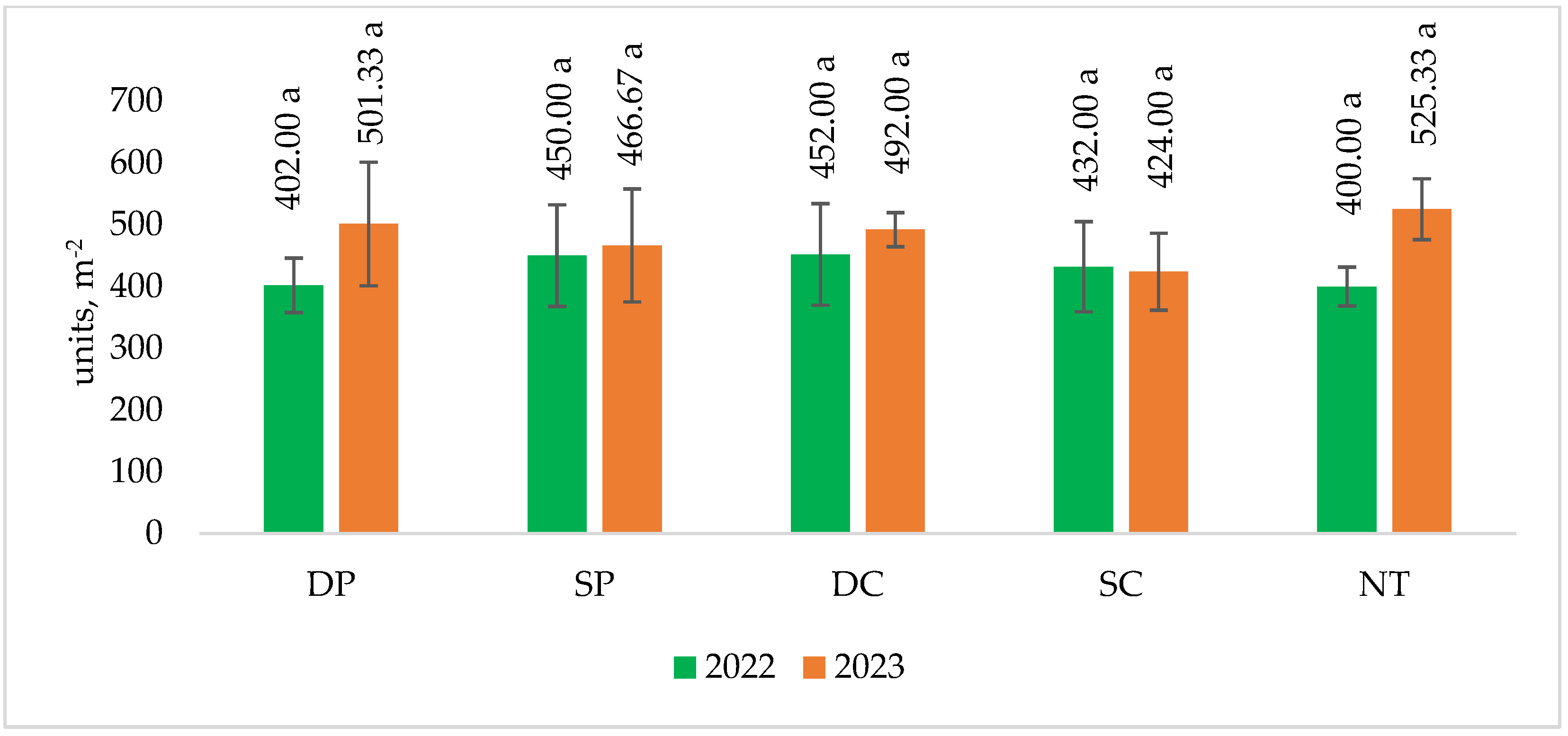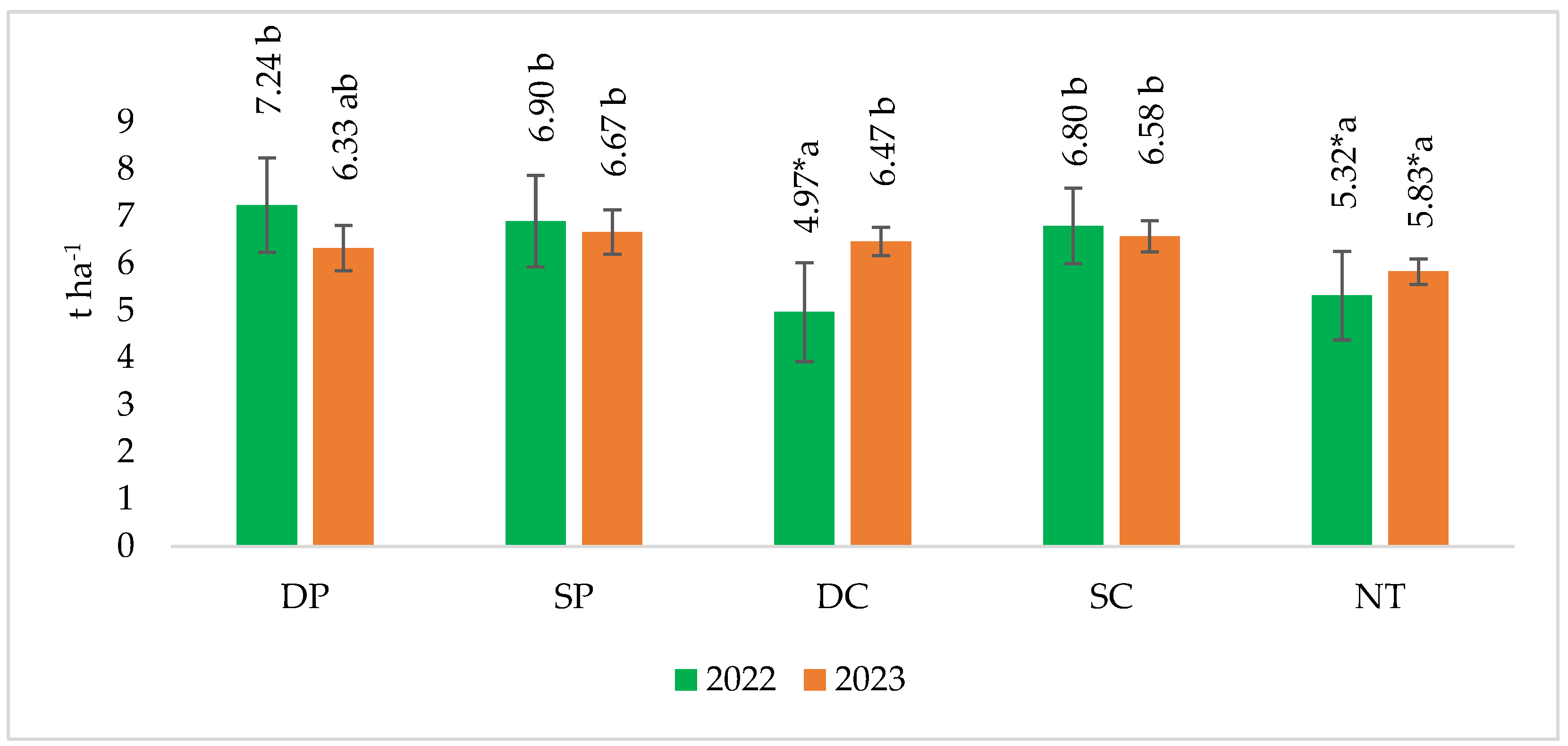Abstract
As the population grows, more food is needed to keep the food supply chain running smoothly. For many years, intensive farming systems have been used to meet this need. Currently, due to intense climate change and other global natural problems, there is a shift towards sustainable use of natural resources and simplified methods of tillage. Soil tillage intensity influences the distribution of nutrients, and soil’s physical and mechanical properties, as well as gas flows. The impact of reduced tillage on these indices in spring barley cultivation is still insufficient and requires more analysis on a global scale. This study was carried out at Vytautas Magnus University, Agriculture Academy (Lithuania) in 2022–2023. The aim of the investigation was to determine the effect of the tillage systems on the soil temperature, moisture content, CO2 respiration and concentration in spring barley cultivation. Based on a long-term tillage experiment, five tillage systems were tested: deep and shallow moldboard ploughing, deep cultivation-chiseling, shallow cultivation-chiseling, and no tillage Shallow plowing technology has been found to better conserve soil moisture and maintain higher temperatures in most cases. During almost the entire study period, the spring barley crop with deep cultivation had lower moisture content and lower soil temperature. Shallow cultivation fields in most cases increased CO2 emissions and CO2 concentration. When applying direct sowing to the uncultivated soil (10–20 cm), the concentration of CO2 decreased from 0.01 to 0.148 percent. pcs. The results show that in direct sowing fields, most cases had a positive effect on crop density. Direct sowing fields resulted in significantly lower, from 7.9 to 26.5%, grain yields of spring barley in the years studied.
1. Introduction
Soil preparation is one of the most important tasks in agriculture, as it is essential for plant growth and soil health. For plants to grow well, you need to ensure that the soil has the right amount of air, water, and nutrients. A prerequisite for this operation is the right soil structure, which can be affected by different tillage techniques. Soil properties directly impact the root system and growth of plants. The traditional tillage system, mainly involving ploughing and supplementary tillage, is widespread in Central Europe. However, for ecological and economic reasons, increasing attention is being paid to alternative tillage systems that aim to improve soil health and energy efficiency.
A study by Feizos et al. [1] argues that CO2 emissions are determined by the depth and intensity with which the soil is mechanically tilled. The authors believe that CO2 emissions are directly increased by intensive tillage. Other researchers point out that intensive tillage increases CO2 emissions to the atmosphere [2]. Increasing concentrations of CO2 in the air, together with other gases (CH4 and N2O), accelerate climate change. To reduce CO2 emissions from the soil, the use of no-till farming systems should be increased. The data obtained by scientists in Lithuania and many other countries around the world on reduced tillage are often different and contradictory. The impact and benefits of tillage are often related to the quality of soil preparation, previous agrotechnical measures such as pesticide use, fertilizer intensity, and plant species grown [3]. Reduced tillage reduces soil erosion, and improves soil structure, and durability, and other physical properties [3,4,5]. Avižienytė et al. [6] argue that minimum tillage before sowing intensifies the activity of microorganisms, causes less damage to the soil structure, and reduces the mixing of crop residues in the top layer of the soil. Tillage with implements determines the soil‘s physical properties, which are important for nutrient supply to the plant, and also influence the soil‘s air and moisture regime. Intensive tillage can have a negative impact on soil mobilization. Ecosystem functioning is influenced by soil temperature gradients, which are also important for ecological processes. Various factors such as soil moisture, climatic conditions, and land use affect soil temperature gradients. Soil temperature and soil moisture are very closely linked. Wet soils can store more heat. Wet soils need more heat to evaporate the water in the soil [7]. The soil moisture regime depends on its physical properties, granulometric composition, temperature, precipitation, etc. [8]. Soil moisture is also thought to be affected by tillage. Soil microorganisms help determine the stability of the ecosystem, nutrient cycling, and soil fertility. Factors such as the environment, tillage, and crop residues determine the biological activity of the soil. Different tillage techniques lead to different levels of organic residue incorporation and their incorporation affects the decomposition of organic matter [9]. The activity of microorganisms is essential for soil fertility and soil fertilization. Microorganisms are involved in the decomposition of organic matter, leading to an increase in minerals and biologically active substances needed by plants [10]. To provide good conditions for soil microorganisms and earthworms, it is important to choose the right tillage system [11,12,13]. Studies have shown that in fields with direct sowing, the growth and activity of microorganism populations in the top layer of the soil studied was higher due to the higher organic matter and moisture content compared to deep ploughing fields [14]. It was also found that in fields where direct sowing into uncultivated soil was applied, biodiversity and activity increased, and a higher amount of organic matter was accumulated, which is necessary for the growth of crop plants and their fertility, as well as for the improvement of the yield quality indicators [9,15,16]. A study by Toth et al. [17] showed that the organic carbon content in the 0–20 cm soil layer was significantly increased under no tillage (46 mg C ha−1) compared to conventional tillage (26 mg C ha−1). The authors point out that direct sowing and mulching improve the durability of the soil structure and the water-holding capacity.
Photosynthesizing living organisms take up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and use it during photosynthesis when the carbon is converted into carbohydrates, or otherwise energy reserves [18]. Organic carbon makes up approximately 58% of the organic matter in soil [19]. Krauss et al. [20] report that reduced tillage compared to deep ploughing increased SOC stocks in the surface layer by 20.8% and total SOC stocks by 1.7%, but biomass production was also reduced by 8% due to reduced tillage.
The most commonly studied enzymes are urease and sucrase, belonging to the class of hydrolases. The enzyme activity depends on indicators such as the intensity of beetle infestation, the abundance of microorganisms, the levels of mobile phosphorus, potassium, and humus, the acidity (pH) of the soil, and the plant yield [21]. Different tillage practices also change soil properties, which are closely linked to enzyme activity. Reduced tillage systems leave more crop residues such as straw. This intensifies the activity of enzymes in the soil and increases soil fertility [22,23]. The activity of soil enzymes affects the mineralization of crop residues, the increase in organic matter, soil structure, and nutrient cycling [24,25].
Soil biological indicators are crucial for soil quality. This is becoming increasingly important in today‘s farming, which is moving towards sustainability, cost reduction, and soil conservation [26]. Soil fauna helps plants obtain nutrients, improve soil structure, and regulate soil water levels [27]. The soil‘s biological properties are very sensitive and responsive to change [28]. Another factor influencing plants and microbes is soil water content. Plants and organisms rely heavily on water in soils and water is essential for nutrient cycling. It is essential for the development of plants that the soil provides favorable conditions for the growth of plant roots and the uptake of water, thus allowing yields to increase. Proper tillage has a positive effect on aeration, density, and water holding capacity, and therefore on root biomass and microorganism content. CO2 emissions are directly linked to the biological activity of microorganisms and root respiration. These processes are mainly influenced by soil structure, temperature, and moisture [29].
The aim of the investigation was to determine the effect of the tillage systems on the soil temperature, moisture content, CO2 respiration and concentration in spring barley cultivation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Experimental Site
The long-term stationary field experiment was performed at the Experimental Station of Vytautas Magnus University Agriculture Academy (former Aleksandras Stulginskis University) (54°52′ N, 23°49′ E). The experiment was initiated in 1988 and modified in 2001 when a direct sowing treatment was added. The research data, presented in this article, are from 2022 to 2023. The soil in the experimental field (2022) was silty loam (45.6% sand, 41.7% silt, 12.7% clay) Planosol (WRB 2014). The depth of the arable layer was 25–27 cm. The pHKCL of the soil surface was 6.4–7.7, the amount of available phosphorus varied from 194 to 384 mg kg−1, and potassium from 85 to 206 mg kg−1. Andriuškaitė (2022) found that in 2019 (0–20 cm) soil pH: deep ploughing—7.2; shallow ploughing—6.9; deep cultivation—7.1; shallow cultivation—6.9; no tillage—6.5. Mobile phosphorus (mg kg−1): deep ploughing—238.8; shallow ploughing—258.4; deep cultivation—264.9; shallow cultivation—252.1; no tillage—330.7. Mobile potassium (mg kg−1): deep ploughing—295.4; shallow ploughing—400.8; deep cultivation—330.9; shallow cultivation—357.9; no tillage—572.3. Total nitrogen (%): deep ploughing—0.111, shallow ploughing—0.134; deep cultivation—0.126; shallow cultivation—0.126; no tillage—0.163. Organic carbon (g kg−1): deep ploughing—14.6; shallow ploughing—18.3; deep cultivation—16.8; shallow cultivation—18.7; no tillage—22.0 [30]. The variation and location of elements depended on long-term soil tillage practices.
2.2. Experiment Design and Agricultural Practices
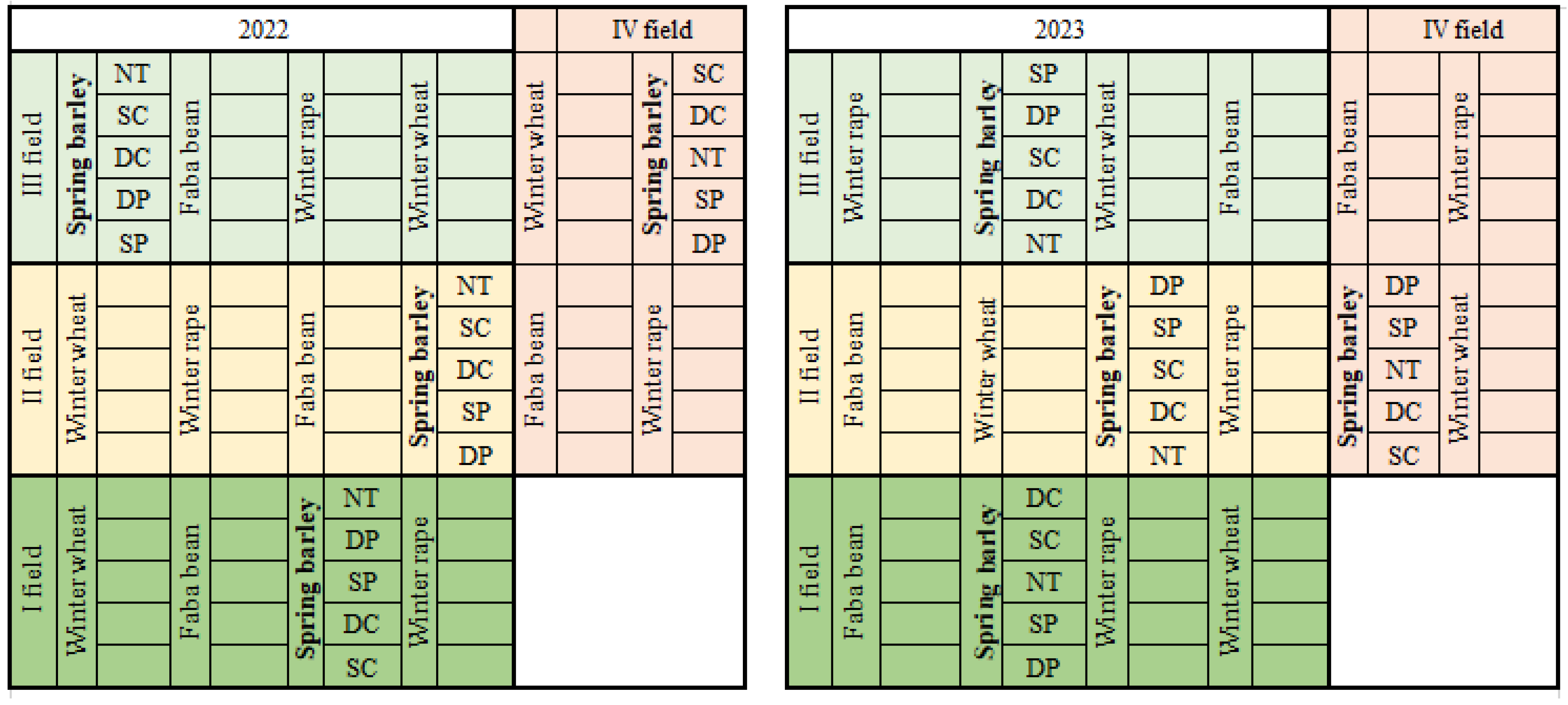
The experimental design (Table 1, Figure 1) consisted of four randomized main plots with four replications: spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), winter rape (Brassica napus L.), and faba bean (Vicia faba L.) with plant residues and winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with plant residues and cover crops. Tillage treatments were applied to five subplots: conventional ploughing (CP) at a depth of 22–25 cm (control treatment), shallow ploughing (SP) at a depth of 12–15 cm, deep cultivation (DC, chiseling) at a depth of 25–30 cm, shallow cultivation (SC, chiseling) at a depth of 10–12 cm, and no tillage (NT) (Table 1, Figure 1).

Table 1.
Tillage practice in the experiment (according to Romaneckas et al. [31]).
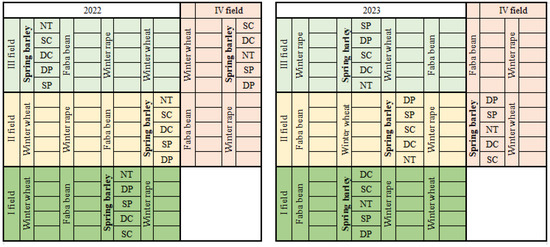
Figure 1.
The experiment plan of spring barley crop rotation (in 2022–2023). Note: NT—(no tillage); SC—(shallow cultivation); DC—(deep cultivation); DP—(deep ploughing); SP—(shallow ploughing).
There were 16 main plots of 126 m2 (14 × 9 m) and a protection zone of 1 m. In this study, soil samples were used only from a field of spring barley. A randomized design of the plot’s distribution was used. The buffer strip was 1 m wide between the experimental plots and 9 m between the blocks. The spring barley crop consisted of 20 subplots, each of 70 m2 (10 × 7 m). The main tillage operation for the treatments was performed during September–October.
Under NT treatment, there was no soil cultivation in spring, and the crops were directly planted. Moreover, weeds were chemically controlled with the herbicide Glyphogan 360 SL (De Bron, South Africa). The main cultivations were performed in September–October (2022 and 2023). For DP, SP ploughing was used as a plough Gamega PP-3-43 (Gamega Ltd., Lithuania). For DC, and SC tillage, a chisel cultivator KRG-3.6 (Laumetris Ltd., Keleriškiai, Lithuania) was used. The pre-sowing tillage operation was performed with a complex cultivator KLG-3.6 (Laumetris Ltd., Keleriškiai, Lithuania) in April–May. Spring barley was sown at a row spacing of 12.5 cm, at a depth of 3 cm and at a rate of 180 kg ha–1 with a drill Väderstad Rapid 300C Super XL (Väderstad AB, Väderstad, Sweden) in April–May. The application of NPK (16:16:16) and ammonium nitrate (N 34.4) fertilizers was 300 kg ha–1 and 200 kg ha–1, respectively. There was the same rate for all plots. The crops were sprayed using insecticide Karate Zeon 5 CS (50 g L−1 lamda cyhalothrin), herbicide Elegant 2FD (florasulam 6.25 g L−1 + 2.4-D 300 g L−1) and fungicide Mirador 250 SC (azoxystrobin 250 g L−1 (22.81%)). Insecticides and herbicides were applied twice per season.
Soil CO2 emissions were measured using an Infra-Red Gas Analyzer to measure the soil CO2 efflux (μmol m−2 s−1). The portable, automated soil gas flux system LI-8100A with an 8100-103 chamber and the analyzer LI-8100A (LI-COR Inc., Lincoln, NE, USA) was used. In spring, 20 cm-diameter rings were installed in the soil in each plot, and there were no growing plants. Two days before the measurements, all grown plants were removed. Three measurements were made in each plot. CO2 efflux was determined three times per growing season, at the same time of the day (from 10 a.m. to 3 p.m.) and at designated locations in the field. Soil moisture was measured with the sensor LI-8100-204 (LI-COR Inc.), and soil temperature with the sensor LI-8100-203 (LI-COR Inc.), included in the chamber control of the LI-8100A automated soil gas flux system (LI-COR Inc.).
Soil CO2 concentration (%) at the 0–10 cm and 10–20 cm layers was determined using the device Screenalyt honold umweltmesstechnik. Measurements were carried out in each accounting field during plant vegetation from 8 to 11 a.m. and from 2 to 5 p.m.
2.2.1. Assessment of Crop Density
The crop density (the number of productive stems) is determined at maturity, in 50 × 50 cm frames, at 4 points in the field, and expressed in pcs. m2. The spring barley density is determined at post-harvest, in 50 × 50 cm frames, at four locations in the field, and expressed in pcs. m2.
Yield. Spring barley are harvested in the experimental fields with a combine harvester, weighed, and expressed as the weight of grains of 14% moisture content for cereal with 100% purity. To determine the purity, a pooled sample of approximately 2 kg of grain or 0.5 kg of seed is made from all replicates of each variant. The cereal is poured into cloth bags. 2 samples from each variant of the pooled sample are counterbalanced. The impurities are removed, and the clean grains or seeds are weighed.
2.2.2. Statistical Analysis
The research data were processed by a one-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) using the F test of the computer software package SPSS Statistics I [32]. The research data were processed by the method of analysis of variance using the computer program SYSTAT 12. The significance of differences between the means of the variants was assessed using the LSD test at 95.99 and 99.9% confidence levels [33]. Inter-relationships between characteristics were evaluated by the method of correlation analysis by calculating the correlation coefficient r and its reliability at 95 and 99% probability levels and calculating regression equations with the computer program STAT from the program package SELECTION [33]. Standard errors of the means are indicated by whiskers.
In case of a significant difference between a given variant and the control, its confidence level is denoted as follows:
* for p ≤ 0.050 > 0.010 (the differences are significant at the 95% confidence level);
** for p ≤ 0.010 > 0.001 (differences are significant at the 99% confidence level);
*** for p ≤ 0.001 (differences are significant at the 99.99% confidence level).
p > 0.050—no significant differences (differences significant at less than 95% confidence level).
Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatments (p ≤ 0.05).
During the statistical analysis of research data, a significant interaction between years was found in many cases; therefore, research data for each year are presented separately.
2.3. Meteorological Conditions
The climate of the experimental site is identified as boreal (subarctic). During the last 100 years, the average annual temperature increased from 6.3 to 6.7 °C, and the precipitation rate—was from 590 to 625 mm. The length of vegetation season with active temperatures (SAT, ≥ 10°C) is approximately 6 months. The SAT in 1990 was 2132 °C, in 1995—2371 °C, and 2018—2965 °C. The average air temperatures across 24 h and the precipitation rates are presented in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
The average air temperature across 24 h during spring barley vegetative seasons, Kaunas Meteorological Station.

Table 3.
Precipitation (mm) during spring barley vegetative seasons, Kaunas Meteorological Station.
The start of the 2022 vegetative season was colder than normal and precipitation increased. July and August were warmer and precipitation was similar to the long-term average. In May 2023, temperatures were cooler and precipitation was very low. In June and August, temperatures and precipitation were similar to the long-term average. However, in July, precipitation was very low and temperatures were lower.
Looking at 2022 and 2023, it can be seen that the temperatures at the beginning of the crop vegetative season were cooler and those at the end of the vegetative season were warmer. In 2022, precipitation was higher in May, June and July, but the precipitation dropped drastically in April. In 2023, the opposite trend was observed.
A rise in air temperatures is a positive trend for the realization of cereal productivity; however, higher temperatures, due to decreased precipitation, destroy soil aggregates, increase soil compaction and reduce biological activity [34,35].
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Tillage Intensity on Soil Physical Properties
Analysis of the results showed that reduced tillage significantly affected soil moisture (Table 4).

Table 4.
The soil moisture content of spring barley crop, %.
The first measurement (6 June 2022, BBCH39) showed that the field with shallow ploughing (SP) and shallow cultivation (SC) had a significantly higher soil moisture content of 2.46 to 2.61 percentage points compared to deep ploughing (DP). When comparing different tillage systems with each other (6 June 2022), it was found that soil moisture in shallow plowing (SP) and shallow cultivation (SC) plots was significantly higher, compared to deep plowing (DP) and deep cultivation (DC).
In the third measurement (25 July 2022, BBCH71), shallow cultivation (SC) fields showed a significantly lower moisture content of 3.19 percentage points compared to conventional tillage (DP) fields. At the end of spring barley vegetation (12 August 2022), no-tillage (NT) plots had the lowest soil moisture compared to shallow plowing SP, deep cultivation (DC) and shallow cultivation (SC). Comparing 2022 and 2003 precipitation (mm) in spring barley vegetation seasons (May–August), 88.7 mm less precipitation fell in 2023. The 2023 drought also affected other barley spring results.
A linear very strong negative and statistically significant correlation (r = −0.91, y = 30.58 − 0.77x, p < 0.05) was found between soil moisture at BBCH47 and spring barley yield.
When the experiment was repeated in 2023 and measurements were taken, we received opposite results (Table 4).
The measurements in the fields of reduced tillage showed higher soil moisture, but not significantly. Further measurements in the spring barley crop during the vegetative season showed that the different tillage practices did not significantly affect soil moisture. The last measurement (4 August 2023, BBCH 89) before the spring barley harvest did not show any soil moisture content.
A linear positive very strong and statistically significant correlation (r = 0.92, y = 0.75 + 1.01x, p < 0.01) was found between soil moisture content on 28 June 2023 and soil temperature on 28 June 2023. A linear positive correlation (r = 0.98, y = 2.60 + 17.69x, p < 0.01) was found between the soil moisture content on 28 June 2023 and the soil CO2 emission (28 June 2023).
At the time of the measurement on 06 June 2022, when the plants had reached growth stage 37, the results showed that in all fields with reduced tillage, soil temperatures were significantly lower compared to the fields of deep ploughing (DP) (Table 5). Soil temperature measurements on 28 June and on 12 August in the reduced tillage fields did not show a significant difference in soil temperature compared to the deep ploughing fields (DP).

Table 5.
Soil temperature in spring barley crop, °C.
Soil temperature (6 June 2022; 25 July 2022) significantly increased with deep plowing (DP) compared to deep cultivation (DC), shallow cultivation (SC) and no tillage (NT). On 25 July 2022 (BBCH 71), the results showed that the fields with deep cultivation (DC), shallow cultivation (SC) and no tillage (NT) showed a significant decrease of 5.4 to 10.1% in soil temperature compared to deep ploughing (DP).
Soil temperature measurements for 2023, during the spring barley vegetation, showed that although six measurements were made, no significant differences were found (Table 6).

Table 6.
Soil CO2 concentration in spring barley crop, %.
A linear positive correlation was found between soil temperature (28 June 2023) and soil CO2 emissions (28 June 2023), with a very strong and statistically significant correlation (r = 0.97, y = −0.87 + 17.06x, p < 0.01).
In the year under study, the moisture content at the time of the first measurement was higher in the reduced tillage field compared to the control field (DP). During the period under study, the temperature was lower in all reduced tillage fields at the time of the first measurement, compared to deep ploughing fields (DP). In the third measurement, deep cultivation (DC) fields showed lower moisture content compared to deep ploughing (DP). Shallow ploughing (SP) fields showed higher temperatures in the second and third measurements compared to the control (DP).
3.2. The Effect of Tillage Intensity on Soil Biological Properties
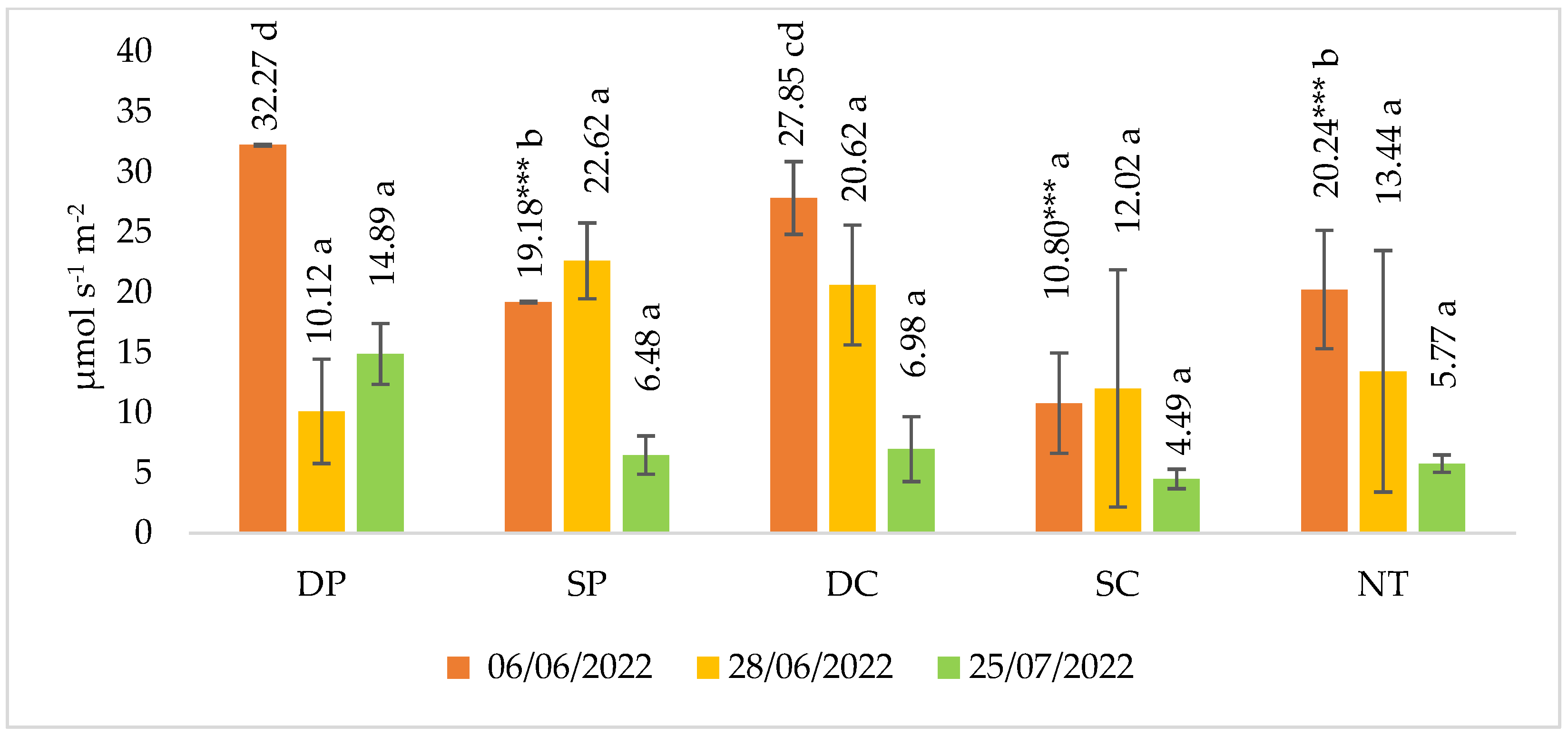
In 2022, three measurements of CO2 emissions were made during the spring barley vegetative season (Figure 2). The results of the first measurement (6 June 2022) showed that the CO2 emissions from the soil were significantly lower by a factor of 1.59 to 2.98 in the fields of shallow ploughing (SP), shallow cultivation (SP) and no tillage (NT) compared to deep ploughing (DP). A significantly higher release of CO2 emissions from the soil (6 June 2022) was found in deep plowing (DP) plots compared to shallow plowing (SP), shallow cultivation (SC) and no tillage (NT).
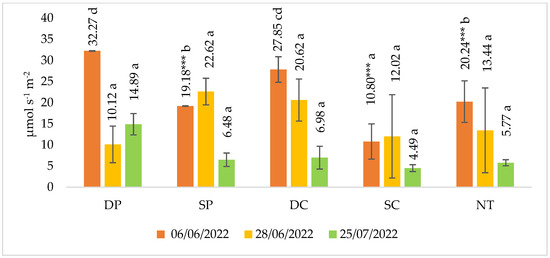
Figure 2.
Soil CO2 emissions in spring barley crop in 2022. Note. A confidence level of significant difference: *** p ≤ 0.001. Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatments (p ≤ 0.05). Whiskers indicate standard errors of the means. 1. DP—Deep ploughing 22–25 cm depth (control—comparable variant); 2. SP—Shallow ploughing 12–15 cm depth; 3. DC—Deep cultivation (chisel cultivator) 25–30 cm depth; 4. SC—Shallow cultivation (chisel cultivator) 10–12 cm depth; 5. NT—No tillage.
Other measurements showed that different tillage practices did not significantly affect the CO2 emissions from the soil.
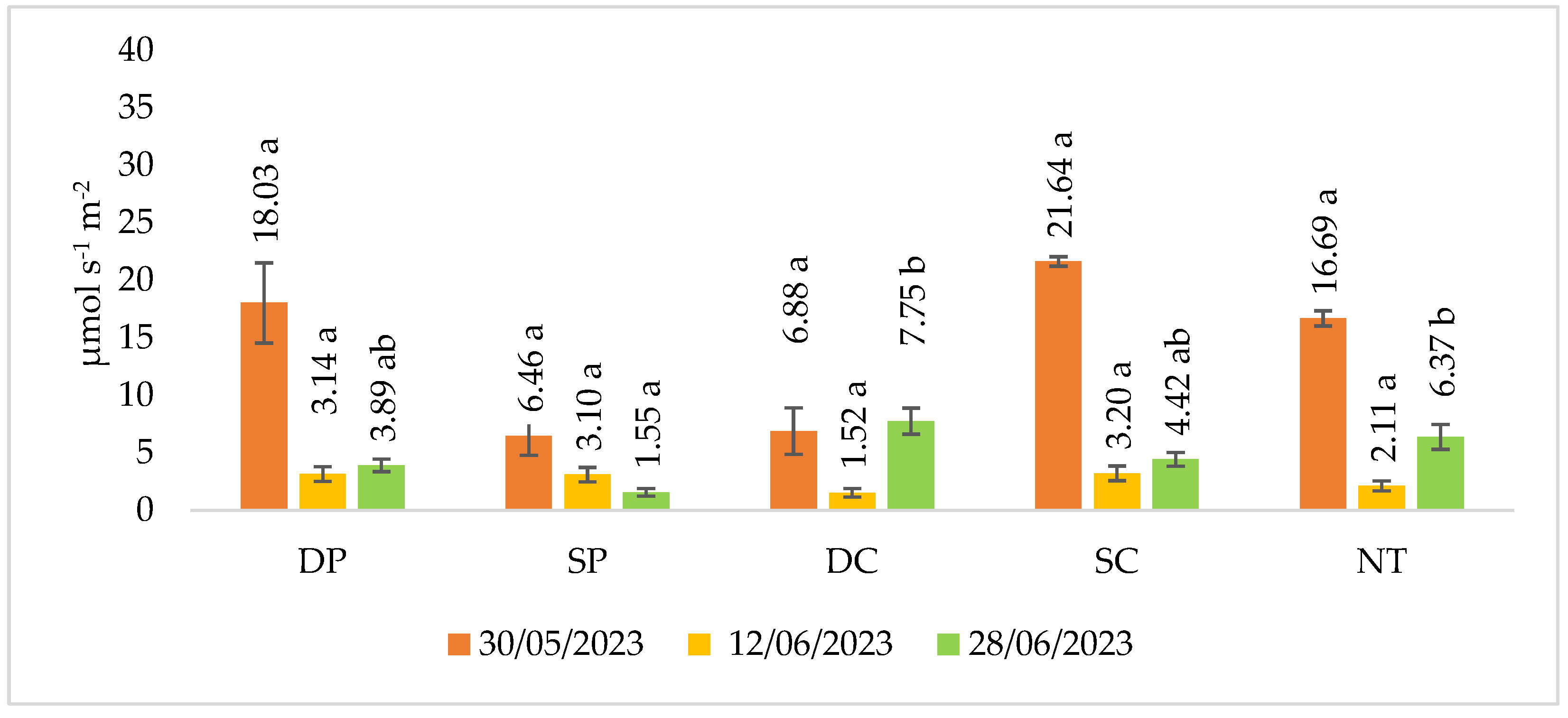
The experimental studies were continued in 2023, but the measurements were made three times (Figure 3).
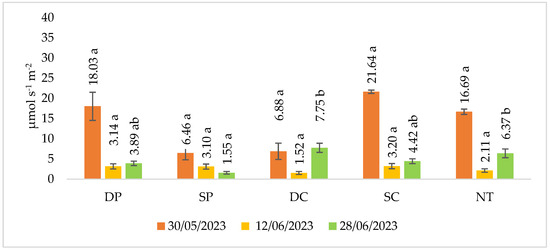
Figure 3.
Soil CO2 emissions in spring barley crop in 2023. Note. No significant differences: p > 0.050. Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatments (p ≤ 0.05). Whiskers indicate standard errors of the means. 1. DP—Deep ploughing 22–25 cm depth (control—comparable variant); 2. SP—Shallow ploughing 12–15 cm depth; 3. DC—Deep cultivation (chisel cultivator) 25–30 cm depth; 4. SC—Shallow cultivation (chisel cultivator) 10–12 cm depth; 5. NT—No tillage.
A review of the results shows no significant differences compared to the control (DP). A significantly lower release of CO2 emissions from the soil (28 June 2023) was found in shallow plowing (SP) plots compared to deep cultivation (DC) and no tillage (NT).
In the year studied, the CO2 emissions obtained in the shallow ploughing (SP) fields were higher compared to the control fields. In most of the reduced tillage fields, lower emissions were obtained in the third (2022) and second (2023) measurements.
A linear positive very strong and statistically significant correlation (r = 0.92, y = −113.04 + 0.30x, p < 0.05) was found between the soil CO2 emissions and the grain yield of spring barley.
Three measurements of CO2 concentration in the spring barley crop were carried out between 2022 and 2023 in different soil layers (Table 6).
In 2022, no significant differences were found in the topsoil (0–10 cm) in the fields with reduced tillage systems tested.
Significant differences in the amount of CO2 concentration in the studied soil layers between different tillage systems were determined only in 2023. In 2023, in deep cultivation (DC) and no-tillage (NT) fields, the first measurement (23 May 2023) showed significantly lower CO2 concentrations in the top (0–10 cm) layer of the soil by 0.71 and 0.67 percentage points, respectively, compared to deep ploughing (DP). In contrast, shallow ploughing (SP) and shallow cultivation (SC) plots showed significantly lower CO2 concentrations of 0.42 and 0.40 percentage points compared to conventional tillage (DP). In the second measurement (26 June 2023), which was carried out one month later, the shallow cultivation (SC) fields showed a significant decrease of 0.02 percentage points in CO2 concentration compared to deep ploughing (DP). The other reduced tillage treatments showed a non-significant decrease in CO2 concentration in the soil layer studied compared to deep ploughing (DP) fields. In the third measurement (4 August 2023) no CO2 concentration was detected due to drought.
In 2022, in the deeper (10–20 cm) soil layer, only the no-tillage (NT) plots showed a lower CO2 concentration of between 0.035 and 0.210 percentage points for the whole period studied, compared to the deep ploughing (DP) plots (Figure 3). In the lower (10–20 cm) soil layer, similar trends were found as in the upper (0–10 cm) soil layer studied in the third measurement (12 August 2022), with the shallow ploughing (SP) fields showing the highest CO2 concentrations compared to the deep ploughing (DP) fields.
Measurements in the deeper (10–20 cm) soil layer were also made in 2023. The first measurement in the reduced tillage fields showed lower CO2 concentrations of between 0.16 and 0.052 percentage points compared to the deep ploughing (DP) fields. In the second measurement (28 June 2023), also in the reduced tillage fields, the CO2 concentration was 0.007 to 0.014 percentage points lower compared to deep ploughing fields (DP). In contrast, the third measurement (4 August 2023) showed significantly lower CO2 concentrations of 0.158, 0.150, 0.140 and 0.148 percentage points in fields with shallow ploughing (SP), deep cultivation (DC), shallow cultivation (SC) and no tillage (NT) compared to deep ploughing (DP).
A linear negative very strong and statistically significant correlation (r = −0.98, y = 2861.83 + 267.84x, p < 0.01) was found between soil CO2 (10–20) concentration and spring barley productivity.
In the year under study, the lower arable layer received lower CO2 levels in the first measurement. No-tillage (NT) fields showed lower amounts in all measurements (Figure 4). In the topsoil, shallow ploughing (SP) and shallow cultivation (SC) fields showed lower CO2 yields.
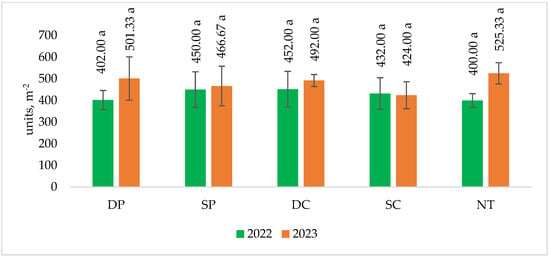
Figure 4.
The effect of tillage intensity on crop density (2022–2023). Note. No significant differences: p > 0.050. Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatments (p ≤ 0.05). Whiskers indicate standard errors of the means. 1. DP—Deep ploughing 22–25 cm depth (control—comparable variant); 2. SP—Shallow ploughing 12–15 cm depth; 3. DC—Deep cultivation (chisel cultivator) 25–30 cm depth; 4. SC—Shallow cultivation (chisel cultivator) 10–12 cm depth; 5. NT—No tillage.
3.3. The Effect of Tillage Intensity on Spring Barley Productivity Indicators
The crop density is calculated for the years 2022–2023 (Figure 4). When comparing different tillage systems, no significant effect on spring barley crop density was found.
In 2022, shallow cultivation (SC) plots showed a predominant increase in crop density of between 7.5 and 12.4% plants m−2 compared to deep ploughing (DP). In no-tillage (NT) fields, less than 1% (0.49%) of spring barley pcs. m−2 were found compared to deep ploughing (DP). In 2023, similar results were obtained. Deep ploughing (DP) and shallow cultivation (SC) plots showed non-significantly lower yields of 9.8 and 13.8%, respectively, compared to deep ploughing (DP). Shallow ploughing (SP) had a lower spring barley density (6.9%) compared to deep ploughing (DP). No-tillage (NT) plots showed a non-significant increase (4.8%) in spring barley density compared to deep ploughing (DP) plots.
In 2022, significantly lower yields were found in deep cultivation (DC) and no-tillage (NT) fields, 31.4 and 26.5%, respectively (Figure 5). The highest yield of 7.24 t ha−1 of spring barley grain was obtained in deep ploughing (DP) fields. In the fields with reduced tillage technology, spring barley grain yields were between 4.7 and 31.4% lower compared to the yields obtained in the control (DP).
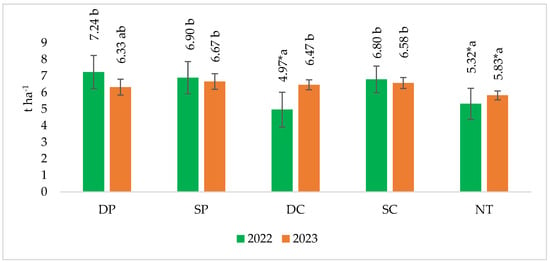
Figure 5.
The effect of tillage intensity on spring barley grain yields in 2022–2023. Note. A confidence level of significant difference: * p ≤ 0.050. Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatments (p ≤ 0.05). Whiskers indicate standard errors of the means. 1. DP—Deep ploughing 22–25 cm depth (control—comparable variant); 2. SP—Shallow ploughing 12–15 cm depth; 3. DC—Deep cultivation (chisel cultivator) 25–30 cm depth; 4. SC—Shallow cultivation (chisel cultivator) 10–12 cm depth; 5. NT—No tillage.
In 2023 the results were different. The highest grain yield of spring barley was found in the fields of shallow ploughing (SP), where it was 6.67 t ha−1. Both deep cultivation (DC) and shallow cultivation (SC) plots showed 2.2 and 3.9% lower grain yields, respectively, compared to the control plots (DP). Only the no-tillage (NT) plots showed a 7.9% significantly lower grain yield of spring barley compared to the deep ploughing (DP) plots. Significantly lower spring barley yields were found in both study years when no till (NT) was compared with shallow tillage (SP) and shallow tillage (SC).
4. Discussion
The water that naturally accumulates in soil pores, cracks and cavities is soil moisture [36]. Soil moisture depends on several factors such as physical properties, soil grain size, soil temperature and others [8]. The soil moisture regime is also thought to be influenced by the method of tillage. Soil temperature and soil moisture are closely linked. Wet soils can store more heat. Such soils require more heat to warm up to evaporate the water in the soil [7]. Deep ploughing promotes evaporation of moisture from the soil. Moisture is particularly important in spring and evaporation should be avoided. Shallow ploughing, on the other hand, inhibits this process. Loose topsoil reduces heat radiation. Shallowly incorporated plant residues benefit the soil, as shallowly incorporated plant residues decompose more quickly, thus improving the structure of the topsoil. Adequate heat and humidity are essential for quality shallow cultivation [36]. The heat exchange process in the soil is influenced by meteorological conditions, the thermal conductivity of the soil, the water content of the soil and other properties [37]. The most important factors influencing the thermal process in soil are tillage and the coverage of the soil surface by vegetation or its remains.
Researchers Buragienė [38], Steponavičienė et al. [5], Sinkevičius [39], and Andruškaitė [30] in their articles have investigated and discussed the scientific results, which we have also analyzed.
In a spring barley crop, Andriuškaitė [30], Buragienė [38] and Sinkevičius [39] carried out measurements of CO2 emissions. The research aimed to compare traditional tillage—deep ploughing—with soil conservation tillage and to compare the benefits and harms of the increasingly popular no-till methods.
Sinkevičius [39] made three measurements of CO2 emissions from the soil during the crop vegetative season. The first measurement (12 May 2021) showed that the reduced tillage fields had a higher CO2 release from the soil compared to the control fields. The results of Dencso et al. [40] showed that the no-tillage soil had 2.9 times higher CO2 emissions compared to the shallow-tilled soil. According to the authors, grassy no-till soils emit more CO2 due to root respiration rather than soil microbial activity. The study also highlighted the importance of GHG emission measurement timing, as a few days of heavier precipitation can significantly reduce GHG emissions. Buragienė et al. [4] also carried out measurements in 2009, 2010, and 2011. The researcher noted that in the years studied, the fields under reduced tillage had higher CO2 emissions after the test tillage compared to the results obtained when measurements were taken before reduced tillage. She also pointed out that in the study years, all the reduced tillage fields showed lower CO2 emissions than the control. Buragienė [38] found a negative correlation between soil temperature and CO2 emissions before autumn tillage (r = −0.98). Liu et al. [41] suggested that GHG emissions can also depend strongly on soil temperature so that CO2 emissions from soil decrease at higher temperatures. Steponavičienė et al. [42] found that soil temperature and moisture content are more influenced by meteorological conditions than by different tillage practices. Andruškaitė [30] also carried out CO2 measurements. The study reports that the measurements were carried out every two weeks in May, June and July. The results obtained in May 2018 showed that the fields of shallow ploughing had higher CO2 emissions from the soil compared to the control fields. The June results showed that the shallow ploughing and shallow cultivation fields had higher CO2 emissions, while the deep ploughing and direct sowing fields had lower CO2 emissions. The measurements continued and in June 2019, the results showed that shallow ploughing and direct sowing fields had lower CO2 emissions, while in July, deep ploughing and shallow cultivation fields had higher CO2 emissions. The results of Du et al. [43] showed that CO2 emissions are not influenced by the tillage method but by soil moisture content. Furthermore, their study showed that neither crop productivity nor soil microbial biomass differed significantly between tillage practices (p > 0.05). Bogužas et al. [44] showed that direct sowing resulted in higher CO2 emissions compared to the control. In our field experiment in 2022, a total of three measurements were made. The first (6 June 2022) and the third (25 July 2022) measurements gave opposite results. That is, in all reduced tillage fields CO2 emissions were found to be lower compared to deep ploughing. Meanwhile, in 2023, the first measurement (30 May 2023) showed similar results to those of Sinkevičius [39]. Uncultivated fields showed higher CO2 emissions compared to the control. Measurements carried out by the researcher on 17 July 2021 and 3 August 2021 showed that reduced tillage fields with and without cover crops had lower CO2 emissions compared to deep ploughing fields. Meanwhile, our second measurement on 28 June 2022 showed higher CO2 emissions in the reduced tillage fields compared to the control fields. In 2023, the results of the first (30 May 2023) and second (12 June 2023) measurements showed that shallow ploughing, deep cultivation and direct sowing fields had lower CO2 emissions compared to deep ploughing fields. In contrast, shallow cultivation fields showed higher results compared to the control. The third measurement (28 June 2023) showed that shallow ploughing fields had lower CO2 concentrations compared to the control fields. The remaining reduced tillage fields showed higher CO2 concentrations compared to the deep ploughing fields. Comparing the different studies and the data obtained, we can say that the results obtained in 2021 and 2023 were similar. The vegetative season is also very important for the overall soil respiration values, as CO2 emissions in the soil can decrease significantly after harvest [45]. According to these researchers, soil respiration was significantly higher under no tillage compared to arable farming, irrespective of crop type or meteorological conditions.
Lu et al. [46] argue that the 6 years of conventional tillage and no-till practices, conducted between the growth of wheat and corn, resulted in significant differences in the soil properties not only in their mean values but also in their temporal variability. The NT treatment resulted in lower soil CO2 emissions when compared to the conventional tillage treatment. This seemed to be related to the differences observed in certain physical, chemical, and biological soil properties, especially the temperature and C stock. A positive linear correlation between the CO2 emissions and soil organic carbon stock indicated that the soil C losses could be due to the decomposition of soil organic carbon.
Bogužas et al. [44] present yield results for different tillage treatments. In 2015, the spring barley crop showed the highest yields in direct sowing fields. In our field experiment, yield comparisons for spring barley grain were also established. In 2023, we found that the direct sowing fields produced the lowest yields. In 2022–2023, the highest yields were obtained in shallow ploughing fields. Similar results have been obtained by Niether et al. [47], where higher yields were obtained with deep and shallow ploughing compared to direct sowing in no tillage While reduced tillage is an important practice to limit disturbance to soil structure and biota, deep ploughing is still commonly used in conventional farming as the most effective way to control weeds and aerate heavy soils. According to Piggin et al. [48], zero tillage and early sowing time had an effect of 12% higher yield of spring barley compared to traditional tillage. Kauppi et al. [49] obtained opposite results and reported that spring barley yield was 12–13% higher with deep tillage and reduced tillage than with no tillage. This coincides with the data of our experiment, since the yield of spring barley grains in no-tillage (NT) fields was significantly lower compared to the yield of deep plowing fields (DP).
So, although we are comparing the work of only a few researchers who carried out similar studies in different years, we can see that the results obtained in each year sometimes differ. There are many different reasons for this, but one of the main ones is the different meteorological conditions in each of the years studied. Evaluation of the obtained results, analysis of scientific literature, technical indicators, impact on climate change, it can be said that simplified land systems are more efficient than deep plowing technology.
5. Conclusions
Comparing the reduced-intensity tillage system with the deep plowing (DP) technology, we can say that the shallow plowing (SP) tillage technology was more efficient. When comparing different tillage systems, deep plowing (DP) in most cases had a negative effect on the studied indicators. Shallow plowing (SP) and shallow cultivation (SC) had a positive influence on the obtained results. The shallow plowing (SP) tillage system was almost twice as efficient as the deep plowing (DP) tillage technology.
In shallow plowing (SP) fields, soil moisture and temperature increased, but CO2 emission and concentration in the soil. The established soil CO2 indicators was also improved by no-tillage (NT) technology compared to deep plowing (DP). The yield of spring barley decreased with no-tillage (NT) tillage technology compared to deep plowing (DP). Spring barley yield was related to soil moisture (r = −0.91, p < 0.05) and CO2 emissions from the soil (r = 0.92, p < 0.05). When comparing the systems with each other, deep plowing (DP) had the greatest negative effect on the CO2 concentration in the deeper soil layer.
In order to further highlight the differences between the studied tillage systems, it would be appropriate to perform agrochemical and microbiological analyzes of the soil and to determine the activity of enzymes in each studied year.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.K., K.R., A.S., J.B., T.P. and K.J.; methodology, A.S.; software, R.K.; formal analysis, A.S.; investigation, K.J. and T.P.; data curation, J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S. and R.K.; writing—review and editing, K.R.; visualization, R.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Feiza, V.; Feizienė, D.; Auškalnis, A.; Kadžienė, G. Sustainable tillage: Results from long-term field experiments on Cambisol. Zemdirb. Agric. 2010, 97, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Maikštėnienė, S.; Šlepetienė, A.; Masilionytė, L. Verstuvinio ir nevertuvinio pagrindinio žemės dirbimo poveikis glėjiškų rudžemių savybėms ir agrosistemų energetiniam efektyvumui. Žemdirbystė 2007, 94, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jodaugienė, D. The peculiarities of underground and overground parts of Triticum aestivum winter varieties ‘Širvinta 1’ and ‘Zentos’ under the conditions of different soil tillage. Žemdirbystė 2002, 77, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Buragienė, S.; Šarauskis, E.; Romaneckas, K.; Sasnauskienė, J.; Masilionytė, L.; Kriaučiūnienė, Z. Experimental analysis of CO2 emissions from agricultural soils subjected to five different tillage systems in Lithuania. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steponavičienė, V.; Bogužas, V.; Sinkevičienė, A.; Skinulienė, L.; Vaisvalavičius, R.; Sinkevičius, A. Soil Water Capacity, Pore Size Distribution, and CO2 Emission in Different Soil Tillage Systems and Straw Retention. Plants 2022, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avižienytė, D.; Romaneckas, K.; Pališkytė, R.; Bogužas, V.; Pilipavičius, V.; Šarakauskis, E.; Adamavičienė, A.; Vaiciukevičius, V. The impact of long-term reduced primary soil tillage on maize (Zea mays L.) productivity. Agriculture 2023, 100, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veršulienė, A.; Kadžienė, G.; Kochiieru, M.; Pranaitienė, S.; Meškauskienė, L.; Auškalnienė, O. Vasarinių miežių šaknų ir dirvožemio fizikinių savybių atsakas į pokyčius po denginiu pasėliu ir skirtingu žemės dirbimu. Zemdirb. Agric. 2022, 4, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kažys, J.; Rimkus, E.; Bukantis, A. Gausūs krituliai Lietuvoje 1961–2008 metais. Geografija 2009, 45, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Cesevičius, G.; Janušauskaitė, D. Dirvožemio mikrobiologinės ir fizikinės savybės įvairiose žemės dirbimo sistemose. Žemdirbystė 2006, 93, 18–34. [Google Scholar]
- Piaulokaitė-Motuzienė, L.; Končius, D. Azotą transformuojančių mikroorganizmų paplitimas esant skirtingoms aplinkos sąlygoms. Žemės Ūkio Moksl. 2007, 14, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sparovek, G. Earthworm (Pontoscolex corethrurus) and organic matter effects on the reclamation of an eroded Oxisol. Pedobiologic 1999, 43, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogužas, V.; Kairytė, A.; Jodaugienė, D. Soil physical properties and earthworms as affected by soil tillage systems, straw and green manure management. Žemdirbystė 2010, 97, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Juchnevičienė, A.; Raudonius, S.; Avižienytė, D.; Romaneckas, K.; Bogužas, V. Ilgalaikio supaprastinto žemės dirbimo ir tiesioginės sėjos įtaka žieminių kviečių pasėliui. Žemės Ūkio Mokslai 2012, 19, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, R.; Furtini-Neto, A.E.; Guedes, G.A.A.; Fernandes, L.A. Urease activity and it is relation to soil organic matter, mikcrobia biomass nitrogen and urea−nitrogen assimilation by maize in a Brazilan Oxisoil under no-tillage and tillage systems. Biol. Fertil. Soil 2000, 32, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Effects of straw incorporation on the soil nutrient contents, enzyme activities, and crop yield in a semiarid region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J. The effects of rotating conservation tillage with conventional tillage on soil properties and grain yields in winter wheat−spring maize rotations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 263, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, M.; Stumpp, C.; Klik, A.; Strauss, P.; Shulz, B.; Liebhard, G.; Strohmeier, S. Long-term effects of tillage systems on soil health of a silt loam in Lower Austria. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 241, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Singh, J.; Kumar, P. Impact of bioenergy for the diminution of an ascending global variability and change in the climate. In Microbiome Under Changing Climate; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 21, pp. 469–487. [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl, D.W. A critical review of the conventional SOC to SOM conversion factor. Geoderma 2010, 156, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, M.; Wiesmeier, M.; Don, A.; Cuperus, F.; Gattinger, A.; Gruber, S.; Haagsma, W.K.; Peigné, J.; Chiodelli-Palazzoli, M.; Schulz, F.; et al. Reduced tillage in organic farming affects soil organic carbon stocks in temperate Europe. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 216, 105262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, N.; Singh, D. Enzymes in relation to soil biological properties and sustainability. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 30, 383–406. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, A.D.; Domuta, C.; Ciobanu, C.; Sandor, M. Field management effects on soil enzyme activities. Rom. Agric. Res. 2008, 28, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, C.P.; Kumar, N.; Das, K.; Hazra, K.K.; Praharaj, C.S.; Singh, N.P. Impact of variable tillage-based residue management and legume-based cropping for seven years on enzymes activity, soil quality index and crop productivity in rice ecology. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2021, 10, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trap, J.; Riah, W.; Akpa−Vinceslas, M.; Bailleul, C.; Laval, K.; Trinsoutrot−Gattin, I. Improved effectiveness and efficiency in measuring soil enzymes as universal soil quality indicators using microplate fluorimetry. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 45, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.S.; Grover, M.; Kundu, S.; Desai, S. Soil Enzymes. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2017; pp. 2100–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Brussaard, L.; De Ruiter, P.C.; Brown, G. Soil biodiversity for agricultural sustainability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibblewhite, M.G.; Ritz, K.; Swift, M.J. Soil health in agricultural systems. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Zsolnay, A.; Hernández, T.; García, C. Past, present and future of soil quality indices: A biological perspective. Geoderma 2008, 147, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks Pries, C.E.; Castanha, C.; Porras, R.C.; Torn, M.S. The whole−soil carbon flux in response to warming. Science 2017, 355, 1420–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruškaitė, I. Dirvožemio Tvarumas Didinant Anglies Sankaupų Sluoksniavimąsi Armenyje Skirtingo Žemės Dirbimo Sąlygomis. Ph.D. Thesis, Vytautas Magnus University, Kaunas, Lithuania, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Romaneckas, K.; Adamavičienė, A.; Sinkevičienė, A.; Kimbirauskienė, R.; Bogužas, V.; Šarauskkis, E.; Butkus, V.; Jasinskas, A.; Buragienė, S.; Čekanauskas, S. Influence of five tillage patters on faba bean productivity parameters. In Actual Tasks on Agricultural Engineering. Proceeding of 45 International Symposium on Agricultural Enginiering; University of Zagreb: Opatija, Croatia, 2017; pp. 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- SPSS. Instat 10; Statistics I; SPSS: Chicago, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Raudonius, S. Statistikos taikymas augalų ir pasėlių tyrimuose: Svarbūs klausimai. Zemdirb. Agric. 2017, 104, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badagliacca, G.; Benítez, E.; Amato, G.; Badalucco, L.; Giambalvo, D.; Laudicina, V.A.; Ruisi, P. Long-term no-tillage application increases soil organic carbon, nitrous oxide emissions and faba bean (Vicia faba L.) yields under rain-fed Mediterranean conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhola, S.; Klein, N.; Käyhkö, J.; Neset, T.-S.S. Climate change transformations in Nordic agriculture? J. Rural. Stud. 2017, 51, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirsė, A.; Taparauskienė, L. Drėgmingumo kaita augalų vegetacijos metu ir jo vertinimo metodų palyginimas. Žemės Ūkio Mokslai 2010, 17, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Feizienė, D.; Feiza, V.; Vaidelienė, A.; Povilaitis, V.; Antanaitis, Š. Soil surface carbon dioxide exchange rate as affected by soil texture, different long-term tillage application and weather. Zemdirb. Agric. 2010, 97, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Buragienė, S. Skirtingų Žemės Dirbimo Technologijų Poveikis Aplinkai. Ph.D. Thesis, Vytautas Magnus University, Kaunas, Lithuania, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sinkevičius, A. Žemės Dirbimo Technologijų Ilgalaikis Poveikis Agroekosistemų Tvarumui. Ph.D. Thesis, Vytautas Magnus University, Kaunas, Lithuania, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dencso, M.; Toth, E.; Zsigmond, T.; Saliga, R.; Horel, A. Grass cover and shallow tillage inter-row soil cultivation affecting CO2 and N2O emissions in a sloping vineyard in upland Balaton, Hungary. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 37, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Li, G. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi affect the response of soil CO2 emission to summer precipitation pulse following drought in rooted soils. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 352, 110023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steponavičienė, V.; Žiūraitis, G.; Rudinskienė, A.; Jackevičienė, K.; Bogužas, V. Long-Term Effects of Different Tillage Systems and Their Impact on Soil Properties and Crop Yields. Agronomy 2024, 14, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Li, F.; Qiao, Y.; Leng, P.; Zhao, L.; Ge, J.; Yang, G. Influence of no-tillage and precipitation pulse on continuous soil respiration of summer maize affected by soil water in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogužas, V.; Sinkevičienė, A.; Romaneckas, K.; Steponavičienė, V.; Skinulienė, L.; Butkevičienė, L.M. The impact of tillage intensity and meteorological conditions on soil temperature, moisture content and CO2 efflux in maize and spring barley cultivation. Žemdirbystė 2018, 105, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Gelybo, G.; Barcza, Z.; Dencso, M.; Potyo, I.; Kasa, I.; Horel, A.; Pokovai, K.; Birkas, M.; Kern, A.; Hollos, R.; et al. Effect of tillage and crop type on soil respiration in a long-term field experiment on chernozem soil under temperate climate. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 216, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lu, X.; Liao, Y. Dirvožemio CO2 emisija ir jos ryšys su dirvožemio savybėmis skirtingose žemės dirbimo sistemose. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2015, 62, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niether, W.; Macholdt, J.; Schulz, F.; Gattinger, A. Yield dynamics of crop rotations respond to farming type and tillage intensity in an organic agricultural long-term experiment over 24 years. Field Crops Res. 2023, 303, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggin, C.; Haddad, A.; Khalil, Y.; Loss, S.; Pala, M. Effects of tillage and time of sowing on bread wheat, chickpea, barley and lentil grown in rotation in rainfed systems in Syria. Field Crops Res. 2015, 173, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, K.; Kaseva, J.; Jalli, M.; Palojärvi, A.; Alakukku, L. Long-term nitrogen and phosphorus balances for spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivation as affected by primary tillage of a Nordic clay soil. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 155, 127131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).