Abstract
Wetlands provide essential benefits, including flood control, water quality enhancement, shoreline erosion prevention, natural resource conservation, recreational opportunities, and esthetic value. However, climate change and human activities have recently posed significant threats to these ecosystems. To address this issue, we employed an integrated approach combining remote sensing and the cloud-free Google Earth Engine (GEE) to monitor the impacts of climate change and human activities on Parishan Wetland in Iran. In this study, various climatic and anthropogenic factors, including air temperature (AT), precipitation, built-up area, croplands, and groundwater storage, were analyzed over the period from 2001 to 2010 to explore their potential effects on wetland conditions. The Pearson correlation test was used to assess the relationships between these variables and wetland health. Also, non-parametric Mann–Kendall (MK) and Pettitt tests were employed to identify monotonic trends and shifts in the time series. The findings suggest a complex interplay of climatic and anthropogenic factors impacting the wetland’s ecosystem. Groundwater availability emerged as the most influential factor, with a very strong positive correlation of 0.92, highlighting the critical role of groundwater in sustaining wetland ecosystems. Air temperature values in recent years have shown a significant increasing trend, while precipitation exhibits a statistically significant decreasing trend. These factors, along with the slightly increasing built-up area, which negatively impacts the natural ecosystem, indicate an urgent need to restore the wetland.
1. Introduction
Wetlands contribute to approximately 40% of the total value of ecosystem services, which are the benefits provided by natural systems that enhance social welfare, including food supply, biodiversity preservation, and flood control [1,2]. Wetlands serve as transitional areas between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, where the water table is typically at or near the surface or the land is covered by shallow water [3]. These ecosystems play an essential role in supporting the environment, providing critical habitats for many unique species of plants and animals [4,5].
Wetlands offer numerous benefits, such as water purification, natural hazard protection, soil and water conservation, and recreational opportunities [6,7]. However, in recent decades, both human activities and climate change have impacted ecosystems, particularly in semi-arid and arid regions. Human-induced factors such as urban expansion and intensified agriculture have led to a 35% global loss of natural wetlands since the 1970s, while artificial wetlands have increased by 233% [8,9]. As urban areas expand, impervious surfaces such as roads, buildings, and parking lots multiply, preventing rainwater infiltration, which is essential for recharging local aquifers and sustaining wetlands [10]. Moreover, agricultural practices in these dry regions rely heavily on irrigation, often drawing water from local sources such as rivers, aquifers, and wetlands. Given the naturally low rainfall, the additional demand for irrigation further exacerbates water scarcity [11]. Climate change poses additional threats, including declining freshwater availability and rising sea levels [12]. The warming trend associated with climate change has raised concerns about global ecosystems, particularly wetlands, which are highly sensitive to changes in temperature and precipitation patterns [13]. These changes affect rainfall distribution and evaporation rates, leading to fluctuations in wetland water levels. Many wetland species are adapted to specific environmental conditions, and variations in temperature and water availability threaten their survival, resulting in population shifts, altered migration patterns, and, in some cases, local extinctions [14,15]. Consequently, monitoring wetlands to assess the effects of human activities and climate change is essential to obtain accurate, consistent, and up-to-date data on key attributes such as changes in size, type, and condition.
Remote sensing techniques have proven invaluable in wetland identification and monitoring, offering satellite-based data to track changes in wetland extent, vegetation cover, and water quality [16,17]. These techniques are essential for effective wetland management and conservation, as they reduce the need for extensive fieldwork, provide broad spatial coverage, and are both cost effective and time efficient [18]. Recent advancements in remote sensing have significantly improved the spatial, spectral, and temporal resolution of satellite imagery, providing a golden opportunity for the spatiotemporal monitoring of wetlands [19,20]. However, less attention has been given to using remote sensing to monitor the combined effects of anthropogenic and climatic factors on wetlands. Multispectral satellite imagery, especially from the Landsat series, is widely used for wetland mapping due to its extensive coverage, moderate resolution, long historical record, and free accessibility, making it a primary resource for tracking wetland dynamics [21,22]. With advancements in big data, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, the ability to extract meaningful wetland-related information from remote sensing data has significantly evolved, necessitating the development of efficient processing tools for handling large datasets [23]. Google Earth Engine (GEE), a cloud-based geospatial data processing platform developed by Google in 2010, leverages Google’s server capacity to enable large-scale, long-term geospatial analysis [24,25]. GEE provides access to vast amounts of global remote sensing data, including Landsat, MODIS, Sentinel, and GF-1 imagery, along with thematic datasets covering climate, temperature, ecology, and socioeconomic factors [26]. Additionally, GEE offers free access to anthropogenic data, such as urban development, land use/cover, and surface water consumption, making it a powerful tool for comprehensive, long-term monitoring of human impacts on wetlands [27].
A brief review of the literature shows that numerous studies have evaluated the effects of climate change on wetlands [28,29,30,31,32,33]. However, despite an increasing number of studies on the combined impacts of climate change and anthropogenic factors on wetlands, existing research often considers a limited range of indicators, such as temperature and land cover changes [34,35,36]. In contrast, the present study intends to provide a more comprehensive analysis by examining various climatic and anthropogenic factors, including air temperature (AT), precipitation, built-up areas, croplands, and groundwater storage. This study focused on the Parishan Wetland in Iran and investigated environmental challenges from 2001 to 2010, a period chosen due to the near-complete drying of the wetland in 2010. Furthermore, this study aimed to employ the cloud-based capabilities of GEE to monitor the impacts of climate change and human activities on wetlands, offering a data-driven approach to sustainable wetland management.
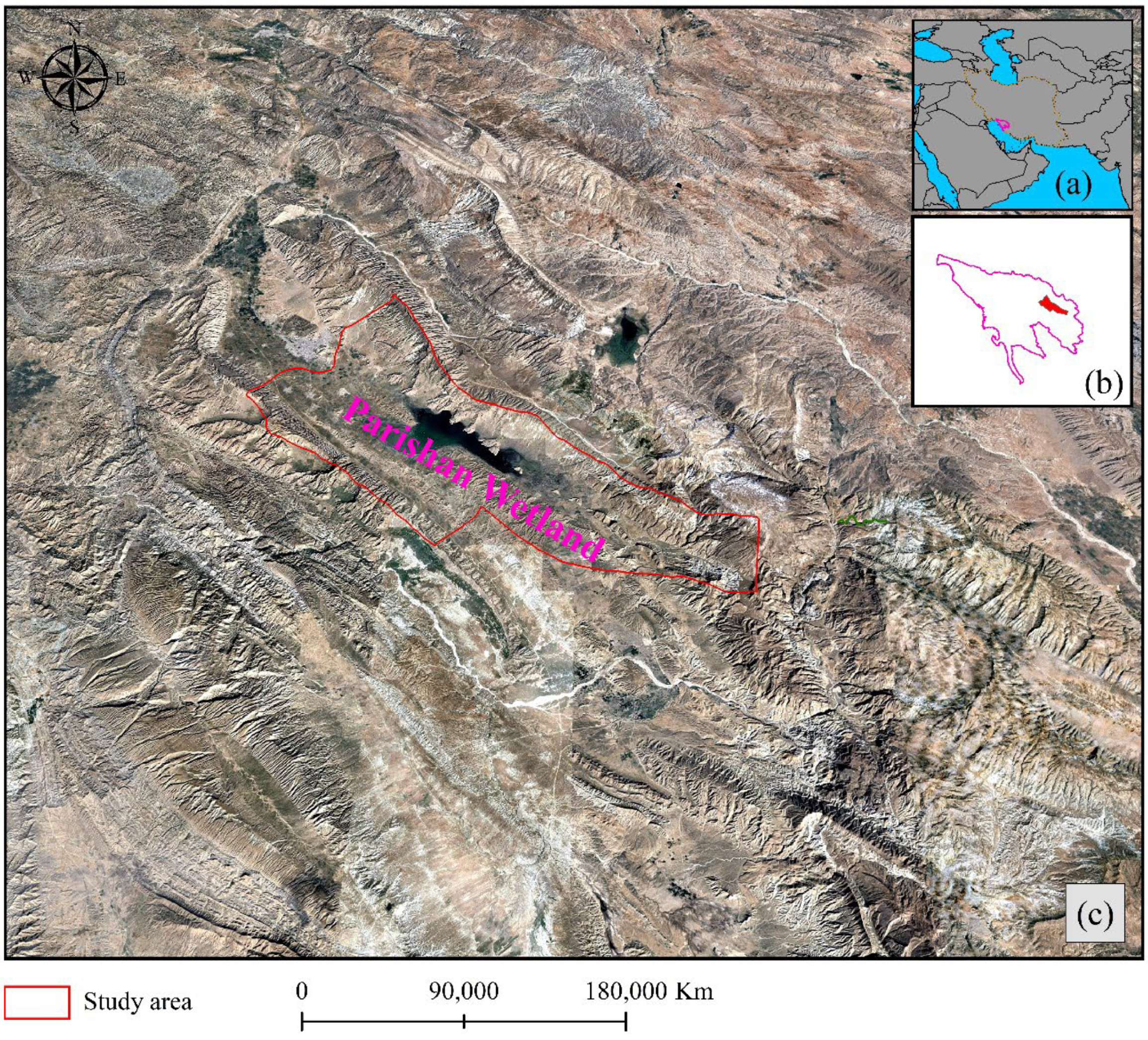
2. Location of Study Area
The Parishan Wetland, a permanent freshwater lake fed by springs and seasonal streams, is located in Fars Province, approximately 12 km southeast of Kazeroun (Figure 1). The wetland’s average depth fluctuates between 2 and 2.5 m, depending on annual rainfall variations. Situated at an elevation of 820 m above sea level, Parishan Wetland experiences warm, dry summers and mild winters [37]. It plays a crucial role as a habitat for a diverse range of wintering waterfowl, as well as breeding waterfowl populations, especially during wetter years. Located in an enclosed drainage basin within a broad valley, the wetland’s water ranges from brackish to saline, with salinity levels varying according to the wetland’s size [38].
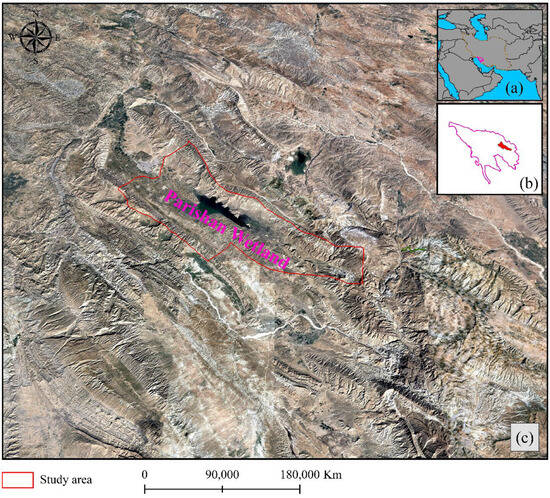
Figure 1.
Location of study: (a) in the southwest of Iran, (b) basins, and (c) Parishan Wetland represented on the satellite image for the year 2002, when water was available.
From a climatic perspective, Parishan Wetland lies within the warm zone of Fars Province, specifically in the Persian precipitation zone. This zone extends from the central region near the Persian Gulf to southern Kerman and Fars and receives approximately 60% of its precipitation during winter, making it the region with the highest winter rainfall concentration in Iran [39]. In recent years, declining annual rainfall has caused the wetland’s water levels to drop significantly, bringing it close to drying up. Seasonal temperature fluctuations range from approximately 4 °C in winter to around 32 °C in summer. In addition to climatic challenges, anthropogenic activities have significantly impacted the wetland over the past few decades, exacerbating its environmental challenges [40].
3. Materials and Methodology
3.1. Materials
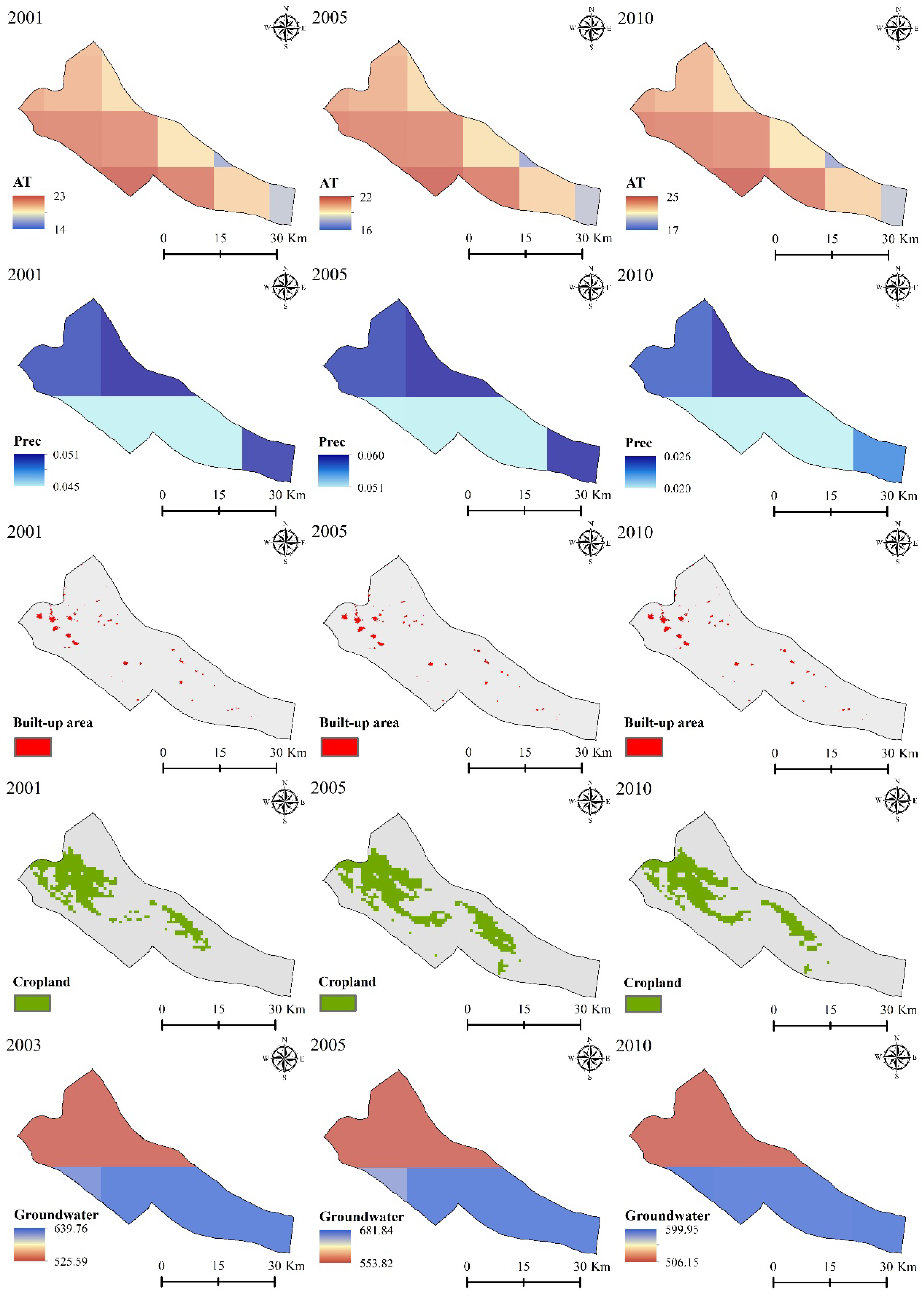
The present study investigated the relationship between wetland and various climatic and anthropogenic factors over the period from 2001 to 2010. The analyzed variables included AT, precipitation, built-up areas, croplands, and groundwater storage. Table 1 provides detailed information on these selected variables, while Figure 2 illustrates the range of climatic and anthropogenic factors used to assess the impacts of climate change and human activities on wetlands during this period.

Table 1.
Further details on the various climatic and anthropogenic variables employed, including their full names, products, and spatial resolutions, to assess their effects on Parishan Wetland.
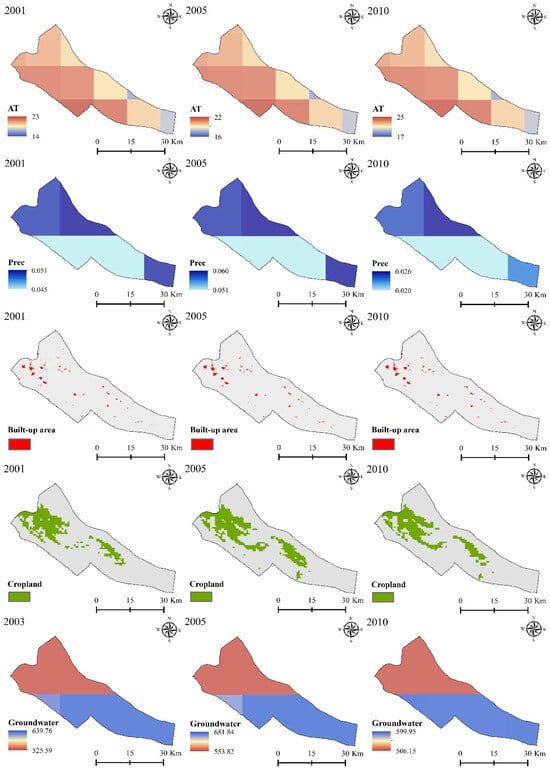
Figure 2.
Examples of the climatic and anthropogenic variables employed for the years 2001, 2005, and 2010, along with their respective ranges in different units, were used to assess their effects on Parishan Wetland.
3.2. Methodology
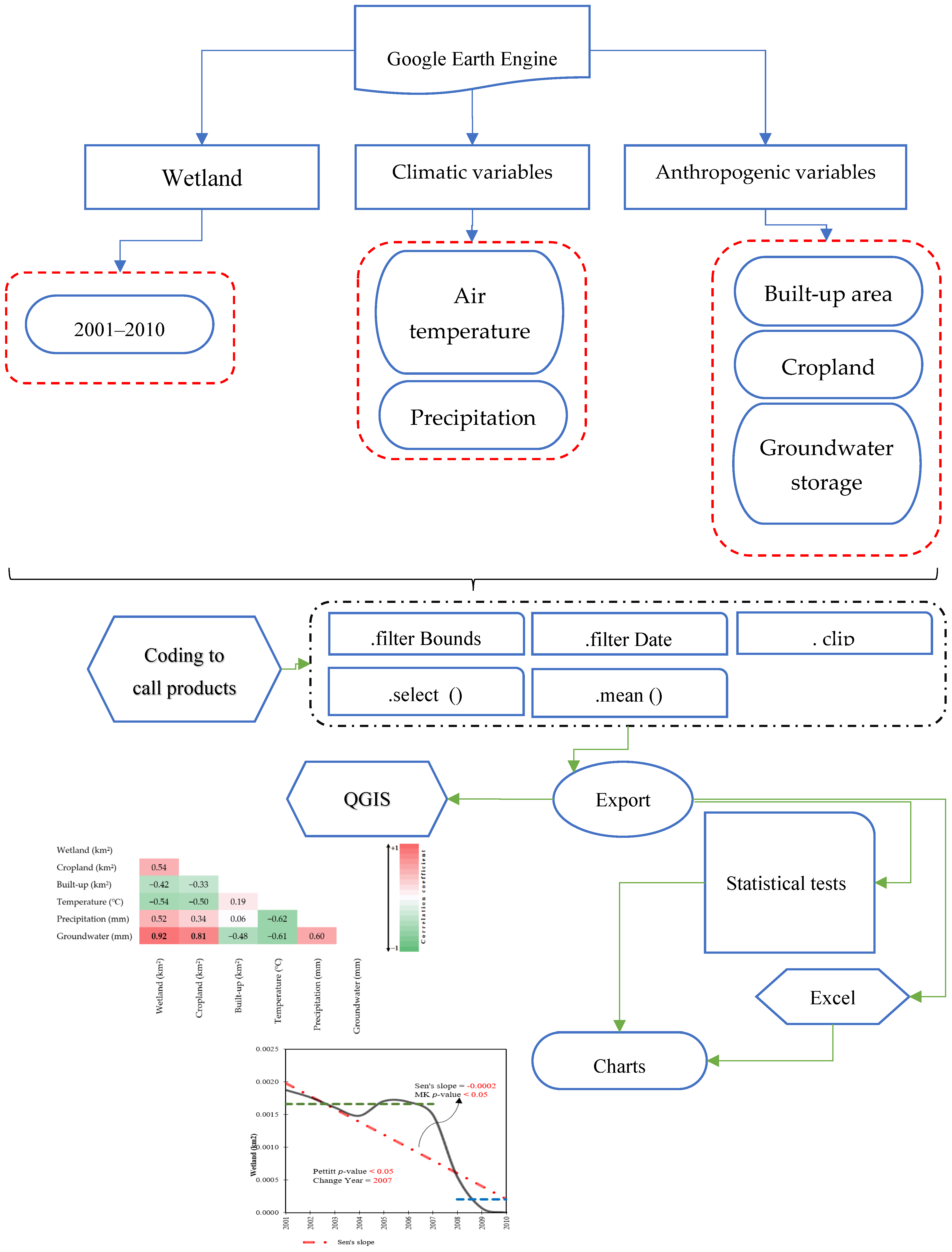
- To assess the impacts of climate change and human activities on wetlands, various climatic and anthropogenic variables were analyzed within GEE. GEE supports two geographic data structures: raster-based Images and vector-based Features. This flexibility enhances the interpretation of environmental phenomena [45]. For this study, Images were chosen to represent our datasets due to their suitability for handling large-scale environmental data and performing extensive analyses. Features in GEE, in contrast, consist of geometric elements such as points, lines, or polygons, each accompanied by a property dictionary that provides detailed spatial attributes. This dual structure in GEE provides flexibility in manipulating geographic data, making it easier to analyze environmental changes [46]. We began by delineating both the study area and the study period. Using QGIS Desktop version 3.30.3, we outlined Parishan Wetland as the area of interest. The study period was set from 2001 to 2010, covering a decade of data that reflect both climate variability and human influences. Next, we extracted key variables from GEE that are critical for understanding the impacts of climate and human activities on wetlands. These included AT, precipitation, built-up areas, cropland extent, and groundwater storage. Each variable was sourced from specialized satellite products and environmental datasets, ensuring a comprehensive analysis of the relationships between climate factors, human activity, and wetland health. All variables were exported in GeoTIFF and CSV formats to enable detailed analysis. The implemented code facilitated the execution operations, including (a) spatial subset on the interested area, (b) temporal subset on the collection datasets, (c) selecting the targeted datasets, and (d) exporting the selected datasets to perform further analysis. Figure 3 shows an overview of the applied methodology.
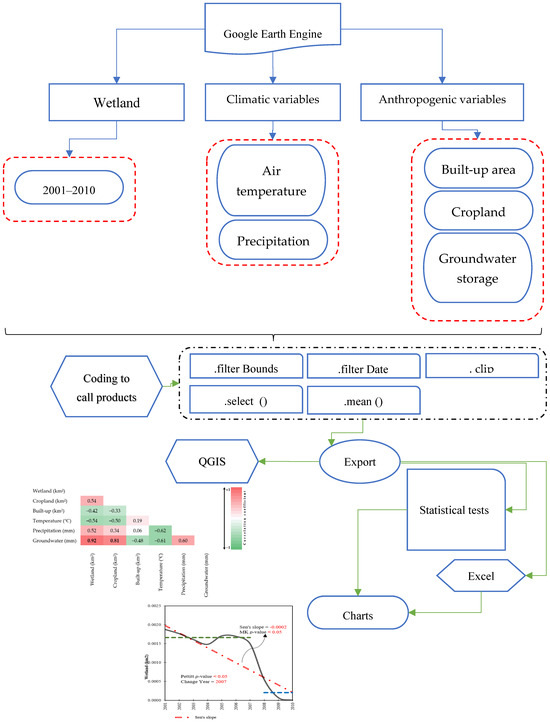 Figure 3. An overview of the applied methodology for detecting the effects of climate change and anthropogenic activities on wetlands.
Figure 3. An overview of the applied methodology for detecting the effects of climate change and anthropogenic activities on wetlands.
Statistical Analysis
To assess the relationships between climate, anthropogenic variables, and wetlands, we applied the Pearson correlation coefficient. Furthermore, the Mann–Kendall (MK) test was used to detect significant long-term trends. The effect of autocorrelation was addressed using the modified MK test proposed by Hamed and Rao [46]. The magnitude of the trend was quantified using Sen’s slope estimator [47]. The Pettitt test [48] was employed to identify abrupt shifts in the time series. These tests have been extensively applied in numerous studies investigating the impacts of climate change on Earth’s natural systems and processes [49,50,51]. All these statistical methods are comprehensively described in Sadeqi et al. [52].
4. Results
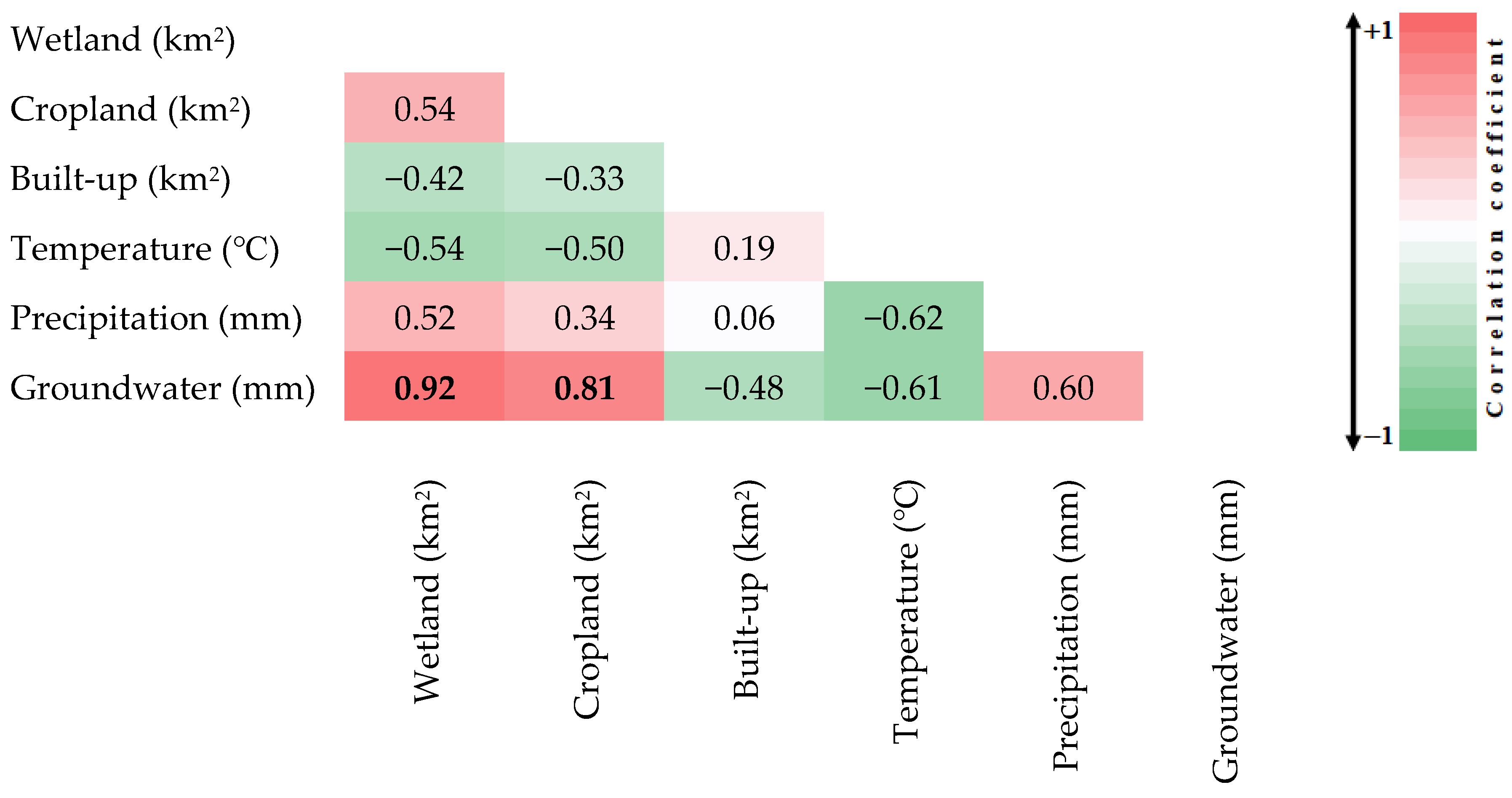
An integrated approach combining remote sensing and GEE is employed to monitor the impacts of climate change and anthropogenic activities on wetlands in southwest Iran. The results demonstrate significant correlations between climatic factors, namely AT and precipitation, and wetland conditions, as shown in Figure 4. This study found that AT negatively correlated with wetland area (−0.54) from 2001 to 2010. This suggests that as AT increased, the wetland area decreased. These findings align with [53], which also reported the harmful effect of rising AT on wetland health in Iran. Furthermore, a positive correlation coefficient of 0.52 was found between precipitation and Parishan Wetland conditions, indicating that decreased rainfall negatively impacted wetland preservation. This result is consistent with the findings of [54], which documented a similar relationship between precipitation and wetland sustainability. In terms of anthropogenic variables, a negative correlation of −0.42 was identified between the expansion of built-up areas and wetland health, highlighting the detrimental impact of urbanization on wetlands. Groundwater availability was identified as the most influential factor, with a very high positive correlation coefficient of 0.92 with wetland conditions, indicating that groundwater plays a crucial role in maintaining wetland ecosystems in the Parishan Wetland ecosystem. Previous studies showed the adverse effects of groundwater decline in water resources in Iran [55,56].
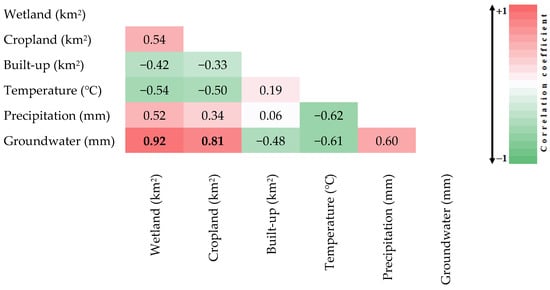
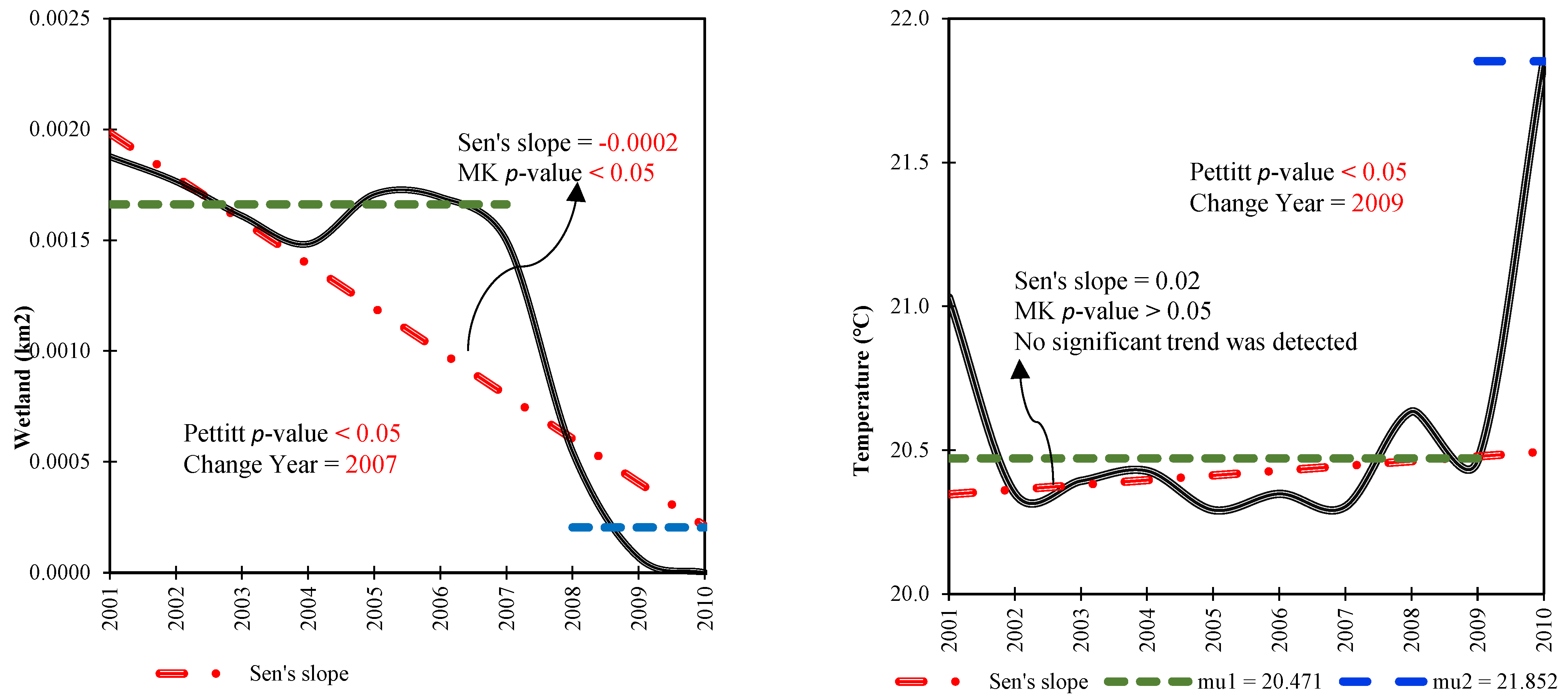
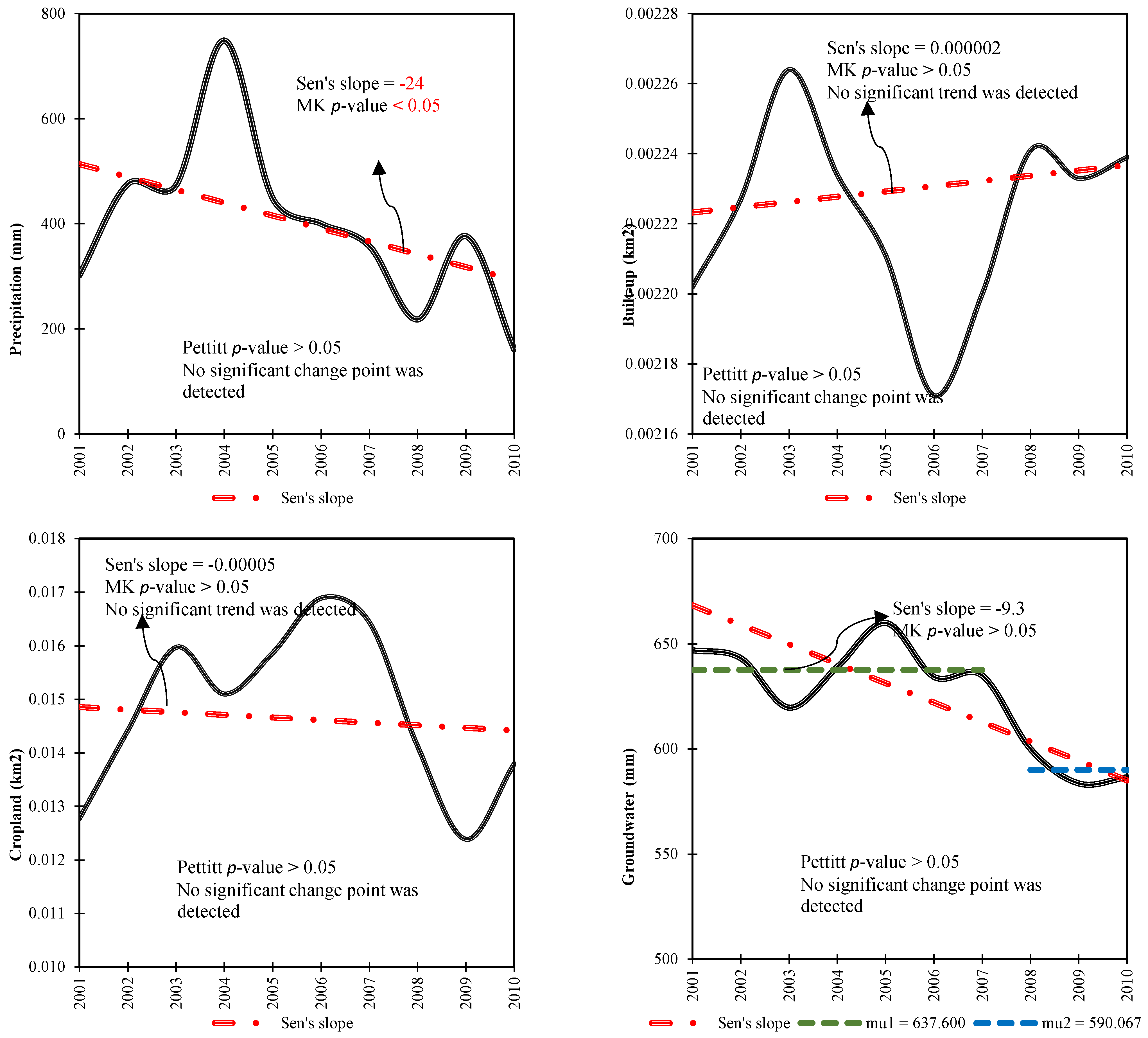
Figure 4.
Correlations between various climatic and anthropogenic variables and Parishan Wetland. Bold values indicate statistically significant correlations (p-value < 0.05).
From 2001 to 2010, Parishan Wetland underwent significant changes due to both climatic and human-induced factors, as illustrated in Figure 4 and Figure 5. These influences led to a reduction in the wetland area by 2.041 km2, with a noticeable decline beginning in 2007, signaling a dramatic shift in the region’s environmental health. Prior to this critical year, the wetland’s average area was approximately 2.043 km2, which gradually shrank over time, eventually decreasing drastically to just 0.002 km2 by the end of the decade, highlighting a severe loss in wetland habitat. Regarding average AT, the study found an increase of 1.38 °C over the same period, with the highest temperature recorded in 2009. Before this peak year, the average AT was around 20.47 °C, which subsequently rose to 21.85 °C, reflecting a clear upward shift in regional temperatures. Conversely, precipitation data from 2001 to 2010 showed a statistically significant negative trend. Additionally, no significant changes were observed for the built-up areas and croplands within the study region. In stark contrast, groundwater storage exhibited a statistically significant decrease of 47.54 mm (p < 0.05), indicating a worrying decline in the region’s water resources. The average groundwater storage level dropped from 637.60 mm to 590.06 mm during this period, contributing further stress to the wetland ecosystem. Groundwater in Iran is frequently used for agricultural and domestic purposes, highlighting the significant anthropogenic impacts on natural resources. This comprehensive analysis highlights the diverse and interconnected impacts of both climatic and anthropogenic factors on the Parishan Wetland, underscoring the urgent need for integrated management strategies to ensure its sustainability and mitigate the adverse effects of ongoing environmental changes.
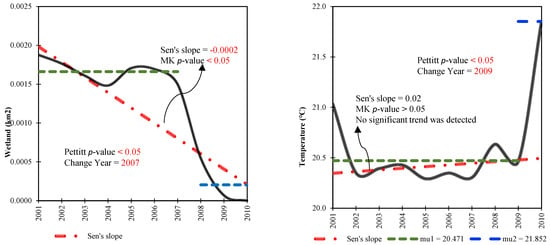
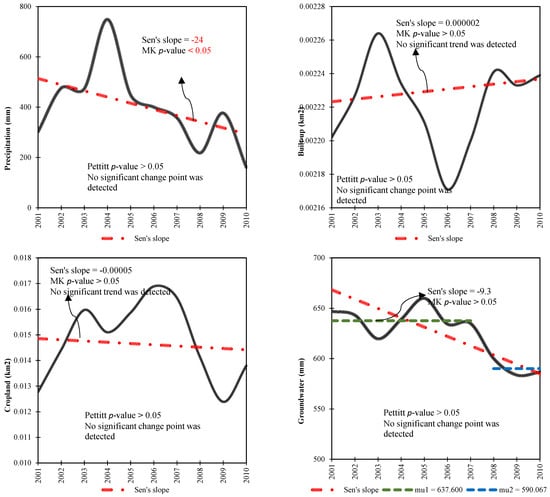
Figure 5.
Time series monotonic analysis depicting the annual variations and trends in climatic and anthropogenic variables throughout the Parishan Wetland from 2001–2010. Mu denotes the average of the pre- and post-breakpoint sub-series.
5. Discussion
Wetlands are recognized for the valuable benefits they provide to society, such as enhancing food supply, preserving biodiversity, and offering flood control. Understanding the changes in wetlands and their impacts, driven by climate change and human activities, is, therefore, of great importance. Previous research [30,31,32,33,34,35,36] has typically focused on a limited number of climatic and anthropogenic variables when assessing the effects of climate change and human activities on wetlands. Chen et al., [34] analyzed the spatiotemporal changes in land use and land cover (LULCC), focusing particularly on the conversion of marshland to other LULCC types (e.g., croplands) in northeast China from 1980 to 2015. The relative impacts of human activities and climatic changes on wetland and agricultural dynamics were quantitatively distinguished and evaluated across different periods using a seven-stage LULC dataset. Their findings indicated that human activities such as population expansion, socioeconomic development, and institutional policies related to wetlands and agriculture were the primary driving forces of LULCC over the past decades. However, this study also identified an increasing contribution of climatic changes. Yan et al., [36] also examined the impact of climatic and anthropogenic pressures on the net primary production (NPP) of wetlands on the Zoige Plateau from 1990 to 2015. They assessed and quantified the effects of various climatic and anthropogenic factors such as NDVI, precipitation, temperature, and solar radiation on NPP using a simulated process model (LPJ_WHyMe) and a remote sensing model (CASA). Their simulations indicated that the annual average potential net primary production (NPPp) fluctuated throughout the study period, peaking in 2008 at 347.37 g C m−2 year−1, while the total wetland NPPp peaked in 2000 at 1.75 Tg C year−1. The results also revealed that the annual average actual net primary production (NPPa) reached its lowest value of 206.04 g C m−2 year−1 in 2000. The total wetland NPPa ranged from 0.97 to 1.15 Tg C year−1 and exhibited a continuous decline over the study period. Their research demonstrated that human activities contributed to 22.37–36.45% of the reduction in wetland NPP. These findings suggest that minimizing human interventions can enhance the NPP of wetlands. In contrast, the present study focuses on analyzing various climatic and anthropogenic indicators, including AT, precipitation, built-up areas, croplands, and groundwater storage, to provide a comprehensive approach to examining the effects of climate change and human activity on the Parishan Wetland and its associated environmental issues from 2001 to 2010. Additionally, we applied an integrated approach combining remote sensing and GEE to monitor the effects of climatic and anthropogenic variables on wetlands. This approach provides a faster and more efficient method for analyzing the trends and impacts of these variables on wetlands compared with previous research. Besides the applied methodology, developing a framework that identifies key climatic and anthropogenic indicators such as temperature, precipitation, land use changes, and groundwater storage can enhance the efficiency of this approach, making it more applicable to various wetlands worldwide. The results demonstrate that both climatic and human-induced factors significantly influence wetlands, with groundwater storage emerging as a key variable impacting changes in the Parishan Wetland. Additionally, our research highlights the effectiveness of integrating remote sensing with GEE for long-term monitoring of climate change and wetland patterns. The use of GEE enables access to a wide array of free datasets and provides a user-friendly, cloud-based environment, making it an ideal platform for conducting extensive, long-term studies across various scales.
The analysis of various climatic variables highlights their impact on the Parishan Wetland, revealing notable trends in precipitation over the years. Findings show a significant upward shift in temperature values in recent years. Higher temperatures cause more water to evaporate from the wetland’s surface. In the case of Parishan Wetland, which is already experiencing water stress, increased evaporation could significantly lower water levels, worsening the drying process. This also disrupts the regional hydrological cycle. As a result, the amount of water entering the wetland is further limited, leading to prolonged dry periods. Higher temperatures not only accelerate evaporation but also reduce the volume of water in wetlands, which may increase the concentration of salts and other minerals in the remaining water. This salinization can make the wetland inhospitable for many species of plants and animals, leading to a loss of biodiversity. Wetlands like Parishan rely on both groundwater and surface water for replenishment. As temperatures rise, groundwater levels may also decline due to increased evaporation and higher water consumption, causing the wetland to dry out more quickly. As temperatures continue to increase, the types of vegetation and animals that can survive in the wetland will change. Species adapted to cooler, wetter conditions may no longer survive, reducing the diversity of the wetland’s ecosystem and negatively affecting both local wildlife and regional environmental health [57].
The analysis of various anthropogenic factors has revealed significant effects on the Parishan Wetland. Among these factors, changes in cropland and groundwater storage appear to be particularly influential. A closer look at the built-up area shows a steady increase over time. In 2001, the built-up area comprised 9.00% of the study region. This proportion rose gradually, reaching 10.80% by 2010. The expansion of urban areas is a critical factor contributing to the degradation of the wetland, as urbanization typically leads to the reduction in natural habitats and changes in water drainage patterns. The expansion of built-up areas around the Parishan Wetland in Iran has significantly contributed to its drying through various direct and indirect impacts. Urbanization and infrastructure development in the surrounding region have disrupted natural hydrological and ecological dynamics, accelerating the wetland’s degradation. This expansion reduces water inflows, disrupts hydrological processes, introduces pollution, and increases water demand, all of which exacerbate the drying of the wetland. Implementing sustainable urban planning, effective water management, and robust wetland conservation policies is crucial to mitigating these effects and preserving the wetland’s ecological integrity [58]. Similarly, the cropland area within the study zone also experienced significant fluctuations during the period from 2001 to 2010. In 2001, cropland covered 8.64% of the area, and this figure increased over the following years, reaching 11.13% by 2007. This growth can be attributed to the intensification of agricultural practices and the expansion of irrigated lands, which often results in a higher demand for water and contributes to the alteration of local hydrological cycles. However, by 2008, the area under cropland began to decline, dropping to 9.33% by 2010. This decrease may reflect shifting agricultural priorities, land-use policies, or environmental factors such as water scarcity, which may have affected agricultural productivity. The most significant anthropogenic factor impacting the Parishan Wetland, however, is the variation in groundwater storage. Groundwater is a critical resource for the region, particularly in arid and semi-arid areas like the study zone, where it plays a key role in maintaining both agricultural and ecological balance. The study revealed a noticeable decline in groundwater storage from 2001 to 2010. In 2001, the mean annual groundwater storage was 638.55 mm. This value initially increased, reaching 659.97 mm by 2005, possibly due to enhanced recharge from precipitation or changes in water management practices. However, from 2006 onwards, groundwater storage began to decrease sharply, dropping to 586.55 mm by 2010. This significant reduction in groundwater levels could be linked to factors such as over-extraction for agricultural irrigation, reduced precipitation, or ineffective groundwater management practices, all of which exacerbate the stress on the wetland ecosystem. The overall trends observed suggest that the combined pressures of urbanization, agricultural expansion, and declining groundwater storage are contributing to the degradation of the Parishan Wetland. These factors not only alter the local landscape but also disrupt the delicate ecological balance, further threatening the sustainability of the wetland. A decrease in groundwater storage has a profound impact on the drying of Parishan Wetland in Iran. Wetlands like Parishan depend heavily on groundwater to maintain their hydrological balance, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions where surface water is scarce. Groundwater contributions are especially critical during dry seasons or periods of low rainfall. When groundwater storage declines, these inflows are directly reduced, causing water levels in the wetland to drop. Additionally, the regional water table lowers as groundwater storage diminishes, making it more difficult for water to naturally seep into the wetland. This disruption to the wetland’s hydrological balance accelerates the desiccation process [59]. In conclusion, the Parishan Wetland is facing multiple anthropogenic challenges. The continued expansion of built-up areas and cropland, coupled with the decline in groundwater storage, underscores the urgent need for integrated land-use and water management policies to mitigate these negative impacts. Effective conservation strategies are essential to ensure the long-term preservation of the wetland ecosystem, which provides important ecological services such as biodiversity support, water filtration, and climate regulation.
The Parishan Wetland, spanning nearly 4300 hectares at an elevation of 820 m above sea level, is internationally recognized as a Ramsar Convention wetland (https://www.ramsar.org, accessed on 3 November 2024) and designated as a protected area. However, in recent years, it has nearly dried up due to inadequate rainfall and the proliferation of authorized and unauthorized wells drilled for agricultural purposes. Despite its historical resilience and self-regeneration in the absence of human interference, the wetland now faces significant challenges. Although seasonal rains during winter and spring temporarily replenish it, excessive groundwater extraction, deep-well digging, year-round agricultural activities, and high evaporation rates hinder its long-term revival. The dry bed of the Parishan Wetland has been plagued by numerous issues, including land subsidence, soil erosion, encroachment on national lands, unauthorized grazing, illegal wells, and water diversion beyond its boundaries. Rising air temperatures in this arid desert region and declining annual rainfall have exacerbated these problems. Additionally, road construction near the wetland has caused irreparable harm to its ecosystem, further contributing to its desiccation. Another major factor in the wetland’s decline is the operation of a combined-cycle power plant located nearby. While plant officials claim their water sources come from distant wells, the heat generated by the facility significantly increases evaporation in the wetland. Furthermore, unauthorized wells drilled around the wetland to support surrounding agriculture have intensified the crisis. These combined pressures have devastated the Parishan Wetland, threatening its ecosystem and highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive conservation efforts [60]. Therefore, recovering the Parishan Wetland in Iran requires an integrated approach that encompasses water resource management and land-use planning. To enhance water inflows, it is essential to identify and secure natural water sources, such as springs and rivers. Groundwater extraction should be regulated by implementing monitoring systems and restricting well drilling. In terms of land-use planning, establishing protected areas around the wetland is crucial to prevent urban encroachment and limit industrial development in its vicinity. Additionally, promoting the use of drip irrigation and other water-saving techniques can serve as an effective strategy for restoring the wetland ecosystem.
Despite the efficiency of the applied methodology for analyzing the effects of climatic and anthropogenic factors on wetlands, there are two limitations. First, the spatial resolution of some applied products (e.g., groundwater storage) may not be as helpful as other products with medium spatial resolution for understanding trends in small-scale wetland dynamics across various variables. Although accuracy assessments have generally been conducted for each product, it would be better to evaluate the accuracy of the applied data specifically for different regions worldwide before processing using ground control points. Several factors, including spatial and temporal resolution, data collection methodology, classification algorithms, and sensor limitations and calibration, affect data in GEE. Some limitations, such as sensor constraints, cannot be resolved by users. However, others, like classification algorithms, can be improved or at least mitigated by users. In general, using ground control points is the most effective way to check and validate the accuracy of GEE products. Future research is recommended to incorporate high-spatial-resolution data for monitoring small-scale wetlands. Additionally, to gain a deeper understanding of the effects of climate change and anthropogenic factors on wetlands, it is crucial to consider a broader range of ecological and hydrological features. This approach would enhance the efficiency of the results and provide a more comprehensive understanding of how integrated factors impact wetland ecosystems.
6. Conclusions
We monitored the Parishan Wetland from 2001 to 2010 to explore the effects of climatic and anthropogenic variables using an integrated approach of remote sensing and GEE. Our findings highlight that both climatic and anthropogenic factors have a significant effect on the wetland. Groundwater availability was identified as the most significant factor, showing a strong positive correlation of 0.92 with wetland conditions. This highlights the critical role of groundwater in sustaining the Parishan Wetland ecosystem. The results of this study demonstrate the effectiveness of the cloud-free GEE platform in monitoring wetland trends and assessing the impacts of climate change and human activities. Additionally, our findings highlight the efficiency of this integrated approach for large-scale and long-term wetland monitoring. This methodology offers valuable insights for researchers studying the impacts of climate change on Earth’s features, particularly wetlands. The findings of this research can contribute to developing effective management strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change and anthropogenic activities on wetlands, particularly in semi-arid and arid regions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing—original draft, and methodology: M.K.G.; methodology, investigation, writing—review and editing, and supervision: K.V.K. and B.F.; formal analysis, data curation, and writing—original draft: O.G.A. and M.S.; methodology and validation: A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions, which contributed to improving this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mitsch, W.J.; Gosselink, J.G. The value of wetlands: Importance of scale and landscape setting. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 35, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, M.; Yang, G.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, J. Wetland ecosystem services research: A critical review. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, J.; Wania, R.; Hodson, E.; Poulter, B.; Ringeval, B.; Spahni, R.; Bohn, T.; Avis, C.; Beerling, D.; Chen, G. Present state of global wetland extent and wetland methane modelling: Conclusions from a model inter-comparison project (WETCHIMP). Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 753–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Jafarzadeh, H.; Granger, J.E.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Brisco, B.; Salehi, B.; Homayouni, S.; Weng, Q. A large-scale change monitoring of wetlands using time series Landsat imagery on Google Earth Engine: A case study in Newfoundland. GIScience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 1102–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannezhad, M.; Sadeqi, A.; Liu, J.; Chen, D. Building on Iran’s Gorgan Bay restoration. Science 2024, 383, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zuo, X.; Dou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhai, X.; Lei, Y.; Li, J.; Pan, X.; Li, W. Plant identification of Beijing Hanshiqiao wetland based on hyperspectral data. Spectrosc. Lett. 2021, 54, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Ouyang, Y. Dynamic simulation of coastal wetlands for Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay area based on multi-temporal Landsat images and FLUS model. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, N.C. How much wetland has the world lost? Long-term and recent trends in global wetland area. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Sharifi, A.; Hosseingholizadeh, M.; Tariq, A. Detection of oil pollution using SAR and optical remote sensing imagery: A case study of the Persian Gulf. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.; Jones, M.D.; Hunt, L.H.; Saulnier-Talbot, É.; Elias, D.; Nankabirwa, A.; Lejju, J.B.; Gell, P.A. Cultural landscapes: Human impacts on wetlands. In Ramsar Wetlands; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 237–258. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Vignat, J.; Lorenzoni, V.; Eslahi, M.; Ginsburg, O.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; Arbyn, M.; Basu, P.; Bray, F.; Vaccarella, S. Global estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2020: A baseline analysis of the WHO Global Cervical Cancer Elimination Initiative. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 11, e197–e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, R.W.; Shu, H.; Javid, K.; Pervaiz, S.; Mustafa, F.; Raza, D.; Ahmed, B.; Quddoos, A.; Al-Ahmadi, S.; Hatamleh, W.A. Wetland identification through remote sensing: Insights into wetness, greenness, turbidity, temperature, and changing landscapes. Big Data Res. 2024, 35, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, C.; Davis, J.A.; Gell, P.A.; Kingsford, R.; Parton, K. The status of wetlands and the predicted effects of global climate change: The situation in Australia. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 75, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Christian, R.R.; Boesch, D.M.; Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Morris, J.; Twilley, R.R.; Naylor, L.; Schaffner, L.; Stevenson, C. Consequences of climate change on the ecogeomorphology of coastal wetlands. Estuaries Coasts 2008, 31, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieger, R.; Capon, S.J.; Hadwen, W.L.; Mackey, B. Between a bog and a hard place: A global review of climate change effects on coastal freshwater wetlands. Clim. Chang. 2020, 163, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, K.V.; Feizizadeh, B.; Khorrami, B.; Ebadi, Y. A comparative approach of support vector machine kernel functions for GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping. Appl. Geomat. 2021, 13, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, M.; Abbasi-Moghadam, D.; Sharifi, A.; Tariq, A.; Li, Q. Hyperspectral image band selection based on CNN embedded GA (CNNeGA). IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 1927–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.; Jin, D.; Kim, C.-S. Change detection in high resolution satellite images using an ensemble of convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 November 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 509–515. [Google Scholar]
- Feizizadeh, B.; Garajeh, M.K.; Lakes, T.; Blaschke, T. A deep learning convolutional neural network algorithm for detecting saline flow sources and mapping the environmental impacts of the Urmia Lake drought in Iran. Catena 2021, 207, 105585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizizadeh, B.; Mohmmadzadeh Alajujeh, K.; Lakes, T.; Blaschke, T.; Omarzadeh, D. A comparative approach of integrated fuzzy object-based deep learning and machine learning techniques for monitoring land use/cover changes and environmental impacts assessment. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 1543–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garajeh, M.K.; Malakyar, F.; Weng, Q.; Feizizadeh, B.; Blaschke, T.; Lakes, T. An automated deep learning convolutional neural network algorithm applied for soil salinity distribution mapping in Lake Urmia, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizizadeh, B.; Omarzadeh, D.; Kazemi Garajeh, M.; Lakes, T.; Blaschke, T. Machine learning data-driven approaches for land use/cover mapping and trend analysis using Google Earth Engine. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2023, 66, 665–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiminia, H.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.; Adeli, S.; Brisco, B. Google Earth Engine for geo-big data applications: A meta-analysis and systematic review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N. Google earth engine. In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts; American Geophysical Union: Vienna, Austria, 2013; p. 11997. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi Garajeh, M.; Salmani, B.; Zare Naghadehi, S.; Valipoori Goodarzi, H.; Khasraei, A. An integrated approach of remote sensing and geospatial analysis for modeling and predicting the impacts of climate change on food security. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firatli, E.; Dervisoglu, A.; Yagmur, N.; Musaoglu, N.; Tanik, A. Spatio-temporal assessment of natural lakes in Turkey. Earth Sci. Inform. 2022, 15, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moomaw, W.R.; Chmura, G.; Davies, G.T.; Finlayson, C.; Middleton, B.A.; Natali, S.M.; Perry, J.; Roulet, N.; Sutton-Grier, A.E. Wetlands in a changing climate: Science, policy and management. Wetlands 2018, 38, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, U.K.; Borah, B.C. Flood plain wetland fisheries of India: With special reference to impact of climate change. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehvar, S.; Filatova, T.; Sarker, M.H.; Dastgheib, A.; Ranasinghe, R. Climate change-driven losses in ecosystem services of coastal wetlands: A case study in the West coast of Bangladesh. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 169, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bortolotti, L.E.; Li, Z.; Armstrong, L.M.; Bell, T.W.; Li, Y. Heterogeneous changes to wetlands in the Canadian prairies under future climate. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Zibaei, M. Water conflict management between agriculture and wetland under climate change: Application of economic-hydrological-behavioral modelling. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epele, L.B.; Grech, M.G.; Williams-Subiza, E.A.; Stenert, C.; McLean, K.; Greig, H.S.; Maltchik, L.; Pires, M.M.; Bird, M.S.; Boissezon, A. Perils of life on the edge: Climatic threats to global diversity patterns of wetland macroinvertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; Nie, N. Climate change and anthropogenic impacts on wetland and agriculture in the Songnen and Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Gu, J.-D. Ecological responses, adaptation and mechanisms of mangrove wetland ecosystem to global climate change and anthropogenic activities. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 162, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wang, Y.; Chaudhary, P.; Ju, P.; Zhu, Q.; Kang, X.; Chen, H.; He, Y. Effects of climate change and human activities on net primary production of wetlands on the Zoige Plateau from 1990 to 2015. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 35, e02052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.D.; Djamali, M.; Holmes, J.; Weeks, L.; Leng, M.J.; Lashkari, A.; Alamdari, K.; Noorollahi, D.; Thomas, L.; Metcalfe, S.E. Human impact on the hydroenvironment of Lake Parishan, SW Iran, through the late-Holocene. Holocene 2015, 25, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafilzadeh, F.; Shiva, A.H.; Malekpour, R.; Azad, H.N. Determination of organochlorine pesticide residues in water, sediments and fish from Lake Parishan, Iran. World J. Fish Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Noorollahi, D.; Lashkari, H.; Amirzade, M.; Azizi, G.; Sharafi, S. Climatic and environmental reconstruction based on stable isotopes of Parishan lake (Iran). J. Rangel. Sci. 2011, 1, 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei Tavabe, K.; Tabibian, S.; Samadi-kouchaksaraei, B.; Bagherzadeh Karimi, M.; Gholamzadeh, P. Estimation of environmental water requirement and ecological water level of parishan wetland with the purpose of transferring water from nargesi dam and restoration of the wetland. Iran. J. Soil Water Res. 2022, 53, 435–446. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H. ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Stocker, E.; Bolvin, D.; Nelkin, E.; Tan, J. GPM IMERG Final Precipitation L3 1 Month 0.1 Degree x 0.1 Degree V06; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P. GHS-BUILT-S R2023A-GHS Built-Up Surface Grid, Derived from Sentinel2 Composite and Landsat, Multitemporal (1975–2030); European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC): Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Rodell, M.; Kumar, S.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Getirana, A.; Zaitchik, B.F.; de Goncalves, L.G.; Cossetin, C.; Bhanja, S.; Mukherjee, A. Global GRACE data assimilation for groundwater and drought monitoring: Advances and challenges. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7564–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Mahdavi, S.; Afshar, M.; Brisco, B.; Huang, W.; Mohammad Javad Mirzadeh, S.; White, L.; Banks, S.; Montgomery, J.; Hopkinson, C. Canadian wetland inventory using Google Earth Engine: The first map and preliminary results. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, J.N.; DeLancey, E.R.; McDermid, G.J.; Kariyeva, J. Google Earth Engine, open-access satellite data, and machine learning in support of large-area probabilistic wetland mapping. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi Garajeh, M.; Akbari, R.; Aghaei Chaleshtori, S.; Shenavaei Abbasi, M.; Tramutoli, V.; Lim, S.; Sadeqi, A. A Comprehensive Assessment of Climate Change and Anthropogenic Effects on Surface Water Resources in the Lake Urmia Basin, Iran. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi Garajeh, M.; Haji, F.; Tohidfar, M.; Sadeqi, A.; Ahmadi, R.; Kariminejad, N. Spatiotemporal monitoring of climate change impacts on water resources using an integrated approach of remote sensing and Google Earth Engine. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi Garajeh, M.; Abdoli, N.; Seyedebrahimi, E.; Naboureh, A.; Kurdpour, I.; Bakhshi Lomer, A.R.; Sadeqi, A.; Mirzaei, S. Impact of Long-Term Drought on Surface Water and Water Balance Variations in Iran: Insights from Highland and Lowland Regions. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeqi, A.; Tabari, H.; Dinpashoh, Y. Spatio-temporal analysis of heating and cooling degree-days over Iran. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 869–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, S.; Yazdanpanah, H.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.A.; Pourmanafi, S.; Dorigo, W. The Gavkhouni wetland dryness and Its impact on air temperature variability in the eastern part of the Zayandeh-Rud River Basin, Iran. Water 2022, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbakhsh Ganjeh, M.; Khorasani, N.; Morshedi, J.; Danehkar, A.; Naderi, M. An investigation on spatial changes of parishan international wetland using remote sensing methods. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Nazemi, A.; AghaKouchak, A. Anthropogenic drought dominates groundwater depletion in Iran. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, R.; Maghrebi, M.; Jessen, S.; Bateni, S.M.; Heggy, E.; Javadi, S.; Noury, M.; Pistre, S.; Abolfathi, S.; AghaKouchak, A. Decline in Iran’s groundwater recharge. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosleh, L.; Asadi, F.; Safaian, R. Investigation on the values of International Parishan Lake’s plants. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biom. Res. 2013, 1, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Ansarifard, S.; Ghorbanifard, M.; Boustani, F.; Abdolazimi, H. Hydrological simulation and evaluation of drought conditions in the ungauged watershed Parishan lake Iran, using the SWAT model. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2024, 15, 4666–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, S.; Hatami, A.; Julaie, L. Parishan, a declining wetland. Iran Nat. 2018, 3, 84–93. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).