Abstract
The development of green spaces in urban parks can significantly enhance the quality of the urban and ecological environment. This paper utilizes 2021 Gaofen-7 (GF-7) satellite remote sensing images as its primary data source and uses deep learning algorithms for the precise extraction of the green space coverage within Beijing’s fifth ring road. It also incorporates the park points of interest (POI) information, road data, and other auxiliary data to extract green park space details. The analysis focuses on examining the relationship between supply and demand in the spatial allocation of green park spaces from an accessibility perspective. The main findings are as follows: (1) The application of deep learning algorithms improves the accuracy of green space extraction by 10.68% compared to conventional machine methods. (2) The distribution of parks and green spaces within the fifth ring road of Beijing is uneven, showing a clear pattern of “more in the north and less in the south”. The accessibility within a five-minute service radius achieves a coverage rate of 46.65%, with a discernible blind zone in the southeast. (3) There is an imbalance in the per capita green space location entropy within the fifth ring road of Beijing, there is a big difference in per capita green space location entropy (44.19), and social fairness needs to be improved. The study’s outcomes unveil the intricate relationship between service capacity and spatial allocation, shedding light on the supply and demand dynamics of parks and green spaces within Beijing’s fifth ring road. This insight will contribute to the construction of ecologically sustainable and aesthetically pleasing living spaces in modern megacities.
1. Introduction
Urban green space is an important part of the urban environment, often referred to as the “kidney of the city”. These spaces fulfill various needs such as daily leisure, recreation, exercise, and socialization [1]. As a typical green space type in cities, urban parks play a crucial role in improving the urban ecological environment [2,3], maintaining the carbon cycle of urban ecosystems [4], improving the urban microclimate [5,6,7], promoting sustainable urban development, and improving residents’ quality of life [8,9], among other benefits. Increasing green spaces in cities can effectively improve air quality because plants can clean the atmosphere by absorbing pollutants such as PM2.5, NOx, and other pollutants in the air through surface blockage and stomata [10,11]. Moreover, plants can release negative ions and beneficial BVOCs, which can not only inhibit bacteria and sterilize and repel insects, but also play a therapeutic and healthcare role in the human body, mind, and spirit [12,13]. Therefore, in the development of cities, the status of green park space cannot be overlooked.
However, with the rapid pace of urbanization and an influx of rural populations into cities, the built-up area has been expanding continuously [14]. This has led to a serious inadequacy in the supply of urban green park space resources, diminishing the fairness in residents’ access to these resources [15]. This imbalance poses a challenge to the sustainable and healthy development of cities. In Beijing, a mega-city in China, this problem is especially obvious, as it is London, Paris, and New York. These three city center areas are similar, in which London and Paris are two cities with green characteristics in a ring distribution pattern, New York has a corridor network green space layout pattern, and Beijing has a ring network radial distribution pattern; however, the density of the road network in the main urban area of Beijing is significantly lower than that of the other three cities, about 1/4 of the average value of the other three cities, and the density of green park space in its core area is the least [16]. Therefore, it is of great significance to rationalize the allocation of green space in Beijing parks. As urbanization progresses, the demand of urban residents for recreational and open spaces, such as green park space, continues to rise. The spatial configuration of urban parks and green spaces has the potential to impact the equity of social benefits. Studies indicate that balancing the supply and demand of green park space resources can effectively address heart health problems among urban residents, enhance people’s overall sense of well-being [17,18,19,20], and contribute to the sustainable development of social equity and justice. Most existing studies have focused on park renovations and ecological service functions [21,22,23]. Fewer studies have delved into the spatial layout of urban parks and green spaces and the equity of their distribution. Moreover, many studies have been conducted on individual parks or specific districts and counties [24,25,26,27]. These studies often have a limited scope or a single research index, making it challenging to assess the spatial configuration and social service capacity of urban parks and green spaces comprehensively. In addition, with the rapid urban regeneration, the number of small green spaces with small areas, diverse types, and blurred boundaries are difficult to identify efficiently. There is also a problem of inaccurate green space information within these parks due to later alterations, etc., and the research on green space planning information as spatial configuration and equity has a lagging effect.
To assess the spatial configuration for effective social service capacity in a more timely and accurate manner, scholars have used geographic information systems and low- and medium-resolution images such as Landsat to determine the urban greening coverage rate, distribution of green space, scale, and three-dimensional green volume [28,29], however, due to their low spatial resolution, there are a large number of mixed pixels in remote sensing images, which affects the accuracy of the estimation of green space area and greening rate [30]. The successful implementation of China’s “High-Resolution Earth Observation System of Systems” (Gaofen special project) major project has marked a breakthrough in China’s ultra-high-resolution spatial detector technology, providing crucial data support for more the accurate real-time monitoring of urban feature information [31]. However, urban green space extraction is a complex data-processing process, and there are many difficulties in urban green space categorization, especially for high-resolution remote sensing images: (1) the vegetation types of urban green spaces are diverse, with significant differences in multispectral features; (2) green space patches are highly heterogeneous and dispersed, with fragmented and irregular shapes; and (3) high-resolution remote sensing images provide high-definition detail information about features while also increasing intra-class variation [32]. There are image classification methods with strict requirements for the data themselves, it is difficult to train effective classifiers from massive data to fully explore the association between the data, a weak generalization ability, and time-consuming and labor-intensive processes [33]. Deep learning has great advantages in segmenting images for recognition and autonomous learning [34] and sufficient algorithmic support for the intelligent extraction of urban green spaces [35,36]. Based on high-resolution remote sensing images, using typical green spaces as deep learning recognition samples and applying deep learning models for the semantic segmentation of the images, the distribution of urban green spaces can be quickly determined [37]. For problems such as the blurring of urban green space boundaries, spectral information differences can be utilized to separate similar features that are easily confused [38]. The flexibility of deep learning allows researchers to improve the accuracy of urban green space extraction by adding model modules, model optimization, and the construction of variant models [39]. The advantage of deep learning methods over shallow machine learning is that they can more fully mine the spectral, textural, and potential feature information of massive data, automatically perform feature selection and feature extraction, and achieve better classification results in image classification. The U-Net model has been improved on the basis of Fully Convolutional Network [40], which combines the Inverse Convolutional Network and the jump structure to obtain an urban green space extraction accuracy that is better than that of the machine learning method and can reach more than 90% [41,42,43]. It has become an important technical method for extracting information about urban green spaces [44,45,46].
China is presently in a critical phase of upgrading the quality of its urban spaces, and enhancing the sense of access and happiness among residents is a central concern for the government, scholars, residents, and other stakeholders [47]. As a vital component of urban space, urban parks are a key focus for improving residents’ sense of access and well-being. Conventional indicators such as green space per capita, green coverage rate, and urban green space rate have proven inadequate for spatially describing the layout of urban parks and green spaces [48,49]. They struggle to authentically reflect the effectiveness of urban parks and green spaces in delivering services to urban residents. Studies on the rapid acquisition of high-precision and high-resolution urban green space information in Beijing using high-resolution remote sensing data respond to the evolving needs of urban gardening, landscape planning, and the development of refined green space configurations.
Therefore, this paper focuses on the urban green park space within the fifth ring road of Beijing. It uses Gaofen-7 (GF-7) ultra-high spatial resolution remote sensing images and a deep learning model to extract the green space information within the fifth ring road of Beijing. Different streets serve as the spatial units of the analysis. The paper adopts accessibility analysis and location entropy methods to analyze the urban green park spaces within the fifth ring road from the perspectives of demand–supply alignment and social equity, exploring the spatial allocation and supply–demand relationship of urban parks and green spaces within the fifth ring road of Beijing, analyzed in terms of the following three issues: (1) How can high-spatial-resolution imagery and deep learning algorithms be scientifically applied to identify the green spaces in urban parks? (2) What is the impact of parkland service capacity on per capita access to parkland resources? (3) How does equity in the layout of the city’s parks relate to residents’ accessibility to the parks? The aim is to provide a scientific reference for optimizing the spatial pattern of urban green space.
Study Area
Located in northern China, Beijing is positioned at 116.20° E longitude and 39.56° N latitude, featuring a terrain that is high in the northwest and low in the southeast. The city experiences a warm–temperate semi-humid continental climate characterized by high temperatures and rainy summers, cold and dry winters, and short springs and autumns. The average temperature is 13.8 °C, and the average annual precipitation from 2017 to 2021 is approximately 548.12 mm [50]. As the center of China’s political, cultural, and technological innovation, Beijing holds the distinction of being the world’s first “Double Olympic City”. Covering a total area of 16,410.54 km2, urban green spaces in Beijing are primarily distributed within the fifth ring road, encompassing numerous urban parks, as well as small and micro green spaces. For this study, the fifth ring area of Beijing is chosen as the research area, which includes the entire Dongcheng District, the complete Xicheng District, and parts of the Haidian, Chaoyang, Fengtai, Shijingshan, and Daxing districts. This area totals 666 km2, and 46.83 km2 of green park space, constituting 7% of the total area. (Figure 1) shows the GF-7 image of the fifth ring area of Beijing.
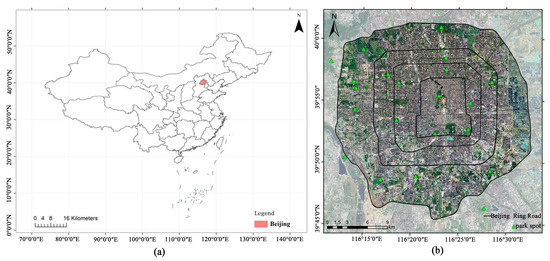
Figure 1.
Research area. GF-7 images within the fifth ring road of Beijing: (a) map of China and (b) Beijing fifth ring road area.
2. Materials and Methods
The method flowchart is shown in (Figure 2).
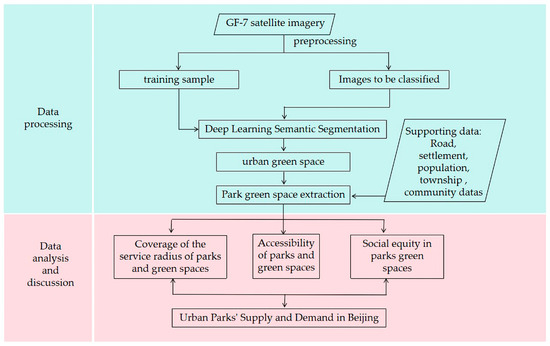
Figure 2.
Theoretical–methodological flowchart.
2.1. Data Sources and Processing
2.1.1. Remote Sensing Data
The Gaofen-7 (GF-7) satellite was successfully launched on 3 November 2019. Equipped with a dual-linear array stereo camera, laser altimeter, and other Earth observation instruments, it has pioneered sub-meter stereo mapping camera technology [51]. Capable of capturing high-spatial-resolution optical stereo observation data and high-precision laser altimetry data, the GF-7 is China’s first civilian high-resolution stereo mapping satellite. This study uses domestically produced GF-7 satellite remote sensing imagery as its primary data source. The satellite imagery includes panchromatic stereo images and a 4-band multispectral image (Table 1), with a return period of approximately 60 days, facilitating the effective acquisition of vegetation detection parameters. The image data were obtained from the Land Observing Data Satellite Data Service website (https://data.cresda.cn/#/home, accessed on 14 March 2023). The study predominantly relies on four GF-7 remote sensing image datasets captured between April and October 2021. The basic remote sensing image data processed through resampling had a resolution of 0.6 m, encompassing the blue, green, red, and near-infrared bands.

Table 1.
Parameters of domestic Gaofen-7 remote sensing image data sensor.
2.1.2. Measured Data
In the field survey for this study, parks and green spaces were primarily chosen as the subjects of investigation. The selected survey areas were evenly distributed within each administrative district and each ring, with the actual number of surveys appropriately adjusted based on the district’s area and the number of parks. Sixteen parks of various types were selected in the fifth ring area of Beijing, resulting in a total of 35 survey sample points and 510 survey sample squares. The surveys were conducted in October 2021 and from July to October 2022. For each park, 2–3 survey sample points were selected, and within each sample point, 9–16 sample squares were chosen. Each sample square measured 5 m × 5 m and was divided into 25 evenly spaced 1 m × 1 m sample grids. The latitude and longitude of the midpoints of the sample squares were recorded using a handheld GPS instrument. Moreover, the type of inland features, distribution characteristics, height of features, and characteristics of the surroundings for each sample square were documented and photographed. This information was crucial for the subsequent validation of the accuracy of the urban green space classification data. The details regarding the type of features, distribution characteristics, height of features, and characteristics of the surrounding environment in each sample plot were recorded using a handheld GPS device, with accompanying photos taken for the subsequent verification of the accuracy of urban green space classification.
2.1.3. Supporting Data
Road, settlement, population, township (Figure 3), and community data of the study area were collected as auxiliary data sources. The geographic coordinate system of all the data used in this study was GCS_WGS_1984, and the projected coordinate system was WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_50N. Specifically, the road network data for Beijing were sourced from Open Street Map (OSM). For residential areas and park information, we used the Web API service in the AutoNavi open platform https://lbs.amap.com (accessed on 23 May 2023) to obtain Point of Interest (POI) data. Data on the resident population within the fifth ring road came from the Seventh Population Census [52], and township and community data were sourced from the official website of the National Bureau of Statistics (http://www.stats.gov.cn accessed on 27 May 2023.).
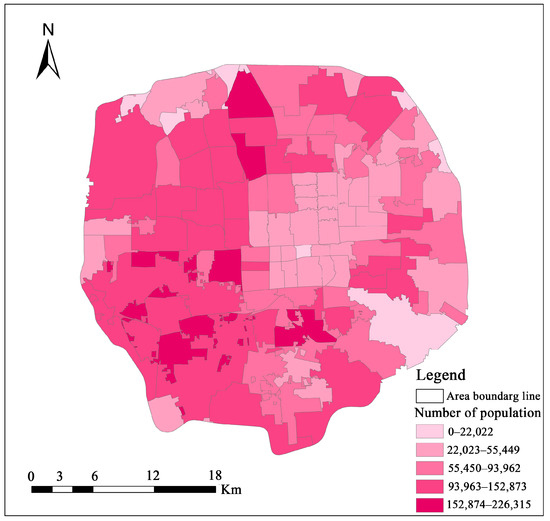
Figure 3.
Population date. The distribution of population in each region within the fifth ring road of Beijing. (These data are from the Seventh Population Census.).
2.2. Green Park Space Extraction
In this study, a deep learning model was used to extract the overall green space coverage information within the fifth ring road. The U-Net model, known for its relatively stable classification results, was chosen as the final classifier. Following the structure of a previous work [40], the U-Net model consists of an encoder and a decoder (Figure 4). The encoder is composed of modular convolutional and maximum pooling layers, effectively extracting contextual information in the input image. The image is then restored to its initial resolution after convolution by the decoder.
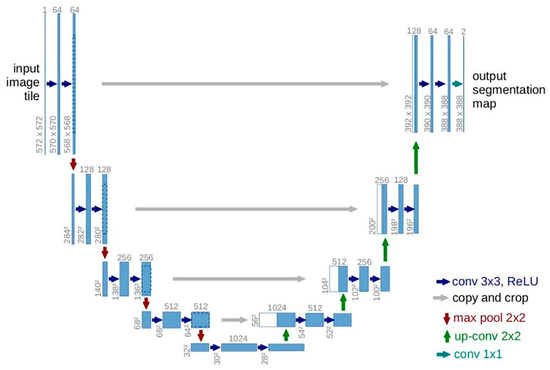
Figure 4.
U-Net network structure [40].
A U-Net model was trained based on a training sample dataset of 7350 manually created 256 × 256-pixel images in conjunction with a field survey. Data augmentation was performed on the green space sample dataset by the means of horizontal flipping, vertical flipping, and diagonal flipping (Figure 5). Network parameters, such as the batch size and learning rate, were continuously adjusted during the training process to enhance the accuracy of the detail information extraction. The number of categories was set to 2, the number of iterations to 20,000, the batch size to 10, and the base learning rate to 1e-3. Green park space information was obtained by combining the extracted urban green space information with other auxiliary data, such as park Point of Interest (POI) information and road data. The distribution of green park space within the fifth ring road was obtained by analyzing the kernel density and standard ellipse difference of the park point data. To validate the accuracy of the extraction results of the Beijing urban green space extraction and classification system established in this paper, we chose to compare the accuracy with the results extracted only by SVM. A confusion matrix was established between the urban green space prediction results extracted by the two methods and the true value data. Precision evaluation indices were calculated based on the confusion matrix to evaluate the accuracy of the classification results (refer to Table 2 for the calculation method).
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of sample library date: (a) original drawing; (b) flip horizontal; (c) flip vertical; and (d) diagonal flip.

Table 2.
Accuracy verification evaluation indicators of urban green space extraction results.
The average nearest neighbor (ANN) index of parkland within the fifth ring road was computed using the average nearest neighbor tool in ArcGIS to determine the distribution pattern of parkland:
2.3. Capacity of Green Park Space Services
2.3.1. Coverage of the Service Radius of Green Park Spaces
The service radius coverage rate of urban green park space is determined based on the National Garden City Selection Criteria issued by China’s Ministry of Housing and Urban–Rural Development in 2022. This criterion entails the percentage of residential land area covered within the service radius of the green park space. For green park space below 5000 m2, a 300 m service radius is employed, while green park spaces of 5000 m2 and above use a 500 m service radius. Buffer zones of 300 m and 500 m were established based on the size of the park area, and the area of residential land covered by these buffer zones was calculated to derive the coverage ratio of the service radius of urban parks and green spaces:
in which C is the coverage rate of the service radius of the green park space (%), r is the area of residential land covered by the service radius of the urban buffer zone (m2), and R is the area of urban residential land (m2).
2.3.2. Accessibility of Parks and Green Spaces
Accessibility refers to the availability and proximity of parks and green spaces within a specified spatial range. It is influenced not only by spatial distance, but also by information and behavior [53]. Accessibility is a vital element in measuring the rationality of the spatial layout of urban services and the quality of life for residents [54,55]. In terms of the accessibility of green spaces in urban parks, walking is the most common mode of travel, unaffected by road traffic conditions. Most residents prefer to walk no more than five minutes to reach green park spaces, with a maximum acceptable walk of 30 min [56]. Taking into account residents’ willingness to travel, this study adopts the concept of the “15-min city” and divides walking time into three levels: no more than 5 min, 15 min, and 30 min. We considered an average walking speed of 5 km/h [57] and corresponding walking distances of 420 m, 1250 m, and 2500 m, respectively. Buffer zones for different time ranges were established accordingly, and the coverage area and the number of neighborhoods covered by different buffer zones were calculated to assess the accessibility of green park space within different time ranges.
2.4. Social Equity in Green Park Spaces
The social supply of green park spaces is evaluated through their social service capacity, employing the density of the resident population as an indicator of residents’ demand for green park spaces. Generally, the higher the population density, the greater the overall demand for green park spaces. In this study, focusing on social equity, we adopted the method of location entropy to calculate the per capita green park space location entropy [58], representing the actual amount of green park space resources per capita in a specific area to analyze the social equity of green park space resources in Beijing. The entropy of green park space per capita can be expressed as:
where Tdg is the total area of green park space in each street, Pd is the number of residents in each street, Tqg is the total area of green park space in each park within the study area, and Pq is the total resident population within the study area. The per capita green park space service area entropy is expressed as:
where Tds is the total area of a number of green park spaces accessible to residential land in each street within an effective service radius, Pd is the number of residents on each street, Tqs is the total area of a number of green park spaces accessible to residential land in the study area within an effective service radius, and Pq is the total resident population in the study area. If the location entropy of a street is greater than 1, it indicates that the public per capita enjoyment of parkland in the area is higher than the overall level of the study area. If the location entropy is less than 1, it indicates that the per capita enjoyment of parkland in the area is lower than the overall level of the study area.
3. Results
3.1. Urban Green Space Extraction Validation and Patterns of Green Space Distribution in Parks
As depicted in Figure 6a, areas with a high density of green park space distribution within the fifth ring road of Beijing are concentrated in the northern region, primarily around the Summer Palace and the Olympic Park. The area of a high distribution density within the center city is evident around Tiantan Park. Overall, the distribution density of parks and green spaces within the fifth ring road follows a “more in the north and less in the south” pattern. The standard deviation ellipse method helped to determine the specific direction of green park space distribution. As shown in Figure 5b, the trend of the standard deviation ellipse direction within the fifth ring road of Beijing was not pronounced, mainly due to large-scale green areas like Beihai Park and Tiantan Park within the second ring road controlling the overall trend of green park space size distribution. However, the general tendency is in the direction of a northwestern–southeastern distribution. To assess the accuracy of the Beijing urban green space extraction and classification system established in this study, we compared its results with those of SVM.
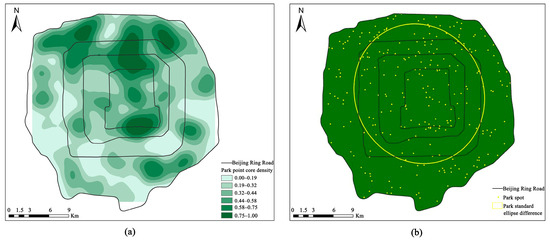
Figure 6.
Distribution density and distribution trend of green spaces in parks within the fifth ring road in Beijing: (a) kernel density map of park sites and (b) park distribution standard deviation ellipse.
The z-score for green park space within the fifth ring road of Beijing was −1.68, indicating an aggregation pattern, as illustrated in Figure 7. The closest ratio index was 0.94, with the ratio value being between 0.6 and 1, suggesting that the aggregation of green park space is not significant.
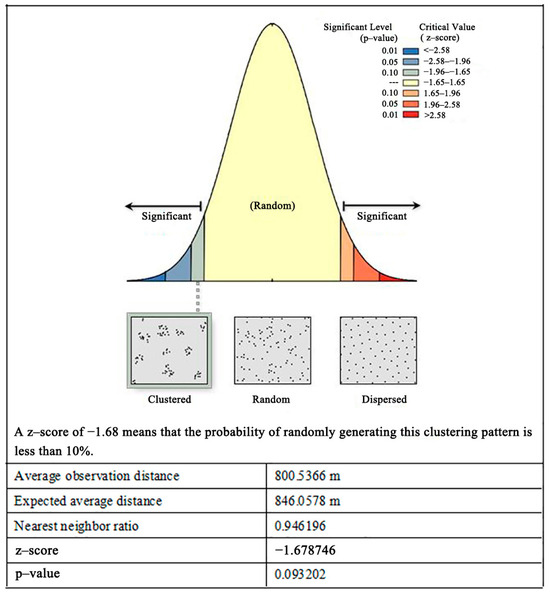
Figure 7.
Analysis of green space distribution patterns in parks within the fifth ring road of Beijing.
In this study, the results extracted by the two methods were individually compared with the true value data, producing a confusion matrix. Four assessment metrics, namely UA, PA, OA, and Kappa coefficient, were used to evaluate the accuracy of the extracted classification results. The true value data were combined with field survey sample data, and 300 areas of interest were randomly constructed as validation samples, with sample sizes of 100 for trees, shrubs, and non-green areas, totaling 262,518 image elements.
The results presented in Table 3 demonstrate that the accuracy of the results extracted by the Beijing Urban Green Space Extraction Classification System was significantly higher than that of SVM, with an overall classification accuracy improvement of 10%. Specifically, the overall classification accuracy of the Beijing urban green space information extraction classification system was 94.31% and the Kappa coefficient was 0.88. In contrast, the overall classification accuracy of SVM was 83.63%, with a Kappa coefficient of 0.71.

Table 3.
Comparison of classification results accuracy for the two classification methods.
From Figure 8, it can be observed that the parks within the fifth ring road of Beijing are primarily concentrated within the fourth to fifth ring road. In this study, a total of 46.82 km2 of green park space was extracted from the fifth ring road area, with parks exhibiting extensive green space coverage mainly concentrated in the western and northern regions of the fourth and fifth rings.
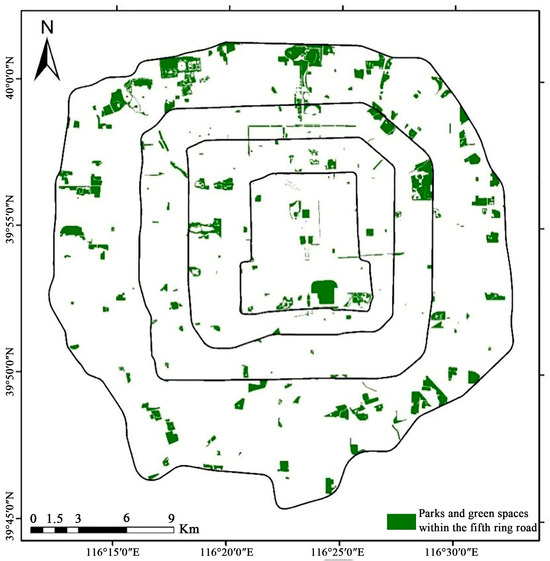
Figure 8.
Green space information extraction results of parks within the fifth ring road of Beijing.
3.2. Capacity of Urban Parks Green Space Services
3.2.1. Service Radius Coverage of Urban Parks and Green Spaces
In this study, a total of 266 parks and green spaces were extracted from the fifth ring road area, of which 96.6% had an area exceeding 5000 m2. The total area covered by parks and green spaces is 4682.63 hectares, while the residential area within the fifth ring road is 14,753.54 hectares. The total residential area covered by the service radius of parks within the fifth ring road is 6882.65 hectares, resulting in a coverage rate of 46.65%. Specifically, the residential area covered by a 500 m service radius of parks and green spaces larger than 5000 m2 within the fifth ring road is 6787.99 hectares, with a coverage rate of 46.01%. Examining the spatial distribution, the service radius coverage area of parks in the southern part of the fourth to fifth ring is relatively small, indicating service blind spots.
Looking at different rings (Figure 9), the coverage of the service radius of parks and green spaces is higher within the first three rings compared to areas outside the third ring. The service radius coverage within the second ring area is the largest at 57.16%, covering 555.35 hectares of residential area within the service radius. In contrast, the service radius coverage within the third to fourth ring area is the smallest at 42.31%, covering 1935.15 hectares of residential area. The second ring, as the center of Beijing, has a green park space coverage of 589.89 hectares, surpassing the coverage within the second to third rings (407.54 hectares).
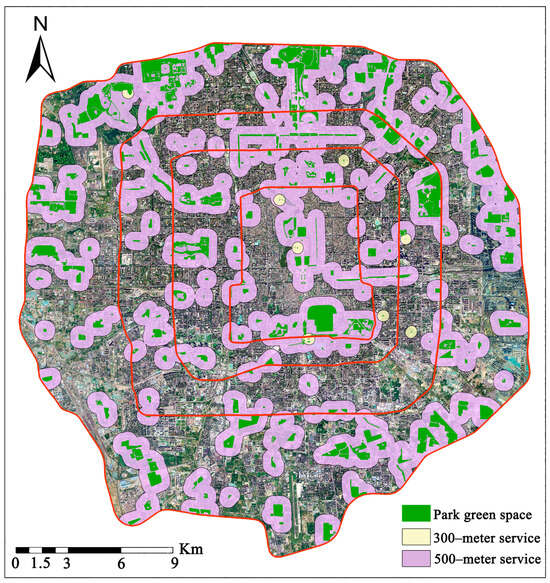
Figure 9.
Coverage of service radius of parks within the fifth ring road in Beijing.
3.2.2. Accessibility of Urban Parks Green Spaces
According to the statistical results (Figure 10), parks and green spaces within the fifth ring area are primarily located within the fourth to fifth ring. Using the buffer zone method for analysis, the total buffer zone area was computed at 30,772.86 hectares, constituting 46.17% of the entire study area for the five-minute time range. For the 15-min interval, the total buffer zone area extended to 92.38% of the total study area. Extending the time range to 30 min, accessibility covered almost the entire area, with the total buffer area encompassing 99.95% of the study area. The spatial distribution map highlights red areas (15–30 min) primarily in the southeastern part of the third to fourth ring, the southwestern part of the fourth to fifth ring, and the eastern segment, indicating areas with a limited accessibility to parks. In addition, a blank area in the southeastern part of the third to fourth ring indicates service blind spots, taking more than 30 min to reach.
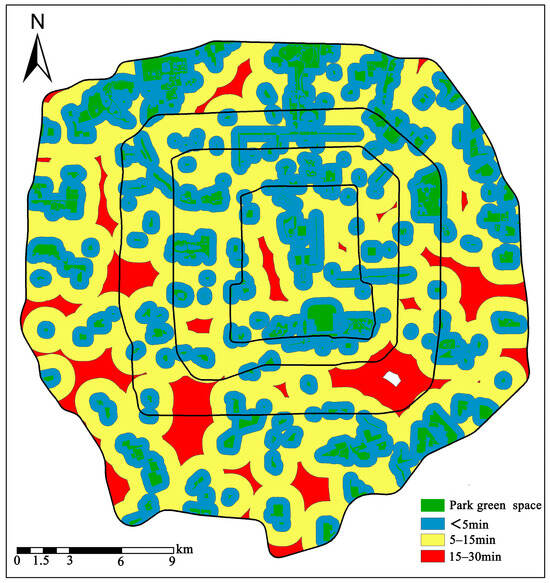
Figure 10.
Statistics of accessible range and residential area covered by different walking durations.
An analysis of the number of residential subdivisions within each buffer level reveals 2474 residential subdivisions within the five-minute reach, compared to 2420 within 5–15 min, and only 239 within 15–30 min. Comprehensive statistical results indicate that the reachable area within Beijing’s fifth ring road, satisfying urban residents’ five-minute access to parks and green spaces, encompasses nearly half of the study area. The number of residential neighborhoods covered within this reachable area constitutes 48% of the total neighborhoods, while achieving 15-min accessibility to parks accounts for 92% of the total neighborhoods. These results underscore the high serviceability of parkland in the study area, ensuring that a substantial majority of residents benefit from accessible green spaces.
3.3. Social Equity in Urban Parks Green Spaces
The entropy of per capita green park space location within the five rings of Beijing reveals an uneven distribution of green park space resources across each ring belt (Figure 11). At the district level, six out of seven districts have a district entropy higher than one, with Chaoyang District ranking the highest (5.44), followed by Haidian District (4.33), and Xicheng District registering the lowest (0.89). On the street scale, streets with a higher entropy per capita green park area are concentrated in Cuigezhuang Street (44.19), Qinglongqiao Street (31.52), Maizidian Street (31.10), Tiantan Street (28.55), and Shibaridian Street (24.86), and Olympic Village Street (20.13). In contrast, streets such as Chaoyangmen Street, Chongwenmenwai Street, Sanlitun Street, Jianwai Street, Jiuxianqiao Street, Niujie Street, Dazhalan Street, Financial Street, Tsubaki Street, Donggomen Street, Dahongmen Street, You’anmen Street, and College Road Street exhibit zero actual green park space ownership.
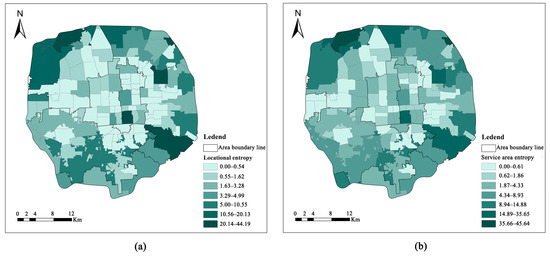
Figure 11.
Equity of green space in parks of streets within the fifth ring road of Beijing city. (a) Equity of park green area location and (b) entropy of the park’s green space service.
The results for parkland and parkland service location entropy per capita were generally similar, but exhibited slight differences. Regarding regions, Haidian District shows the highest per capita green park space service area entropy (8.13), followed by Chaoyang District (7.23), while Xicheng District has the smallest (1.30). On the street scale, streets like Chaoyangmen, Chongwenmenwai, Sanlitun, Jianwai, Jiuxianqiao, Dashilan, Financial Street, Dahongmen, You’anmen, and College Road demonstrate zero actual green park space ownership. However, the per capita parkland service area entropy values for those streets were 0.15, 0.85, 0.08, 2.27, 1.48, 0.19, 0.22, 0.41, 1.74, and 0.07, respectively. The entropy of park space per capita in Xiaoguan, Liulitun, Anzhen, Fa-tou, Gym, and Qianmen streets is lower than the district average, yet the per capita parkland service area entropy is slightly higher than the regional average. This suggests that, in the spatial configuration of urban park green space, landscape patterns such as aggregation and fragmentation impact the social service level and social publicness of urban parks. When the entropy of per capita park green space location is lower than the regional level, increasing the green park space in the effective service range of neighboring areas can enhance the entropy of per capita green park space service in the region.
4. Discussion
This study focuses on the spatial configuration of urban parks and green spaces within the fifth ring road of Beijing, and their supply and demand relationships. The results showed that the area covered by urban parks within the fifth ring road of Beijing has reached 46.82 km2, but its overall spatial distribution is uneven, showing a pattern of more in the north and less in the south, and more outside and less inside. The entropy distribution of per capita parks and green areas is uneven, and the entropy of per capita parks and green areas services is low. This is highly influenced by the historical development within the fifth ring road of Beijing, showing more historical buildings and a high building density in the center of the city, rich natural plant resources in the north, and a low density of road networks [59]. The distribution pattern of urban parks and green spaces can be improved in the future through the development of new urban areas and expansion of the road network.
4.1. Analysis of Information Extraction Results of Urban Park Green Space
In this study, GF-7 satellite images were used to extract green spaces in urban parks, employing deep learning algorithms combined with the POI information of park points, roads, and other auxiliary data. This approach, which is more time-sensitive, provides a clear spatial distribution of green spaces. The extracted results offer more precise green space information for subsequent categorization compared to the conventional SVM, which extracts the complete edges of green space information and mitigates the impact of other features such as building shadows and mulch. Deep learning was utilized in the study to carry out the extraction of greenfield information, i.e., greenfield and non-greenfield information was extracted. Deep learning algorithms for extracting classifications need to be trained using a large amount of labeled data, and the more classification categories there are, the greater the number of training samples required. Therefore, a lot of manual work is still required to label the training sample set when preparing it. In this study, we chose to combine deep learning and machine learning models to classify green spaces using SVM methods based on deep learning to extract green spaces with a higher accuracy, and the overall classification accuracy of the final extraction results was 94.31%. This accuracy is comparable to the results of urban green space information in Nanming District of Guiyang City and Shanghai City [60,61]. Compared with the extraction accuracy of green spaces in urban parks within the fifth ring road of Beijing by using GF-2 multispectral remote sensing images combined with U-Net deep learning, the accuracy was improved by 1.23% [33], good results were achieved in image classification, and the edge aliasing problem of traditional algorithms was effectively solved. The accuracy of using high-resolution image data and deep learning algorithms to extract urban park green space was further demonstrated. The results showed that the deep learning model can play an important role in the extraction of urban green space and can provide urban green space information data with a high accuracy and better extraction effect for urban green space monitoring, effectively addressing the edge jaggedness issue of the traditional algorithm. Despite potential errors caused by image quality, building shadow occlusion, and other factors, leading to the extracted green space information being smaller than the actual situation, future improvements to the algorithm can reduce such errors.
4.2. Service Capacity and Supply–Demand Dynamics of Urban Park Green Spaces
In this study, two key indicators, namely, park service radius coverage and park accessibility, were chosen to evaluate the influence of the spatial distribution of urban parks on the effective capacity of social services. Urban green space accessibility is impacted by various factors, with time and access distance being crucial considerations [62,63]. Embracing the “15-min city” concept, prioritizing non-driving individuals, and considering residents’ expected shortest walking time to reach parks, we employed the buffer zone method to establish zones with different time levels to assess the degree of serviceability of green park space. The findings indicated that the northern part of the study area exhibits a high parkland accessibility coverage and a well-balanced supply and demand scenario. However, the southeastern area experiences service blindness, highlighting the need for enhanced accessibility and a more equitable supply and demand balance for parkland. This aligns with observations in Ilam city, Iran, and Guangzhou and Shanghai, China [64,65,66], revealing accessibility imbalances and disparities in the supply and demand dynamics of urban parks. This phenomenon may be attributed to rapid urbanization, extensive industrial zones, roads, and commercial land uses compressing urban green spaces, leading to their reduction or disappearance. Additionally, urban planning often prioritizes hard structures like buildings, neglecting the effective protection and use of green space and coverage [67]. The burgeoning urban population exacerbates the imbalance between the supply and demand for green space in urban parks.
Considering 15-min park accessibility, which constitutes 92% of the total number of districts, it is evident that Beijing’s city parks within the fifth ring road are well constructed, effectively meeting the daily life needs of urban residents. However, the presence of service blind zones in the southeast area indicates room for improvement. To enhance the construction of the 15-min city, the optimization of green spaces in city parks should be prioritized, aiming for a more people-centered service orientation.
4.3. Equity in the Layout of City Parks and Their Accessibility to Residents
In this study, per capita park green space location entropy and per capita park green space service location entropy were employed as indicators to evaluate the spatial alignment between the service capacity of urban park green space and the population. The findings revealed significant variation in the per capita enjoyment of green space resources in Beijing, with an insufficient equity. The entropy of per capita park green space location ranged from a maximum of 44.19 to a minimum of 0, with an average of 3.39. This aligns with the outcomes of equity studies on spatial layouts in Xuhui District, Shanghai, and five urban parks and green spaces in Chengdu [68,69].
The Cuigezhuang area within the study zone exhibits the highest per capita enjoyment of parkland, primarily due to its small area within the fifth ring road, a limited resident population, and concentrated parkland resources, resulting in a high level of per capita enjoyment of parkland resources in the region. At the same time, the phenomenon of “work–life separation” exists, as people’s places of residence and places of work are usually not in the same place. The average commuting time for Beijing residents in a single day is more than 90 min [70], resulting in a significant reduction in the amount of time residents are able to spend outdoors during the day, especially visiting green spaces [71]. In megacities, green space resources are often not evenly distributed, and there may be some areas with abundant green space resources while others are relatively scarce. Office space within the fifth ring road of Beijing is mainly concentrated in Zhongguancun in Haidian District, Financial Street in Xicheng District, Wangfujing and Dongdan areas in Dongcheng District, and CBD in Chaoyang District, etc. The entropy of per capita parkland services in these areas is higher than the actual per capita entropy of parkland services. In residential areas such as Ox Street Street, Dashilar Street, Financial Street Street, Tsubaki Street, Chaoyangmen Street, and Chongwenmenwai, there are fewer parks and green spaces and the population is more concentrated, resulting in a low entropy in the area. In addition, the entropy of per capita parkland service area surpasses that of per capita parkland area, mainly because many parks intersect in different regions or are situated at regional boundaries, enabling simultaneous service provision to urban residents across various areas. The overall per capita enjoyment of parkland resources in the study area follows a pattern of abundance in the north and scarcity in the south, influenced by Beijing’s geographic location and its distribution of natural resources, particularly the Yanshan mountain range in the north, rich in natural parkland resources, with the total area of parkland in the southern part of the city being less than 1/3 of the northern part.
The phenomenon of occupational and residential segregation has had a negative impact on the equity of green space in mega-cities like Beijing. In order to improve this situation, green space planning needs to take the actual needs and commuting conditions of residents more into account to ensure the equitable distribution and effective utilization of green space resources. Improving the entropy of the service area involves optimizing the spatial layout, introducing pocket parks, incorporating three-dimensional greenery into existing public service zones, and enhancing the sharing of public service facilities with neighboring areas [72,73] to address issues such as insufficient urban park green space.
5. Conclusions
This study employed remote sensing technology to extract park green space information. It analyzed the service capacity of green park space within the fifth ring road of Beijing using a buffer zone analysis and the location entropy method. A quantitative analysis of the balance between the supply and demand of park green space in each street was conducted based on POI data. The study explored the current spatial layout and supply–demand relationship of urban park green space from the perspective of social equity, yielding the following conclusions: (1) The extraction efficiency of the Beijing urban green space extraction and classification system, established in this study using the deep learning U-net model, outperformed that of SVM. The overall classification accuracy improved by 10.68% to 94.31%, providing reliable foundational data for monitoring and evaluating urban green space. (2) The coverage area of parks within the fifth ring road of Beijing is substantial, with an overall distribution density showing a pattern of “more outside and less inside”. This pattern aligns with the service capacity of parks and the level of per capita enjoyment of parks and green space resources. (3) The entropy of per capita green space location in the five rings of Beijing is uneven, indicating a significant variation in the level of per capita enjoyment of green space resources. Social fairness in this aspect needs improvement.
This study constructed an evaluation index of park accessibility in Beijing and explored the walkability and service of urban parks within the fifth ring road of Beijing, which can provide a certain reference for the improvement of human settlements and optimization of the layout of public parks in Beijing. However, this study only used walking time distance as an accessibility factor, and did not consider the connectivity of roads, which has certain limitations. At the same time, in terms of population, this study focused solely on the equity of green park space services for the number of permanent residents within the same time period and did not consider the psychological needs of different groups of people. Future research can delve into the psychological needs of individuals of different ages and occupations for urban parks. This approach will enhance the promotion of human-centered urbanization, scientific planning, and the layout of the city’s production, living, and ecological spaces, creating a city that harmoniously coexists with humans and nature, becoming a beautiful home.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L.; formal analysis, J.F.; funding acquisition, B.L., S.L. (Shaowei Lu) and X.X.; investigation, B.L., C.L. and X.X.; methodology, B.L., S.L. (Shaoning Li) and H.L.; project administration, S.L. (Shaowei Lu) and X.X.; resources, B.L. and X.X.; software, H.L.; supervision, S.L. (Shaoning Li) and X.X.; validation, H.L., N.Z. and X.L.; visualization, B.L., H.L., C.L., J.F. and X.L.; writing—original draft, H.L. and C.L.; writing—review and editing, B.L., S.L. (Shaoning Li), N.Z., S.L. (Shaowei Lu) and X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Director’s Foundation of Institute of Forestry and Pomology in Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences (LGSSZJJ202302), and Innovation Capacity Building of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry (KJCX20230306) and (KJCX20220412).
Data Availability Statement
Due to property rights, the data cannot be made public, but the authors can be contacted if needed.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the following units for supporting: Instiyute of Forestry and Pomology, Beijing of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences; Beijing Yanshan Forest Ecosystem Observation and Research Station; and Forestry College of Shenyang Agricultural University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Wu, J. Landscape sustainability science: Ecosystem services and human well-being in changing landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.L.; Lin, L.; Zhou, W.Q. Quantifying the characteristics of particulate matters captured by urban plants using an automatic approach. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 39, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Yan, J.L.; Ma, K.M.; Zhou, W.Q.; Chen, G.J.; Tang, R.L.; Zhang, Y.X. Characterization of particulate matter deposited on urban tree foliage: A landscape analysis approach. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 171, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, A.A.; Sabir, S. Benefits of a forested urban park: What is the value of Allan Gardens to the city of Toronto, Canada? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.P.; Smith, P.L. A systematic approach to model the influence of the type and density of vegetation cover on urban heat using remote sensing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 132, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenerette, G.D.; Harlan, S.L.; Buyantuev, A.; Stefanov, W.L.; Declet-Barreto, J.; Ruddell, B.L.; Myint, S.W.; Kaplan, S.; Li, X. Micro-scale urban surface temperatures are related to land-cover features and residential heat related health impacts in Phoenix, AZ USA. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toparlar, Y.; Blocken, B.; Maiheu, B.V.; Van Heijst, G.J.F. The effect of an urban park on the microclimate in its vicinity: A case study for Antwerp, Belgium. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, e303–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.W.; Roe, J.; Aspinall, P.; Mitchell, R.; Clow, A.; Miller, D. More green space is linked to less stress in deprived communities: Evidence from salivary cortisol patterns. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.Y.; Huang, G.L.; Wu, J.G. Review of the relationship between urban greenspace accessibility and human well-being. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 421–431. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.X.; Li, S.N.; Zhao, N.; Xu, X.T.; Zhou, Y.B.; Lu, S.W. Uptake and distribution of the inorganic components NH4+ and NO3− of PM2.5 by two Chinese conifers. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 907, 167573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.S.; Liu, H.Q.; Mo, D.L. The role of Guangzhou Urban vegetation in removing atmospheric Sulfur. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1999, 38, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, R.H.; Gan, W.Z. Study on negative air ions concentration in 5 kinds of indoor ornamental plants. Build. Sci. 2018, 34, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.N.; Li, X.H.; Lei, H.J.; Zhao, N.; Xu, X.T.; Lu, S.W. Components and change laws of volatile organic compounds from peach leaves. Non-Wood For. Res. 2023, 41, 40–51+78. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Xia, J.; Xiao, R.; He, T. Urban expansion patterns of 291 Chinese cities, 1990–2015. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 12, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Zhang, Y. Mini-Park Layout Formation Method in High-Density Cities. Chin. Gard. 2021, 37, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Liu, R.; Su, M.T. A Quantitatively Comparative Study on Green Pattern of Urban Park in Beijing, London, Paris and New York Using Spatial Statistics Model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 267, 052004. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, J.; Verheij, R.A.; Groenewegen, P.P.; De Vries, S.; Spreeuwenberg, P. Green space, urbanity, and health: How strong is the relation? J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2006, 60, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yañez, D.V.; Barboza, E.P.; Cirach, M.; Daher, C.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Mueller, N. An urban green space intervention with benefits for mental health: A health impact assessment of the Barcelona Eixos Verds Plan. Environ. Int. 2023, 174, 107880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Teimouri, R.; Degirmenci, K.; Alanjagh, F.A. Association between park visits and mental health in a developing country context: The case of Tabriz, Iran. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 199, 103805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wen, J.; Lu, Y.; Peng, Q.Z. A quasi-experimental study on the impact of park accessibility on the mental health of undergraduate students. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 86, 127979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Q.; Bai, W.L.; Cao, B.X. Study on emergency shelter function of urban green space: A case study at Chaoyang district in Beijing. Harmony and Common Prosperity: Inheritance of Tradition and Sustainable Development: Chinese Society of Landscape Architecture. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference, Volume I; China Urban Construction Design & Research Institute: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Xiu, C.L.; Wei, Y.; He, H.S. Evaluating methodology for the service extent of refugee parks in Changchun, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyando, S.B.; Mziray, L.F. The Kitulo National Park Transformation and the Implications on Sustainable Livelihoods to Adjacent Local Communities in Makete District, Tanzania. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 1539–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Su, Q. Does spatial layout matter to theme park tourism carrying capacity? Tour. Manag. 2017, 61, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.Y.; Hu, H.; Sun, B.D. Elderly Suitability of Park Recreational Space Layout Based on Visual Landscape Evaluation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.X. Research on the Relationship between Park Green Space Accessibility, Place attachment and health benefit assessment: A case Study of Xiamen Island. People’s City, Planning Empowerment. In Proceedings of the 2023 China Annual Conference on Urban Planning; School of Architecture, Huaqiao University: Quanzhou, China, 2023; pp. 260–273. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.R.; Huang, W.Y. The Impact of Urban Park Green Space Accessibility on Neighboring Settlements under the Perspective of Social Equity—The Case of Yuexiu Park in Guangzhou. People’s City, Planning for Empowerment. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Urban Planning in China 2022 (19 Housing and Community Planning); Guangdong University of Technology: Guangzhou, China, 2023; pp. 912–921. [Google Scholar]
- Di, S.C.; Li, Z.L.; Tang, R.L.; Pan, X.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Niu, Y. Urban green space classification and water consumption analysis with remote-sensing technology: A case study in Beijing, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 1909–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Q.S.; Wang, H.L. A Summary of Study on Urban Green Space; Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Agricultural Sciences: Shanghai, China, 2001; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, P. Assessing impacts of urban form on landscape structure of urban green spaces in China using Landsat images based on Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.R. Information Extraction and Landscape Pattern of Urban Green Space Based on GF-1 Satellite Image: A Case Study of Lanzhou. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Lanzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.W.; Han, L.; Han, X.Y. High spatial resolution remote sensing image classification based on deep learning. Acta Opt. Sin. 2016, 36, 0428001. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, L.T.; Wang, Z.Q. U-Net for urban green space classification in Gaofen-2 remote sensing images. J. Image Graph. 2021, 26, 700–713. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Garcia, A.; Orts-Escolano, S.; Oprea, S.; Villena-Martinez, V.; Garcia-Rodriguez, J. A Review on Deep Learning Techniques Applied to Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.06857. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, G.M.A.; Lngkvist, M.; Loutfi, A. Deep learning based automated estimation of urban green space index from satellite image: A case study. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 97, 128373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Ren, Z.P.; Zhao, Y.F.; Liao, Y.L.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.; He, J.X.; Gu, Y.K.; Wang, Y.X.; et al. Multi-scale Feature Fusion and Transformer Network for urban green space segmentation from high-resolution remote sensing images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, R.; Hikosaka, S. Building detection from satellite imagery using ensemble of size-specific detectors. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 223–2234. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Song, W.; Dai, J.; Chen, Y. Road Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Using Refined Deep Residual Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.D.; Tran, X.L. Remote sensing–based urban green space detection using marine predators algorithm optimized machine learning approach. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5586913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.F.; Zou, W.B. Review of remote sensing image classification based on deep learning. Appl. Res. Comput. 2018, 35, 3521–3525. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; He, G.; Yin, R.; Zheng, K.; Wang, G. Comparative study of marine ranching recognition in multi-temporal high-resolution remote sensing images based on DeepLab-v3+ and U-Net. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, Z.; Seddouki, M.; Himmy, O.; Maanan, M.; Tahiri, M.; Rhinane, H. Rural Settlements Segmentation Based on Deep Learning U-Net Using Remote Sensing Images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Sui, Y. Automatic extraction of green tide from GF-3 SAR images based on feature selection and deep learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10598–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Chehri, A.; Jeon, G. A sustainable deep learning-based framework for automated segmentation of COVID-19 infected regions: Using U-Net with an attention mechanism and boundary loss function. Electronics 2022, 11, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Lu, P.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, N. U-Net: A deep-learning method for improving summer precipitation forecasts in China. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2023, 16, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Fang, C.L.; Mu, X.F.; Li, G.D.; Xu, G.Y. Urban green space quality in China: Quality measurement, spatial heterogeneity pattern and influencing factor. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 66, 127381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, Y.; Yang, G.; Wu, Z.; Mao, F.; Liu, S.; Xu, R.H.; Qu, Z.L.; Xu, B.; Chang, J. Inequalities of urban green space area and ecosystem services along urban center-edge gradients. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 217, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.M.; Chen, B.; Ho, H.C.; Kwan, M.P.; Liu, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.H.; Cai, J.X.; Li, X.J.; Xu, Y.; et al. Observed inequality in urban greenspace exposure in China. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Statistical Yearbook Editorial Committee. China Statistical Yearbook 2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.R.; Cui, X.M.; Guo, L.; Wu, L.; Tang, X.M.; Liu, S.H.; Yuan, D.B.; Wang, X. Satellite Laser Altimetry Data-Supported High-Accuracy Mapping of GF-7 Stereo Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of the Leading Group of Beijing Municipality for the Seventh National Population Census; Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing (China) Population Census Yearbook 2020; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pooler, J.A. The use of spatial separation in the measurement of transportation accessibility. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 1995, 29, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.Y.; Samsudin, R. Effects of spatial scale on assessment of spatial equity of urban park provision. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 158, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulak, M.B.; Yazici, A.; Aljarrah, M. Value of convenience for taxi trips in New York City. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 142, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Ma, L.; Huang, C. Factors affecting the use of urban green spaces for physical activities: Views of young urban residents in Beijing. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Sun, Z.; Bao, Z. Landscape perception and recreation needs in urban green space in Fuyang, Hangzhou, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.L.; Gu, S. An evaluation of social performance in the distribution of urban parks in the central city of Shanghai: From social equity justice. J. Urban Plan. 2016, 227, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.F.; Qiu, J.X.; Breuste, J.; Friedman, C.; Zhou, W.Q.; Wang, X.K. Variations of urban greenness across urban structural units in Beijing, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.X. Research on Green Space Information Extraction and Application Based on Deep Learning Algorithms. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Fei, X.Y.; Gao, X.W.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhao, H.M. Extraction of urban green space with high resolution remote sensing image segmentation. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 12, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, D. Racial/ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in urban green space accessibility: Where to intervene? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 102, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Lin, T.; Zhang, G.Q.; Jones, L.; Xue, X.; Ye, H.; Liu, Y.Q. Spatiotemporal patterns and inequity of urban green space accessibility and its relationship with urban spatial expansion in China during rapid urbanization period. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasihi, H.; Parizadi, T. Analysis of spatial equity and access to urban parks in Ilam, Iran. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.L.; Wu, Z.F.; Zhang, H.; Wei, J.Y. Comprehensive evaluation of park green space service capability in central city: Models and cases. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2020, 29, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.H.; He, K.; Wang, B.Y.; Yu, G. Research on the Planning Layout and Supply Demand Relationship of Pocket Park in Minhang District of Shanghai from the Perspective of Social Equity. Landsc. Archit. 2023, 40, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, H.J. Analysis of the Coordination Relationship between the Green Principle of Civil Law and Environmental Law in Environmental Pollution and Ecological Destruction. J. Environ. Public Health 2022, 1, 2536704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, A.N.; Wang, J.Q.; Lu, T.F. Supply and demand analysis of urban park distribution based on social equity and justice: A case study of Xuhui District, Shanghai. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7035–7046. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Xie, J.C.; Yew, M.K.; Ding, T.C.; Le, Y.Y.; Lu, Y.X. Research on fairness evaluation of park and green space layout in five urban areas of Chengdu city. Shanxi Archit. 2024, 50, 10–13+37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, H.Y. Long commutes and transport inequity in China’s growing megacity: New evidence from Beijing using mobile phone data. Travel Behav. Soc. 2020, 20, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Li, Z.G.; Chen, H.S.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, J. Subjective well-being in China: How much does commuting matter? Transportation 2019, 46, 1505–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.J.; Schroeder, T.; Bekkering, J. Designing with nature: Advancing three-dimensional green spaces in architecture through frameworks for biophilic design and sustainability. Front. Archit. Res. 2023, 12, 732–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.X.; Zhai, X.Q.; Hu, Y.L.; Cheng, B.K.; Wang, P. Based on the “sponge city” construction concept of three-dimensional greening engineering construction technology analysis. China Build. Decor. Furnish. 2023, 18, 154–156. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).