Abstract
Faced with the dual challenges of ecological degradation and economic deceleration, promoting urban green high-quality development (UGHQD) is pivotal for achieving economic transformation, ecological restoration, and regional sustainable development. While the existing literature has delved into the theoretical dimensions of UGHQD, there remains a notable dearth of empirical studies that quantitatively assess its developmental levels, spatio-temporal evolution, and driving factors. This study examines 107 cities of China’s five major urban agglomerations from 2003 to 2020, constructing a comprehensive evaluation indicator system for UGHQD. By employing methodologies, including the Dagum Gini coefficient, Kernel density estimation, Markov chain, and geographical detector, this study extensively assesses the spatial difference, dynamic evolution, and underlying driving forces of UGHQD in these urban agglomerations. The findings indicate: (1) The UGHQD level of the five major urban agglomerations has witnessed a consistent year-over-year growth trend, with coastal agglomerations like the Pearl River Delta (PRD) and Yangtze River Delta (YRD) outperforming others. (2) Pronounced regional differences exist in UGHQD levels across the urban agglomerations, with inter-regional differences primarily contributing to these differences. (3) The dynamic evolution of UGHQD distribution generally transitions from a centralized to a decentralized pattern, with a marked “club convergence” characteristic hindering cross-type leaps. (4) While a range of factors drive UGHQD in these agglomerations, technological innovation stands out as the principal factor inducing spatial differentiation. The comprehensive analysis and findings presented in this research not only contribute to academic knowledge but also hold practical implications for policymakers and practitioners striving for environmentally conscious land use planning and urban management.
1. Introduction
Currently, the world faces increasingly serious climate change and ecological degradation issues, which are progressively becoming major challenges to green economic recovery and sustainable social development [1]. In this context, there is a growing international consensus on the urgent need to foster green growth and cultivate a low-carbon, circular economy [2,3]. The United Nations World Commission on Environment and Development initially introduced the concept of sustainable development in 1987 through Our Common Future. Subsequently, David Pearce expanded upon this concept in his seminal work Blueprint for a Green Economy, which closely aligns with the central tenets of sustainable development and provides key guidelines for balancing economic growth with environmental preservation [4,5,6]. As the world’s highest consumer of energy and a significant source of carbon emissions, China has undergone a phase of rapid economic growth marked by intensive resource use and elevated energy consumption [7,8]. Although China has successfully realized its aspirational objective of creating a comprehensively moderately prosperous society, this achievement has come at considerable environmental and resource costs [9,10]. Given the dual challenges of limited resources and ecological vulnerability, China’s traditional development model, primarily reliant on increasing inputs of production factors, is no longer sustainable [11]. Consequently, China urgently needs to accelerate the transformation of its development model and shift its economy from being factor-driven to one focused on green, low-carbon development through “quality change”, “efficiency change”, and “driving force change” [12,13].
As key vehicles for industrialization and modernization, cities are experiencing significant expansion in size and population. Forecasts suggest that by 2050, nearly 67% of the global populace will inhabit urban areas. This heightened urban concentration promotes industrialization while simultaneously exacerbating environmental and resource-related challenges [14,15]. Using China as an illustrative case, data from the National Bureau of Statistics indicate that urban energy consumption constituted 85% of the national total in 2020 [16], thereby aggravating environmental degradation. Recently, urban agglomerations—advanced forms of spatial organization at mature stages of urban development—have emerged as strategic epicenters for regional economic and social advancement. China’s 14th Five-Year Plan (2020–2025) emphasizes the role of such agglomerations in propelling innovations in intelligent manufacturing; the digital economy; and sustainable, low-carbon industries [17]. Notably, the five major urban agglomerations, the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), the Pearl River Delta (PRD), Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH), the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River (MYR), and Chengdu-Chongqing (CC), are the most economically advanced and talent-attractive regions in China, serving as primary conduits linking China’s economy with the global economic landscape [18]. However, due to the influence of various factors, such as population, geography, policies, educational resources, and development patterns, urban agglomerations differ greatly with respect to development potential, technological innovation capacity, and infrastructure development [19]. Thus, will these differences in development factors lead to serious spatial imbalances in urban green high-quality development (UGHQD) among urban agglomerations? Moreover, China is at a pivotal juncture in its urbanization trajectory, and high-pollution and high-energy-consumption industries still play an important role in pulling economic growth in development [20]. As crucial nodes of China’s new urbanization agenda, these agglomerations are inevitably the hotspots for various environmental pollution issues [21,22]. Within this context, UGHQD, as an innovative development concept that is green-oriented and takes into account the synergistic progress of the economy, society, and technological innovation as well as the ecological environment, offers a strategic approach to solving the problem.
In view of this, this study focuses on a representative sample of 107 cities in China’s five major urban agglomerations selected for their typicality in terms of economic scale, regional attributes, and policy environments. A multidimensional evaluation framework is constructed to assess UGHQD, incorporating factors related to economic development, social livelihood, ecological environment, and technological innovation. Initially, the entropy value method is employed to quantify composite scores for UGHQD across these urban agglomerations for the period 2003–2020. Subsequently, spatial differences and the sources of the differences are scrutinized using Dagum’s Gini coefficient and its decomposition techniques. Kernel density estimation and Markov chain analyses are applied to systematically examine the spatio-temporal distribution and evolutionary dynamics of UGHQD within these urban agglomerations. Lastly, the geographical detector is employed to examine the driving factors behind spatial differences in UGHQD. The theoretical contributions of this study can be distilled into three main points. Firstly, this study delves deeper by shifting the empirical research focus to the city level, moving beyond the more commonly referenced provincial samples in the existing literature. Such an approach paves the way for more precise and detailed empirical conclusions. An in-depth examination of spatial differences and the dynamic evolution of UGHQD within China’s five major urban agglomerations helps sharpen our understanding of strategies and pivotal aspects for the future promotion of UGHQD. Secondly, in contrast to existing studies that predominantly utilize green total factor productivity as the primary indicator, this paper constructs a comprehensive evaluation system for UGHQD. This system evaluates based on four dimensions, economic development, social livelihood, ecological environment, and technological innovation, thereby more closely aligning with the objectives of UGHQD. Thirdly, beyond simply examining the spatio-temporal evolution of UGHQD in China’s five major urban agglomerations, this study employs appropriate methodologies to unveil the driving factors in spatial differences of UGHQD, offering empirical insights for crafting sustainable development strategies for contemporary urban agglomerations.
2. Literature Review
As a hot topic in recent years, high-quality development serves as a major strategic plan designed to address the shortcomings of previous development approaches, overcome technological bottlenecks, and reduce income inequality [23]. It signifies a strategic evolutionary path and an institutional innovation process that shifts economic growth from “scale expansion” and “factor-driven” to innovation-driven [24,25]. Integrating the concept of high-quality development into the framework of socialist modernization is pivotal as China’s economy transitions to a new era [26]. In this context, “green” has emerged as an essential aspect of economic development. The new focus is on balancing economic efficiency with environmentally friendly development models, taking into full account resource utilization efficiency and environmental pollution emissions [27,28]. UGHQD represents a high degree of integration between “green development” and “high-quality development” [29]. Its connotations are multifaceted: it advocates for low-carbon, low-pollution, and high-efficiency production modes while sustaining economic growth [30]. These modes foster the advancement and deployment of clean energy, refine the composition of the energy matrix, alleviate ecological burdens, and improve resource utilization efficiency [31,32]. Furthermore, UGHQD places a heightened focus on social sustainability, emphasizing that economic growth should not solely prioritize material gains but that social benefits such as equity, sharing, and inclusivity should also be considered [33]. This necessitates addressing issues like job creation, narrowing income gaps, and improving education and healthcare conditions [34,35]. Lastly, UGHQD underscores the importance of innovation and technological progress [36,37]. This development paradigm, which places a premium on innovation, is positioned to markedly elevate production efficiency and expedite the transition and enhancement of industrial structures [38]. Overall, UGHQD aims to envision a “win-win-win” scenario for the economy, society, and the environment.
In the realm of assessing the UGHQD level, existing scholarly contributions predominantly fall into two categories: single-indicator and multi-indicator approaches. The single-indicator method primarily evaluates efficiency to determine the UGHQD level, typically using green total factor productivity as the metric. Earlier methodologies tended to rely on traditional approaches such as the Cobb–Douglas production function [39,40]. However, these traditional methods often overlooked the extensive impact of environmental costs and undesirable outputs on economic efficiency, revealing limitations in non-parametric estimations [41]. Consequently, they have evolved into more sophisticated methods, including data envelopment analysis (DEA) [42], super efficiency slacks-based measure (SBM) [43], and stochastic frontier analysis (SFA) [44,45,46]. Although a single total factor productivity measure cannot fully encapsulate all aspects of social economic operation and falls short of capturing the complex nuances of UGHQD, it does provide valuable insights for establishing a more comprehensive measurement system for UGHQD [47,48]. As for multi-indicator measurements, existing studies primarily focus on comprehensive assessments of high-quality developmental levels. Early studies often equated economic growth quality with efficiency, necessitating a more precise delineation of its broader implications [49]. In recent years, scholars have increasingly adopted a more comprehensive view of economic growth quality, arguing that it should possess a richer connotation to complement development speed. Consequently, factors such as green growth [50], industrial upgrading [51], and technological innovation [52] have been incorporated into assessments of economic growth quality. Existing literature mainly employs the five development concepts of innovation, coordination, greenness, openness, and sharing [53] or their derivatives as subsystems [54], or studies construct an indicator system from three subsystems: economic, social, and ecological [55]. Some scholars have also expanded the understanding of high-quality development, constructing indicator systems that consider dimensions like economic structure optimization, resource allocation efficiency, social services, and industrial recycling development [56,57].
From a regional perspective, factors such as geographical location, resource endowment, and environmental regulations collectively contribute to notable differences in green development and high-quality development levels across regions [58,59]. Numerous scholars have conducted in-depth analyses to elucidate these differences’ characteristics and underlying causes, aiming to formulate more precise and targeted strategies for regional synergistic development [60,61]. In the study of regional differences in green development levels and convergence characteristics, the Theil index and β-convergence model are widely used [62]. However, the Theil index cannot describe the dynamic distribution of subgroup samples, nor can it decompose the sources of spatial differences in detail, limiting the accuracy of spatial difference analysis. Researchers have increasingly turned to the Dagum Gini coefficient to circumvent these issues and investigate the regional differences in urban green development along with their root causes [63]. The Dagum Gini coefficient addresses data overlap within sample sets and can effectively identify and trace the sources of regional differences. To describe the evolution of absolute differences in green development levels more accurately, scholars have employed Kernel density estimation methods to analyze the distributional dynamics of regional green development [64,65]. Building on this, some have introduced the Markov transition probability matrix to enhance data expressiveness and explanatory power [66]. While the spatial Durbin model [67] and the dynamic panel quantile model [68] are commonly applied to study the causes of regional differences, they fail to address endogeneity issues in regression analyses adequately. Researchers have adopted the geographical detector model to resolve this, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of interactions among multiple factors and thereby identifying the causes of differences [69]. The geographical detector model is gaining traction in economic, social, and environmental research, offering a valuable tool for scholars in these domains [70,71].
In surveying existing studies, it is evident that research on UGHQD has yielded certain results, establishing a theoretical foundation for this study while leaving room for further exploration. First, concerning the measurement of UGHQD levels, existing studies have predominantly utilized metrics such as green total factor productivity. Comprehensive evaluation frameworks based on an integrated set of indicators are notably scarce. This limitation often hampers the accurate and comprehensive depiction of UGHQD. Second, the majority of existing studies have exclusively explored the spatio-temporal differences in either green development or high-quality development, with few examining the spatio-temporal disparities in UGHQD and the driving factors that contribute to them. As a critical indicator for sustainable urban development, the study of these differences and their drivers holds practical significance; its absence hinders further in-depth research in this area. Third, the existing literature predominantly focuses on nations, provinces, and occasionally inter-provincial regions or watersheds as units of empirical analysis. In contrast, studies employing cities as the spatial dimension for investigation are relatively rare. This paper selects cities as the spatial research unit to more accurately capture the nuanced and precise dynamics of UGHQD.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
Guided by policy frameworks, such as Outline of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Cooperative Development Plan, Pearl River Delta Reform and Development Plan (2008–2020), Integrated Development Plan for the Yangtze River Delta Region, Development Plan for the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration, and Development Plan for the Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration, and drawing on existing research [72], this study systematically categorizes 107 cities within these five major urban agglomerations. The specific distribution of these cities is detailed in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Spatial distribution of China’s five major urban agglomerations.
3.2. Data Sources
This study focuses on China’s five major urban agglomerations, covering the period from 2003 to 2020. The primary data sources included China Statistical Yearbook, China Urban Statistical Yearbook, China Urban and Rural Construction Statistical Yearbook, statistical yearbooks of various prefectures and cities, and the EPS database (https://www.epsnet.com.cn, accessed on 26 April 2023). The number of authorized green patents was obtained from the patent search database of China’s State Intellectual Property Office (SIPO). For data gaps, interpolation methods were employed for imputation. Notably, the per capita real GDP used in this study was based on the GDP deflator of the province where the city is located and was adjusted to constant 2003 prices. Additionally, the urban population figures used in the calculations were based on the total urban population recorded at the end of each year.
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Indicator System
Establishing a scientifically rigorous and practical evaluation indicator system is essential to deeply explore the UGHQD levels of China’s five major urban agglomerations. Three primary considerations were emphasized in developing this system: policy documents, academic research findings, and data availability. Policy documents provided directive guidance for the construction of the indicator system. This study thoroughly reviewed numerous policy documents issued by the Chinese government related to UGHQD. Academic research offered a theoretical foundation for the system’s design. We incorporated insights from scholars on the definition, characteristics, and potential indicator systems of high-quality development and green development, ensuring scientific integrity and the forward-thinking nature of our indicator choices [51,52,53,54,55]. Data availability ensured the operability of the indicator system. Meticulous review and selection processes were applied to each potential indicator’s data sources, guaranteeing representativeness and reliability. The collected data were rigorously pre-processed and validated to mitigate potential biases, ensuring the accuracy and authenticity of the evaluation results. Integrating these considerations, this study proposes a UGHQD indicator system that encompasses four main dimensions, economic development (ED), social livelihood (SL), ecological environment (EE), and technological innovation (TI), featuring a total of 27 fundamental indicators. To ensure the objectivity and rationality of the weights for each indicator, this study calculates the weights of the fundamental indicators within the UGHQD indicator system using the entropy value method. Table 1 provides descriptions of the relevant indicators.
Economic development is a fundamental means to resolve major societal contradictions. To foster UGHQD and enhance both the quality and quantity of economic development, upgrading the driving forces behind economic development while maintaining stable economic growth is essential. Consequently, this study employed real GDP per capita, fixed-asset investment, logistics accessibility, intensity of social consumption, foreign trade dependence, foreign investment dependence, upgradation of the industrial structure, and rationalization of the industrial structure as the foundational indicators to assess the level of economic development.
The social livelihood dimension emphasizes the well-being of individuals, advocating for the continual improvement of people’s livelihoods and social justice. This dimension focuses on elevating the populace’s living standards, ensuring that every resident experiences tangible benefits, happiness, and security. This not only facilitates robust economic development but also lays the groundwork for social stability. Moreover, when people’s livelihoods are adequately safeguarded, cities are more inclined to prioritize environmental sustainability, resulting in a symbiotic relationship between green development and the welfare of the populace. Consequently, this study employs the basic education level, transport infrastructure, public culture level, average wage level, health and medicine level, and internet penetration rate as the key indicators of the social livelihood dimension.
Regarding the ecological environment dimension, the growing global focus on environmental issues has positioned the ecological health of cities as a central evaluative dimension of UGHQD. A thriving ecological environment guarantees a healthy existence for citizens and underpins sustainable economic and social development. Consequently, this study employs green innovation achievements, intensity of science expenditure, intensity of education expenditure, cultivation of innovative talents, and technological innovation achievements as the key indicators of the ecological environment dimension.
The rationale for including technological innovation as a dimension in the UGHQD evaluation index system is derived from its pivotal role in facilitating economic transformation and enhancing resource efficiency. Technological innovation can drive the shift from traditional, polluting industries to low-carbon, clean industries and provide cutting-edge solutions to urban environmental challenges. Therefore, technological innovation is indispensable in steering cities toward green, high-quality development. Consequently, this study employs green innovation achievements, intensity of science expenditure, intensity of education expenditure, and cultivation of innovative talents as the core indicators of the technological innovation dimension.
3.3.2. Dagum Gini Coefficient
Dagum (1997) [73] decomposed the overall Gini coefficient into three components: the intra-regional differences Gw, the inter-regional differences Gnb, and the super-variable density Gt. Due to its capability to effectively decompose and elucidate regional differences, the Dagum Gini coefficient addresses the limitations of traditional measurement methods. In this study, the Dagum Gini coefficient and its decomposition method are employed to systematically investigate the sources of regional differences in the UGHQD level in China’s five major urban agglomerations. This approach allows for the examination of sub-sample distributions that are unaffected by sample overlap. The formula for calculating the Dagum Gini coefficient is as follows:
where G represents the overall Gini coefficient of the UGHQD level of the five major urban agglomerations, yji(yhr) is the UGHQD level of any city within j(h) urban agglomeration, and nj(nh) is the number of cities within j(h) urban agglomeration.
If only the Gini coefficient of the UGHQD level of each city within a region (e.g., within urban agglomeration j) is considered, the formula is as follows:
where μj is the expected value of the UGHQD level of each city in urban agglomeration j, yji(yjr) is the UGHQD level of any city in urban agglomeration j, and nj is the number of cities in urban agglomeration j.
The contribution of intra-regional differences is:
where pj = nj/n, sj = njμj/nμ, and Gw can be interpreted as a weighted average of the Gini coefficients within regions.
If the Gini coefficient of the UGHQD level of cities between regions (e.g., between urban agglomerations j and h) is considered, the formula is as follows:
where uj (uh) is the expected value of the UGHQD level of each city in the j(h) urban agglomeration, yji (yjr) is the UGHQD level of any city in the j(h) urban agglomeration, and nj (nh) is the number of cities in the j(h) urban agglomeration.
The contribution of the inter-regional differences and the contribution of the super-variable density are, respectively:
where Djh is the relative impact of the UGHQD level among j(h) urban agglomerations and Djh is defined as shown in the following equation under the premise that μj > μi:
where the formulas for djh and pjh are shown below:
where Fh(Fj) is the cumulative density distribution function for the j(h) urban agglomerations.
Furthermore, utilizing the aforementioned Gini coefficient decomposition formula allows us to derive the decomposition equation for the overall Gini coefficient of the UGHQD levels across China’s five major urban agglomerations:
3.3.3. Kernel Density
Kernel density estimation serves as a method for analyzing data distribution characteristics drawing directly from the data itself. This method relaxes prior assumptions about data distribution, is not bound by specific functional expressions, and avoids logical inconsistencies arising from predetermined function forms. Given that the distribution of the UGHQD levels in China’s five major urban agglomerations changes over time and exhibits significant uncertainty and complexity, the nonparametric Kernel density estimation method is well-suited for estimating its dynamic distribution trend. This study uses Kernel density estimation to systematically describe the distribution’s location, shape, extensibility, and polarization characteristics for the UGHQD levels of the five major urban agglomerations throughout the sample period. Let the density function f(c) for the random variable X at point c be formulated as [64,74]:
In Equation (11), N is the number of observations, Ci is the independent and equally distributed observations, is the mean value, ρ is the bandwidth, and K(·) is the kernel function. This study chooses the more commonly used Gaussian kernel function to estimate the dynamic evolution trend of the distribution of the UGHQD level in the five major urban agglomerations. The kernel function expression is:
3.3.4. Markov Chain
The Markov chain represents a discrete-time, discrete-state stochastic process. It captures the growth change of a variable by segmenting the data into λ categories and determining the growth change by calculating the probability distribution for each category and its evolutionary trend over time. One of the distinguishing features of the Markov chain is its “memory lessness”; the conditional distribution of state Xt+1 is solely dependent on state Xt and is independent of prior states. In this study, we construct a transition probability matrix over a time span of d. When categorizing the UGHQD level into λ groups, one can establish a transition probability matrix of order λ × λ. The transition probability formula is as follows:
where is the probability that the UGHQD level of a given urban agglomeration shifts from type i in year t to type j in year t + d, denotes the number of regions belonging to type i in year t during the sample examination period that transition to type j after d years, and n represents the number of regions belonging to type i in year t.
The spatial Markov chain expands upon the traditional Markov chain by introducing the notion of “spatial lag”. It transforms the two-dimensional transition probability matrix of λ × λ into a three-dimensional matrix of λ × λ × λ. This allows the spatial Markov chain to assess whether the UGHQD level of neighboring cities influences the transition probability of a city’s UGHQD state.
3.3.5. Geographical Detector
The geographical detector is a statistical instrument designed to discern spatial disparities in geographic elements and investigate the driving factors underlying these differences. This methodology partitions the study area into several specific subregions and compares the overall variance within each region with the sum of variances across these subregions to determine if the geographic elements exhibit significant spatial heterogeneity. In this study, we use the q-value as a criterion to quantify the influence of various factors affecting the spatial differences in UGHQD levels among the five major urban agglomerations. The q-value ranges from 0 to 1; a q-value closer to 1 indicates a stronger explanatory power for the spatial differences in UGHQD. Specifically, a q-value of 1 or 0 suggests a high degree of consistency or lack of correlation, respectively, between the factor and the spatial differences in UGHQD.
Furthermore, this study introduces the concept of an interaction detector, which identifies the existence and strength of an interaction effect between bivariate variables. This is achieved by comparing the difference between the spatially superimposed q-values of two factors and the q-values of each individual factor [69].
where h = 1, 2,…, m represents the partition of the independent or dependent variable, n is the total number of samples in the study area, σ2 is the total discrete variance in the study area, nh is the number of samples in partition h, and is the discrete variance of the dependent variable in partition h.

Table 1.
Indicator system of UGHQD.
Table 1.
Indicator system of UGHQD.
| Dimension Layer | Sub-Level | Explanation | Attributes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED | Economic development level | Real GDP per capita | Positive | [26,49,57] |
| Fixed-asset investment | Per capita investment in fixed assets | Positive | [26] | |
| Logistics accessibility | Per capita road freight volume | Positive | [55] | |
| Intensity of social consumption | Total retail sales of consumer goods per capita | Positive | [52] | |
| Foreign trade dependence | Ratio of total exports and imports to GDP | Positive | [49,55] | |
| Foreign investment dependence | Actual utilized of foreign capital to GDP | Positive | [55] | |
| Upgradation of industrial structure | Value added of tertiary industry to value added of secondary industry | Positive | [52,56] | |
| Rationalization of industrial structure | New Theil index | Reverse | [52,55,70] | |
| SL | Basic education level | Number of primary and secondary school teachers per student | Positive | [27] |
| Transport infrastructure | Road mileage per unit area | Positive | [65] | |
| Public culture level | Number of library books per 10,000 people | Positive | [57] | |
| Average wage level | Average wage of urban employees | Positive | [66] | |
| Health and medicine level | Number of hospital beds per 10,000 people | Positive | [27,57] | |
| Internet penetration rate | Number of internet users per 100 people | Positive | [60] | |
| EE | Urban wastewater treatment rate | Concentrated treatment rate of wastewater treatment plants | Positive | [55,56] |
| Harmless treatment rate of garbage | Harmless treatment rate of household garbage | Positive | [55,56] | |
| Solid waste utilization rate | Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste | Positive | [52,55,56] | |
| Greening coverage in built-up areas | Area of landscaped green space to built-up area | Positive | [55,56,57] | |
| Air particulate pollution | Annual average of PM2.5 | Reverse | [52,75] | |
| Industrial SO2 emission | Industrial SO2 emission to industrial output value | Reverse | [52,55] | |
| Industrial wastewater discharges | Industrial wastewater discharge to industrial output value | Reverse | [52,55,56] | |
| Industrial dust emission | Industrial smoke (dust) emission to industrial output value | Reverse | [55,56] | |
| TI | Green innovation achievements | Number of green patent authorizations per 10,000 people | Positive | [52] |
| Intensity of science expenditure | Per capita science expenditure | Positive | [55,56] | |
| Intensity of education expenditure | Per capita expenditure on education | Positive | [55] | |
| Cultivation of innovative talents | Number of university students per 10,000 people | Positive | [56] | |
| Technological innovation achievements | Number of patent authorizations per 10,000 people | Positive | [52] |
4. Results
4.1. Level Measurement
This study employs the entropy method [76,77] to systematically evaluate the UGHQD levels of China’s five major urban agglomerations, the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), the Pearl River Delta (PRD), Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH), the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River (MYR), and Chengdu-Chongqing (CC), from 2003 to 2020. The study performs meanization processing on the urban sample data and, based on this, depicts the evolutionary trends of the UGHQD levels for these urban agglomerations, as shown in Figure 2. Drawing on existing studies [78,79] and using the “natural breaks” as a delineation criterion, this research identifies 2003, 2008, 2014, and 2020 as pivotal study years. The spatial distribution of UGHQD across the five major urban agglomerations is depicted in Figure 3, revealing the regional disparities in their development. As seen in Figure 2, two key features emerge: First, there was a clear upward trajectory in UGHQD levels across these urban agglomerations. However, the overall development level remained relatively low despite this progressive trend. The annual growth rate was modest, and noticeable differences among the different urban agglomerations were evident. A detailed analysis follows.
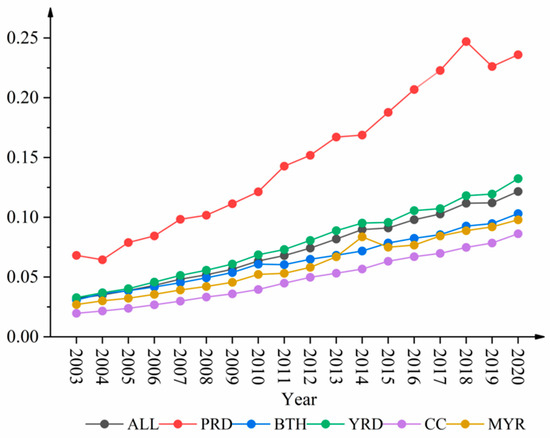
Figure 2.
Evolutionary trend of the UGHQD level in China’s five major urban agglomerations.
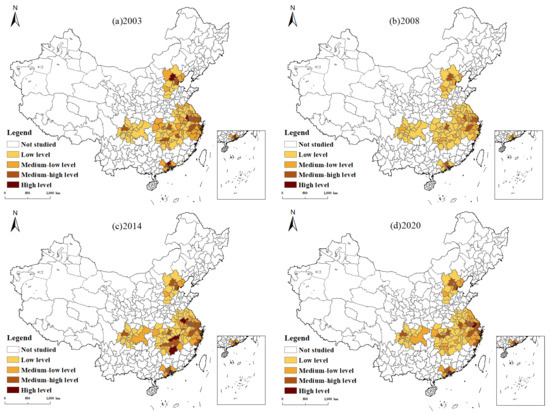
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of UGHQD level in China’s five major urban agglomerations.
From 2003 to 2020, the average UGHQD level in these urban agglomerations increased from 0.0321 to 0.1216, marking a cumulative growth of 179.45%. From a spatio-temporal perspective, pronounced differences existed in the UGHQD levels across the five major urban agglomerations. The PRD and YRD exhibited average UGHQD levels that surpassed the collective mean. Notably, despite its relative strength, the PRD experienced a downturn in its development level in 2004 and again in 2018. Conversely, the YRD consistently showed a steady year-over-year ascent in its development. However, BTH, CC, and the MYR lagged in this metric. Specifically, the average UGHQD level in CC stood at just 0.0863 in 2020, consistently trailing other urban agglomerations throughout the sample period.
Analyzing the average annual growth rates, the combined rate for the five major urban agglomerations stood at 7.69%. Specifically, the YRD and CC registered growth rates of 8.06% and 8.56%, respectively, surpassing the aggregate average. This suggests that although the YRD currently leads in UGHQD, its potential for further growth is substantial. Conversely, CC, starting from a lower baseline, demonstrated the most robust annual growth, indicating potential for convergence with its peers in the future. Meanwhile, the growth rates for the PRD, BTH, and the MYR were 7.15%, 6.93%, and 7.42%, respectively, all falling below the aggregate average.
4.2. Spatial Differences
Utilizing the Dagum Gini coefficient and its decomposition methodology, this study quantitatively assesses the overall, intra-regional, and inter-regional differences and the super-variable density in the UGHQD level among China’s five major urban agglomerations. The aim is to reveal the characteristics of spatial differences in UGHQD levels and their sources, as depicted in Figure 4.
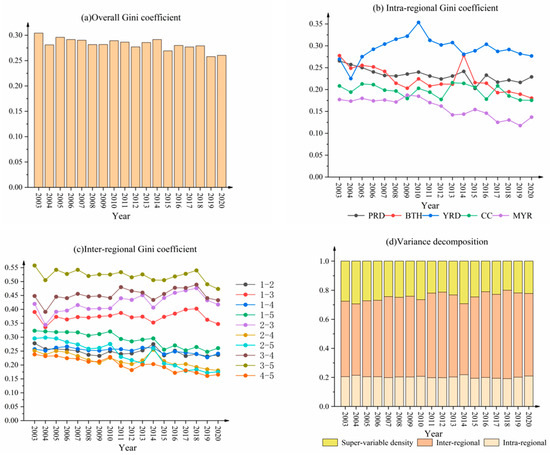
Figure 4.
Gini coefficients and their decompositions in China’s five major urban agglomerations.
4.2.1. Overall Differences and Evolutionary Trends
Figure 4a illustrates the evolutionary trends of the overall Gini coefficient for UGHQD across the five major urban agglomerations. From a static perspective, the Gini coefficient ranged from 0.2578 to 0.3043 during the sample period, with an average value of 0.2822, signifying a marked spatial imbalance. This difference largely stemmed from the persistently low development levels in CC and the MYR as opposed to the more developed PRD and YRD. From a dynamic perspective, the Gini coefficient gradually declined from 0.3043 in 2003 to 0.2604 in 2020, with an annual average decrease rate of approximately 0.87%. Although this trend suggests that regional imbalances are slowly evolving toward regional synergy, the pace of this progress is relatively slow and inconsistent. The PRD and YRD showed limited growth rates, whereas CC and the MYR, starting from a lower baseline, are growing more rapidly, contributing to the observed fluctuations and narrowing of the Gini coefficient.
4.2.2. Intra-Regional Differences and Evolutionary Trends
Figure 4b illustrates the evolutionary trends of the intra-regional Gini coefficients for UGHQD across the five major urban agglomerations. From a static perspective, the Gini coefficients for the study period ranged from 0.1175 to 0.3535. The mean values for these urban agglomerations were as follows: the MYR (0.1585), CC (0.1964), BTH (0.2231), the PRD (0.2223), and the YRD (0.2954). These figures indicate significant differences in the levels of development within the urban agglomerations. Among them, the average value for the coastal YRD and PRD exceeded 0.2000, which is significantly higher than for other urban agglomerations. From a dynamic perspective, except for the YRD, all other urban agglomerations showed a declining trend in spatial differences. The average annual decrease rates were: the PRD (0.83%), CC (0.96%), the MYR (1.44%), and BTH (2.42%). In contrast, the YRD’s intra-regional differences have expanded gradually by approximately 0.15% annually. CC, interestingly, exhibited considerable short-term fluctuations—for example, sharply rising from 0.1775 in 2012 to 0.2143 in 2014 before dropping to 0.1782 in 2016. This volatility may be attributed to its lower initial level of UGHQD, making it more vulnerable to unstable economic conditions. In conclusion, a higher UGHQD level correlates with more significant spatial disequilibrium within a region and vice versa.
4.2.3. Inter-Regional Differences and Evolutionary Trends
Figure 4c illustrates the evolutionary trends of the inter-regional Gini coefficients for UGHQD among the five major urban agglomerations. From a static perspective, the inter-regional Gini coefficients during the sample period ranged from 0.1608 to 0.5577, and the average values exceeded 0.2000. These data highlight pronounced spatial imbalances in UGHQD across these urban agglomerations. The most significant difference was observed between the YRD and MYR, registering an average Gini coefficient of 0.5212. In contrast, more modest disparities were evident between the MYR and CC, with average Gini coefficients of 0.2017. From a dynamic perspective, the spatial differences between urban agglomerations exhibited fluctuations during the study period, with most inter-regional differences showing a declining trend, although a few still displayed a minor increase. For instance, in the case of the PRD and YRD, the difference narrowed from 0.5577 in 2003 to 0.5052 in 2004, rebounded to 0.5424 in 2007, fell to 0.5052 in 2015, rebounded to 0.5401 in 2018, and then declined rapidly again. The evolutionary patterns of the Gini coefficients among the other urban agglomerations are broadly similar, albeit with some variations in specific fluctuation nodes and magnitudes.
4.2.4. Sources of Differences in the UGHQD Level and Their Contribution
Figure 4d illustrates the sources of differences in the UGHQD level among the five major urban agglomerations and their respective contributions. From a static perspective, inter-regional differences dominated the overall differences, with contribution rates ranging from 48.91% to 60.87% and an average of 55.34%. In contrast, intra-regional differences accounted for between 19.13% and 21.45% of the total differences, averaging 20.26%. Furthermore, the fluctuating contribution of super-variable density fell between 20.01% and 29.26%, with an average of 24.40%. This evidence suggests that efforts to mitigate the prevalent spatial differences in UGHQD should focus on bridging the development gap between urban agglomerations, particularly those between the coastal and central-western regions. From a dynamic perspective, the contribution rate of inter-regional differences followed a “decreasing-then-increasing” pattern throughout the study period, with comparable magnitudes of decline and ascent. The contribution rate of super-variable density oscillated more frequently, albeit within a narrower range. Meanwhile, the contribution rate of intra-regional differences remained relatively stable, showing only minor fluctuations between 2012 and 2018. Collectively, these trends indicated an anticipated stabilization in the respective contribution rates of the differences mentioned above.
4.3. Dynamic Evolution
Figure 5 illustrates the Kernel density estimation for the overall and individual UGHQD levels across the five major urban agglomerations. Subsequent sections delve deeper, analyzing the Kernel density curves with a focus on attributes such as location, shape, ductility, and polarization features.

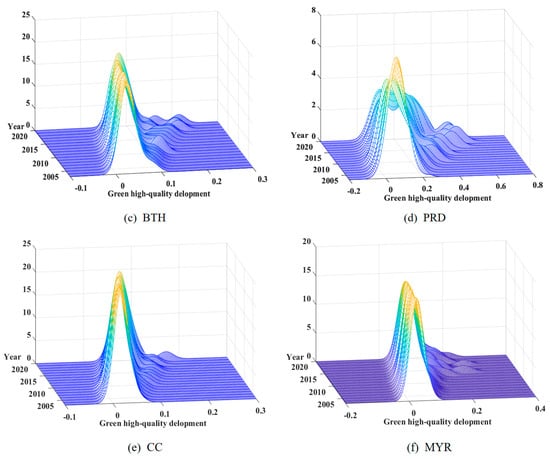
Figure 5.
Evolution of the distribution of UGHQD in China’s five major urban agglomerations.
From the perspective of spatial distribution, the Kernel density distribution curves for the five major urban agglomerations—both collectively and individually—manifested discernible rightward shifts over time. This finding corroborates the substantial improvements in UGHQD levels, as elaborated in preceding sections. CC and the YRD exhibited the most pronounced rightward shifts, signifying faster UGHQD improvement rates. In contrast, the weaker shift in the PRD suggests a relatively sluggish pace of improvement.
From the perspective of distributional shape, a decreasing peak height and widening curve in Kernel density distribution indicate a transition from a centralized to a more dispersed spatial pattern among the five agglomerations. A more granular analysis uncovers that the majority of urban agglomerations in the PRD, the YRD, BTH, and the MYR exhibited expanding development profiles. CC, however, demonstrated a unique pattern: the height of the main peak decreased before increasing, followed by a narrowing of the peak’s width, indicating a more concentrated form of UGHQD.
From the perspective of distributional ductility, all urban agglomerations displayed varying degrees of the “right-tail” phenomenon, meaning that some cities within each agglomeration were leading in UGHQD levels. Specifically, Guangzhou and Shenzhen in the PRD, Beijing and Tianjin in BTH, Shanghai and Hangzhou in the YRD, Chengdu and Chongqing in CC, and Wuhan and Changsha in the MYR, were all leading in terms of UGHQD. Furthermore, some urban agglomerations exhibited annual extension trends, indicative of a growing difference between leading cities and others, potentially due to policy preferences and resource allocation advantages.
From the perspective of distributional polarization, all five major urban agglomerations generally displayed characteristics of a “single main peak with multiple side peaks”, showing an evolutionary trend towards multi-level differentiation. Further analysis of each urban agglomeration substantiates an orderly transition from single-peak to multiple-peak distributions, highlighting the increasing feature of multi-polarization in UGHQD.
4.4. Transfer Probabilities
By leveraging the quartile method, our study categorizes the UGHQD scores of 107 cities in China’s five major urban agglomerations into four distinct classes: low, medium-low, medium-high, and high. To ascertain the probability and direction of categorical transitions for each city, we employ Markov chain analysis using Matlab 2022b software, resulting in transition probability matrices as depicted in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
Traditional Markov transfer probability matrix for UGHQD.

Table 3.
Spatial Markov transfer probability matrix for UGHQD.
4.4.1. Traditional Markov Chain Analysis
Table 2 provides the transition probability matrices for UGHQD levels in China’s five major urban agglomerations across one-, two-, and three-year time horizons. The diagonal entries in these matrices signify the likelihood of UGHQD levels remaining constant within the respective time horizons, while the off-diagonal entries indicate transition probabilities. During the study period, diagonal probabilities ranged from 43.11% to 97.41%, substantially exceeding off-diagonal values. This suggests that UGHQD levels are more likely to remain stable within 1–3 years, displaying a clear pattern of “club convergence”. Importantly, areas with higher UGHQD levels demonstrated greater stability, while less-developed regions exhibited increased fluidity. In terms of stability, the ranking is as follows: medium-low < low < medium-high < high. Examining specific urban agglomerations, such as the YRD, the PRD, BTH, and the MYR, largely corroborates these overall trends, pointing to more entrenched developmental patterns. In contrast, CC demonstrated lower stability but a higher proclivity for upward movement, suggesting a self-reinforcing growth trajectory. Further analysis reveals that lower-tiered regions are expected to experience diminishing stability and a growing likelihood of upward mobility within the next 1–3 years as we extend the time horizon. Although these less-developed areas face increased odds of improvement, transitioning across categorical boundaries at this stage remains a formidable challenge.
4.4.2. Spatial Markov Chain Analysis
Traditional Markov chains depict the trend of type transitions in the UGHQD level within the five major urban agglomerations. However, it is essential to recognize that cities exhibit specific spatial correlations in this development. Given these urban agglomerations’ geographic dispersion and their limited mutual influence, this study predominantly examines the interaction and impact of UGHQD within each urban agglomeration. Consequently, using the first-order neighboring spatial weight matrix, this study constructs the spatial Markov transition probability matrix for these urban agglomerations’ UGHQD, as presented in Table 3.
Table 3 reveals that, after accounting for spatial lag, the values on the diagonal significantly exceeded those off-diagonal. This indicates that even when considering spatial lag, the UGHQD of the five major urban agglomerations maintained a “club convergence” feature. Transitions mainly occurred between adjacent types, and inter-type transition probabilities were nearly negligible. As spatial lag increased, the developmental stability of low and medium-low regions declined, accompanied by a rise in their upward transition probability. In contrast, the stability of medium-high and high regions showed an increasing trend. For instance, in the YRD, the diagonal values in the transition probability matrix ranged between 50.00% and 100.00%, underscoring the distinct “club convergence” feature. As spatial lag increased, the likelihood of retaining the status quo in the low-level regions decreased from 89.70% to 50.00%, while the probability of upward transition jumps from 10.30% to 50.00%. The medium-low region’s probability of maintaining the status quo decreased from 91.30% to 50.00%, while its likelihood for upward transition increased from 8.70% to 26.50%. The probabilities for the medium-high and high-level regions varied between 70.60% and 100.00%. While other urban agglomerations showed different transition probabilities, their characteristics largely align with those of the YRD.
4.5. Driving Factors
To elucidate systematically and scientifically the intrinsic drivers behind the spatial and temporal differences in UGHQD across the five major urban agglomerations, this study draws on methodologies from the existing literature [80,81], with a focus on four dimensions of driving forces for the spatial difference of UGHQD levels in 2020: economic development (X1), social livelihood (X2), ecological environment (X3), and technological innovation (X4). Initially, with the assistance of ArcGIS, “natural breaks” were used to convert each detector factor into a type variable. Subsequently, the geographical detector model was employed to quantify each factor’s influence on the spatial differences in development quality, as reflected by their respective q-values; higher q-values indicate stronger influence. Detailed findings are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Power of factors to drive UGHQD in 2020.
4.5.1. Factor Detection Analysis
The results in Table 4 reveal that each factor has a differentiated impact on the spatial difference of UGHQD across the five major urban agglomerations. Viewed as a whole, the driving effects of the factors are ranked as follows: technological innovation (0.8074) > economic development (0.6550) > social livelihood (0.6513) > ecological environment (0.1834). Notably, technological innovation significantly outperformed the other factors, establishing it as the principal driver of spatial difference in UGHQD. This underscores the increasing global reliance on innovative and knowledge-based economies. Concurrently, economic development and social livelihood were secondary drivers, providing essential material and economic foundations. However, in CC, economic development surpassed technological innovation as the primary driver, registering a value below 0.5000, thus indicating untapped potential for technological innovation. Intriguingly, for all five major urban agglomerations, the ecological environment factor was the weakest driver and failed to achieve statistical significance, highlighting pressing challenges in resource utilization and ecological governance as critical bottlenecks in their path toward UGHQD.
4.5.2. Interactive Detection Analysis
By using interaction detectors, this study quantitatively evaluates the potential additive effects among the driving factors. Figure 6 shows the outcomes of interaction detection for spatial differences in UGHQD across the five major urban agglomerations. As evidenced by Figure 6, the influence of bi-factor interactions consistently exceeded that of single-factor interactions, exhibiting a “bi-variable enhancement”. Specifically, the joint influence of two interacting drivers surpassed the contribution of any single factor toward UGHQD yet fell short of the sum of the influences of the two individual factors. Notably, the q-value arising from the interaction of technological innovation (TI) with the other factors was prominent. In contrast, the q-value for economic development’s interaction with other factors was less marked. These findings highlight the crucial role of TI in guiding the spatio-temporal evolution of UGHQD within these urban agglomerations, providing invaluable insights for policymaking. Notably, the synergistic effect of technological innovation’s interaction with the ecological environment substantially outweighs their individual impacts, underscoring the importance of STI in enhancing urban resource utilization and ecological governance.
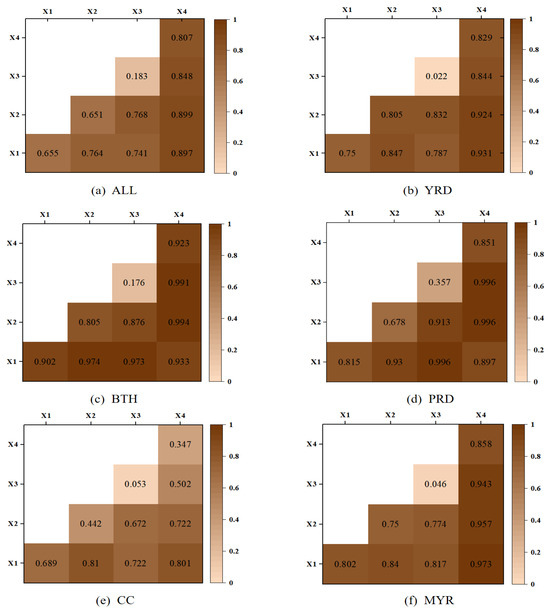
Figure 6.
Results of interaction detection.
5. Discussion
Given the pressing challenges posed by global climate change and ecological degradation, the significant threats to societal and economic activities are increasingly garnering widespread attention. Specifically, establishing a nexus between “ecological welfare” and “economic prosperity”—ensuring ecological sustainability while concurrently fostering economic growth—has become a pivotal discourse among scholars and policymakers. As China transitions from high-speed to high-quality growth, it becomes imperative to deepen our understanding of the theories underpinning UGHQD. Although existing literature has engaged with the theoretical aspects of UGHQD, there is a significant lack of empirical studies quantitatively assessing its developmental levels, spatio-temporal evolution, and driving factors. Departing from previous research that employed green total factor productivity to gauge UGHQD [31,47,48], this study introduces a comprehensive evaluative framework incorporating four key dimensions: economic development (ED), social livelihood (SL), ecological environment (EE), and technological innovation (TI). Unlike prior works focusing on China’s provincial-level administrative regions [52,56], this paper analyzes 107 cities across China’s five major urban agglomerations, offering an in-depth exploration of UGHQD’s spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and its key drivers. Our research furnishes a robust empirical methodology for the nuanced and exhaustive measurement of UGHQD and establishes valuable yardsticks for mapping the trajectory of sustainable urban development in this transformative era. Furthermore, the synergistic advancement of UGHQD is pivotal not just for China’s contemporary socio-economic progress but also serves as an innovative blueprint for sustainable development that can be considered by countries globally.
The empirical findings of this study indicate that the five major urban agglomerations exhibited a gradual improvement in UGHQD. However, the spatial and temporal differences during the sample period were marked by a significant gap, particularly between the coastal urban agglomerations and those in the central and western regions. Due partly to the early implementation of open economy policies and unique resource endowments, coastal areas have attracted substantial foreign investment and high-quality talent. They have also introduced advanced technologies, collectively contributing to the optimization and transformation of their economic structures and lending robust support to UGHQD. Taking the YRD as an example, 2021 data indicate that the GDP of eight cities within the urban agglomeration—including Shanghai, Suzhou, and Hangzhou—has exceeded one trillion dollars. These cities maintain an unassailable lead in economic strength among the five major urban agglomerations. Benefiting from geographic advantages and supportive macro policies, the YRD had already constructed a more mature industrial and service system by the 1990s. Its highly advanced industrial structure provides abundant employment opportunities and economic growth points, thereby offering a solid foundation for UGHQD. Like the YRD, the nine cities in the PRD have also succeeded in attracting considerable talent and capital driven by reform and opening up policies. These cities excel in several industry sectors, including advanced manufacturing, high-tech industries, and financial services. By contrast, the urban agglomerations in central and western China manifest apparent deficiencies in these areas, characterized by relatively weak industrial and service systems and an over-reliance on low value-added and resource-intensive traditional industries. This not only constrains their rate of economic growth but also imposes significant ecological and environmental pressure. In aspects such as foreign investment, technological innovation, and government incentives, urban agglomerations in the central and western regions also display evident shortcomings. These multilevel and multidimensional factors lead to the relative lag in UGHQD observed in central and western urban agglomerations.
The empirical findings of this study further reveal that technological innovation is the core driver of the spatio-temporal difference in UGHQD across the five major urban agglomerations. The possible explanations for this conclusion are as follows: Firstly, technological innovation catalyzes the transformation and upgrading of economic structures, enabling a shift from low-value-added, pollutant-intensive traditional industries to high-value-added, low-carbon, and eco-friendly emerging sectors. For example, the YRD has successfully pivoted from traditional manufacturing to advanced manufacturing and services, particularly in integrated circuits, biomedicine, and electric vehicles. Secondly, technological innovation often enhances resource utilization efficiency while minimizing carbon emissions and environmental degradation. For instance, innovative cleaner production technologies in the PRD have led many manufacturing enterprises to reduce carbon emissions and environmental pollution while improving productivity significantly. Additionally, urban agglomerations with strong innovation capabilities tend to attract skilled talent and foreign investment, creating a positive feedback loop that further fuels technological advancement. The problem of brain drain in some cities in the MYR is partly due to the relatively weak capacity of scientific and technological innovation, which is unable to attract and retain high-level talent. Lastly, technological innovation also offers cost-effective and efficient solutions for environmental governance, thus reinforcing its role as a prerequisite for sustainable development. Collectively, technological innovation is the key to economic transformation and talent attraction as well as a necessary condition for environmental governance and sustainable development, which explains why technological innovation is the chief factor causing spatial differences in UGHQD in the five major urban agglomerations.
In light of the findings presented in this paper, we propose the following policy recommendations. Firstly, there is an urgent need to reassess the traditional focus on GDP-centric development, promoting instead a coordinated approach between economic growth and ecological sustainability. Local governments should prioritize environmentally efficient and people-centered development strategies. Secondly, regional characteristics should be acknowledged, and barriers should be broken to optimize resource allocation, restructure industries, and foster technological innovation. Lastly, given the critical role of technological advancement, sustained governmental support in R&D investment, tax incentives, and talent development are imperative for continuous technological and economic progress.
The limitations of this study are twofold. On the one hand, the present study investigates the UGHQD of 107 cities in China’s five major urban agglomerations, a focus that holds unique value and significance from a geographical standpoint. However, this scope means that the role of other small and medium-sized cities, as well as rural areas, is not adequately addressed in this paper. In an era of accelerated globalization, the study also needs a comparative analysis of UGHQD with international cities, thereby missing an international perspective. Future research might consider expanding the geospatial sample and conducting more systematic comparative studies across different spatial and temporal scales. On the other hand, the analysis in this paper covers the driving factors of economic development, social livelihood, ecological environment, and technological innovation, providing a diversified perspective for understanding the complex phenomenon of UGHQD. Nonetheless, additional soft factors such as cultural influences, educational systems, public environmental awareness, and external variables like policy landscapes and global trends require further exploration for their potential impact on UGHQD. Therefore, future research should analyze external drivers, including the policy environment, in greater depth to better understand how they influence the process of UGHQD in urban agglomerations.
6. Conclusions
This study took 107 cities of China’s five major urban agglomerations as research objects, constructed a comprehensive evaluation indicator system of UGHQD level based on four dimensions (economic development, social livelihood, ecological environment, and technological innovation), and empirically examined the spatio-temporal difference in the UGHQD level of the five major urban agglomerations and the trend of dynamic evolution by using the analytical methods, such as the Dagum Gini coefficient, the Kernel density estimation, and the Markov chain. Further, the driving factors behind the spatial differences in the UGHQD level were analyzed in depth using geographic detectors. The research revealed several key findings:
- (1)
- The UGHQD levels of the five major urban agglomerations demonstrated a consistent upward trajectory during the period of 2003–2020. Coastal regions, specifically the PRD and YRD, consistently outperformed inland agglomerations. The Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration, however, persistently lagged behind its counterparts, necessitating close scrutiny.
- (2)
- Significant spatial differences existed in the UGHQD levels among the urban agglomerations. Inter-regional differences among the sub-clusters primarily drove these differences. Coastal urban agglomerations consistently led in terms of UGHQD, creating a pronounced development gap when compared to the central and western urban agglomerations.
- (3)
- The spatio-temporal evolution of UGHQD levels in 107 cities within these five major urban agglomerations exhibited a trend of moving from a concentrated to a dispersed pattern. The dynamism of this distribution varied among different urban agglomerations. Additionally, the phenomenon of “club convergence” was observed in UGHQD levels, making it challenging to achieve a leap across different types. Upon accounting for spatial lag effects, the potential for upward mobility was more prominent in low-level areas.
- (4)
- Diverse driving factors underpinned UGHQD levels in the five major urban agglomerations. Among them, the impact of technological innovation (TI) notably surpassed other factors. Interactive detection analysis further revealed a prominent synergistic effect between technological innovation (TI) and other driving factors, affirming that technological innovation served as the primary driver behind the spatial differentiation of UGHQD.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.Y. and X.H.; methodology, X.H. and S.J.; writing—original draft preparation, T.Y. and X.H.; writing—review and editing, T.Y. and X.C.; funding acquisition, T.Y. and X.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
National Social Science Foundation of China: 22BZZ039; Major Project of Philosophy and Social Sciences in Higher Education Institutions in Hubei Province of China: 22ZD015.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, H.; Qi, S.; Tan, X. Decomposition and prediction of China’s carbon emission intensity towards carbon neutrality: From perspectives of national, regional and sectoral level. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Liu, Z. Spatial heterogeneity of demographic structure effects on urban carbon emissions. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 95, 106790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andiappan, V.; Foo, D.C.Y.; Tan, R.R. Process-to-Policy (P2Pol): Using carbon emission pinch analysis (CEPA) tools for policy-making in the energy sector. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Ye, Q. The Marxist green development concept and green development in contemporary China: Comment on incompatibility theory between environment and development. Econ. Res. J. 2017, 52, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wen, S.; Tao, C.Q. Impact of environmental tax on pollution control: A sustainable development perspective. Econ. Anal. Policy 2023, 79, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, L. The challenge of sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2003, 11, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Du, C.; Chen, X.; Jia, L.; Guo, X.; Chen, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H. Carbon peak and carbon neutrality in China: Goals, implementation path and prospects. China Geol. 2021, 4, 720–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, B. Energy and CO2 emissions efficiency of major economies: A network DEA approach. Energy 2018, 147, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. Understanding China’s growth: Past, present, and future. J. Econ. Perspect. 2012, 26, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Cai, T.; Deng, W.; Zheng, R.; Jiang, Y.; Bao, H. Indicators for Evaluating High-Quality Agricultural Development: Empirical Study from Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Soc. Indic. Res. 2022, 164, 1101–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.R.; Stauvermann, P.J.; Patel, A. Exploring the link between research and economic growth: An empirical study of China and USA. Qual. Quant. 2016, 50, 1073–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Revive China’s green GDP programme. Nature 2016, 534, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Norris, M. Productivity growth, technical progress, and efficiency change in industrialized countries: Reply. Am. Econ. Rev. 1997, 87, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Xiong, Y. Impact of Climate on the Carbon Sink Capacity of Ecological Spaces: A Case Study from the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Land 2023, 12, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Alam, K. Impact of industrialization and non-renewable energy on environmental pollution in Australia: Do renewable energy and financial development play a mitigating role? Renew. Energy 2022, 195, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lee, J. Dynamic convergence of green total factor productivity in Chinese cities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Yu, D. Urban agglomeration: An evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, X.; Huang, H. The spatial-temporal evolution and influencing factors of eco-efficiency in the five major urban agglomerations of China. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Ren, Y. A spatial effect study on financial agglomeration promoting the green development of urban agglomerations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 70, 102900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, J. Ecological total-factor energy efficiency of regions in China. Energy Policy 2012, 46, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, T. Potential heterogeneity in the relationship between urbanization and air pollution, from the perspective of urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Liang, L. Spatio-temporal evolution of ozone pollution and its influencing factors in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhibiao, L.; Yonghui, L. Structural transformation, TFP and high-quality development. China Econ. 2022, 17, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Shen, K. Modernized economic system, total factor productivity and high quality development. Shanghai J. Econ. 2018, 6, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, W. Evaluation of ecological city and analysis of obstacle factors under the background of high-quality development: Taking cities in the Yellow River Basin as examples. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, F. Exploring the role of green finance and energy development towards high-quality economic development: Application of spatial Durbin model and intermediary effect model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Song, D.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X. Evolving Trends and Influencing Factors of the Rural Green Development Level in Chongqing. Land 2023, 12, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickel, J.; Kallis, G. Is green growth possible? New Political Econ. 2020, 25, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y. How to evaluate the green and high-quality development path? An FsQCA approach on the China pilot free trade zone. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, L. Green total factor productivity and its decomposition of Chinese manufacturing based on the MML index: 2003–2015. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhu, Q. Innovation in emerging economies: Research on the digital economy driving high-quality green development. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 145, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schandl, H.; West, J. Resource use and resource efficiency in the Asia–Pacific region. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2010, 20, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, R.J. Quantity and Quality of Economic Growth; Banco Central de Chile: Santiago, Chile, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, A. Jobs and climate policy: Evidence from British Columbia’s revenue-neutral carbon tax. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2017, 83, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Fang, B.; Xie, X. Temporal and Spatial Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Urban Ecological Welfare Performance from the Perspective of High-Quality Development: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province, China. Land 2022, 11, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, K.; Dong, X. Green energy as a new determinant of green growth in China: The role of green technological innovation. Energy Econ. 2022, 114, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, L.; Arvidsson, A. Green innovation networks: A research agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 131926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Cai, X.; Song, X. How does renewable energy technology innovation affect the upgrading of industrial structure? The moderating effect of green finance. Renew. Energy 2022, 197, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, P.; Milios, J. TFP change, output gap and inflation in the Russian Federation (1994–2006). J. Econ. Bus. 2009, 61, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, G.H.; Rawski, T.G.; Zhang, Y. Productivity growth and convergence across China’s industrial economy. J. Chin. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2008, 6, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrouznejad, A.; Yang, G. A survey and analysis of the first 40 years of scholarly literature in DEA: 1978–2016. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2018, 61, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Qian, W. Efficiency evaluation and dynamic evolution of China’s regional green economy: A method based on the Super-PEBM model and DEA window analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Liu, P.; Zhong, F.; Yang, C.; Luo, X. Borrowing Size and Urban Green Development Efficiency in the City Network of China: Impact Measures and Size Thresholds. Land 2022, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto-Millán, P.; de la Fuente, M.; Fernández, X.L. Determinants of the European electricity companies efficiency: 2005–2014. Energy Strategy Rev. 2018, 21, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, L.; Qayyum, M. Energy efficiency comparison amongst service industry in Chinese provinces from the perspective of heterogeneous resource endowment: Analysis using undesirable super efficiency SBM-ML model. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qin, Y.; Xu, J.; Ren, W. Analysis of the Evolution Characteristics and Impact Factors of Green Production Efficiency of Grain in China. Land 2023, 12, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Jiang, P.; Wang, D.; Wu, J. Can smart city construction facilitate green total factor productivity? A quasi-natural experiment based on China’s pilot smart city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Nakonieczny, J.; Jabeen, F.; Shahzad, U.; Jia, W. Does green innovation induce green total factor productivity? Novel findings from Chinese city level data. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 185, 122021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, X.; Ren, B. The fluctuation and regional difference of quality of economic growth in China. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 46, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Ren, S.; Zhang, P. Environmental decentralization, local government competition, and regional green development: Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Chen, Z. Business environment, technological innovation and government intervention: Influences on high-quality economic development. Manag. Decis. 2023, 61, 2413–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ding, T.; Wang, H. Digital economy, technological innovation and green high-quality development of industry: A study case of China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Huang, J. Analysis of the spatio-temporal coupling coordination mechanism supporting economic resilience and high-quality economic development in the urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. High-quality development in China: Measurement system, spatial pattern, and improvement paths. Habitat Int. 2021, 118, 102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Liu, J. Theoretical connotation, evaluation criteria and path to realization of high quality green development. Inn. Mong. Soc. Sci. 2019, 40, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J. Green credit, carbon emission and high quality development of green economy in China. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 12215–12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Qin, Q.; Li, L. A comprehensive evaluation paradigm for regional green development based on “Five-Circle Model”: A case study from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J. Different types of environmental regulations and heterogeneous influence on “green” productivity: Evidence from China. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 132, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, W.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, T. Spatiotemporal and driving forces of Ecological Carrying Capacity for high-quality development of 286 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gu, T.; Wang, H. The Coupling Coordination between Digital Economy and Industrial Green High-Quality Development: Spatio-Temporal Characteristics, Differences and Convergence. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, X. Guided High-Quality Development, Resources, and Environmental Forcing in China’s Green Development. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, W. The measurement and analysis of the inclusive green growth in China. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2018, 8, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, N.; Lu, X.; Kuang, B.; Zhang, X. Regional disparities and evolution trend of city-level carbon emission intensity in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 88, 104288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zou, R.; Cheng, J.; Geng, Z.; Li, Q. Environmental technical efficiency and its dynamic evolution in China’s industry: A resource endowment perspective. Resour. Policy 2023, 82, 103451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Hu, B.; Kuang, B.; Zhou, M. Regional differences and dynamic evolution of urban land green use efficiency within the Yangtze River Delta, China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wakasi, R.A. A research of the regional disparities and distributional dynamic evolution of high-quality agricultural development in China. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2021, 6, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wu, J.; Song, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y. Spatiotemporal regularity and spillover effects of carbon emission intensity in China’s Bohai Economic Rim. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z. The heterogeneous effect of driving factors on carbon emission intensity in the Chinese transport sector: Evidence from dynamic panel quantile regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Kuang, T.; Tao, S. Quantifying influences of natural factors on vegetation NDVI changes based on geographical detector in Sichuan, western China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Peng, W.; Zhang, L. Estimate of population density and diagnosis of main factors of spatial heterogeneity in the metropolitan scale, western China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Shi, X. Industrial Agglomeration, Technological Innovation and High-quality Economic Development: Empirical Research based on China’s Five Major Urban Agglomerations. Reform 2022, 36, 68–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dagum, C. A New Approach to the Decomposition of the Gini Income Inequality Ratio. Empir. Econ. 1997, 22, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Liu, C.; Shan, L.; Jiang, Y. Spatial Pattern and Mechanism of the Life Service Industry in Polycentric Cities: Experience from Wuhan, China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2023, 149, 05023015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, G.; Liang, B.; Li, F. An Exploration of a Synthetic Construction Land Use Quality Evaluation Based on Economic-Social-Ecological Coupling Perspective: A Case Study in Major Chinese Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yi, Y.; Sun, J. Entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, G.; Cushman, S.A.; Wang, X.; László, K.; Su, R.; Yuan, L.; Li, B.; et al. The seeds of ecological recovery in urbanization–Spatiotemporal evolution of ecological resiliency of Dianchi Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y. Fostering green development with green finance: An empirical study on the environmental effect of green credit policy in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, R.; He, Z. The impact of environmental pollution and green finance on the high-quality development of energy based on spatial Dubin model. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M. Spatiotemporal Variation in Ecosystem Health and Its Driving Factors in Guizhou Province. Land 2023, 12, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, L.; Yang, D.; Liu, Y. Quantifying the spatial heterogeneity influences of natural and socioeconomic factors and their interactions on air pollution using the geographical detector method: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).