Spatial Differentiation of Ecotourist Perceptions Based on the Random Forest Model: The Case of the Gansu Section of the Yellow River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Study Area and Data Source
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Sources
3.2.1. Fundamental Data
3.2.2. Remote Sensing Data
3.2.3. Questionnaire Data
4. Methods
4.1. Ecotourist Perception Evaluation Index System
4.2. One-Way ANOVA
4.3. Random Forest Models (RF)
4.3.1. Decision Trees
4.3.2. Random Forest
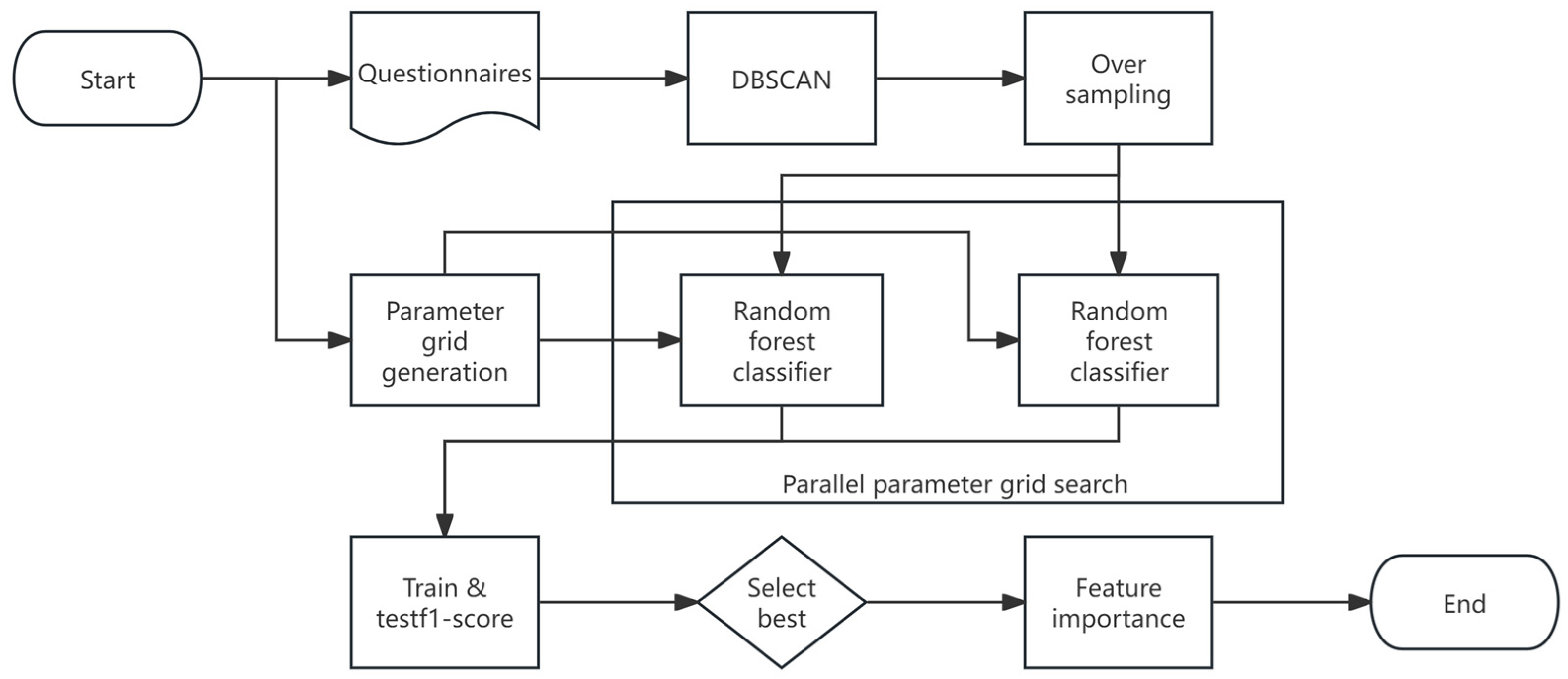
4.3.3. Overall Procedure
5. Result Analysis
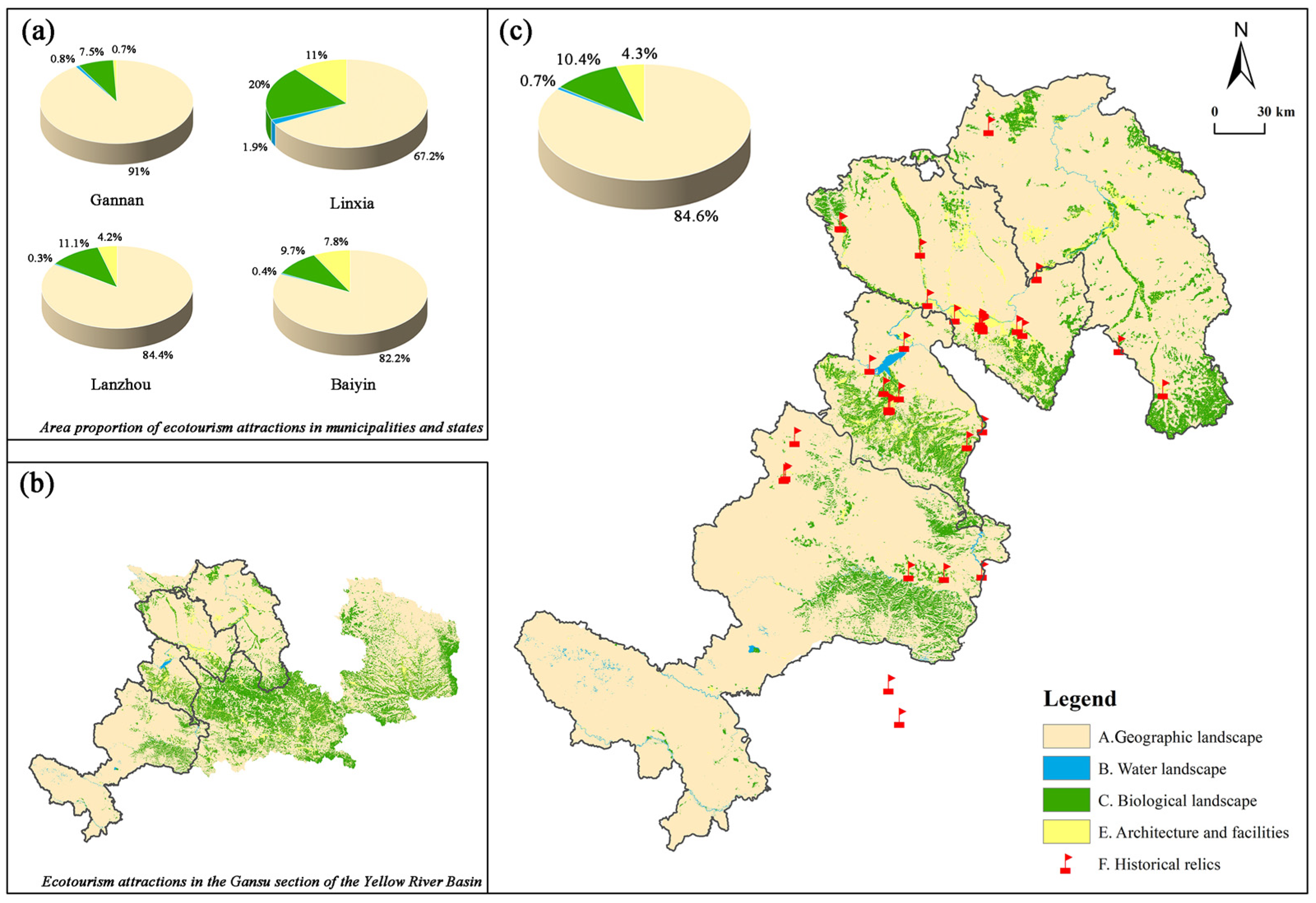
5.1. The Identification and Classification of Ecotourism Attractions
5.2. Analysis of Tourists’ Knowledge in Ecotourism
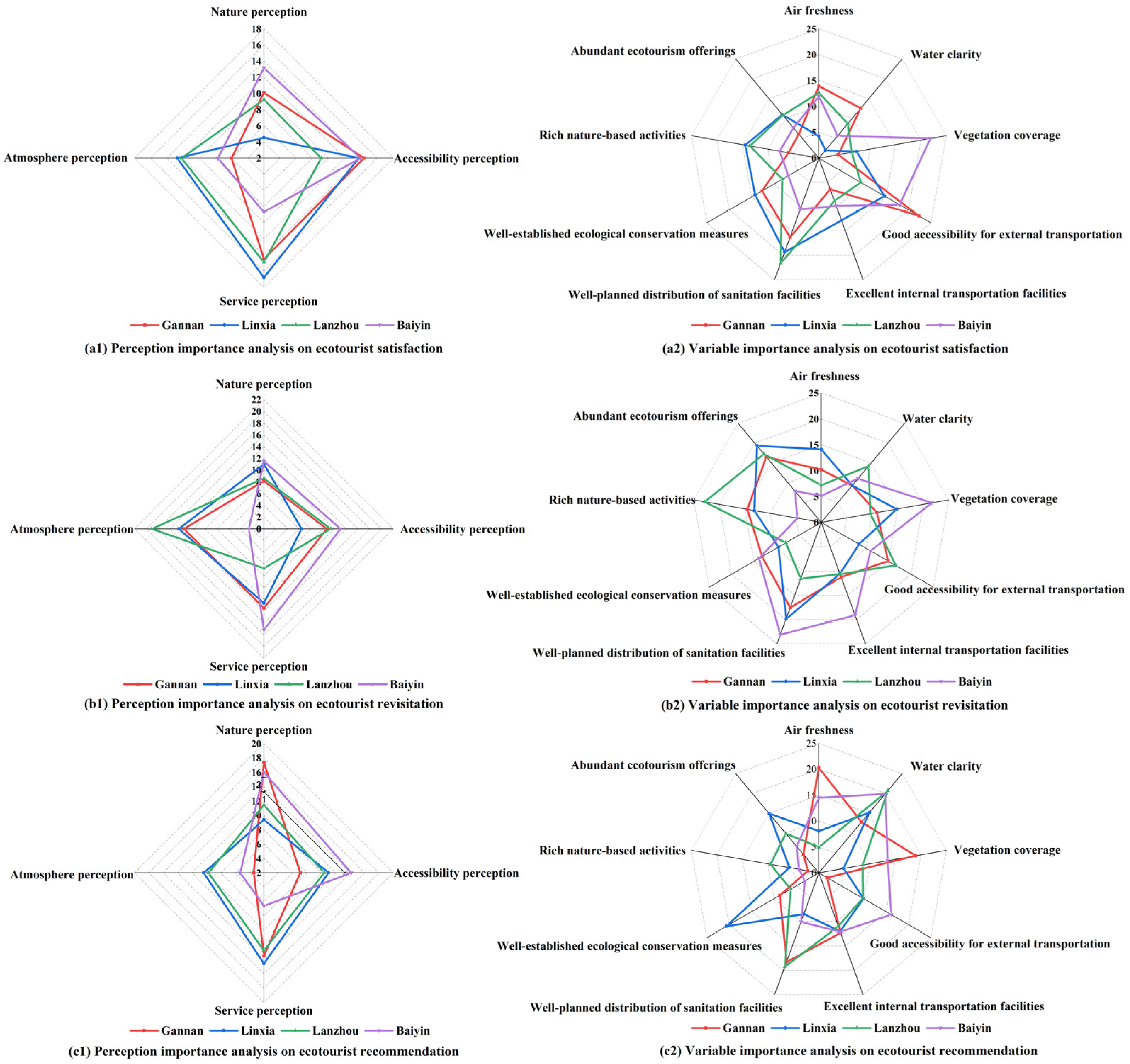
5.3. Spatial Disparity of Ecotourists’ Perceptions
5.4. The Importance of Influencing Factors on Ecotourist Satisfaction, Revisitation, and Recommendation
6. Conclusions and Implications
6.1. Conclusions and Discussion
6.2. Implications for the Development of Ecotourism
6.2.1. Emphasize the Development of Ecotourism Resources
6.2.2. Implement Targeted Ecotourism Development Strategies in Different Regions
6.2.3. Implement Differentiated Ecotourism Development Strategies in Different Regions
6.2.4. Promote the Dissemination of Ecotourism Awareness
6.3. Limitations and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shasha, Z.T.; Geng, Y.; Sun, H.; Musakwa, W.; Sun, L. Past, Current, and Future Perspectives on Eco-Tourism: A Bibliometric Review between 2001 and 2018. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 2020, 27, 23514–23528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanra, S.; Dhir, A.; Kaur, P.; Mäntymäki, M. Bibliometric Analysis and Literature Review of Ecotourism: Toward Sustainable Development. Tour. Manag. Pers. 2021, 37, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, P.S. Ecotourism and Nature Conservation: A Definition with Some Recent Developments in Micronesia. Tour. Manag. 1993, 14, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Liu, J.-S.; Ma, T.-B. Dynamics and Changes in Spatial Patterns of Land Use in Yellow River Basin, China. Land. Use Policy 2010, 27, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, D.; Tang, C.; Zhao, Y. Facilitating Sustainable Tourism by Endogenization: China as Exemplar. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 81, 102890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Liu, Z.; Mao, X.; Song, C. International experience of national park funding patterns and its enlightenment to China. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 39, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Liao, Y.; Song, B.; Huang, H.; Wang, X. Ecological protection and high quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Reg. Econ. Rev. 2020, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, F.; Soutar, G.N. Experiences, Post-Trip Destination Image, Satisfaction and Loyalty: A Study in an Ecotourism Context. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 19, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Thapa, B. Perceived Value and Flow Experience: Application in a Nature-Based Tourism Context. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 8, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Han, H. Tourist Experience Quality and Loyalty to an Island Destination: The Moderating Impact of Destination Image. J. Travel. Tour. Mark. 2019, 36, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-T.H.; Lee, W.-I.; Chen, T.-H. Environmentally Responsible Behavior in Ecotourism: Antecedents and Implications. Tour. Manag. 2014, 40, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Choi, Y.; Lee, C.-K.; Ahmad, M.S. Effects of Place Attachment and Image on Revisit Intention in an Ecotourism Destination: Using an Extended Model of Goal-Directed Behavior. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Guan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q. Assessment of Ecotourism Environmental Carrying Capacity in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraphin, H.; Sheeran, P.; Pilato, M. Over-Tourism and the Fall of Venice as a Destination. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 9, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidmamatov, O.; Matyakubov, U.; Rudenko, I.; Filimonau, V.; Day, J.; Luthe, T. Employing Ecotourism Opportunities for Sustainability in the Aral Sea Region: Prospects and Challenges. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajer, E.; Demir, S. Ecotourism Strategy of UNESCO City in Iran: Applying a New Quantitative Method Integrated with BWM. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Ecotourism Society What Is Ecotourism. TIES 2015. Available online: https://ecotourism.org/what-is-ecotourism/ (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Zhong, L.; Ma, X.; Kang, W. Progresses and prospects of ecotourism research in China. Progress. Geogr. 2016, 35, 679–690. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zeng, Y. Study on development of urban tourism based on dissipative structure theory. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2007, 23, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Uddhammar, E. Development, Conservation and Tourism: Conflict or Symbiosis? Rev. Int. Political Econ. 2006, 13, 656–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A Model Study in the Development of Ecotourism Destination. Tour. Trib. 2006, 4, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wondirad, A.; Tolkach, D.; King, B. Stakeholder Collaboration as a Major Factor for Sustainable Ecotourism Development in Developing Countries. Tour. Manag. 2020, 78, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beall, J.M.; Boley, B.B.; Landon, A.C.; Woosnam, K.M. What Drives Ecotourism: Environmental Values or Symbolic Conspicuous Consumption? J. Sustain. Tour. 2021, 29, 1215–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L. New Development Direction on Worse Ecological System Resource of China Eco-Tourism. Energy Procedia 2012, 14, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Zheng, X.; Li, J.; Jia, J.; Hayat, K. Tourists’ wilingness to pay for the non-use values of ecotourism resources in a national forest park. J. Resour. Ecol. 2023, 14, 331–343. [Google Scholar]
- Garrod, B.; Fennell, D.A. Strategic Approaches to Accessible Ecotourism: Small Steps, the Domino Effect and Not Paving Paradise. J. Sustain. Tour. 2023, 31, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. An image perception research on ecotourism destination under the Internet word of mouth and horizon:Take Wanlv Lake scenic spot in Guangdong as an example. Tour. Res. 2016, 8, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H.S.T.; Khanh, C.N.T. Ecotourism Intention: The Roles of Environmental Concern, Time Perspective and Destination Image. Tour. Rev. 2020, 76, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romão, J.; Neuts, B.; Nijkamp, P.; Shikida, A. Determinants of Trip Choice, Satisfaction and Loyalty in an Eco-Tourism Destination: A Modelling Study on the Shiretoko Peninsula, Japan. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 107, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, W.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. The formation mechanism of tourist loyalty in ecotourism scenic spots from the perspective of tourist perceived value: Evidence from Xixi National Wetland Park. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 7135–7147. [Google Scholar]
- Lian Chan, J.K.; Baum, T. Ecotourists’ Perception of Ecotourism Experience in Lower Kinabatangan, Sabah, Malaysia. J. Sustain. Tour. 2007, 15, 574–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Xue, D. Tourists’spatial perception and place imagination in frontier ecotourism destination: A case of Ejin Oasis, Inner Mongolia. Arid. Land Geogr. 2022, 45, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Wong, I.A.; Wearing, S.; McDonald, M. Ecotourism Social Media Initiatives in China. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 25, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Fan, J.; Qiao, Q. The Multi-Player Evolutionary Game Analysis for the Protective Development of Ecotourism. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 126, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, G.; Tyllianakis, E.; Luisetti, T.; Ferrini, S.; Turner, R.K. Prospective Tourist Preferences for Sustainable Tourism Development in Small Island Developing States. Tour. Manag. 2021, 82, 104178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhu, K.; Kang, L.; Dávid, L.D. Tea Culture Tourism Perception: A Study on the Harmony of Importance and Performance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Kang, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, B.; Liu, P. Spatiotemporal Behavior Pattern Differentiation and Preference Identification of Tourists from the Perspective of Ecotourism Destination Based on the Tourism Digital Footprint Data. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, C.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y. Evaluation and Spatial Characteristics of Cooperation among Tourist Attractions Based on a Geographic Information System: A Case Study of The Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Z. An analysis on residents tourism perceptions differences and influential factors in Wetland ecotourism destination. J. Nanjing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 34, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Boley, B.B.; McGehee, N.G.; Tom Hammett, A.L. Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA) of Sustainable Tourism Initiatives: The Resident Perspective. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, C.; Knight, D. Research on the spatial differentiation and influence mechanism of sustainable tourism perception among Shennongjia National Park residents. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 2854–2865. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. The spatial response and its formation mechanism of community residents perceived conflicts in nature reserve: A case study of Qionghai National Wetland Park. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-García, M.Á.; Castellanos-Verdugo, M.; Vega-Vázquez, M.; Orgaz-Agüera, F. The Mediating Roles of the Overall Perceived Value of the Ecotourism Site and Attitudes Towards Ecotourism in Sustainability Through the Key Relationship Ecotourism Knowledge-Ecotourist Satisfaction. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2017, 19, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, T.-B. Eco-Destination Image, Environment Beliefs, Ecotourism Attitudes, and Ecotourism Intention: The Moderating Role of Biospheric Values. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2023, 57, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Sun, D. Development and management tasks of the Yellow River Basin: A preliminary understanding and suggestion. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Gao, W.; Gao, X.; Ma, M.; Zhou, M.; Du, K.; Ma, X. Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity of Air Pollution and Its Key Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Economic Belt of China from 2014 to 2019. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, W.; Li, M.; Meng, L. Coupling Coordination Degree of Production, Living and Ecological Spaces and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Gan, Z.; Wang, Y. Scientific discussion and ponder on the coordination of naturaenvironmental in the upper Yellow River Basin. Adv. Eath Sci. 2023, 38, 320–329. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C. Land Policy Reform in China: Assessment and Prospects. Land. Use Policy 2003, 20, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qin, C.; Hong, X.; Kang, G.; Qin, M.; Yang, D.; Pang, B.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Dick, R.P. Risk Assessment and Source Analysis of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution from Lower Reaches of Yellow River Irrigation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Kou, J.; Ma, W.; Jian, Y.; Yang, H.; Xue, B.; Gou, X. Scale Effect of Population and Area Exposed to Water Scarcity Based on Different Recurrence Periods: A Case Study of Gansu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Shi, P. Optimization and arrangament of natural ecotouris resources in Gansu. J. Arid. Land. Resour. Environ. 2009, 23, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- China Knowledge Centre for Engineering Sciences and Technology. Available online: https://www.ckcest.cn/ (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform. Available online: https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Lu, W.; Stepchenkova, S. Ecotourism Experiences Reported Online: Classification of Satisfaction Attributes. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Lv, J.; Huang, X. Evaluation and countermeasure research on the competitiveness of rural tourism in urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of Changiiang river. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2020, 36, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Du, Y. Empirical study on perceptive image formation of tourists on tourism destination:A case study of Nantong, Jiangsu Province. Geogr. Res. 2011, 30, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Carvache-Franco, M.; Carvache-Franco, O.; Carvache-Franco, W. Exploring The Satisfaction of Ecotourism In Protected Natural Areas. Geoj. Tour. Geosites 2020, 29, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Research on the experience products development of forest tour based on tourists’ satisfaction:Taking 49 national forest parks in Shandong province as examples. For. Econ. 2021, 43, 62–79. [Google Scholar]
- Mafi, M.; Pratt, S.; Trupp, A. Determining Ecotourism Satisfaction Attributes—A Case Study of an Ecolodge in Fiji. J. Ecotourism 2020, 19, 304–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Verdugo, M.; Vega-Vázquez, M.; Oviedo-García, M.Á.; Orgaz-Agüera, F. The Relevance of Psychological Factors in the Ecotourist Experience Satisfaction through Ecotourist Site Perceived Value. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.F.; Wagner, M.R. Chapter 15—ANOVA: Testing for Differences Among Many Samples and Much More. In Practical Business Statistics, 8th ed.; Siegel, A.F., Wagner, M.R., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 485–510. ISBN 978-0-12-820025-4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Broughton, M.; Mohseni, M.; Babbush, R.; Boixo, S.; Neven, H.; McClean, J.R. Power of Data in Quantum Machine Learning. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulova, A.; Jokar Arsanjani, J. Exploratory Analysis of Driving Force of Wildfires in Australia: An Application of Machine Learning within Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 18972-2017; Classification, Investigation, and Evaluation of Tourism Resources. China National Tourism Administration: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Cui, M.; Liu, R. A study on the coupling coordination and obstacle factors of ecotourism and rural revitalization in the Yellow River Basin. J. Henan Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2024, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, C.; Su, W.; Ma, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W.; Zhu, G. Spatiotemporal Evaluation of Alpine Pastoral Ecosystem Health by Using the Basic-Pressure-State-Response Framework: A Case Study of the Gannan Region, Northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 108000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Plathong, S.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Z.; Munnoy, T.; Ma, L.; Jantharakhantee, C.; Tanboot, L. Analysis of the Island Tourism Environment Based on Tourists’ Perception—A Case Study of Koh Lan, Thailand. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2020, 197, 105326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrväinen, L.; Uusitalo, M.; Silvennoinen, H.; Hasu, E. Towards Sustainable Growth in Nature-Based Tourism Destinations: Clients’ Views of Land Use Options in Finnish Lapland. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2014, 122, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H. The Antecedents of Memorable Tourism Experiences: The Development of a Scale to Measure the Destination Attributes Associated with Memorable Experiences. Tour. Manag. 2014, 44, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya, G.J.; Lehto, X. ‘Moments to Be Had’: Understanding The Experience of Memorable Tourism Moments. Tour. Manag. 2023, 95, 104674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ecotourism Perception | Indicators |
|---|---|
| Nature perception | Air freshness |
| Water clarity | |
| Vegetation coverage | |
| Accessibility perception | Good accessibility for external transportation |
| Excellent internal transportation facilities | |
| Service perception | Well-planned distribution of sanitation facilities |
| Well-established ecological conservation measures | |
| Atmosphere perception | Rich nature-based activities |
| Abundant ecotourism offerings | |
| Overall perception | I am satisfied with this visit |
| I would repeat the visit | |
| I will recommend the visit to my families and friends |
| Basic Land Cover Types | The Subclass of Tourism Resources | The Class of Tourism Resources (Area Ratio %) |
|---|---|---|
| Sparse plants/valley bare land (hilly valleys, stratigraphic profiles, vertical natural zones and other natural landmarks and natural landscape structural phenomena) | AA Natural landscape complex AB Geology and structural traces AC Surface configuration AD Natural markers and natural phenomena | A geographic landscape (82.480%) |
| Natural water bodies (rivers, lakes, waterfalls, and wetlands) | BA/BB Rivers/lakes | B Water landscape (0.698%) |
| Snow/ice (snow cover with relatively low temperature) | BD Snow and ice land | |
| Crops (wheat and flower) Woodland (single tree and jungle) | CA Vegetation landscape | C Biological landscape (12.784%) |
| Water-flooded vegetation (aquatic animals and birds) Sand/shrub (terrestrial animals and butterflies) | CB Wildlife habitat | |
| Construction area/human activity site (social and commercial activities, cultural activities, human settlements, bridges and roads, pavilions and other buildings) | EA Human landscape complex EB Practical architecture and core facilities EC Landscape and sketch architecture | E Architecture and facilities (4.038%) |
| National key cultural relics protection units (4 in Gannan; 7 in Linxia; 10 in Lanzhou; 3 in Baiyin) National historical and cultural town (1 in Gannan; 3 in Lanzhou) Historical and cultural blocks in Gansu Province (2 in Gannan; 2 in Linxia; 5 in Lanzhou) National intangible cultural heritage (Gannan: 13 of national and 49 of provincial; Linxia: 11 of national and 28 of provincial; Lanzhou: 5 of national and 42 of provincial; Baiyin: 2 of national and 21 of provincial) | FA Tangible cultural heritage FB Intangible cultural heritage | FA Tangible historical relics (37 in total) FB Intangible historical relics (171 in total) |
| Tourist Demographic | Ecotourists | Total | % | Tourist Demographic | Ecotourists | Total | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 296 | 545 | 54.31 | Household monthly income (Yuan) | No | 152 | 260 | 58.46 |
| Female | 236 | 442 | 53.39 | Less than 3000 | 67 | 151 | 44.37 | ||
| Age | <18 | 28 | 67 | 41.79 | 3000–5000 | 155 | 299 | 51.84 | |
| 18–30 | 265 | 449 | 59.02 | 5000–8000 | 93 | 171 | 54.39 | ||
| 30–45 | 130 | 221 | 58.82 | More than 8000 | 65 | 106 | 61.32 | ||
| 45–60 | 90 | 188 | 47.87 | Occupation | Student | 21 | 34 | 61.76 | |
| 60–77 | 17 | 57 | 29.82 | Civil servant | 91 | 186 | 48.92 | ||
| >77 | 2 | 5 | 40.00 | Company employees | 60 | 100 | 60.00 | ||
| Education | High school or below | 76 | 219 | 34.70 | Senior management | 49 | 69 | 71.01 | |
| Junior college | 89 | 172 | 51.74 | Teachers | 175 | 297 | 58.92 | ||
| Undergraduate | 320 | 538 | 59.48 | Workers | 22 | 69 | 31.88 | ||
| Graduate and above | 47 | 58 | 81.03 | Retired personnel | 58 | 104 | 55.77 | ||
| Self-employment | 14 | 52 | 26.92 | ||||||
| Others | 42 | 76 | 55.26 | ||||||
| Ecotourist Perception | Variables | Mean of Ecotourist Perception | Mean of Variables | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GN | LX | LZ | BY | GN | LX | LZ | BY | F-Value | p-Value | ||
| Nature perception | Air | 4.076 | 3.99 | 4.107 | 4.138 | 4.16 | 4.16 | 4.36 | 4.26 | 0.44 | 0.72 |
| Water | 4.08 | 4.09 | 3.95 | 4.08 | |||||||
| Vegetation | 3.99 | 3.72 | 4.01 | 4.07 | |||||||
| Accessibility perception | External transportation | 3.503 | 3.836 | 4.050 | 3.954 | 3.47 | 3.84 | 4.05 | 4.03 | 15.9 | 0.00 |
| Internal transportation | 3.53 | 3.83 | 4.05 | 3.87 | |||||||
| Service perception | Sanitation facilities | 3.605 | 3.914 | 4.073 | 4.069 | 3.56 | 3.92 | 4.16 | 4.03 | 14.5 | 0.00 |
| Conservation measures | 3.65 | 3.91 | 3.99 | 4.10 | |||||||
| Atmosphere perception | Nature-based activities | 3.281 | 3.445 | 3.476 | 3.586 | 3.11 | 3.37 | 3.34 | 3.60 | 2.84 | 0.00 |
| Ecotourism offerings | 3.45 | 3.52 | 3.61 | 3.58 | |||||||
| Ecotourist Perception | Satisfaction(%) | Revisitation (%) | Recommendation (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GN | LX | LZ | BY | GN | LX | LZ | BY | GN | LX | LZ | BY | |
| Nature perception | 10.1 | 4.5 | 9.2 | 13.2 | 8.2 | 11.0 | 8.6 | 11.5 | 17.4 | 9.4 | 11.4 | 16.0 |
| Accessibility perception | 14.4 | 13.7 | 9.1 | 13.9 | 10.7 | 6.4 | 11.3 | 13.0 | 7.1 | 11.0 | 10.4 | 14.1 |
| Service perception | 14.5 | 16.8 | 14.9 | 8.7 | 13.5 | 12.6 | 6.7 | 17.2 | 13.5 | 14.6 | 12.8 | 6.6 |
| Atmosphere perception | 6.0 | 12.7 | 12.2 | 7.7 | 13.6 | 14.5 | 19.1 | 2.6 | 3.4 | 10.4 | 9.7 | 5.3 |
| Ecotourist Perception | Variables | Satisfaction (%) | Revisitation (%) | Recommendation (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GN | LX | LZ | BY | GN | LX | LZ | BY | GN | LX | LZ | BY | ||
| Nature perception | Air | 13.9 | 4.2 | 12.6 | 11.9 | 10.2 | 14.1 | 7.2 | 5.1 | 20.3 | 8.1 | 5.0 | 14.5 |
| Water | 12.6 | 2.0 | 8.7 | 5.6 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 12.0 | 8.3 | 12.8 | 15.2 | 20.7 | 19.9 | |
| Vegetation | 3.8 | 7.4 | 6.4 | 21.9 | 8.1 | 12.7 | 6.6 | 21.0 | 19.0 | 4.9 | 8.6 | 13.5 | |
| Accessibility perception | External transportation | 22.3 | 14.7 | 9.4 | 18.0 | 12.9 | 5.1 | 14.9 | 8.2 | 1.8 | 10.0 | 9.8 | 16.1 |
| Internal transportation | 6.4 | 12.8 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 8.5 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 17.9 | 12.3 | 12.0 | 11.0 | 12.1 | |
| Service perception | Sanitation facilities | 16.3 | 19.3 | 21.6 | 10.5 | 16.1 | 18.8 | 8.9 | 22.7 | 18.3 | 8.5 | 19.2 | 10.1 |
| Conservation measures | 12.7 | 14.2 | 8.2 | 6.8 | 10.8 | 6.5 | 4.5 | 11.7 | 8.7 | 20.6 | 6.3 | 3.1 | |
| Atmosphere perception | Nature-based activities | 6.0 | 14.4 | 13.5 | 7.7 | 12.4 | 10.8 | 22.4 | 0.6 | 2.2 | 5.8 | 9.5 | 3.9 |
| Ecotourism offerings | 6.0 | 11.0 | 10.8 | 7.7 | 14.8 | 18.2 | 15.7 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 15.0 | 9.9 | 6.7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Gao, H.; Shen, Y.; Ma, G. Spatial Differentiation of Ecotourist Perceptions Based on the Random Forest Model: The Case of the Gansu Section of the Yellow River Basin. Land 2024, 13, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040560
Yuan J, Gao H, Shen Y, Ma G. Spatial Differentiation of Ecotourist Perceptions Based on the Random Forest Model: The Case of the Gansu Section of the Yellow River Basin. Land. 2024; 13(4):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040560
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Jing, Hang Gao, Yanlong Shen, and Guoqiang Ma. 2024. "Spatial Differentiation of Ecotourist Perceptions Based on the Random Forest Model: The Case of the Gansu Section of the Yellow River Basin" Land 13, no. 4: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040560
APA StyleYuan, J., Gao, H., Shen, Y., & Ma, G. (2024). Spatial Differentiation of Ecotourist Perceptions Based on the Random Forest Model: The Case of the Gansu Section of the Yellow River Basin. Land, 13(4), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040560






