Pix2Pix-Based Modelling of Urban Morphogenesis and Its Linkage to Local Climate Zones and Urban Heat Islands in Chinese Megacities
Abstract
1. Introduction
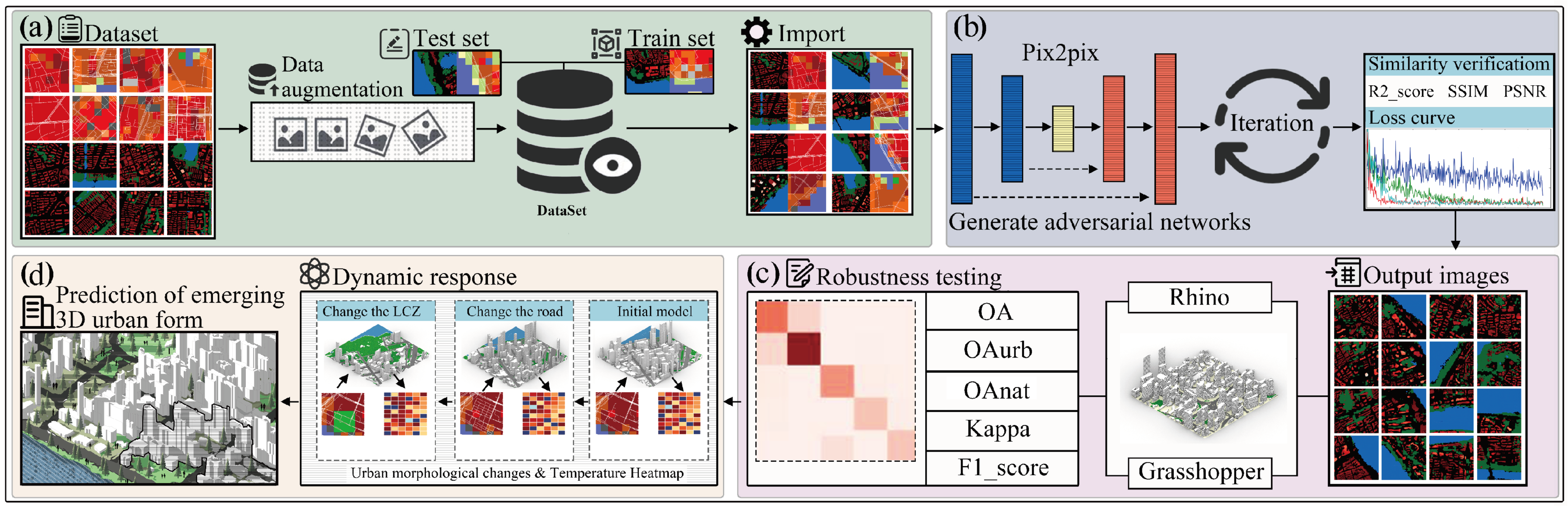
2. Materials and Methods
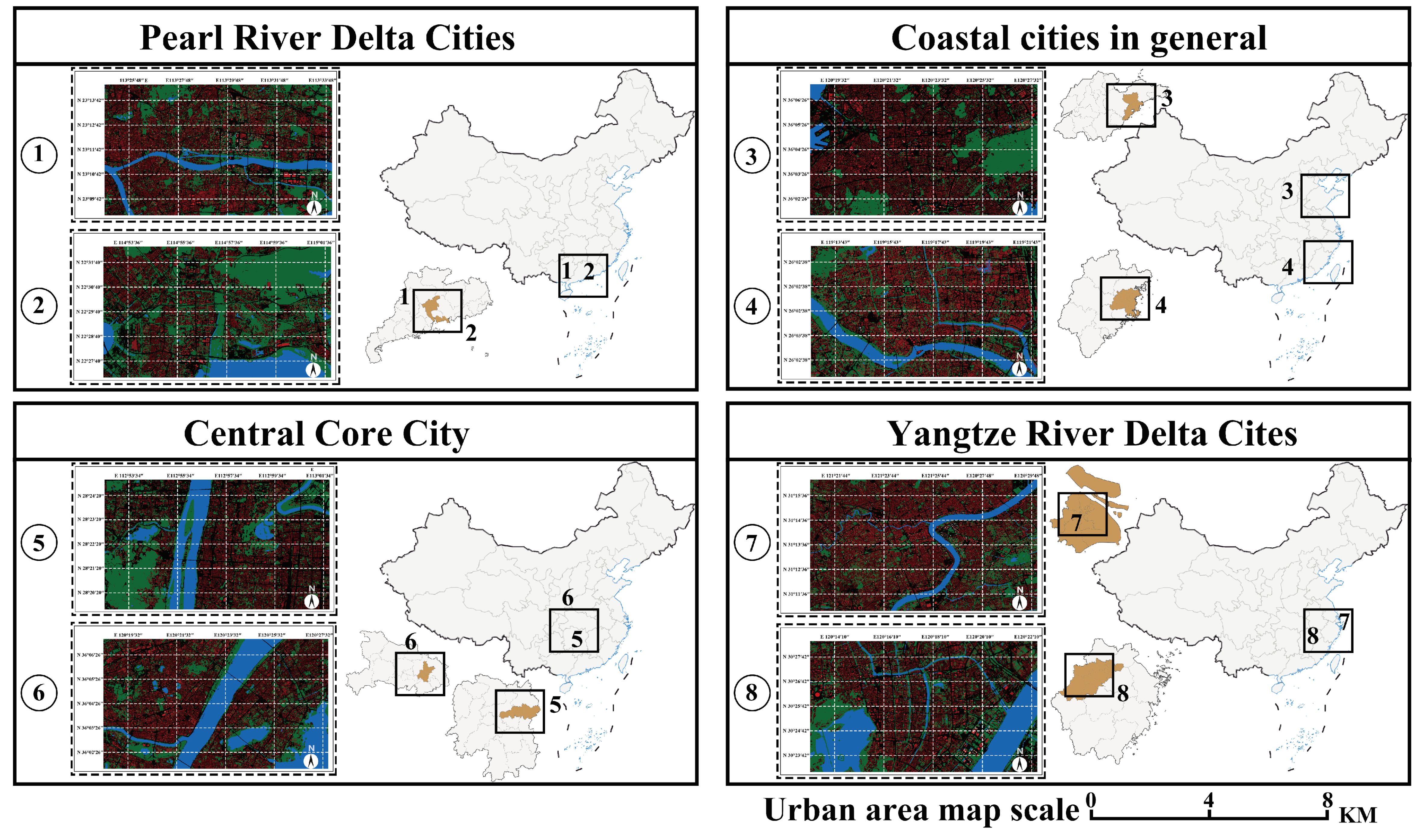
2.1. Urban Form Data Acquisition
2.1.1. Preparation of Urban Morphology Data
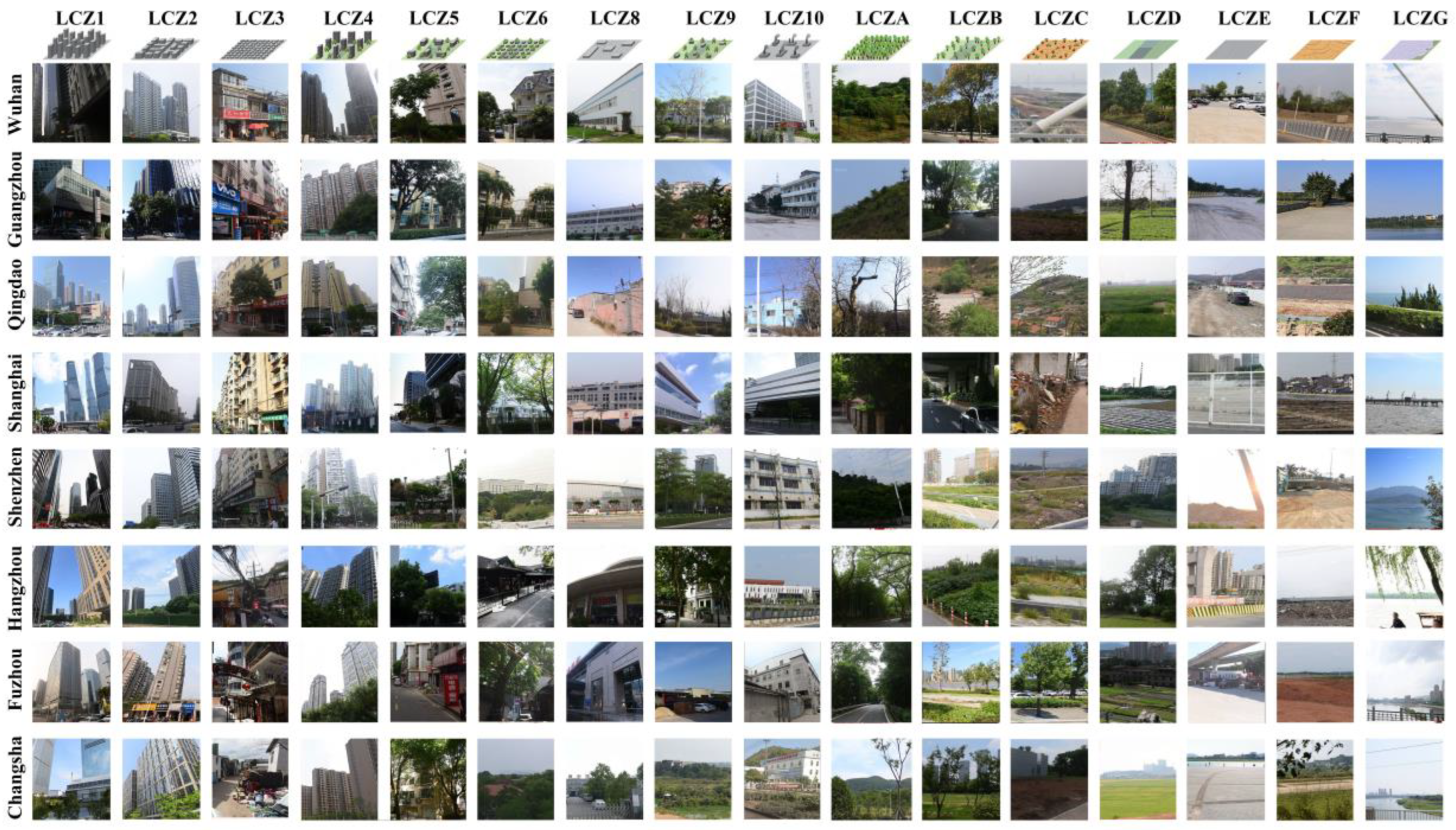
2.1.2. Preparation of LCZ Data
2.1.3. Encoding and Enhancement of Data
2.1.4. Accuracy and Validation of Model
2.1.5. Calculation of Urban Geometric Properties
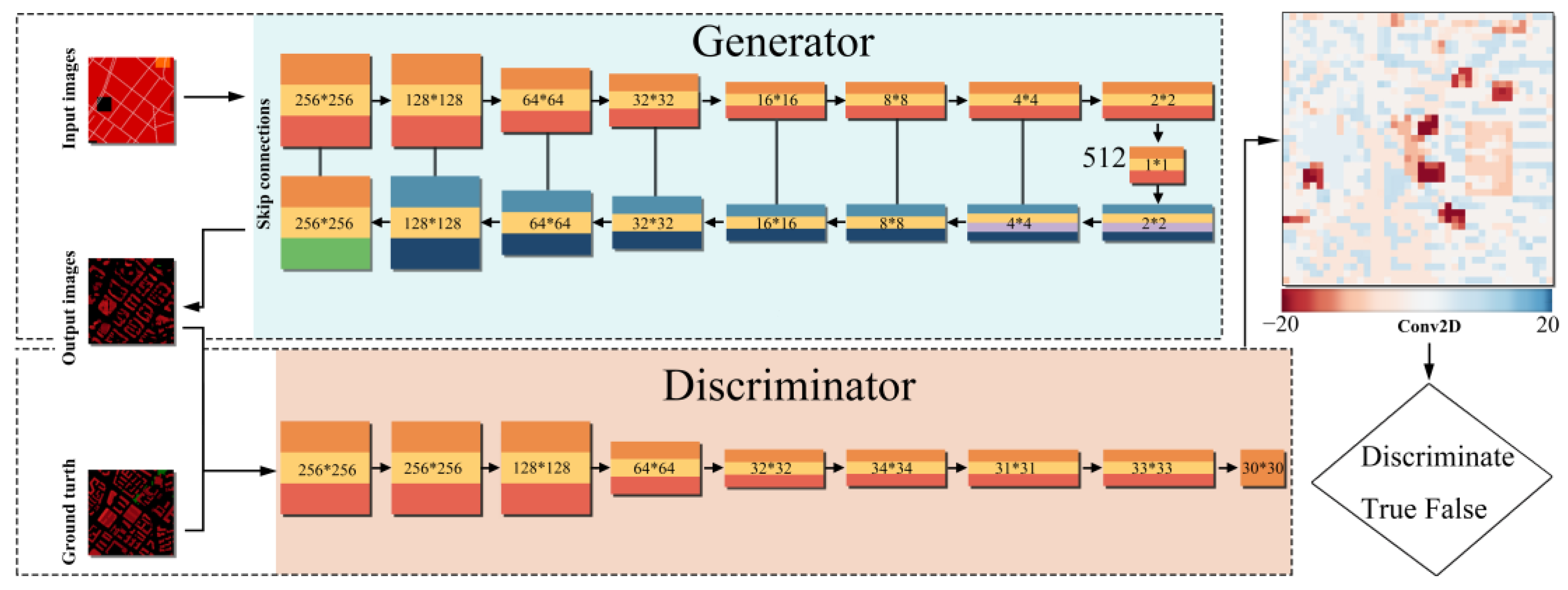
2.2. Pix2pix Model Training Framework
3. Results
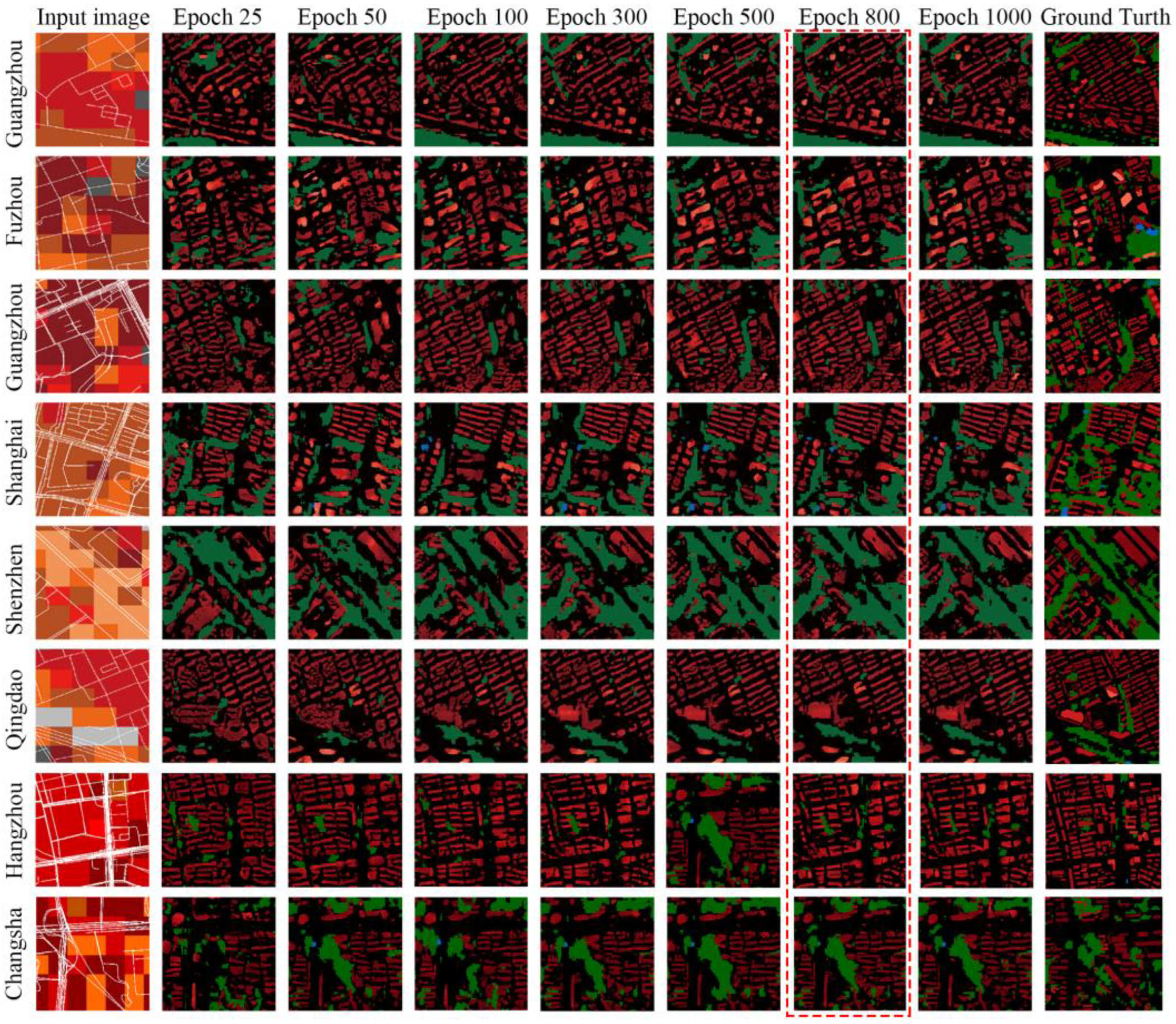
3.1. Iteration Selection in pix2pix Model
3.2. Monitoring and Summarizing the Training Process
3.3. Urban Morphology Generation and Accuracy
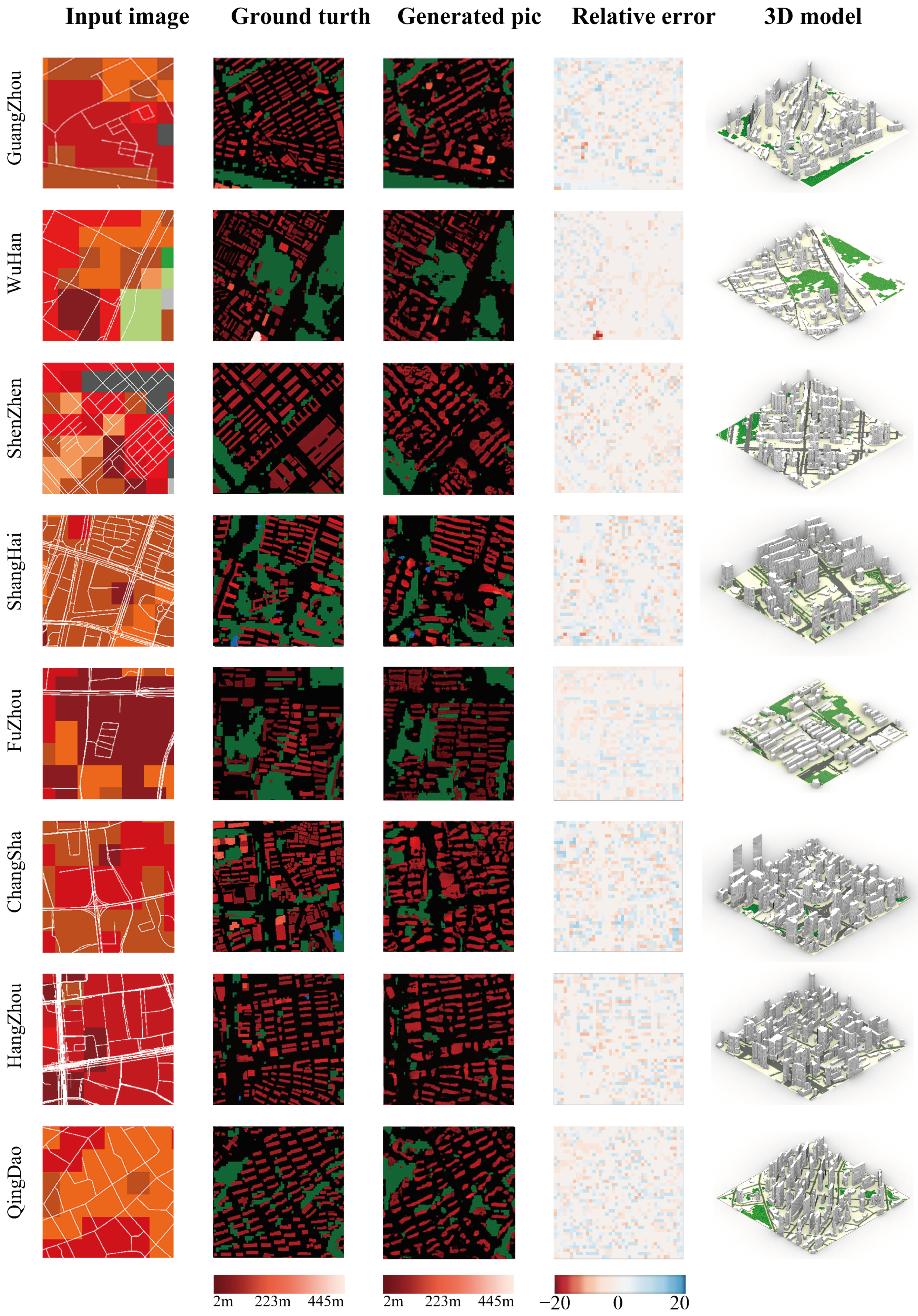
3.3.1. 3D Urban Morphology Generation
3.3.2. Evaluation of the Accuracy of the Model Based on LCZ Classification
3.3.3. Dynamic Response of 3D Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Prediction of Future Urban Morphology
4.2. Computational Efficiency and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, Y.; Wong, M.; Kwan, M.-P.; Pearce, J.; Feng, Z. Assessing multi-spatial driving factors of urban land use transformation in megacities: A case study of Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area from 2000 to 2018. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 27, 1090–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, C.; Zhang, D. Opportunities and challenges in green stormwater infrastructure (GSI): A comprehensive and bibliometric review of ecosystem services from 2000 to 2021. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtat, N.; Khirfan, L. The climate justice pillars vis-à-vis urban form adaptation to climate change: A review. Urban Clim. 2021, 39, 100951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzhaf, E.; Hofer, R. Monitoring Urban Structure Types as Spatial Indicators with CIR Aerial Photographs for a More Effective Urban Environmental Management. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2008, 1, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Jing, Y.; Yang, G.; Sun, R. A New Urban Functional Zone-Based Climate Zoning System for Urban Temperature Study. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.D.; Oke, T. Local Climate Zones for Urban Temperature Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1879–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jin, S.; Xiao, X.; Jin, C.; Xia, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S. Local climate zone ventilation and urban land surface temperatures: Towards a performance-based and wind-sensitive planning proposal in megacities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, Y.; Qiang, B.; Shang, J. Wasserstein Generative Recurrent Adversarial Networks for Image Generating. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Tang, P. Urban Morphological Feature Extraction and Multi-Dimensional Similarity Analysis Based on Deep Learning Approaches. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Shi, Y.; Ren, C.; Lau, K.K.-L.; Ng, E.Y.Y. Impact of Urban Overheating and Heat-Related Mortality in Hong Kong. In Urban Overheating: Heat Mitigation and the Impact on Health; Aghamohammadi, N., Santamouris, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 275–292. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Kwon, Y. Novel CNN-Based Approach for Reading Urban Form Data in 2D Images: An Application for Predicting Restaurant Location in Seoul, Korea. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, F. Integrating cellular automata with long short-term memory neural network to simulate urban expansion using time-series data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 127, 103676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Fujioka, T.; Katsuta, L.; Kikuchi, Y.; Oda, G.; Nakagawa, T.; Kitazume, Y.; Kubota, K.; Tateishi, U. Feasibility of new fat suppression for breast MRI using pix2pix. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2020, 38, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cira, C.-I.; Manso-Callejo, M.-Á.; Alcarria, R.; Fernández Pareja, T.; Bordel Sánchez, B.; Serradilla, F. Generative Learning for Postprocessing Semantic Segmentation Predictions: A Lightweight Conditional Generative Adversarial Network Based on Pix2pix to Improve the Extraction of Road Surface Areas. Land 2021, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, G.; Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Calautit, J.K.; Zhao, C.; An, N.; Peng, X. Accelerated environmental performance-driven urban design with generative adversarial network. Build. Environ. 2022, 224, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sabbagh, S.; Robles-Kelly, A.; Gao, S. Scene-cGAN: A GAN for underwater restoration and scene depth estimation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2025, 250, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, S.; Sojka, A.; Davila, C.C. Conditional generative adversarial networks for pedestrian wind flow approximation. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Symposium on Simulation for Architecture and Urban Design, Vienna, Austria, 25–27 May 2020; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Jia, W.; Wang, M.; Wu, Y.; Qiao, R.; Wu, Z. Automatic responsive-generation of 3D urban morphology coupled with local climate zones using generative adversarial network. Build. Environ. 2023, 245, 110855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Leng, H.; Yuan, Q.; Song, S. Impact of urban form on carbon emissions of residents in counties: Evidence from Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 56332–56349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Cloud and Shadow Removal for Sentinel-2 by Progressively Spatiotemporal Patch Group Learning. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019–2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 775–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Ren, C.; Xu, Y.; Lau, K.K.-L.; Shi, Y. Mapping the local climate zones of urban areas by GIS-based and WUDAPT methods: A case study of Hong Kong. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonck, M.-L.; Okujeni, A.; van der Linden, S.; Demuzere, M.; De Wulf, R.; Van Coillie, F. Influence of neighbourhood information on ‘Local Climate Zone’ mapping in heterogeneous cities. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 62, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerberg, K.; Brousse, O.; Martilli, A.; Mahdavi, A. Implications of employing detailed urban canopy parameters for mesoscale climate modelling: A comparison between WUDAPT and GIS databases over Vienna, Austria. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, e1241–e1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtel, B.; Alexander, P.J.; Beck, C.; Böhner, J.; Brousse, O.; Ching, J.; Demuzere, M.; Fonte, C.; Gál, T.; Hidalgo, J.; et al. Generating WUDAPT Level 0 data—Current status of production and evaluation. Urban Clim. 2019, 27, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; van Nistelrooij, M.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Sutar, P.; Houweling, S.; Varon, D.J.; Tol, P.; Gains, D.; Worden, J.; Aben, I. Daily detection and quantification of methane leaks using Sentinel-3: A tiered satellite observation approach with Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-5p. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 296, 113716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Ma, A.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cao, L. Self-Training Classification Framework with Spatial-Contextual Information for Local Climate Zones. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Keskar, R.; Kotharkar, R. Classifying heterogeneous urban form into local climate zones using supervised learning and greedy clustering incorporating Landsat dataset. Urban Clim. 2024, 53, 101770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, S.; He, S.; Lv, H. Generative adversarial network in mechanical fault diagnosis under small sample: A systematic review on applications and future perspectives. ISA Trans. 2022, 128, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Jiang, S.; Zhan, W.; Bechtel, B.; Liu, Z.; Demuzere, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, L.; Xia, W.; et al. Mapping local climate zones for cities: A large review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 292, 113573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touya, G.; Lokhat, I. Deep Learning for Enrichment of Vector Spatial Databases: Application to Highway Interchange. ACM Trans. Spat. Algorithms Syst. 2020, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugros, A.; Caplier, A.; Ospici, M. Are Adversarial Robustness and Common Perturbation Robustness Independent Attributes? In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1045–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.; Qi, J.; Huang, H.; Li, L. Combining 3D Radiative Transfer Model and Convolutional Neural Network to Accurately Estimate Forest Canopy Cover from Very High-Resolution Satellite Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10953–10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Hu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Feng, Z. Mapping Local Climate Zones in the Urban Environment: The Optimal Combination of Data Source and Classifier. Sensors 2022, 22, 6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Zou, B.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, X. Exploring the relationship between air temperature and urban morphology factors using machine learning under local climate zones. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 55, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzourides, P.; Eleftheriou, A.; Kyprianou, A.; Ching, J.; Neophytou, M.K.A. Linking local-climate-zones mapping to multi-resolution-analysis to deduce associative relations at intra-urban scales through an example of Metropolitan London. Urban Clim. 2019, 30, 100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Liu, L.; Ma, H. ESR-GAN: Environmental Signal Reconstruction Learning with Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Kong, X.; Luo, J. Curb-GAN: Conditional Urban Traffic Estimation through Spatio-Temporal Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Virtual, 6–10 July 2020; pp. 842–852. [Google Scholar]
- Pazhani, A.A.J.; Periyanayagi, S. A novel haze removal computing architecture for remote sensing images using multi-scale Retinex technique. Earth Sci. Inform. 2022, 15, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, X. Single Image Cloud Removal Using U-Net and Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 6371–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Shen, X.; Sun, M.; Li, B. β-Dropout: A Unified Dropout. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36140–36153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, E.J. Observations on the tanh–coth expansion method for finding solutions to nonlinear evolution equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 217, 1749–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, A.R.; Kang, D.-K. A Novel Diminish Smooth L1 Loss Model with Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Human Computer Interaction, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 24–26 November 2020; pp. 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Gong, J.; Fu, H.; Liu, W. Fabric Defect Detection Method Using SA-Pix2pix Network and Transfer Learning. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, C.; Yang, R.; Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y. Multisource Data Fusion and Adversarial Nets for Landslide Extraction from UAV-Photogrammetry-Derived Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, F.; Yi, B.; Wei, Z.; Liu, L. Pix2Pix-based DOA Estimation with Low SNR. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 10th Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and Propagation (APCAP), Xiamen, China, 4–7 November 2022; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Gomi, T.; Kijima, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Koibuchi, Y. Evaluation of a Generative Adversarial Network to Improve Image Quality and Reduce Radiation-Dose during Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, T.; Ren, T.; Chen, D.; Li, W.; Qiu, W. Day-to-Night Street View Image Generation for 24-Hour Urban Scene Auditing Using Generative AI. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Llabres-Valls, E.; Jiang, M.; Chen, F. Meta-Connectivity in Urban Morphology: A Deep Generative Approach for Integrating Human–Wildlife Landscape Connectivity in Urban Design. Land 2024, 13, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Hanna, S. Fluid grey 2: How well does generative adversarial network learn deeper topology structure in architecture that matches images? J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binarti, F.; Pranowo, P.; Aditya, C.; Matzarakis, A. Characterizing the local climate of large-scale archaeological parks in the tropics. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.Y.; Chun, K.P.; Mijic, A.; Mah, D.N.-Y.; He, Q.; Choi, B.; Lam, C.K.C.; Yetemen, O. Spatially-heterogeneous impacts of surface characteristics on urban thermal environment, a case of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, H.; Bian, H. Image to Image Translation Based on Differential Image Pix2Pix Model. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 77, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wu, Z. UDGAN: A new urban design inspiration approach driven by using generative adversarial networks. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2024, 11, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, E.; Ishida, Y.; Wang, Z.; Mochida, A. Proposal of LCZs categories and standards considering super high-rise buildings suited for Asian cities based on the analysis of urban morphological properties of Tokyo. Jpn. Archit. Rev. 2022, 5, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| City Sample | Pix2pix | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | R2 | PSNR | |
| Guangzhou | 0.617 | 0.780 | 13.905 |
| Wuhan | 0.580 | 0.787 | 14.115 |
| Shenzhen | 0.712 | 0.805 | 14.540 |
| Shanghai | 0.630 | 0.814 | 13.752 |
| Fuzhou | 0.723 | 0.862 | 16.029 |
| Hangzhou | 0.660 | 0.832 | 15.001 |
| Changsha | 0.653 | 0.839 | 15.229 |
| Qingdao Average | 0.611 0.648 | 0.795 0.814 | 14.165 14.592 |
| City Name | OA % | OAurb % | OAnat % | Kappa | F1_Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangzhou | 75.6% | 77.3% | 73.8% | 0.72 | 0.74 |
| Wuhan | 80.8% | 79.7% | 78.2% | 0.77 | 0.79 |
| Shenzhen | 79.2% | 80.2% | 79.4% | 0.81 | 0.83 |
| Shanghai | 86.5% | 83.4% | 87.1% | 0.83 | 0.86 |
| Fuzhou | 83.2% | 81.1% | 84.5% | 0.86 | 0.88 |
| Hangzhou | 83.1% | 82.8% | 85.3% | 0.84 | 0.85 |
| Changsha | 81.3% | 79.8% | 82.2% | 0.80 | 0.82 |
| Qingdao | 82.2% | 80.7% | 83.1% | 0.82 | 0.84 |
| Average | 81.5% | 80.6% | 81.7% | 0.81 | 0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Q. Pix2Pix-Based Modelling of Urban Morphogenesis and Its Linkage to Local Climate Zones and Urban Heat Islands in Chinese Megacities. Land 2025, 14, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040755
Wang M, Xiong Z, Zhao J, Zhou S, Wang Q. Pix2Pix-Based Modelling of Urban Morphogenesis and Its Linkage to Local Climate Zones and Urban Heat Islands in Chinese Megacities. Land. 2025; 14(4):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040755
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mo, Ziheng Xiong, Jiayu Zhao, Shiqi Zhou, and Qingchan Wang. 2025. "Pix2Pix-Based Modelling of Urban Morphogenesis and Its Linkage to Local Climate Zones and Urban Heat Islands in Chinese Megacities" Land 14, no. 4: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040755
APA StyleWang, M., Xiong, Z., Zhao, J., Zhou, S., & Wang, Q. (2025). Pix2Pix-Based Modelling of Urban Morphogenesis and Its Linkage to Local Climate Zones and Urban Heat Islands in Chinese Megacities. Land, 14(4), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040755








