Interaction Effect of Carbon Emission and Ecological Risk in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: New Insights into Multi-Simulation Scenarios
Abstract
1. Introduction
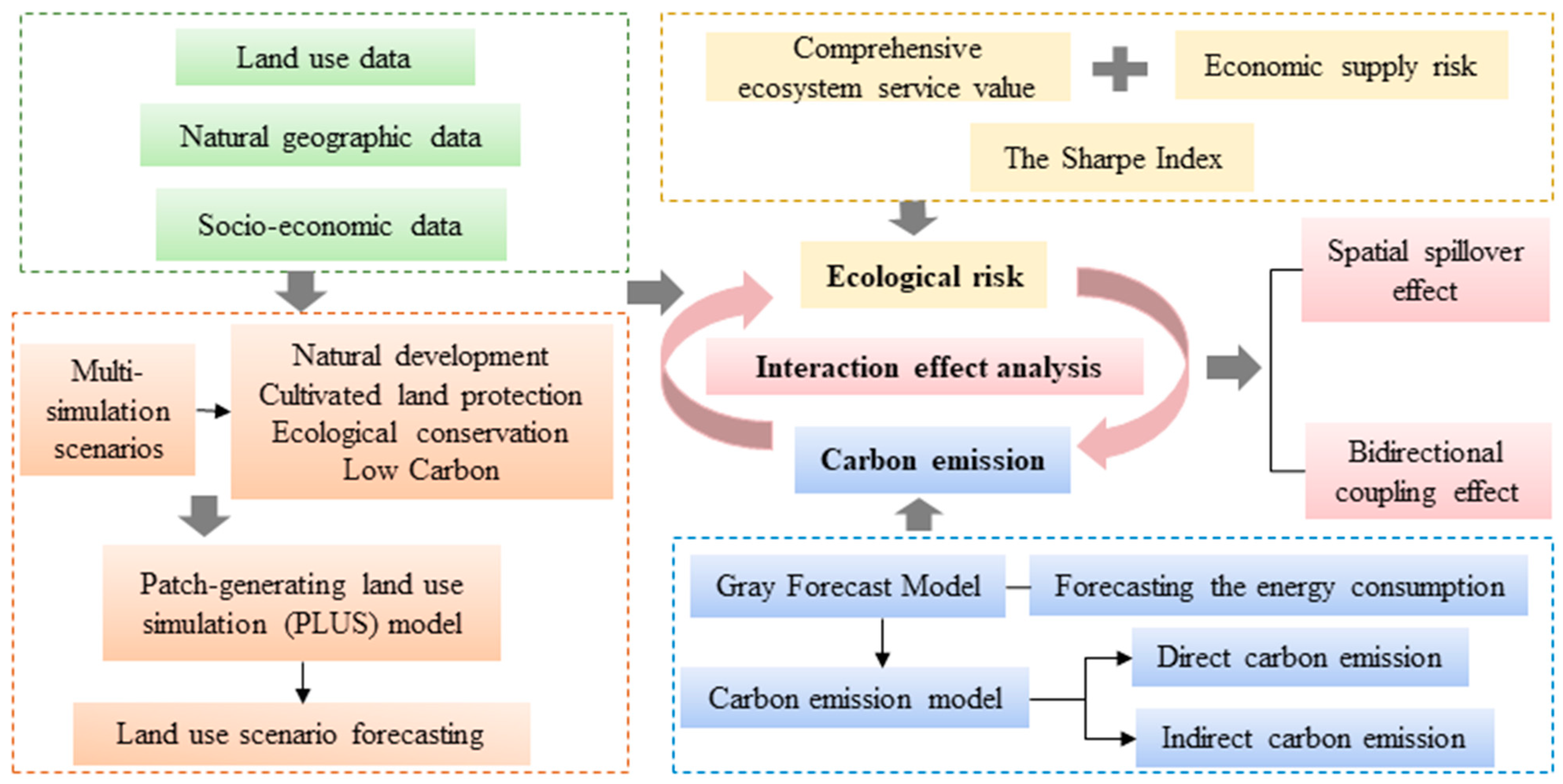
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Geoinformation Tupu Method
2.3.2. Land Use Simulation
2.3.3. Gray Forecast Model
2.3.4. Land Use Carbon Emission (LUCE) Model
2.3.5. Calculation of the ERI
2.3.6. Interaction Effect Analysis
3. Results
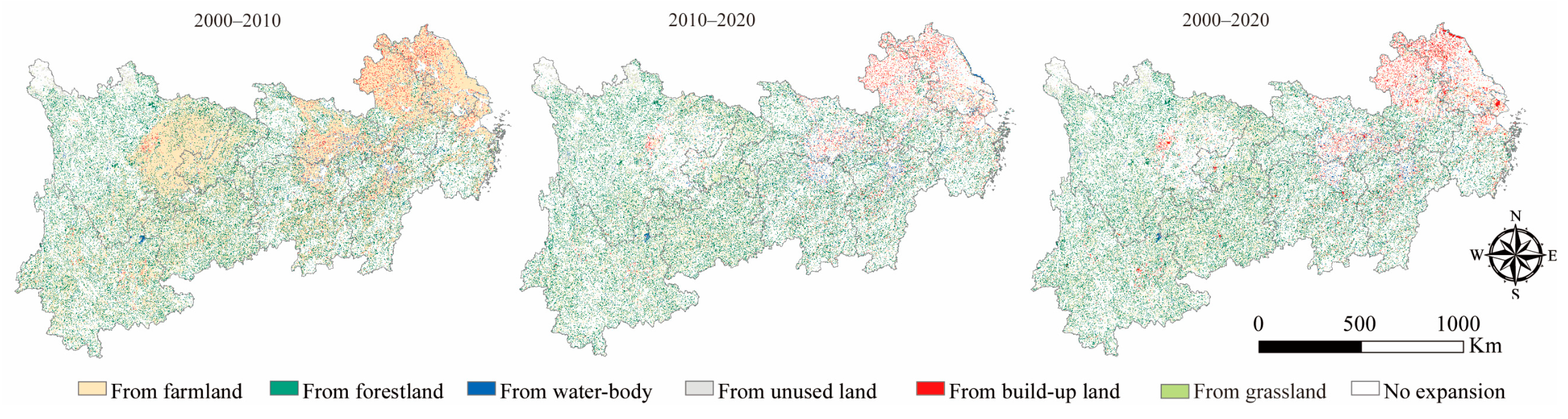
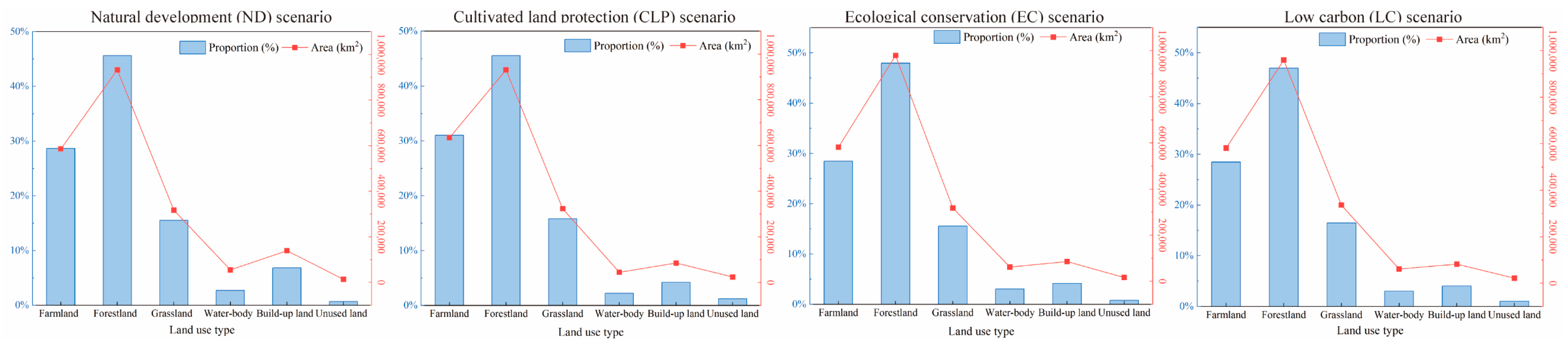
3.1. Land Utilization Pattern under Multi-Scenario Simulations in YREB
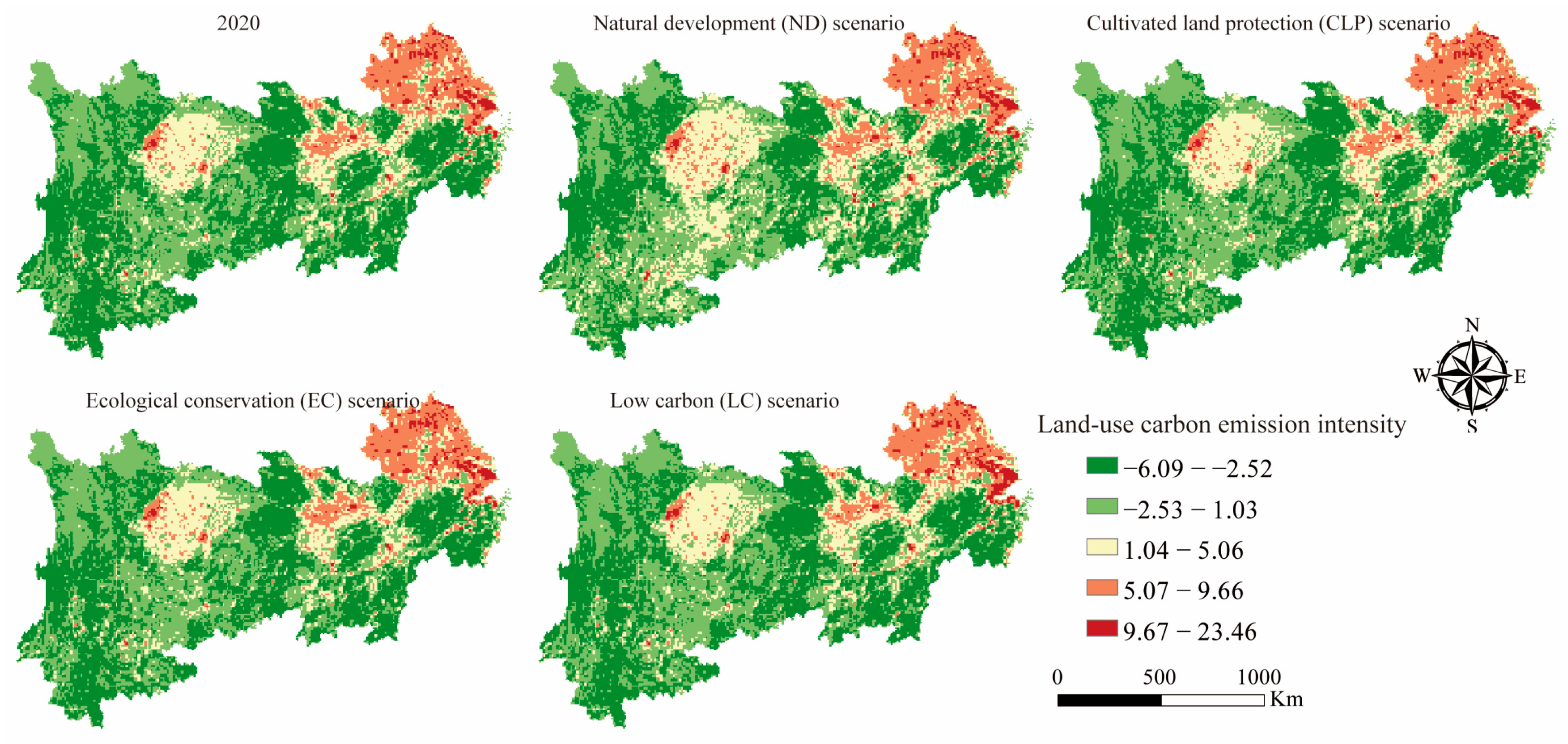
3.2. Spatial Pattern of Land Use Carbon Emission
3.2.1. Forecasting the Energy Consumption
3.2.2. Land Use Carbon Emission under Multi-Scenario Simulations in YREB
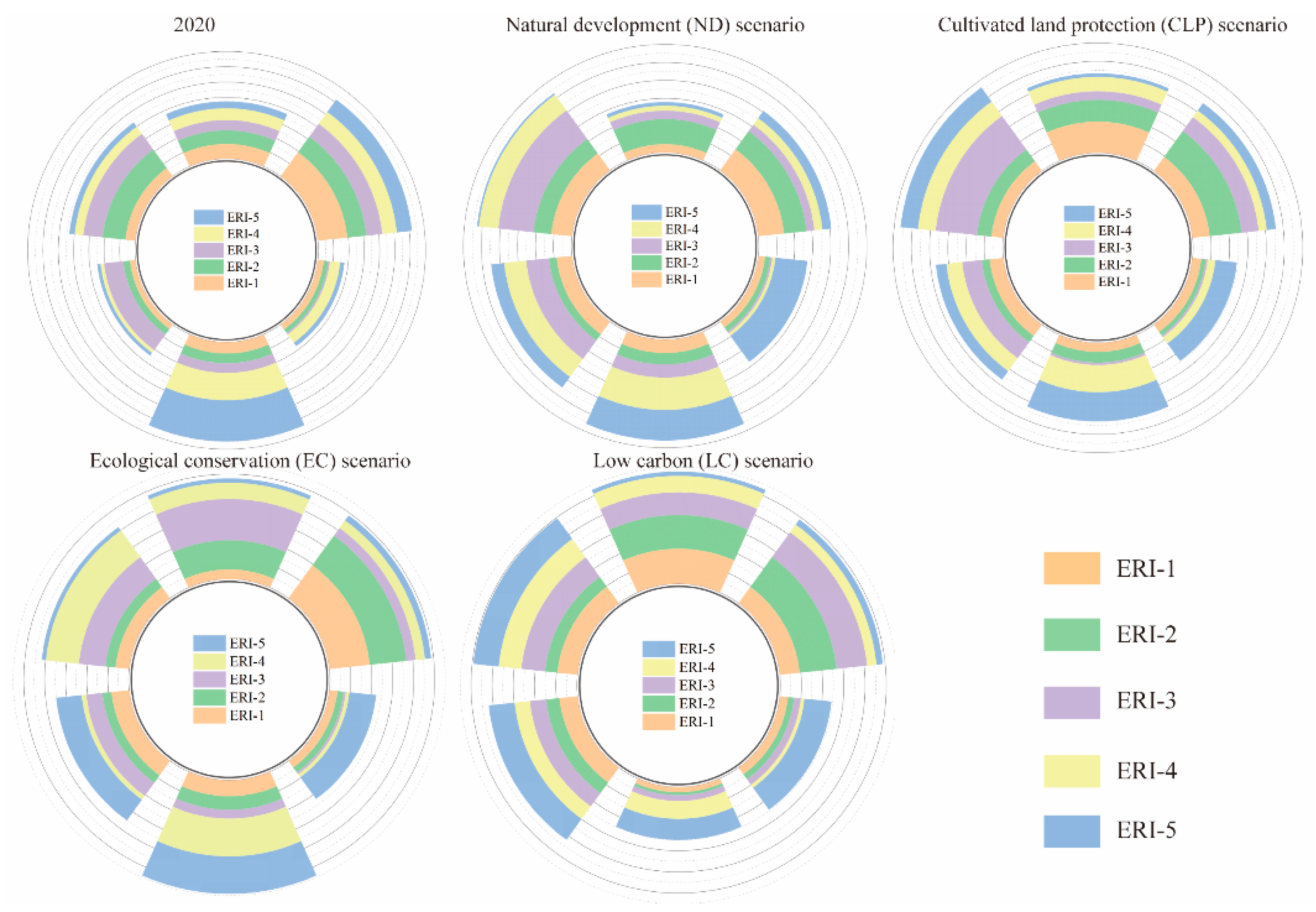
3.3. Spatial Pattern of Ecological Risk in YREB
3.3.1. Spatial Pattern of Ecological Risk Index Considering Uncertainty
3.3.2. Ecological Risk Index under Multi-Scenario Simulations in YREB
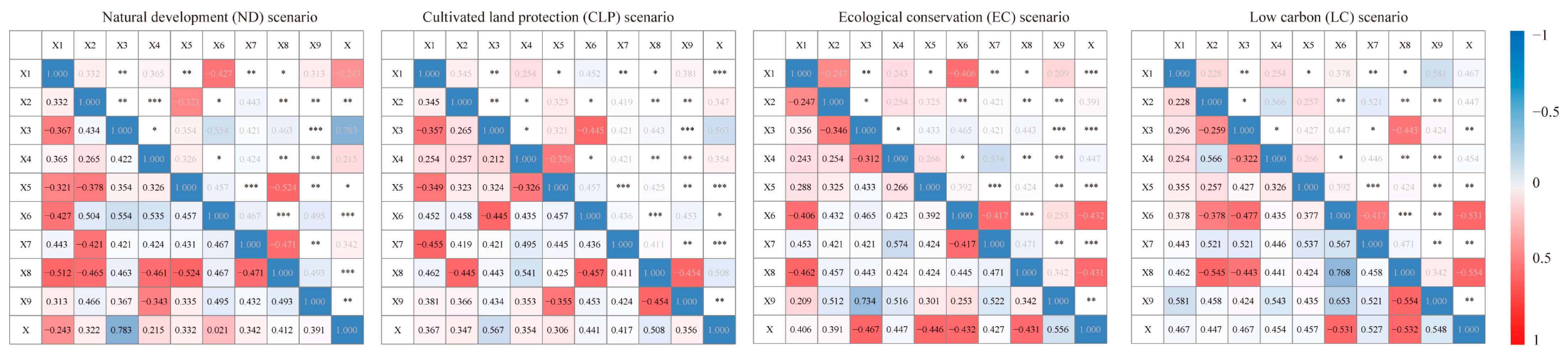
3.4. Interaction Effect Analysis of ERI and LUCE in YREB
3.4.1. Spatial Spillover Effects Analysis
3.4.2. Coupling Coordination Effects Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Further Comprehension of Carbon Emissions with Land Use
4.2. Comprehensive Analysis of Ecological Risk Considering Land Utilization
4.3. Interaction Effect and Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, M.; Chang, L.J.; Ma, S.J.; Zhao, Z.J.; Wu, K.; Hu, X.; Gu, Q.S.; Lü, G.N.; Chen, M. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use for Sustainable Development Goals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warchold, A.; Pradhan, P.; Thapa, P.; Putra, M.P.I.F.; Kropp, J.P. Building a unified sustainable development goal database: Why does sustainable development goal data selection matter? Sustain. Dev. 2022, 30, 1278–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Dong, Y.X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H.O.; Wang, C.J.; Du, Z.W. Temporal and spatial differences in carbon emissions in the Pearl River Delta based on multi-resolution emission inventory modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wen, X.; Guo, Y.T.; Gao, T.M.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L. Spatiotemporal Variability of Carbon Flux from Different Land Use and Land Cover Changes: A Case Study in Hubei Province, China. Energies 2014, 7, 2298–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Sengupta, T.; Alvarado, R. Interplay between technological innovation and environmental quality: Formulating the SDG policies for next 11 economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, M.; Gao, L.J.; Yang, B.; Shi, L.Y. Development and application of a comprehensive ecological risk assessment indicator system in Xiamen, China. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2018, 25, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Zhao, Y.H.; Luo, M.Y.; Han, L.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, L. The Effect of the Human Footprint and Climate Change on Landscape Ecological Risks: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau, China. Land 2022, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.R.; Niu, C.Y.; Zhang, S.R.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, Z.Y.; Cui, Y.R. Spatiotemporal patterns and modifiable areal unit problems of the landscape ecological risk in coastal areas: A case study of the Shandong Peninsula, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.B.; Zong, H.N.; Su, D.S.; Ping, Z.L.; Guan, M. Land Use Change and Its Impact on Landscape Ecological Risk in Typical Areas of the Yellow River Basin in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ma, W. Assessment and management of urbanization-induced ecological risks. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2018, 25, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Guo, P.; Jin, M.T.; Qi, J.F. Multi-scenario landscape ecological risk assessment based on Markov-FLUS composite model. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 1448–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.S.; Chen, Q.; Liu, F.G.; Zhou, Q.; He, W.X.; Guo, Y.Y. Land Use Simulation and Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land 2023, 12, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Yue, S.J.; Chen, H.T. Carbon emission efficiency of China’s industry sectors: From the perspective of embodied carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, X. Imbalance of carbon embodied in South-South trade: Evidence from China-India trade. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 134473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuai, X.W.; Huang, X.J.; Wang, W.J.; Zhao, R.Q.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C.Y. Land use, total carbon emission’s change and low carbon land management in Coastal Jiangsu, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, S.C.; Zhang, H.W. Impact of Land Urbanization on Carbon Emissions in Urban Agglomerations of the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Pandey, M.; Mishra, V.N.; Kumar, R.; Rai, P.K.; Costache, R.; Punia, M.; Di, L.P. Comparative evaluation of geospatial scenario-based land change simulation models using landscape metrics. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Li, X.; Wen, Y.Y.; He, P.T. Modeling urban land-use changes using a landscape-driven patch-based cellular automaton (LP-CA). Cities 2023, 132, 103906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.Y.; Hu, Y.C. Assessing temporal-spatial land use simulation effects with CLUE-S and Markov-CA models in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32231–32245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.F.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, B.Y.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.S.; Bi, C.J.; Jia, J.P.; Deng, L.; Chen, Z.L. Impact of intensive land use on heavy metal concentrations and ecological risks in an urbanized river network of Shanghai. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitts, L.A.; Russell, M.B.; Domke, G.M.; Knight, J.K. Modeling land use change and forest carbon stock changes in temperate forests in the United States. Carbon Balance Manag. 2021, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Abudureheman, M.; Halike, A.; Yao, K.-F.; Yao, L.; Tang, H.; Tuheti, B. Temporal and spatial variation analysis of habitat quality on the PLUS-InVEST model for Ebinur Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Du, Q.; Xiao, X.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Mi, J. Simulation of future land use/cover change (LUCC) in typical watersheds of arid regions under multiple scenarios. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Xiong, L.Y.; Tang, G.A.; Strobl, J.; Xue, K.K. Spatial-temporal variation of land use and land cover change in the glacial affected area of the Tianshan Mountains. Catena 2021, 202, 105256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, B.M.; Reis, E.; Reis, R.; Vale, M.J. The Effects of Land Use and Land Cover Geoinformation Raster Generalization in the Analysis of LUCC in Portugal. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Hu, M.S.; Wang, Y. Integrating ecosystem services value and uncertainty into regional ecological risk assessment: 29. A case study of Hubei Province, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeSage, J.P. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.H.; Zhong, Q.L.; Cheng, D.L.; Xu, C.B.; Chang, Y.N.; Lin, Y.Y.; Li, B.Y. Landscape ecological risk projection based on the PLUS model under the localized shared socioeconomic pathways in the Fujian Delta region. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.F. Quantifying the spatial impact of landscape fragmentation on habitat quality: A multi-temporal dimensional comparison between the Yangtze River Economic Belt and Yellow River Basin of China. Land Use Policy 2023, 125, 106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.M.; Gao, B.P.; Zheng, K.J.; Wu, Y.; Li, C. Multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service value for optimization of land use in the Sichuan-Yunnan ecological barrier, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltagi, B.H.; Heun Song, S.; Cheol Jung, B.; Koh, W. Testing for serial correlation, spatial autocorrelation and random effects using panel data. J. Econom. 2007, 140, 5–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.M. A summary of grey forecasting models. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2022, 12, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, T.; Guo, L.; Zou, H.; Shi, Y. Integrating ecosystem services supply and demand on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau using scarcity value assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.L.; Zhang, C.L.; Su, J.J.; Yang, L.X. Panel threshold spatial Durbin models with individual fixed effects. Econ. Lett. 2021, 201, 109778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.Z.; He, J.H.; Liu, D.F.; Wang, J.W.; Guo, X.A. Ecosystem health assessment based on ecological integrity and ecosystem services demand in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 144837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.F. Urban agglomeration ecological risk transfer model based on Bayesian and ecological network. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Du, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Dong, T.X. Watershed landscape ecological risk assessment and landscape pattern optimization: Take Fujiang River Basin as an example. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2021, 27, 2254–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, P.J.; Zhou, G.H.; Xing, X.D.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use and Landscape Ecological Risk Response Based on Planning Control. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, P.L.; Hu, S.G.; Frazier, A.E.E.; Qu, S.J.; Yu, D.; Tong, L.Y. Exploring changes in landscape ecological risk in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from a spatiotemporal perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, G.; Zhuo, Y.F.; Xu, Z.G.; Ye, Y.M.; Thorn, J.P.R.; Marchant, R. Trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Response to urbanizing variation. Urban Ecosyst. 2022, 25, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| 2020–2030 | ND Scenario | CLP Scenario | EC Scenario | LC Scenario | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | d | e | f | a | b | c | d | e | f | a | b | c | d | e | f | a | b | c | d | e | f | |
| a | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| b | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| c | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| d | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| e | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| f | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Scenarios | Neighborhood Weights | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | Forestland | Grassland | Water Body | Built-Up Land | Unused Land | |
| ND scenario | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 1.00 | 0.25 |
| CLP scenario | 0.80 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.25 |
| EC scenario | 0.20 | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.25 |
| LC scenario | 0.20 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.25 |
| Energy Type | SCCC (kgce·t−1, kgce·kw−1·h−1) | CEC (t·t−1) | Energy Type | SCCC (kgce·t−1, kgce·kw−1·h−1) | CEC (t·t−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| run-of-coal | 0.7143 | 0.7559 | kerosene | 1.4714 | 0.5714 |
| coke | 0.9714 | 0.8550 | Diesel oil | 1.4571 | 0.5921 |
| gasoline | 1.4714 | 0.5538 | Fuel oil | 1.4286 | 0.6185 |
| Crude oil | 1.4286 | 0.5857 | Natural gas | 1.3300 | 0.4483 |
| Energy Type | Energy Consumption/t | Posterior Difference Ratio (C) | Mean Relative Error /% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2030 | |||
| run-of-coal | 5,556,851 | 15,693,697 | 22,519,700 | 31,499,661 | 0.023 | 4.53 |
| coke | 580,819 | 2,085,717 | 3,048,500 | 3,760,847 | 0.033 | 4.86 |
| gasoline | 17,864 | 13,245 | 11,343 | 12,264 | 0.133 | 6.19 |
| Crude oil | 3,464,925 | 5,352,902 | 6,343,200 | 8,796,598 | 0.217 | 7.62 |
| kerosene | 978 | 584 | 358 | 312 | 0.029 | 17.12 |
| Diesel oil | 27,537 | 43,674 | 24,732 | 21,475 | 0.319 | 8.35 |
| Fuel oil | 369,521 | 140,540 | 13,151 | 1312 | 0.118 | 3.42 |
| Natural gas | 46,283 | 162,539 | 235,211 | 361,652 | 0.028 | 6.07 |
| ND Scenario | CLP Scenario | EC Scenario | LC Scenario | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUCE | 0.8853 *** | 0.8533 *** | 0.8621 *** | 0.8021 *** |
| z-score | 22.2187 | 19.3325 | 18.5412 | 19.4431 |
| p-value | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| ERI | 0.7028 *** | 0.7932 *** | 0.7887 *** | 0.7135 *** |
| z-score | 18.1124 | 18.2235 | 16.3373 | 17.9921 |
| p-value | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Variables | ND Scenario | CLP Scenario | EC Scenario | LC Scenario | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFE | TFE | STFE | SFE | TFE | STFE | SFE | TFE | STFE | SFE | TFE | STFE | |
| LUCE | 4.5543 *** (−25.9843) | 0.4529 *** (−4.9821) | 6.9032 *** (−26.9832) | 3.7893 *** (−20.0921) | 0.2134 *** (−2.9311) | 4.5642 *** (−18.8932) | 3.0983 *** (−19.8921) | 0.1549 *** (−3.9021) | 4.2351 *** (−18.8932) | 4.5621 *** (−27.3391) | 0.5521 *** (−4.8921) | 6.0921 *** (−26.7821) |
| W * LUCE | 2.4609 *** (7.5067) | −0.3414 *** (−3.9846) | 2.2818 *** (7.0703) | 1.6743 *** (5.9032) | −0.7832 *** (−2.9013) | 1.8932 *** (5.9021) | 1.8954 *** (6.0921) | −0.2145 *** (−4.9021) | 1.4532 *** (6.9021) | 2.6701 *** (8.0912) | −0.5732 *** (−5.9921) | 2.8901 *** (8.0121) |
| ρ | −0.9110 *** (97.1879) | −0.9100 *** (97.2978) | −0.8820 *** (68.1151) | −0.8821 *** (88.9012) | −0.8912 *** (87.1286) | −0.7891 *** (77.9012) | −0.7821 *** (83.9901) | −0.7912 *** (80.9045) | −0.7714 *** (63.9012) | −0.9312 *** (102.9012) | −0.9123 *** (105.9034) | −0.9034 *** (78.0932) |
| R2 | 0.9659 | 0.8109 | 0.9648 | 0.8878 | 0.7012 | 0.7435 | 0.8012 | 0.8823 | 0.8901 | 0.9023 | 0.9123 | 0.8702 |
| σ2 | 0.0007 | 0.0173 | 0.0032 | 0.0001 | 0.0214 | 0.0013 | 0.0014 | 0.0002 | 0.0045 | 0.0022 | 0.0023 | 0.0012 |
| Log-L | 2314.4079 | 837.5126 | 2334.5706 | 2125.4462 | 670.8923 | 2209.8912 | 1989.9023 | 903.8912 | 2214.9023 | 2090.3131 | 987.8912 | 2289.9012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, H.; Wang, W.; You, C.; Guo, L. Interaction Effect of Carbon Emission and Ecological Risk in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: New Insights into Multi-Simulation Scenarios. Land 2024, 13, 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13070937
Qu H, Wang W, You C, Guo L. Interaction Effect of Carbon Emission and Ecological Risk in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: New Insights into Multi-Simulation Scenarios. Land. 2024; 13(7):937. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13070937
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Hongjiao, Weiyin Wang, Chang You, and Luo Guo. 2024. "Interaction Effect of Carbon Emission and Ecological Risk in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: New Insights into Multi-Simulation Scenarios" Land 13, no. 7: 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13070937
APA StyleQu, H., Wang, W., You, C., & Guo, L. (2024). Interaction Effect of Carbon Emission and Ecological Risk in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: New Insights into Multi-Simulation Scenarios. Land, 13(7), 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13070937









