The Impact of Anthropogenic Activities and Natural Factors on the Grassland over the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Inner Mongolia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
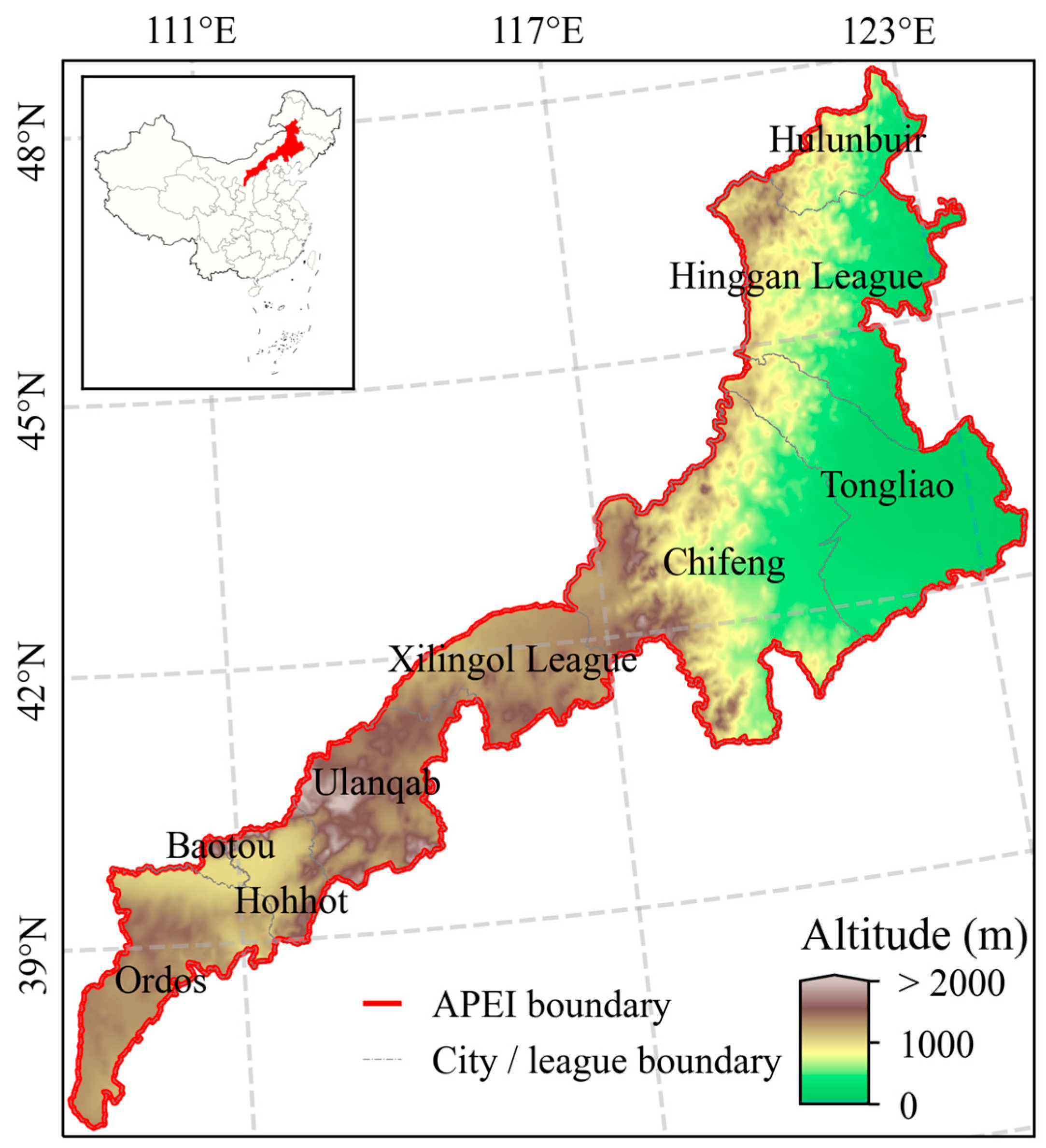
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Quantity and Quality Change
2.3.2. Driving Mechanism of Grassland Quality Change
2.3.3. Classification of Grassland Types Based on Driving Forces
2.3.4. Influencing Factor Analysis for Grassland Quality
3. Results
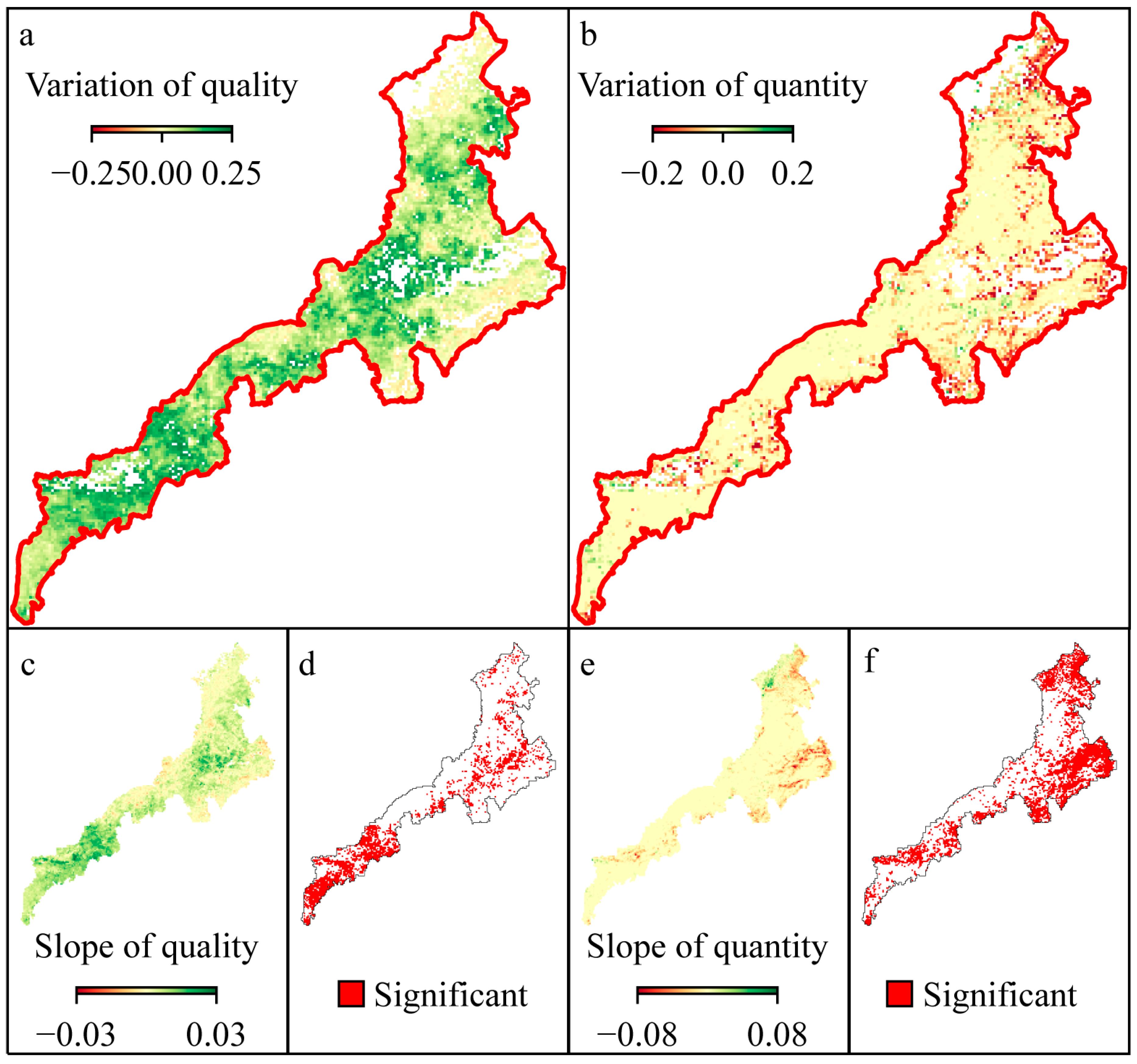
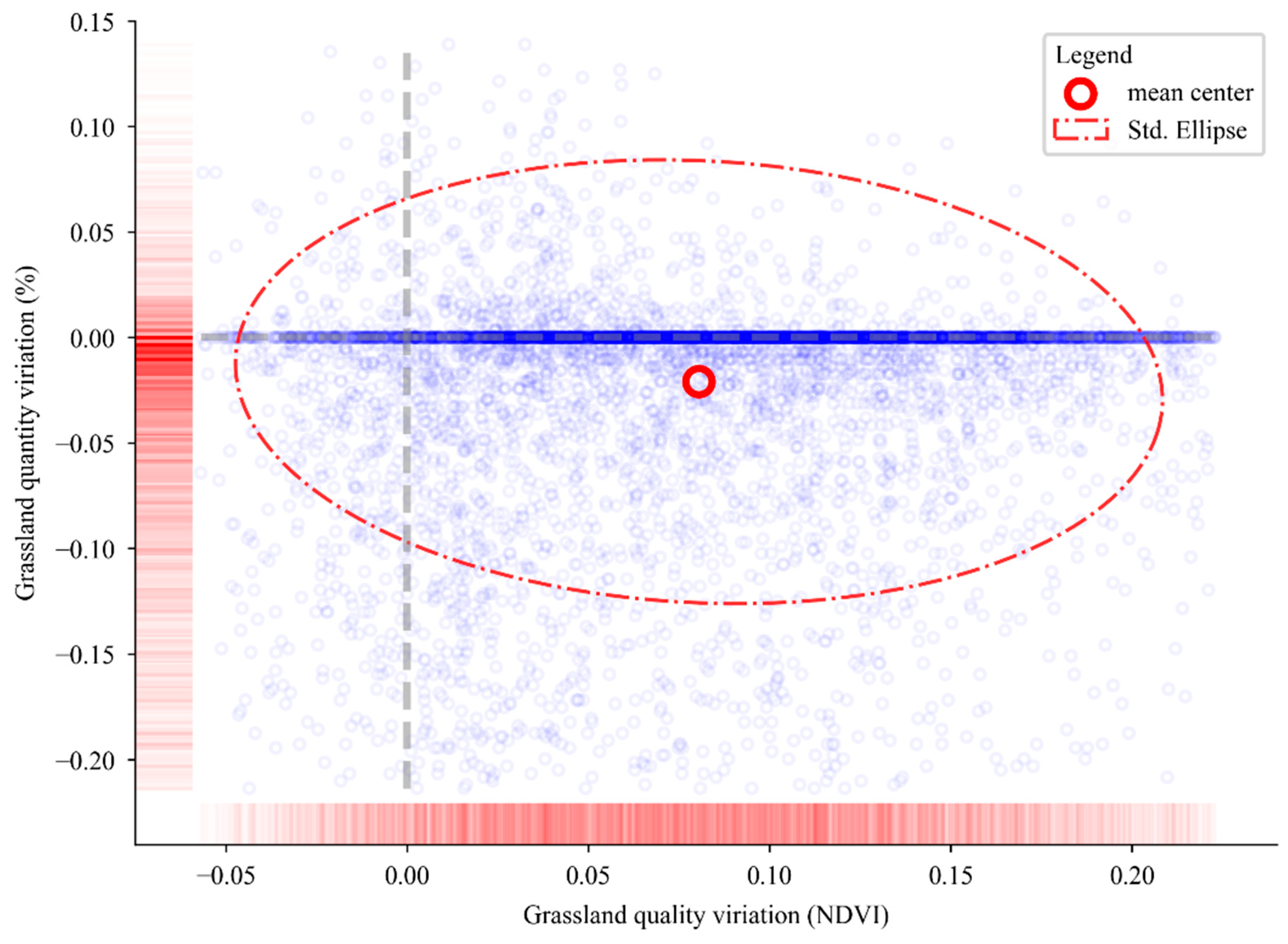
3.1. Variations of Grassland in APEI from 2010 to 2020
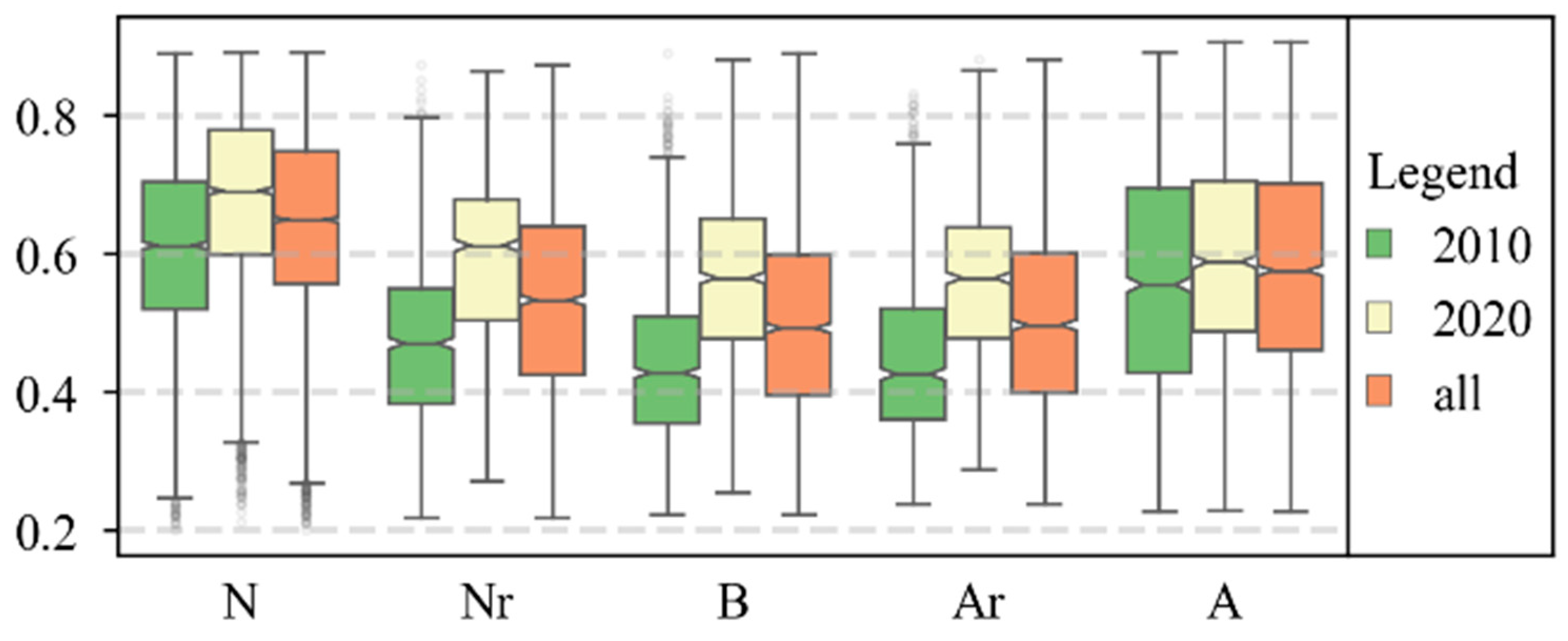
3.2. Classification and Characterization of Grassland Based on Driving Mechanisms
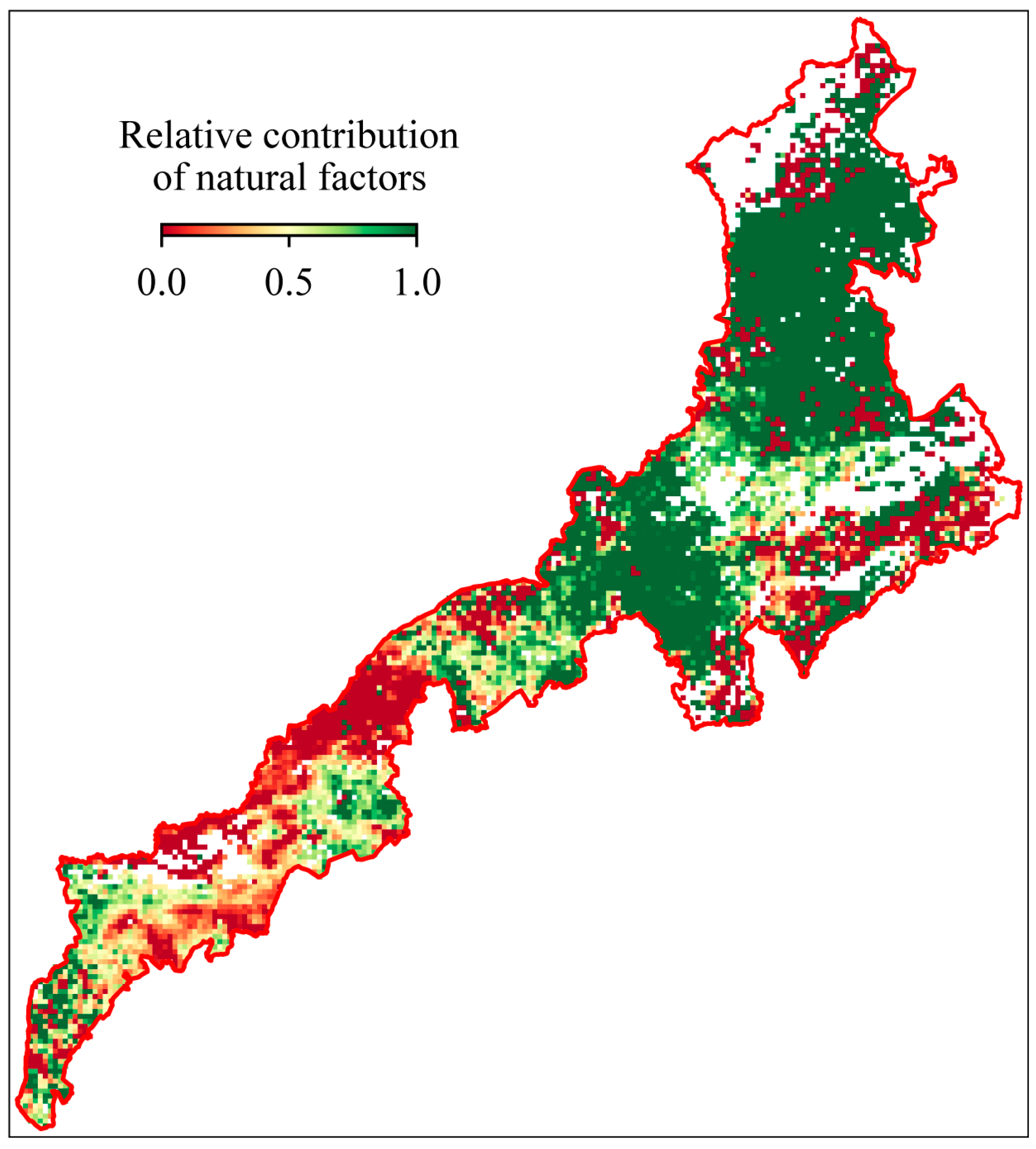
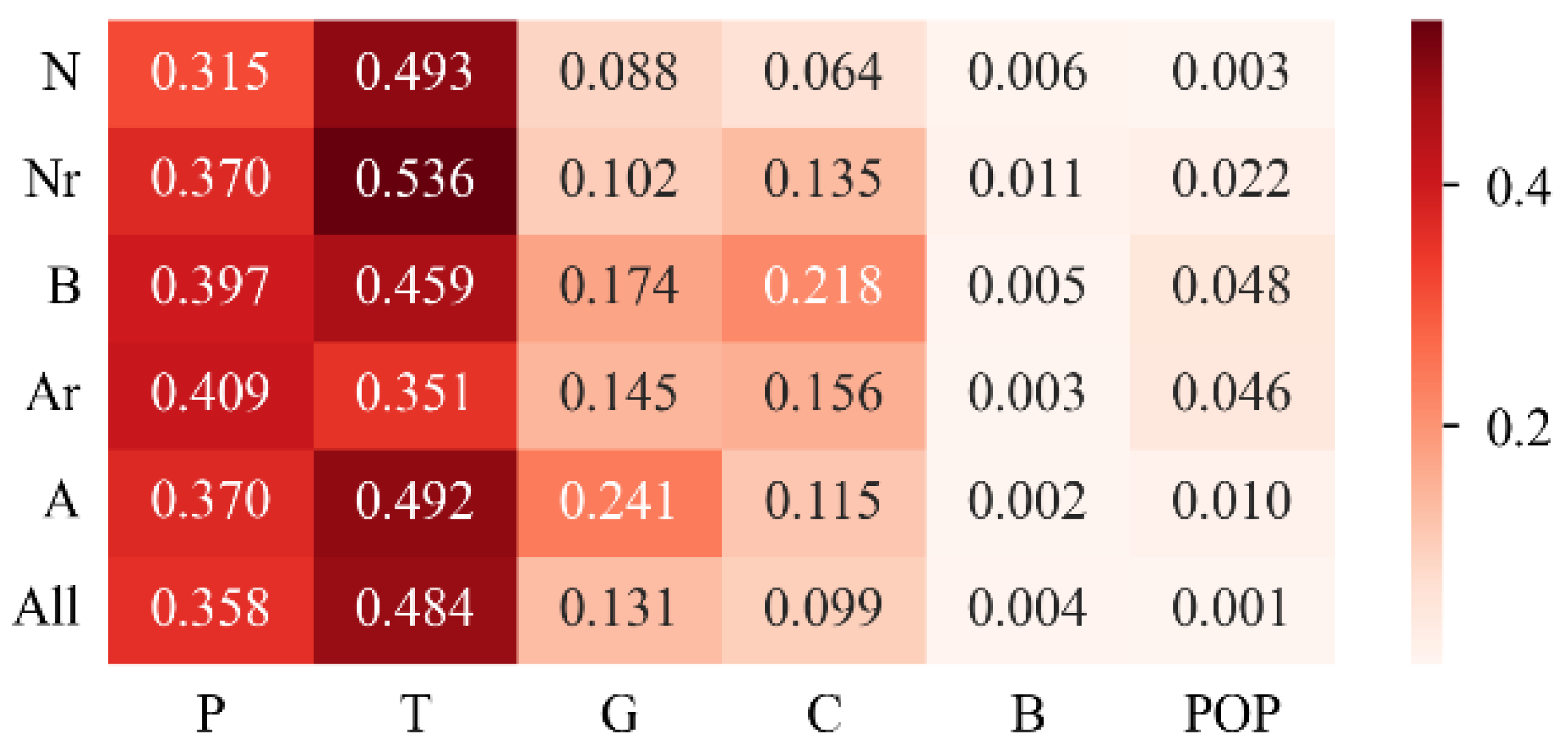
3.3. Analysis of the Influencing Factors of Grassland Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial-Temporal Evolution Determination
4.2. Anthropogenic and Climatic Attributes
4.3. Grassland Quality Change Drivers
4.4. Limitations and Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global Consequences of Land Use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pielke, R.A. Land Use and Climate Change. Science 2005, 310, 1625–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Global Land Use Change, Economic Globalization, and the Looming Land Scarcity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S. Economic geographical survey in one of farming-grazing transitional zones-North Cha, Cha League and Xi League. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1953, 19, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Man, W.; Liu, W.; Nie, Q. Spatial Change of the Farming–Pastoral Ecotone in Northern China from 1985 to 2021. Land 2022, 11, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X. Development of Quantitative Methods for Detecting Climate Contributions to Boundary Shifts in Farming-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Yu, D.; Georgescu, M.; Han, Z.; Wu, J. Impacts of Land Use and Land Cover Change on Regional Climate: A Case Study in the Agro-Pastoral Transitional Zone of China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Ouyang, Z. Responses of Landscape Structure to the Ecological Restoration Programs in the Farming-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuyun, D.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.; Hou, A.; Crusiol, L.G.T.; Yu, L.; Chen, R.; Sun, Z. The Spatiotemporal Change of Cropland and Its Impact on Vegetation Dynamics in the Farming-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 805, 150286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, M.; Xie, G.; Zhen, L. Evaluating the Impacts of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Service Values under Multiple Scenarios in the Hunshandake Region of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, D.; Zhao, X.; Fan, J. Effects of Land-Use Conversions on the Ecosystem Services in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, B.; He, C.; Shao, R. Detecting Vegetation Variations and Main Drivers over the Agropastoral Ecotone of Northern China through the Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, X. Impact of Extreme Climates on Vegetation from Multiple Scales and Perspectives in the Agro-Pastural Transitional Zone of Northern China in the Past Three Decades. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Lv, S.-H.; Han, Y.; Nie, Y. Shifting Farming–Pastoral Ecotone in China under Climate and Land Use Changes. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y. The Trend of Vegetation Greening and Its Drivers in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China, 2000–2020. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Yu, D.; Wu, J. Relationship between Paired Ecosystem Services in the Grassland and Agro-Pastoral Transitional Zone of China Using the Constraint Line Method. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 240, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Tang, H.; Lu, Y. Exploring Subjective Well-Being and Ecosystem Services Perception in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, A.; Liang, C. Historical Landscape Dynamics of Inner Mongolia: Patterns, Drivers, and Impacts. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1579–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.A.; Borjigin, E.; Zhang, H. Mongolian Nomadic Culture and Ecological Culture: On the Ecological Reconstruction in the Agro-Pastoral Mosaic Zone in Northern China. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 62, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, Z.; Tan, M.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X. Changing Patterns in Farming–Pastoral Ecotones in China between 1990 and 2010. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, D.; Zhao, X.; Fan, J.; Li, J.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhan, R. Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics of Ecosystem Service Losses in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Pei, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Revegetation Projects Significantly Improved Ecosystem Service Values in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China in Recent 20 Years. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, H.; Liu, M.; Shen, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Luo, J. Quantifying Impacts of Climate Dynamics and Land-Use Changes on Water Yield Service in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 809, 151153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Chen, L.; Shankman, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Excessive Reliance on Afforestation in China’s Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: Lessons in Ecological Restoration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 104, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Lü, Z. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Variations in Land Use on the Loess Plateau of China during 1986–2010. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohabir, N.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, R. Chinese Floating Migrants: Rural-Urban Migrant Labourers’ Intentions to Stay or Return. Habitat Int. 2016, 60, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Zhang, J. The Preference for Larger Cities in China: Evidence from Rural-Urban Migrants. China Econ. Rev. 2017, 43, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Song, X.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G. Spatiotemporal Vegetation Cover Variations Associated with Climate Change and Ecological Restoration in the Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 209–210, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Guo, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, S. How Did the Chinese Loess Plateau Turn Green from 2001 to 2020? An Explanation Using Satellite Data. CATENA 2022, 214, 106246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, K. Quantitative Contributions of Climate Change and Human Activities to Vegetation Changes over Multiple Time Scales on the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, L.; Cao, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, J.; Xu, X.; Tian, H. Benefits, Potential and Risks of China’s Grassland Ecosystem Conservation and Restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Cao, S. Net Value of Grassland Ecosystem Services in Mainland China. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, D.R.; Guodong, H.; Xiangyang, H.; Michalk, D.L.; Fujiang, H.; Jianping, W.; Yingjun, Z. Innovative Grassland Management Systems for Environmental and Livelihood Benefits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8369–8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mara, F.P. The Role of Grasslands in Food Security and Climate Change. Ann. Bot. 2012, 110, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafalska, A.; Walkiewicz, A.; Osborne, B.; Klumpp, K.; Bieganowski, A. Variation in Methane Uptake by Grassland Soils in the Context of Climate Change—A Review of Effects and Mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, X.; Tang, Y.; Gu, S.; Zhou, L. Alpine Grassland Degradation and Its Control in the Source Region of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Grassl. Sci. 2005, 51, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Tang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, H.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, G.; Chen, X. Unraveling the Relative Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Grassland Productivity in Central Asia over Last Three Decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Hou, M.; Liang, T.; Feng, Q.; Meng, X.; Liu, J.; Bao, X.; Gao, H. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Grassland Aboveground Biomass and Its Driving Factors in North China over the Past 20 Years. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souther, S.; Loeser, M.; Crews, T.E.; Sisk, T. Drought Exacerbates Negative Consequences of High-intensity Cattle Grazing in a Semiarid Grassland. Ecol. Appl. 2019, 30, e02048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Anthropogenic Contributions Dominate Trends of Vegetation Cover Change over the Farming-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dietz, T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Alberti, M.; Folke, C.; Moran, E.; Pell, A.N.; Deadman, P.; Kratz, T.; Lubchenco, J.; et al. Complexity of Coupled Human and Natural Systems. Science 2007, 317, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Wu, J.; Huang, J. Distinguishing between Human-Induced and Climate-Driven Vegetation Changes: A Critical Application of RESTREND in Inner Mongolia. Landsc. Ecol. 2012, 27, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Fiedler, S.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, W.; Hassan, W.; Mărgărint, M.C.; Tarolli, P.; et al. Disentangling Climatic and Anthropogenic Contributions to Nonlinear Dynamics of Alpine Grassland Productivity on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 281, 111875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Xia, F.; Chen, Q.; Huang, J.; He, Y.; Rose, N.; Rozelle, S. Grassland Ecological Compensation Policy in China Improves Grassland Quality and Increases Herders’ Income. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Xu, L.; Pan, X.; Hu, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Shao, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, X. Spatio-Temporal Variations in Vegetation Types Based on a Climatic Grassland Classification System during the Past 30 years in Inner Mongolia, China. CATENA 2019, 185, 104298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, J. Monthly Precipitation Data Set with 1 Km Resolution in China from 1960 to 2020. Sci. Data Bank 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Vegetation in the Yellow River Basin, China during 2000–2020. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Geerken, R. Discrimination between Climate and Human-Induced Dryland Degradation. J. Arid Environ. 2003, 57, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. The Relative Roles of Climate Variations and Human Activities in Vegetation Change in North China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 87–88, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, G.F. The Data Model Concept in Statistical Mapping. Int. Yearb. Cartogr. 1967, 7, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Liu, M.; Gao, H.; Gong, P. Urban Growth Rates, Trajectories, and Multi-Dimensional Disparities in China. Cities 2022, 126, 103717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Lyu, F.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal Change and Drivers of Ecosystem Quality in the Loess Plateau Based on RSEI: A Case Study of Shanxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.-F. Optimal Discretization for Geographical Detectors-Based Risk Assessment. GIScience Remote Sens. 2018, 50, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q. Geemap: A Python Package for Interactive Mapping with Google Earth Engine. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshan, T.M.; Li, Z.; Kang, W.; Wolf, L.J.; Fotheringham, A.S. Mgwr: A Python Implementation of Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression for Investigating Process Spatial Heterogeneity and Scale. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordahl, K.; Bossche, J.V.D.; Fleischmann, M.; Wasserman, J.; McBride, J.; Gerard, J.; Tratner, J.; Perry, M.; Badaracco, A.G.; Farmer, C.; et al. Geopandas/Geopandas: V0.8.1. 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/3946761 (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer, S.; Hamman, J. Xarray: N-D Labeled Arrays and Datasets in Python. J. Open Res. Softw. 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Su, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, J. Assessing the Impacts of Grain-for-Green Programme on Ecosystem Services in Jinghe River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau Is Approaching Sustainable Water Resource Limits. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; John, R.; Sun, G.; Fan, P.; Henebry, G.M.; Fernández-Giménez, M.E.; Zhang, Y.; Park, H.; Tian, L.; Groisman, P.; et al. Prospects for the Sustainability of Social-Ecological Systems (SES) on the Mongolian Plateau: Five Critical Issues. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 123004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Xue, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T. Wind Erosion Occurrence Probabilities Maps in the Watershed of the Ningxia–Inner Mongolia Reach of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 75, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Ye, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Prediction of Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Ecosystem Service Variation in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Jiang, D.; Musa, A.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, M.; Wang, Y. Effectiveness of Shrub Planting and Grazing Exclusion on Degraded Sandy Grassland Restoration in Horqin Sandy Land in Inner Mongolia. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 74, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, O.J. Grassland Ecosystems in China: Review of Current Knowledge and Research Advancement. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Piao, S.; Myneni, R.B.; Huang, M.; Zeng, Z.; Canadell, J.G.; Ciais, P.; Sitch, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Arneth, A.; et al. Greening of the Earth and Its Drivers. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Datasets | Spatial Resolution | Year | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use/cover | 250 m | 2010, 2020 | MODIS |
| Temperature | 1000 m | 2010, 2020 | MODIS |
| Precipitation | 1000 m | 2010, 2020 | SCIENCE DATA BANK |
| Population | 1000 m | 2010, 2019 | REDC |
| NDVI | 250 m | 2010, 2020 | MODIS |
| SOB | Driver | Driver Division | Contribution Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCI | SAI | CCI | CAI | ||
| >0 | CI & AI | >0 | >0 | SCI/SOB | SAI/SOB |
| CI | >0 | <0 | 1 | 0 | |
| AI | <0 | >0 | 0 | 1 | |
| <0 | CI & AI | <0 | <0 | SAI/SOB | SCI/SOB |
| CI | <0 | >0 | 1 | 0 | |
| AI | >0 | <0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Name of Indices | Quality | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Proportion of grid cells where the index variations increased | 89.80% | 8.94% |
| Proportion of grid cells where the index variations decreased | 10.20% | 91.06% |
| Mean values of the variations | 0.08 | −2.10% |
| Regions | Contribution of Anthropogenic | Contribution of Natural Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Areas where the grassland quality improved | 33.23% | 66.77% |
| Areas where the grassland quality declined | 74.96% | 25.04% |
| Areas where the grassland quantity improved | 42.28% | 57.72% |
| Areas where the grassland quantity declined | 36.53% | 63.47% |
| APEI | 37.48% | 62.52% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, F.; Pan, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z. The Impact of Anthropogenic Activities and Natural Factors on the Grassland over the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Inner Mongolia. Land 2023, 12, 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12112009
Lyu F, Pan Y, Yu L, Wang X, Yu Z. The Impact of Anthropogenic Activities and Natural Factors on the Grassland over the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Inner Mongolia. Land. 2023; 12(11):2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12112009
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Feinan, Ying Pan, LinJun Yu, Xiang Wang, and Zhenrong Yu. 2023. "The Impact of Anthropogenic Activities and Natural Factors on the Grassland over the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Inner Mongolia" Land 12, no. 11: 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12112009
APA StyleLyu, F., Pan, Y., Yu, L., Wang, X., & Yu, Z. (2023). The Impact of Anthropogenic Activities and Natural Factors on the Grassland over the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Inner Mongolia. Land, 12(11), 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12112009






