Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystems Based on Adaptive Restoration to Promote Human–Nature Harmony: A Case Study of Loess Hills Micro-Watershed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
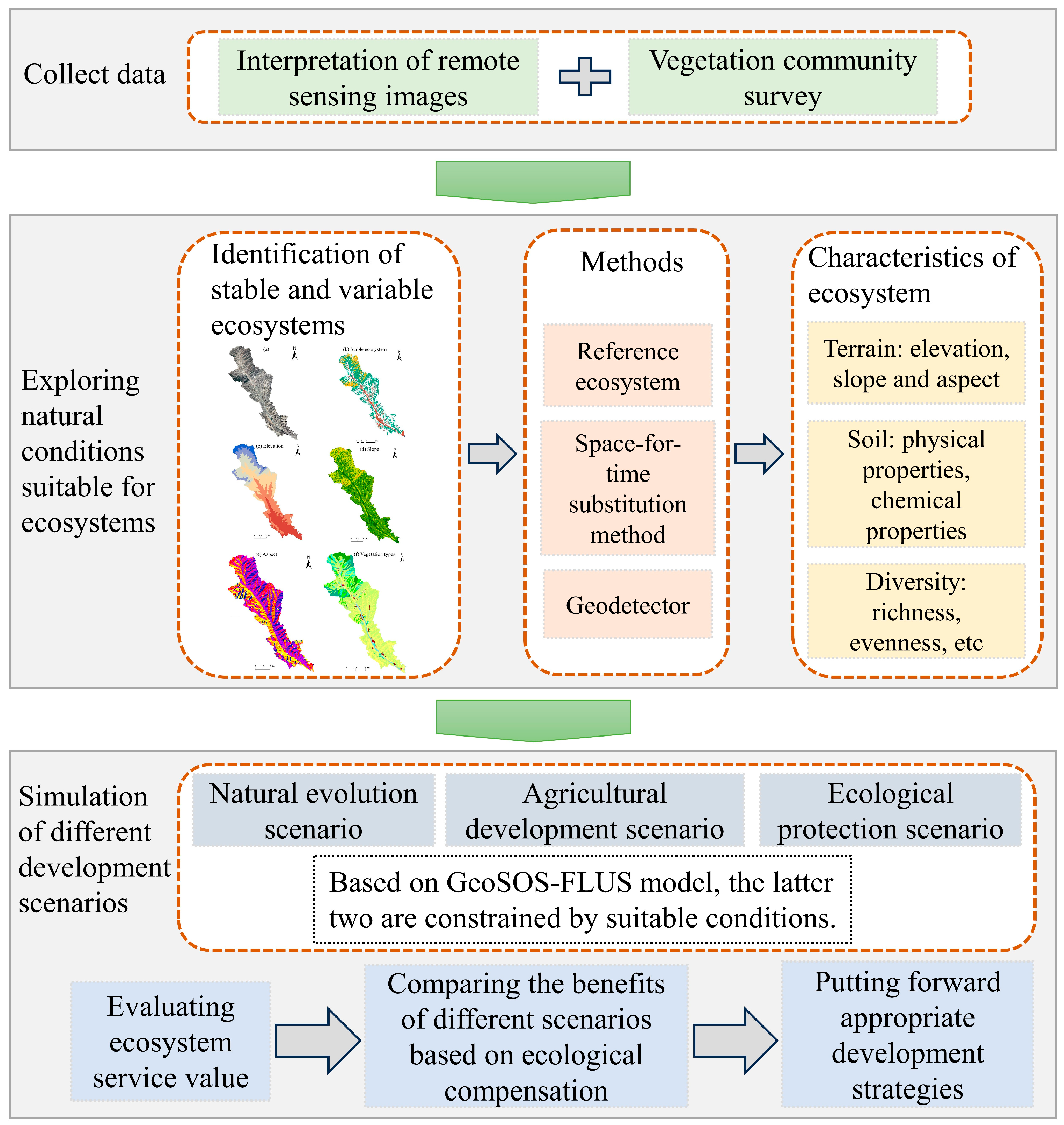
2.2. Research Framework
2.3. Data Sources
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Reference Ecosystem
2.4.2. GeoSOS-FLUS Model
2.4.3. Estimation of Ecosystem Service Value
2.4.4. Ecological Compensation
3. Results
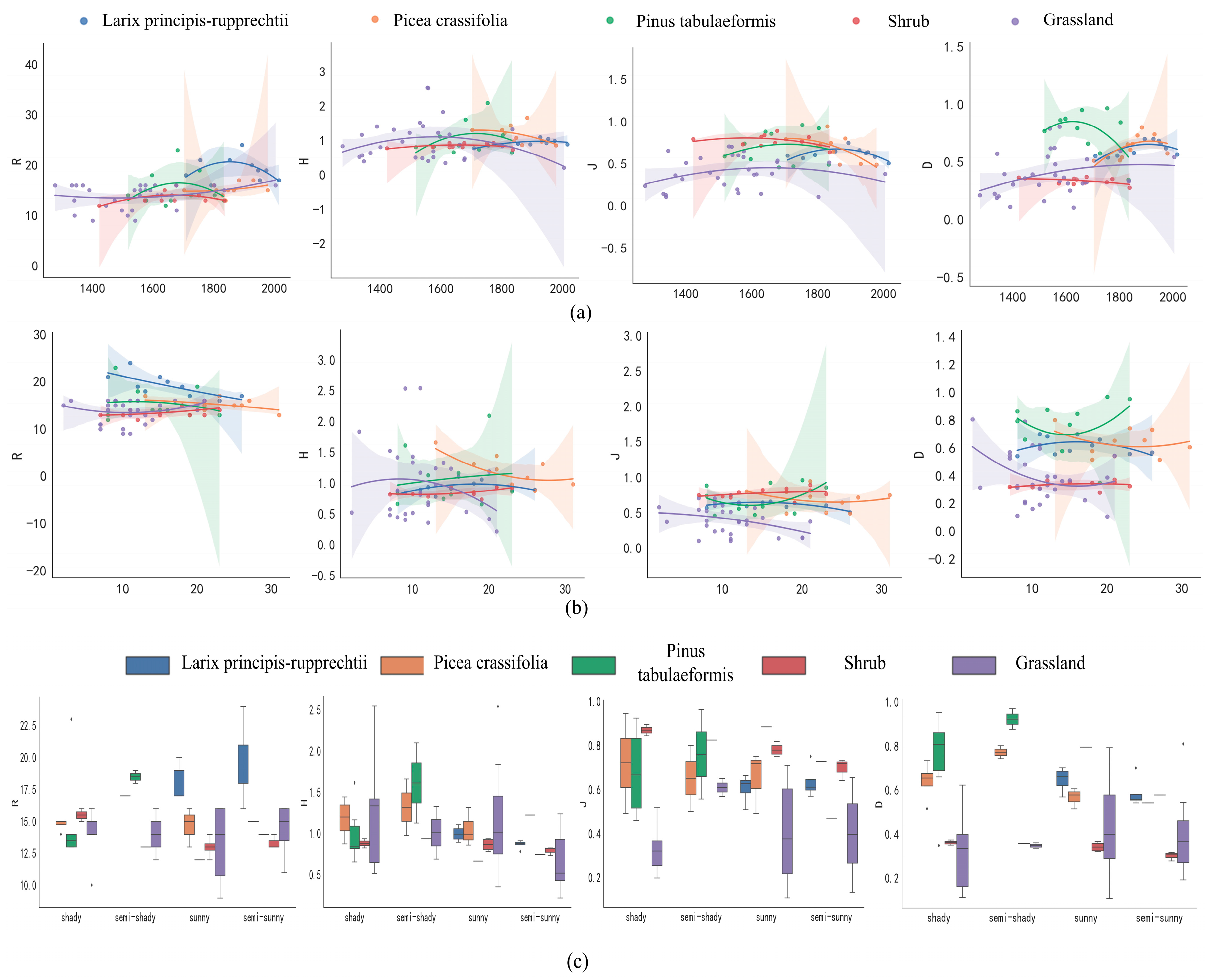
3.1. Natural Conditions Suitable for Ecosystems in Different Situations
3.2. Multi-Scenario Simulation Based on GeoSOS-FLUS Model
3.3. Ecosystem Service Value in Different Scenarios
3.4. Comprehensive Benefits of Different Scenarios Based on Ecological Compensation Mechanisms
4. Discussion
4.1. Adaptive Restoration of Ecosystems
4.2. Comparison of Ecosystem Service Value
4.2.1. Comparison of Comprehensive Benefits of Ecosystems under Different Scenarios
4.2.2. Restoration Effects of Different Natural Conditions under Ecological Protection Scenario
4.3. Innovation and Uncertainty
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernández-Blanco, M.; Costanza, R.; Chen, H.; deGroot, D.; Jarvis, D.; Kubiszewski, I.; Montoya, J.; Sangha, K.; Stoeckl, N.; Turner, K.; et al. Ecosystem health, ecosystem services, and the well-being of humans and the rest of nature. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 5027–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ji, H.; Hao, M. A Review on Experiment and Demonstration Effects of Comprehensive Management and Research Perspectives on Regional High-quality Development in Highland Region of Loess Plateau. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 40, 318–324. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Meadows, M.E. Ecological restoration for sustainable development in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Fan, Y.; Bai, Z.; Shi, X.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bai, D. Diagnosis of ecological problems and exploration of ecosystem restoration practices in the typical watershed of loess plateau: A case study of the pilot project in the middle and upper reaches of Fen River in Shanxi Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 8817–8825. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, F.; Hou, P. National Ecosystem Survey and Assessment of China (2000–2010). Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2014, 29, 462–466. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhao, W.; Gulinck, H.; Liu, G.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Y. Temporal change in land use and its relationship to slope degree and soil type in a small catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. CATENA 2006, 65, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; He, G. Topographic gradient effect and spatial pattern of land use in Baota District. Arid Land Geogr. 2020, 43, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Frietsch, M.; Loos, J.; Löhr, K.; Sieber, S.; Fischer, J. Future-proofing ecosystem restoration through enhancing adaptive capacity. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maure, L.A.; Diniz, M.F.; Pacheco Coelho, M.T.; Molin, P.G.; Rodrigues da Silva, F.; Hasui, E. Biodiversity and carbon conservation under the ecosystem stability of tropical forests. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, X.; Wu, A.; Li, R. Simulation and Optimization of Multi-objective Land Use Pattern Based on the CLUE-S Model: A Case Study of the Three Northern Counties of Langfang in Hebei Province. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 34, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F. Simulation and prediction of land use change in Three Gorges Reservoir Area based on MCE-CA-Markov. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 268–277. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Jin, X.; Yang, X.; Sun, R.; Liu, J.; Han, B.; Xu, W.; Zhou, Y. Coupled MOP and GeoSOS-FLUS Models Research on Optimization of Land Use Structure and Layout in Jintan District. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Pei, F. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Hou, M.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yao, S. Ecological compensation strategy of the old revolutionary base areas along the route of Long March based on ecosystem service value evaluation. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.; Zhao, X. Ecological Compensation in the Loess Plateau of East Gansu Based on the Value of Ecosystem Service. Soil Water Conserv. China 2023, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H. Estimating inter-regional payments for ecosystem services: Taking China’s Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region as an example. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 168, 106514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadyari, F.; Tavakoli, M.; Zarandian, A.; Abdollahi, S. Optimization land use based on multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service for sustainable landscape planning in a mixed urban–Forest watershed. Ecol. Model. 2023, 483, 110440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Wang, Z.; Xu, F. Multi-scenario simulation of China’s dynamic relationship between water–land resources allocation and cultivated land use based on shared socioeconomic pathways. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 118062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Shi, X.; Wu, Q. Exploring suitable topographical factor conditions for vegetation growth in Wanhuigou catchment on the Loess Plateau, China: A new perspective for ecological protection and restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 158, 106053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, I.; Dorrough, J.; Travers, S.K. The acceptable range of variation within the desirable stable state as a measure of restoration success. Restor. Ecol. 2023, 31, e13800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Xu, L.; He, H. The methods of evaluation ecosystem quality: Ideal reference and key parameters. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 637–650. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, S. Improvement of the Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Service Value Based on Per Unit Area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Evolutionary game and simulation of management strategies of fallow cultivated land: A case study in Hunan province, China. Land Use Policy 2018, 71, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, U.; Phelps, J.; Garmendia, E.; Brown, K.; Corbera, E.; Martin, A.; Gomez-Baggethun, E.; Muradian, R. Social Equity Matters in Payments for Ecosystem Services. BioScience 2014, 64, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Gao, P.; Tian, B.; Wu, C.; Mu, X. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of NDVI and Its Influencing Factors Based on the ESTARFM in the Loess Plateau of China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.; Kottkamp, A.; Williams, M.; Palmer, M. Setting a reference for wetland carbon: The importance of accounting for hydrology, topography, and natural variability. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 064014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Jiang, J. Coupling effects of soil and vegetation from an ecosystem service perspective. CATENA 2023, 231, 107354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Q. Ecological restoration in the source region of Lancang River: Based on the relationship of plant diversity, stability and environmental factors. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 180, 106649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrière, N.; Locatelli, B.; Laumonier, Y.; Freycon, V.; Bernoux, M. Soil erosion in the humid tropics: A systematic quantitative review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, T.; Cai, Y.; Fei, T.; Zhai, C.; Qi, W.; Dong, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Stable or unstable? Landscape diversity and ecosystem stability across scales in the forest–grassland ecotone in northern China. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 3889–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, R.; Sulser, T.B.; Huefner, R.; Mason-D’Croz, D.; Dunston, S.; Nautiyal, S.; Ringler, C.; Schuengel, J.; Tikhile, P.; Wimmer, F.; et al. Agricultural Development and Land Use Change in India: A Scenario Analysis of Trade-Offs Between UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Earth’s Future 2020, 8, e2019EF001287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, D.; Liu, C.; Liao, Q. Integrating territorial pattern and socioeconomic development into ecosystem service value assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 100, 107088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Yu, S. Ecological compensation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on ecosystem services flow. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Bryan, B.A. Finding pathways to national-scale land-sector sustainability. Nature 2017, 544, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Ren, J.; Hai, W.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; Gao, Y. Research on the Slope Gradient Effect and Driving Factors of Construction Land in Urban Agglomerations in the Upper Yellow River: A Case Study of the Lanzhou-Xining Urban Agglomerations. Land 2023, 12, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Qiao, F.; Che, L.; Pu, L. Layout optimization and multi-scenarios for land use: An empirical study of production-living-ecological space in the Lanzhou-Xining City Cluster, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianjiao, F.; Dong, W.; Ruoshui, W.; Yixin, W.; Zhiming, X.; Fengmin, L.; Yuan, M.; Xing, L.; Huijie, X.; Caballero-Calvo, A.; et al. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of environmental factors and ecosystem functions in farmland shelterbelt systems in desert oasis ecotones. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 271, 107790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, D.; Shi, W.; Du, J.; Huang, Z.; Liu, B. Spatio-temporal changes in ecosystem service value: Evidence from the economic development of urbanised regions. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 193, 122626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
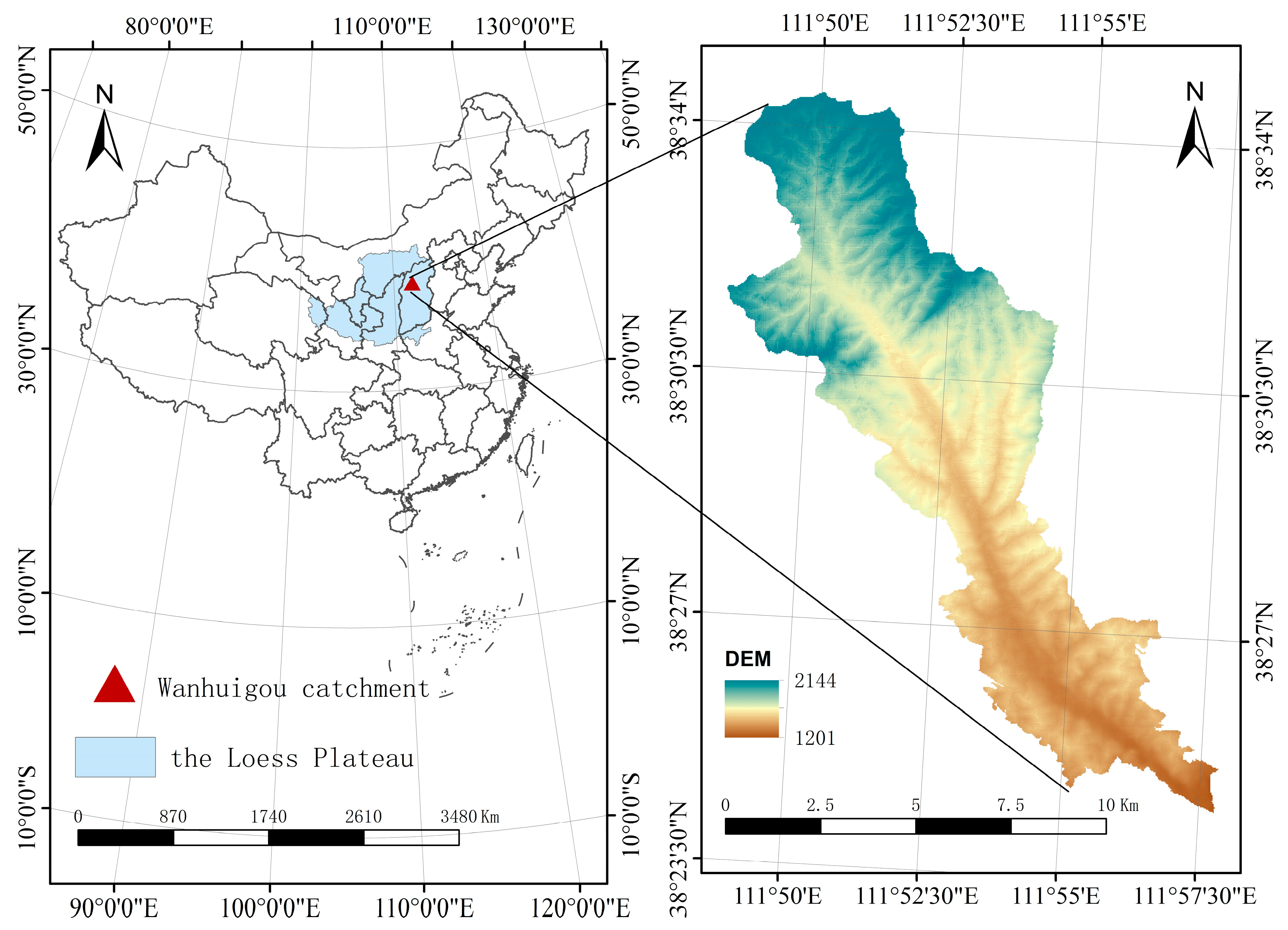


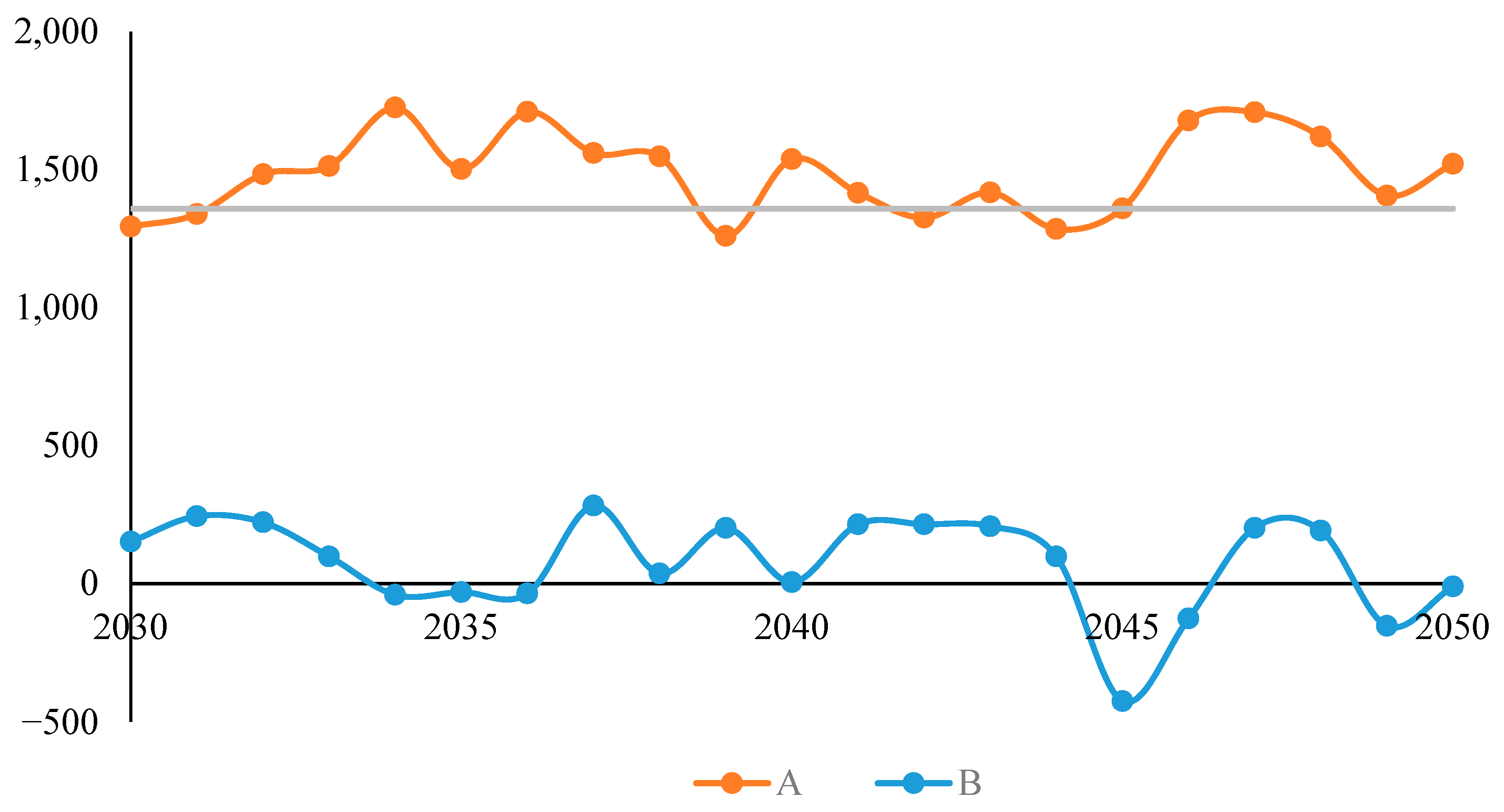
| Elevation (m) | Slope (°) | Aspect (°) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1201–1379 | 1 (Flat slope) | 0–5 | 0 (no aspect) | −1 |
| 2 | 1379–1483 | 2 (Gentle slope) | 5–15 | 1 (shady aspect) | 337–360, 0–67 |
| 3 | 1483–1594 | 3 (Slope) | 15–25 | 2 (semi-shady aspect) | 67–112, 292–337 |
| 4 | 1594–1715 | 4 (Steep slope) | 25–35 | 3 (sunny aspect) | 157–247 |
| 5 | 1715–1856 | 5 (Sharp slope) | 35–45 | 4 (semi-sunny aspect) | 112–157, 247–292 |
| 6 | 1856–2144 | 6 (Dangerous slope) | Above 45 | ||
| Ecosystem Service Functions | Farmland | Forest | Shrub | Grassland | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply service | Food production | 1586.50 | 324.78 | 272.43 | 1003.19 |
| Raw materials production | 746.59 | 767.66 | 616.55 | 1478.38 | |
| Water resources supply | 13.42 | 148.92 | 150.56 | 234.92 | |
| Adjustment service | Gas regulation | 1250.54 | 2509.65 | 2021.70 | 5200.74 |
| Climate regulation | 671.93 | 7484.66 | 6065.10 | 7828.31 | |
| Purify the environment | 186.65 | 2199.63 | 1835.30 | 4540.75 | |
| Hydrological regulation | 181.16 | 1842.18 | 2292.56 | 2894.81 | |
| Support service | Soil conservation | 10,725.97 | 12,376.12 | 4133.38 | 9873.60 |
| Maintaining nutrient cycling | 223.98 | 236.20 | 186.40 | 475.19 | |
| Biodiversity | 242.64 | 2775.38 | 2251.11 | 5755.13 | |
| Cultural service | Aesthetic landscape | 111.99 | 1210.54 | 989.34 | 2534.37 |
| Summation | 15,941.37 | 31,875.70 | 20,814.41 | 41,819.40 | |
| Ecosystem Types | Elevation | Slope | Percentage (%) | Ecosystem Types | Elevation | Slope | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | 1 | 1 | 22.93 | Grassland | 1 | 2 | 9.85 |
| 2 | 29.47 | 2 | 2 | 11.55 | |||
| 2 | 1 | 9.68 | 3 | 2 | 16.28 | ||
| 2 | 18.38 | 3 | 3 | 5.38 | |||
| 3 | 2 | 5.91 | 4 | 2 | 14.40 | ||
| Forest | 2 | 2 | 5.89 | 4 | 3 | 8.81 | |
| 3 | 2 | 6.33 | 5 | 2 | 5.14 | ||
| 4 | 2 | 7.97 | 5 | 3 | 7.15 | ||
| 3 | 11.42 | Urban | 1 | 1 | 27.28 | ||
| 5 | 2 | 8.92 | 1 | 2 | 42.73 | ||
| 3 | 20.19 | 1 | 3 | 5.45 | |||
| 6 | 2 | 7.37 | 3 | 2 | 16.36 | ||
| 3 | 9.75 | ||||||
| Shrub | 1 | 2 | 11.56 | ||||
| 2 | 2 | 17.49 | |||||
| 3 | 2 | 18.51 | |||||
| 4 | 2 | 9.70 | |||||
| 4 | 3 | 5.17 | |||||
| 5 | 3 | 5.66 |
| Soil Properties | Units | Variable Ecosystems | Stable Ecosystems | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| es12 | es22 | es32 | es42 | Forest | Shrub | Grassland | Farmland | ||
| bdod | g/cm3 | 1.313 | 1.312 | 1.285 | 1.262 | 1.162 | 1.202 | 1.217 | 1.310 |
| cfvo | cm3/100 cm3 | 16.972 | 16.961 | 16.403 | 15.715 | 15.540 | 13.810 | 14.763 | 16.616 |
| sand | g/100 g | 47.846 | 45.967 | 41.964 | 41.898 | 45.253 | 45.870 | 45.820 | 46.229 |
| silt | g/100 g | 36.708 | 37.650 | 39.137 | 38.750 | 38.017 | 37.340 | 37.653 | 37.374 |
| clay | g/100 g | 15.420 | 16.362 | 18.848 | 19.335 | 16.723 | 16.760 | 16.520 | 16.395 |
| ocd | kg/dm3 | 11.437 | 11.788 | 13.719 | 17.036 | 47.863 | 33.340 | 30.340 | 11.867 |
| soc | g/kg | 7.095 | 8.275 | 11.703 | 14.573 | 43.363 | 29.310 | 25.567 | 8.207 |
| pH | 8.151 | 8.115 | 8.009 | 7.783 | 7.120 | 7.640 | 7.790 | 8.114 | |
| CEC | mmol/kg | 161.145 | 163.085 | 171.211 | 181.477 | 204.467 | 202.500 | 208.800 | 161.747 |
| nitrogen | g/kg | 0.893 | 0.917 | 1.017 | 1.210 | 3.840 | 2.833 | 2.578 | 0.918 |
| tk | g/kg | 15.719 | 16.303 | 17.038 | 17.716 | 18.338 | 17.365 | 16.465 | 16.324 |
| tp | g/kg | 0.451 | 0.460 | 0.471 | 0.468 | 0.522 | 0.483 | 0.508 | 0.463 |
| Year | Natural Evolution Scenario | Agricultural Development Scenario | Ecological Protection Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2030 | 32,796.40 | 32,644.49 | 33,937.87 |
| 2031 | 33,207.72 | 32,963.91 | 34,302.51 |
| 2032 | 33,627.60 | 33,406.12 | 34,889.32 |
| 2033 | 34,056.10 | 33,958.15 | 35,471.02 |
| 2034 | 34,493.26 | 34,534.67 | 36,259.23 |
| 2035 | 34,939.16 | 34,970.43 | 36,472.22 |
| 2036 | 35,393.86 | 35,429.78 | 37,139.07 |
| 2037 | 35,857.43 | 35,575.62 | 37,135.22 |
| 2038 | 36,329.93 | 36,293.32 | 37,841.21 |
| 2039 | 36,811.45 | 36,609.71 | 37,869.45 |
| 2040 | 37,302.05 | 37,297.35 | 38,835.11 |
| 2041 | 37,801.82 | 37,587.40 | 39,003.00 |
| 2042 | 38,310.85 | 38,096.05 | 39,421.37 |
| 2043 | 38,829.22 | 38,621.74 | 40,038.84 |
| 2044 | 39,357.02 | 39,259.07 | 40,543.91 |
| 2045 | 39,894.34 | 40,320.60 | 41,680.01 |
| 2046 | 40,441.29 | 40,567.76 | 42,245.38 |
| 2047 | 40,997.96 | 40,796.64 | 42,504.69 |
| 2048 | 41,564.45 | 41,372.72 | 42,992.20 |
| 2049 | 42,140.88 | 42,294.43 | 43,700.26 |
| 2050 | 42,727.34 | 42,737.89 | 44,258.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Q. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystems Based on Adaptive Restoration to Promote Human–Nature Harmony: A Case Study of Loess Hills Micro-Watershed. Land 2024, 13, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020233
Li Q, Shi X, Zhao Z, Wu Q. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystems Based on Adaptive Restoration to Promote Human–Nature Harmony: A Case Study of Loess Hills Micro-Watershed. Land. 2024; 13(2):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020233
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qiang, Xueyi Shi, Zhongqiu Zhao, and Qingqing Wu. 2024. "Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystems Based on Adaptive Restoration to Promote Human–Nature Harmony: A Case Study of Loess Hills Micro-Watershed" Land 13, no. 2: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020233
APA StyleLi, Q., Shi, X., Zhao, Z., & Wu, Q. (2024). Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystems Based on Adaptive Restoration to Promote Human–Nature Harmony: A Case Study of Loess Hills Micro-Watershed. Land, 13(2), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020233






