Segmentation Performance and Mapping of Dunes in Multi-Source Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
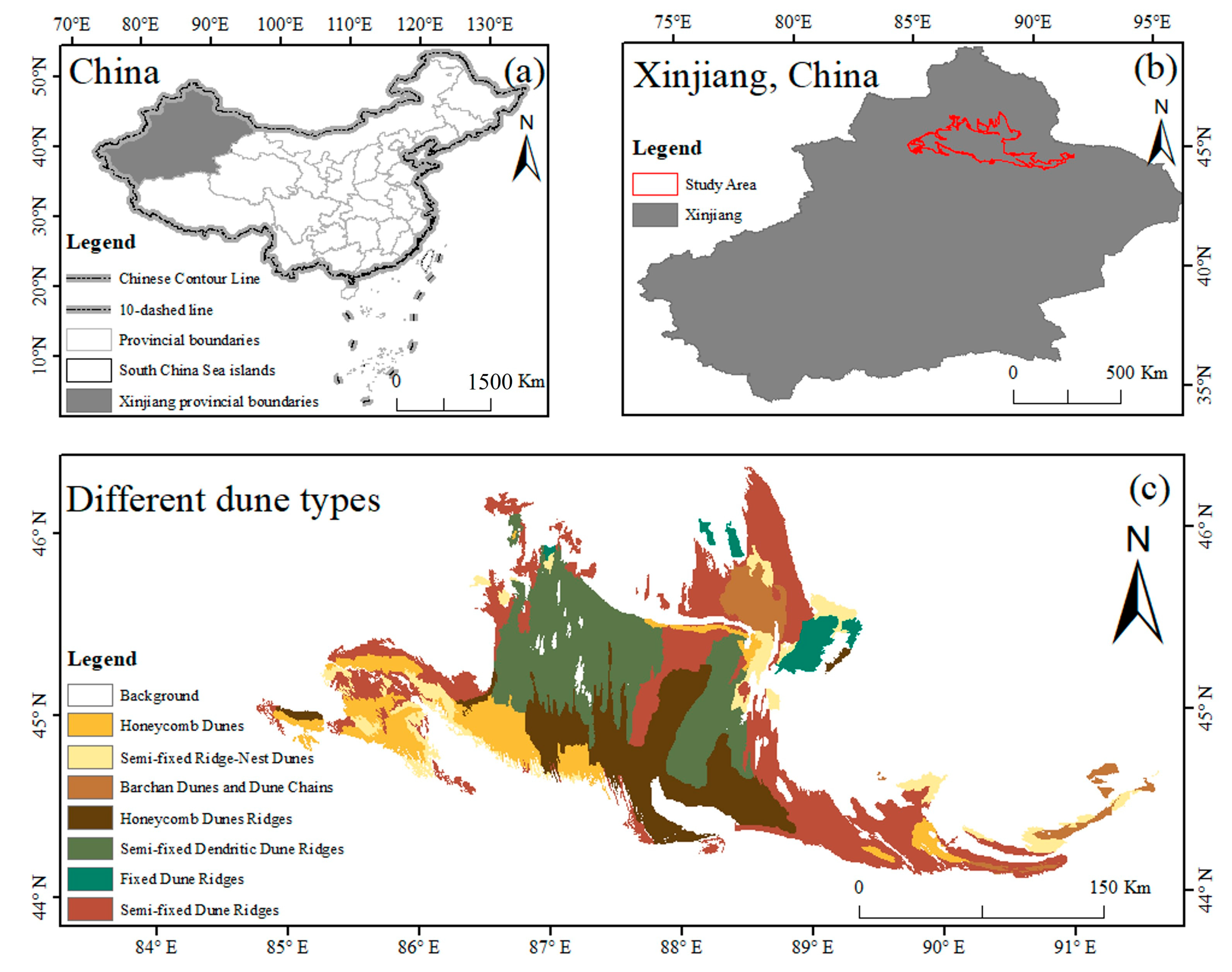
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Image Acquisition and Processing
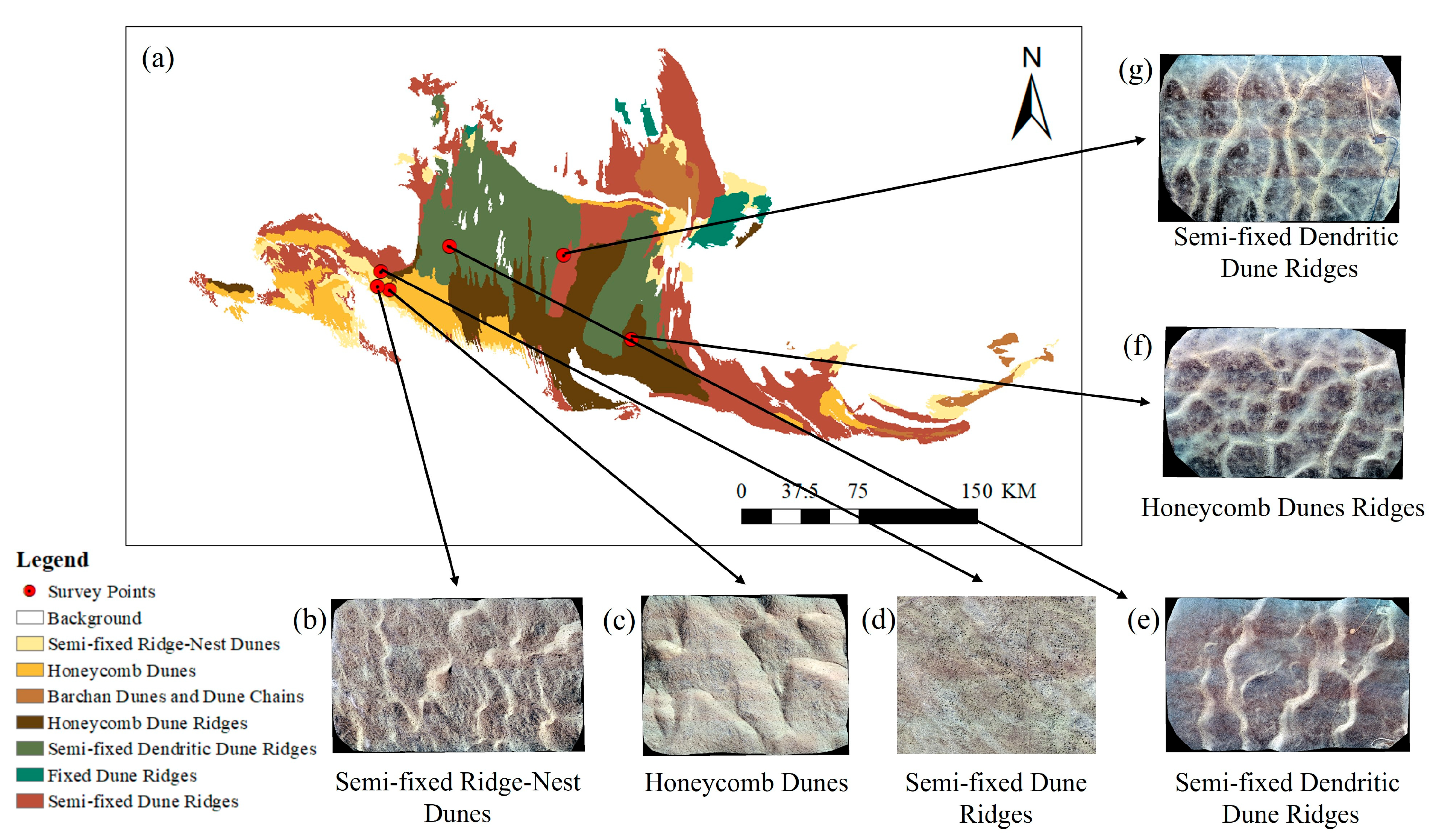
2.2.2. Label Data
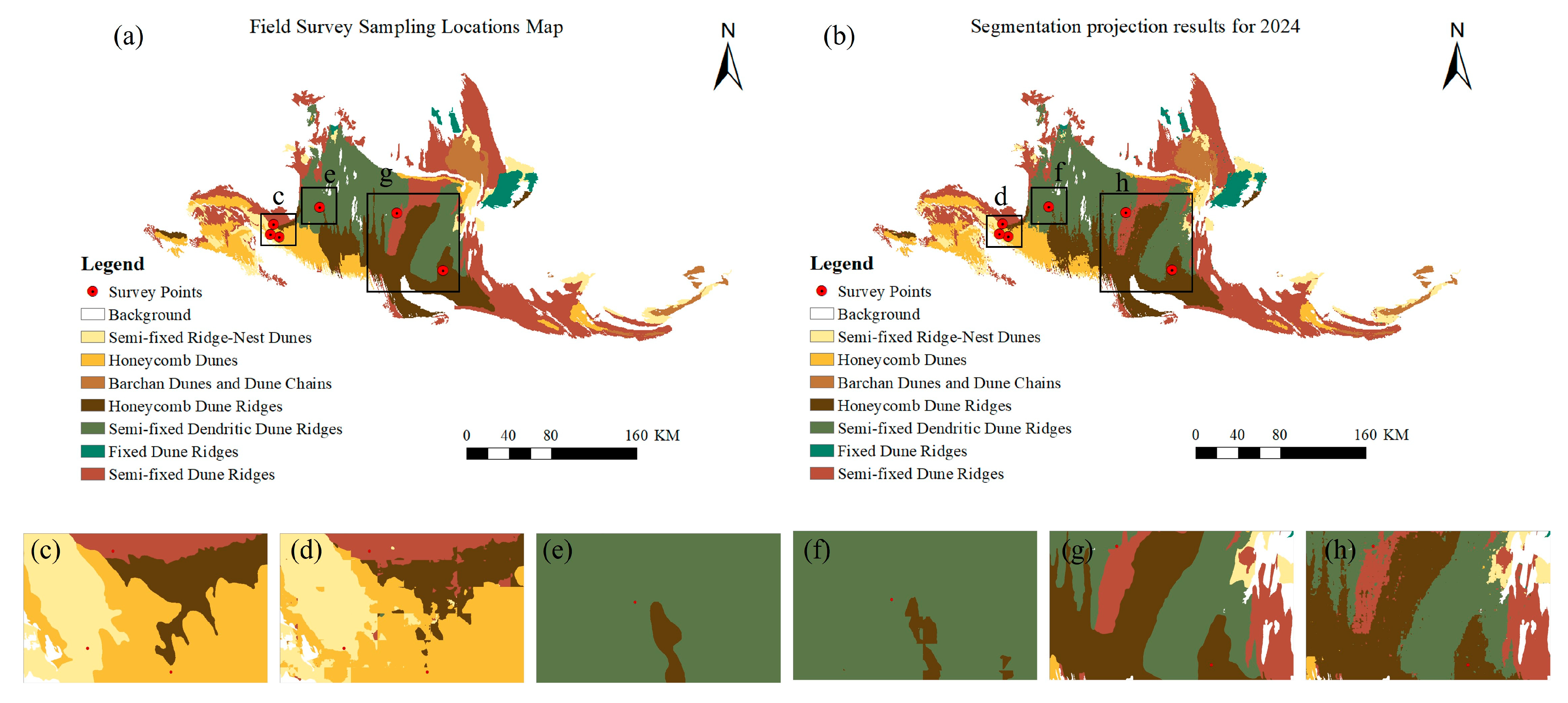
2.2.3. Field Validation Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. DeepLab v3
2.3.2. U-Net
2.3.3. U-Net++
2.4. Experiment Introduction
2.4.1. Dataset Construction
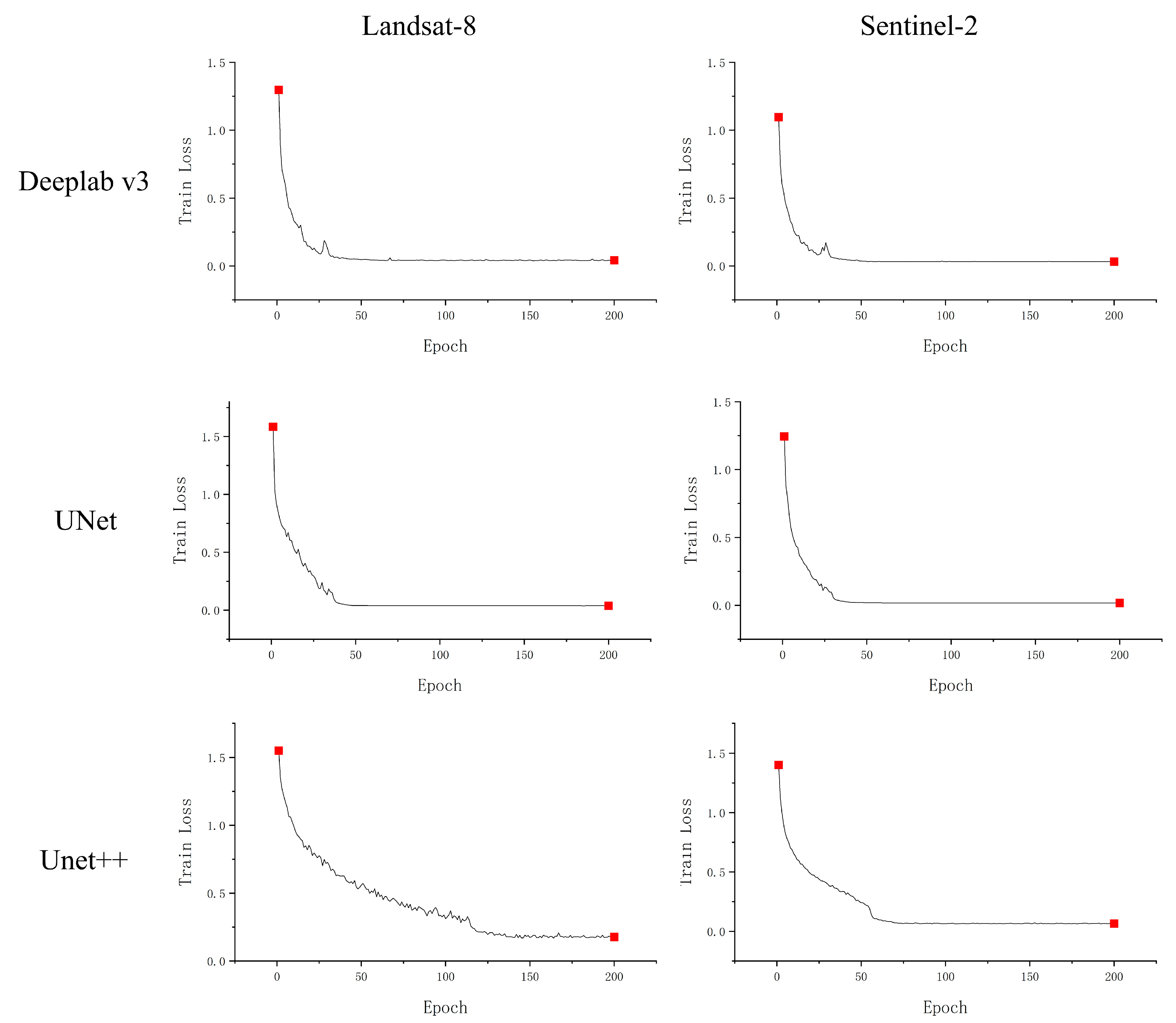
2.4.2. Experimental Setup
2.4.3. Model Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Segmentation Performance with Different Batch Sizes
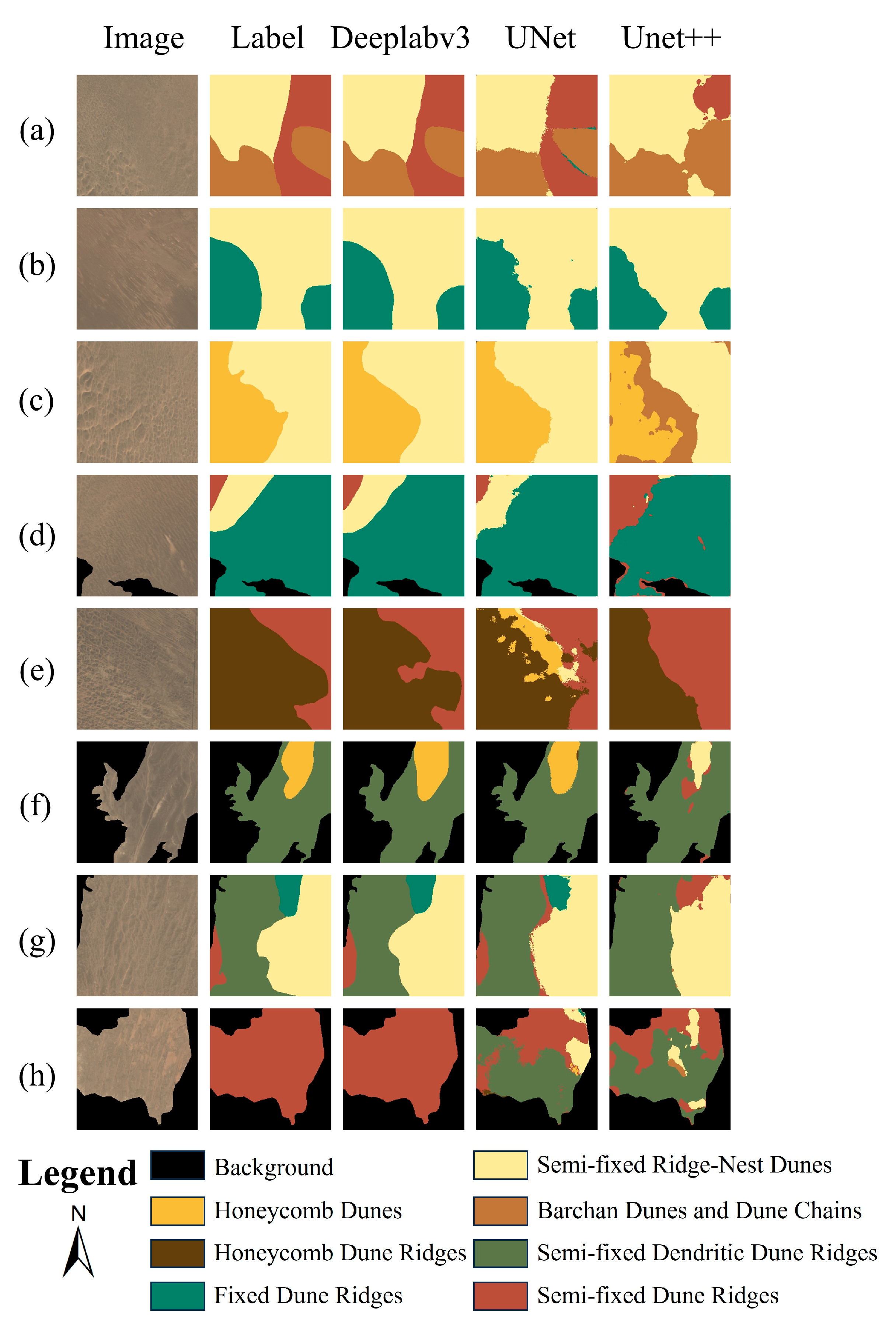
3.2. Segmentation Performance of Different Models
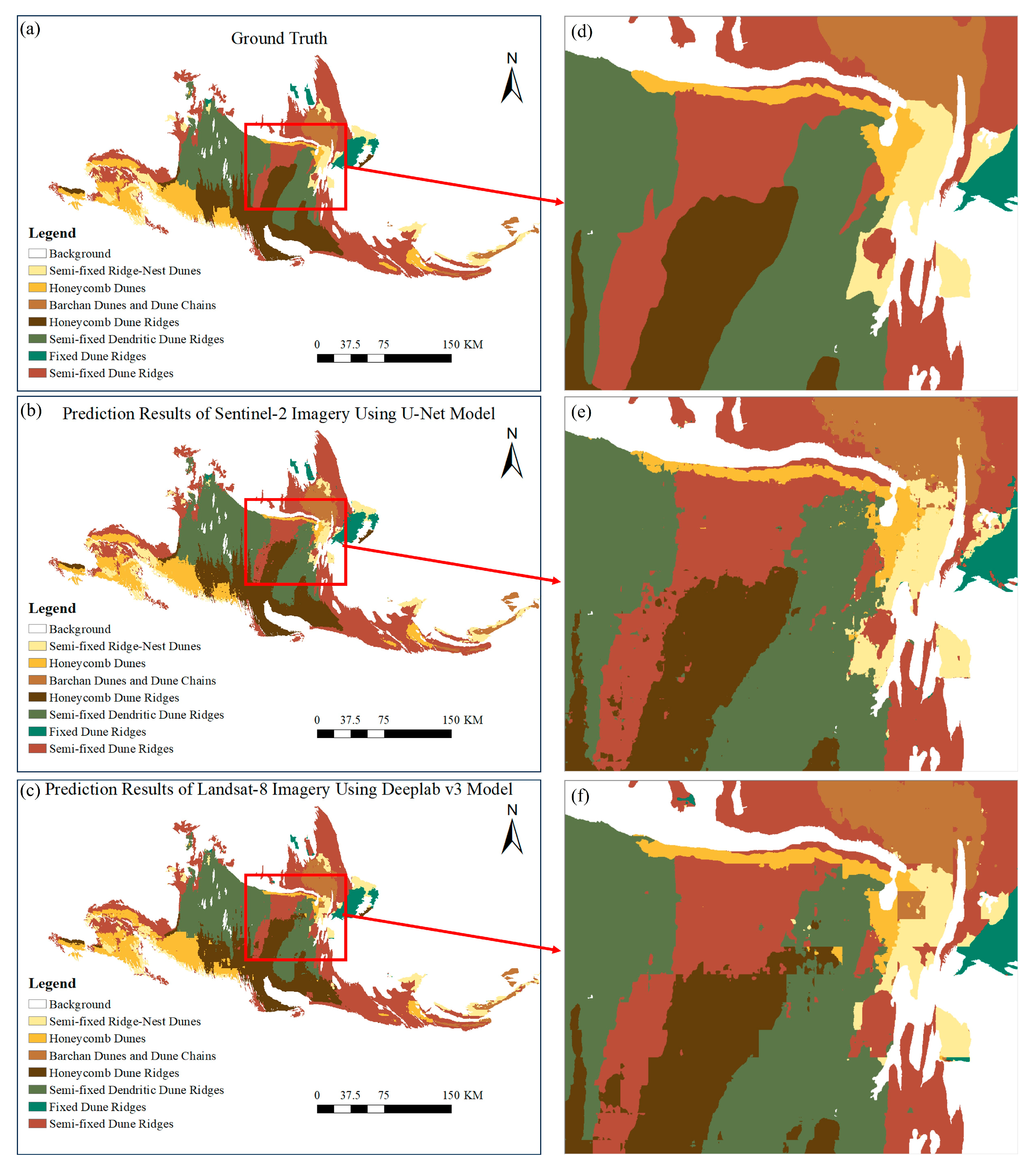
3.3. Segmentation Mapping of the Gurbantünggüt Desert
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- As the batch size increases, the segmentation performance improves. When the batch size reaches 12, the model’s performance improvement slows down, and the optimal batch size is 16. The number of epochs required for model convergence varies with different models and image data sources, and appropriate epoch values should be set according to the actual training process.
- The segmentation performance when using Sentinel-2 images is generally superior to that with Landsat-8 images, providing more detailed features for model recognition.
- The segmentation performance of U-Net on Sentinel-2 images was the best among all experiments, with overall accuracy (OA) of 92.45%. On Landsat-8 images, DeepLab v3 achieved the best segmentation performance, with OA of 86.63%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrera, D.; Bandeira, L.; Santana, R.; Lozano, J.A. Detection of sand dunes on Mars using a regular vine-based classification approach. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 163, 858–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Kennedy, D.M.; Konlechner, T.M. Coastal dune mobility over the past century: A global review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2020, 44, 814–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loope, D.B.; Rowe, C.M.; Joeckel, R.M. Annual monsoon rains recorded by Jurassic dunes. Nature 2001, 412, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.B.; Qu, J.J.; Qian, G.Q.; Zhang, Z.S. Classification of Aeolian and Sand Dune Landforms in the Kumtag Desert. China Desert. 2011, 31, 805–814. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vitousek, S.; Buscombe, D.; Vos, K.; Barnard, P.L.; Ritchie, A.C.; Warrick, J.A. The future of coastal monitoring through satellite remote sensing. Camb. Prism. Coast. Futures 2023, 1, e10. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, W. An Auto-Detection and classification algorithm for identification of sand dunes based on remote sensing images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 125, 103592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownett, J.; Mills, R. The development and application of remote sensing to monitor sand dune habitats. J. Coast. Conserv. 2017, 21, 643–656. [Google Scholar]
- de Figueiredo Meyer, M. The Effect of Spatial Resolution on Biomass Estimation Through Multispectral Imagery: A Case Study on C. edulis. Master’s Thesis, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz, C.H.; Levin, N.; Barchyn, T.E.; Baddock, M.C. Remote sensing and spatial analysis of aeolian sand dunes: A review and outlook. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2012, 111, 319–334. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, P. Automated measurement of sand dune migration using multi-temporal lidar data and GIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 5426–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.C. Research on Dune Morphology Classification Based on Deep Learning and Multi-Source Remote Sensing Imagery: A Case Study of the Southern Edge of the Gurbantünggüt Desert. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang University, Urumchi, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.M. Research on Dune Type Information Extraction Based on Deep Learning. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang University, Urumchi, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Ali, E.; Yu, J.; Du, S. Global perspectives on sand dune patterns: Scale-adaptable classification using Landsat imagery and deep learning strategies. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 218, 781–801. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yan, J.H.; Ye, W.Z.; Dong, S.; Yang, Z.K. Automatic Dune Morphology Classification Method Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Arid. Zone Resour. Environ. 2024, 38, 121–129. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Diniega, S.; Kreslavsky, M.; Radebaugh, J.; Silvestro, S.; Telfer, M.; Tirsch, D. Our evolving understanding of aeolian bedforms, based on observation of dunes on different worlds. Aeolian Res. 2017, 26, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.D.; Wu, Z.; Liu, S.; Di, X.M. Introduction to the Deserts of China; Revised Edition; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1980; p. 107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdsson, J.; Armannsson, S.E.; Ulfarsson, M.O.; Sveinsson, J.R. Fusing Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 Satellite Images Using a Model-Based Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Song, H.; Huang, J.; Zhong, H.; Zhan, R.; Teng, X.; Qiu, Z.; He, M.; Cao, J. Flood Detection in Dual-Polarization SAR Images Based on Multi-Scale Deeplab Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, M. Bag of tricks for image classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, C. On the sand surface stability in the southern part of Gurbantünggüt Desert. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2005, 48, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.B. Environmental Studies of the Gurbantünggüt Desert; China Basic Education Subject Yearbook. Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011; p. 489. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fearnehough, W.; Fullen, M.; Mitchell, D.; Trueman, I.; Zhang, J. Aeolian deposition and its effect on soil and vegetation changes on stabilised desert dunes in northern China. Geomorphology 1998, 23, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeloff, V.C.; Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Anderson, M.; Cook, B.; Crawford, C.J.; Friedl, M.; Gao, F.; Gorelick, N.; Hansen, M.; et al. Need and vision for global medium-resolution Landsat and Sentinel-2 data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 300, 113918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, L.; Li, X.; Peng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, P. Progress and trends in the application of Google Earth and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essel, B. Developing an Enhanced Photogrammetric Methodology for Mapping Water Bodies Using Low-Cost Drones. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Ireland, Maynooth, Ireland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Aizatin, A.; Nugraha, I.G.B.B. Comparison of semantic segmentation deep learning methods for building extraction. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Computer Engineering, Network, and Intelligent Multimedia (CENIM), Surabaya, Indonesia, 22–23 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: DLMIA ML-CDS 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11045, pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, X.; Pang, Y.; Han, J.; Pan, J. Cascaded hierarchical atrous spatial pyramid pooling module for semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 110, 107622. [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum, M.; Souri, H.; Ni, R.; Shu, M.; Prabhu, V.; Somepalli, G.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Ibrahim, M.; Bardes, A.; Hoffman, J.; et al. Battle of the backbones: A large-scale comparison of pretrained models across computer vision tasks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 29343–29371. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenhende, S.; Georgoulis, S.; Van Gansbeke, W.; Proesmans, M.; Dai, D.; Van Gool, L. Multi-task learning for dense prediction tasks: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3614–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.X.; Huang, M.E.; Gao, F.; Tao, T.Y.; Wu, Z.F.; Zhu, Y.C. Water Body Extraction from Remote Sensing Imagery Based on U-Net, U-Net++, and Attention-U-Net Networks. Surv. Mapp. Bull. 2024, 8, 26–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, F. The Effect of Batch Normalization on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Master’s Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, A.; Mohri, M.; Zhong, Y. Cross-entropy loss functions: Theoretical analysis and applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 23803–23828. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-H.; Chuang, J.-H.; Liu, T.-L. Regularized background adaptation: A novel learning rate control scheme for Gaussian mixture modeling. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 20, 822–836. [Google Scholar]
- Acun, B.; Murphy, M.; Wang, X.; Nie, J.; Wu, C.-J.; Hazelwood, K. Understanding training efficiency of deep learning recommendation models at scale. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 February–3 March 2021; pp. 802–814. [Google Scholar]
- Susmaga, R. Confusion matrix visualization. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Information Processing and Web Mining: Proceedings of the International IIS: IIPWM ‘04 Conference; Zakopane, Poland, 17–20 May 2004, pp. 107–116.
- Du Pont, S.C.; Rubin, D.M.; Narteau, C.; Lapôtre, M.G.; Day, M.; Claudin, P.; Livingstone, I.; Telfer, M.W.; Radebaugh, J.; Gadal, C. Complementary classifications of aeolian dunes based on morphology, dynamics, and fluid mechanics. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 255, 104772. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R. The Development of Barchan Dunes and the Evolution of Aeolian Environment in Western Gurbantunggut Desert. Master’s Thesis, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China, 2023. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]





| Data | Training Set | Validation Set | Test Set | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-8 | 653 | 326 | 109 | 1088 |
| Sentinel-2 | 1372 | 686 | 229 | 2287 |
| Data | Batch Size | OA | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-8 | 16 | 86.63% | 80.46% | 74.62% | 76.82% |
| 12 | 84.90% | 79.05% | 74.12% | 75.92% | |
| 8 | 74.71% | 65.27% | 58.63% | 60.92% | |
| 4 | 69.65% | 52.67% | 43.73% | 43.84% | |
| Sentinel-2 | 16 | 92.32% | 89.96% | 90.38% | 90.13% |
| 12 | 92.03% | 89.22% | 89.88% | 89.51% | |
| 8 | 91.37% | 89.69% | 87.72% | 88.63% | |
| 4 | 89.19% | 87.42% | 84.09% | 85.60% |
| Model | Data | OA | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLab v3 | Landsat-8 | 86.63% | 80.46% | 74.62% | 76.82% |
| Sentinel-2 | 92.32% | 89.96% | 90.38% | 90.13% | |
| U-Net | Landsat-8 | 85.61% | 78.63% | 73.91% | 75.85% |
| Sentinel-2 | 92.45% | 90.03% | 90.94% | 90.45% | |
| U-Net++ | Landsat-8 | 86.02% | 78.65% | 76.98% | 77.71% |
| Sentinel-2 | 89.15% | 86.50% | 86.06% | 86.24% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, P.; An, J.; Zheng, J.; Han, W.; Tuerxun, N.; Cui, B.; Zhao, X. Segmentation Performance and Mapping of Dunes in Multi-Source Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Learning. Land 2025, 14, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040713
Zhao P, An J, Zheng J, Han W, Tuerxun N, Cui B, Zhao X. Segmentation Performance and Mapping of Dunes in Multi-Source Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Learning. Land. 2025; 14(4):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040713
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Pengyu, Jiale An, Jianghua Zheng, Wanqiang Han, Nigela Tuerxun, Bochao Cui, and Xuemi Zhao. 2025. "Segmentation Performance and Mapping of Dunes in Multi-Source Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Learning" Land 14, no. 4: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040713
APA StyleZhao, P., An, J., Zheng, J., Han, W., Tuerxun, N., Cui, B., & Zhao, X. (2025). Segmentation Performance and Mapping of Dunes in Multi-Source Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Learning. Land, 14(4), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040713





