The Effect of Bedrock Differences on Plant Water Use Strategies in Typical Karst Areas of Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
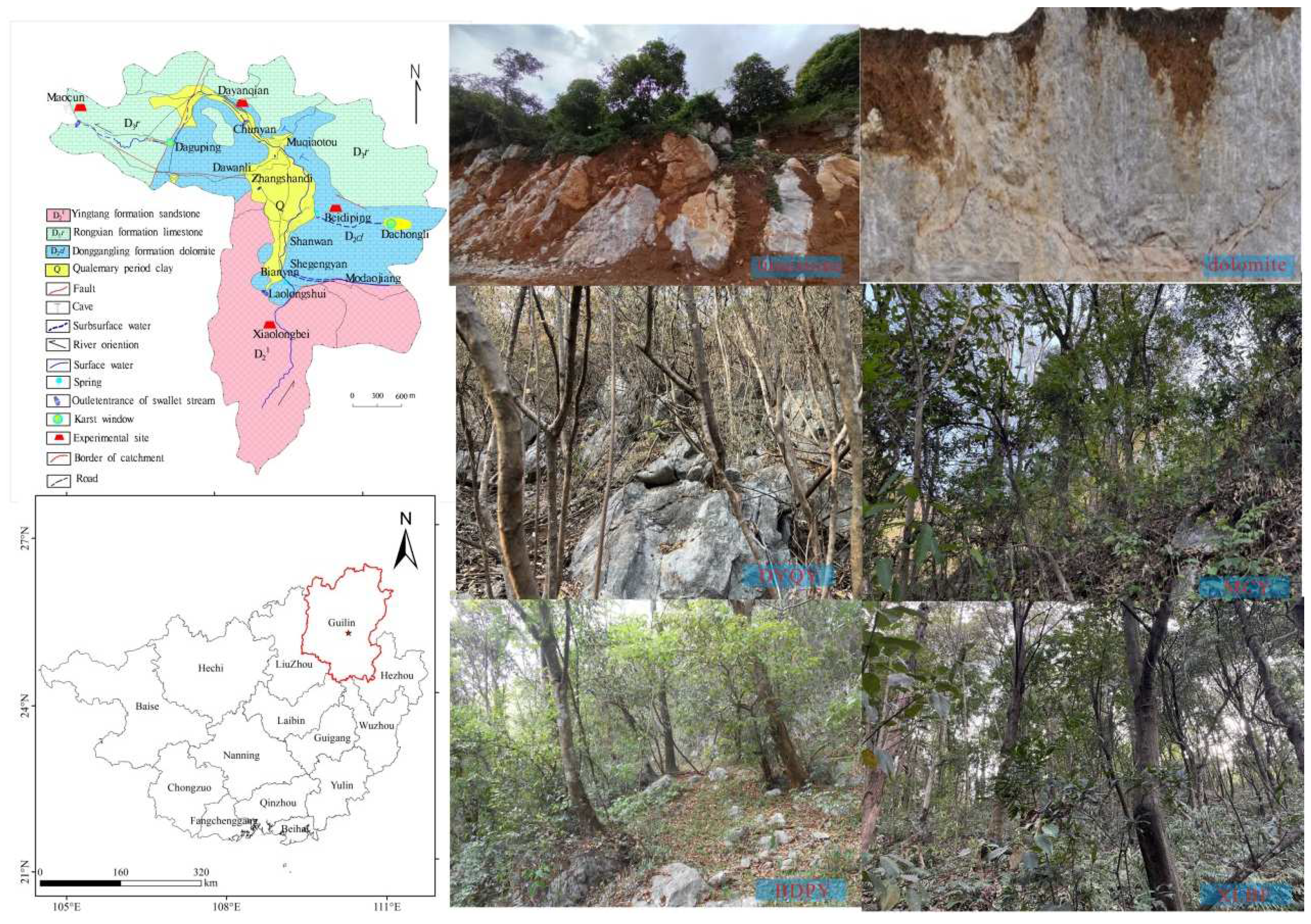
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Determination
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Variation Characteristics of δD and δ18O of Precipitation and Groundwater
3.2. Characteristics of Soil Water Variation in Karst and Nonkarst Areas
3.2.1. Variation in Soil Water Content with Depth
3.2.2. Characteristics of δD and δ18O Variation in Soil Water under Different Geologies
3.3. Sources of Plant Water in Karst and Nonkarst Areas
3.3.1. Direct Correlation Method to Determine the Source of Plant Water Uptake
3.3.2. Proportion of Plant Water Use
3.4. Variation in the SW-Excess of Plant Stem Water in Karst and Nonkarst Areas
4. Discussion
4.1. Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotope Characteristics and Their Influencing Factors
4.2. Factors Influencing the Source of Plant Water
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, X.M.; Xu, X.L.; Zhong, F.X.; Yi, R.Z.; Xu, C.W.; Zhang, Y.H. Comparative study of MixSIAR and IsoSource models in the analysis of plant water sources. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5611–5619. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pauses, J.G.; Austin, M.P. Patterns of plant species richness in relation to different environments: An appraisal. J. Veg. Sci. 2001, 12, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, M.B.; Martin, J.B.; Kurz, M.J. Synoptic estimates of diffuse groundwater seepage to a spring-fed karst river at high spatial resolution using an automated radon measurement technique. J. Hydrol. 2016, 544, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Jiang, Y.J.; Shen, L.C.; Liu, J.C.; He, R.L. Response of water use efficiency of typical plants to tunnel construction in karst trough valley. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 4032–4040. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, J. Point-recharge of limestone aquifers-a model from new zealand karst. J. Hydrol. 1983, 61, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trcek, B. How can the epikarst zone influence the karst aquifer hydraulic behaviour? Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.X.; Jiang, R.J.; Shen, L.C.; Pu, J.B.; Xiao, C. Modern Karstololgy; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 292–316. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.C. Features of epikarst zone in south China and formation mechanism. Trop. Geogr. 1998, 18, 322–326. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.P.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, K.L. Seasonal variation of water sources for plants growing on continuous rock outcrops in limestone area of Southwest China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 35, 1029–1037. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.P.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, K.L.; Yang, J. Water source utilization by woody plants growing on dolomite outcrops and nearby soils during dry seasons in karst region of Southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420–421, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wan, H.; Deng, Z.M.; Pan, G.Y.; Xia, J. Using stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes to study water movement in soil-plant-atmos-phere continuum at Lake Poyang wetland China. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 25, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Shen, L.C.; Wang, Z.X.; Duan, S.H.; Wu, W.; Peng, X.Y.; Wu, C.; Jiang, Y.J. Response of plants water uptake patterns to tunnels excavation based on stable isotopes in a karst trough valley. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ke, J.; Wu, S.; Jiang, G.H.; Jiang, Z.C.; Zhu, A.J. Responses of plant water uptake to groundwater depth in limestone outcrops. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Behzad, H.M.; He, Q.F.; Wu, Y.B.; Jiang, Y.J. Seasonal transpiration dynamics of evergreen Ligustrum lucidum linked with water source and water-use strategy in a limestone karst area, Southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Dai, J.Y.; Wu, X.C.; Peng, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Meersmans, J.; Green, S.M.; Quine, T.A. Rock crevices determine woody and herbaceous plant cover in the karst critical zone. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 49, 8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S.; Hu, K.; Nie, Y.P.; Wang, K.L. Analysis of soil water movement inside a footslope and a depression in a karst catchment, Southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Z.D.; Guan, H.D.; Zhang, X.P.; Xu, X.; Dai, J.J.; Hua, M.Q. Examination of the ecohydrological separation hypothesis in a humid subtropical area: Comparison of three methods. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthias, S.; Doerthe, T.; Chris, S. No influence of CO2 on stable isotope analyses of soil waters with off-axis integrated cavity output spectroscopy. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 21, 430–436. [Google Scholar]
- Diner, T.; Davis, G.H. Application of environmental isotope tracers to modeling in hydrology. J. Hydrol. 1984, 68, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Z.C.; Qin, X.M. Water source partitioning among trees growing on carbonate rock in a subtropical region of Guangxi, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Luo, Z.D.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.L.; He, X.G.; Rao, Z.G.; Guan, H.D. Variation of the stable isotopes of water in the soil-plant-atmosphere continuum of a Cinnamomum camphora woodland in the East Asian monsoon region. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125199–125210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, J.P.; Walker, G.R.; Kennett-Smith, A.K. Field validation of isotopic procedures for determining sources of water used by plants in a semi-arid environment. J. Hydrol. 1995, 167, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbjornsen, H.; Shepherd, G.; Helmers, M.; Mora, G. Seasonal patterns in depth of water uptake under contrasting annual and perennial systems in the Corn Belt Region of the Midwestern US. Plant Soil 2008, 308, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G.; Tsujimura, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Sasaki, L.; Yamanaka, T.; Davaa, G.; Oyunbaatar, D.; Sugita, M. Seasonal variation in oxygen isotope composition of waters for a montane larch forest in Mongolia. Trees 2006, 20, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.P.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, K.L.; Tan, W.; Deng, P.Y.; Yang, J. Seasonal water use patterns of woody species growing on the continuous dolostone outcrops and nearby thin soils in subtropical China. Plant Soil 2011, 341, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.P.; Chen, H.S.; Ding, Y.L.; Yang, J.; Wang, K.L. Comparison of rooting strategies to explore rock fractures for shallow soil-adapted tree species with contrasting aboveground growth rates: A greenhouse microcosm experiment. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Q.; Fan, Y.; Guan, W.; Tan, N. Soil-water utilization levels in a Cyclobalanopsis glaucoides virgin forest on the Central Yunnan Karst Plateau. J. Zhejiang A F Univ. 2014, 31, 690–696. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.P.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, P.Y.; Li, J.T. Plant Water Use Strategies in a Limestone Tropical Seasonal Moist Rainforest in Xishuangbanna, SW China. Acta Bot. Yunnanica 2008, 30, 496–504. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.R.; Barnard, H.R.; Coulombe, R.; McDonnell, J.J. Ecohydrologic separation of water between trees and streams in a Mediterranean climate. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araguás-Araguás, L.; Rozanski, K.; Gonfiantini, R.; Louvat, D. Isotope effects accompanying vacuum extraction of soil water for stable isotope analyses. J. Hydrol. 1995, 168, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B.; Hanshaw, B.B. Ultrafiltration by a compacted clay membrane—I. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic fractionation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1973, 37, 2295–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerter, E.; Finstad, K.; Schaefer, J.; Goldsmith, G.R.; Dawson, T.; Amundson, R. Oxygen isotope fractionation effects in soil water via interaction with cations (Mg, Ca, K, Na) adsorbed to phyllosilicate clay minerals. J. Hydrol. 2014, 515, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.; Schaffer, B.; Yuhong, L.; Sternberg, L.D.S.L. Testing plant use of mobile vs immobile soil water sources using stable isotope experiments. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, N.N.; Wang, Z.C.; Ma, X.Y.; Liu, W.N.; Chen, H.S.; Nie, Y.P. Isotopic deviations of water extracted from carbonate soil by cryogenic vacuum extraction: Implication for root water uptake analysis. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Jiang, G.H.; Gong, X.P.; Yin, J.J.; Wu, X. Recharge processes on typical karst slopes implied by isotopic and hydrochemical indexes in Xiaoyan Cave, Guilin, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.B.; Zeng, S.M.; Qin, H.L.; Zhou, K.X.; Yang, H.; Lan, F.; Huang, F.; Cao, J.H.; Müller, C. Low nitrate retention capacity in calcareous soil under woodland in the karst region of southwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Garousi, F.; Wang, J.; Cao, J.H.; Xu, X.L.; Zhu, T.B.; Mueller, C. Land use effects on gross soil nitrogen transformations in karst desertification area. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.Y.; Zhang, M.J.; Qu, D.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.Y.; Xiao, H.T. Contrasting water use strategies of Tamarix ramosissima in different habitats in the northwest of Loess Plateau, China. Water 2020, 12, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.L.; Gregg, J.W. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too many sources. Oecologia 2003, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeta, A.; Jones, S.P.; Clavé, L.; Wingate, L.; Gimeno, T.E.; Fréjaville, B.; Wohl, S.; Ogée, J. Unexplained hydrogen isotope offsets complicate the identification and quantification of tree water sources in a riparian forest. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 2129–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Zhang, M.L.; Wu, X.; Pan, M.C. The relationship between δ18O characteristics of the precipitation (heavy rainfall or rainstorm) and its water vapor sources in Guilin, China. Carsologica Sin. 2017, 36, 139–161. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Seasonal variations in depth of water uptake for a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to drought in an East Asian monsoon region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansguaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tell Us 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Sun, Z.Y.; Zhou, A.G.; Yu, S.W.; Cao, H. Using 18O stable isotopes to trace the water sources of riparian Tamarix in middle reaches of Heihe River. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2014, 28, 150–155. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Zheng, X.J.; Tang, L.S.; Li, Y. Stable oxygen isotopes reveal distinct water use patterns of two Haloxylon species in the Gurbantonggut Desert. Plant Soil 2015, 389, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Yu, X.X.; Jia, G.D.; Jia, J.B.; Lou, Y.H.; Lu, W.W. Contrasting water sources of evergreen and deciduous tree species in rocky mountain area of Beijing, China. Catena 2017, 150, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.N.; Chen, H.S.; Zou, Q.Y.; Nie, Y.P. Divergent root water uptake depth and coordinated hydraulic traits among typical karst plantations of subtropical China: Implication for plant water adaptation under precipitation changes. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 249, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.A.; Jia, G.D.; Yu, X.X.; Liu, W.W.; Sun, L.B.; Wang, Y.S.; Baheti, Z. Morphological trait as a determining factor for Populus simonii Carr. to survive from drought in semi-arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 253, 106943. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lu, N.; Fu, B.J. Inter-comparison of stable isotope mixing models for determining plant water source partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, H.S.; Nie, Y.P.; Wang, K.L. Dynamic variations in profile soil water on karst hillslopes in Southwest China. Catena 2019, 172, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.B.; Moore, L.A.; Hoffmann, W.A.; Pockman, W.T.; Linder, C.R. Ecosystem rooting depth determined with caves and DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11387–11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshun, J.; Dietrich, W.E.; Dawson, T.E.; Fung, I. Dynamic, structured heterogeneity of water isotopes inside hillslopes. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 164–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meißner, M.; Köhler, M.; Schwendenmann, L.; Hölscher, D.; Dyckmans, J. Soil water uptake by trees using water stable isotopes (δ2H andδ18O)-a method test regarding soil moisture, texture and carbonate. Plant Soil 2014, 376, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, D.R.; Schulze, E.S.; Hall, S.J. Revisiting streamside trees that do not use stream water: Can the two water worlds hypothesis and snowpack isotopic effects explain a missing water source? Ecohydrology 2017, 10, e1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonnell, J.J. The two water worlds hypothesis: Ecohydrological separation of water between streams and trees? WIREs Water 2014, 1, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geris, J.; Tetzlaff, D.; Mcdonnell, J.; Anderson, J.; Paton, G.; Soulsby, C. Ecohydrological separation in wet, low energy northern environments? A preliminary assessment using different soil water extraction techniques. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 5139–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorburn, P.J.; Hatton, T.J.; Walker, G.R. Combining measurements of transpiration and stable isotopes of water to determine groundwater discharge from forests. J. Hydrol. 1993, 150, 563–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.H.; Sternberg, L.S.L. Hydrogen isotopic fractionation by plant roots during water uptake in coastal wetland plants. In Stable Isotopes and Plant Carbon/Water Relations; Ehleringer, J.R., Hall, A.E., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 497–510. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.H.; Yuan, D.X.; Pan, G.X. Soil in karst ecosystem. Adv. Earth Sci. 2003, 18, 37–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wu, H. Mapping karst rocky desertification using Landsat 8 images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.A.; Shen, Y.X.; He, B.B.; Zhao, Z.M. Humus soil as a critical driver of flora conversion on karst rock outcrops. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagy, K.A. Doubly-Labeled Water Studies of Vertebrate Physiological Ecology. Stable Isot. Ecol. Res. 1989, 68, 270–287. [Google Scholar]
- Josep, P.; Iolanda, F.; Jaume, T. Variability of plant nitrogen and water use in a 100-m transect of a subdesertic depression of the Ebro valley (Spain) characterized by leaf δ13C and δ15N. Acta Oecologica 1999, 20, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Yakir, D.; Sternberg, Y.L. The Use of Stable Isotopes to Study Ecosystem Gas Exchange. Oecologia 2000, 123, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, R.; Anfodillo, T.; Eeleringer, J.R. Water sources and carbon isotope composition (δ13 C) of selected tree species of the Italian Alps. Can. J. For. Res. 1994, 24, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.H.; Chen, J.H.; Mou, Y.; Fang, W.; Kuang, Y.Y.; Fan, Y. Differences of Water Use Strategies of Pinus yunnanensis in Different Recovery Modes in Karst Mountains in Southeast Yunnan. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2021, 36, 37–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- McCole, A.A.; Stern, L.A. Seasonal water use patterns of Juniperus ashei on the Edwards Plateau, Texas, based on stable isotopes in water. J. Hydrol. 2007, 342, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sampling Site | Sampling Points | Vegetation Category | Advantageous Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clastic rock (XLBF) | 1-1 | tree forest | Castanopsis fargesii Franch |
| 1-2 | tree and shrub forest | Machilus grijsii Hance, Castanopsis hystrix J.D.Hooker | |
| 1-3 | scrub | Castanopsis fargesii Franch | |
| 1-4 | bare land | ||
| Dolomite (BDPY) | 2-1 | tree forest | Loropetalum chinense(R.Br.) Oliver |
| 2-2 | tree and shrub forest | Loropetalum chinense(R.Br.) Oliver, Murraya paniculata(L.) Jack | |
| 2-3 | tree forest | Osmanthus fragrans(Thunb.)Loureiro | |
| 2-4 | bare land | ||
| Limestone (MCY) | 3-1 | tree forest | Cyclobalanopsis glauca(Thunberg)Oersted |
| 3-2 | tree and shrub forest | Cyclobalanopsis glauca(Thunberg)Oersted, Miliusa philippensis(Lam.)Muell.Arg | |
| 3-3 | scrub | Miliusa balansae Finet Gagnep | |
| 3-4 | bare land | ||
| Dolomite (DYQY) | 4-1 | scrub | Loropetalum chinense(R.Br.) Oliver |
| 4-2 | bare land |
| Sampling Site | δD | δ18O | Soil Water Lines (SWL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clastic rock (XLBF) | −53.5‰~−30.0‰ (average −41.8‰) | −7.8‰~−4.3‰ (average −6.1‰) | δD = 6.17δ18O − 4.30 (R2 = 0.85) |
| Dolomite (BDPY) | −55.0‰~−40.1‰ (average −48.1‰) | −8.7‰~−6.2‰ (average −7.4‰) | δD = 5.68δ18O − 6.89 (R2 = 0.82) |
| Limestone (MCY) | −60.4‰~−42.2‰ (average −52.8‰) | −9.7‰~−5.3‰ (average −8.0‰) | δD = 4.76δ18O − 14.74 (R2 = 0.84) |
| Dolomite (DYQY) | −51.4‰~−39.4‰ (average −46.0‰) | −7.9‰~−5.4‰ (average −6.7‰) | δD = 5.08δ18O − 11.94 (R2 = 0.87) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, H.; Ma, J.; Cao, J. The Effect of Bedrock Differences on Plant Water Use Strategies in Typical Karst Areas of Southwest China. Land 2023, 12, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010012
Ning J, Liu X, Wu X, Yang H, Ma J, Cao J. The Effect of Bedrock Differences on Plant Water Use Strategies in Typical Karst Areas of Southwest China. Land. 2023; 12(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Jing, Xiang Liu, Xia Wu, Hui Yang, Jie Ma, and Jianhua Cao. 2023. "The Effect of Bedrock Differences on Plant Water Use Strategies in Typical Karst Areas of Southwest China" Land 12, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010012
APA StyleNing, J., Liu, X., Wu, X., Yang, H., Ma, J., & Cao, J. (2023). The Effect of Bedrock Differences on Plant Water Use Strategies in Typical Karst Areas of Southwest China. Land, 12(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010012






