Abstract
As a vital part of smart city development, smart community development is in full swing, aiming to improve residents’ sense of safety (RSS). Most research focuses on the technological innovation and infrastructure construction of smart communities; few studies have evaluated smart community development from the perspective of the RSS. Thus, this paper aims to propose a system of evaluation indicators for assessing the RSS of smart community development. After the relevant evaluation indicators were identified, an evaluation method was proposed using the CRITIC-FCE approach. To validate the feasibility of this method, 31 smart communities in China were selected in this study. The results showed the following: (1) The indicator of the highest weight was ‘cultural activities for the elderly’, while ‘overall design’ had the lowest weight, highlighting the importance of community services in enhancing the RSS of smart community development. (2) The selected cities and communities achieved a generally high level in the RSS of smart community development, and some differences were observed among them. (3) Emergency services and property services play an important role in enhancing the RSS of smart community development, with communities excelling in these areas, achieving higher overall rankings. Conversely, the score of pension service was relatively low, which is a common problem in the evaluation results, reflecting the shortcomings of the current smart community in providing pension service. Consequently, several strategies are suggested to enhance the RSS of smart community development, such as building an emergency information system based on advanced technology, establishing mobile and Internet of Things-based emergency assistance services for the elderly, and enhancing the maintenance of public facilities. This research enriches the knowledge of RSS and provides guidance for further research for the RSS of smart community development.
1. Introduction
In an era of rapid digitalization, Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) play a critical role in decision-making processes across political, administrative, and personal spheres [1,2]. The integration of ICTs with urban management has led to the emergence of the smart city concept, which is pivotal in advancing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) outlined by the United Nations [3]. Smart cities aim to optimize resources, enhance governance, and improve the quality of life of residents by leveraging data-driven decision-making processes [4]. However, the deployment of smart city technologies raises concerns about equitable access to ICTs and the capacity of institutions to implement these innovations effectively [5]. Addressing these challenges is essential for ensuring that smart cities are both inclusive and sustainable [3,5]. Within this context, a smart community, as an important part of the development of a smart city, is a new community form for the future; it utilizes internet technology to improve work and life experiences in many areas, including personal health, home care, hospitals, urban networks, and residential housing, meeting the diverse needs of residents [6,7]. The concept of smart communities has seen extensive implementation across regions such as the United States, Europe, the United Kingdom, Japan, and Singapore [8]. For example, smart communities in Singapore provide residents with a comprehensive ‘one-stop’ service portal, as well as infrastructure such as smart parking and smart electric fans within the community [9]. These innovations aim to create a community environment that is safe, comfortable, convenient, and aligned with modern living standards [9,10]. The city of Dubuque in the US launched the first smart community project in the US and the world in 2009; technologies of this project such as the Internet of Things, energy sensing, and big data analytics were used to better serve the needs of residents’ lives [11]. Finland’s smart communities use an interactive interface to enable smart metering of the community, both for the purpose of controlling energy use and to provide a more satisfying service to community residents [12]. However, current smart communities still lack a focus on people, with low resident awareness, mismatched needs, and a shortage of funding leading to low levels of satisfaction among smart community residents [13]. The purpose of a smart community is to improve the quality of life of residents [14], and it is a basic project providing residents with precise and refined services, which directly affects people’s sense of safety, happiness, and gain [15]. The “sense of safety” is the subjective feeling of whether a human is safe in their main areas of life and whether they have the ability to deal with risks in the present and future period of time. Residents’ sense of safety (RSS) is crucial in the process of smart community development and directly affects the effectiveness of smart community development. The gas explosion incident at the bazaar market in Yanbu Community, Shiyan City, China, in June 2021, serves as a significant example; it resulted in significant financial losses, disruption, and human casualties, and the RSS of the local community was greatly affected due to the serious lack of community emergency response capacity [16]. Therefore, evaluating the RSS of smart community development can help to understand the actual level of the RSS and provide recommendations for improving the RSS of smart community development.
The development of smart communities has garnered increasing attention, with significant progress made in various aspects of their implementation. This includes advancements in smart infrastructure construction [17], the development of service systems for smart communities [10,12,18,19], and the establishment of cooperation mechanisms among stakeholders [20]. As the construction of smart communities deepens, greater attention is being paid to the experiences of residents. Researchers have developed measurement models to assess smart community construction from the perspective of residents’ perceptions and sense of gain, exploring how smart community construction can enhance these residents’ perceptions and sense of gain [9,21]. By integrating security management with community development, the concept of a safer smart community has been proposed. Concurrently, from the residents’ perspective, the sense of safety is being extensively studied and has become a significant research focus. At the city level, an evaluation system for the sense of safety was developed, focusing on urban safety and residents’ perceived safety, and was successfully applied in Xiamen [22]. At the community level, studies have analyzed the current state of community RSS, identified influencing factors, and proposed measures to enhance the RSS [23]. Furthermore, the relationship between community governance and residents’ sense of safety has been explored [24]. In terms of quantitative research on RSS, Maslow pioneered a safety sense questionnaire in the 1950s, consisting of 75 questions with a three-level scoring system [25]. An analysis of this questionnaire identified three key factors—safety, belonging, and respect—that demonstrated good reliability and validity, laying the groundwork for subsequent safety scale development. Gao Xing’s research furthered the measurement of RSS in safe communities by establishing an evaluation model based on questionnaires and operational rules [26]. Moreover, some methods were used to evaluate the sense of safety such as the Best–Worst Scaling method [27], the Logit model [28], Principal Component Analysis [29], Grey relational analysis [30], and other methods. However, previous research on the evaluation of smart communities has largely overlooked the aspect of the RSS, resulting in three primary research gaps: (1) Most smart community evaluation systems focus on only one area, such as technological advancements and infrastructure development. Few studies have explored the evaluation of smart community development from the perspective of residents’ sense of safety. (2) There are few reports on evaluation indicators for the RSS of smart community development. (3) Establishing an objective and universally applicable standard for evaluating the RSS of smart community development remains challenging.
This paper aims to develop a novel evaluation method from the perspective of residents’ sense of safety to assess the development of smart communities, with the goal of advancing their overall progress. The objectives of this study are (1) to identify key evaluation indicators that reflect the RSS of smart community development; (2) to develop an evaluation method for assessing the RSS of smart community development using the CRITIC-FCE method, and (3) to offer actionable recommendations aimed at improving the RSS in both current and future smart community development.
2. Methodology
To quantify residents’ sense of safety (RSS) of smart community development, an evaluation indicator system was developed. An evaluation model was then proposed by integrating the CRITIC (Criteria Importance Through Intercriteria Correlation) method with the Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation (FCE) approach. The combination of CRITIC and FCE can make full use of their respective advantages and complement each other, thus improving the accuracy of evaluation. On the one hand, the CRITIC method allocates weight scientifically and reasonably by considering the correlation and conflict among evaluation indicators and reduces subjective interference [10,31]. The FCE method uses fuzzy mathematics theory to transform qualitative evaluation into quantitative evaluation, which enhances the objectivity and accuracy of evaluation [9]. On the other hand, the weight determined by the CRITIC method provides a scientific weight allocation basis for the FCE method, while the FCE method carries out a more accurate quantitative evaluation of the evaluated object through the fuzzy mathematical theory. In addition, CRITIC and FCE are both evaluation methods based on scientific theories, and their combined use can further enhance the scientificity and credibility of evaluation [32,33]. By comprehensively considering multiple evaluation indices and fuzziness factors, the evaluation results can be more objective and credible. The evaluation process is detailed as follows (as shown in Figure 1): Step 1: Initial evaluation indicators for RSS were identified through a systematic literature review (SLR). Step 2: These indicators were further refined and selected through in-depth expert interviews. Step 3: The evaluation results for the RSS of smart community development were determined using the CRITIC-FCE method.
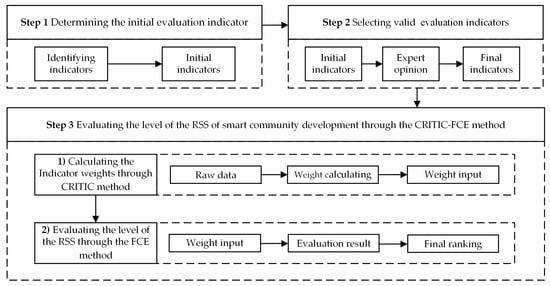
Figure 1.
The evaluation process diagram for the RSS of smart community development using CRITIC-FCE methodologies.
2.1. Identification of Evaluation Indicators for Assessing the RSS of Smart Community Development
The selection of scientific and reasonable indicators is fundamental for evaluating the RSS of smart community development. To this end, a systematic literature review (SLR) was employed to determine the initial evaluation indicator system (as shown in Figure 2). The identification process adhered to the following criteria: (1) Indicators with obviously similar concepts should be considered for merging; otherwise, each indicator should remain as a distinct evaluation dimension. (2) Indicators mentioned fewer than three times in the literature can be discarded. (3) Indicators deemed significant for RSS evaluation should be selected, even if they are mentioned only once [33]. Based on these criteria, and considering the specific service contents of various smart communities and the concept of RSS in these contexts, a preliminary evaluation indicator system was established using the SLR method. The initial system comprises 9 first-level indicators and 43 second-level indicators [10,29,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44], as detailed in Supplementary File S1.
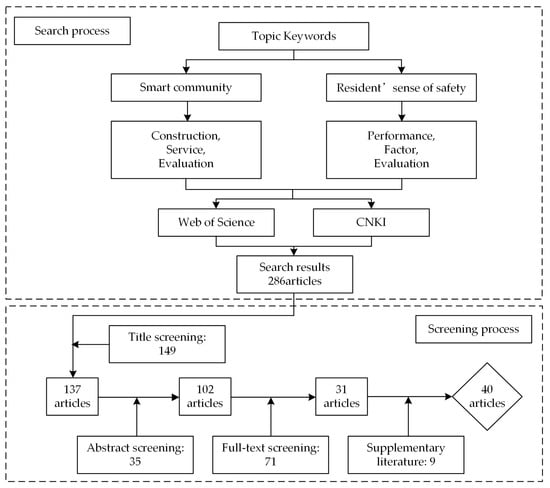
Figure 2.
The flow chart of the SLR process.
The initial evaluation indicators for the RSS of smart community development are primarily derived from the literature. However, these indicators require optimization to more accurately reflect the actual level of RSS of smart community development. To achieve this, several experts specializing in smart community development, community safety, and residents’ sense of safety were selected, ensuring their extensive experience and knowledge in the field [33]. In June and July 2022, 27 scholars and experts for the RSS domain of smart communities were interviewed via VooV Meeting. Detailed information of the participating experts is presented in Supplementary File S2. The expert questionnaire used for indicator optimization is provided in Supplementary File S3. During the meeting, the importance of the initial assessment indicators was discussed, and the evaluation indicators were adjusted based on the experts’ feedback. Ultimately, 7 first-level indicators and 23 second-level indicators were selected for the final evaluation indicators, as shown in Table 1. An explanation for the evaluation indicator system is provided in Supplementary File S4.

Table 1.
The evaluation indicators for the RSS of smart community development.
2.2. Determination of Indicator Weights for the RSS of Smart Community Development Using the CRITIC Method
The CRITIC (Criteria Importance Through Intercriteria Correlation) method offers several advantages for assessing the RSS of smart community development [33]. Firstly, the CRITIC method provides an objective approach to determining the weights of evaluation indicators by considering both the contrast intensity and conflict among criteria. This ensures that the derived weights reflect the true importance of each indicator in the context of the RSS, leading to more accurate and reliable evaluation results [10]. Secondly, the CRITIC method effectively handles the complexity and inter-dependencies among various indicators, which is crucial in the multifaceted environment of smart communities. By capturing the intrinsic relationships between indicators, it enhances the comprehensiveness of the assessment. Furthermore, the CRITIC method’s reliance on statistical measures to derive weights mitigates potential biases inherent in subjective weighting approaches, thereby improving the credibility and validity of the evaluation outcomes. These strengths make the CRITIC method a valuable tool in advancing the understanding and enhancement of safety perceptions in smart communities. The process of determining indicator weights using the CRITIC method involves the following detailed steps:
(a) Standardization of the Sense of Safety Indicator Data.
To eliminate the influence of different units, the raw data should be standardized. The standardized value zij can be calculated using the following formula:
where min(xij) and min(xij) are the minimum and maximum values of the j-th RSS evaluation indicator, respectively.
(b) Calculation of the Standard Deviation of the RSS Evaluation Indicators.
The standard deviation σj for each RSS evaluation indicator in the standardized matrix is calculated as follows:
where is the mean of the j-th indicator of the RSS.
(c) Calculation of the Correlation Coefficient Matrix Between the RSS Evaluation Indicators.
The correlation coefficient rjk between each pair of the RSS evaluation indicators in the standardized matrix is computed as follows:
(d) Calculation of the Information Content of Each RSS Evaluation Indicator.
The information content Cj of each RSS evaluation indicator is calculated using the following formula:
(e) Calculation of the Weights of the RSS Evaluation Indicators.
Finally, the weight wi of each RSS evaluation indicator is determined by the following formula:
2.3. Evaluating the Level of the RSS of Smart Community Development Using the FCE Method
The Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation (FCE) method is a mathematical model that utilizes specific techniques of fuzzy measurement, fuzzy statistics, and fuzzy evaluation during its computational process [45,46]. Compared to other evaluation methods, FCE excels in handling fuzzy and uncertain information, thereby producing results that are more aligned with real-world conditions. By transforming qualitative indicators into quantitative evaluations and integrating expert insights with empirical data, the FCE method delivers more scientific and rational outcomes. Its results are characterized by clarity, systematic rigor, and broad applicability, effectively synthesizing various evaluation metrics to yield more accurate and comprehensive assessments. Consequently, the FCE method holds significant advantages in evaluating residents’ sense of safety, offering a more holistic, scientific, and reasonable assessment of the RSS of smart community development.
(1) Establishing a Factor Set of Quantitative Indicators.
The quantitative indicators for the RSS in smart communities are organized into a factor set, denoted by U, which is a set.
(2) Determining the Evaluation Indicator Set.
The various quantitative indicators within the set U have different levels of significance for the Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation. Hence, a set Ci of indicator weights is established.
(3) Establishing an Evaluation Set.
Drawing from existing research on the development of perception scales for the RSS, the evaluation set consists of five elements: very poor, poor, average, good, and very good, corresponding to V1 to V5, respectively. For quantification purposes, V1 to V5 are assigned scores of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 points, respectively.
(4) Determining the Judgment Matrix for Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation
For the i-th indicator, the fuzzy subset on the membership V of each comment is represented as follows:
In the set Ri, rim denotes the membership degree of the i-th indicator to the m-th evaluation level, which reflects the proportion of the indicator ui receiving the evaluation Vm.
In the set Ri, rim represents the degree to which the i-th indicator belongs to the m-th evaluation level, indicating the proportion of the indicator ui that is evaluated as Vm. The formula for calculating rim is
where Eim represents the number of respondents who rated the indicator ui as Vm, and N is the total number of respondents. rim indicates the probability of the indicator ui belonging to the m-th evaluation level.
Consequently, the fuzzy comprehensive judgment matrix of the indicators is derived.
(5) Calculating the Community’s Comprehensive Quantization Score
The comprehensive quantization score for the community is calculated as follows:
where Bi denotes the weighted final degree of membership for each second-level indicator of a single community.
(6) Obtaining the Final Evaluation Results
The final evaluation results are obtained by comparing the scores of elements Vi in the evaluation set. The results corresponding to the RSS of the smart community are determined by combining the scores using the following formula:
3. Empirical Study
3.1. Study Area
Six cities in China—Shenzhen, Huizhou, Dongguan, Putian, Zhengzhou, and Luoyang—were selected as investigation sites to collect data on the RSS of smart community development. On the one hand, these cities have been at the forefront of smart community development, accumulating extensive experience and demonstrating strong comprehensive capabilities. For instance, Shenzhen, Dongguan, and Huizhou, located in Guangdong Province, are leaders in smart community initiatives, boasting advanced technology and management expertise. Similarly, Zhengzhou and Luoyang in Henan Province have made significant strides in this area, while Putian in Fujian Province has also garnered valuable experience in smart community development. On the other hand, these cities’ smart communities stand out in their use of technology and the effectiveness of service delivery. Most of these communities have developed integrated platforms for intelligent management of community affairs, particularly excelling in the precise and efficient delivery of community services [21].
Among the six cities selected, 17 administrative districts, such as Nanyuan District of Shenzhen City, Huiyang District of Huizhou City, Luolong District of Luoyang City, Chengxiang District of Putian City, Zhongyuan District of Zhengzhou City, and Dongguan City, were selected because these administrative districts have a relatively developed economy and large resident population and play an important role in smart community development [10]. For example, Shenzhen Nanyuan has achieved good results in community governance and proposed innovative methods for the national smart community governance pilot base. The development of smart communities in these areas is more diverse and mature, which provides a reliable dataset for a comprehensive analysis of the RSS of smart community development [32]. Other administrative areas were not included in this study; the main reason is that smart communities of the same level were not developed at the time of our study. This selection strategy is conducive to the centralized collection of data for the construction of an intelligent community.
From these six cities, 31 smart communities that have made significant progress in smart community services were selected. Due to the achievements in smart management, smart services, and emergency response, these communities are an ideal paradigm for evaluating the RSS of smart community development. For example, these communities used digital technologies to collect residents’ health data and built smart infrastructure to respond to emergencies. Consequently, the selection of these 31 communities was made to ensure that the data used to evaluate the RSS of smart community development are comprehensive, scientifically sound, and accurate. Figure 3 illustrates the locations of the chosen smart communities. The name and code of each community are detailed in the Supplementary File S5.
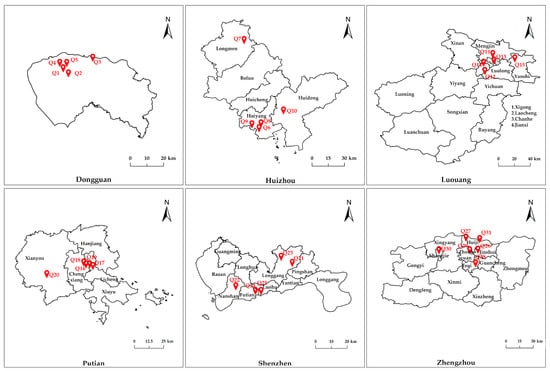
Figure 3.
Location of the smart communities for evaluating the RSS of smart community development.
3.2. Data Collection
During the data collection process, to ensure consistency and representativeness, questionnaires were uniformly distributed and collected across six major cities: Dongguan, Huizhou, Luoyang, Putian, Shenzhen, and Zhengzhou. Residents were invited to rate the evaluation indicators of the RSS of smart community development on a scale from 1 (very unimportant) to 5 (very important). The resulting ratings were then used to determine the weight of each evaluation indicator. The questionnaires were distributed in equal proportions according to the number of residents in different communities, using a random sampling pattern to ensure the quality and fairness of the data. A total of 2242 questionnaires were gathered via the Wenjuanxing platform, with 2128 being valid. Wenjuanxing is a specialized online tool for conducting surveys, exams, assessments, and polls. The distribution of surveyed residents was comprehensive and reasonable in terms of age, education, occupation, political affiliation, form of housing, length of residence, and average monthly income. The questionnaire data were used to determine weights using the CRITIC method. Subsequently, based on the collected data, the level of RSS in each smart community was calculated using the FCE method to further analyze the evaluation results. The detailed contents of the questionnaire are found in Supplementary File S6.
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics of the Respondents
Table 2 presents the basic demographic statistics of the respondents. In terms of socio-demographic characteristics, the sample consisted of 42.2% male and 57.8% female respondents. Nearly half of the respondents were between the ages of 21 and 35 (66.49%). In terms of educational attainment, 75.98% of the population had a college education or above. As for the residents’ characteristics, most respondents have resided in the community for over 3 years (65.27%) and are homeowners (66.82%). In terms of economic characteristics, respondents were categorized by disposable income, with 66.78% earning more than RMB 5000 (approximately USD 690) per month. According to official data from the National Bureau of Statistics of China, the average disposable income for urban residents in China was approximately RMB 36,883 annually (about USD 5092), or about RMB 3073 (approximately USD 424) per month (National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2023) [47]. This indicates that a significant portion of respondents earn above the average level of disposable income.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of individual characteristics.
4.2. Results of Indicator Weights for the RSS of Smart Community Development Using the CRITIC Approach
The results of the indicator weights are obtained through Equations (1)–(5) of the CRITIC method. The results of the weights of the evaluation indicators are shown in Table 3. The results show that ‘Smart community emergency service (ES)’ is the most important, followed by ‘Smart community property service (ProS)’. Meanwhile, ‘Smart community medical service (MS)’ has the lowest weight. In addition, the three highest weights in the second-level indicator are PS2 (Cultural activities for the elderly), BS1 (Electric vehicle charging pile), and BS2 (Smart catering service), while the three lowest weights are SS1 (Overall design), ES5 (Emergency assistance alarm), and SS3 (Platform data security). This shows that cultural activities for the elderly and emergency services for the elderly should be the priorities of the RSS of smart community development.

Table 3.
The results of the indicator weights of the RSS of smart community development.
4.3. Results of the RSS Evaluation of Smart Community Development through the FCE Method
After the determination of the weight of each evaluation indicator, the performance of the sampled smart communities was assessed using the FCE method. Performance scores were standardized to a range between 0 and 5. Accordingly, the total score was categorized into five levels: highest performance (4–5), high performance (3–4), average performance (2–3), low performance (1–2), and lowest performance (0–1) [9]. The evaluation results of the RSS in 6 cities and 31 communities are shown in Table 4 and Table 5.

Table 4.
Evaluation results of the RSS for the six-city sample.

Table 5.
Evaluation results of the RSS for the smart community sample.
The RSS of smart community development in six cities was evaluated; the results are shown in Table 4. The findings indicate that the overall scores for these cities range from 3.725 to 3.869, demonstrating a high level of smart community development. Specifically, Putian City secured the top position with an overall score of 3.869, showcasing comprehensive strengths across various indicators, particularly excelling in ‘Smart community safety safeguard’ (SS), ‘Smart community medical service’ (MS), and ‘Smart community pension service’ (PS). Dongguan City follows closely with an overall score of 3.794, highlighting significant advantages in ‘Smart community emergency service’ (ES) and ‘Smart community governance service’ (GS). Zhengzhou City ranks third with an overall score of 3.777, with notable performance in ‘Smart community medical service’ (MS) and ‘Smart community property service’ (ProS). Huizhou City, with a score of 3.767, ranks fourth, excelling in ‘Smart community safety safeguard’ (SS) and ‘Smart community emergency service’ (ES). Luoyang City, with an overall score of 3.744, ranks fifth, demonstrating competitiveness in ‘Smart community medical service’ (MS) and ‘Smart community pension service’ (PS). Shenzhen City, with a score of 3.725, ranks sixth; despite its lower overall score, it performs well in ‘Smart community property service’ (ProS) and ‘Smart community governance service’ (GS).
As presented in Table 5, the Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation (FCE) method was employed to assess the level of 31 smart communities, yielding total scores between 3.305 and 3.980. According to the rating scale, all these communities fall within the high-performance category. Notably, the Q17 community achieved the highest score of 3.980, securing the top rank and demonstrating exceptional performance across several metrics, particularly in ‘Smart community safety safeguard’ (SS), ‘Smart community medical service’ (MS), and ‘Smart community pension service’ (PS). Following closely, the Q21 community, with a score of 3.906, excelled notably in ‘Smart community property service’ (ProS). The Q19 community, ranked third with a score of 3.891, also exhibited substantial strengths across all evaluated metrics. Conversely, the Q15 community, although ranked 31st with a score of 3.305, exhibited relatively weaker performance compared to other communities across various indicators but remained within the high-performance range.
5. Discussion
5.1. Differences in Weights of the RSS of Smart Community Development
ES (Smart community emergency service) and ProS (Smart community property service) are two of the higher-weighted first-level indicators. This indicates the importance residents attach to the issue of emergency services and property services. As for ES, the reason for this may be related to the residents’ mindset of being prepared for danger in times of peace [48]. At the same time, in the event of an incident, the community’s reaction time and ability to deal with the emergency is crucial as most ordinary residents are not equipped to deal with it [49]. As for ProS, with the development of urbanization in China, property services are gradually playing an important role in the daily management of communities [50,51]. Property management companies currently have problems such as low service quality, irregular work processes, few service items, and low staff dedication [52,53]. These problems have seriously affected the RSS. Thus, the sense of safety in smart property services is valued by community residents, which is the reason for the high weight of ProS. Among the seven first-level indicators, MS (Smart community medical service) and GS (Smart community governance service) have the lowest weights. This indicates that for respondents currently living in these smart communities, the health screening services and the open access to emergency assistance provided by the community are meeting the needs of residents [54]. The majority of respondents are young and middle-aged with higher education, and there are fewer older people. As a result, there is a lower demand for community-organized legal and cultural activities, which leads to the lower weighting of GS (Smart community governance service) [55].
According to Table 5, the results show some variability in the weights of secondary indicators. On one hand, the indicators PS2 (Cultural activities for the elderly), BS1 (Electric vehicle charging pile), and BS2 (Smart catering service) hold the highest weight values. The reasons are as follows: Cultural activities for the elderly foster social interaction and a sense of community belonging, which helps maintain cognitive function, reduce loneliness, and enhance emotional well-being among older residents [56]. This, in turn, significantly improves their sense of safety and overall quality of life. The installation of electric vehicle charging stations increases convenience and promotes sustainability, reducing travel concerns and enhancing community safety by encouraging green travel and reducing traffic accident risks [57]. Smart catering provides healthy, nutritionally balanced meal options that meet residents’ daily needs and can swiftly respond to public health emergencies, ensuring food safety and supply chain stability. This enhances residents’ life satisfaction and sense of safety [10]. In summary, these three indicators are highly prioritized in the evaluation of the RSS in smart communities due to their substantial impact on improving residents’ quality of life and sense of safety. On the other hand, the weight values of the three indicators SS3 (Platform data security), ES5 (Emergency assistance alarm), and SS1 (Overall design), are usually low, because their direct impact on residents’ sense of safety is not as significant as other factors. Platform data security focuses on safeguarding residents’ personal information and preventing data breaches. While crucial for protecting privacy, it has a limited influence on residents’ daily sense of safety [32]. The emergency assistance alarm system is essential for responding to emergencies; however, in everyday situations, residents seldom use this service directly, which diminishes its impact on enhancing daily safety perceptions [33,58]. Overall design pertains to the comprehensive planning and layout of the community. Although a well-thought-out design enhances the community’s functionality and aesthetics, its direct influence on residents’ sense of safety is not as pronounced as that of specific services and amenities [59]. Consequently, residents’ sense of safety is more closely tied to tangible service experiences and the availability of smart facilities, such as cultural activities and intelligent services, which more directly improve their quality of life and safety perception [60]. As a result, these three indicators have lower weight values relative to other indicators.
5.2. Differences in the Level of the RSS at the City Level
The city rankings can be clearly observed from high to low: Putian City, Dongguan City, Zhengzhou City, Huizhou City, Luoyang City, and Shenzhen City.
Putian City was the best performer in the RSS evaluation, with high scores across all indicators. The reasons may be related to several factors, including Putian City’s economic development, government investment, policy support, community facilities, and community management. The Putian City government has invested a lot of funds and resources to promote the development of smart communities, including smart security systems and smart car parks, which are conducive to improving residents’ sense of safety and quality of life [61]. Compared with other first-level indicators, Putian City has a low score on PS (Smart community pension service). The main reason may be that there is an uneven distribution of economic resources in the field of elderly care services, resulting in some important elderly care service projects and facilities not having enough financial support. Putian City may still be in the exploratory stage of the development of a smart community, and the promotion and application of smart elderly care services may not be widespread enough, resulting in the elderly being unable to fully experience the convenience and security brought by wisdom. Therefore, Putian City should formulate corresponding improvement measures according to the actual situation. Community responsibility departments should establish effective feedback and communication mechanisms to gradually enhance the sense of safety for elderly care services [53].
It is notable that Shenzhen, renowned for its advanced technological innovation and digitalization, ranks lowest in residents’ perceived sense of safety. This paradoxical situation can be attributed to several factors, including the city’s rapid urban development, the investment and spatial distribution in smart community infrastructure, and the disparity between residents’ expectations and perceptions. Firstly, as a special economic zone and a front-runner in China’s reform and opening-up, Shenzhen’s rapid growth has led to high population density and diverse demands, posing significant challenges to the comprehensive coverage and precision of smart community services [62]. Second, despite substantial investments in smart city infrastructure, Shenzhen may not have evenly distributed these resources across all communities. Older and remote areas, in particular, exhibit relatively low levels of smart technology integration. Furthermore, Shenzhen’s smart community initiatives have predominantly emphasized technological innovation and demonstration projects, potentially at the expense of enhancing residents’ actual experiences and quality of life [63]. Lastly, Shenzhen’s residents generally have a high standard of living and elevated expectations, leading to greater anticipation for the development of smart communities. If the actual experience falls short of these expectations, it may result in lower assessments of their sense of safety [64,65]. Therefore, to enhance the RSS in Shenzhen’s smart communities, it is crucial to comprehensively consider these factors. This includes optimizing resource allocation, promoting balanced development across communities, and paying greater attention to residents’ actual needs and perceptions. These steps are essential for achieving comprehensive, in-depth, and sustainable development of smart communities.
Dongguan ranks below Putian, while Zhengzhou and Huizhou are ranked third and fourth, respectively, with Luoyang’s ranking being only slightly higher than that of Shenzhen. According to Figure 4, Dongguan excels across various indicators, including ‘Smart community safety safeguard’ (SS), ‘Smart community medical service’ (MS), ‘Smart community pension service’ (PS), and ‘Smart community business service’ (BS), reflecting a comprehensive and balanced approach to smart community development. As a significant city in the Pearl River Delta, Dongguan’s rapid economic development and strong technological capabilities have facilitated substantial investments in smart community development, improving community management, service facilities, and safety measures, thus enhancing residents’ sense of safety. Zhengzhou’s overall score is slightly lower than Dongguan’s but higher than the other cities, with particularly high scores in ‘Smart community property service’ (ProS) and ‘Smart community emergency service’ (ES). As the capital of Henan Province, Zhengzhou has made significant progress in smart city and community development, driven by increased government investment in community governance, environmental improvement, and professional services, thereby enhancing residents’ quality of life and sense of safety. Huizhou’s indicators are relatively balanced, without particularly outstanding highlights. As a livable city in the Pearl River Delta, Huizhou emphasizes ecological protection and community governance. Its smart community initiatives focus on improving residents’ convenience and comfort, contributing to a good sense of safety. Stable economic growth in Huizhou also supports the development of smart communities. Luoyang, while ranking relatively low among the four cities, maintains high levels across various indicators. As a historic cultural city, Luoyang has promoted smart city development while preserving its cultural heritage, integrating cultural preservation with technological innovation to enhance residents’ sense of safety through improved ‘Smart community governance service’ (GS) and service quality. However, compared to cities in the Pearl River Delta, Luoyang faces economic and technological challenges that may affect the pace and effectiveness of its smart community development. In summary, the reasons these four cities rank second to fifth in residents’ sense of safety in smart communities are primarily due to their comprehensive investment and balanced development in smart community development. Each city has achieved significant success in different aspects of smart community development based on its unique characteristics and circumstances, enhancing residents’ sense of safety and satisfaction [40].
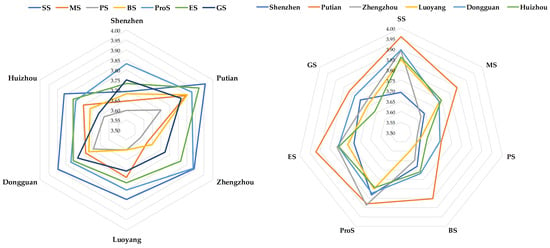
Figure 4.
Score analysis chart for six cities for the different first-level indicators.
5.3. Differences in Level of the RSS at the Community Level
The community ranking results show that the three best-performing communities are Q17 in Putian City, Q21 in Shenzhen City, and Q19 in Putian City. Q17 and Q19 are both located in Putian City. This result is due to the overall high level of development in Putian City, with both communities performing better on all indicators. Q21 is a newer community, close to many high-tech companies and schools with excellent educational resources, and offers smarter and more convenient living and a safer environment. This may be the reason for the large gap between it and Q22 and Q24. However, three smart communities fell short of achieving the highest RSS level, indicating the presence of certain obstacles that may impact the RSS in these communities. As shown in Table 5, the PS scores of the three communities are relatively low: 3.700 (Q17), 3.729 (Q21), and 3.731 (Q19). This indicates that the elderly care service is a common area that the three communities need to strengthen, and there may be problems such as insufficient elderly care service facilities, single service content, or low service quality. Therefore, through targeted improvement measures and policy support, the development level of smart elderly care services in these communities can be gradually improved, and residents’ sense of safety can be improved.
Meanwhile, the three worst-performing communities are Q15 in Luoyang City and Q24 and Q22 in Shenzhen City. Q15 is located in Yanshi District, Luoyang City. In the FCE results for the Xinglong community, all indicators scored in the range of 55–58, and none of them were at a better level. This indicates that it is difficult for residents to feel a higher level of safety from any of the indicators. As smart communities are currently funded by the government, the level of economic activity often determines the level of capital investment in smart communities [9]. Luoyang City has the lowest GDP per capita among the six cities, with Yanshi District exhibiting an even lower economic level. The poor investment capacity of government funds may be one of the reasons for the low ranking of Q15. In addition, the fact that Q15, one of the older neighborhoods, has old infrastructure, inadequate roads, and insufficient community management has led to residents having difficulty trusting the community’s ability to provide emergency services [37]. Therefore, strengthening financial support for smart communities and accelerating infrastructure renewal are important initiatives for improving the RSS in smart communities.
Q24 and Q22 are two of the poorer-level communities, both located in Shenzhen City. As indicated by Table 5, both the Fuguang and Nanyuan communities in Shenzhen, China, exhibit lower scores in MS (Smart community medical service), PS (Smart community pension service), and ES (Smart community emergency service). Despite their geographical proximity, disparities in their developmental stages, population structure and demand, resource allocation and management, geographical and environmental factors, resident participation and satisfaction, and policy frameworks have led to distinct differences in their security, medical services, and property management. Fuguang Community (Q22), being relatively new, has yet to fully develop its security measures and medical facilities, and its supporting services remain inadequate. Conversely, Nanyuan Community (Q24) is more established but faces significant challenges in property management and security due to its high population density [66]. To enhance the RSS in these smart communities, it is essential to strengthen security measures by increasing the presence of security personnel and installing surveillance equipment. Improving the quality of medical services is crucial to ensure residents’ health and safety. Furthermore, enhancing property management practices, including service quality and response times, is vital. Additionally, optimizing business services can help mitigate security risks. By comprehensively addressing these factors and implementing targeted solutions, the overall sense of safety and satisfaction among community residents can be significantly improved [67].
5.4. Suggestions for Enhancing the RSS of Smart Community Development
According to the research results, several recommendations have been proposed to enhance the RSS of smart community development. These suggestions aim to guide community decision-makers in creating safer and more efficient smart communities.
First, safety facilities directly affect the RSS of smart community development, so it is necessary to promptly update and improve the infrastructure construction of emergency services in the development of smart communities. During the initial stages of smart community development, it is crucial to prepare and regularly update emergency plans to improve the effectiveness of emergency services within these communities [68]. At the same time, advanced information technologies, including big data, cloud computing, the internet, and blockchain, should be utilized to establish an emergency information system, which can enhance the timeliness and accuracy of emergency information in smart communities. This system should include multi-level emergency linkages, cross-platform monitoring, and warning integration, a flexible and efficient mobile command platform [12,36,54,69]. In addition, the channels for residents’ participation will also be broadened, and residents will be encouraged to participate in emergency services for community emergencies, which is conducive to enhancing the RSS of smart community development [70].
Second, the research results indicate that pension services play a significant role in evaluating the residents’ sense of safety (RSS) of smart community development. To enhance the RSS, it is crucial to improve smart community pension services, particularly by offering timely emergency services and cultural activities for the elderly. On the one hand, mobile and Internet of Things-based emergency services for the elderly should be established to shorten the response time of emergencies and improve the survival rate of patients [71]. On the other hand, community service providers should pay more attention to the emotional needs of the elderly, and the community can regularly organize group cultural activities for them [72]. At the same time, publicity and education for young people about supporting and caring for the elderly should be strengthened to enhance the sense of safety in elderly services.
Third, with the continuous improvement of people’s requirements for life quality, traditional property management is no longer able to meet the needs and reliance of modern residents. To reduce labor costs and conflicts between properties and residents, property management systems with more intelligence, flexibility, and safety should be established, with professional safety staff and timely updates for maintaining public facilities [73]. These measures will enhance the RSS of smart community development. In addition, to build a community with a higher sense of safety and greater satisfaction, the most important thing is to strengthen residents’ participation [70]. Resident involvement is essential for both the development of new smart communities and the renovation of existing ones. It is also necessary to provide multi-process management measures according to residents’ needs.
6. Conclusions
To help the community decision-makers accurately determine the RSS of smart community development, a novel method for determining the RSS of smart community development was developed, and the levels for the RSS in 31 smart communities were analyzed in this paper. Several key findings merit attention. First, an evaluation indicator system was proposed, and a novel approach for assessing the RSS of smart community development was introduced using the CRITIC-FCE method. To ensure the practical application of the proposed evaluation indicator system and the CRITIC-FCE method, community decision-makers are the main agents responsible for mainstreaming and implementing these tools. These stakeholders have the capacity to integrate the evaluation system into existing governance structures by aligning it with ongoing smart community development. Specifically, community decision-makers can incorporate the indicator system into urban planning and community management processes, ensuring that the RSS of smart community development is improved. Second, the analysis of indicator weights revealed that ‘Cultural activities for the elderly’ had the highest weight, while ‘Overall design’ had the lowest. In addition, the indicators of business services, medical services, and pension services are integral components of the RSS of smart community development. Therefore, these aspects should be prioritized during smart community development. Third, the evaluation results show that the performance of the selected cities and smart communities is at a high level. Specifically, these cities and smart communities receive high scores in emergency services and property services, but there are shortcomings in pension services, which is a common problem. Additionally, significant differences are observed between cities. For instance, Shenzhen, despite its technological advancements, ranks lower in the RSS due to uneven resource distribution and gaps between residents’ expectations and actual experiences. These findings suggest that community decision-makers should focus on strengthening weak areas to enhance the RSS of smart community development. This study makes a significant contribution to the field of smart community development by introducing a novel quantitative method for evaluating the RSS. The CRITIC-FCE method developed in this research provides a quantitative approach to assess the RSS of smart community development, thereby enriching the existing body of knowledge in this area. In practice, this paper offers clear guidance for community decision-makers, highlighting key areas such as medical service, pension service, and business service that require prioritization. By focusing on these critical areas, community decision-makers can effectively allocate resources and implement policies that directly improve the safety and well-being of residents. Moreover, experts can use the evaluation framework to identify gaps and guide targeted interventions, ensuring that smart community development is both effective and responsive to residents’ needs.
However, two research limitations are discovered in this paper. First, due to the limited survey area, the sample data in this paper have some limitations, and some investigations are inefficient. Second, the evaluation method proposed in this study is static, while the RSS of smart communities is dynamic in real life. Therefore, the evaluation method requires adjustment. Future research will involve collecting larger datasets from similar studies conducted in China and other countries to obtain more reliable data. Given that the RSS in smart communities is subject to change, a more complex and dynamic evaluation method should be developed to enhance RSS and support the sustainable development of smart communities. Moreover, this indicator system holds the potential for adaptation and implementation across various countries and regions outside China. Ensuring the framework’s replicability and effectiveness in different contexts will be crucial, necessitating a consideration of local constraints and opportunities. This approach will provide a valuable tool for decision-makers worldwide.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/land13091434/s1. File S1: Preliminary indicator of the evaluation of the RSS in smart communities. File S2: Detailed information on effective experts. File S3: Questionnaire about assessment of residents’ sense of safety for smart communities. File S4: Detailed information about the evaluation indicator system of smart community residents’ sense of safety. File S5: The name and code of each community. File S6: Questionnaire about Evaluation of Residents’ Sense of Safety in Smart Community. Refs. [9,10,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44] are cited in the Supplementary Materials file.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.W., Y.C. and T.G.; materials and methods, C.W., L.W. and T.G.; formal analysis, C.W., H.Z. and L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, C.W., H.Z. and Y.C.; writing—review and editing, C.W., L.W., T.G. and E.H.; supervision, L.W. and T.G.; funding acquisition, L.W. and T.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 72104233), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Certificate Number: 2023M743767), Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities of China University of Mining and Technology (Number: XJ2023002901).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors hereby express their special gratitude to all the respondents who presented the needed data with great patience, as well as the surveyors and interviewers who did their best in terms of data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Huanjie Zhang was employed by the company China Three Gorges New Energy (Group) Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| RSS | Residents’ sense of safety |
| SS | Smart community safety system |
| MS | Smart community medical service |
| PS | Smart community pension service |
| BS | Smart community business service |
| ProS | Smart community property service |
| ES | Smart community emergency service |
| GS | Smart community governance service |
References
- Aceto, G.; Persico, V.; Pescapé, A. The role of Information and Communication Technologies in healthcare: Taxonomies, perspectives, and challenges. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 107, 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhassan, M.D.; Adam, I.O. The effects of digital inclusion and ICT access on the quality of life: A global perspective. Technol. Soc. 2021, 64, 101511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, S.; Ganzaroli, A.; De Noni, I. Smartening sustainable development in cities: Strengthening the theoretical linkage between smart cities and SDGs. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toli, A.M.; Murtagh, N. The Concept of Sustainability in Smart City Definitions. Front. Built Environ. 2020, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Allam, Z.; Bibri, S.E.; Khavarian-Garmsir, A.R. Smart cities and sustainable development goals (SDGs): A systematic literature review of co-benefits and trade-offs. Cities 2024, 146, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ling, W. Impact of Smart City Planning and Construction on Community Governance under Dynamic Game. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6690648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Guo, J. Development of smart city community service integrated management platform. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Networks 2019, 15, 1550147719851975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duanmu, Y.; Chai, Y.; Zhou, W. Standardization of Smart Community Construction at Home and Abroad. Constr. Sci. Technol. 2017, 13, 49–52+59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Yin, J.; Xiang, J.; Chang, Z.; Gu, T.; Han, F. EWM-FCE-ODM-Based Evaluation of Smart Community Construction: From the Perspective of Residents’ Sense of Gain. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Hao, E.; Wang, C.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y. CRITIC-PROMETHEE II-Based Evaluation of Smart Community Services: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Kim, K.J.; Maglio, P.P. Smart cities with big data: Reference models, challenges, and considerations. Cities 2018, 82, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, R.; Liang, X.; Shen, X.; Chen, J.; Lin, X. Smart community: An internet of things application. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2011, 49, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P. Influencing factors of smart community service quality: Evidence from china. Teh. Vjesn. 2021, 28, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, H. Information and communication platform for providing smart community services: System implementation and use case in Saitama city. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Lyon, France, 20–22 February 2018; pp. 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Hou, T. Building Smart Communities in the Context of the New Era: Values, Logic and Pathways. Soc. Sci. GUANGXI 2021, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, J. Common safety issues and solutions in community management in the context of public management. China Manag. Informationization 2022, 25, 213–217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y. Create synergies and inspire collaborations around the development of intelligent infrastructure for human-centered communities. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2019, 70, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Edge, D. The social shaping of technology. Res. Policy 1996, 25, 865–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, J.C. Juan Carlos Augusto Past, Present and Future of Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments. In International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Chai, Y.; Ma, X. Concept, Model and Framework of Human-Oriented Smart Community. Mod. Urban Res. 2014, 10, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Hao, E.; Wang, C.; Xie, M. Quantifying Residents’ Perceptions of Smart Community Construction through a Hybrid EWM-PROMETHEE II Method: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. Land 2024, 13, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Lai, H. A preliminary study on the construction of the «safest city» in Xiamen. J. Fujian Police Coll. 2019, 33, 1–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Lai, T. An Empirical Study of Factors Influencing Community Residents’ Sense of Security—A Survey Based on Shanghai. Chang. J. (In Chinese). 2020, 69–77+2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Lv, X.; Luan, H.; Li, Y. Community Governance and Citizens’ Security in the Post-Epidemic Era. Archicreation 2020, 203–209. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Maslow, A.H. A Theory of Human Motivation. Psychol. Rev. 1943, 2, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X. A Study on the Measurement of Residents’ Sense of Security in Safe Communities. China Saf. Sci. J. 2011, 21, 152–158. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, V.; Ravillion, A.; Houix, O.; Susini, P. Best-worst scaling, an alternative method to assess perceptual sound qualities. JASA Express Lett. 2022, 2, 064404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Shen, J. A comparison between mixed logit model and latent class logit model for multi-profile best-worst scaling: Evidence from mobile payment choice dataset. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2022, 29, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, S. Evaluation of public safety perceptions in cities based on combined empowerment and grey correlation. Stat. Decis. 2019, 35, 45–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, W.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of Public Safety Index in Chinese Cities Based on Entropy TOPSIS Method. Math. Pract. Theroy 2018, 48, 126–133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, T. Performance evaluation and obstacle factors analysis of urban public transport priority. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2019, 42, 696–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Gu, T.; Yin, J.; Hao, E. CRITIC-TOPSIS-Based Evaluation of Smart Community Safety: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Chang, Z. CRITIC-TOPSIS Based Evaluation of Smart Community Governance: A Case Study in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitzman, C. Community Safety Indicators: Are We Measuring What Counts? Urban Policy Res. 2008, 26, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, A.; Tawodzera, M. Communities’ perceptions of health hazards induced by climate change in Mount Darwin district, Zimbabwe. Jamba 2019, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Lorenzo, S.; Goya, J.; Anorga, J.; Adin, I.; Mendizabal, J.; Arrizabalaga, S. Alarm Collector in Smart Train Based on Ethereum Blockchain Events-Log. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13306–13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solansky, S.T.; Beck, T.E. Enhancing Community Safety and Security Through Understanding Interagency Collaboration in Cyber-Terrorism Exercises. Adm. Soc. 2009, 40, 852–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.L. Community Public Safety Evaluation System Based on Location Information Service Architecture. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 6694757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Deng, H.; Dang, X. Preference Preserved Privacy Protection Scheme for Smart Home Network System Based on Information Hiding. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 40767–40776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Tsai, S.-B.; Lin, X.; Zhang, T. How to Evaluate Smart Cities’ Construction? A Comparison of Chinese Smart City Evaluation Methods Based on PSF. Sustainability 2017, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Wang, N.; Yao, S.; Wu, J.; Fang, L. Towards healthy aging: Influence of the built environment on elderly pedestrian safety at the micro-level. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Dang, Y.; She, B.; Li, Y. Sharing intention of electronic health records in online health communities: Patients’ behavioral decisions in the context of privacy protection measures. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1047980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.M.; Kane, K. The effective enforcement of HACCP based food safety management systems in the UK. Food Control 2014, 37, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, H.K.; Hung, K.K.C.; MacDermot, M.K.; Hubloue, I.; Barone-Adesi, F.; Ragazzoni, L.; Della Corte, F.; Acharya, R.; Graham, C.A. Role of Community Health Volunteers since the 2015 Nepal Earthquakes: A Qualitative Study. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2023, 17, e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, X. Fuzzy-based methodology for performance assessment of emergency planning and its application. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2009, 22, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S. A New Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Model Based on the Support Vector Machine. Fuzzy Inf. Eng. 2010, 2, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Statistical Yearbook 2023-National Bureau of Statistics of China Disponible. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2023/indexch.htm (accessed on 31 August 2024).
- Chen, H.; Cao, Y.; Cao, Y. Reflections on nuclear safety culture from the perspective of traditional Chinese culture. Radiat. Med. Prot. 2022, 3, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J. Incident command in the time of COVID-19. Lab Med. 2021, 51, E78–E82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Monkkonen, P. The value of property management services: An experiment. Prop. Manag. 2014, 32, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, B.; Brown, R.J. Optimization of residential property management. Prop. Manag. 2006, 24, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, T. Intelligent Community and Real Estate Management Based on Machine Learning. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, C.X.; Shi, J.L. Study on the Influence Factors of Satisfaction Level to City Property Management in China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 709, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.S.; Luther, B.L.; Sisler, S.M.; Wong, B.; Guo, J.-W. Integrating social determinants of health screening and referral during routine emergency department care: Evaluation of reach and implementation challenges. Implement. Sci. Commun. 2021, 2, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñiz, C.; Rodríguez, P.; Suárez, M.J. Participation in cultural activities: Specification issues. J. Cult. Econ. 2017, 41, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; García-Mollá, A.; Oliver, A.; Sansó, N.; Tomás, J.M. The role of social and intellectual activity participation in older adults’ cognitive function. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2023, 107, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Akul Krishnan, K.; Pandey, A.C. A Novel Blockchain and Internet of Things-Based Food Traceability System for Smart Cities. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2023, 129, 2157–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesus, T.C.; Portugal, P.; Costa, D.G.; Vasques, F. Reliability and Detectability of Emergency Management Systems in Smart Cities under Common Cause Failures. Sensors 2024, 24, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Jia, T.; Yan, P.; Wang, D.; Liu, G. The sense of community revisited in Hankow, China: Combining the impacts of perceptual factors and built environment attributes. Cities 2021, 111, 103108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Smith, M.K. Residents’ Quality of Life in Smart Cities: A Systematic Literature Review. Land 2023, 12, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boella, G.; van der Torre, L. Security policies for sharing knowledge in virtual communities. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2006, 36, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharum, Z.A.; Nawawi, A.H.; Saat, Z.M. Assessment of Property Management Service Quality of Purpose Built Office Buildings. Int. Bus. Res. 2009, 2, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Failler, P.; Ding, Y. Enterprise financialization and technological innovation: Mechanism and heterogeneity. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W. Research on the Problems in the Construction of Smart Community in China and Its Countermeasures; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Dongfang, N.; Zhaoli, S.; Meibo, H. China—Africa Joint Construction of “Digital Africa”: Driving Force and Development Path. West Asia Africa 2022, 66–87+158. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Meng, L.; Wu, Q.; Gong, P.; Seto, K.C. Satellite mapping of urban built-up heights reveals extreme infrastructure gaps and inequalities in the Global South. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2214813119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierendeels, G.; Reniers, G.; van Nunen, K.; Ponnet, K. An integrative conceptual framework for safety culture: The Egg Aggregated Model (TEAM) of safety culture. Saf. Sci. 2018, 103, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skryabina, E.; Reedy, G.; Amlôt, R.; Jaye, P.; Riley, P. What is the value of health emergency preparedness exercises? A scoping review study. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 21, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Rao, K.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Z. An investigation into local government plans for public health emergencies in China. Health Policy Plan. 2007, 22, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.Q.; Alamsyah, N. Citizen empowerment and satisfaction with smart city app: Findings from Jakarta. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 174, 121304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intawong, K.; Boonchieng, W.; Lerttrakarnnon, P.; Boonchieng, E.; Puritat, K. A- SA SOS: A Mobileand IoT-based Pre- hospital Emergency Service for the Elderly and Village Health Volunteers. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C. Community-based elderly care services in China: An analysis based on the 2018 wave of the CLHLS Survey. China Popul. Dev. Stud. 2020, 3, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y. Design and implementation of intelligent community information system based on WSN technology. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 686, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
