Assessment of Urban Ecological Resilience Based on PSR Framework in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
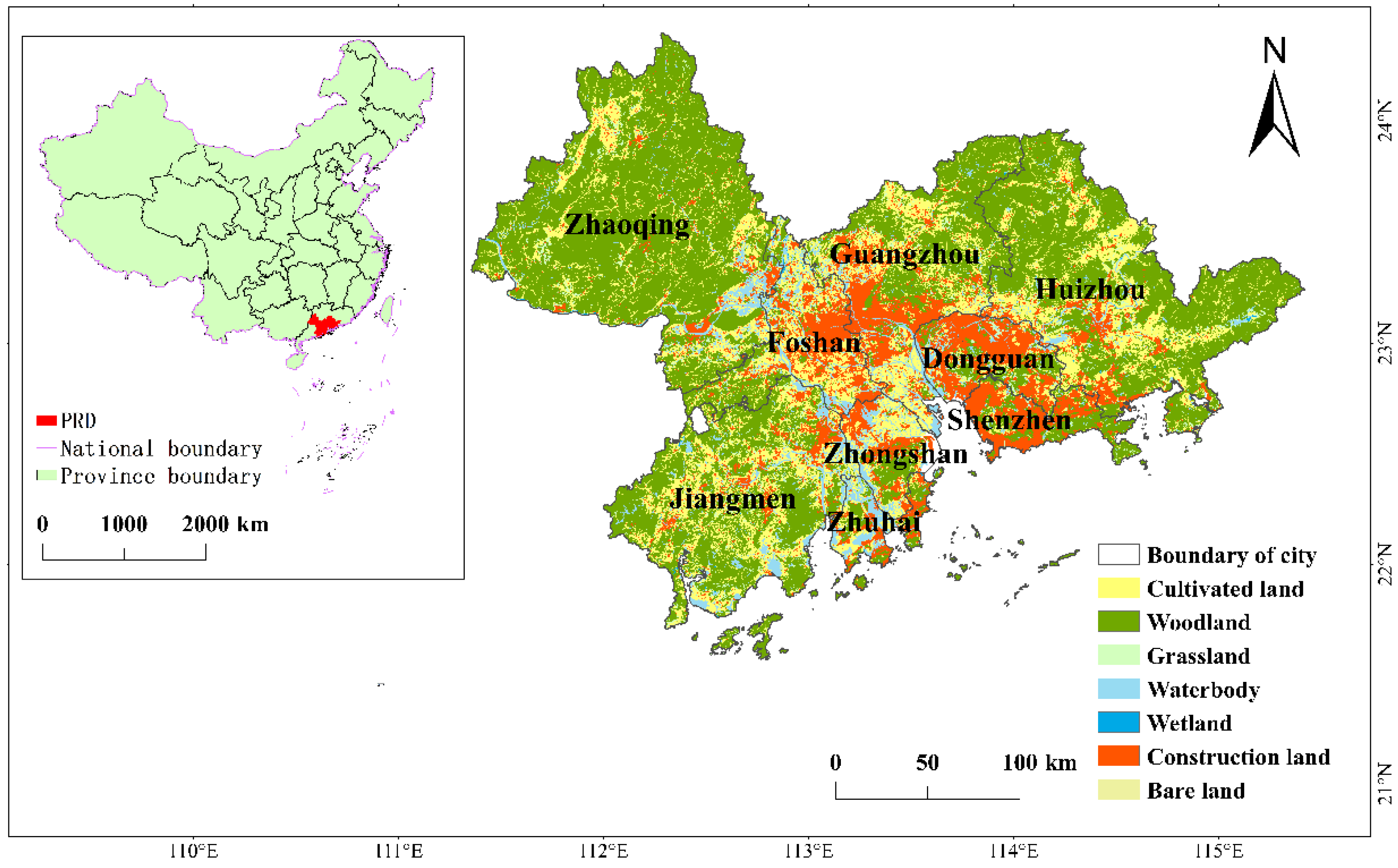
2.1. Study Area
2.2. UER Evaluation Framework Construction
2.3. Methods of Evaluating UER Indicators
2.3.1. Evaluating Morphological Resilience
2.3.2. Evaluating Density Resilience
2.3.3. Evaluating Economic Resilience
2.3.4. Evaluating Comprehensive UER
3. Results
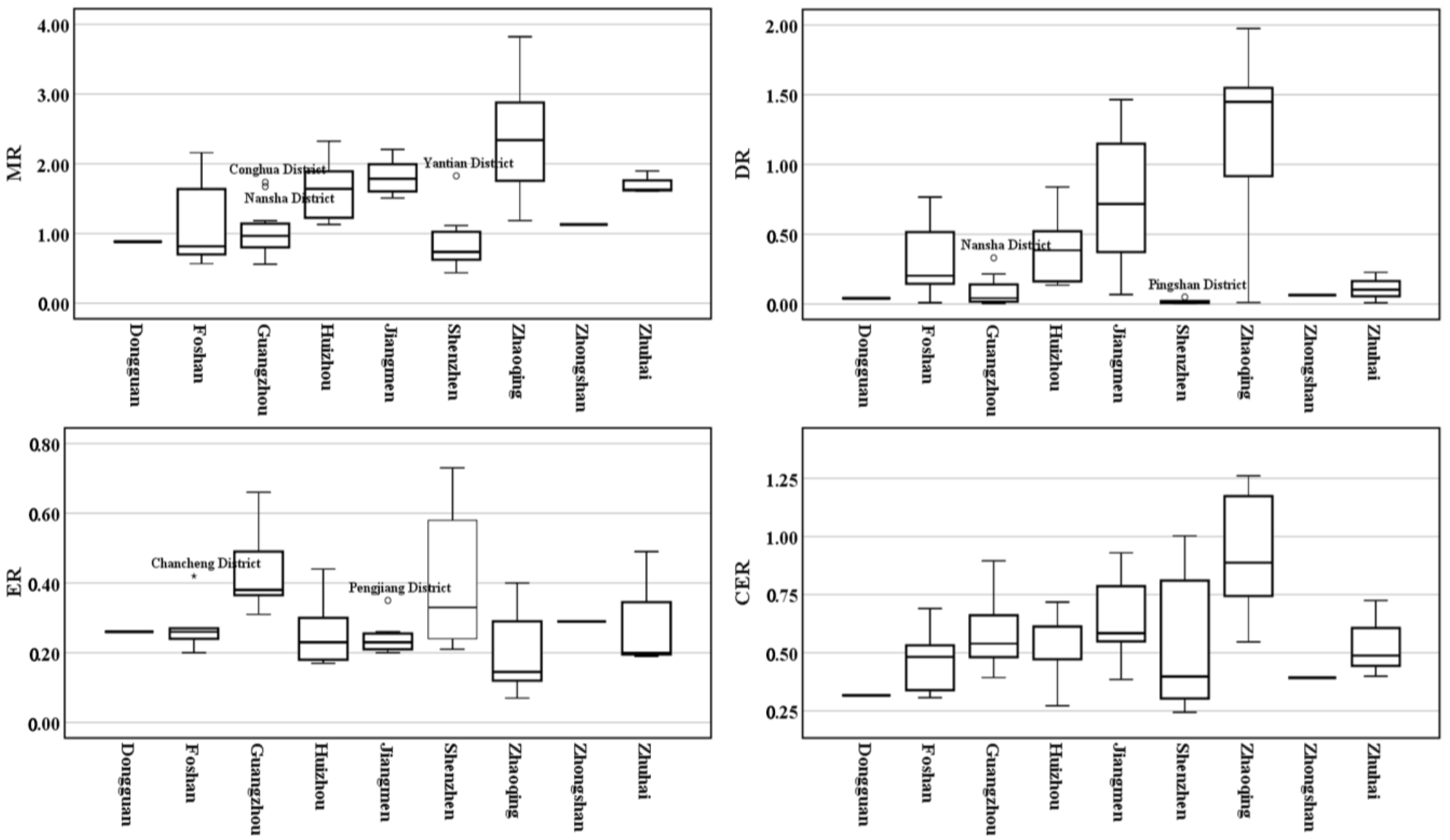
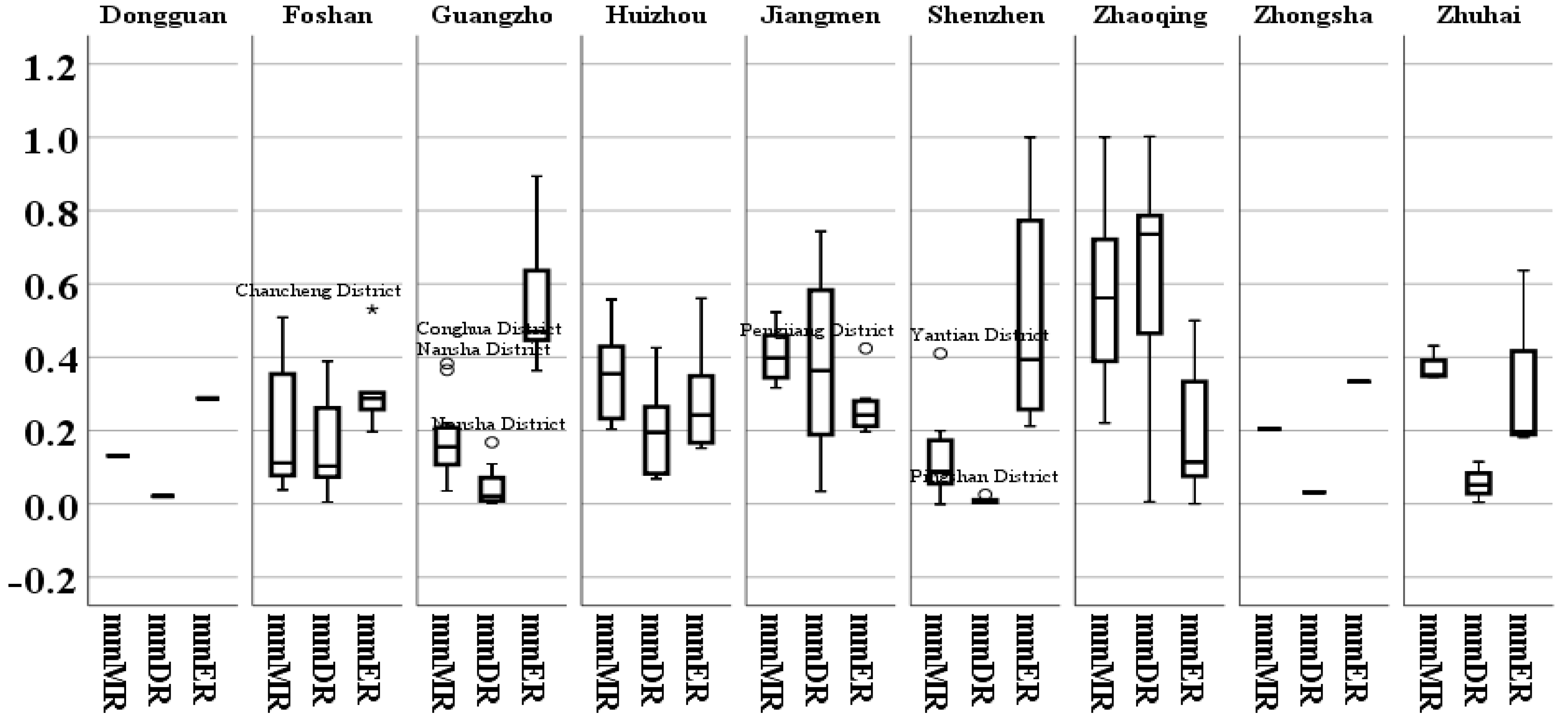
3.1. Morphological Resilience
3.2. Density Resilience
3.3. Economic Resilience
3.4. Comprehensive UER
4. Discussion
4.1. Framework of UER Evaluation
4.2. Evaluation and Spatial Difference of UER Indicators
4.3. Policy Implications for Improving UER
4.4. Limits of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alberti, M.; Marzluff, J.M. Ecological resilience in urban ecosystems: Linking urban patterns to human and ecological functions. Urban Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhai, G.; Xu, L.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, W. Assessment methods of urban system resilience: From the perspective of complex adaptive system theory. Cities 2021, 112, 103141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cui, Z.; Lin, J.; Xie, J.; Kun, S.U. The coupling relationship between urbanization and ecological resilience in the Pearl River Delta. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, G.; Zheng, J. A framework for measuring urban ecological resilience under high-quality development. J. Nat. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ. 2022, 56, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- McPhearson, T.; Andersson, E.; Elmqvist, T.; Frantzeskaki, N. Resilience of and through urban ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaans, M.; Waterhout, B. Building up resilience in cities worldwide—Rotterdam as participant in the 100 Resilient Cities Programme. Cities 2017, 61, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Hamann, M.; Kuiper, J.J.; Andersson, E.; Guerry, A.D. Blending Ecosystem Service and Resilience Perspectives in Planning of Natural Infrastructure: Lessons from the San Francisco Bay Area. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 601136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Nagargoje, S.; Dey, S.; Nandish, S.K.; Jaiswal, A. Urban Vulnerability: A Review of the Methodologies Adopted Globally to Assess Vulnerability of Cities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Construction Real Estate Infrastructure and Projects (CRIP) Management, Pune, India, 23–25 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Xiu, C.; Feng, X.; Mei, D.; Wei, Y. A comprehensive assessment of urban resilience and its spatial differentiation in China. World Reg. Stud. 2019, 28, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Rafael, S.; Martins, H.; Sá, E.; Carvalho, D.; Borrego, C.; Lopes, M. Influence of urban resilience measures in the magnitude and behaviour of energy fluxes in the city of Porto (Portugal) under a climate change scenario. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, M.; Saini, M.; Areendran, G.; Imdad, K.; Sarma, K.; Sajjad, H. Assessing Wetland ecosystem health in Sundarban Biosphere Reserve using pressure-state-response model and geospatial techniques. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 26, 100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazbavi, Z.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Gholamalifard, M.; Davudirad, A.A. Watershed health assessment using the pressure-state-response (PSR) framework. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhu, L.; Meng, J. Fuzzy evaluation of the ecological security of land resources in mainland China based on the Pressure-State-Response framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D. Urban Resilience Assessment Based on Pressure-State-Response Model—A Case Study of HuangShi City. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Friend, A.M.; Rapport, D.J. Evolution of macro-information systems for sustainable development. Ecol. Econ. 1991, 3, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, L.; Xu, S. The Relationships of Supporting Services and Regulating Services in National Forest City. Forests 2022, 13, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, F.; Yan, H.; Zhang, F.; Wei, X. Impacts of urbanization-induced land-use changes on ecosystem services: A case study of the Pearl River Delta Metropolitan Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Yuan, M.J.; Hu, M.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Xia, B.C. Evaluation of ecological security and influencing factors analysis based on robustness analysis and the BP-DEMALTE model: A case study of the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, Y.P.; Gao, P.P.; Xia, B.C. A Mamdani fuzzy inference approach for assessing ecological security in the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, C.L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q. Evaluation of urban resilience of Dalian city based on the perspective of “Size-Density-Morphology”. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 2315–2328. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.L.; Zhang, G.Y.; Xue, D.S. High-quality development of urban agglomerations in China and construction of science and technology collaborative innovation community. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2898–2908. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Chen, J.; Xue, T.; Shen, H. The Economic Resilience Cycle Evolution and Spatial-Temporal Difference of Tourism Industry in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from 2000 to 2019. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Noble, I.; Hellmann, J.; Coffee, J.; Murillo, M.; Chawla, N. University of Notre Dame Global Adaptation Index Country Index Technical Report; University of Notre Dame: Notre Dame, IN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kouklis, G.R.; Yiannakou, A. The Contribution of Urban Morphology to the Formation of the Microclimate in Compact Urban Cores: A Study in the City Center of Thessaloniki. Urban Sci. 2021, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.P. Study on the Temporal and Spatial Features of Urban Resilience in Lanzhou. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Q. Analysis on the Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Urban Resilience Based on “Size-Density-Morphology”—A Case of Cheng Demian Development Zone. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan Normal University, Sichuan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Li, D.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, J. Influencing factors and their influencing mechanisms on urban resilience in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.W.; Zaidi, S.; Khan, N.R.; Mirza, F.M.; Ou, F.H.; Kirmani, S. The impact of natural resources, human capital, and foreign direct investment on the ecological footprint: The case of the United States. Resour. Policy 2019, 63, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.D.; Fu, B.J.; Zhao, W.W. Source-sink landscape theory and its ecological significance. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Han, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z. Application of the source–sink landscape method in the evaluation of agricultural non-point source pollution: First estimation of an orchard-dominated area in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 252, 106910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, M.; Rees, W. Our Ecological Footprint: Reducing Human Impact on the Earth; New Society Publishers: Gabriola Island, BC, Canada, 1997; Volume 19, pp. 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.C. Temporal Dynamics and Spatial Patterns of China’s Ecological Footprints; Chemical Industry Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 006–012. [Google Scholar]
- Special Report on the Per Capita Consumption of Main Food in Guangdong Households (Edition 2019). Available online: https://www.docin.com/p-2379423978.html (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Guangdong Statistical Yearbook. 2021. Available online: http://stats.gd.gov.cn/gdtjnj/content/post_3557537.html (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Monfreda, C.; Wackernagel, M.; Deumling, D. Establishing national natural capital accounts based on detailed Ecological Footprint and biological capacity assessments. Land Use Policy 2004, 21, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.Y. Temporal and Spatial Changes of Land Natural Capital in Xianyang City Based on Improved Three-Dimensional Ecological Footprint Model. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qing, F.; Fang, D. Study on the Influencing factors of urban economic resilience in post epidemic Era—A case study of Kunming City. J. Urban Manag. 2021, 10, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuguang, S.; Gang, P.; Yunyun, M.; Nan, Z. Testing the applicability of Wagner’s Law in China based on reconstruction of government expenditure indicators. China Financ. Econ. Rev. 2015, 4, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhtarov, S.; Mammadov, I.; Humbatova, S. The Relationship Between Government Expenditures on Education and Economic Growth: The Case of Azerbaijan. Res. World Econ. 2020, 11, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Duan, J.; Xu, X.R. Comprehensive measure methods of regional multi-dimensional development and their applications. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar]
- WWF; OPF; Institute of Geographical Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Ecological Footprint Report 2019; Guangdong People’s Press: Guangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Q.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mou, F. Research Progress in Ecological Carrying Capacity Implications, Assessment Methods and Current Focus. J. Resour. Ecol. 2017, 8, 514–525. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Tian, H.; Fu, B.; Zhao, X. Development of a new index for integrating landscape patterns with ecological processes at watershed scale. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, P.C.; Graham, D.J.; Noland, R.B. A meta-analysis of estimates of urban agglomeration economies. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2009, 39, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; He, S.; Zhang, F.Q. Relationship between FDI, fiscal expenditure and green total-factor productivity in China: From the perspective of spatial spillover. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.L. Spatial Optimization Path of Urban Agglomerations from an Ecosystem-Like Perspective: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Filho, W.L.; Barbir, J.; Sima, M.; Kalbus, A.; Nagy, G.J.; Paletta, A.; Villamizar, A.; Martinez, R.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Pereira, M.J.; et al. Reviewing the role of ecosystems services in the sustainability of the urban environment: A multi-country analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Indicator | Data | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| MR | Land use data | Geographic Data Sharing Infrastructure, Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn) (accessed on date 14 May 2023) Guangdong Statistical Yearbook 2021 (http://stats.gd.gov.cn/) (accessed on date 14 May 2023) |
| DR | Average food consumption; fossil energy consumption; number of permanent residents; various types of land use. | |
| ER | Proportion of GDP of tertiary industry (30%); per capita GDP (30%); total retail sales of social consumer goods (15%); education investment (10%); science and technology investment (15%). | Guangdong Statistical Yearbook 2021 (http://stats.gd.gov.cn/) (accessed on date 14 May 2023) |
| MR | DR | ER | CER | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | |
| PRD | 1.443 | 0.716 | 0.407 | 0.542 | 0.318 | 0.151 | 0.617 | 0.249 |
| Guangzhou | 1.035 | 0.385 | 0.090 | 0.110 | 0.428 | 0.115 | 0.591 | 0.153 |
| Shenzhen | 0.874 | 0.414 | 0.017 | 0.014 | 0.418 | 0.202 | 0.556 | 0.302 |
| Foshan | 1.177 | 0.690 | 0.328 | 0.307 | 0.278 | 0.084 | 0.470 | 0.155 |
| Dongguan | 0.884 | / | 0.041 | / | 0.260 | / | 0.317 | / |
| Huizhou | 1.642 | 0.491 | 0.408 | 0.289 | 0.264 | 0.111 | 0.538 | 0.172 |
| Zhongshan | 1.131 | / | 0.063 | / | 0.290 | / | 0.392 | / |
| Zhuhai | 1.712 | 0.161 | 0.113 | 0.109 | 0.293 | 0.170 | 0.537 | 0.168 |
| Jiangmen | 1.814 | 0.261 | 0.756 | 0.538 | 0.244 | 0.052 | 0.653 | 0.188 |
| Zhaoqing | 2.369 | 0.861 | 1.227 | 0.605 | 0.198 | 0.115 | 0.927 | 0.256 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Xu, S. Assessment of Urban Ecological Resilience Based on PSR Framework in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Land 2023, 12, 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12051089
Zhang Q, Huang T, Xu S. Assessment of Urban Ecological Resilience Based on PSR Framework in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Land. 2023; 12(5):1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12051089
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiongrui, Tao Huang, and Songjun Xu. 2023. "Assessment of Urban Ecological Resilience Based on PSR Framework in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China" Land 12, no. 5: 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12051089
APA StyleZhang, Q., Huang, T., & Xu, S. (2023). Assessment of Urban Ecological Resilience Based on PSR Framework in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Land, 12(5), 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12051089












