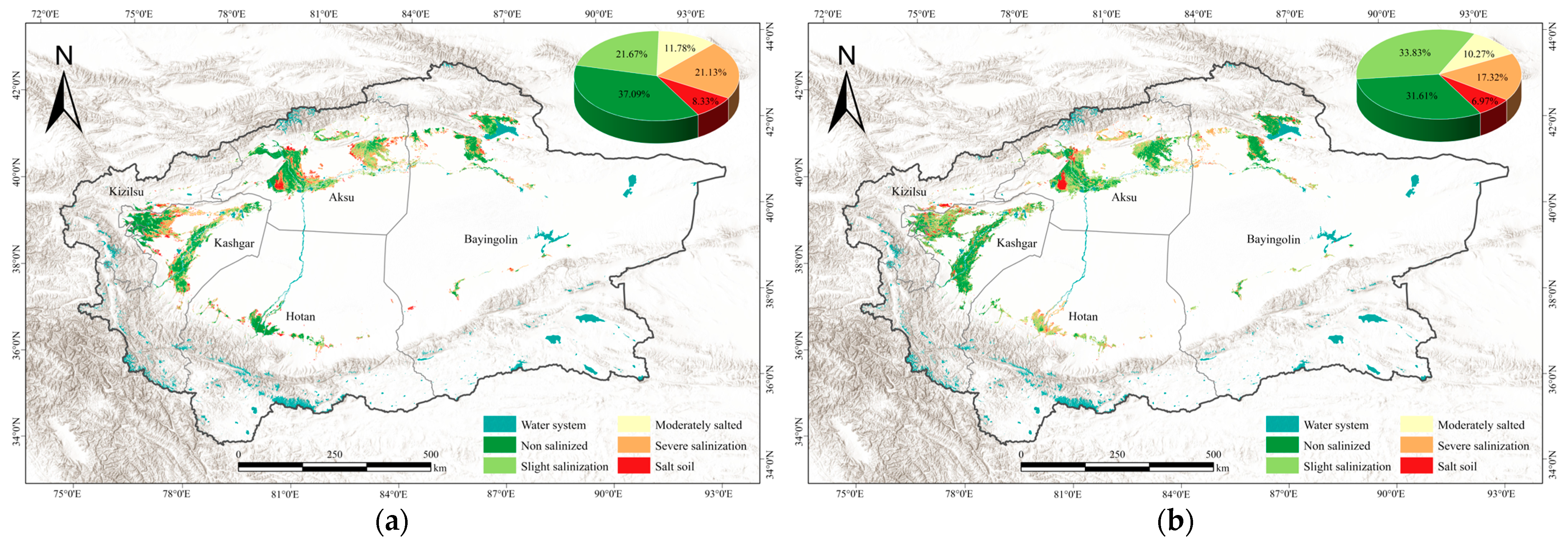
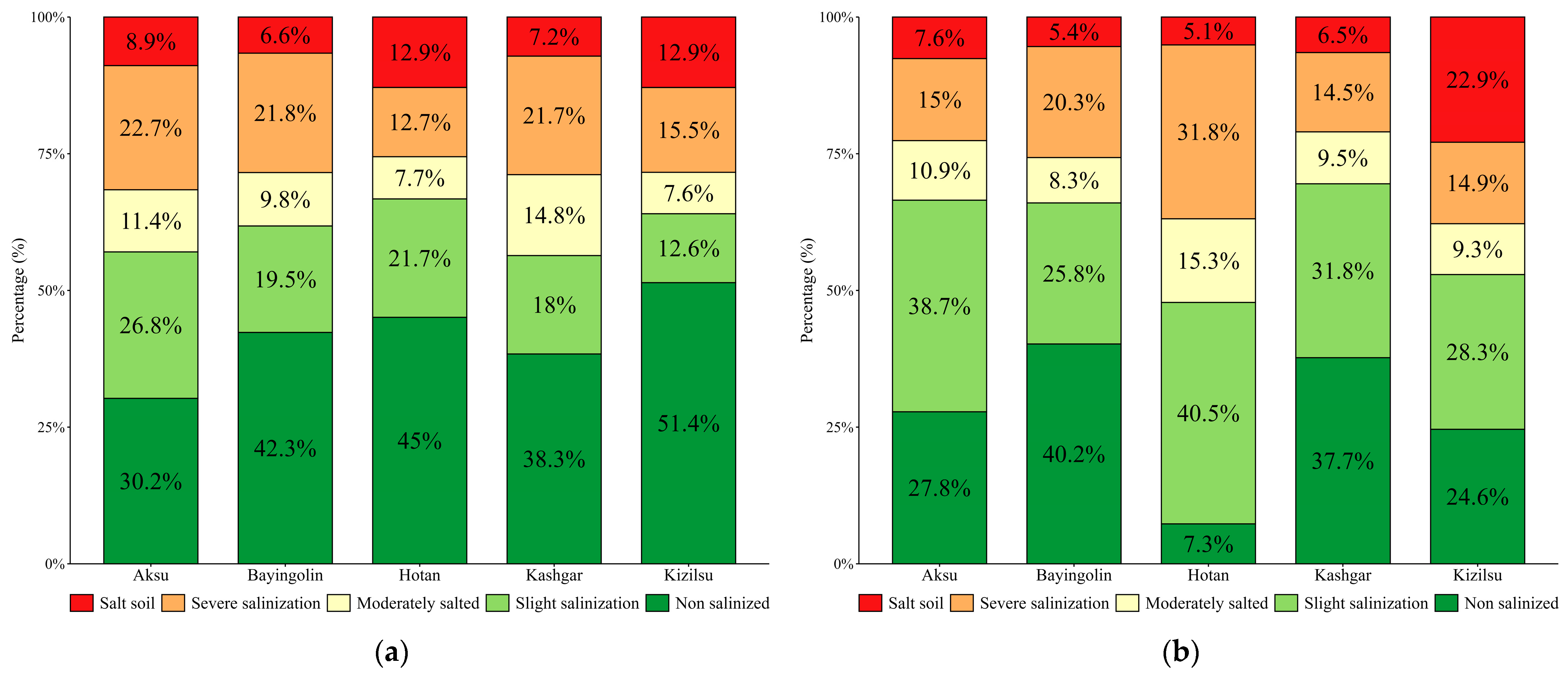
3.4. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Variations in Soil Salinization
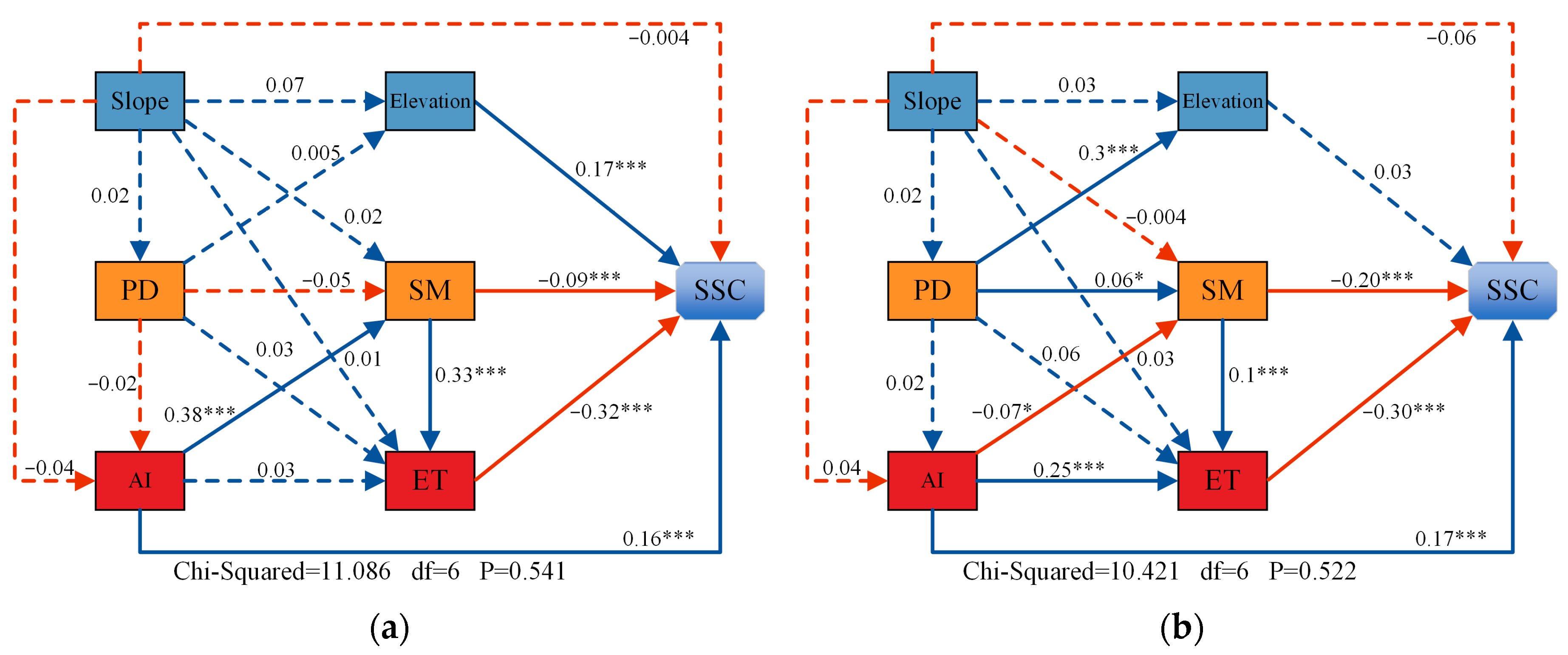
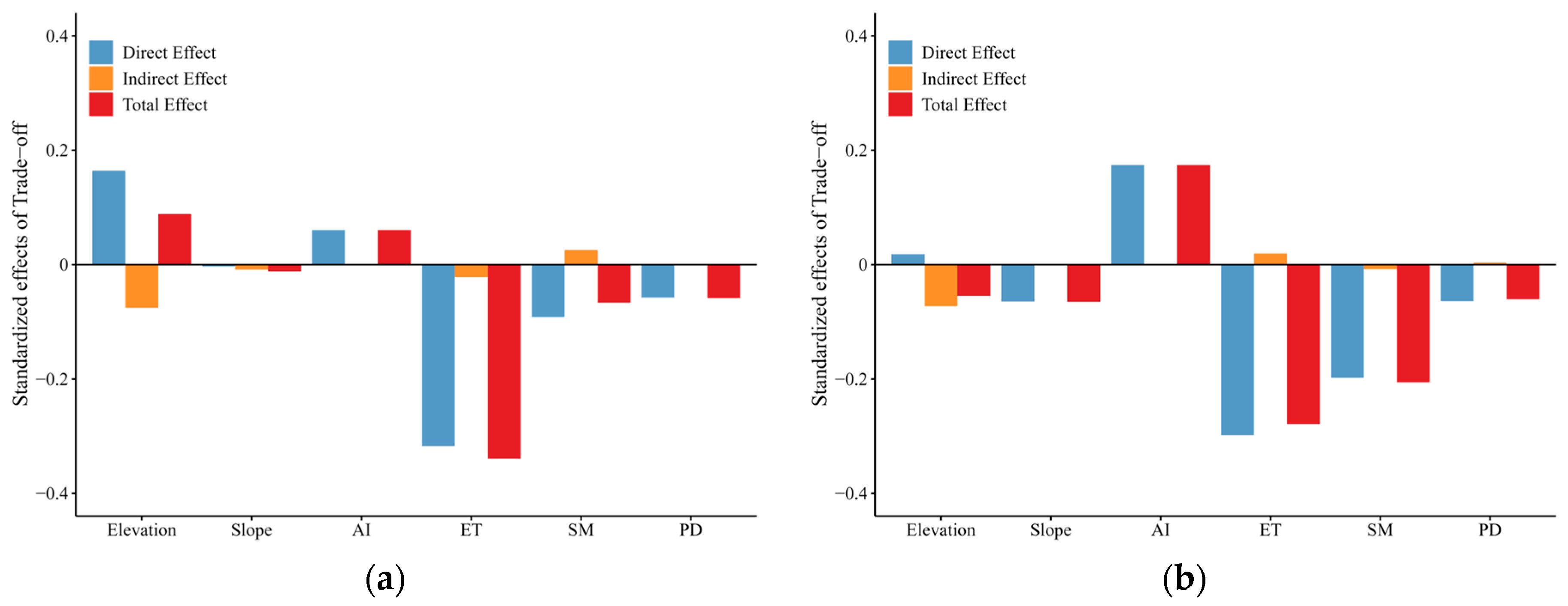
3.5. Analysis of the Drivers of Soil Salinization
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of Inversion Variables for Soil Salinity
4.2. Evaluation of Inversion Models for Soil Salinization
4.3. Drivers of Soil Salinization Changes in the Oasis of South Xinjiang
4.4. Future Challenges and Perspectives
5. Conclusions
- 1.
- Among the environmental variables such as spectra, vegetation, climate and topography, Red, NDSI, kNDVI, SDI, ET, elevation and SM variables have significant relationships with soil salinity; among the four machine models, their accuracies are ranked as RF > GBDT > SVM > CART, which fully proves the superiority of the RF method in monitoring soil salinity at a large scale range.
- 2.
- Over the past decade, the study area in the oasis region of southern Xinjiang exhibited a general trend of soil salinization mitigation, with a 3.81% reduction in severely salinized areas and a 1.36% decline in saline soil proportion. However, the extent of mildly salinized areas expanded significantly, indicating a redistribution of soil salinity within the region, where both the effectiveness of salinization control and potential risks coexist. Additionally, this study focused exclusively on two specific periods; therefore, future research should incorporate data from additional years to characterize the temporal dynamics of soil salinization.
- 3.
- Evapotranspiration (ET) and soil moisture (SM) were identified as the primary driving factors influencing soil salinity dynamics. The impact of SM on soil salinity intensified throughout the study period, suggesting that anthropogenic irrigation has emerged as the dominant factor regulating soil salinity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, A. Soil salinity: A global threat to sustainable development. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 39–67. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, N.; Rai, A.K.; Barman, A.; Mandal, S.; Sundha, P.; Bedwal, S.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, R.K.; Sharma, P.C. Salt affected soils: Global perspectives. In Soil Health and Environmental Sustainability: Application of Geospatial Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 107–129. [Google Scholar]
- Haj-Amor, Z.; Araya, T.; Kim, D.-G.; Bouri, S.; Lee, J.; Ghiloufi, W.; Yang, Y.; Kang, H.; Jhariya, M.K.; Banerjee, A. Soil salinity and its associated effects on soil microorganisms, greenhouse gas emissions, crop yield, biodiversity and desertification: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gang, N.; Gu, F.; Burrill, H.M.; Jianfang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. Saline-alkali soil reclamation and utilization in China: Progress and prospects. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 216. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Wei, Y.; Shi, Q.; Ding, J. Characterizing soil salinity at multiple depth using electromagnetic induction and remote sensing data with random forests: A case study in Tarim River Basin of southern Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142030. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Shi, Z. Estimating soil salinity from remote sensing and terrain data in southern Xinjiang Province, China. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Qin, G. Characterizing spatiotemporal variations of soil salinization and its relationship with eco-hydrological parameters at the Regional Scale in the Kashi Area of Xinjiang, China from 2000 to 2017. Water 2021, 13, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakak, H.; Huang, J.; Zouahri, A.; Douaik, A.; Triantafilis, J. Mapping soil salinity in 3-dimensions using an EM38 and EM4Soil inversion modelling at the reconnaissance scale in central Morocco. Soil Use Manag. 2017, 33, 553–567. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, D.; Van Niekerk, A. Machine learning performance for predicting soil salinity using different combinations of geomorphometric covariates. Geoderma 2017, 299, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiee, M.; Ghazavi, R.; Pakparvar, M.; Vali, A. Mapping spatial variability of soil salinity in a coastal area located in an arid environment using geostatistical and correlation methods based on the satellite data. Desert 2018, 23, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Webster, R.; Shi, Z. Mapping soil salinity in the Yangtze delta: REML and universal kriging (E-BLUP) revisited. Geoderma 2015, 237, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, C.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Z.; Li, Y. Identifying change in spatial accumulation of soil salinity in an inland river watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahbeni, G.; Székely, B. Spatial modeling of soil salinity using kriging interpolation techniques: A study case in the Great Hungarian Plain. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2022, 11, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulatov, A.; Khamidov, A.; Akhmatov, D.; Pulatov, B.; Vasenev, V. Soil salinity mapping by different interpolation methods in Mirzaabad district, Syrdarya Province. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 883, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X. The inversion of arid-coastal cultivated soil salinity using explainable machine learning and Sentinel-2. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G. Upscaling remote sensing inversion and dynamic monitoring of soil salinization in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, J. Inversion of salinization in multilayer soils and prediction of water demand for salt regulation in coastal region. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 301, 108970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G. Remote sensing prediction and characteristic analysis of cultivated land salinization in different seasons and multiple soil layers in the coastal area. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102838. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, G.; Chang, C.; Yang, W.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G. Soil salinity inversion in coastal corn planting areas by the satellite-UAV-ground integration approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, A.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Wei, Y. Soil salinity inversion based on differentiated fusion of satellite image and ground spectra. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 101, 102360. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Yu, D.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, X.; Teng, D.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Lizaga, I. Capability of Sentinel-2 MSI data for monitoring and mapping of soil salinity in dry and wet seasons in the Ebinur Lake region, Xinjiang, China. Geoderma 2019, 353, 172–187. [Google Scholar]
- Bandak, S.; Movahedi-Naeini, S.A.; Mehri, S.; Lotfata, A. A longitudinal analysis of soil salinity changes using remotely sensed imageries. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10383. [Google Scholar]
- Avdan, U.; Kaplan, G.; Matcı, D.K.; Avdan, Z.Y.; Erdem, F.; Mızık, E.T.; Demirtaş, İ. Soil salinity prediction models constructed by different remote sensors. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 128, 103230. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, A.; Kumar, N.; Sinha, N.K.; Kumar, J. Identification of salt-affected soils using remote sensing data through random forest technique: A case study from India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elaziz, A.E.A.; Soliman, K.G.; Abu-Hashim, M.S.; Hamed, E.A.; Metwally, M.S. Enhancing soil salinity prediction in semi-arid regions using machine learning models technology. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. IJCBS 2023, 24, 565–574. [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy, S.; Sertel, E.; Roscher, R.; Tanik, A.; Hamzehpour, N. Assessment of soil salinity using explainable machine learning methods and Landsat 8 images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 130, 103879. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J. Performance comparison of machine learning algorithms for estimating the soil salinity of salt-affected soil using field spectral data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tashpolat, N. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Soil Salinity in Weigan River–Kuqa River Delta Oasis Based on Two-Dimensional Feature Space. Water 2023, 15, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yang, F.; Han, B.; Fan, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, W.; Jiang, L. A model for the rapid monitoring of soil salinization in the Yellow River Delta using Landsat 8 OLI imagery based on VI-SI feature space. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 796–805. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, B.; Ji, W.; Li, S.; Hong, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X. Global soil salinity prediction by open soil Vis-NIR spectral library. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Min, L.; Guo, Z.; Li, N. Retrieval of farmland surface soil moisture based on feature optimization and machine learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrelst, J.; Malenovský, Z.; Van der Tol, C.; Camps-Valls, G.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.-P.; Lewis, P.; North, P.; Moreno, J. Quantifying vegetation biophysical variables from imaging spectroscopy data: A review on retrieval methods. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 589–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, W.; Duan, W.; Ma, F.; Li, C.; Li, Z. Inversion model of soil salinity in alfalfa covered farmland based on sensitive variable selection and machine learning algorithms. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, G.; Wang, X.; Han, J. UAV remote sensing inversion of soil salinity in field of sunflower. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 178–191. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Van, C.P.; Nguyen, T.G.; Dang, D.K.; Pham, T.T.N.; Nguyen, Q.-H.; Bui, Q.-T. Soil salinity prediction using hybrid machine learning and remote sensing in Ben Tre province on Vietnam’s Mekong River Delta. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 74340–74357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Duan, H.; Liao, J.; Guo, P.; Huang, C.; Xue, X. Estimation of soil salinization by machine learning algorithms in different arid regions of northwest China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Ding, J.; Huang, W.; Ma, X. Spatiotemporal variation and future predictions of soil salinization in the Werigan–Kuqa river delta oasis of China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Han, B. Spatiotemporal changes of soil salinization in the Yellow River Delta of China from 2015 to 2019. Sustainability 2021, 13, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Feng, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X. Analysis of spatial and temporal changes in vegetation cover and its drivers in the Aksu River Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Zhang, Q.; Pilla, F.; Joshi, P.K.; Basu, B.; Keesstra, S.; Roy, P.; Wang, Y.; Sutton, P.C.; Chakraborti, S. Responses of ecosystem services to natural and anthropogenic forcings: A spatial regression based assessment in the world’s largest mangrove ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 137004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Yang, T.; Gao, G.-F.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H. Contrasting patterns for bacteria and archaea in response to salt stress across alpine wetlands of the Tibetan Plateau. Fundam. Res. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Spatial distribution patterns and drivers of above-and below-biomass in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 944, 173922. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.; He, B.; Luo, X.; Ma, S.; Song, Y.; Yang, W. Spatio-Temporal Variation Analysis of Soil Salinization in the Ougan-Kuqa River Oasis of China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Nurmemet, I.; Gao, M.; Xie, B. Inversion of soil salinity using multisource remote sensing data and particle swarm machine learning models in Keriya Oasis, northwestern China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, G.; Mei, Y. Spatio-temporal changes of soil salinity in arid areas of south Xinjiang using electromagnetic induction. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, B.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. Effects of Potential Large-Scale Irrigation on Regional Precipitation in Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Deng, X.; Ren, C.; Deng, M.; Wang, S.; Lai, X.; Long, A. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Trends of Ecological Environment Quality and Influencing Factors in Xinjiang Oasis. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Chao, G.; Bin, X.; Yunxiang, J.; Jinya, L.; Hailong, M.; Fen, Z.; Jian, G.; Xiuchun, Y. Quantitative inversion of soil salinity and analysis of its spatial pattern in agricultural area in Shihezi of Xinjiang. Geogr. Res. 2015, 33, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L.; Aldakheel, Y.Y. Assessing soil salinity using soil salinity and vegetation indices derived from IKONOS high-spatial resolution imageries: Applications in a date palm dominated region. Geoderma 2014, 230, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Khan, S. Using remote sensing techniques for appraisal of irrigated soil salinity. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Modelling and Simulation (MODSIM), Christchurch, New Zealand, 10–13 December 2007; pp. 2632–2638. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting salinity hazards within a semiarid context by means of combining soil and remote-sensing data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.M.; Rastoskuev, V.V.; Sato, Y.; Shiozawa, S. Assessment of hydrosaline land degradation by using a simple approach of remote sensing indicators. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 77, 96–109. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khaier, F. Soil Salinity Detection Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Master’s Thesis, International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation, University of Twente, Enscheda, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.M.; Rastoskuev, V.V.; Shalina, E.V.; Sato, Y. Mapping salt-affected soils using remote sensing indicators-a simple approach with the use of GIS IDRISI. In Proceedings of the 22nd Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Singapore, 5–9 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Camps-Valls, G.; Campos-Taberner, M.; Moreno-Martínez, Á.; Walther, S.; Duveiller, G.; Cescatti, A.; Mahecha, M.D.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; García-Haro, F.J.; Guanter, L. A unified vegetation index for quantifying the terrestrial biosphere. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Minasny, B.; Sarmadian, F.; Malone, B. Digital mapping of soil salinity in Ardakan region, central Iran. Geoderma 2014, 213, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Gao, S.; Chi, H.; Qi, J.; Song, W.; Tong, Y.; Mu, X.; Yan, G. Evaluation of the vegetation-index-based dimidiate pixel model for fractional vegetation cover estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4400514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Hao, D.; Huete, A.; Dechant, B.; Berry, J.; Chen, J.M.; Joiner, J.; Frankenberg, C.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Ryu, Y. Optical vegetation indices for monitoring terrestrial ecosystems globally. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Sun, D.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J. Mapping soil salinity using a combination of vegetation index time series and single-temporal remote sensing images in the Yellow River Delta, China. Catena 2023, 231, 107313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Al-Shafie, W.M.; Mhaimeed, A.S.; Ziadat, F.; Nangia, V.; Payne, W.B. Soil salinity mapping by multiscale remote sensing in Mesopotamia, Iraq. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4442–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fern, R.R.; Foxley, E.A.; Bruno, A.; Morrison, M.L. Suitability of NDVI and OSAVI as estimators of green biomass and coverage in a semi-arid rangeland. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.R.; Pattey, E.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Strachan, I.B. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: Modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lei, S.; Bian, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. Study of the desertification index based on the albedo-MSAVI feature space for semi-arid steppe region. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Zeng, P.; Wang, T.; Geng, Y.; Wang, H. Soil salinization in the irrigated area of the Manas River basin based on MSAVI-SI feature space. Arid Zone Res 2016, 33, 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Han, B.; Yang, F.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, S.; Yang, W.; Gong, R.; Liang, T. Salinization information extraction model based on VI–SI feature space combinations in the Yellow River Delta based on Landsat 8 OLI image. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 1863–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-T.; Zhao, B. Impact of anthropogenic land-uses on salinization in the Yellow River Delta, China: Using a new RS-GIS statistical model. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 947–952. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, T.P.; Ahler, S.J.; Mathers, A.; Ziter, C.D.; Dugan, H.A. Road salt impact on soil electrical conductivity across an urban landscape. J. Urban Ecol. 2020, 6, juaa006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Shi, F.; Schneider, M.; Lv, G.; Li, Y. Impact of groundwater depth and soil salinity on riparian plant diversity and distribution in an arid area of China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Ding, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, S. Digital mapping of soil salinization based on Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data combined with machine learning algorithms. Reg. Sustain. 2021, 2, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Feng, X.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Y.; Huang, J.; Cheng, J. A framework for soil salinity monitoring in coastal wetland reclamation areas based on combined unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) data and satellite data. Drones 2022, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, M.S.; Dahms, T.; Kuebert-Flock, C.; Rummler, T.; Arnault, J.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Ullmann, T. Integrating random forest and crop modeling improves the crop yield prediction of winter wheat and oil seed rape. Front. Remote Sens. 2023, 3, 1010978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Zamanian, K.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X. Combination of hyperspectral and machine learning to invert soil electrical conductivity. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M. Google Earth Engine (GEE) cloud computing based crop classification using radar, optical images and Support Vector Machine Algorithm (SVM). In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 3rd International Multidisciplinary Conference on Engineering Technology (IMCET), Beirut, Lebanon, 8–10 December 2021; pp. 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.K. On classification and regression trees for multiple responses and its application. J. Classif. 2006, 23, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tian, J.; Lu, X.; Tian, Q. Temporal and spatial dynamics distribution of organic carbon content of surface soil in coastal wetlands of Yancheng, China from 2000 to 2022 based on Landsat images. Catena 2023, 223, 106961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Dong, S.; Xu, Y.; Fry, E.L.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Shen, H.; Xiao, J.; Wu, S.; Yang, M. Plant biomass allocation and driving factors of grassland revegetation in a Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau chronosequence. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar]
- Naimi, S.; Ayoubi, S.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Dematte, J.A.M. Ground observations and environmental covariates integration for mapping of soil salinity: A machine learning-based approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhetaer, N.; Nurmemet, I.; Abulaiti, A.; Xiao, S.; Zhao, J. A quantifying approach to soil salinity based on a radar feature space model using ALOS PALSAR-2 data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, F.; Li, J.; Gu, Q.; Yang, S.; Wu, D.; Feng, J.; Ding, J. Characterizing and modeling regional-scale variations in soil salinity in the arid oasis of Tarim Basin, China. Geoderma 2017, 305, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Chan, N.W.; Ariken, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y. Regional suitability prediction of soil salinization based on remote-sensing derivatives and optimal spectral index. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145807. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, P.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; Yuan, D.; Hu, Y.; Zamanian, K.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X. Inversion of different cultivated soil types’ salinity using hyperspectral data and machine learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; He, Y.; Shi, Z. Integrating remote sensing and landscape characteristics to estimate soil salinity using machine learning methods: A case study from Southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Kang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; He, F. Mapping the Soil Salinity Distribution and Analyzing Its Spatial and Temporal Changes in Bachu County, Xinjiang, Based on Google Earth Engine and Machine Learning. Agriculture 2024, 14, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehla, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Jhorar, R. Soil salinity assessment and mapping using spectral indices and geostatistical techniques-concepts and reviews. In Remote Sensing of Soils; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 429–437. [Google Scholar]
- Boudibi, S.; Sakaa, B.; Benguega, Z.; Fadlaoui, H.; Othman, T.; Bouzidi, N. Spatial prediction and modeling of soil salinity using simple cokriging, artificial neural networks, and support vector machines in El Outaya plain, Biskra, southeastern Algeria. Acta Geochim. 2021, 40, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. Mapping multi-depth soil salinity using remote sensing-enabled machine learning in the yellow river delta, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; He, B.; Xie, B.; Ge, X.; Han, L. Investigation of the spatial and temporal variation of soil salinity using Google Earth Engine: A case study at Werigan–Kuqa Oasis, West China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-T.; Wu, H.-Q.; Gu, H.-B.; Feng, G.-L.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, J.-D. Variability of soil salinity at multiple spatio-temporal scales and the related driving factors in the oasis areas of Xinjiang, China. Pedosphere 2014, 24, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Guo, M.; Yue, W.; Teng, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Yang, J.; Zuo, R. Evaluating the impact of flood irrigation on spatial variabilities of soil salinity and groundwater quality in an arid irrigated region. Hydrol. Res. 2021, 52, 229–240. [Google Scholar]
| Degree of Soil Salinization | Non Salinized | Slight Salinization | Moderately Salted | Severe Salinization | Salt Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil salinity (S, g·kg−1) | 0 ≤ S < 3 | 3 ≤ S < 6 | 6 ≤ S < 10 | 10 ≤ S < 20 | S ≥ 20 |
| Factor Types | Variable Name | Data Sources | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral index | Blue, Green, Red, NIR, SWIR1, SWIR2 | Landsat 5/9 | 30 m |
| Salinity index | SI1, SI2, SI3, SI4, SI5, SI6, SI7, SI8, SI9, SI10, NDSI, SI-T | Landsat 5/9 | 30 m |
| Vegetation index | NDVI, EVI, OSAVI, MSAVI, CRSI, GDVI, DVI, kNDVI | Landsat 5/9 | 30 m |
| Composite index | Albedo, AM, SDI, ASI, NAS, MAS | Landsat 5/9 | 30 m |
| Climatic factor | Evapotranspiration (ET) | MOD16A2GF | 500 m |
| Precipitation | CHIRPS Daily 2.0 Final | 500 m | |
| Aridity Index (AI) | TerraClimate | 0.04° | |
| Soil factor | Soil Moisture (SM), Soil Temperature (ST) | Global Land Data Assimilation System | 0.25° |
| Topographic factor | Elevation, Slope, Aspect | SRTM | |
| Human activities | Population Density (PD) | LandScan | |
| Night Lights (NTL) | NCEI |
| Factor Types | Variable Name | Abbreviation | Calculation Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity index | Salinity index 1 | SI1 | [49] | |
| Salinity index | SI-T | [49] | ||
| Salinity index 2 | SI2 | [50] | ||
| Salinity index 3 | SI3 | [50] | ||
| Salinity index 4 | SI4 | [50] | ||
| Salinity index 5 | SI5 | [50] | ||
| Salinity index 6 | SI6 | [51] | ||
| Salinity index 7 | SI7 | [51] | ||
| Salinity index 8 | SI8 | [52] | ||
| Salinity index 9 | SI9 | [53] | ||
| Salinity index 10 | SI10 | [53] | ||
| Normalized difference salinity index | NDSI | [54] | ||
| Vegetation index | kernel normalized difference vegetation index | kNDVI | [55] | |
| Normalized difference vegetation index | NDVI | [56] | ||
| Difference vegetation index | DVI | [57] | ||
| Enhanced vegetation index | EVI | [58] | ||
| Canopy redness index | CRSI | [59] | ||
| Generalized difference vegetation index | GDVI | ) | [60] | |
| Optimized soil-adjusted vegetation index | OSAVI | [61] | ||
| Modified soil-adjusted vegetation index | MSAVI | [62] | ||
| Composite index | Albedo | Albedo | [63] | |
| SI1-NDVI | SDI | [64] | ||
| Albedo-MSAVI | AM | [64] | ||
| SI1-Albedo | ASI | [64] | ||
| Albedo-SI1 | NAS | [64] | ||
| SI1-Albedo-MSAVI | MAS | [65] |
| Degree of Soil Salinization | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Median | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non salinized | 0.12 | 2.93 | 1.82 | 0.60 | 1.80 | 33.09 |
| Slight salinization | 3.00 | 5.95 | 3.94 | 0.72 | 3.84 | 18.31 |
| Moderately salted | 6.00 | 9.88 | 7.19 | 1.33 | 6.50 | 18.46 |
| Severe salinization | 12.60 | 19.74 | 15.48 | 2.47 | 14.56 | 15.97 |
| Salt soil | 20.51 | 23.80 | 22.65 | 1.26 | 23.03 | 5.59 |
| Degree of Soil Salinization | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Median | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non salinized | 0.30 | 3.00 | 1.55 | 0.74 | 1.50 | 47.61 |
| Slight salinization | 3.01 | 6.00 | 4.29 | 0.87 | 4.20 | 20.34 |
| Moderately salted | 6.07 | 10.00 | 7.75 | 1.09 | 7.70 | 14.03 |
| Severe salinization | 10.10 | 19.80 | 13.21 | 2.65 | 12.55 | 20.10 |
| Salt soil | 20.30 | 58.30 | 32.41 | 10.32 | 30.95 | 31.85 |
| Model | R2 | RMSE/(g·kg−1) | MAE/(g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.756 | 2.265 | 1.468 |
| GBDT | 0.734 | 2.608 | 1.634 |
| SVM | 0.570 | 1.663 | 1.266 |
| CART | 0.502 | 3.648 | 2.145 |
| Factor Types | Variable Name |
|---|---|
| Human activities | Soil moisture, population density, night lighting, distance from road (DFR) |
| Topographic attributes | Elevation, slope, aspect |
| Natural factors | Evaporation, aridity index, precipitation, soil temperature, proximity to river (PTR) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Fan, Y.; Xuan, J.; Shi, M.; Wang, D.; Wu, H.; Bi, Y.; Li, Y. Monitoring of Soil Salinization and Analysis of Driving Factors in the Oasis Zone of South Xinjiang. Land 2025, 14, 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040803
Zhao J, Fan Y, Xuan J, Shi M, Wang D, Wu H, Bi Y, Li Y. Monitoring of Soil Salinization and Analysis of Driving Factors in the Oasis Zone of South Xinjiang. Land. 2025; 14(4):803. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040803
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jiahao, Yanmin Fan, Junwei Xuan, Mingjie Shi, Dejun Wang, Hongqi Wu, Yanan Bi, and Yunhao Li. 2025. "Monitoring of Soil Salinization and Analysis of Driving Factors in the Oasis Zone of South Xinjiang" Land 14, no. 4: 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040803
APA StyleZhao, J., Fan, Y., Xuan, J., Shi, M., Wang, D., Wu, H., Bi, Y., & Li, Y. (2025). Monitoring of Soil Salinization and Analysis of Driving Factors in the Oasis Zone of South Xinjiang. Land, 14(4), 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040803






