A Geospatial Model of Periurbanization—The Case of Three Intermediate-Sized and Subregional Cities in Chile
Abstract
1. Introduction
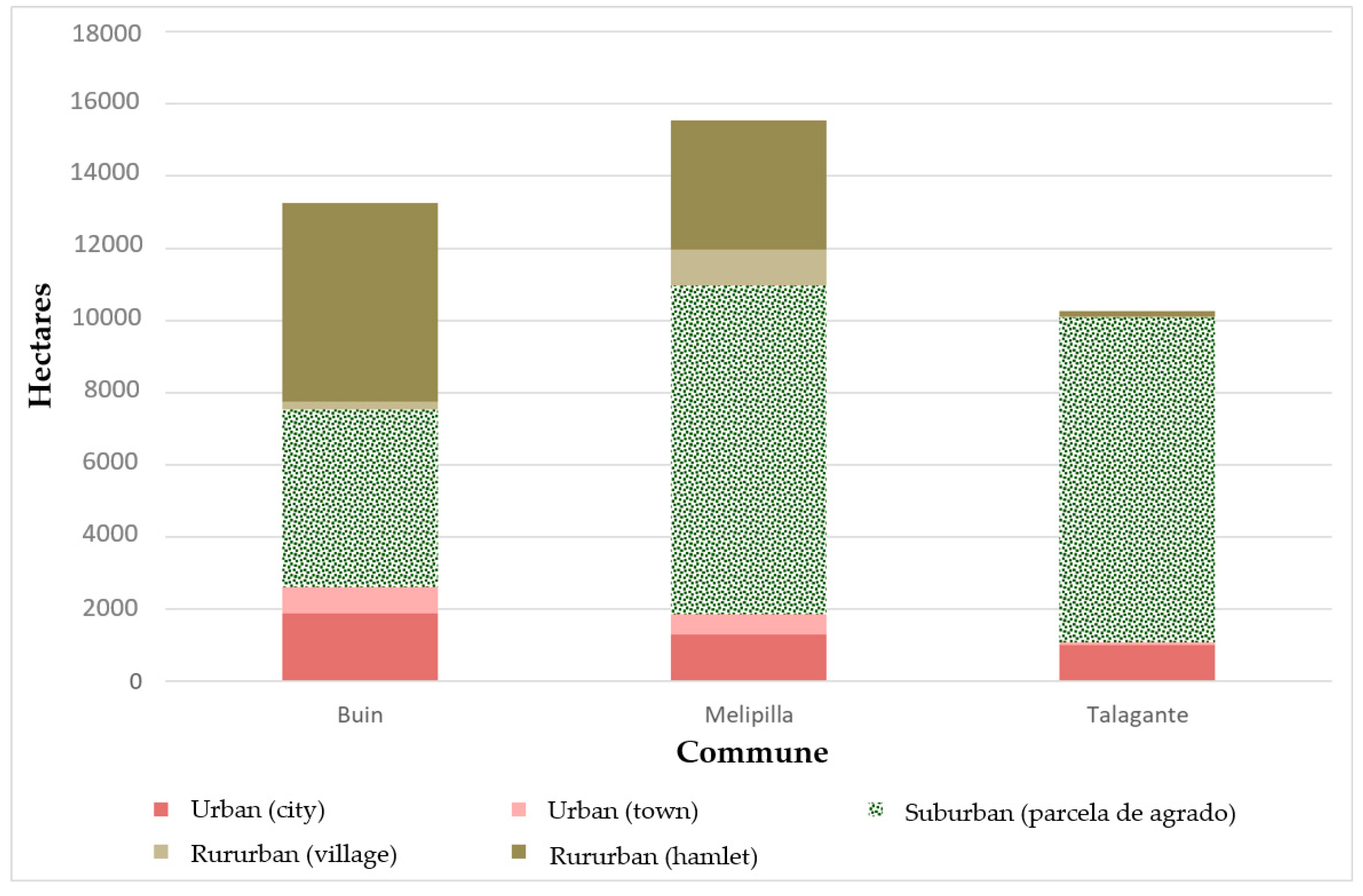
1.1. State of the Literature and Conceptual Framework: General Context of Urban Expansion in Latin America and Chile
1.2. Key Concepts, Research Problem, and Hypotheses
2. Materials and Methods
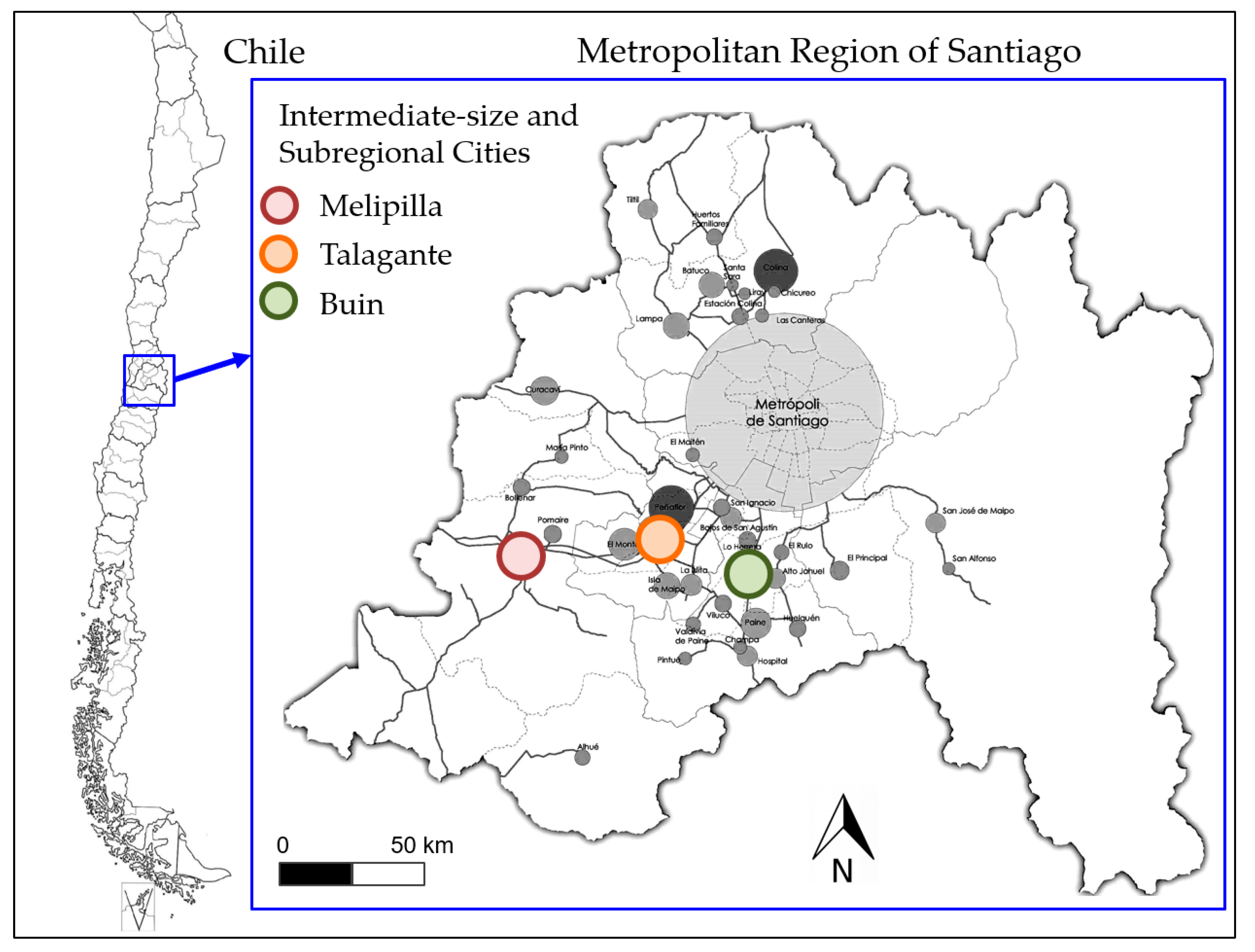
2.1. Selection and Justification of the Study Area
2.2. Compilation, Analysis, and Representation of Geospatial Data
3. Results: Geospatial Dynamics
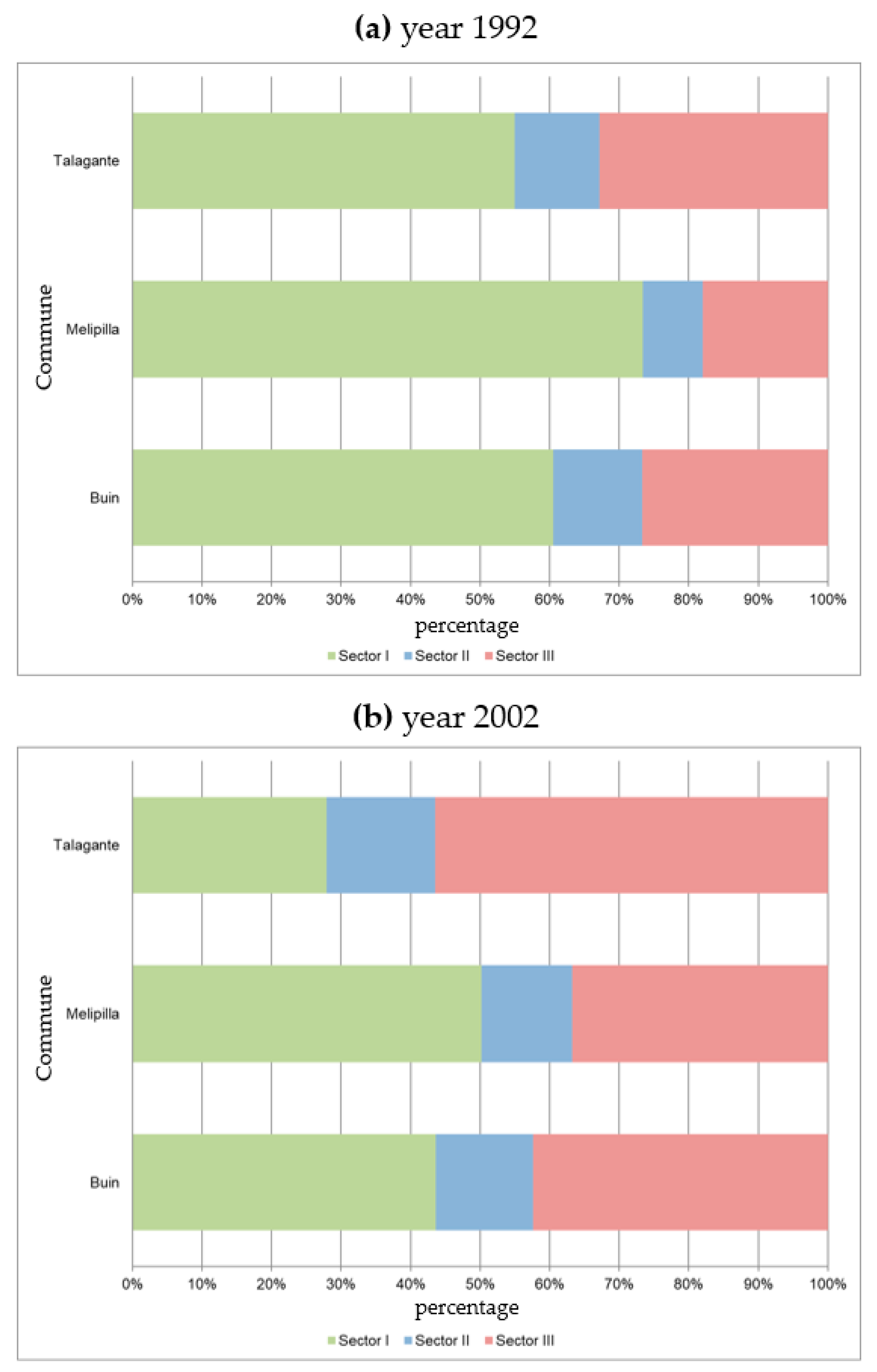
3.1. Sociodemographic and Socioeconomic Dynamics
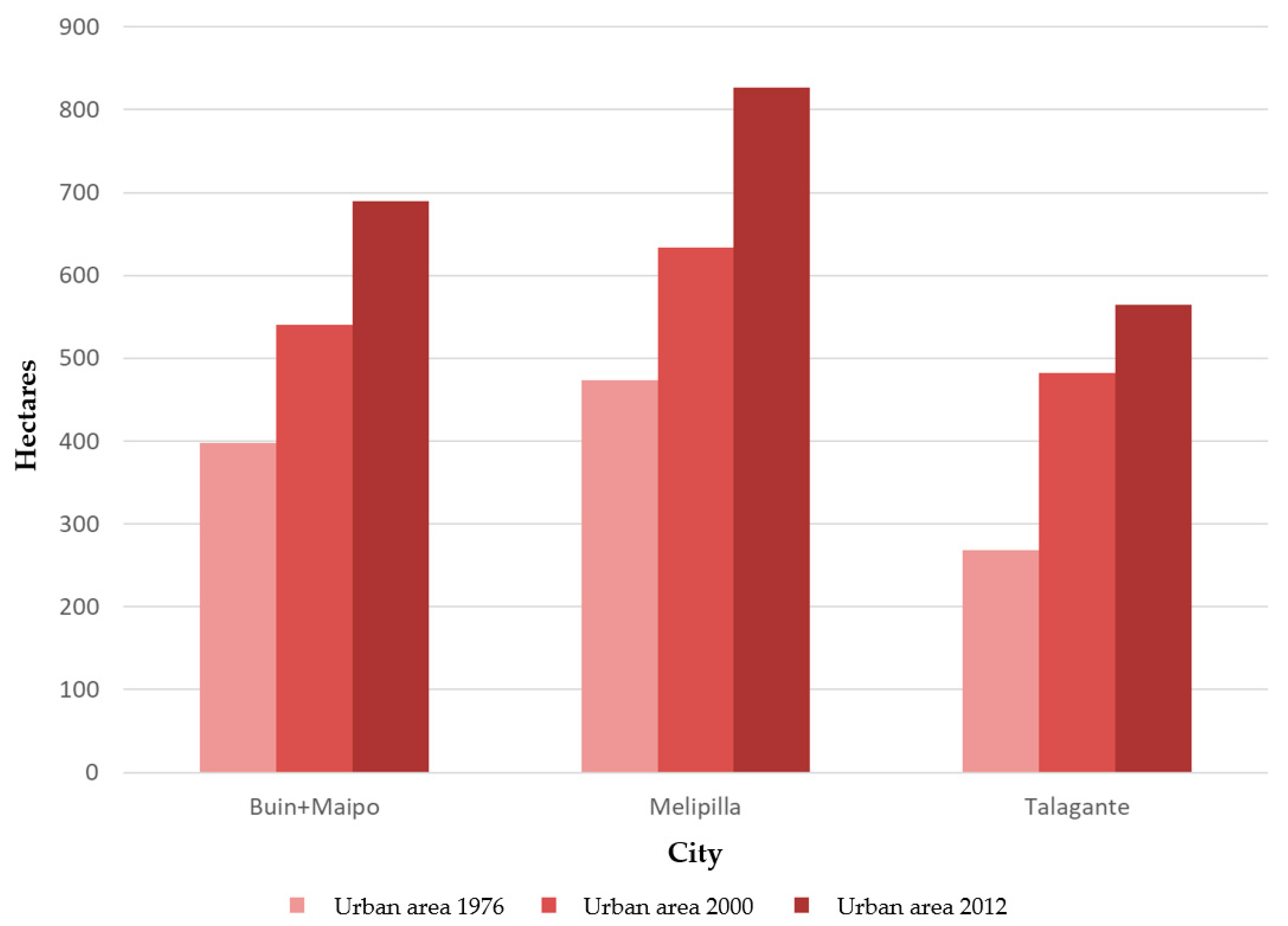
3.2. Dynamics of Urban Expansion and Distribution of Other Associated Land Uses
3.3. Evolution of Land Use and Cover in the Peri-Urban Area
4. Discussion and Proposal of the Periurbanization Geospatial Model
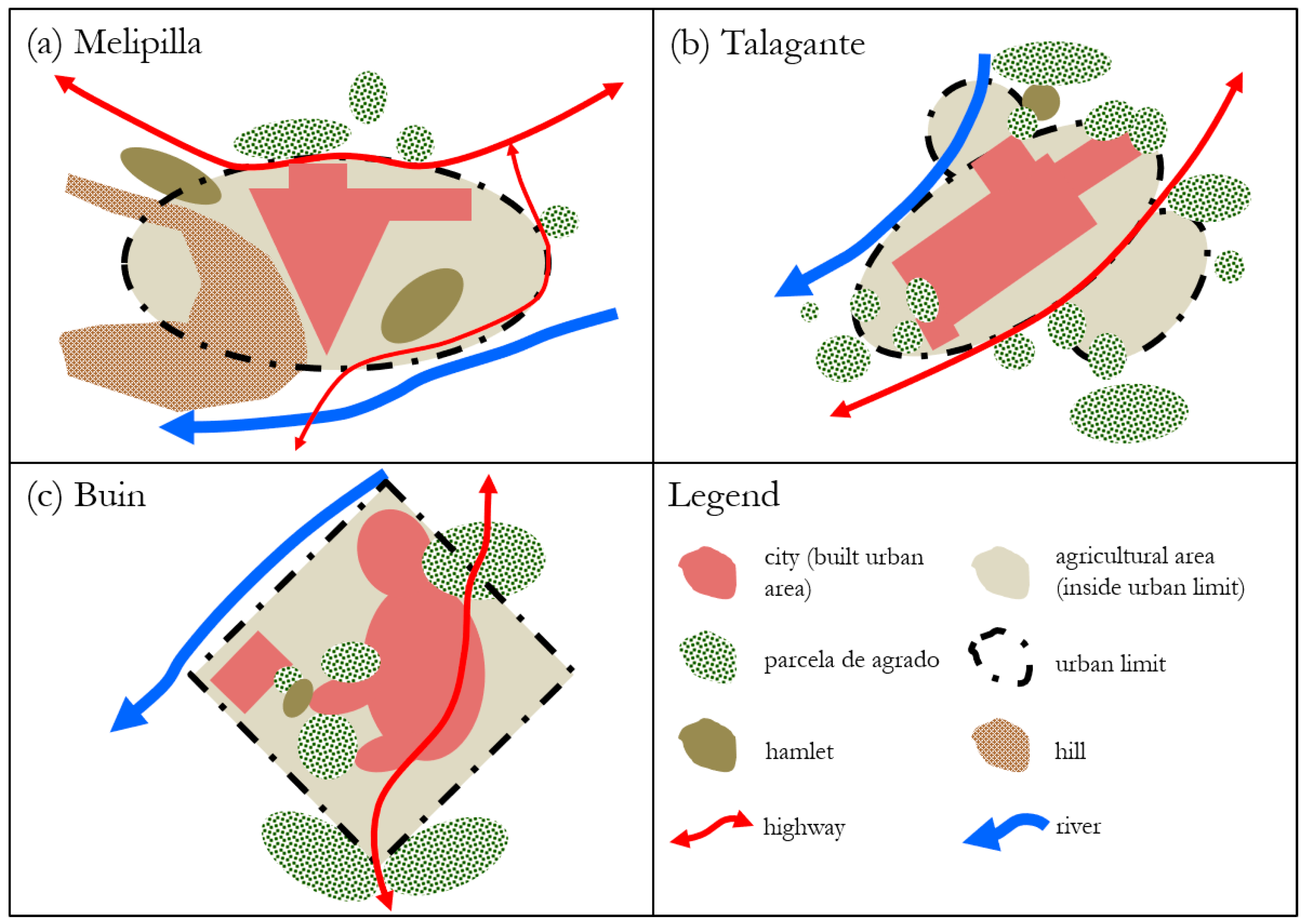
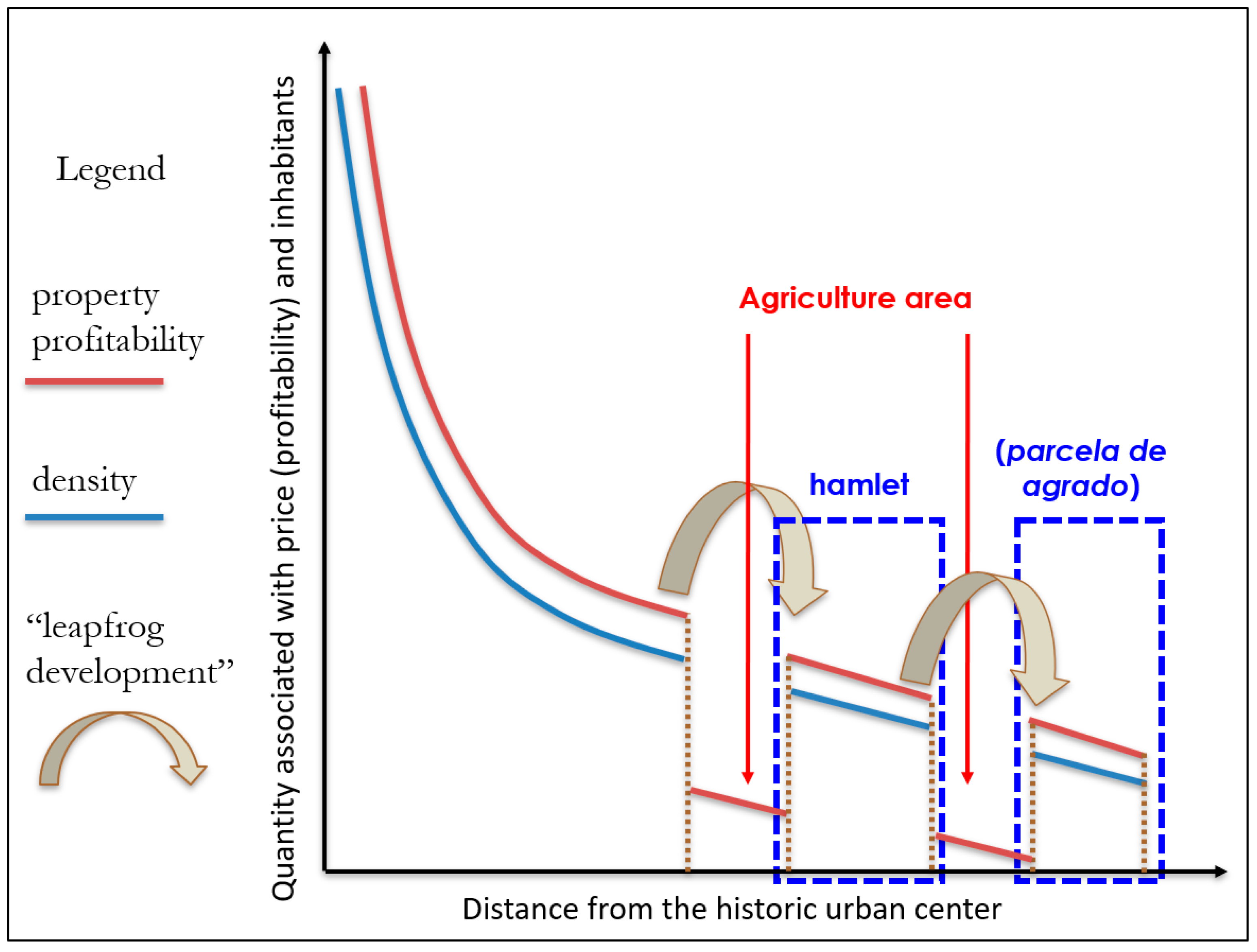
4.1. Dynamics in the Periurban Areas of Subregional Intermediate-Sized Cities in Chile
4.2. Projection of the Three Cases of Subregional Intermediate-Sized Cities
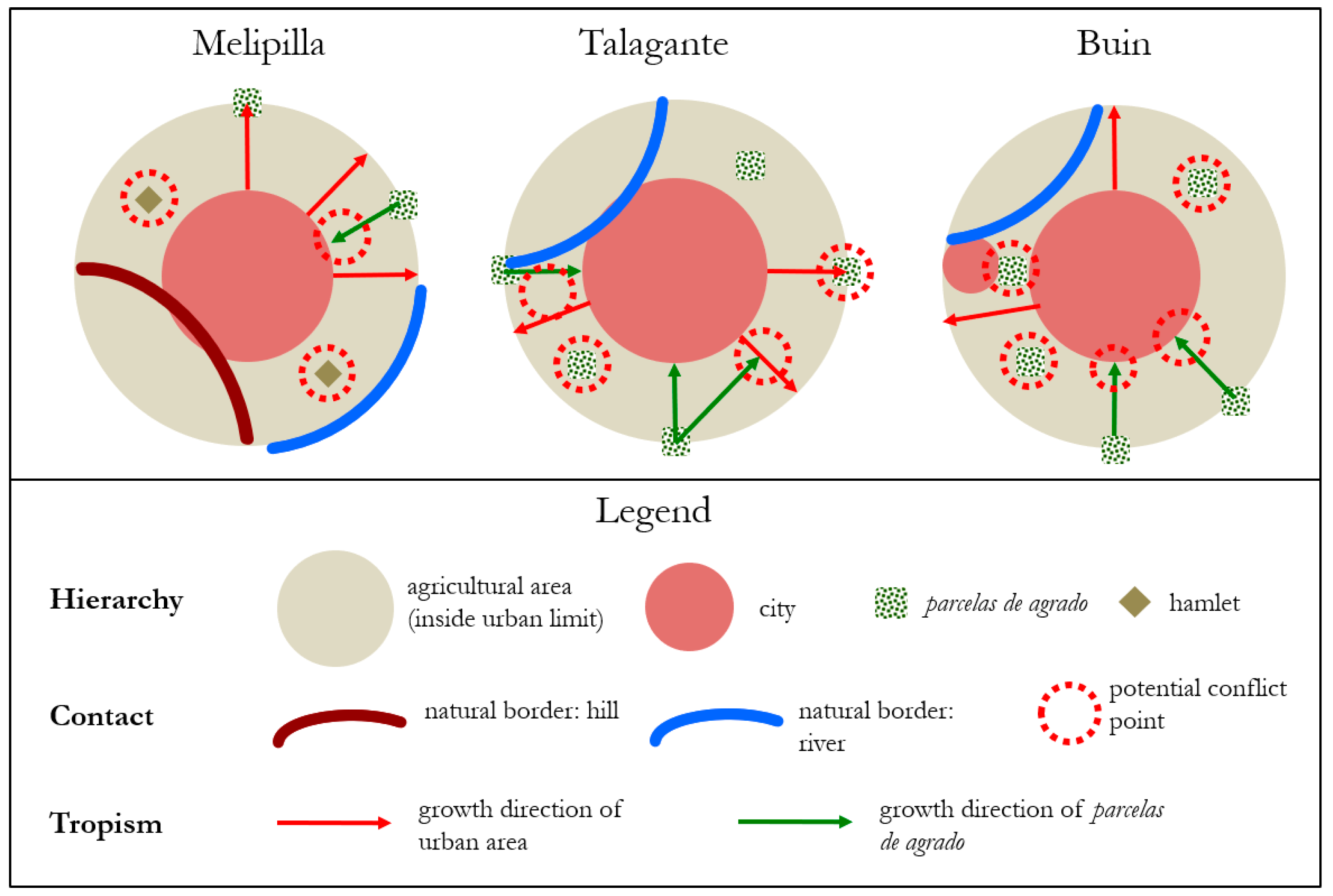
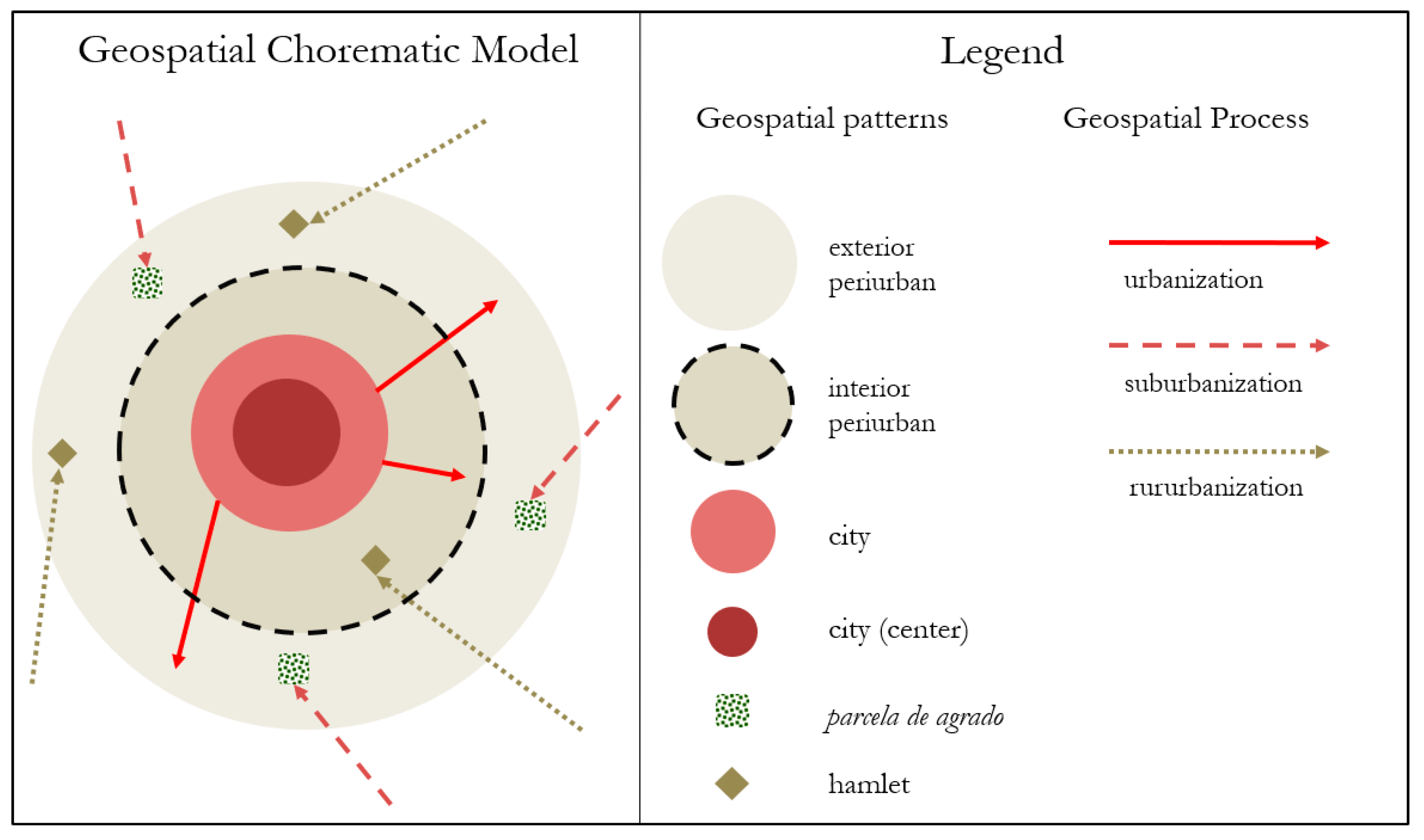
4.3. Composition of the Periurbanization Process in Chile: Proposal of a Geospatial Chorematic Model for Subregional Intermediate-Sized Cities and Its contribution to Latin America and the Global South
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B


| 1 | Satellites images of each city are in Appendix A, Figure A1. |
| 2 | Only the years 1992 and 2002 were taken into consideration, as this question was not included in the 2017 Census. Consequently, they represent the most recent publicly available data. |
| 3 | It should be noted that the surfaces of the urban, suburban, and rururban categories were employed for human settlements. Thus, the percentage pertains to these categories and does not encompass the entirety of the commune, which includes other uses and coverages. |
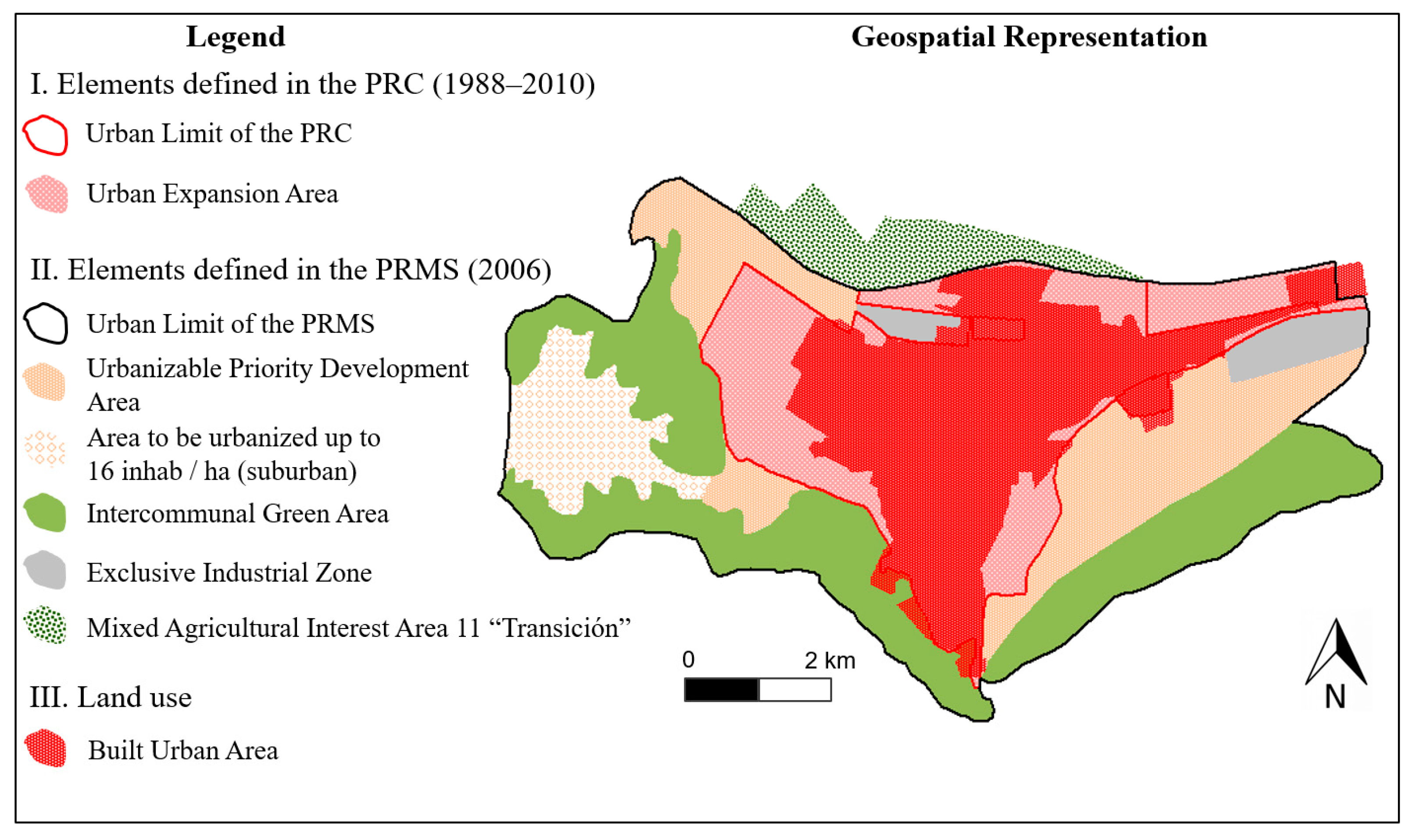
| 4 | Geospatial elements defined by the Communal Regulatory Plan (PRC) and the Metropolitan Regulatory Plan of Santiago (PRMS) of the urban and periurban areas of each city are in Appendix B. |
References
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hejazi, M.; Wise, M.; Vernon, C.; Iyer, G.; Chen, W. Global Urban Growth between 1870 and 2100 from Integrated High Resolution Mapped Data and Urban Dynamic Modeling. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A Meta-Analysis of Global Urban Land Expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.; Knox, P.K. The New Metropolis: Rethinking Megalopolis. Reg. Stud. 2009, 43, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubilla-Bravo, G. Gouvernance Territoriale et Politiques D’aménagement. Cas du Périurbain au Chili, 1960–2015. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paul-Valéry, Montpellier III, Montpellier, France, 2020. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-03094889/ (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Bolay, J.C. Planning the Intermediate City, or How to Do Better with Little: The Case of the City of Nueve de Julio, Argentina. Curr. Urban Stud. 2018, 6, 366–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, N.; Theodore, N. Neoliberalism and the Urban Condition. City 2005, 9, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precedo, A. Capítulo 1. Las respuestas de los territorios locales a la globalización. In Nuevas Realidades Territoriales para el Siglo XXI: Desarrollo Local, Identidad Territorial y Ciudad Difusa; Espacios y Sociedades. Serie Mayor; Editorial Síntesis S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 2004; pp. 13–32. ISBN 978-84-9756-163-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Varquez, A.C.G.; Kanda, M. High-Resolution Global Urban Growth Projection Based on Multiple Applications of the SLEUTH Urban Growth Model. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlon, B. Sprawl. In The Wiley Blackwell Encyclopedia of Urban and Regional Studies; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 4, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iracheta Cenecorta, A.; Jaloma López, L.; Soto Alva, E. Suelo Urbano en México: Retos y Oportunidades para su Administración y Registro; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Mexico City, Mexico, 2019; ISBN 978-607-30-1624-7. [Google Scholar]
- Coq-Huelva, D.; Asián-Chaves, R. Urban Sprawl and Sustainable Urban Policies. A Review of the Cases of Lima, Mexico City and Santiago de Chile. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usach, N.; Gallo-Rivera, M.T.; Garrido-Yserte, R. La Dinámica Espacial en el Área Metropolitana de Buenos Aires: ¿De la Dispersión al Policentrismo? XXXIX Reunión de Estudios Regionales: Oviedo, Spain, 2013; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Change Detection: How Has Urban Expansion in Buenos Aires Metropolitan Region Affected Croplands. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2018, 11, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Vergara-Perucich, F. Determinants of Urban Sprawl in Latin America: Evidence from Santiago de Chile. SN Soc. Sci. 2021, 1, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Criado, F.; Ubilla-Bravo, G. Movilidad en transporte privado y emisión de CO2: Patrones geoespaciales e implicancias en el ordenamiento territorial para el Área Metropolitana de Santiago, Chile. Rev. Transp. Territ. 2023, 169–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, G.N.; Magaña Rueda, V.O. The Urban Growth of the Metropolitan Area of Sao Paulo and Its Impact on the Climate. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2018, 21, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inostroza, L. Informal Urban Development in Latin American Urban Peripheries. Spatial Assessment in Bogotá, Lima and Santiago de Chile. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 165, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, E.; Henríquez, C.; Durán, G.; Qüense, J.; Puente-Sotomayor, F. How to Define a New Metropolitan Area? The Case of Quito, Ecuador, and Contributions for Urban Planning. Land 2021, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzai, G.D. Urban Models in the Study of Latin American Cities. In Die Welt Verstehen-Eine Geographische Herausforderung: Eine Festschrift der Geographie Innsbruck für Axel Borsdorf; Innsbrucker Geographische Studien: Innsbruck, Austria, 2016; pp. 271–288. ISBN 978-3-901182-43-3. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, A.; Soltani, A.; Abdi, M.H.; Zarei, M. Driving Forces behind Land Use and Land Cover Change: A Systematic and Bibliometric Review. Land 2022, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, M. Compact City. In The Wiley Blackwell Encyclopedia of Urban and Regional Studies; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Cirella, G.T. Modern Compact Cities: How Much Greenery Do We Need? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouratidis, K. Compact City, Urban Sprawl, and Subjective Well-Being. Cities 2019, 92, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precedo, A. Capítulo 7. La ciudad regional difusa. In Nuevas Realidades Territoriales para el Siglo XXI: Desarrollo Local, Identidad Territorial y Ciudad Difusa; Espacios y Sociedades. Serie Mayor; Editorial Síntesis S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 2004; pp. 165–180. ISBN 978-84-9756-163-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bartels, L.E.; Bruns, A.; Simon, D. Towards Situated Analyses of Uneven Peri-Urbanisation: An (Urban) Political Ecology Perspective. Antipode 2020, 52, 1237–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubilla-Bravo, G. Relaciones de poder entre los actores del periurbano en torno al Plan Regulador Comunal: Analizando la gobernanza territorial. Cuad. Geogr. Rev. Colomb. Geogr. 2020, 29, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubilla-Bravo, G. Aprendizaje en la gobernanza territorial: Construcción de lenguaje, coordinación y acuerdos entre los actores del periurbano. Rev. Geogr. Norte Gd. 2023, 1–25. Available online: https://revistanortegrande.uc.cl/index.php/RGNG/article/view/38655 (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Chapuis, R. Géographie. Agrégation-Capes D’histoire et de Géographie. Crises et Mutations des Agricultures et D’espaces Ruraux; Institut de Vanves du CNED: Vanves, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, A. La interfase periurbana como escenario de cambio y acción hacia la sustentabilidad del desarrollo. Cuad. Cendes 2003, 20, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sereno, C.A.; Santamaría, M.; Santarelli, S. El rururbano: Espacio de contrastes, significados y pertenencia, ciudad de Bahía Blanca, Argentina. Cuad. Geogr. Rev. Colomb. Geogr. 2010, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila Sánchez, H. Periurbanización y espacios rurales en la periferia de las ciudades. Estud. Agrar. 2009, 15, 93–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ubilla-Bravo, G. Rururbanización, suburbanización y reconcentración de la tierra: Efectos espaciales de instrumentos rurales en las áreas periurbanas de Chile. AGER Rev. Estud. Sobre Despoblación Desarro. Rural. 2020, 28, 75–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armijo, G. La urbanización del campo metropolitano de Santiago: Crisis y desaparición del hábitat rural. Rev. Urban. 2000, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubilla-Bravo, G.; Rodríguez-Seguel, V. Asentamientos Humanos en Chile: Revisión General en Torno al Cambio Climático y Ambiental para Ciudades Grandes e Intermedias. Estado de la Materia en 2022; Universidad de Chile: Santiago, Chile, 2022; p. 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamizar-Santamaría, S. Gated Communities/Fortified Enclaves. In The Wiley Blackwell Encyclopedia of Urban and Regional Studies; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decreto No 47. In Fija Nuevo Texto de la Ordenanza General de la Ley General de Urbanismo y Construcciones; Bilbioteca del Congreso Nacional de Chile: Valparaiso, Chile, 1992; p. 237.
- Ubilla Bravo, G. Entidades rurales aisladas de la Región Metropolitana de Santiago de Chile-RMS: Localización y vulnerabilidad. Cuad. Geogr. Rev. Colomb. Geogr. 2012, 21, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INE Chile. Chile: Ciudades, Pueblos y Aldeas. Censo 1992; Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas: Santiago, Chile, 1995; ISBN 0717-1463. [Google Scholar]
- INE Chile. Chile: Ciudades, Pueblos, Aldeas y Caseríos. Censo 2002; Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas: Santiago, Chile, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- INE Chile. Chile: Ciudades, Pueblos, Aldeas y Caseríos 2019; Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas: Santiago, Chile, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Resolución No 76. In Deja Sin Efecto Resolución No 115, de 2005 y Modifica Plan Regulador Metropolitano de Santiago; Bilbioteca del Congreso Nacional de Chile: Valparaiso, Chile, 2006.
- Pouyanne, G. Théorie économique de la ville discontinue. Rev. D’économie Régionale Urbaine 2014, 587–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras Alonso, M.; Opazo, D.; Núñez Pino, C.; Ubilla Bravo, G. Informe Final del Proyecto “Ordenamiento Territorial Ambientalmente Sustentable” (OTAS); Contreras Alonso, M., Ed.; Gobierno Regional Metropolitano de Santiago, Universidad de Chile y Agencia Técnica Alemana: Santiago, Chile, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubilla Bravo, G.; Robles Vargas, R.; González, D.; Garay, N.; Norambuena Vega, P.; Sandoval Verdugo, G.; Muñoz Muñoz, F. Carta de Cobertura y Uso del Suelo en la Región Metropolitana de Santiago; Plan Regional de Ordenamiento Territorial de la Región Metropolitana de Santiago. Etapa 2: Diagnóstico Prospectivo Territorial; Gobierno Regional Metropolitano de Santiago y Edáfica: Santiago, Chile, 2012; p. 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAF Chile; Sud-Austral Consulting SpA. Diagnóstico de la Desertificación en Chile y Sus Efectos en el Desarrollo Sustentable: Alineación de los Contenidos del Actual PANCD Con la Estrategia Decenal de la Convención (CNULD), la Iniciativa de Degradación Neutral de la Tierra y Los Objetivos del Desarrollo Sostenible; CONAF: Santiago, Chile, 2016; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, W.K.D. Centrality and the Central Place Hierarchy. Urban Stud. 1967, 4, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti Gallardo, M.P.; Saa Vidal, R.; Rodríguez Rojas, J.; Contreras Alonso, M.; Montecinos Concha, T.; Ibáñez Zamora, J.; Núñez Pino, C.; Ubilla Bravo, G. Atlas Socioeconómico de la Región Metropolitana de Santiago; Gobierno Regional Metropolitano de Santiago: Santiago, Chile, 2006; ISBN 956-8583-00-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubilla-Bravo, G.; Chia, E. Construcción del periurbano mediante instrumentos de regulación urbana: Caso de ciudades intermedias en la Región Metropolitana de Santiago-Chile. Cuad. Geográficos 2021, 60, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, M.; Ravetz, J.; Patel, P.P.; Dadashpoor, H.; Follmann, A. Where Is the Peri-Urban? A Systematic Review of Peri-Urban Research and Approaches for Its Identification and Demarcation Worldwide. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, R. La composition des modèles dans l’analyse spatiale. Spgeo 1980, 9, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, R. Sustainable Geography; Geographical Information Systems Series; ISTE; Wiley: London, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-118-55784-6. [Google Scholar]
- INE Chile. Resultados Generales. Censo de Población y la Vivienda. Chile 1992; Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas: Santiago, Chile, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- INE Chile. Chile: XVII Censo de Población y VI de la Vivienda año 2002. Volumen I: Población, País-Región; Morales, H., Ed.; Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas: Santiago, Chile, 2003; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- INE Chile Resultados de Comunas–Censo 2017. 2017. Available online: http://www.censo2017.cl/descargue-aqui-resultados-de-comunas/ (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Apey Guzmán, A. El proceso de reestructuración económica nacional y su impacto en el sistema regional: 1976–1981. Investig. Geográficas 1983, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffo Rosas, M. Globalización de La Economía e Impacto Espacial En Las Áreas Rurales de La Zona Central de Chile. Rev. Chil. Hist. Geogr. 1998, 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- CNR Chile; Agrolog Chile Ltda. Estudio de Suelos del Proyecto Maipo año 1976. Tomo I; Comisión Nacional de Riego: Santiago, Chile, 1981; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- GORE RMS; Universidad de Chile; GTZ. Carta Uso del Territorio. Región Metropolitana de Santiago; Gobierno Regional Metropolitano de Santiago: Santiago, Chile, 2003; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- INE Chile. Cartografía Precenso 2016 Región Metropolitana de Santiago 2016. Available online: https://www.ide.cl/index.php/sociedad/item/1740-cartografia-precenso-2016-region-metropolitana-de-santiago (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- DL No 3.516. In Establece Normas Sobre División de Predios Rústicos; Bilbioteca del Congreso Nacional de Chile: Valparaiso, Chile, 1980.
- MINVU Chile. Política Nacional de Desarrollo Urbano; Ministerio de Vivienda y Urbanismo: Santiago, Chile, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Decreto No 420. In Modifica Plan Intercomunal de Santiago y su Ordenanza; Bilbioteca del Congreso Nacional de Chile: Valparaiso, Chile, 1979.
- Gordon, P.; Richardson, H.W. Are Compact Cities a Desirable Planning Goal? J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1997, 63, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R. Is Los Angeles-Style Sprawl Desirable? J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1997, 63, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decreto No 78. In Aprueba Política Nacional de Desarrollo Urbano y Crea Consejo Nacional de Desarrollo Urbano; Bilbioteca del Congreso Nacional de Chile: Valparaiso, Chile, 2014.
- Decreto No 19. In Aprueba Política Nacional de Desarrollo Rural; Bilbioteca del Congreso Nacional de Chile: Valparaiso, Chile, 2020.
- Decreto No 469. In Aprueba Política Nacional de Ordenamiento Territorial; Bilbioteca del Congreso Nacional de Chile: Valparaiso, Chile, 2021.
- Gasic Klett, I.R. Mercado del suelo urbano y reserva financiera de terrenos para producción de vivienda en el Área Metropolitana de Santiago. Rev. Geogr. Norte Gd. 2020, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa Angulo, J.; Vidal Domínguez, M.J. Capítulo 1. Los procesos de urbanización desde una perspectiva geográfica. In Los Procesos de Urbanización; Espacios y Sociedades. Serie General; Editorial Síntesis S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 1999; pp. 9–31. ISBN 84-7738-110-0. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez-Lemus, Y.; Vieyra, A.; Poncela, L.; de la Tejera, B.; Ruiz-López, C. Peripheralization, Ejidos and Agricultural Livelihoods in Intermediate Mexican Cities: The Importance of Collective Agency to Reduce Vulnerabilities. Front. Sustain. Cities 2022, 4, 816649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decreto No 458. In Aprueba Nueva Ley General de Urbanismo y Construcciones; Bilbioteca del Congreso Nacional de Chile: Valparaiso, Chile, 1976.
- Bryant, C.R.; Russwurm, L.H.; McLellan, A.G. The City’s Countryside: Land and Its Management in the Rural-Urban Fringe; Longman: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1982; ISBN 978-0-582-30045-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bryant, C.R. L’évolution de la ville régionale en Amérique du Nord: Le cas de Toronto. Geo 1986, 95, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekers, M.; Hamel, P.; Keil, R. Governing Suburbia: Modalities and Mechanisms of Suburban Governance. Reg. Stud. 2012, 46, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydalot, P.; Garnier, A. Périurbanisation et suburbanisation: Des concepts à définir. disP-Plan. Rev. 1985, 21, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsin, L. La reprise démographique rurale en Wallonie et en Europe du Nord-Ouest. Espace Popul. Sociétés 2000, 18, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follmann, A. Geographies of Peri-Urbanization in the Global South. Geogr. Compass 2022, 16, e12650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A. Peri-Urbanization, Global South. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, D. An Overdue Agenda: Systematizing East Asian Peri-Urban Research. Pac. Aff. 2011, 84, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Mei, L. Characterizing Growth Types and Analyzing Growth Density Distribution in Response to Urban Growth Patterns in Peri-Urban Areas of Lianyungang City. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, J. Becoming Urban: Periurban Dynamics in Vietnam and China—Introduction. Pac. Aff. 2011, 84, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Gupta, K. Mapping Peri-Urbanization in a Non-Primate City: A Case Study of Burdwan, India. Eur. Acad. Res. Rom. 2018, 5, 6065–6081. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Narain, V. Lost in Transition: Perspectives, Processes and Transformations in Periurbanizing India. Cities 2020, 97, 102494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, M.; Choy, D.L. Change in Peri-Urban Australia: Implications for Land Use Policies. In Proceedings of the 3rd State of Australian Cities National Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 28–30 November 2007; pp. 291–302. Available online: https://apo.org.au/node/60246 (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Liu, Z.; Robinson, G.M. Residential Development in the Peri-Urban Fringe: The Example of Adelaide, South Australia. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedire, F.M. Peri-Urban Expansion in Ikorodu, Lagos: Extent, Causes, Effects, and Policy Response. Urban Forum 2018, 29, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afriyie, K.; Abass, K.; Adomako, J.A.A. Urbanisation of the Rural Landscape: Assessing the Effects in Peri-Urban Kumasi. Int. J. Urban Sustain. Dev. 2014, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoateng, P.; Cobbinah, P.B.; Owusu-Adade, K. Managing Physical Development in Peri-Urban Areas of Kumasi, Ghana: A Case of Abuakwa. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2013, 7, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, L.E. Peri-Urbanization as “Quiet Encroachment” by the Middle Class. The Case of P&T in Greater Accra. Urban Geogr. 2020, 41, 524–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daga, D.Y.; Vazquez, P.; Sequeira, N.D. Sistemas hortícolas del periurbano de Mar del Plata (Argentina): Implicancias ambientales y necesidad de una clasificación tipológica para la evaluación de la sustentabilidad. Papeles Geogr. 2021, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorda, M.A. Lógicas socioespaciales en el espacio periurbano de Bahía Blanca. Huellas 2008, 90–112. [Google Scholar]
- Pola-Villaseñor, S.; Méndez-Lemus, Y.M.; Vieyra Medrano, A. Acceso al suelo ejidal periurbano: Análisis desde el capital social. Econ. Soc. Territ. 2017, 429–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubilla Bravo, G. Diagnóstico y Propuesta de Ordenamiento Territorial para la Comuna de Melipilla, Región Metropolitana de Santiago-Chile. Terra Aust. 2008, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxar Technologies Inc. Constellation-WorldView Legion-Earth Observation Satellites. Available online: https://www.maxar.com/constellation (accessed on 10 December 2023).
| Criteria | Source | Subregional Intermediate-Sized Cities in the Human Settlement System |
|---|---|---|
| (i) Potential to be a subregional center based on population size | [43] | (i) Tiltil, (ii) Colina, (iii) Curacaví, Melipilla, (iv) San José de Maipo, (v) Buin, (vi) Talagante and (vii) Alhué. |
| [40] | (i) Peñaflor, (ii) Colina, (iii) Melipilla, (iv) Talagante, (v) Buin and (vi) Padre Hurtado. | |
| (ii) Competition for land use | [44,45] | (i) Buin, (ii) Isla de Maipo, (iii) Talagante, (iv) El Monte and (v) Melipilla. |
| (iii) Functional centrality of cities | [47] | (i) Melipilla, (ii) Talagante and (iii) Buin. |
| Dynamics Category | Geospatial Indicator | Year or Period | Data Source Institution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic | Variation in Urban Population | 1982–2017 | INE Chile |
| Variation in Rural Population | 1982–2017 | INE Chile | |
| Variation in Population in Communal Capital Cities | 1982–2017 | INE Chile | |
| Socioeconomic | Variation in Rural Economically Active Population Structure | 1992–2002 | INE Chile |
| Urban Expansion and Distribution of Associated Land Uses | Variation in Urban Area | 1976–2012 | GORE RMS |
| Proportion of Urban, Rururban, and Suburban Areas | 2016 | INE Chile | |
| Land Use in the Peri-urban Area | Evolution of Land Use and Cover | 2016 | INE Chile y SEREMI VyU RMS |
| Commune | Urban Human Settlement Name | Census Year |
|---|---|---|
| Buin | Buin (communal capital) | 1982, 1992, 2002, 2017 |
| Maipo | 1982, conurbation with “Buin” since 1992 | |
| Linderos | 1982, conurbation with “Buin” since 1992 | |
| Alto Jahuel | 1982, 1992, 2002 and 2017 | |
| Valdivia de Paine | 1982, 1992, 2002 and 2017 | |
| El Rulo | 2002 and 2017 | |
| Viluco | 2002 and 2017 | |
| Melipilla | Melipilla (communal capital) | 1982, 1992, 2002 and 2017 |
| Pomaire | 1982, 1992, 2002 and 2017 | |
| Bollenar | 1982, 1992, 2002 and 2017 | |
| Talagante | Talagante (communal capital) | 1982, 1992, 2002 and 2017 |
| Variation Period | 1982–1992 | 1992–2002 | 2002–2017 | 1982–2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commune | |||||
| Buin | 33.21% | 35.29% | 54.96% | 179.27% | |
| Melipilla | 23.31% | 18.70% | 39.12% | 103.63% | |
| Talagante | 46.77% | 34.30% | 18.52% | 133.62% | |
| Variation Period | 1982–1992 | 1992–2002 | 2002–2017 | 1982–2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commune | |||||
| Buin | 9.44% | −25.15% | 38.23% | 13.23% | |
| Melipilla | 27.75% | 16.21% | 15.64% | 71.67% | |
| Talagante | 12.57% | 27.73% | 52.60% | 119.42% | |
| Variation Period | 1982–1992 | 1992–2002 | 2002–2017 | 1982–2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commune | |||||
| Buin | 82.94% | 21.27% | 63.65% | 263.05% | |
| Melipilla | 35.74% | 17.06% | 34.92% | 114.38% | |
| Talagante | 49.49% | 34.30% | 13.85% | 128.57% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ubilla-Bravo, G.F. A Geospatial Model of Periurbanization—The Case of Three Intermediate-Sized and Subregional Cities in Chile. Land 2024, 13, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050694
Ubilla-Bravo GF. A Geospatial Model of Periurbanization—The Case of Three Intermediate-Sized and Subregional Cities in Chile. Land. 2024; 13(5):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050694
Chicago/Turabian StyleUbilla-Bravo, Gerardo Francisco. 2024. "A Geospatial Model of Periurbanization—The Case of Three Intermediate-Sized and Subregional Cities in Chile" Land 13, no. 5: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050694
APA StyleUbilla-Bravo, G. F. (2024). A Geospatial Model of Periurbanization—The Case of Three Intermediate-Sized and Subregional Cities in Chile. Land, 13(5), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050694






