Research on Climate Resilience Assessment and Enhancement Strategies for Hebei Province in Response to Climate Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
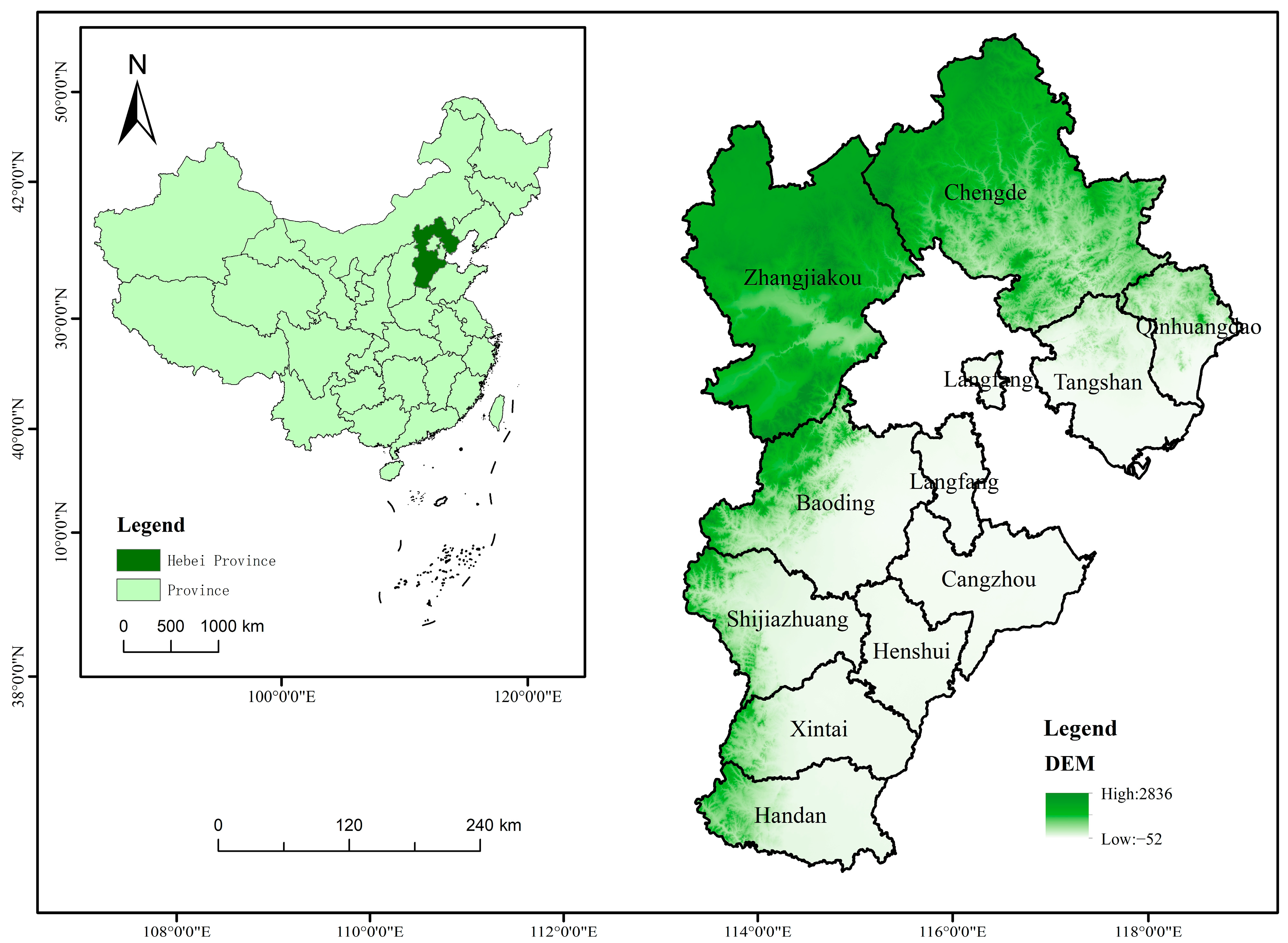
2. Research Area Overview
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data Source
3.2. Data Processing
3.3. Research Methods
- (1)
- Entropy weight method
- (2)
- Urban Climate Resilience Assessment Model
- (3)
- Obstacle Degree Model
4. Analysis of Results
4.1. Climate Resilience Assessment Results for Hebei Province
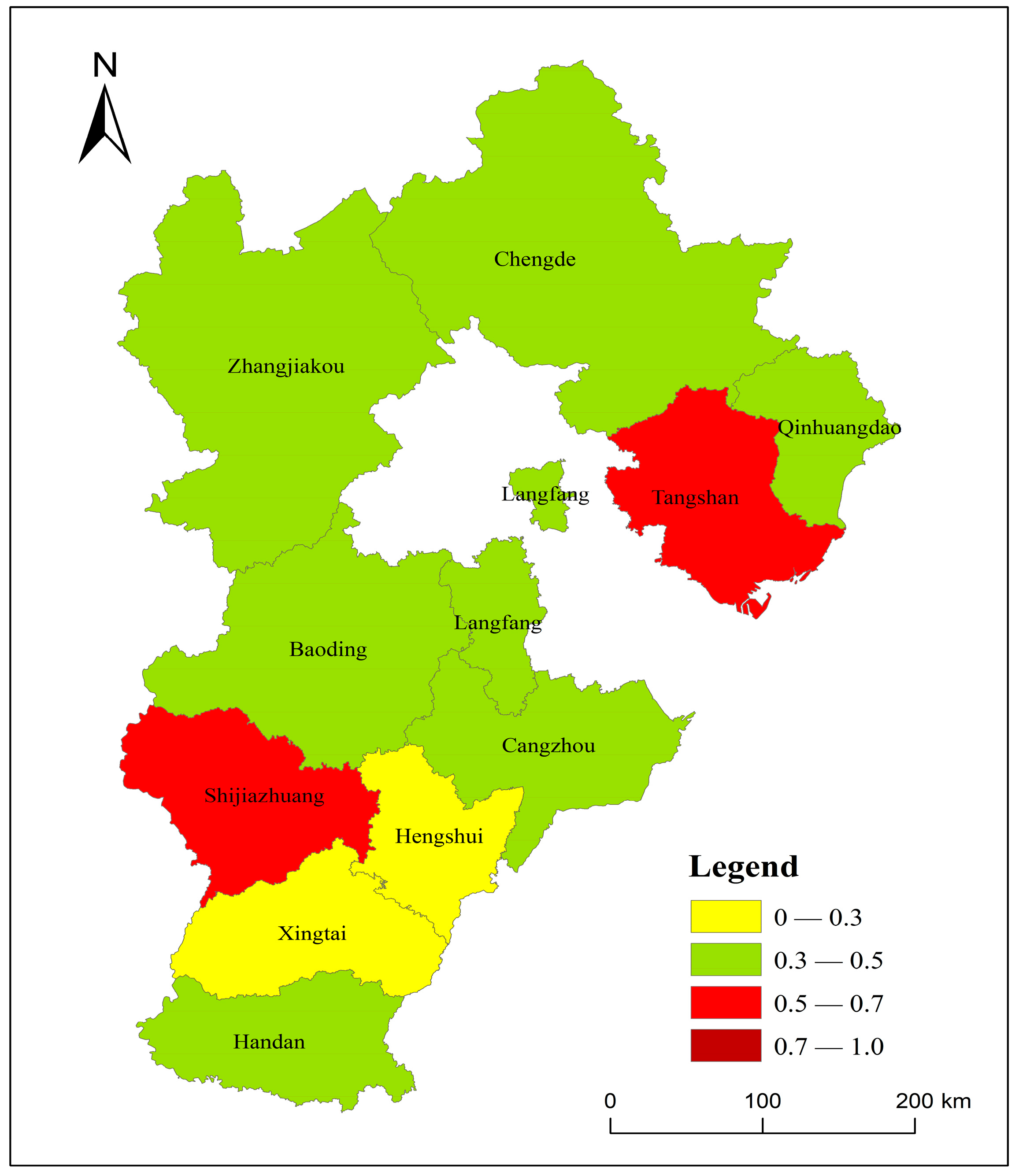
4.1.1. Analysis of the Overall Climate Resilience Assessment Results for Hebei Province
4.1.2. Analysis of the Assessment Results for the Climate Resilience Subsystem
4.2. Study on Climate Resilience Barriers in Hebei Province
4.2.1. Barrier Factor Analysis
4.2.2. Resilience Subsystem Failure Analysis
4.2.3. Enhancement Strategy
5. Conclusions and Discussion
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.C.; Xiong, M.Y.; Jia, Q.; Li, F.T. Assessing resilience of sustainability to climate change in China’s cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Wei, H.B.; Hassan, H.; He, X.Y. Research progress and prospects of urban resilience in the perspective of climate change. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1247360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.S.; Zheng, J.Y.; Hao, Z.X.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.Q. Recent advances on reconstruction of climate and extreme events in China for the past 2000 years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 827–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.S.; Zheng, J.Y.; Hao, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Fang, X.Q.; Wang, H.; Yan, Z.H. State-of-the-arts in the study of climate changes over China for the past 2000 years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadnabizadeh, M. Critical findings of the sixth assessment report (AR6) of working Group I of the intergovernmental panel on climate change (IPCC) for global climate change policymaking a summary for policymakers (SPM) analysis. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2023, 15, 652–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wu, L.F.; Liu, X.G.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Cui, Y.K. Long-term forecast of heatwave incidents in China based on numerical weather prediction. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 599–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.Z.; Gao, H.; Gao, R.; Ding, T. Extreme characteristics and causes of the drought event in the whole Yangtze River Basin in the midsummer of 2022. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2023, 14, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.L.; Clark, R.; Furtado, K.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Q.L.; Sun, R.Z. A case study of the July 2021 Henan extreme rainfall event: From weather forecast to climate risks. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2023, 40, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.H.; Luo, L.; Zhang, X.W.; Yang, R.J. Assessment of the urban climate resilience in China during 2002 to 2020. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, Y.X.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Yin, L.; Li, L.G.; Zhang, B.L. A new framework for assessing and dealing with heat risk from an urban resilience perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 479, 144008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, E.; Dedekorkut-Howes, A.; Howes, M. A framework for using the concept of urban resilience in responding to climate-related disasters. Urban Res. Pract. 2022, 15, 561–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; Sim, J.; Kwon, Y. Recognition Changes of the Concept of Urban Resilience: Moderating Effects of COVID-19 Pandemic. Land 2021, 10, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.H.; Zhai, G.F. The spatiotemporal evolution pattern of urban resilience in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration based on TOPSIS-PSO-ELM. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.J.G.; Gonçalves, L.A.P.J. Urban resilience: A conceptual framework. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Benayas, J.; Tilbury, D. Towards an Urban Resilience Index: A Case Study in 50 Spanish Cities. Sustainability 2016, 8, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumastuti, R.D.; Viverita; Husodo, Z.A.; Suardi, L.; Danarsari, D.N. Developing a resilience index towards natural disasters in Indonesia. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2014, 10, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.Y.; Jia, W.J.; Zhao, H.; Xiang, P.C. A framework for urban resilience measurement and enhancement strategies: A case study in Qingdao, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 122047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Guan, H.M.; Wang, S.J.; Yang, Z.P.; Li, Z.W.; Sun, Y.S. Measurement of Urban and Rural Resilience and Their Coupling Coordination Relationship in Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 35, 612–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.W.; Su, Y.Q.; Ren, K.F.; Song, F.; Xue, R.X. Measurement and influencing factors of urban traffic ecological resilience in developing countries: A case study of 31 Chinese cities. Reg. Sustain. 2021, 2, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Ren, R.X.; Wang, Y.F. Comprehensive evaluation and spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of urban resilience in Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 22, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.L.; Lin, J.Z.; Zhou, L.F.; Niu, L.D. A study on the spatial and temporal evolution and dynamic simulation of urban resilience in Yunnan Province. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2023, 26, 382–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Wang, Z.H.; Sun, Q.P.; Yuen, K.F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Xue, H.F.; Zhao, S.M. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Urban Resilience and Its Influencing Factors: Evidence from the Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.M.; Nie, Z.L.; Wang, K.Y.; Xu, M.X.; Fang, Y.H. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of urban resilience in the Yellow River Basin, China. Reg. Sustain. 2024, 5, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. An Analysis of Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Urban Resilience: A Case Study of Liaoning Province, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.T.; Sun, Y.A.; Liu, J.W. Evolution and analysis of urban resilience and its influencing factors: A case study of Jiangsu Province, China. Nat. Hazards 2022, 113, 1751–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Feng, X.G.; Zuo, W.J.; Xia, Z.C.; Niu, J.Y. Interactive stress effect and collaborative response of urban resilience level and tourism environmental carrying capacity: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2024, 44, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; An, Z.X.; Wang, H.K.; Zhang, P.H.; Wang, G.Y.; Wang, Z. The coupling of urban resilience and innovation efficiency for coordinated spatio-temporal evolution and spatial heterogeneity in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Geogr. Res. 2025, 44, 577–602. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Yu, W.B.; Baklanov, A.; He, B.J.; Ge, Q.S. Mainstreaming the local climate zone framework for climate-resilient cities. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Xiu, C.L.; Xiao, X.M.; Xia, J.H.; Jin, C. Optimizing local climate zones to mitigate urban heat island effect in human settlements. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrabo, M.A.; Hassaan, M.A. An integrated framework for urban resilience to climate change—Case study: Sea level rise impacts on the Nile Delta coastal urban areas. Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.S.; Yang, Y.G.; Li, H.H.; van Dijk, M.P. Measuring Urban Resilience to Climate Change in Three Chinese Cities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A.I.; Cobbinah, P.B. Framing resilience in Saudi Arabian cities: On climate change and urban policy. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 101, 105172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, R.X.; Xiao, X.M.; Xia, J.H. Contribution of urban functional zones to the spatial distribution of urban thermal environment. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 109000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, F.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.M.; Xia, J.H. Regional thermal environment changes: Integration of satellite data and land use/land cover. iScience 2023, 26, 105820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, W.B.; Cong, N.; Xiao, X.M.; Xia, J.H.; Li, X.M. Investigating the attribution of urban thermal environment changes under background climate and anthropogenic exploitation scenarios. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 107, 105466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ren, J.Y.; Creutzig, F.; Zhao, B.Y.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.M.; Xia, J.H.; Ge, Q.S. Continuous assessment of the factors driving the urban surface thermal environment in 1469 cities worldwide. Cell Rep. Sustain. 2025, 2, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.; Yu, W.B.; Ren, J.Y.; Xiao, X.M.; Xia, J.H. XGBoost-Based Analysis of the Relationship Between Urban 2-D/3-D Morphology and Seasonal Gradient Land Surface Temperature. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 4109–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.J.; Li, Y.Z.; Gao, G.H.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.C. Temporal and spatial characteristics of high temperatures, heat waves, and population distribution risk in China from 1951 to 2019. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 96629–96646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Xin, J.X.; Yu, W.B.; Ren, J.Y.; Xiao, X.M.; Xia, J.C. Building a climate-adaptative city: A study on the optimization of thermal vulnerability. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 490, 144768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.J. Variation in community heat vulnerability for Shenyang City under local climate zone perspective. Build. Environ. 2025, 267, 112242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, J.; Ma, X.Y.; Xiao, X.M.; Xia, J.H. Optimal allocation of local climate zones based on heat vulnerability perspective. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.S.; Jiang, S.L.; Xu, L.S.; Xu, H.G.; Guan, N.N. Resilience assessment and obstacle factor analysis of urban areas facing waterlogging disasters: A case study of Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 65455–65469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Feng, Z.L.; Zhang, M.F.; Yao, Y.H. Influence of large-scale climate indices and regional meteorological elements on drought characteristics in the Luanhe River Basin. Atmos. Res. 2024, 300, 107219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.L.; Zhang, P.; Yu, F.; Zhu, X.Y. A review on resilient cities research from the perspective of territorial spatial planning: A bibliometric analysis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1300764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteska, A.; Sharif, T.; Bhuiyan, F.; Abedin, M.Z. Impacts of the changing climate on agricultural productivity and food security: Evidence from Ethiopia. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Wu, H.; Xie, C.K.; Wan, Y.S.; Qin, Y.F.; Jiang, R.Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Che, S.Q. Community future climate resilience assessment based on CMIP6, A case study of communities along an urban-rural gradient in Shanghai. Urban Clim. 2024, 56, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Chen, Y.N.; Chen, A. Evaluating urban climate resilience in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration: A novel method integrating the DPSIR model and Sustainable Development Goals. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Bai, H.; Zhong, S.C.; Wu, Z.F. Prediction of CO2 emission peak and reduction potential of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, X. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Red Industrial Heritage in Hebei, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.F.; Zeng, W.; Feng, D. Coupling Coordination of Urban Resilience and Urban Land Use Efficiency in Hunan Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.P.; Lei, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.G. Differentiation of Rural Development Driven by Natural Environment and Urbanization: A Case Study of Kashgar Region, Northwest China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.M.; Yang, S.; Wu, Z.L.; Si, Z.J. Analysis of Water Rights Allocation in Heilongjiang Province Based on Stackelberg Game Model and Entropy Right Method. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Y.; Miao, C.L.; Yang, L. Ecological-economic efficiency evaluation of green technology innovation in strategic emerging industries based on entropy weighted TOPSIS method. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, A.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhou, X.X.; Yang, Y.F. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Obstacle Factors of New-Quality Productivity in Water Conservancy in China Based on RAGA-PP and Obstacle Degree Model. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Ma, C.; Tan, Z.W.; Wu, T.H. Low-carbon development pathways for the water-energy-food-carbon nexus in the Yangtze river economic Belt: Insights from coupling coordination and obstacle degree analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 523, 146399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Goal Level | Guideline Level | Indicator Level | Interpretations | Indicator Attributes | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban climate resilience | Ecological Resilience (0.2008) | Greening coverage in built-up areas (A1) Parkland area per capita (A2) Sewage treatment rate (A3) Ratio of good air quality days (A4) Soil erosion control area (A5) | Urban ecological regulation capacity | Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive | 0.0305 0.0227 0.0227 0.0391 0.0856 |
| Economic Resilience (0.2803) | Per capita GDP (B1) Per capita fiscal revenue (B2) Number of patents granted (B3) Local general public finance budget expenditure (B4) Average annual disposable income per urban resident (B5) Financial investment in science and technology (B6) | Government capacity to regulate resources and household economic buffers | Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive | 0.0483 0.0431 0.0503 0.0406 0.0384 0.0594 | |
| Social Resilience (0.3172) | population density (C1) Disaster prevention and emergency management expenditure (C2) Food production per capita (C3) Number of employees in public administration and social organizations (C4) Number of urban and rural residents guaranteed minimum subsistence allowance (C5) Number of beds in medical institutions per 1000 population (C6) Health technicians per 1000 population (C7) University students per 10,000 population (C8) Percentage of vulnerable population (elderly + children) (C9) | Reflecting the Government’s capacity for disaster preparedness | Negative Positive Positive Positive Negative Positive Positive Positive Negative | 0.0201 0.0396 0.0467 0.0390 0.0194 0.0258 0.0348 0.0528 0.0388 | |
| Infrastructure Resilience (0.2015) | Total water resources (D1) Road network density (D2) Density of drainage pipes (D3) Density of water pipes (D4) Total water supply (D5) | Reflects the capacity of the city to prevent flooding and the coverage of the water supply system | Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive | 0.0508 0.0087 0.0193 0.0447 0.0777 |
| Region | Ecological Resilience | Economic Resilience | Social Resilience | Infrastructure Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shijiazhuang | A5 (0.2627) | B1 (0.2038) | C3 (0.4683) | D1 (0.1625) |
| Tangshan | A5 (0.2611) | B3 (0.1425) | C3 (0.4082) | D5 (0.1597) |
| Qinhuangdao | A5 (0.1886) | B6 (0.2106) | C3 (0.3587) | D5 (0.1532) |
| Cangzhou | A5 (0.2191) | B6 (0.1743) | C8 (0.3437) | D5 (0.1904) |
| Xingtai | A5 (0.1633) | B6 (0.1742) | C8 (0.3398) | D5 (0.1675) |
| Baoding | A5 (0.1570) | B1 (0.1789) | C8 (0.3443) | D5 (0.1754) |
| Zhangjiakou | A1 (0.0597) | B6 (0.2086) | C8 (0.3113) | D5 (0.1892) |
| Handan | A5 (0.1817) | B1 (0.1469) | C8 (0.3747) | D5 (0.1397) |
| Langfang | A5 (0.2462) | B6 (0.1623) | C3 (0.3889) | D5 (0.2055) |
| Hengshui | A5 (0.2005) | B6 (0.1546) | C8 (0.3740) | D5 (0.1825) |
| Chengde | A1 (0.0602) | B6 (0.2290) | C8 (0.3407) | D5 (0.2190) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Du, M.; Song, Y. Research on Climate Resilience Assessment and Enhancement Strategies for Hebei Province in Response to Climate Change. Land 2025, 14, 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112189
Li X, Du M, Song Y. Research on Climate Resilience Assessment and Enhancement Strategies for Hebei Province in Response to Climate Change. Land. 2025; 14(11):2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xueming, Meishuo Du, and Yishan Song. 2025. "Research on Climate Resilience Assessment and Enhancement Strategies for Hebei Province in Response to Climate Change" Land 14, no. 11: 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112189
APA StyleLi, X., Du, M., & Song, Y. (2025). Research on Climate Resilience Assessment and Enhancement Strategies for Hebei Province in Response to Climate Change. Land, 14(11), 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112189





