Integrating Ecosystem Service Values into Urban Planning for Sustainable Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
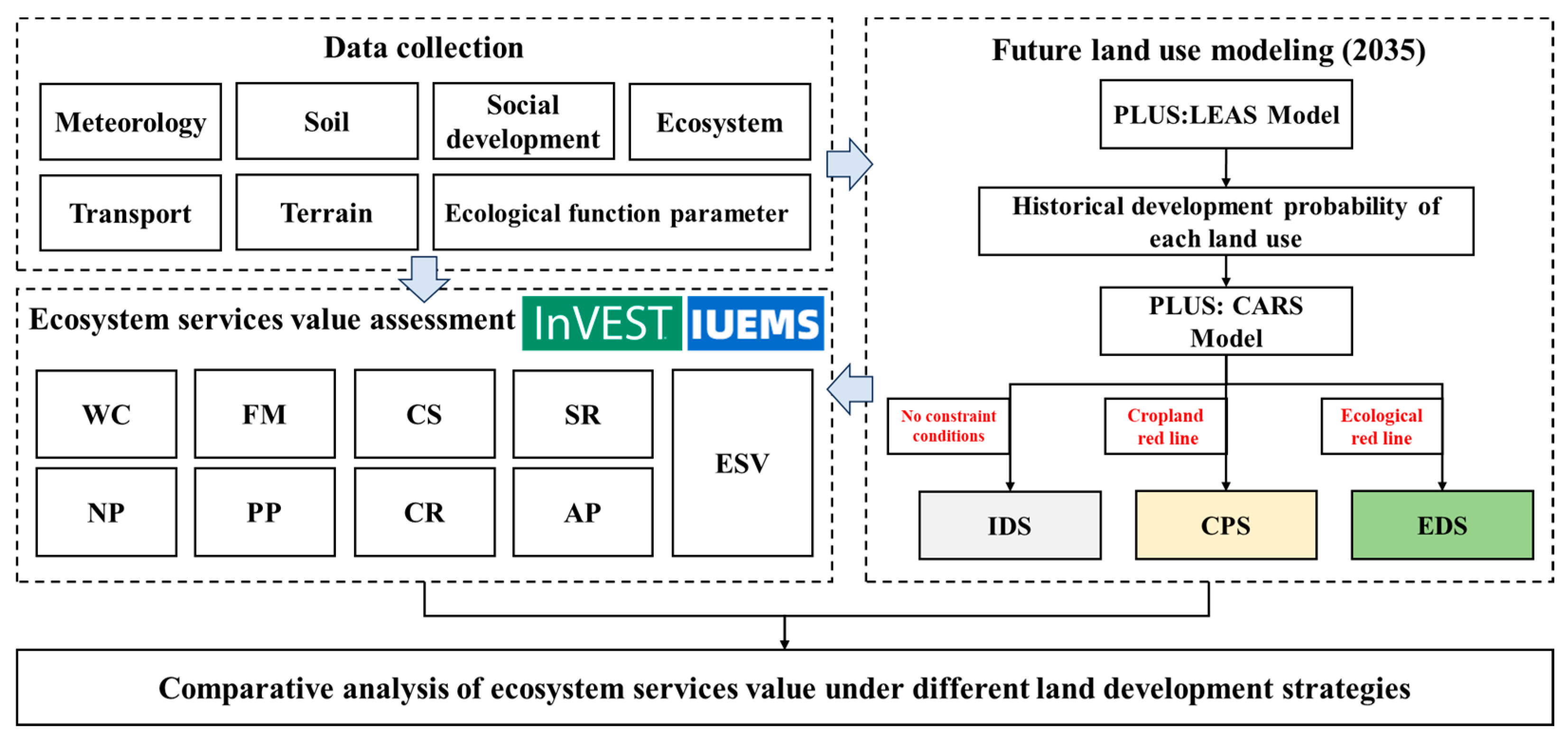
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Future Development Strategies Simulation
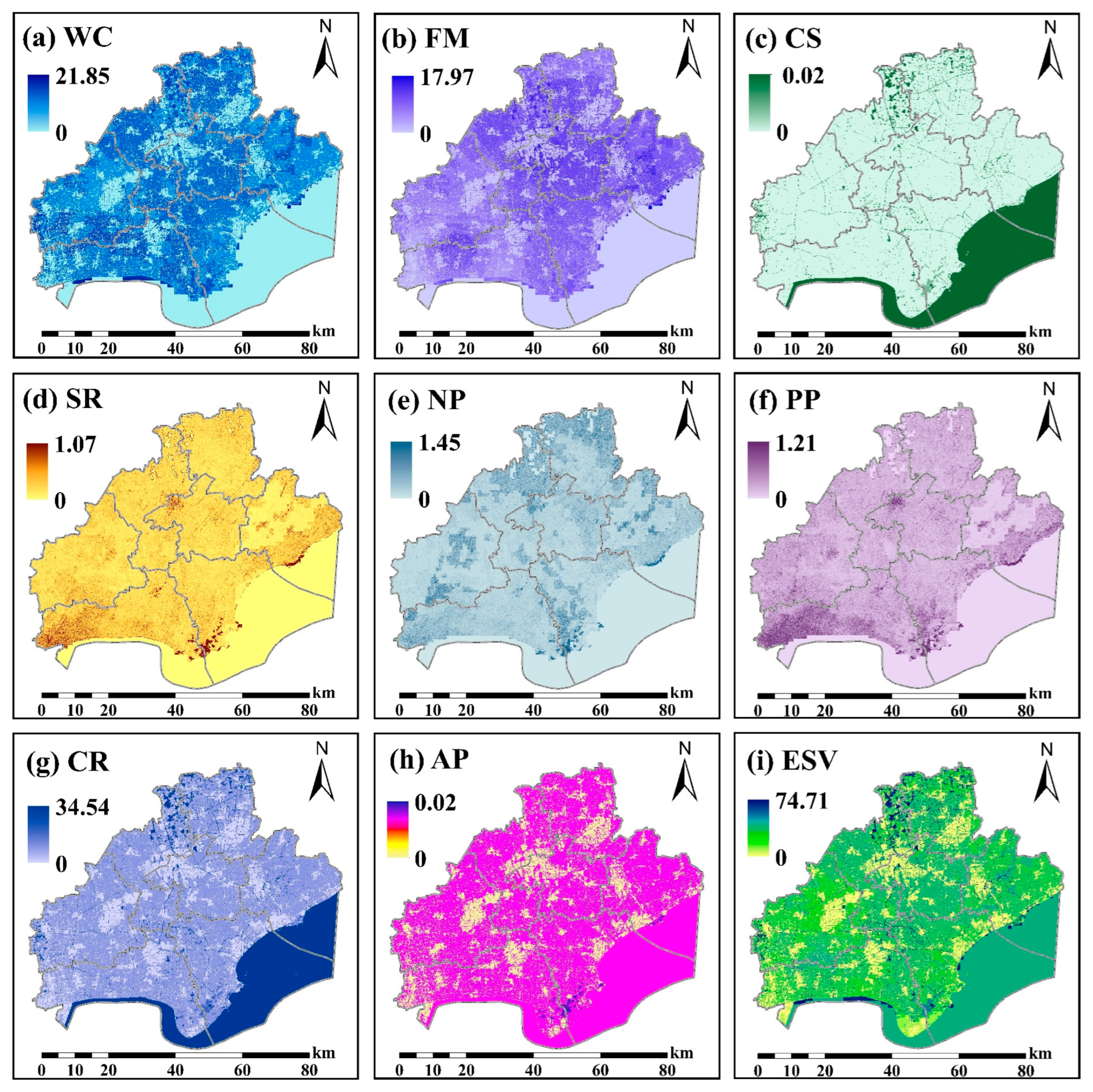
2.3. Ecosystem Services Evaluation and Valuation
2.4. Data Collection
3. Results
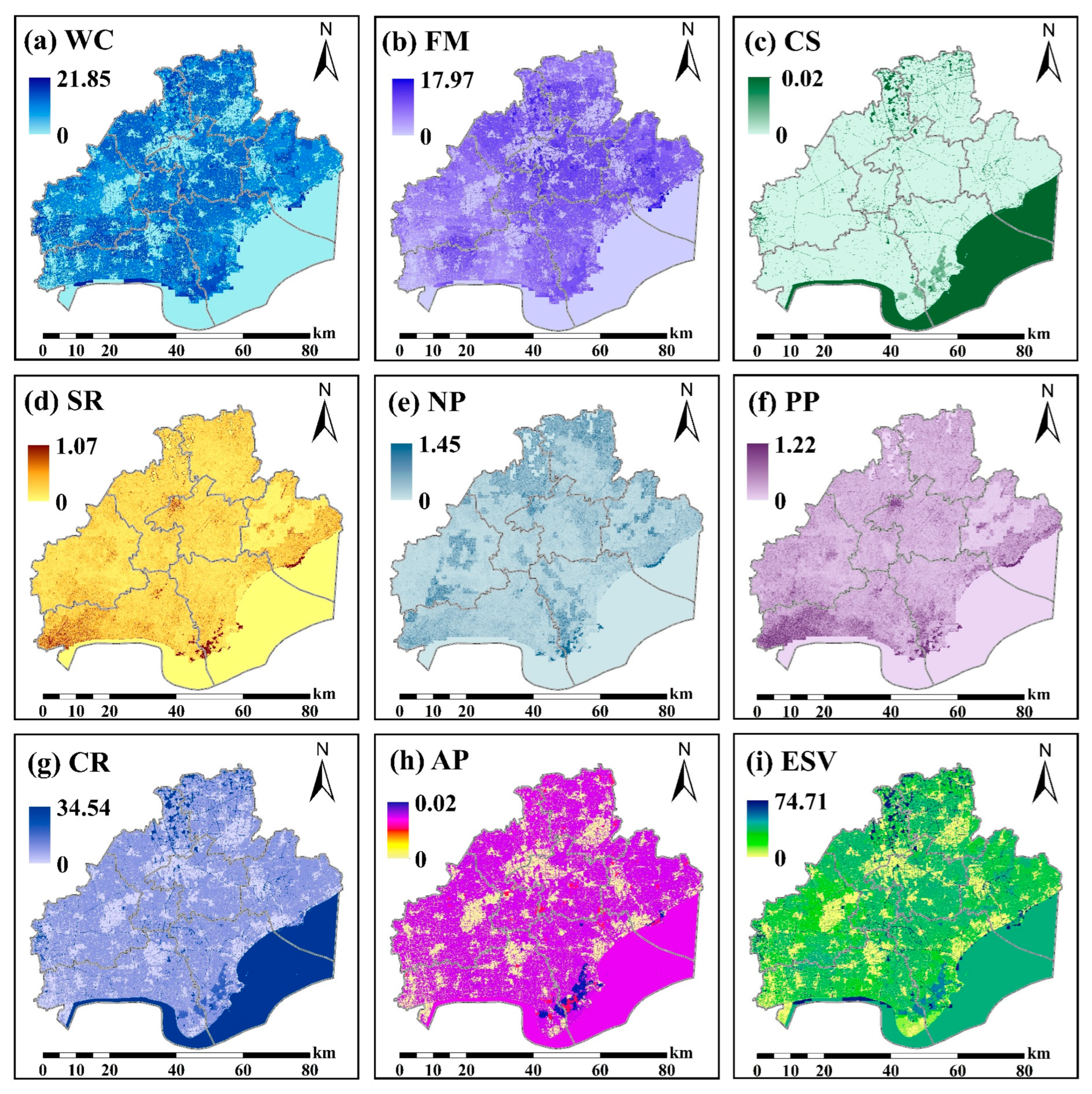
3.1. The Current Status of Ecosystem Services Values Supply
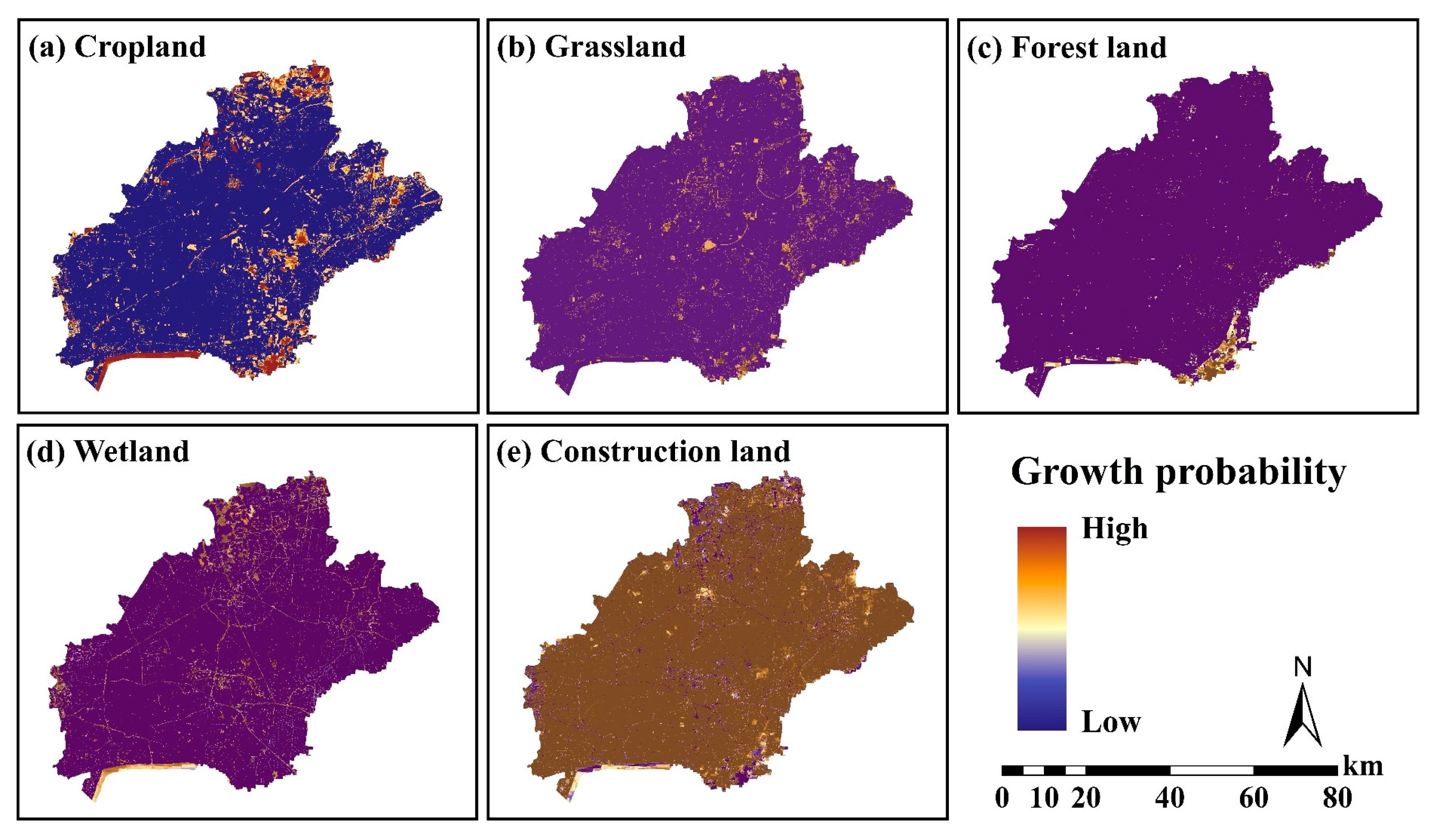
3.2. Driving Factors of Historical Land Use Change
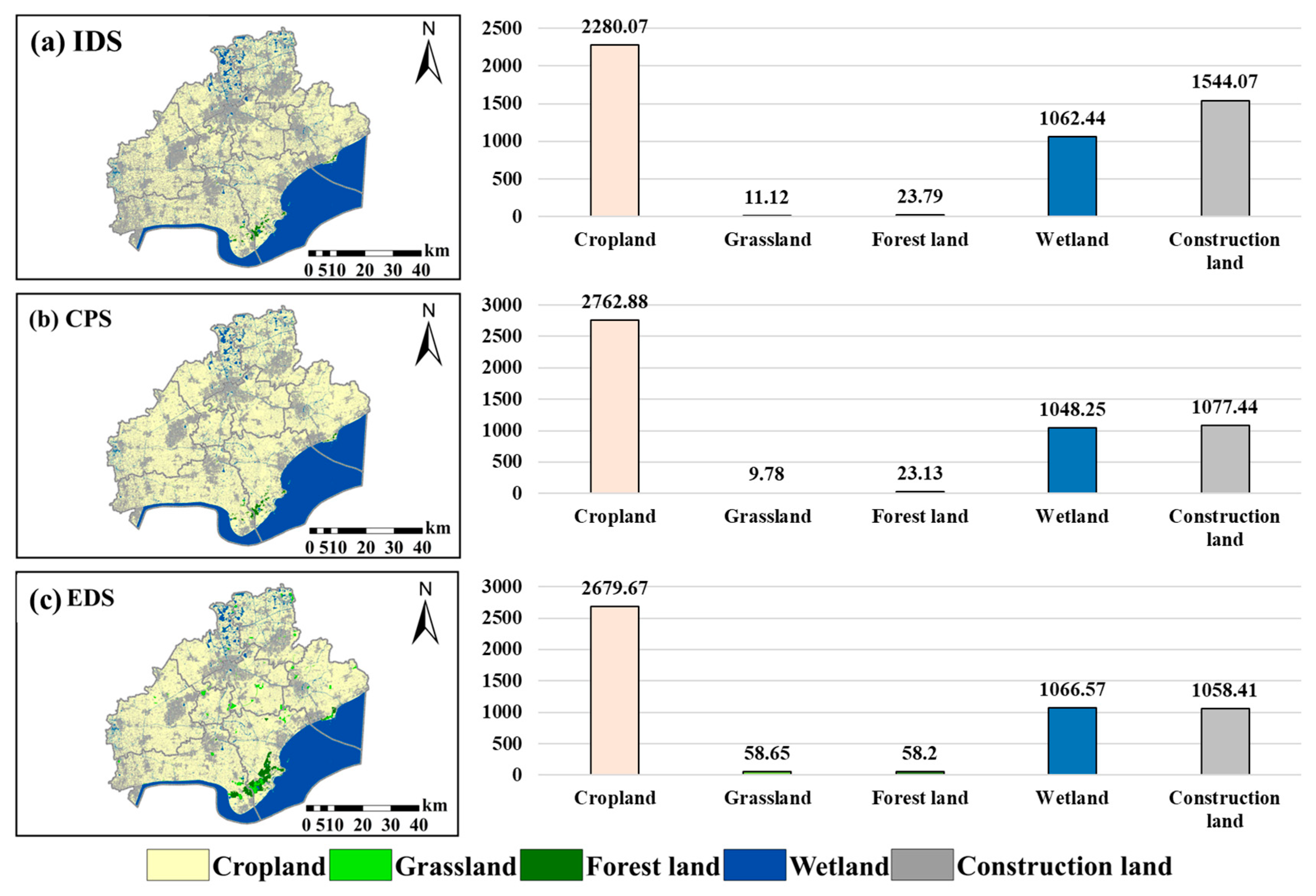
3.3. Land Use Distribution Patterns Under Different Development Strategies
3.4. Differences in Ecosystem Service Values Under Various Land Development Strategies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hejazi, M.; Wise, M.; Vernon, C.; Iyer, G.; Chen, W. Global urban growth between 1870 and 2100 from integrated high resolution mapped data and urban dynamic modeling. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmqvist, T.; Andersson, E.; McPhearson, T.; Bai, X.; Bettencourt, L.; Brondizio, E.; Colding, J.; Daily, G.; Folke, C.; Grimm, N.; et al. Urbanization in and for the Anthropocene. Npj Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A Meta-Analysis of Global Urban Land Expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolking, S.; Mahtta, R.; Milliman, T.; Esch, T.; Seto, K.C. Global urban structural growth shows a profound shift from spreading out to building up. Nat. Cities 2024, 1, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Habitat. World Cities Report 2022: Envisaging the Future of Cities; United Nations Fund for Population Activities: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, F. Urban Agglomeration Formation and Its Spatiotemporal Expansion Process in China: From the Perspective of Industrial Evolution. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M. Urbanization can help reduce income inequality. Npj Urban Sustain. 2022, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Clemente, R.; Strano, E.; Batty, M. Urbanization and economic complexity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K. Urban planning and quality of life: A review of pathways linking the built environment to subjective well-being. Cities 2021, 115, 103229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, H.; Yadav, R.K.; Patra, S.K. Global impact of urbanization on ecosystems: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis. Nat. Hazards Res. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, D.; Zhou, W. Global Megacities and Frequent Floods: Correlation between Urban Expansion Patterns and Urban Flood Hazards. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Hutchins, M. The impacts of urbanisation and climate change on urban flooding and urban water quality: A review of the evidence concerning the United Kingdom. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 12, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhan, W.; Hu, L.; Chakraborty, T.C.; Wang, Z.; Fu, P.; Wang, D.; Liao, W.; Huang, F.; Fu, H.; et al. Divergent urbanization-induced impacts on global surface urban heat island trends since 1980s. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Fu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, P.; He, X. Rapid urbanization and climate change significantly contribute to worsening urban human thermal comfort: A national 183-city, 26-year study in China. Urban Clim. 2022, 43, 101154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Bryan, B.A. Future global urban water scarcity and potential solutions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Du, X. Urban Land Expansion and Air Pollution: Evidence from China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 05018017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Gross ecosystem product:concept, accounting framework and case study. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 6747–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Song, C.S.; Zheng, H.; Polasky, S.; Xiao, Y.; Bateman, I.J.; Liu, J.G.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Shi, F.Q.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Using gross ecosystem product (GEP) to value nature in decision making. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14593–14601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauman, K.A.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Polasky, S.; Aumeeruddy-Thomas, Y.; Brancalion, P.H.S.; DeClerck, F.; Jacob, U.; Mastrangelo, M.E.; Nkongolo, N.V.; Palang, H.; et al. Global trends in nature’s contributions to people. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32799–32805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, P.; Dong, K.; Sun, J. Formation of the National Territory Development Planning System Under the Background of Ecological Civilization. Urban Plan. Forum 2019, 4, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Fan, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, K.; Wu, S.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, P.; Guo, W. Research review on land development rights and its implications for China’s national territory spatial planning. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Yi, F.; Wang, S.; Wei, H.; Wang, S. Blue-Green Space Pattern and Indicator System in Territorial Planning. City Plan. Rev. 2022, 46, 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, K. Greenway Planning and Construction Strategy in Metropolitan AreasTake Xuhui Greenway in Shanghai as an Example. Urban Plan. Forum 2018, 3, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Borowiecka, M.; Alcaraz, M.; Manzano, M. Assessment of Ecosystem Services with numerical modelling to support groundwater dependent ecosystems and aquifer management: A demo study in the Medina del Campo Groundwater Body, Spain. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercambre, G.; Mirás-Avalos, J.M.; Juillion, P.; Moradzadeh, M.; Plenet, D.; Valsesia, P.; Memah, M.-M.; Launay, M.; Lesniak, V.; Cheviron, B.; et al. Analyzing the impacts of climate change on ecosystem services provided by apple orchards in Southeast France using a process-based model. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molla Sitotaw, T.; Willemen, L.; Tsegaye Meshesha, D.; Nelson, A. Empirical assessments of small-scale ecosystem service flows in rural mosaic landscapes in the Ethiopian highlands. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 67, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscieme, L.; Marchettini, N.; Niccolucci, V.; Sporchia, F. Mapping the flows of ecosystem service values in the global land market: The winners and losers of large-scale land acquisitions. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 67, 101629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Roldán, E.; Lorenzetti, R.; Calzolari, C.; Ungaro, F. Disentangling soil-based ecosystem services synergies, trade-offs, multifunctionality, and bundles: A case study at regional scale (NE Italy) to support environmental planning. Geoderma 2024, 448, 116962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Ayala, A.; Jiménez-Aceituno, A.; Meacham, M.; Rozas-Vásquez, D.; Mancilla García, M.; Rocha, J.; Rincón-Ruíz, A. Mapping ecosystem services in Colombia: Analysis of synergies, trade-offs and bundles in environmental management. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 66, 101608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, W. Ecosystem service value and ecological compensation in Qilian Mountain National Park: Implications for ecological conservation strategies. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Río-Mena, T.; Willemen, L.; Vrieling, A.; Nelson, A. How remote sensing choices influence ecosystem services monitoring and evaluation results of ecological restoration interventions. Ecosyst. Serv. 2023, 64, 101565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtbozorgi, F.; Hedayatiaghmashhadi, A.; Dashtbozorgi, A.; Ruiz–Agudelo, C.A.; Fürst, C.; Cirella, G.T.; Naderi, M. Ecosystem services valuation using InVEST modeling: Case from southern Iranian mangrove forests. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 60, 102813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isely, E.S.; Isely, P.; Seedang, S.; Mulder, K.; Thompson, K.; Steinman, A.D. Addressing the information gaps associated with valuing green infrastructure in west Michigan: INtegrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services Tool (INVEST). J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Yang, S.; Xiang, M.; Li, W.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of ecosystem service value in the Upper Minjiang River of China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Ouyang, Z. The comparing and applying Intelligent Urban Ecosystem Management System (IUEMS)on ecosystem services assessment. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 8697–8708. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, P. Evaluation on Ecological Security of Regional Land Resources: A Case Study of Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province. Resour. Sci. 2004, 26, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Guo, X.; Lian, G.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Service Value in Rapid Urbanization Areas in Yangtze River Deltaa Case Study of Jiaxing City. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2017, 26, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Xu, Y.; Han, L.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Xu, G. Spatial-temporal changes of river systems in Jiaxing under the background of urbanization. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Wu, L.; Miao, H.; Liu, J.; Jiang, K.; Ding, H.; Gao, W.; Liu, T. Prediction of land use for the next 30 years using the PLUS model’s multi-scenario simulation in Guizhou Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jia, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, K. Evaluation and multi scenario simulation of ecosystem service value in Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area based on PLUS model. Meas. Sens. 2024, 32, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, Y. A cellular automata model coupled with partitioning CNN-LSTM and PLUS models for urban land change simulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, L.; Xia, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal variations and multi-scenario simulation of urban thermal environments based on complex networks and the PLUS model: A case study in Chengdu central districts. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 115, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Meng, H.; Han, B.; Yang, H.; Pan, X.; Lin, L.; Ouyang, Z. Impact of precipitation factors on gross ecosystem product. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Shu, C. Integrating System Perspectives to Optimize Ecosystem Service Provision in Urban Ecological Development. Systems 2024, 12, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 28592-2012; Grade of Precipitation. China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2012.
- DB33/T 2274-2020; Technical Specification for Accounting Gross Ecosystem Product (GEP)—Terrestrial Ecosystems. Zhejiang Province Market Supervision Administration: Hangzhou, China, 2020.
- Lin, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, Z. Assessing the realization of the values of ecosystem products:A case study of Lishui, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, S.; Moksnes, P.-O.; Söderqvist, T.; Wikström, S.A.; Sundblad, G.; Hasselström, L.; Bergström, U.; Kraufvelin, P.; Bergström, L. Environmental compensation for biodiversity and ecosystem services: A flexible framework that addresses human wellbeing. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 50, 101319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, S.; Venkatesh, P.; Singh, D.R.; Renjini, V.R.; Jha, G.K.; Sharma, D.K. Ecosystem valuation and eco-compensation for conservation of traditional paddy ecosystems and varieties in Kerala, India. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 49, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wübbelmann, T.; Förster, K.; Bouwer, L.M.; Dworczyk, C.; Bender, S.; Burkhard, B. Urban flood regulating ecosystem services under climate change: How can Nature-based Solutions contribute? Front. Water 2023, 5, 1081850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzetti, B.; Lanzanova, D.; Liquete, C.; Reynaud, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Assessing water ecosystem services for water resource management. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 61, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Chai, B.; Jin, C.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, X.; Wang, W. Response and prediction of ecosystem service values to land use change resulting from underground coal mining in high groundwater table areas: A case study of Jining City, China. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2024, 23, 100441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, J. Multi-objective land use optimization based on integrated NSGA–II–PLUS model: Comprehensive consideration of economic development and ecosystem services value enhancement. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Number | Data | Year | Resolution | Data Type | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Land use and land cover | 2005, 2020 | 30 m | Raster | Institute of Space and Astronautical Information Innovation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://data.casearth.cn/), accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 2 | Soil Attributes Data (clay, sand, silt, organic matter content, nitrogen content, phosphorus content, soil bulk density) | / | 1000 m | Raster | Harmonized World Soil Database v2.0 (https://www.fao.org/home/en/), accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 3 | Ecosystem Type CN Values | / | / | Text | Literature data |
| 4 | Digital Elevation Model | / | 30 m | Raster | ASTER GDEM V3 |
| 5 | Meteorological data (Precipitation, Temperature) | 2020 | / | Text | Chinese Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/), accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 6 | Daily Heavy Rainfall Standards | - | - | Text | China Meteorological Administration GB/T28592-2012 [48], accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 7 | Ecosystem Evapotranspiration Data | 2020 | 500 m | Raster | The Earth Science Data Systems (ESDS) Program (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/), accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 8 | Carbon sequestration rates for various ecosystem types | / | / | Text | Standard: DB33/T 2274-2020 [49], accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 9 | Air pollutants purification rates for various ecosystems | / | / | Text | Standard: DB33/T 2274-2020, accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 10 | Heat consumption coefficients for various ecosystems | / | / | Text | Standard: DB33/T 2274-2020, accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 11 | Latent heat of evaporation | / | / | Text | Literature data |
| 12 | Pricing of various ecosystem services | / | / | Text | Standard: DB33/T 2274-2020, accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 13 | Normalized Difference Veg-etation Index Data | 2020 | 30 m | Raster | Chinese Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/), accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| Type | Potential Driving Forces | Abbreviation | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Socio-economic factors | 1: Population | POP | Chinese Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/), accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 2: Gross domestic product | GDP | ||
| 3: Night-time light | NL | ||
| 4: Proximity to railway station | PRS | OpenStreetMap (https://www.openstreetmap.org/), accessed on 1 August 2024 | |
| 5: Proximity to railway | PR | ||
| 6: Proximity to trunk | PT | ||
| 7: Proximity to highway | PH | ||
| 8: Proximity to primary roads | PPR | ||
| 9: Proximity to secondary roads | PSR | ||
| 10: Proximity to tertiary roads | PTR | ||
| 11: Proximity to government | PG | ||
| Climate and environmental factors | 12: Proximity to open water | POW | OpenStreetMap (https://www.openstreetmap.org/), accessed on 1 August 2024 |
| 13: Digital Elevation | DE | ASTER GDEM V3 | |
| 14: Slope | SL | ASTER GDEM V3 | |
| 15: Annual mean temperature | AMT | Chinese Academy of Sciences Resource and Environmental Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/), accessed on 1 August 2024 | |
| 16: Annual precipitation | AP | ||
| 17: Soil type | ST | Harmonized World Soil Database v2.0 (https://www.fao.org/home/en/), accessed on 1 August 2024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, W.; Shu, C.; Lin, L. Integrating Ecosystem Service Values into Urban Planning for Sustainable Development. Land 2024, 13, 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13121985
Cai W, Shu C, Lin L. Integrating Ecosystem Service Values into Urban Planning for Sustainable Development. Land. 2024; 13(12):1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13121985
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Wenbo, Chengji Shu, and Li Lin. 2024. "Integrating Ecosystem Service Values into Urban Planning for Sustainable Development" Land 13, no. 12: 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13121985
APA StyleCai, W., Shu, C., & Lin, L. (2024). Integrating Ecosystem Service Values into Urban Planning for Sustainable Development. Land, 13(12), 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13121985








