Ecologically Regenerative Building Systems through Exergy Efficiency: Designing for Structural Order and Ecosystem Services
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Need for Regenerative Buildings and Building Systems
2. Theoretical Background
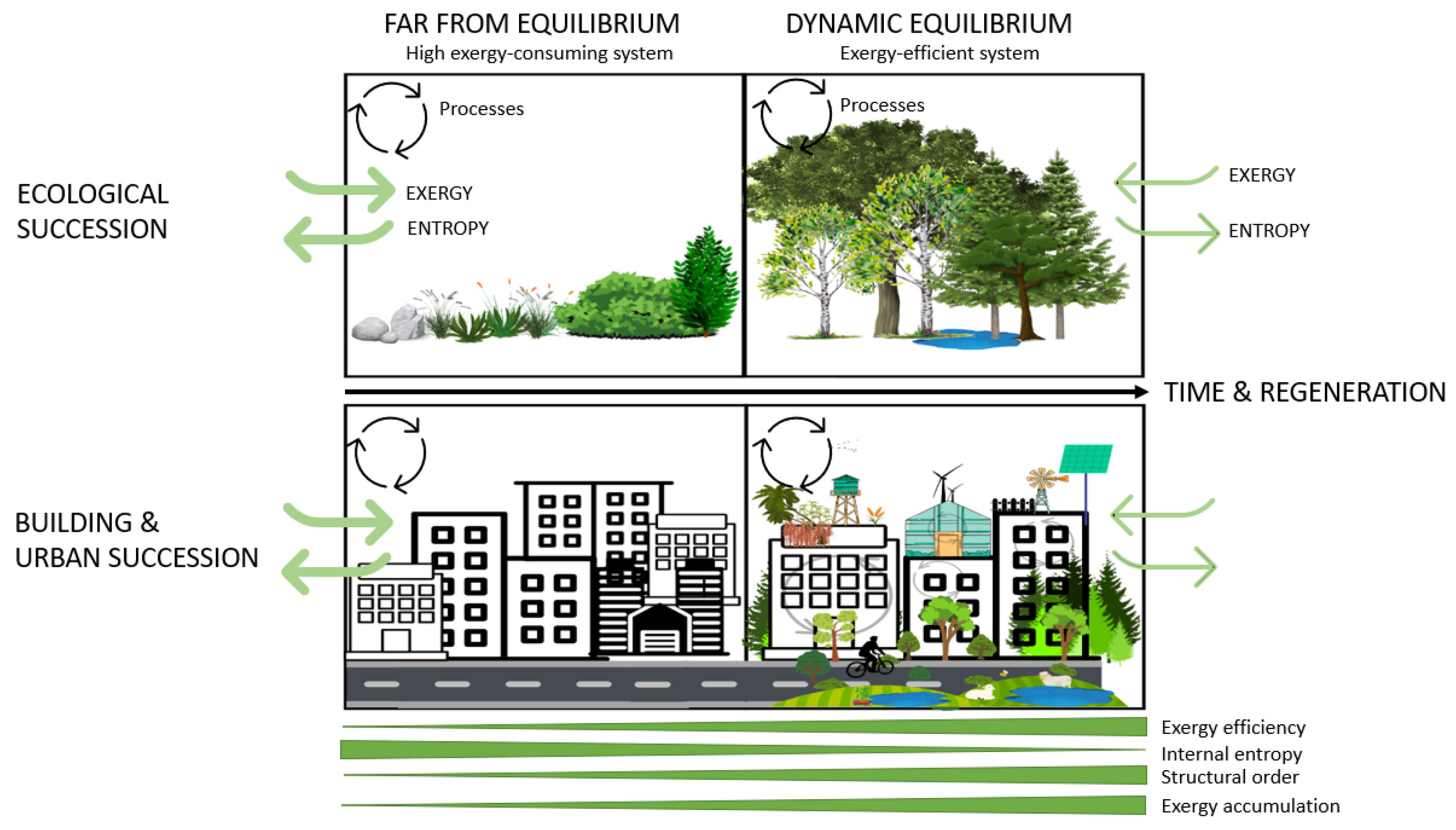
2.1. The Concept of Regeneration
2.2. Thermodynamical Functioning and Exergy Analyses for Regenerative Systems
2.3. Entropy Generation in Exergy-Efficient Systems
2.4. Ecosystem Service Generation with Building Systems
2.5. System Thinking for More Regenerative Buildings
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Conceptual Model for Evaluating Regenerative Performance of Building Systems
4.2. Thermodynamic Design Strategies for Regenerative-Building Systems
- Strategy 1: Provide habitat/physical space for ecologies
- Strategy 2: Integrate ((un)-managed) living systems
- Strategy 3: Increase biomass of autotropic communities
- Strategy 4: Increase biodiversity
- Strategy 5: Increase multifunctionality
- Strategy 6: Design for dynamic structures
- Strategy 7: Develop dissipative structures
- Strategy 8: Develop reversible processes
- Strategy 9: Design for symbiotic and synergetic interactions
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
References
- Sharifi, A. Trade-offs and conflicts between urban climate change mitigation and adaptation measures: A literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 122813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iea50 Buildings-Tracking Buildings. Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/buildings (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Zhong, X.; Hu, M.; Deetman, S.; Steubing, B.; Lin, H.X.; Hernandez, G.A.; Harpprecht, C.; Zhang, C.; Tukker, A.; Behrens, P. Global greenhouse gas emissions from residential and commercial building materials and mitigation strategies to 2060. Nat. Commun. 2021, 121, 6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, A.; Drago, C. A taxonomy of energy resilience. Energy Policy 2020, 136, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E. Exergy. In Encyclopedia of Ecology (5-Volume Set); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1498–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Fu, F.; Li, H.; Campbell, D.E.; Ren, H. Eco-exergy and emergy based self-organization of three forest plantations in lower subtropical China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, S.; Hinman, G.W. Ecological exergy analysis: A new method for ecological energetics research. Ecol. Modell. 1996, 84, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, F.; Luisi, P.L. The Systems View of life: A Unifying Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 1–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedri, K.; Salem, M.; Assad, M.E.H.; Rungamornrat, J.; Malek Mohsen, F.; Buswig, Y.M. PV/Thermal as promising technologies in buildings: A comprehensive review on exergy analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, R.M.; Garcia-Acevedo, L.E. Thermodynamic assessment of cities applying exergetic efficiency as evaluation index. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 50, 101801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causone, F.; Sangalli, A.; Pagliano, L.; Carlucci, S. An exergy analysis for Milano Smart City. Energy Procedia 2017, 111, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggers, F.; Leibundgut, H. The reference environment: Utilising exergy and anergy for buildings. Int. J. Exergy 2012, 11, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggers, F.; Ritter, V.; Goffin, P.; Baetschmann, M.; Leibundgut, H. Low exergy building systems implementation. Energy 2012, 41, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evola, G.; Costanzo, V.; Marletta, L. Exergy analysis of energy systems in buildings. Buildings 2018, 8, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, P.; Zari, M.P.; Chapman, R.; Randal, E.; Perry, M.; Howden-Chapman, P.; Gyde, E. Multiple roles of green space in the resilience, sustainability and equity of Aotearoa New Zealand’s cities. Land 2024, 13, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen Zari, M.; MacKinnon, M.; Varshey, K.; Bakshi, N. Regenerative living cities and the urban climate-biodiversity-wellbeing nexus. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen Zari, M. Regenerative Urban Design and Ecosystem Biomimicry; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–260. [Google Scholar]
- Fish, F.E. Biomimetics and the application of the leading-edge tubercles of the humpback whale flipper. In Flow Control through Bio-Inspired Leading-Edge Tubercles; New, D., Ng., B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlyn, M. Biomimicry in Architecture, 2nd ed.; RIBA Publishing: Portland, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen Zari, M. Ecosystem processes for biomimetic architectural and urban design. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2015, 58, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Pedersen Zari, M.; Raskin, K.; Clergeau, P. Urban ecosystem-level biomimicry and regenerative design: Linking ecosystem functioning and urban built environments. Sustainability 2021, 13, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morseletto, P. Restorative and regenerative: Exploring the concepts in the circular economy. J. Ind. Ecol. 2020, 24, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, C.G.; Dobrev, S.V. Cities as convergent autopoietic systems. In Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Optimization Tools for Smart Cities: Designing for Sustainability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 186, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyke, J.G.; Weaver, I.S. The emergence of environmental homeostasis in complex ecosystems. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, G.W.F. Thermodynamics. Britannica. 2024. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/thermodynamics (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Rosen, M.A. Exergy analysis as a tool for addressing climate change. Eur. J. Sustain. Dev. Res. 2021, 5, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.A. Exergy analysis. In Design and Performance Optimization of Renewable Energy Systems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; pp. 43–60. [CrossRef]
- Giordano, M. Homeostasis: An underestimated focal point of ecology and evolution. Plant Sci. 2013, 21, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyak, N.; Deshko, V.; Bilous, I.; Biriukov, D.; Voloshchuk, V. Applying dynamic energy and exergy analysis to a building envelope. Int. J. Exergy 2024, 43, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susani, L.; Pulselli, F.M.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Bastianoni, S. Comparison between technological and ecological exergy. Ecol. Modell. 2006, 193, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, P. Thermal and mechanical aspect of entropy-exergy relationship. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2012, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihervaara, P.; Franzese, P.P.; Buonocore, E. Information, energy, and eco-exergy as indicators of ecosystem complexity. Ecol. Modell. 2019, 395, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, R.; Bastianoni, S. Emergy. In Encyclopedia of Ecology (5-Volume Set); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1218–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Demirel, Y. Entropy and exergy. In Nonequilibrium Thermodyn; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silow, E.A.; Mokry, A.V. Exergy as a tool for ecosystem health assessment. Entropy 2010, 12, 902–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastianoni, S.; Coscieme, L.; Pulselli, F.M. Ecological indicators: Eco-exergy to emergy flow. In Managing Biological and Ecological Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledari, M.B.; Saboohi, Y.; Valero, A.; Azamian, S. Exergy analysis of a bio-system: Soil–plant interaction. Entropy 2020, 23, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, G.W.F. Entropy. Britannica. 2024. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/entropy-physics (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Sciacovelli, A.; Verda, V.; Sciubba, E. Entropy generation analysis as a design tool—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghasemi, H.R.; Pouyan, S.; Bordbar, M.; Golkar, F.; Clague, J.J. Flood, landslides, forest fire, and earthquake susceptibility maps using machine learning techniques and their combination. Nat. Hazards 2023, 116, 3797–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, B. Entropy perspectives of molecular and evolutionary biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, A.; Ovejas, V.J.; Cuadras, A. Analysis of energy and entropy balance in a residential building. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, J.L.; Bakshi, B.R. Expanding exergy analysis to account for ecosystem products and services. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3768–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, M. Introduction to Ecosystem Services. In Ecosystem Services, 2nd ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakri, A.H.; Watson, R. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being. Available online: https://www.millenniumassessment.org/en/Framework.html (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Pedersen Zari, M.; Hecht, K. Biomimicry for Regenerative Built Environments: Mapping Design Strategies for Producing Ecosystem Services. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines-Young, R. Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services (CICES) V5.2 Guidance on the Application of the Revised Structure. Available online: www.cices.eu (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- IPBES. Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Available online: https://www.ipbes.net/ (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Czúcz, B.; Arany, I.; Potschin-Young, M.; Bereczki, K.; Kertész, M.; Kiss, M.; Aszalós, R.; Haines-Young, R. Where concepts meet the real world: A systematic review of ecosystem service indicators and their classification using CICES. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 29, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würtz, P.; Annila, A. Ecological succession as an energy dispersal process. Biosystems 2010, 100, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, F.; Folke, C. Characteristics of nested living systems. J. Biol. Syst. 2012, 01, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E.; Fath, B.D. Application of thermodynamic principles in ecology. Ecol. Complex. 2004, 1, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera, R.; Fath, B.D.; Herrera, A.M.; Rodríguez, R.A. A strategic roadmap for interdisciplinary modeling in ecology: The result of reading ‘Defining an ecological equation of state: Response to Riera et al. 2023’ (Newman et al., 2023). Ecol. Modell. 2024, 490, 110658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, E.; Vrcelj, Z. Biomimicry and the built environment, learning from nature’s solutions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyus, J.M. Biomimicry-Innovation Inspired by Nature; Harper Perennial: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1–308. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groat, L.N.; Wang, D. Architectural Research Methods, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–480. [Google Scholar]
- Skene, K.R. The energetics of ecological succession: A logistic model of entropic output. Ecol. Modell. 2013, 250, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovisi, A. Exergy vs information in ecological successions: Interpreting community changes by a classical thermodynamic approach. Ecol. Modell. 2009, 220, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.W. Considerations of scale and hierarchy. In Ecological Integrity and the Management of Ecosystems, 1st ed.; Woodly, S., Kay, J., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, T.; Gaur, V.K. Exergy analysis: A guide to sustainability? Ecol. Econ. Soc. 2023, 6, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgen, S.; Sarikaya, I. Exergy for environment, ecology and sustainable development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1115–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perryman, M.E.; Schramski, J.R. Evaluating the relationship between natural resource management and agriculture using embodied energy and eco-exergy analyses: A comparative study of nine countries. Ecol. Complex. 2015, 22, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati-Mehdiabadi, E.; Sarhaddi, F.; Sobhnamayan, F. Exergy performance evaluation of a basin-type double-slope solar still equipped with phase-change material and PV/T collector. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 2409–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihervaara, P.; Mononen, L.; Nedkov, S.; Viinikka, A. Biophysical Mapping and Assessment Methods for Ecosystem Services. Deliv. D3 2018, 3, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellar, J.A.C.; Popartan, L.A.; Pueyo-Ros, J.; Atanasova, N.; Langergraber, G.; Säumel, I.; Corominas, L.; Comas, J.; Acuña, V. Nature-based solutions in the urban context: Teminology, classification and scoring for urban challenges and ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry, H.; Rogers, H. Where to rewild? A conceptual framework to spatially optimize ecological function. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20193017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, L.V. Regenerative—The new sustainable? Sustainability 2020, 12, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, T.T.S.; Koman, V.B.; Gordiichuk, P.; Park, M.; Strano, M.S. The emergence of plant nanobionics and living plants as technology. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açikkalp, E.; Hepbasli, A.; Palmero-Marrero, A.I.; Borge-Diez, D. Application of net zero extended exergy buildings concept for sustainable buildings analysis. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 68, 106095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M.; Barbier, M.; Filotas, E.; Gravel, D.; Isbell, F.; Miller, S.J.; Montoya, J.M.; Wang, S.; Aussenac, R.; Germain, R.; et al. Biodiversity as insurance: From concept to measurement and application. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 2333–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunialti, G.; Frati, L. Biomonitoring with lichens and mosses in forests. Forests 2023, 14, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristić, S.; Šajn, R.; Stamenković, S. Lichens as the main indicator in biological monitoring of air quality. In Contaminant Levels and Ecological Effects. Emerging Contaminants and Associated Treatment Technologies; Balabanova, B., Stafilov, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, A.; Saber, M.; Gadow, S. Biological indicators for pollution detection in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2020, 44, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciubba, E.; Zullo, F. An exergy-based analysis of the oc-evolution of different species sharing common resources. Ecol. Model. 2014, 273, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.N.; Müller, F.; Marques, J.C.; Bastianoni, S.; Jørgensen, S.E. Thermodynamics in ecology—An introductory review. Entropy 2020, 22, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muys, B.; Wagendorp, T.; Aerts, R.; Quijano, J.G. Ecological sustainability assessment of carbon conservation, sequestration and substitution projects using the exergy concept. Travaux 2003, 26, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Oehri, J.; Schmid, B.; Schaepman-Strub, G.; Niklaus, P.A. Biodiversity promotes primary productivity and growing season lengthening at the landscape scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10160–10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.K.R.; Kumar, B.M.; Nair, V.D. Definition and concepts of agroforestry. In An Introduction to Agroforestry; Springer Nature: Argau, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, M.S.; Altieri, A.H.; Angelini, C.; Bishop, M.J.; Bulleri, F.; Farhan, R.; Frühling, V.M.M.; Gribben, P.E.; Harrison, S.B.; He, Q.; et al. Heterogeneity within and among co-occurring foundation species increases biodiversity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Verdin, G.; Monarrez-Gonzalez, J.C.; Tecle, A.; Pompa-Garcia, M. Evaluating the multi-functionality of forest ecosystems in northern Mexico. Forests 2018, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremke, S.; Koh, J. Integration of ecological and thermodynamic concepts in the design of sustainable energy landscapes. Landsc. J. 2011, 30, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W.; Schindler, D.E. Getting ahead of climate change for ecological adaptation and resilience. Science 2022, 376, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perino, M.; Serra, V. Switching from static to adaptable and dynamic building envelopes: A paradigm shift for the energy efficiency buildings. J. Facade Des. Eng. 2015, 3, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doniță, N.; Brad, R.R. Ecological emergences within the multi-individual level of systemic organisation. Contrib. Bot. 2024, 58, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deetman, S.; Marinova, S.; van der Voet, E.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Edelenbosch, O.; Heijungs, R. Modelling global material stocks and flows for residential and service sector buildings towards 2050. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.A.F. On the exergy balance equation and the exergy destruction. Energy 2016, 116, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Thermodynamic analysis on theoretical models of cycle combined heat exchange process: The reversible heat exchange process. Energy 2017, 124, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gracia, A.; Cabeza, L.F. Phase change materials and thermal energy storage for buildings. Energy Build. 2015, 103, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Ali, H.M.; Habib, A.; Bashir, M.A.; Jabbal, M.; Yan, Y. Energy and exergy analysis of fuel cells: A review. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2019, 9, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirbet, A.; Lazár, D.; Guo, Y.; Govindjee, G. Photosynthesis: Basics, history and modelling. Ann. Bot. 2020, 126, 511–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallath, N.; John, N.; Rubeena, K.A.; Thangavel, M. Biomass from terrestrial environments. In Handbook of Biomass; Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2023; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, M.D.; Michaelides, E.E. Grid-independent residential buildings with renewable energy sources. Energy 2018, 148, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Convertino, M. Inferring ecosystem networks as information flows. Sci. Rep. 2021, 111, 7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Rumpel, C.; Paustian, K.; Kuikman, P.J.; Elliott, J.A.; McDowell, R.; Griffiths, R.I.; Asakawa, S.; Bustamante, M.; et al. Biogeochemical cycles and biodiversity as key drivers of ecosystem services provided by soils. Soil 2015, 1, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, D.; Van Passel, S. Advantages and limitations of exergy indicators to assess sustainability of bioenergy and biobased materials. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2014, 45, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolina, A.; Nadalini, V.; De, R.; Kalid, A.; Torres, E.A.; Peri, P. Emergy as a tool to evaluate ecosystem services: A systematic review of the literature. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, N.; Mahmoudi, M.; Bazargan, A.; McKay, G. Exergy and life cycle-based analysis. In Handbook of Environmental Materials Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciubba, E. Exergy-based ecological indicators: From thermo-economics to cumulative exergy consumption to thermo-ecological cost and extended exergy accounting. Energy 2019, 168, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.; Trindade, E.; Alencar, L.; Alencar, M.; Silva, L. Sustainability in the construction industry: A systematic review of the literature. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ESs Categories | ESs Categories | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supporting Services |  | Habitat provision | Cultural services |  | Aesthetic and artistic inspiration - Aesthetic value - Artistic inspiration |
 | Nutrient cycling - Retention of nutrients - Regulation of biogeochemical cycles |  | Recreation and psychological wellbeing - Sports - Outdoor activities - Tourism - Socialization - Relaxation and psychological benefit | ||
 | Species Maintenance |  | Sense of place and cultural diversity - Celebration of cultural diversity/history - Sense of place | ||
 | Fixation of solar energy |  | Spiritual and religious inspiration | ||
 | Soil building - Soil formation - Renewal of soil fertility - Soil quality control - Soil retention |  | Education and knowledge - Educational - Inspiration and innovation - Cognitive development - Knowledge building | ||
| Regulation Services |  | Disturbance prevention - Noise - Wave - Erosion - Earthquake - Drought - Flood/Storm events - Wind | Provisioning Services |  | Provision of fuel and energy - Water energy - Wind energy - Active/passive solar energy - Human body heat - Hydrogen energy - Biomass energy - Geothermal energy |
 | Climate regulation - UV protection - Moderation of temperature - Climate adaptation strategies - GHG mitigation |  | Provision of fresh water - Drinking water - Sanitation - Irrigation - Industrial processes - Recreational | ||
 | Purification - Water purification - Soil purification - Air purification |  | Provision of food - Small-scale to large-scale urban farming | ||
 | Decomposition - Biodegradation - Material reuse/recycling - Consumption reduction |  | Biochemicals - Medicine - Natural chemicals | ||
 | Biological control - Control of invasive species - Disease/pest regulation |  | Raw materials | ||
 | Pollination |  | Genetic resources |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hecht, K.; Ortega Reboso, A.; van der Vegt, M.; Appelman, J.; Pedersen Zari, M. Ecologically Regenerative Building Systems through Exergy Efficiency: Designing for Structural Order and Ecosystem Services. Land 2024, 13, 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091375
Hecht K, Ortega Reboso A, van der Vegt M, Appelman J, Pedersen Zari M. Ecologically Regenerative Building Systems through Exergy Efficiency: Designing for Structural Order and Ecosystem Services. Land. 2024; 13(9):1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091375
Chicago/Turabian StyleHecht, Katharina, Abraham Ortega Reboso, Michelle van der Vegt, Jaco Appelman, and Maibritt Pedersen Zari. 2024. "Ecologically Regenerative Building Systems through Exergy Efficiency: Designing for Structural Order and Ecosystem Services" Land 13, no. 9: 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091375
APA StyleHecht, K., Ortega Reboso, A., van der Vegt, M., Appelman, J., & Pedersen Zari, M. (2024). Ecologically Regenerative Building Systems through Exergy Efficiency: Designing for Structural Order and Ecosystem Services. Land, 13(9), 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091375











