Abstract
The interplay of surface and shallow subsurface fluxes plays a critical role in controlling water movement in hillslope agroecosystems and impacting soil and plant health during prolonged dry periods, demonstrating a need for in-field monitoring. This study was conducted for two years (2021–2022) by combining field monitoring of the grass-covered inter-row area (passive wick lysimeter, surface runoff, and meteorological data), laboratory determination of soil hydraulic properties (SHPs), and numerical modeling with the aim to explore near-surface fluxes at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory (CZO) located on a hillslope vineyard. Additionally, sensitivity analysis for basic root water uptake (RWU) parameters was conducted. The model was evaluated (R2, RMSE, and NSE) with lysimeter (hillslope) and runoff (footslope) data, producing good agreement, but only after the inverse optimization of laboratory estimated hydraulic conductivity was conducted, demonstrating that adequate parameterization is required to capture the hydropedological response of erosion-affected soil systems. Results exhibit the dependence of runoff generation on hydraulic conductivity, rainfall, and soil moisture conditions. The data suggest different soil-rewetting scenarios based on temporal rainfall variability. Sensitivity analysis demonstrated that Leaf Area Index (LAI) was the most responsive parameter determining the RWU. The study offers an approach for the investigation of fluxes in the topsoil for similar sites and/or crops (and covers), presenting the methodology of self-constructed soil–water collection instruments.
1. Introduction
Agroecosystems on hillslopes present a challenge for the estimation of vadose zone dynamics due to a large variety of processes, such as surface runoff and erosion, vertical flow, and subsurface flow, which are greatly affected by soil structure, soil management, and evapotranspiration [1,2,3,4,5]. An improved understanding of water dynamics in hillslopes could lead to more effective management, helping to mitigate the impacts of land use management [6] and climate variability [7].
Surface runoff in hillslope soils has significant impacts on sediment yield, nutrient transport, and consequently water quality [8,9]. In vineyards, heavy rainfall often increases and accelerates several negative impacts, including soil aggregate breakdown, soil sealing, nutrient leaching, excessive vine vegetative growth, and fruit disease [10]. As mitigation practice, cover crops are widely used to increase infiltration [11,12]. High runoff poses a significant problem in all areas, but mainly on compacted soils with low hydraulic conductivity, with tremendous negative impacts on the agroecosystem and surrounding environment [13]. Intensively managed vineyards exposed to heavy machinery traffic and cultivation practices mainly suffer from soil compaction [14], which limits the ability of water to infiltrate into the soil [15], and the possibility of it being plant-available.
The availability of water is a critical factor in determining the growth and productivity of plants. In aerobic soil conditions, as soil moisture increases, potential plant water uptake also increases [16], and conversely, when soil moisture is limited, plants may struggle to obtain the water they need, which can lead to stunted growth [17]. From this perspective, conservation practices like grass cover promote infiltration and can help to conserve water in vineyards for dry periods [18], presenting a need for in-field monitoring.
Various methods are used for the monitoring of soil–water fluxes in the vadose zone, while combining methods is often crucial to unlocking their full potential. For in situ soil water sampling, methods such as suction cups, plates, capillary wicks, and lysimeters are widely used [19,20,21]. Many variants of lysimeters are used, depending on the research needs, as they can generate valuable data by simulating actual field conditions [22,23,24]. Wick lysimeters are sampling devices that sample soil water by the gravitational potential using an inert wick material such as fiberglass [25,26] or rock wool [27]. They are commonly used in remote locations or for low-budget instrumentation, as they are relatively easy to build up and do not need any electrical power supply to generate suction for water extraction. Additionally, they offer a compromise between rather costly matric potential controlled suction plate systems and pan lysimeters [28]. Lysimeters can also be accompanied by surface runoff measuring devices [29], especially on hillslopes for a full hydrology component insight.
Numerical modeling is a useful technique for studying water movement in hillslope systems, where the interactions among factors such as precipitation, soil properties, and vegetation can result in complex hydrological processes [30,31,32]. When models accurately account for these interactions, they can aid in forecasting water availability changes and identifying factors that affect water flow patterns [33]. These models can be employed to test various scenarios and make predictions about the future hydrological behavior of hillslopes [31]. To achieve this, soil hydraulic properties (SHPs) are key factors in determining the water movement in soils. When modeling this movement, the optimization of estimated SHP is important for accurate predictions [21]. One approach to optimizing SHPs through inverse modeling involves comparing observed data with simulated results by iteratively adjusting the parameters of the model [34,35]. For example, optimization of hydraulic conductivity can improve the accuracy of the model and allow for better predictions of water movement in soils [36]. However, the optimization process must be carefully designed to ensure that the model is robust and reliable and that the results are consistent with the observed data [37].
Moreover, as water movement ultimately influences root water uptake (RWU), in order for the simulations to represent the field conditions, an accurate characterization of parameters influencing RWU is crucial. Modeling root zone processes often largely depends on characterizing unsaturated hydraulic conductivity, root growth, and water uptake dynamic parameters [38], showing a need for parameter assessment within the model [38,39,40,41]. Kuhl et al. (2018) [38] highlighted the need for accurate root distribution data to model root water uptake processes within various models. Their approach accurately captured root water dynamics, improving the estimates of transpiration. Hupet et al. (2003) [39] aimed to investigate the feasibility of using an inverse modeling approach to derive RWU parameters from soil water content (SWC) data. Their sensitivity analysis showed that SWC dynamics were relatively insensitive to RWU parameters, and the sensitivity depended on the soil texture. However, they concluded that more research is required to apply the inverse modeling approach to real cases with soil heterogeneity and root dynamics.
This study was conducted for two years (2021–2022) by combining the dataset of field investigation (wick lysimeter outflows, surface runoff observations, and meteorological data), laboratory determination of soil hydraulic properties (SHPs), and numerical modeling (HYDRUS-1D/2D). The research aims were (1) to explore the near-surface fluxes of the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory (CZO) located on a hillslope vineyard with field observations and numerical simulations, (2) to investigate the model performance after the inverse optimization of hydraulic conductivity parameter, and (3) to perform sensitivity analysis with basic root water uptake (RWU) parameters, in order to determine the most sensitive parameters for future modeling purposes and research optimization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
The investigations were conducted at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory (CZO) (https://sites.google.com/view/suprehill/; accessed on 20 April 2022), located in a hillslope vineyard at the experimental field Jazbina (45°51′24″ N, 16°00′22″ E) in Zagreb, Croatia. The hillslope is southwest exposed, with the vineyard rows downslope oriented. In this 15-year-old vineyard, the distance of vine plants within rows is 1.2 m, and the inter-row area is 2 m wide, while the inter-row soil surface is covered by grass. In this vineyard, Syrah, Dornfelder and Frankovka vine (Vitis vinifera L.) varieties are present. The soil type is classified as Dystric (Luvic) Stagnosol (IUSS Working Group WRB, 2022) [42].
The sloping between the segments was determined using an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and Agisoft Metashape software (Agisoft LLC., version 1.7.5., St. Petersburg, Russia), with the sloping between the hilltop and backslope being 17.5%, and between backslope and footslope 25.4% (Figure 1).
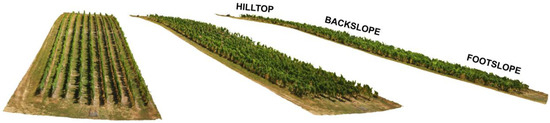
Figure 1.
3D model of the hillslope vineyard at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory (CZO).
2.2. Soil Data
Disturbed soil samples were taken across the inter-row area from three positions (hilltop, backslope, and footslope), covering two soil depths (0–30 and 30–60 cm) at each position. This was replicated in three inter-rows to determine soil texture and soil organic carbon (SOC) [43] (Table 1). The texture was determined by combined sieving and sedimentation (ISO 11277:2020), and the organic carbon content by sulfochromic oxidation (ISO 14235:1998).

Table 1.
Granulometric soil composition with standard deviation (SD). and measured soil organic carbon (SOC) (n = 3) at the hilltop, backslope, and footslope at two depths (0–30 and 30–60 cm).
Undisturbed soil cores (250 cm3) were sampled at the hilltop, backslope, and footslope positions, in three inter-rows, with three soil cores per location and depth (0–20 and 20–40 cm), making a total of nine replications per hillslope position and depth. The sampling campaign was conducted during the lysimeter installation (November 2020), at their installation positions. The undisturbed soil cores were used for determination of SHPs by using the simplified evaporation method with the HYPROP system [44] in combination with the dew point device WP4C (both METER Group, Inc., Pullman, WA, USA) [45]. SHPs were fitted based on the van Genuchten–Mualem (VGM) model using the HYPROP-FIT software (METER Group, Inc., version 4.2.2.0., Pullman, WA, USA) [46] and used for the simulations.
2.3. Meterorological Data
Meteorological data (precipitation, air temperature, relative humidity, vapor pressure deficit and atmospheric pressure, solar radiation, wind speed and direction) were acquired from a meteorological station (ATMOS41, METER Group, Inc., Pullman, WA, USA) installed at the CZO.
The total precipitation recorded at the SUPREHILL CZO in the investigated period (2021–2022) was 1589.5 mm (765.5 in 2021 and 823.9 mm in 2022). The highest daily precipitation recorded was 55 mm (on 16 September 2022). The month with the highest cumulative rainfall was September 2022, with a total of 270.2 mm, while the lowest monthly cumulative rainfall was observed in June 2021, with only 5.3 mm. The mean temperature in 2021 was 12.8 °C (2 m in height). The daily temperatures oscillated between −5.1 °C (recorded on 13 February 2021) and 37.8 °C (recorded on 18 August 2022). Cumulative reference evapotranspiration (ETo) (Allen, 2005) was calculated as 1561 mm (781 mm in 2021 and 780 mm in 2022). The highest monthly cumulative ETo was estimated in June of 2021 (136.7 mm) (Figure 2).
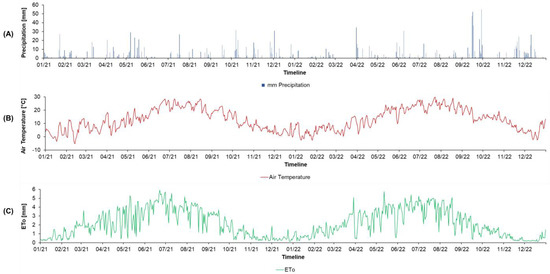
Figure 2.
Total daily precipitation [mm] (A), air temperature (°C) (B), and reference evapotranspiration (ETo) [mm] (C) at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory in 2021-2022.
2.4. Field Monitoring of Soil Water Fluxes
For near-surface drainage measurements, passive wick lysimeters were installed at a soil depth of 40 cm, at the hilltop, backslope, and footslope, in three repetitions (vineyard rows) in the midpoint of the inter-row area, below the grass-covered surface. Lysimeters were constructed out of 1.5 mm thick stainless steel (250 mm × 250 mm × 40 mm) with a drain extension (100 mm in length and 30 mm in diameter) installed at the sunken, fall-providing center point. The surface of the lysimeter was covered with a filter mesh (1 mm × 1 mm) to prevent clogging. Inside the lysimeter, a fiberglass wick was placed at the instrument surface, and through a reinforced flexible pipe mounted on the drain of the lysimeter, to ensure a small negative pressure that enables drainage seepage. The wick leads the sample to the leachate tanks (10 L), which were placed 50 cm deeper than the lysimeters to achieve the required suction. The lysimeters were filled with pre-dried crushed soil of the same profile and applied with a layer of quartz flour (71 µm) on top, moistened after the application to ensure better contact. The lysimeters were placed in a razor-sharp groove with a hammer and lifted with a combination of hard material and metal brackets. The installation process is presented in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Process of installation of passive wick lysimeters: (A) precision cutting, (B) lysimeter assembly and application of crushed soil and quartz flour, and (C) positioning the lysimeter with a hammer at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory (CZO).
To investigate surface water runoff, self-constructed instruments (2 m × 2 m) were installed at the footslope in three repetitions. The instruments collected water runoff through a channel drain. Above and along the drain, a 10 cm deep metal sheet was installed at a depth of 5 cm, to prevent water from percolating underneath the channel. The channel was underlaid with gravel, fixed with concrete, and sealed with silicone. The surface was bordered with galvanized sheets and a letter-J-shaped enforced sheet allowing undisturbed tractor passes in the inter-row sections of the vineyard. The drain channel is connected to a collection container (70 L) through PVC pipes (Figure 4). Schemes for both soil–water collection instruments are presented in Figure 5. In Figure 6, all monitoring points (installation positions) and sampling locations can be seen.

Figure 4.
Process of installation of surface runoff collection instruments: (A) collection tank placement and pipe connection, (B) flow guide placement (C) border and drain channel placement at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory (CZO).
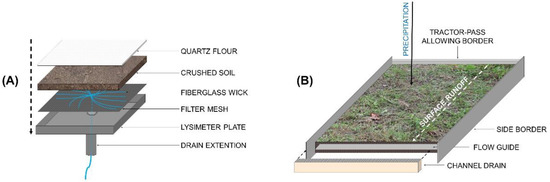
Figure 5.
Scheme of self-constructed (A) passive wick lysimeters and (B) surface runoff collection instruments at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory (CZO).
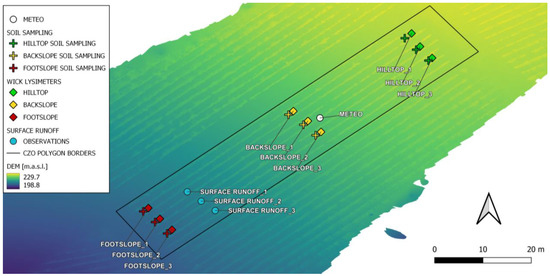
Figure 6.
Scheme of the installed research setup at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory (CZO) (hillslope vineyard), presented on a digital elevation model (DEM).
2.5. Numerical Modeling
Numerical modeling was performed with the HYDRUS (1D/2D) suite (version 5.01.0630 [47,48] using a three-step simulation process:
- Initial one-dimensional modeling based on laboratory determined SHPs, meteorological data and grass cover measurements;
- Inverse one-dimensional modeling based on lysimeter outflow to optimize hydraulic conductivity and to additionally evaluate the model-based surface runoff data;
- Two-dimensional modeling with the optimized parameters to investigate soil moisture in critical seasonal moments.
For the simulation of water flow, the Richards equation for the variably saturated porous medium was solved, which can be written as:
where θ is volumetric soil water content [L3 L−3], h is pressure head [L], K is hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soil [L T−1], z is the gravitational head [L], t is time [T], and S is a sink term for root water uptake (RWU) [T−1].
Soil hydraulic functions were described using the van Genuchten–Mualem (VGM) single porosity model [49]:
where θ(h) is volumetric water content [L3 L−3], K(h) is hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soil at the water pressure head of h [L], θr is residual soil–water content [L3 L−3], θs is water content at saturation [L3 L−3], Se is the effective saturation [-], Ks is the saturated hydraulic conductivity of the soil [L T−1], α is related to the inverse of air-entry value (bubbling pressure) [L−1], n is the dimensionless soil pore size distribution index [-], m is the dimensionless optimization coefficient [-], and l is the pore connectivity parameter [-]. The pore connectivity parameter, l, was fixed to a value of 0.5, as recommended for most soils [50].
Boundary conditions for the simulations were set to atmospheric conditions with surface runoff at the top, while seepage face (pressure head = −50 cm) was applied for the bottom for the one-dimensional simulations (simulating lysimeter outflows) and free drainage for two-dimensional simulations. The domain had a total number of 41 nodes for the 40 cm deep simulation domain (lysimeter depth). The initial conditions were set according to field capacity.
Leaf Area Index (LAI) was calculated based on grass height (hG) measurements (m), using the following equation [51,52]:
LAI = 0.5 (24 hG)
Root water uptake was simulated using the approach of Feddes et al. (1978) [53] setting the parameters P0 to −10 cm, POpt to −25 cm, P2H to −300 cm, P2L to −1000 cm, and P3 to −8000 cm, corresponding for the parameter set available for grass in the HYDRUS integrated library. The maximum rooting depth (linear distribution) was set as 40 cm (corresponding to the lysimeter installation depth).
Sensitivity analysis of parameter changes on basic plant uptake parameters (LAI, root depth and Feddes parameter) within the model was conducted using a method of quantitative sensitivity analysis, where one parameter was systematically decreased (to either 25, 50 and 75% of value or range) while the others were kept constant, in order to determine the most sensitive parameters for future modeling purposes and research optimization. Sensitivity analysis is a method that assesses how changes in input parameters affect a model’s output and is commonly utilized to measure parameter significance [40,54].
The inverse modeling approach was used to optimize Ks. The inverse solution of Ks was obtained by minimization of the objective function using cumulative lysimeter outflow data (50 measurements in total). Minimization of the objective function was accomplished by using the Levenberg–Marquardt nonlinear minimization method, which is a weighted least-squares approach based on Marquardt’s maximum neighborhood method [55]. The method was found to be very effective, and has become a common approach in nonlinear least-squares fitting in soil science and hydrology [56,57].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Model performance evaluation was carried out with the coefficient of determination (R2), the root-mean-square error (RMSE), and the Nash–Sutcliffe model efficiency coefficient (NSE):
where Oi is observation, Pi is prediction, Ō is average observation and is average prediction, while the N is the sample size.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Data
Laboratory determination of SHPs showed that the saturated water content (θs) varied from 0.373 cm3 cm−3 (backslope at 20–40 cm) to 0.426 cm3 cm−3 (hilltop at 0–20 cm). The Ks values varied from 0.306 cm day−1 (hilltop at 0–20 cm) to high as 1.370 cm day−1 (hilltop at 20–40 cm). At each position, θs decreased with depth. Bulk density (BD) varied from 1.48 g cm−3 (hilltop at 0–20 cm) to 1.60 g cm−3 (backslope at 0–20 cm). Values of RMSE (θ) < 0.02 cm3 cm−3 indicated the applicability of VGM at the investigated positions (Table 2). θr was assumed to be 0 for all depths and positions, and was used in this manner as Šimůnek et al. (1998) [58] and González et al. (2015) [59] found that this parameter had little effect on the simulated θ and h time series. The fitted soil water retention curves (SWRCs) are shown in Figure 7.

Table 2.
Van Genuchten-Mualem parameters obtained by HYPROP-FIT: θr represents residual volumetric water content, θs saturated volumetric water content, Ks saturated hydraulic conductivity, Ksopt (inversely optimized saturated hydraulic conductivity after initial simulations) and α and n the empirical retention curve shape parameters with BD.
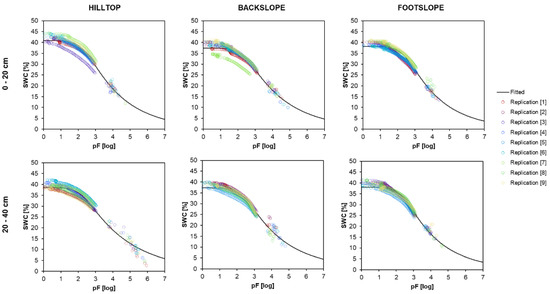
Figure 7.
Soil–water retention curves obtained with HYPROP-FIT software (version 4.2.2.0) for the hilltop, backslope, and footslope at two depths (0–20 and 20–40 cm) and nine replications (soil cores) at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory.
3.2. Lysimeter Outflows and Surface Runoff Observations
The seasonal evaluation revealed that the highest lysimeter outflow (123.8 mm) was found in the winter of 2021 at the hilltop, immediately after the installation of the lysimeter. In the second season, the highest outflow was observed at the footslope in the autumn of 2022, following soil rewetting and extreme rainfall. During both summer seasons, no outflow was captured in lysimeters, due to dry soil conditions, and no significant vertical flux occurred until soil rewetting occurred. The highest measurements of surface runoff were obtained during the winter season of 2021. In 2022, following the highest amount of rainfall in September, the highest surface runoff occurred before/and during the soil-rewetting (Table 3, Figure 8).

Table 3.
Seasonal mean outflow [mm] observed in passive wick lysimeters (in three repetitions) at the hilltop, backslope and footslope and surface runoff [mm] at the footslope at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory in 2021–2022.
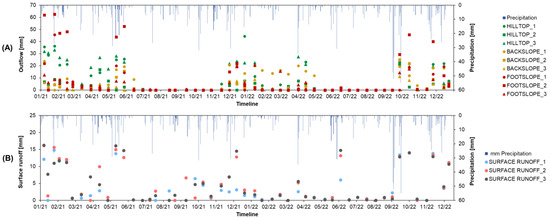
Figure 8.
Observed outflow [mm] in passive wick lysimeters at the hilltop, backslope and footslope (A) and observed surface runoff at the footslope [mm] (B) with daily precipitation [mm] at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory in 2021–2022.
3.3. Numerical Simulations of Soil–Water Fluxes
The initial run of the simulations demonstrated high R2 (0.89–0.90) but low agreement based on high RMSE (83.64–183.81 mm) and negative NSE (ranging from −4.14 to −1.27) values. The highest model performance, based on the lysimeter outflows, was obtained at the backslope during the optimized run, with the highest R2 and NSE (0.95 and 0.90, respectively), and the lowest RMSE (17.71). The RMSE in the optimized simulations ranged from 17.71 to 51.63 mm for the investigated period (2021–2022), while the NSE ranged from 0.38–0.90. Generally, the lowest model performance in the optimized run was obtained at the footslope (Table 4, Figure 9).

Table 4.
Coefficient of determination (R2), root mean square error (RMSE), and Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) for observed lysimeter outflow and simulated outflow (initial/optimized simulations) at the hilltop, backslope and footslope at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory in 2021–2022.
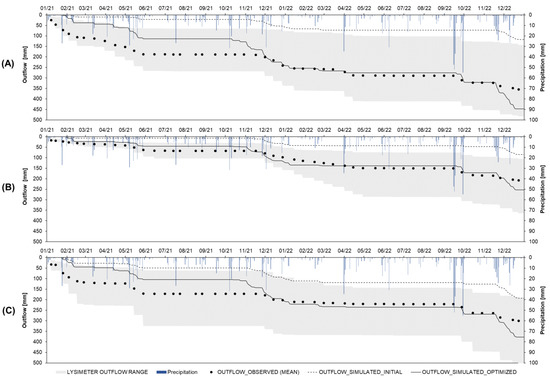
Figure 9.
Observed mean outflow [mm] in wick lysimeters (dots) measured on a 14-day basis with the range of outflow (grey area) and simulated outflow (initial simulation—dashed line; optimized simulation—solid line) with daily precipitation [mm] at the hilltop (A), backslope (B) and footslope (C) at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory in 2021–2022.
The simulated soil water content (SWC) at 5 and 40 cm demonstrates the infiltration effect contributing to the variability of the topsoil moisture at the investigated hillslope. The SWC suggests that in both years, the major soil drying out phase started in the relatively same period, but soil rewetting scenarios were different, with 2022 soil rewetting started to occur in the summer season, in contrast to autumn in 2021. Additionally, in 2021, after the main rewetting phase, soil did not dry out until the next season, contrary to 2022 data that suggests that high intensity rainfall events in September did not rewet the soil to completion (Figure 10). Exemplary instances of the investigated vineyard inter-row topsoil moisture are presented in Figure 11.
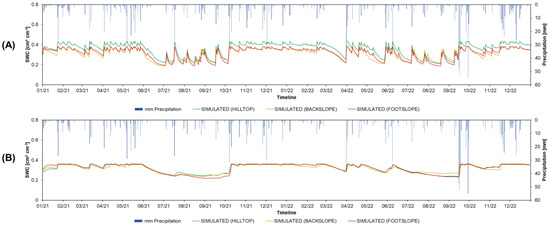
Figure 10.
Simulated soil water content (SWC) [cm3 cm−3] at 5 cm soil depth (A), and at 40 cm soil depth (B) with daily precipitation [mm] at the hilltop, backslope, and footslope at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory in 2021–2022.
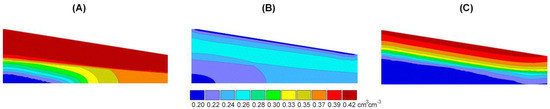
Figure 11.
Exemplary instances of vineyard inter-row topsoil moisture: (A) high-intensity rainfall during unsaturated conditions infiltrating to the topsoil (17 July 2021); (B) dried soil surface controlling surface runoff generation in the summer seasons (16 September 2022); and (C) beginning of soil rewetting (17 September 2021) at the footslope of the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory in 2021–2022.
Model performance evaluation based on surface runoff demonstrated that better model performance was achieved in 2021. Even though high R2 (ranging from 0.88 to 0.97) was obtained in both years, higher model performance is observed in 2021, with all NSE values being higher than 0.5 (ranging from 0.52 to 0.60), and generally lower RMSE (from 20.8 to 23.6 mm) (Table 5, Figure 12).

Table 5.
Coefficient of determination (R2), root mean square error (RMSE), and Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) for observed surface runoff and simulated outflow after the optimization at the footslope at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory in 2021–2022.
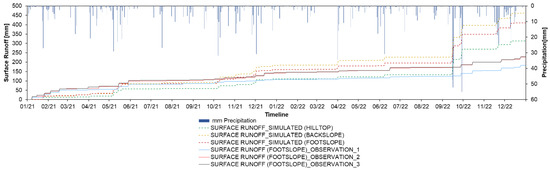
Figure 12.
Simulated surface flux [mm] with daily precipitation [mm] at the hilltop, backslope and footslope at the SUPREHILL Critical Zone Observatory in 2021–2022.
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis for RWU Parameters
The basic plant parameter impact analysis demonstrated that the Leaf Area Index (LAI) was the most responsive parameter determining the RWU dropping almost proportionally to the input. The lowest impact was found for root depth, while the highest uncertainty in the outcome was found for the Feddes parameter. The highest RWU (244 mm) was observed at the backslope (Figure 13).
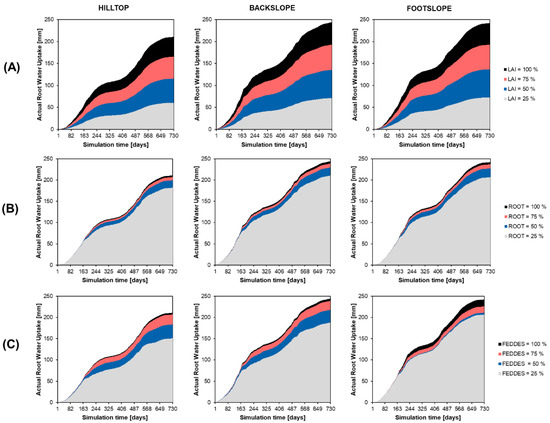
Figure 13.
Model impact analysis for (A) Leaf Area Index (LAI), (B) root depth and (C) Feddes parameters within the HYDRUS-1D model.
4. Discussion
The highest lysimeter outflows were generally observed at the footslope, along with the lowest agreement with the model, suggesting the influence of downward moving water along the hillslope and high-volume rainfall on the vertical flux at the footslope. It is well documented that surface runoff generated on the hillslope can play a significant role in the overall distribution of infiltrated water [60]. Moreover, as rainwater moves downslope, it can encounter variations in soil properties that influence the amount of water retained in the soil, which can lead to variable runoff generation at the hillslope [61,62]. In compacted soils (or dry conditions), runoff may become the dominant pathway for water movement [13], which can result in more water available for infiltration at the footslope. The largest surface runoff volumes were observed after the January (2021) rainfall event, occurring after a month with almost no precipitation, and most likely additionally influenced by freezing conditions, as the lowest temperatures were observed in the winter of 2021 and high soil moisture content. In our study, surface runoff observations demonstrated the influence of temporal rainfall variability on runoff generation (Figure 8).
Even though the lowest R2 in the initial simulations of lysimeter outflows was 0.89, the RMSE and NSE indicate the lower model performance (before the inverse optimization of the hydraulic conductivity), thus demonstrating a need for the use of multiple statistical parameters (such as the combination of R2, RMSE and NSE) in performance evaluation (Table 4). Considering that the model demonstrated dependable outcomes in lysimeter outflows, when observing surface runoff data, the model suggested that in September of 2022, the month with a third (270.2 mm) of total annual rainfall (823.9 mm), the tank for surface runoff collection instrument overflowed due to the extreme rainfall, thus indicating a false low model performance in 2022 (Table 5, Figure 12). In order to prevent this kind of observational problem, the instrument should either be discharged more frequently during extreme events or have higher water storage capacity, or it should be equipped with an automatic discharge and measuring system in future research. Other than this instance, both the lysimeters and surface runoff collection systems produced dependable field values.
The model suggested that within the investigated years (2021 and 2022), different soil-rewetting scenarios occurred (Figure 10), where rather early rewetting in 2022 was triggered by high-volume and high-intensity rainfall in late September. If a prolonged dry period is followed by a sudden rewetting, in some cases, plants may experience a temporary boost in growth due to the sudden availability of water. However, if the extended dry period is followed by intense rainfall events, it can lead to nutrient loss, soil erosion, or waterlogging [63,64,65], negatively impacting crop growth. Moreover, different patterns of rainfall distribution throughout the growing season influence crop development [66,67]; therefore, monitoring the infiltration effects during the year is critical, and this is especially pronounced during dry seasons.
Inter-row vineyard areas provide space for water to infiltrate into the soil (Figure 11A), and when they are covered with grass (instead of bare soil), they aid in reducing overland flow [68], mostly due to the surface roughness and root network. Grass cover enhances soil moisture retention by reducing evaporation and increasing infiltration, helping to mitigate the impacts of dry conditions on soil moisture retention and plant productivity [69]. During prolonged dry periods, soil surface crust can greatly reduce infiltration rates and increase surface runoff, as shown in an exemplary instance in Figure 11B. Soil surface crusts can lead to decreased hydraulic conductivity and water-holding capacity, which can ultimately affect the hydrologic connectivity in the near-surface layer [70]. The surface crusts usually have higher bulk density and smaller pores, and consequently a lower hydraulic conductivity than the underlying soil [58]. Furthermore, when rainfall occurs on uniformly rewetted soil, the soil is able to absorb the water more readily, allowing for increased infiltration and reduced surface runoff. This is because the rewetting process helps to restore the soil’s structure, allowing it to hold more water and promote more efficient water use, while reducing the amount of runoff (Figure 11C). Soil moisture memory (SMM), or the persistence of soil moisture conditions over time, can play an important role in the development and severity of drought [71] and the impact on evapotranspiration. The SMM effect serves as a buffer against the impacts of drought by maintaining the soil structure based on past wet conditions, which influences its future state. Nevertheless, SMM can cause a delay in drought recovery by carrying over its effects from one growing season to the next [72].
The importance of accurately estimating SHPs was highlighted with optimized simulation runs, as they were key factors in determining the water movement in soils. Filipović et al. (2018) [35] used a combination of two- and three-dimensional HYDRUS modeling and inverse optimization to estimate SHPs from field tension disc infiltration experiments and concluded that prolonged dry periods increased soil water repellency in forested hillslopes. Groh et al. (2018) [21] performed an inverse modeling study in which they estimated soil hydraulic parameters and of layered soils from soil water content, matric potential, and stable water isotope measurements in weighable lysimeter systems. In our case, the results demonstrated that the inverse optimization of hydraulic conductivity parameters based on passive wick lysimeter data is feasible, and in our case crucial for obtaining accurate estimations concerning near-surface hydrologic connectivity.
The data suggest that the LAI measurements or estimations are the most dependable of the model outcomes (Figure 13). Zeng et al. (2018) [40] used a variance-based global sensitivity analysis to quantify the sensitivity indices of RWU to Feddes parameters in the HYDRUS-1D model. The study found that wilting point was the most important Feddes parameter for RWU estimation within the model, and suggested that the model should be calibrated based on field measurements. In our case, the highest uncertainty in the outcome was found with the Feddes parameter range change. Furthermore, Cai et al. (2016) [73] conducted an optimization based on the factors determining whether roots absorb water from a certain soil layer and whether the baseline cumulative root efficiency required for maximum plant transpiration is reached. They demonstrated that RWU is an important link in the water and heat exchange between plants and ambient air and that improving its parameterization is key to enhancing the performance of land surface model simulations. In our study, the lowest impact was found for root depth, suggesting that deeper layers do not differ significantly in terms of actual water availability when considering RWU. Angaleeswari and Ravikumar (2019) [74] focused on the practical implementation of HYDRUS in irrigation and fertigation scheduling and demonstrated that the simulations of the root zone processes using HYDRUS largely depended on characterizing parameters related to unsaturated hydraulic conductivity, root growth, and water uptake dynamics, which were found to be most sensitive.
5. Conclusions
The HYDRUS model produced dependable outcomes, but only after the inverse optimization of saturated hydraulic conductivity was executed, demonstrating that an adequate parameterization of SHP is required to capture the hydropedological response of erosion-affected soil systems under complex field conditions. Simulations demonstrated the seasonal interplay of overland flow with hydraulic conductivity and rainfall based on field conditions. Optimization of soil hydraulic conductivity and assessment of basic root water uptake parameters are crucial components of hydrological modeling, as their adjustment enhances the accuracy of models, particularly in areas where soil and vegetation properties differ significantly due to common agroecosystem heterogeneities. Additionally, sensitivity analysis revealed that Leaf Area Index (LAI) was the most responsive parameter determining the plant water uptake within the model and can affect the water balance results greatly. Thus, LAI should be implemented in the model with some caution and preferably using real field data.
The highest lysimeter outflows were observed at the footslope, along with the lowest statistical parameters obtained, pointing to the possibility of the influence of downward-moving water along the hillslope during high-volume rainfall events. These processes should be investigated using a more detailed modeling approach, using the whole hillslope as the domain. However, more soil data should be collected to develop a model showcasing the processes on the hillslope, in order to account for the soil heterogeneities usually present in this kind of agroecosystem, as laboratory measurements of soil hydraulic conductivity suggest. Furthermore, in order to investigate the RWU at the hillslope vineyard scale, a multi-crop root system should be accounted for, in more than two dimensions.
The study also offers a technical overview of applied methodologies for the investigation of fluxes in the topsoil for similar sites and/or crops (and covers), presenting the self-constructed soil–water collection instruments.
It is suspected that the disturbance of the micro-location affected the lysimeter outflows at the beginning of the investigation period, as the highest lysimeter outflows were found in the first winter period, combined with better model performance after the first soil-rewetting (after the installation affected soil settling). As presented, data collected in the first year after this kind of installation should not be disregarded, but they should be handled with circumspection. Additionally, the results indicate the importance of the use of different statistical parameters, as often using only one parameter potentially shows misleading performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.K. and V.F.; Data curation, V.K.; Funding acquisition, L.F. and V.F.; Investigation, V.K., L.F., J.D. and V.F.; Methodology, V.K. and V.F.; Project administration, V.K., L.F. and V.F.; Resources, V.F.; Software, V.K. and J.D.; Supervision, V.F.; Visualization, V.K.; Writing—original draft, V.K. and V.F.; Writing—review and editing, L.F., J.D., I.B., Y.Z., Z.K. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Croatian Science Foundation, grant number UIP-2019-04-5409, project: “Subsurface preferential transport processes in agricultural hillslope soils—SUPREHILL”.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on demand.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Needelman, B.A.; Gburek, W.J.; Petersen, G.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Kleinman, P.J.A. Surface Runoff along Two Agricultural Hillslopes with Contrasting Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo Comino, J.; Senciales, J.M.; Ramos, M.C.; Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Lasanta, T.; Brevik, E.C.; Ries, J.B.; Ruiz Sinoga, J.D. Understanding soil erosion processes in Mediterranean sloping vineyards (Montes de Málaga, Spain). Geoderma 2017, 296, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, S.; Naef, F.; Fach, A.O.; Cordery, I. Formation of runoff at the hillslope scale during intense precipitation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, M. Spatial variability and temporal stability of actual evapotranspiration on a hillslope of the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Arid Land 2021, 13, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, T.; Kuang, F.; Luo, Z.; Tang, J.; Xu, T. Measurements of Nitrate Leaching from a Hillslope Cropland in the Central Sichuan Basin, China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Leys, J.; Gray, J.; Zhang, M. Hillslope erosion improvement targets: Towards sustainable land management across New South Wales, Australia. CATENA 2022, 211, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleda Obando, P.F.; Ducharne, A.; Cheruy, F.; Jost, A.; Ghattas, J.; Colin, J.; Nous, C. Influence of Hillslope Flow on Hydroclimatic Evolution Under Climate Change. Earth’s Futur. 2022, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.B. Soil erodibility and processes of water erosion on hillslope. Geomorphology 2000, 32, 385–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coblinski, J.A.; Favaretto, N.; Goularte, G.D.; Dieckow, J.; de Moraes, A.; de Paula Souza, L.C. Water, Soil and Nutrients Losses by Runoff at Hillslope Scale in Agricultural and Pasture Production in Southern Brazil. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Heuvel, J.; Centinari, M. Under-Vine Vegetation Mitigates the Impacts of Excessive Precipitation in Vineyards. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 713135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahimba, F.C.; Ranjan, R.S.; Froese, J.; Entz, M.; Nason, R. Crop cover effects on infiltration, soil temperature, and soil moisture distribution in the Canadian Prairies. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2008, 24, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lei, T.; Li, S.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, S.; Yang, X. Effects of rye grass coverage on soil loss from loess slopes. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemke, J.J.; Enderling, M.; Klein, A.; Skubski, M. The influence of soil compaction on runoff formation. A case study focusing on skid trails at forested andosol sites. Geosciences 2019, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogunovic, I.; Bilandzija, D.; Andabaka, Z.; Stupic, D.; Rodrigo Comino, J.; Cacic, M.; Brezinscak, L.; Maletic, E.; Pereira, P. Soil compaction under different management practices in a Croatian vineyard. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, R.; de la Fuente, M.; Junquera, P.; Lissarrague, J.R.; Baeza, P. Effects of soil management in vineyard on soil physical and chemical characteristics. BIO Web Conf. 2014, 3, 01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wei, M.; Li, Y.; Feng, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, D. Effects of soil moisture on water transport, photosynthetic carbon gain and water use efficiency in tomato are influenced by evaporative demand. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 226, 105818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.; Hu, X.; Cai, H.; Gu, B. Effects of limited irrigation on yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 55, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celette, F.; Findeling, A.; Gary, C. Competition for nitrogen in an unfertilized intercropping system: The case of an association of grapevine and grass cover in a Mediterranean climate. Eur. J. Agron. 2009, 30, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Hoffland, E. In situ sampling of small volumes of soil solution using modified micro-suction cups. Plant Soil 2007, 292, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.P.; Lin, H. Water and bromide recovery in wick and pan lysimeters under conventional and zero tillage. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, J.; Stumpp, C.; Lücke, A.; Pütz, T.; Vanderborght, J.; Vereecken, H. Inverse Estimation of Soil Hydraulic and Transport Parameters of Layered Soils from Water Stable Isotope and Lysimeter Data. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 170168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffman, P.M.; Williams, C.O.; Pouyat, R.V.; Band, L.E.; Yesilonis, I.D. Nitrate Leaching and Nitrous Oxide Flux in Urban Forests and Grasslands. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1848–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipović, V.; Kodešová, R.; Petošić, D. Experimental and mathematical modeling of water regime and nitrate dynamics on zero tension plate lysimeters in soil influenced by high groundwater table. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2013, 95, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiefenbacher, A.; Weigelhofer, G.; Klik, A.; Pucher, M.; Santner, J.; Wenzel, W.; Eder, A.; Strauss, P. Short-term effects of fertilization on dissolved organic matter in soil leachate. Water 2020, 12, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, M.; Brown, K.W.; Thomas, J.C.; Zabcik, D.; Murray, H.E. Capillary-Wick Unsaturated Zone Soil Pore Water Sampler. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, V.; Coquet, Y.; Pot, V.; Houot, S.; Benoit, P. Modeling the effect of soil structure on water flow and isoproturon dynamics in an agricultural field receiving repeated urban waste compost application. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gal, A.; Shani, U. A highly conductive drainage extension to control the lower boundary condition of lysimeters. Plant Soil 2002, 239, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel-Bothe, S.; Weihermüller, L. (Eds.) Field Measurement Methods in Soil Science; Borntraeger Gebrueder: Stuttgart, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, R.D.; Liu, Z.; Rupp, D.E.; Higgins, C.W.; Selker, J.S. A new instrument to measure plot-scale runoff. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. 2015, 4, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilagyi, J. Analysis of the nonlinearity in the hillslope runoff response to precipitation through numerical modeling. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Clark, M.; Lawrence, D.M.; Swenson, S.; Band, L.E.; Brantley, S.L.; Brooks, P.D.; Dietrich, W.E.; Flores, A.; Grant, G.; et al. Hillslope Hydrology in Global Change Research and Earth System Modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 1737–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, V.; Defterdarović, J.; Krevh, V.; Filipović, L.; Ondrašek, G.; Kranjčec, F.; Magdić, I.; Rubinić, V.; Stipičević, S.; Mustać, I.; et al. Estimation of stagnosol hydraulic properties and water flow using uni-and bimodal porosity models in erosion-affected hillslope vineyard soils. Agronomy 2022, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, H.; Schnepf, A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Javaux, M.; Or, D.; Roose, T.; Vanderborght, J.; Young, M.H.; Amelung, W.; Aitkenhead, M.; et al. Modeling Soil Processes: Review, Key Challenges, and New Perspectives. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, A.; Hupet, F.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Lambot, S.; Vanclooster, M. Using inverse methods for estimating soil hydraulic properties from field data as an alternative to direct methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 59, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, V.; Weninger, T.; Filipović, L.; Schwen, A.; Bristow, K.L.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Leitner, S. Inverse estimation of soil hydraulic properties and water repellency following artificially induced drought stress. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2018, 66, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namitha, M.R.; Ravikumar, V. Determination of Unsaturated Hydraulic Conductivity in Field Conditions through Inverse Modelling Using Hydrus-ID. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2017, 2, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Burns, I.G.; Greenwood, D.J.; Hammond, J.P.; White, P.J. Developing a reliable strategy to infer the effective soil hydraulic properties from field evaporation experiments for agro-hydrological models. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, A.S.; Kendall, A.D.; Van Dam, R.L.; Hyndman, D.W. Quantifying Soil Water and Root Dynamics Using a Coupled Hydrogeophysical Inversion. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupet, F.; Lambot, S.; Feddes, R.A.; Van Dam, J.C.; Vanclooster, M. Estimation of root water uptake parameters by inverse modeling with soil water content data. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Lei, G.; Zha, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, J. Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of the HYDRUS-1D model for root water uptake in saline soils. Crop Pasture Sci. 2018, 69, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Vanderborght, J.; Couvreur, V.; Mboh, C.M.; Vereecken, H. Parameterization of Root Water Uptake Models Considering Dynamic Root Distributions and Water Uptake Compensation. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS) Working Group WRB. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; IUSS: Vienna, Austria, 2022; ISBN 9798986245119. [Google Scholar]
- Krevh, V.; Groh, J.; Weihermüller, L.; Filipović, L.; Defterdarović, J.; Kovač, Z.; Magdić, I.; Lazarević, B.; Baumgartl, T.; Filipović, V. Investigation of Hillslope Vineyard Soil Water Dynamics Using Field Measurements and Numerical Modeling. Water 2023, 15, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- METER. HYPROP Manual; UMS: Munich, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- METER. WP4C Manual; METER: Pullman, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- METER. HYPROP-FIT User’s Manual; METER: Pullman, WA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Šimůnek, J.; Bradford, S.A. Vadose Zone Modeling: Introduction and Importance. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Šejna, M. Recent Developments and Applications of the HYDRUS Computer Software Packages. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A New Model for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Porous Media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pruitt, W.O.; Wright, J.L.; Howell, T.A.; Ventura, F.; Snyder, R.; Itenfisu, D.; Steduto, P.; Berengena, J.; Yrisarry, J.B.; et al. A recommendation on standardized surface resistance for hourly calculation of reference ETo by the FAO56 Penman-Monteith method. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 81, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebler, S.; Hendricks Franssen, H.J.; Pütz, T.; Post, H.; Schmidt, M.; Vereecken, H. Actual evapotranspiration and precipitation measured by lysimeters: A comparison with eddy covariance and tipping bucket. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2145–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddes, R.A.; Kowalik, P.J.; Zaradny, H. Simulation of Field Water Use and Crop Yield; Simulation Monographs; Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yu, H. A sensitivity analysis of simulated infiltration rates to uncertain discretization in the moisture content domain. Water 2019, 11, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.W. An Algorithm for Least-Squares Estimation of Nonlinear Parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, J.B.; Parker, J.C.; van Genuchten, M.T. Determining Soil Hydraulic Properties from One-step Outflow Experiments by Parameter Estimation: I. Theory and Numerical Studies. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, J.B.; Parker, J.C.; van Genuchten, M.T. Parameter estimation for unsaturated flow and transport models—A review. J. Hydrol. 1987, 91, 255–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R.; Schaap, M.G.; Vandervaere, J.P.; Van Genuchten, M.T. Using an inverse method to estimate the hydraulic properties of crusted soils from tension-disc infiltrometer data. Geoderma 1998, 86, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.G.; Ramos, T.B.; Carlesso, R.; Paredes, P.; Petry, M.T.; Martins, J.D.; Aires, N.P.; Pereira, L.S. Modelling soil water dynamics of full and deficit drip irrigated maize cultivated under a rain shelter. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 132, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, R.S.; Song, Y.X.; Han, C.T.; Liu, Z.W.; Liu, J.F. Spatial variability of soil hydraulic conductivity and runoff generation types in a small mountainous catchment. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 2724–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Yi, P.; Frape, S.K.; Gong, M.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of surface water and groundwater interactions in the upstream of Kui river and Yunlong lake, Xuzhou, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S. Infiltration into soils: Conceptual approaches and solutions. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1755–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa, M.S.; Schneider, R.L.; Sullivan, P.J.; Walter, M.T. Drought and post-drought rain effect on stream phosphorus and other nutrient losses in the Northeastern USA. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 28, 100672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandi, S.G.; Rodriguez, J.F.; Saintilan, N.; Wen, L.; Kuczera, G.; Riccardi, G.; Saco, P.M. Resilience to drought of dryland wetlands threatened by climate change. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Shen, Z.; Leng, G.; Wei, G. Synergistic effect of drought and rainfall events of different patterns on watershed systems. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneti, T.Z. Review on the Effect of Moisture or Rain Fall on Crop Production. Civ. Environ. Res. 2019, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, O.I.; Ilunga, M.F. The Rainfall Factor of Climate Change Effects on the Agricultural Environment: A Review. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2017, 14, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horel, Á.; Zsigmond, T. Plant Growth and Soil Water Content Changes under Different Inter-Row Soil Management Methods in a Sloping Vineyard. Plants 2023, 12, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruna, S.I.; Eichas, R.C.; Peters, O.M.; Farmer, A.C.; Lackey, D.Q.; Nichols, J.E.; Peterson, W.H.; Slone, N.A. In situ water infiltration: Influence of cover crops after growth termination. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2022, 86, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahinian, N.; Voltz, M.; Moussa, R.; Trotoux, G. Assessing the impactof the hydraulic properties of a crusted soil on overland flow modelling at the field scale. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 1701–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; González-Zamora, A.; Almendra-Martín, L. Soil moisture memory and soil properties: An analysis with the stored precipitation fraction. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-De La Torre, A.; Miguez-Macho, G. Groundwater influence on soil moisture memory and land-atmosphere fluxes in the Iberian Peninsula. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4909–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Ming, H.; Mi, N.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R. Effects of optimized root water uptake parameterization schemes on water and heat flux simulation in a maize agroecosystem. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angaleeswari, M.; Ravikumar, V. Estimating root water uptake parameters by inverse modelling. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 223, 105681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).